Possible Associations between Space Weather and the Incidence of Stroke
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Environmental Variables
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cornelissen, G.; Halberg, F.; Breus, T.; Syutkina, E.V.; Baevsky, R.; Weydahl, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Otsuka, K.; Siegelova, J.; Fiser, B.; et al. Non-photic solar associations of heart rate variability and myocardial infarction. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2002, 64, 707–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.J.; Rycroft, M.J.; Cermack, M. Solar and geomagnetic activity, extremely low frequency magnetic and electric fields and human health at the Earth’s surface. Surv. Geophys. 2006, 27, 557–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breus, T.K.; Baevskii, R.M.; Chernikova, A.G. Effects of geomagnetic disturbances on humans functional state in space flight. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2012, 5, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caswell, J.M.; Singh, M.; Persinger, M.A. Simulated sudden increase in geomagnetic activity and its effect on heart rate variability: Experimental verification of correlation studies. Life Sci. Space Res. 2016, 10, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilli Vieira, C.L.; Alvares, D.; Blomberg, A.; Schwartz, J.; Coull, B.; Huang, S.; Koutrakis, P. Geomagnetic disturbances driven by solar activity enhance total and cardiovascular mortality risk in 263 U.S. cities. Environ. Health 2019, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrova, S.; Stoilova, I.; Cholakov, I. Influence of local geomagnetic storms on arterial blood pressure. Bioelectromagnetics 2004, 25, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pikin, D.A.; Gurfinkel, I.I.; Oraevskii, V.N. Effect of geomagnetic disturbances on the blood coagulation system in patients with ischemic heart disease and prospects for correction medication. Biofizika 1998, 43, 617–622. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Stoupel, E.; Abramson, E.; Israelevich, P.; Sulkes, J.; Harell, D. Dynamics of serum C-reactive protein (CRP) level and cosmophysical activity. Eur. J. Int. Med. 2007, 18, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Cornellissen, G.; Halberg, F.; Otsuka, K.; Ohkawa, S.I. Associations by signatures and coherences between the human circulation and helio- and geomagnetic activity. Biomed. Pharm. 2001, 55 (Suppl. 1), 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weydahl, A.; Sothern, R.B.; Cornellissen, G.; Wetterburg, L. Geomagnetic activity influences the melatoninsecretion at 70 degrees N. Biomed. Pharmocother. 2001, 55 (Suppl. 1), 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E. The effect of geomagnetic activity on cardiovascular parameters. Biomed. Pharm. 2002, 56, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Kusniec, J.; Golovchiner, G.; Abramson, E.; Kadmon, U.; Strasberg, B. Association of Time of Occurrence of Electrical Heart Storms with Environmental Physical Activity. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2014, 37, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschvink, J.L.; Jones, D.S.; MacFadden, B.J. Magnetite Biomineralization and Magnetoreception in Organisms: A New Biomagnetism; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Binhi, V.N.; Prato, F.S. Biological effects of the hypomagnetic field: An analytical review of experiments and theories. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binhi, V.N.; Prato, F.S. Rotations of macromolecules affect nonspecific biological responses to magnetic fields. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vencloviene, J.; Radisauskas, R.; Vaiciulis, V.; Kiznys, D.; Bernotiene, G.; Kranciukaite-Butylkiniene, D.; Tamosiunas, A. Associations between Quasi-biennial Oscillation phase, solar wind, geomagnetic activity, and the incidence of acute myocardial infarction. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2020, 64, 1207–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Martfel, J.N.; Rotenberg, Z. Paroxysmal atrial fibrillationand stroke (cerebrovascular accidents) in males and females above and below age 65 on days of different geomagnetic activity level. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharm. 1994, 5, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villoresi, G.; Breus, T.K.; Dorman, L.I.; Iuchi, N.; Rapoport, S.I. Effect of interplanetary and geomagnetic disturbances on the increase in number of clinically serious medical pathologies (myocardial infarct and stroke). Biofizika 1995, 40, 983–993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gurfinkel, I.I.; Kuleshova, V.P.; Oraevskiĭ, V.N. Assessment of the effect of a geomagnetic storm on the frequency of appearance of acute cardiovascular pathology. Biofizika 1998, 43, 654–658. (In Russian) [Google Scholar]
- Shaposhnikov, D.; Revich, B.; Gurfinkel, Y.; Naumova, E. The influence of meteorological and geomagnetic factors on acute myocardial infarction and brain stroke in Moscow, Russia. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2013, 58, 799–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feigin, V.L.; Nikitin, Y.P.; Vinogradova, T.E. Solar and geomagnetic activities: Are there associations with stroke occurrence? A population-based study in Siberia, Russia (1982–1992). Cerebrovasc. Dis. 1997, 7, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigin, V.L.; Parmar, P.G.; Barker-Collo, S.; Derrick, A.; Bennett, D.A.; Anderson, C.S.; Thrift, A.G.; Stegmayr, B.; Rothwell, P.M.; Giroud, M.; et al. Geomagnetic Storms Can Trigger Stroke Evidence From 6 Large Population-Based Studies in Europe and Australasia. Stroke 2014, 45, 1639–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Zhemaityte, D.; Drungiliene, D.; Martinkenas, A.; Abramson, E.; Sulkes, J. Klaipėda cardiovascular emergency aid services correlate with 10 cosmophysical parameters by time of occurrence. J. Clin. Basic Cardiol. 2002, 5, 225–227. [Google Scholar]
- Kleimenova, N.G.; Kozyreva, O.V.; Rapoport, S.I. Pc1 Geomagnetic Pulsations as a Potential Hazard of the Myocardial Infarction. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2007, 69, 1759–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenchenko, T.; Poskotinova, L.V.; Rekhtina, A.G.; Zaslavskaya, R.M. Relation between Microcirculation Parameters and Pc3 Geomagnetic Pulsations. Biophysics 2010, 55, 646–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babayev, E.S.; Crosby, N.B.; Obridko, V.N.; Rycroft, R.J. Potential effects of solar and geomagnetic variability on terrestrial biological systems. In Advances in Solar and Solar-Terrestrial Physics; Georgeta, M., Crisan, D., Eds.; Research Signpost: Thiruvananthapuram, India, 2012; pp. 329–376. [Google Scholar]
- Vencloviene, J.; Babarskiene, R.; Slapikas, R.; Sakalyte, G. The association between phenomena on the sun, geomagnetic activity, meteorological variables, and cardiovascular characteristic of patients with myocardial infarction. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2013, 57, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolska, K. The Impact of Ionospheric and Geomagnetic Changes on Mortality from Diseases of the Circulatory System. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2018, 27, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiznys, D.; Vencloviene, J.; Milvidaite, I. The associations of geomagnetic storms, fast solar wind, and stream interaction regions with cardiovascular characteristic in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Life Sci. Space Res. 2020, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannaropoulou, E.; Papailiou, M.; Mavromichalaki, H.; Gigolashvili, M.; Tvildiani, L.; Janashia, K.; Preka-Papadema, P.; Papadima, T. A study on the various types of arrhythmias in relation to the polarity reversal of the solar magnetic field. Nat. Hazards 2014, 70, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vencloviene, J.; Babarskiene, R.M.; Kiznys, D. A possible association between space weather conditions and the risk of acute coronary syndrome in patients with diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2017, 61, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCraty, R.; Atkinson, M.; Stolc, V.; Alabdulgader, A.; Vainoras, A.; Ragulskis, M. Synchronization of human autonomic nervous system rhythms with geomagnetic activity in human subjects. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO MONICA Project, MONICA Manual, Part IV: Event Registration, Section 2: Stroke Event Registration Data Component. 1990. Available online: http://www.ktl.fi/publications/monica/manual/part4/iv-2.htm (accessed on 4 March 2021).
- Radisauskas, R.; Malinauskiene, V.; Milinaviciene, E.; Kranciukaite-Butylkiniene, D.; Tamosiunas, A.; Bernotiene, G.; Luksiene, D.; Milasauskiene, Z.; Sopagiene, D.; Rastenyte, D. Trends in the Attack Rates, Incidence, and Mortality of Stroke during 1986-2012: Data of Kaunas (Lithuania) Stroke Registry. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinheiro, F.J.G.; Barata, M.T.; Fernandes, J.M. Comparison of Space Weather Services: Information Systems, Activity and Forecasts. J. Comp. Int. Sci. 2016, 7, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peng, R.D.; Dominci FBaltimore, M.D. Statistical Methods for Environmental Epidemiology with R: A Case Study of Air Pollution and Health; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Vencloviene, J.; Radisauskas, R.; Kranciukaite-Butylkiniene, D.; Tamosiunas, A.; Vaiciulis, V.; Rastenyte, D. Association between stroke occurrence and changes in atmospheric circulation. BMC Public Health 2021, 21, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, I.G.; Cane, H.V. Near-Earth Interplanetary Coronal Mass Ejections during Solar Cycle 23 (1996–2009): Catalog and Summary of Properties. Solar Physics. Sol. Phys. 2010, 264, 189–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Petrauskiene, J.; Abramson, E.; Kalediene, R.; Sulkes, J. Distribution of monthly deaths, solar (SA) and geomagnetic (GMA) activity: Their interrelationship in the last decade of the second millennium: The Lithuanian study 1990–1999. Biomed. Pharm. 2002, 56, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoupel, E.; Abramson, J.; Domarkiene, S.; Shimshoni, M.; Sulkes, J. Space proton flux and the temporal distribution of cardiovascular deaths. Int. J. Biometeorol. 1997, 40, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seppälä, A.; Verronen, P.T.; Sofieva, V.F.; Tamminen, J.; Kyrölä, E.; Rodger, C.J.; Clilverd, M.A. Destruction of the tertiary ozone maximum during a solar proton event. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L07804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veretenenko, S.V.; Tejll, P. Solar proton events and evolution of cyclones in the North Atlantic. Geomagn. Aeron. 2008, 48, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.; Ruan, Y.; Liang, R.; Liu, X.; Fan, Z. Short-Term Effect of Ambient Temperature and the Risk of Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 9068–9088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buxton, N.; Liu, C.; Dasic, D.; Moody, P.; Hope, D.T. Relationship of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage to changes in atmospheric pressure: Results of a prospective study. J. Neurosurg. 2001, 95, 391–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setzer, M.; Beck, J.; Hermann, E.; Raabe, A.; Seifert, V.; Vatter, H.; Marquardt, G. The influence of barometric pressure changes and standard meteorological variables on the occurrence and clinical features of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Surg. Neurol. 2007, 67, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimez-Conde, J.; Ois, A.; Gomis, M.; Campello, A.R.; Godia, E.C.; Subirana, I.; Roquer, J. Weather as a Trigger of Stroke. Daily meteorological factors and incidence of stroke subtypes. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2008, 26, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Donkelaar, C.E.; Potgieser, A.R.; Groen, H.; Foumani, M.; Abdulrahman, H.; Sluijter, R.; van Dijk, J.M.C.; Groen, R.J. Atmospheric Pressure Variation is a Delayed Trigger for Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2018, 112, e783–e790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, N. Schumann Resonances, a plausible biophysical mechanism for the human health effects of Solar/Geomagnetic Activity. Nat. Hazards 2002, 26, 279–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roldugin, V.C.; Maltsev, Y.P.; Vasiljev, A.N.; Schokotov, A.Y.; Belyajev, G.G. Schumann resonance frequency increase during solar X-ray bursts. J. Geophys. Res. 2004, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

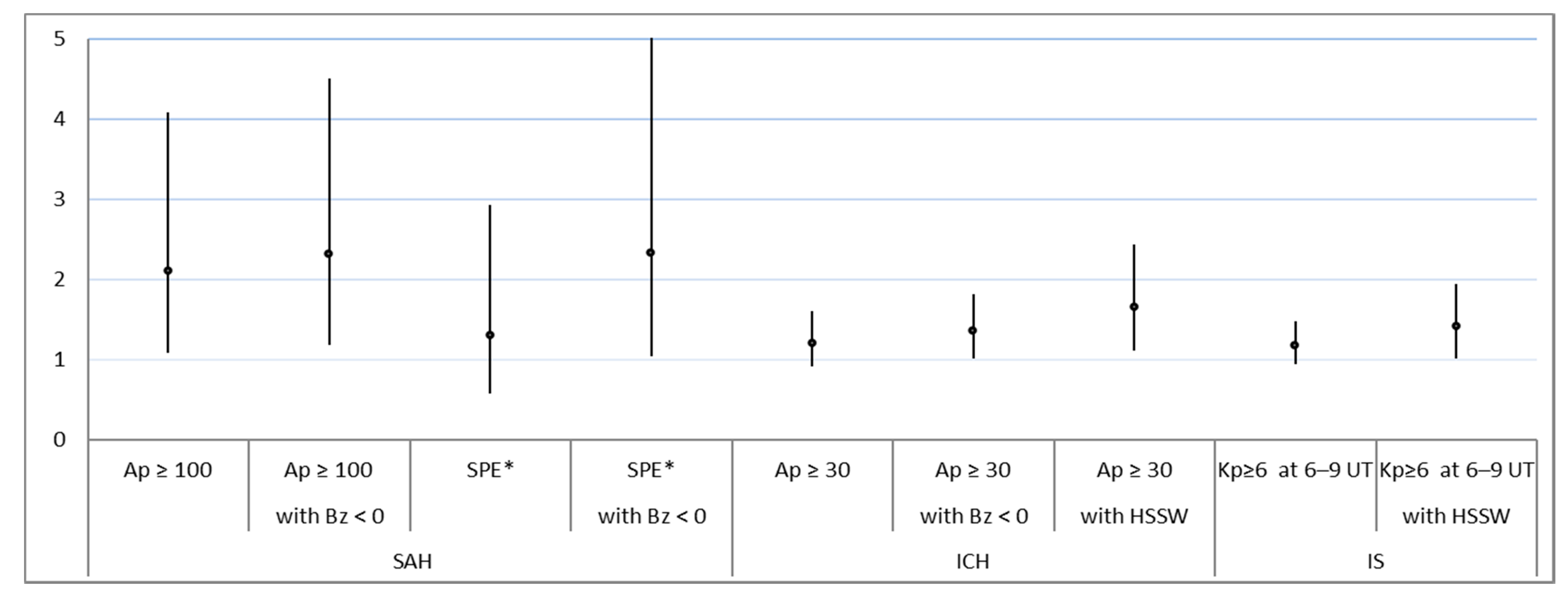
| Sex/Groups | Total | SAH | ICH | HS (SAH + ICH) | IS | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All, n (%) | 9277 (100.0/100.0) | 597 (6.4) | 1147 (12.4) | 1744 (18.8) | 7482 (80.7) | 51 (0.5) |
| Men, n (%) | 5230 (56.4/100.0) | 281 (5.3) | 631 (12.1) | 912 (17.4) | 4294 (82.1) | 24 (0.5) |
| Women, n (%) | 4047 (43.6/100.0) | 316 (7.8) | 516 (12.7) | 832 (20.5) | 3188 (78.8) | 27 (0.7) |
| Variable | N | SAH | ICH | HS | IS | All Types |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| The effects of geomagnetic activity level defined by the Ap index | ||||||
| Ap = 0 | 49 | 0.12 (0.3) | 0.33 (0.5) | 0.45 (0.6) | 1.04 (0.9) | 1.49 (1.0) |
| 0 < Ap < 30 | 8346 | 0.06 (0.3) | 0.12 (0.4) | 0.19 (0.4) | 0.82 (0.9) | 1.01 (1.0) |
| Minor GS (30 ≤ Ap < 50) | 504 | 0.05 (0.2) | 0.13 (0.4) | 0.19 (0.4) | 0.83 (0.9) | 1.02 (1.0) |
| Major GS (50 ≤ Ap < 100) | 186 | 0.08 (0.3) | 0.15 (0.4) | 0.23 (0.5) | 0.86 (0.9) | 1.09 (1.0) |
| Severe GS (Ap ≥ 100) | 46 | 0.17 (0.4) | 0.17 (0.4) | 0.35 (0.5) | 0.78 (0.9) | 1.13 (1.1) |
| p | 0.023 | 0.002 | <0.001 | 0.485 | 0.015 | |
| The effects of GS, defined by 3-h Kp index (days of Ap = 0 excluded) | ||||||
| All 3-h Kp < 5 | 8359 | 0.07 (0.3) | 0.13 (0.4) | 0.19 (0.4) | 0.82 (0.9) | 1.02 (1.0) |
| Minor GS * (Kp = 5) | 1103 | 0.06 (0.3) | 0.12 (0.3) | 0.18 (0.4) | 0.82 (0.9) | 1.01 (1.0) |
| Moderate GS * (Kp = 6) | 450 | 0.05 (0.3) | 0.13 (0.4) | 0.18 (0.4) | 0.82 (0.9) | 0.99 (1.0) |
| Strong/severe GS * (Kp ≥ 7) | 273 | 0.10 (0.3) | 0.14 (0.4) | 0.23 (0.5) | 0.86 (1.0) | 1.09 (1.1) |
| p | 0.108 | ns | 0.273 | ns | ns | |
| The effects of the maximum of SPE | ||||||
| Other days | 9090 | 0.07 (0.3) | 0.13 (0.4) | 0.19 (0.4) | 0.82 (0.9) | 1.02 (1.0) |
| Strong event (1000–9999 pfu) | 31 | 0.10 (0.3) | 0.19 (0.4) | 0.29 (0.4) | 0.84 (0.9) | 1.13 (1.1) |
| Severe event (≥10,000 pfu) | 10 | 0 | 0.40 (0.5) | 0.40 (0.4) | 0.70 (0.9) | 1.10 (1.0) |
| p | ns | 0.039 | 0.151 | ns | ns | |
| The effects of the X-class solar flare | ||||||
| X ≥ 9.0 lag 0–1 ** | 34 | 0.03 (0.2) | 0.15 (0.4) | 0.18 (0.4) | 1.21 (1.12) | 1.38 (1.2) |
| Other days | 9048 | 0.07 (0.3) | 0.12 (0.4) | 0.19 (0.4) | 0.82 (0.9) | 1.01 (1.0) |
| p | 0.426 | ns | ns | 0.013 | 0.034 | |
| Model | Variable | RR (95% CI) | p | RR (95% CI) | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Subarachnoid hemorrhages | Haemorrhagic stroke | ||||
| I | Ap = 0 | 1.88 (0.81–4.34) | 0.142 | 2.33 (1.50–3.61) | <0.001 |
| 50 ≤ Ap < 100 | 1.17 (0.68–2.00) | ns | 1.26 (0.92–1.71) | 0.152 | |
| Ap ≥ 100 | 2.75 (1.35–5.59) | 0.005 | 2.04 (1.24–3.35) | 0.005 | |
| II | Strong/severe GS, defined by daily Kp | 1.58 * (1.07–2.35) | 0.023 | 1.30 * (1.01–1.68) | 0.041 |
| III | Kp = 6 at 06:00–09:00 UT | 1.21 * (0.60–2.45) | ns | ||
| Kp ≥ 7 at 06:00–09:00 UT | 2.65 * (1.49–4.72) | 0.001 | |||
| IV | Extreme GMA (Ap = 0 or Ap ≥ 100) | 2.30 (1.33–3.96) | 0.003 | ||
| Intracerebral hemorrhages | |||||
| V | Ap = 0 | 2.51 (1.50–4.20) | <0.001 | ||
| 30 ≤ Ap < 50 | 1.13 (0.88–1.45) | 0.359 | |||
| 50≤ Ap < 100 | 1.34 (0.89–1.92) | 0.168 | |||
| Ap ≥ 100 | 1.63 (0.81–3.29) | 0.173 | |||
| VI | Kp ≥ 6 at 15:00–21:00 UT | 1.42 * (1.07–1.89) | 0.016 | ||
| VII | Days of the maximum of strong SPE | 1.67 * (0.74–3.77) | 0.214 | ||
| Days of the maximum of severe SPE | 3.33 * (1.23–9.01) | 0.018 | |||
| VIII | Ap = 0 | 2.51 (1.50–4.21) | <0.001 | ||
| Days of the maximum of severe SPE | 2.62 (0.95–7.27) | 0.064 | |||
| Kp ≥ 6 at 15:00–21:00 UT | 1.36 (1.02–1.83) | 0.039 | |||
| IX | Days of the maximum of SPE ** | 1.71 * (0.99–2.98) | 0.056 | ||
| X | 1 day after of the maximum of SPE ** | 2.07 * (1.24–3.47) | 0.006 | ||
| XI | 2 day after of the maximum of SPE ** | 1.51 * (0.83–2.76) | 0.173 | ||
| XII | Ap = 0 | 2.33 (1.50–3.61) | <0.001 | ||
| Ap ≥ 100 | 1.77 (1.05–2.98) | 0.031 | |||
| 1 day after of the maximum of SPE ** | 1.81 (1.06–3.10) | 0.030 | |||
| Variable | RR ♦ (95% CI) | p | RR ♦ (95% CI) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ischemic stroke | All strokes | ||||
| I | Ap = 0 | 1.36 (1.03–1.81) | 0.032 | 1.56 (1.23–1.98) | <0.001 |
| Kp ≥ 6 at 06:00–09:00 UT | 1.17 (1.00–1.36) | 0.047 | 1.18 (1.03–1.36) | 0.016 | |
| II | Kp ≥ 5 at 06:00–09:00 UT and 09:00–12:00 UT | 1.14 * (1.01–1.29) | 0.042 | 1.15 * (1.02–1.28) | 0.019 |
| III | X ≥ 9 lag 0–1 ** | 1.41 * (1.03–1.92) | 0.032 | 1.34 * (1.00–1.79) | 0.048 |
| IV | Ap = 0 | 1.36 (1.03–1.81) | 0.032 | 1.56 (1.23–1.98) | <0.001 |
| Kp ≥ 5 at 06:00–09:00 UT and 09:00–12:00 UT | 1.13 (1.00–1.28) | 0.051 | 1.14 (1.02–1.28) | 0.023 | |
| X ≥ 9 lag 0–1 ** | 1.39 (1.02–1.89) | 0.040 | 1.32 (0.99–1.77) | 0.060 | |
| V | Ap = 0 | 1.36 (1.03–1.81) | 0.033 | 1.56 (1.23–1.98) | <0.001 |
| Kp ≥ 5 at 06:00–09:00 UT and 09:00–12:00 UT | 1.13 (1.00–1.28) | 0.058 | 1.14 (1.02–1.28) | 0.025 | |
| X ≥ 9 lag 0–1 ** and Ap ≥ 30 lag 1–2 | 1.76 (1.18–2.62) | 0.006 | 1.60 (1.09–2.35) | 0.015 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vencloviene, J.; Radisauskas, R.; Tamosiunas, A.; Luksiene, D.; Sileikiene, L.; Milinaviciene, E.; Rastenyte, D. Possible Associations between Space Weather and the Incidence of Stroke. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030334
Vencloviene J, Radisauskas R, Tamosiunas A, Luksiene D, Sileikiene L, Milinaviciene E, Rastenyte D. Possible Associations between Space Weather and the Incidence of Stroke. Atmosphere. 2021; 12(3):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030334
Chicago/Turabian StyleVencloviene, Jone, Ricardas Radisauskas, Abdonas Tamosiunas, Dalia Luksiene, Lolita Sileikiene, Egle Milinaviciene, and Daiva Rastenyte. 2021. "Possible Associations between Space Weather and the Incidence of Stroke" Atmosphere 12, no. 3: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030334
APA StyleVencloviene, J., Radisauskas, R., Tamosiunas, A., Luksiene, D., Sileikiene, L., Milinaviciene, E., & Rastenyte, D. (2021). Possible Associations between Space Weather and the Incidence of Stroke. Atmosphere, 12(3), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12030334









