Performance Comparison of Solid Lead Ion Electrodes with Different Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Electron-Ion Exchangers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Reagents and Materials
2.2. ISEs Fabrication
2.3. Apparatus and Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Micrograph of ElectronIon Exchanger
3.2. CA of Carbon-Based Nanomaterials
3.3. Potentiometric Performance
3.4. Stability and Conductivity of ISEs
3.5. Lifetime of ISEs
3.6. Comprehensive Property and Follow-up Studies
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chon, H.-T.; Ahn, J.S.; Jung, M.C. Heavy Metal Contamination in the Vicinity of Some Base-Metal Mines in Korea; a Review. Geosyst. Eng. 1998, 1, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, M.D.G.A.; De Andrade, J.B.; De Jesus, D.S.; Lemos, V.A.; Bandeira, M.L.; Dos Santos, W.N.; Bezerra, M.A.; Amorim, F.A.; Souza, A.S.; Ferreira, S.L. Separation and preconcentration procedures for the determination of lead using spectrometric techniques: A review. Talanta 2006, 69, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assubaie, F.N. Assessment of the levels of some heavy metals in water in Alahsa Oasis farms, Saudi Arabia, with analysis by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 8, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, X.; Han, Y.; Bian, X.; Zhang, Q. Effective Enrichment and Simultaneous Quantitative Analysis of Trace Heavy Metal Ions Mixture in Aqueous Samples by the Combination of Radial Electric Focusing Solid Phase Extraction, UV-Vis Spectrophotometric Determination and Partial Least Squares Regression. Waterairsoil Pollut. 2017, 228, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Speciation of arsenic and chromium metal ions by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography. Chemosphere 2002, 48, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarazua, G.; Ávila-Pérez, P.; Tejeda, S.; Barcelo-Quintal, I.; Martínez, T. Analysis of total and dissolved heavy metals in surface water of a Mexican polluted river by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry. Spectrochim. Acta Part B At. Spectrosc. 2006, 61, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, C.; Diamond, D. Opportunities and challenges of using ion-selective electrodes in environmental monitoring and wearable sensors. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 84, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, R.S.; Mackey, D.J.; Van Dam, R.; Nowak, B. Copper speciation and toxicity in Macquarie Harbour, Tasmania: An investigation using a copper ion selective electrode. Mar. Chem. 2001, 74, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, G.A. Recent Advances in Ion-selective membrane electrodes for in situ environmental water analysis. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanrahan, G.; Patil, D.G.; Wang, J. Electrochemical sensors for environmental monitoring: Design, development and applications. J. Environ. Monit. 2004, 6, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J.; Ivaska, A.; Lewenstam, A. Potentiometric Ion Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattrall, R.W.; Tribuzio, S.; Freiser, H. Potassium ion responsive coated wire electrode based on valinomycin. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 2223–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janata, J. Principles of Chemical Sensors; Springer Science & Business Media: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2010; pp. 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, G.; Adhikari, R.; Cass, P.; Bown, M.; Gunatillake, P.A. Electrically conductive polymers and composites for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37553–37567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, G.; Seh, Z.W.; Yao, H.; Cui, Y. Understanding the Role of Different Conductive Polymers in Improving the Nanostructured Sulfur Cathode Performance. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 5534–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobacka, J. Conducting Polymer-Based Solid-State Ion-Selective Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalska, A.; Wojciechowski, M.; Jędral, W.; Bulska, E.; Maksymiuk, K. Silver and lead all-plastic sensors—polyaniline vs. poly (3, 4-ethyledioxythiophene) solid contact. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2009, 13, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Driver, N.; Tian, Q.; Jiang, W.; Liu, H. Electrochemical deposition of conductive polymers onto magnesium microwires for neural electrode applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 1887–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fibbioli, M.; Morf, W.E.; Badertscher, M.; de Rooij, N.F.; Pretsch, E. Potential drifts of solid-contacted ion-selective electrodes due to zero-current ion fluxes through the sensor membrane. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2000, 12, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, D.; Anthis, A.H.C.; Afshar, M.G.; Pankratova, N.; Cuartero, M.; Crespo, G.A.; Bakker, E. All-Solid-State Potentiometric Sensors with a Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Inner Transducing Layer for Anion Detection in Environmental Samples. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8640–8645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, Z.; Teter, A.; Lewenstam, A.; Maj-Żurawska, M.; Ivaska, A.; Bobacka, J. Comparison of Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes and Poly(3-octylthiophene) as Ion-to-Electron Transducers in All-Solid-State Potassium Ion-Selective Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2011, 23, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, E.J.; Crespo, G.A.; Riu, J.; Ruiz, A.; Rius, F.X.; Arnó, E.J.P. Ion-selective electrodes using multi-walled carbon nanotubes as ion-to-electron transducers for the detection of perchlorate. Analyst 2009, 134, 1905–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouskaki, M.; Chaniotakis, N. Fullerene-based electrochemical buffer layer for ion-selective electrodes. Analyst 2008, 133, 1072–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, T.; Qin, W. An all-solid-state polymeric membrane Pb2+-selective electrode with bimodal pore C60 as solid contact. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 876, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Ragab, M.T.; Ramadan, N.K.; El-Ragehy, N.A.; El-Zeany, B.A. Design of Solid-contact Ion-selective Electrode with Graphene Transducer Layer for the Determination of Flavoxate Hydrochloride in Dosage Form and in Spiked Human Plasma. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 2803–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaedi, M.; Jaberi, S.Y.S.; Hajati, S.; Montazerozohori, M.; Asfaram, A.; Mirtamizdoust, B.; Zare, M. CuO nanoparticles intermixed with chemically modified multiwalled carbon nanotubes as a novel electrode for Cu2+ ion determination. IEEE Sen. J. 2014, 15, 2882–2890. [Google Scholar]
- Barathi, P.; Senthil Kumar, A. Electrochemical Conversion of Unreactive Pyrene to Highly Redox-Active 1,2-Quinone Derivatives on a Carbon Nanotube-Modified Gold Electrode Surface and Its Selective Hydrogen Peroxide Sensing. Langmuir 2013, 29, 10617–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, C.-C.; Shih, J.-S. Bifunctional Ion-Selective Electrode Based on C60-Cryptand 22 for Silver and Iodine Ions. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2012, 59, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darmanin, T.; Guittard, F. Wettability of conducting polymers: From superhydrophilicity to superoleophobicity. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 656–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, A.M.Y.; Moody, G.J.; Thomas, J.D.R. Studies on lead ion-selective electrodes based on polyalkoxylates. Analyst 1988, 113, 1409–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



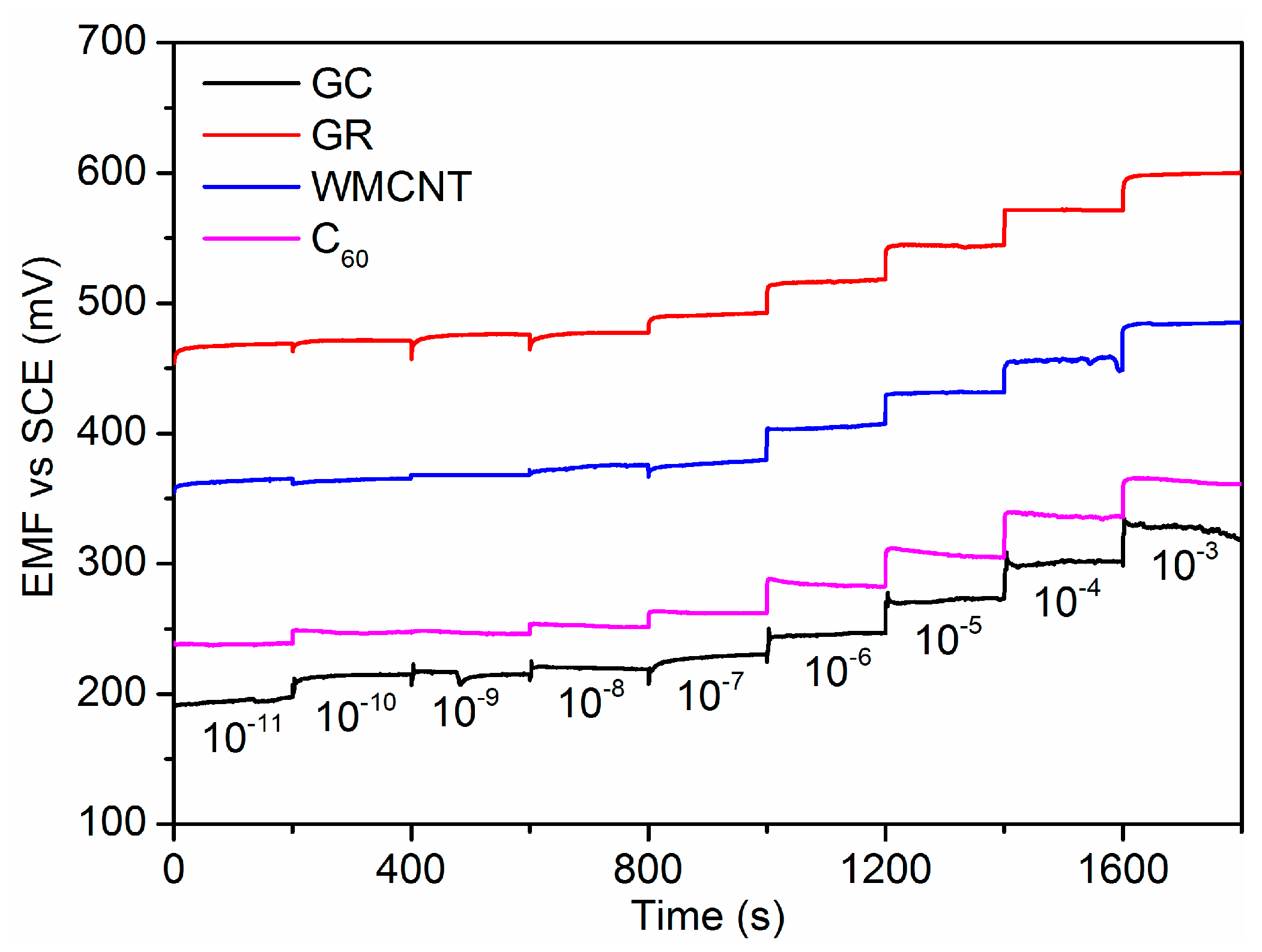

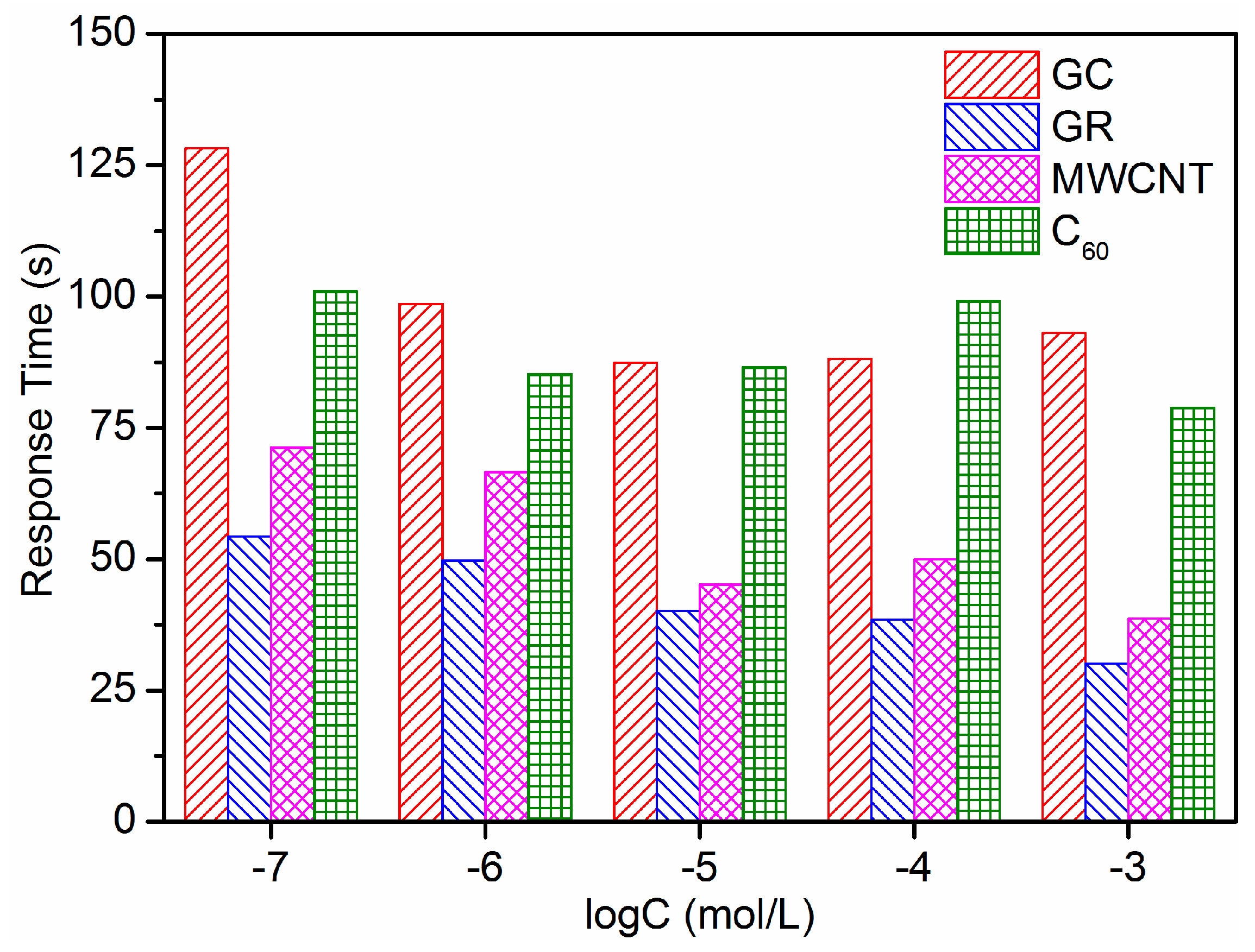
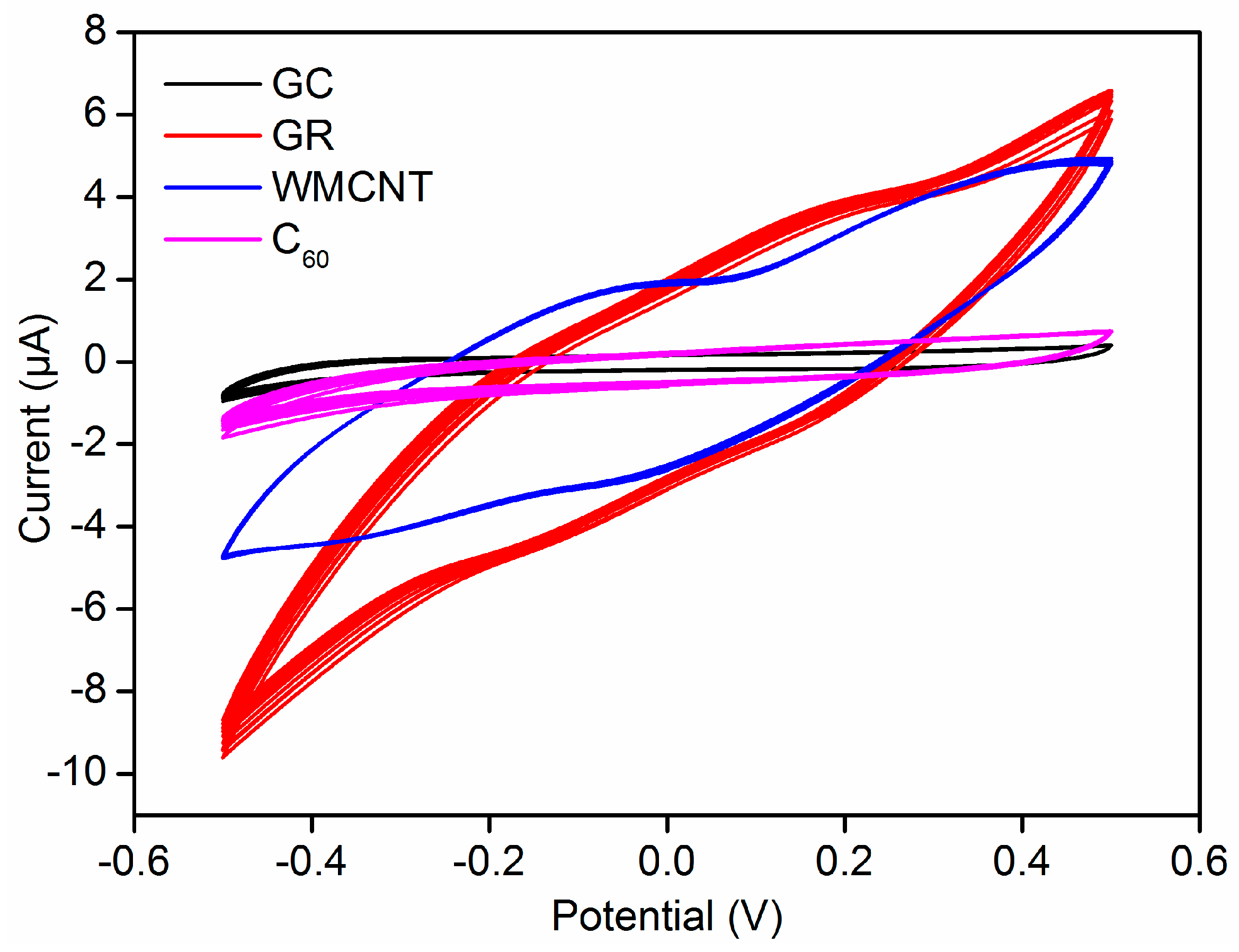

| ISE | Slope (mV/Decade) | LDL (mol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| GC/Pb2+-ISE | 23.2 ± 1.3 | 1.1 × 10−7 |
| GC/GR/Pb2+-ISE | 26.8 ± 0.3 | 3.4 × 10−8 |
| GC/MWCNT/Pb2+-ISE | 25.4 ± 1.5 | 8.7 × 10−8 |
| GC/C60/Pb2+-ISE | 25.0 ± 1.1 | 6.4 × 10−8 |
| No. | Linear Range (mol/L) | Slope (mV/decade) | LDL (mol/L) | Response Time (s) | Lifetime (day) | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10−7~10−3 | 23.24 | 1.10 × 10−7 | 99.12 | 1 | GC/Pb2+-ISE |
| 2 | 10−7~10−3 | 26.79 | 3.44 × 10−8 | 42.58 | 28 | GC/GR/Pb2+-ISE |
| 3 | 10−7~10−3 | 25.39 | 8.65 × 10−8 | 54.34 | 7 | GC/MWCNT/Pb2+-ISE |
| 4 | 10−7~10−3 | 25.01 | 6.39 × 10−8 | 90.22 | 1 | GC/C60/Pb2+-ISE |
| 5 | 10−5~10−1 | 26 | - | 60 | 14 | [30] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Wei, Z.; Liu, P.; Wei, H.; Ma, D. Performance Comparison of Solid Lead Ion Electrodes with Different Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Electron-Ion Exchangers. Sensors 2021, 21, 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051663
Zhang L, Wei Z, Liu P, Wei H, Ma D. Performance Comparison of Solid Lead Ion Electrodes with Different Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Electron-Ion Exchangers. Sensors. 2021; 21(5):1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051663
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei, Zhengying Wei, Pengcheng Liu, Haoran Wei, and Denglong Ma. 2021. "Performance Comparison of Solid Lead Ion Electrodes with Different Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Electron-Ion Exchangers" Sensors 21, no. 5: 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051663
APA StyleZhang, L., Wei, Z., Liu, P., Wei, H., & Ma, D. (2021). Performance Comparison of Solid Lead Ion Electrodes with Different Carbon-Based Nanomaterials as Electron-Ion Exchangers. Sensors, 21(5), 1663. https://doi.org/10.3390/s21051663







