Sources, Status, and Potential Risks of Microplastics in Marine Organisms of the Bohai Sea: A Systematic Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bibliometric Perspective and Current State of Research
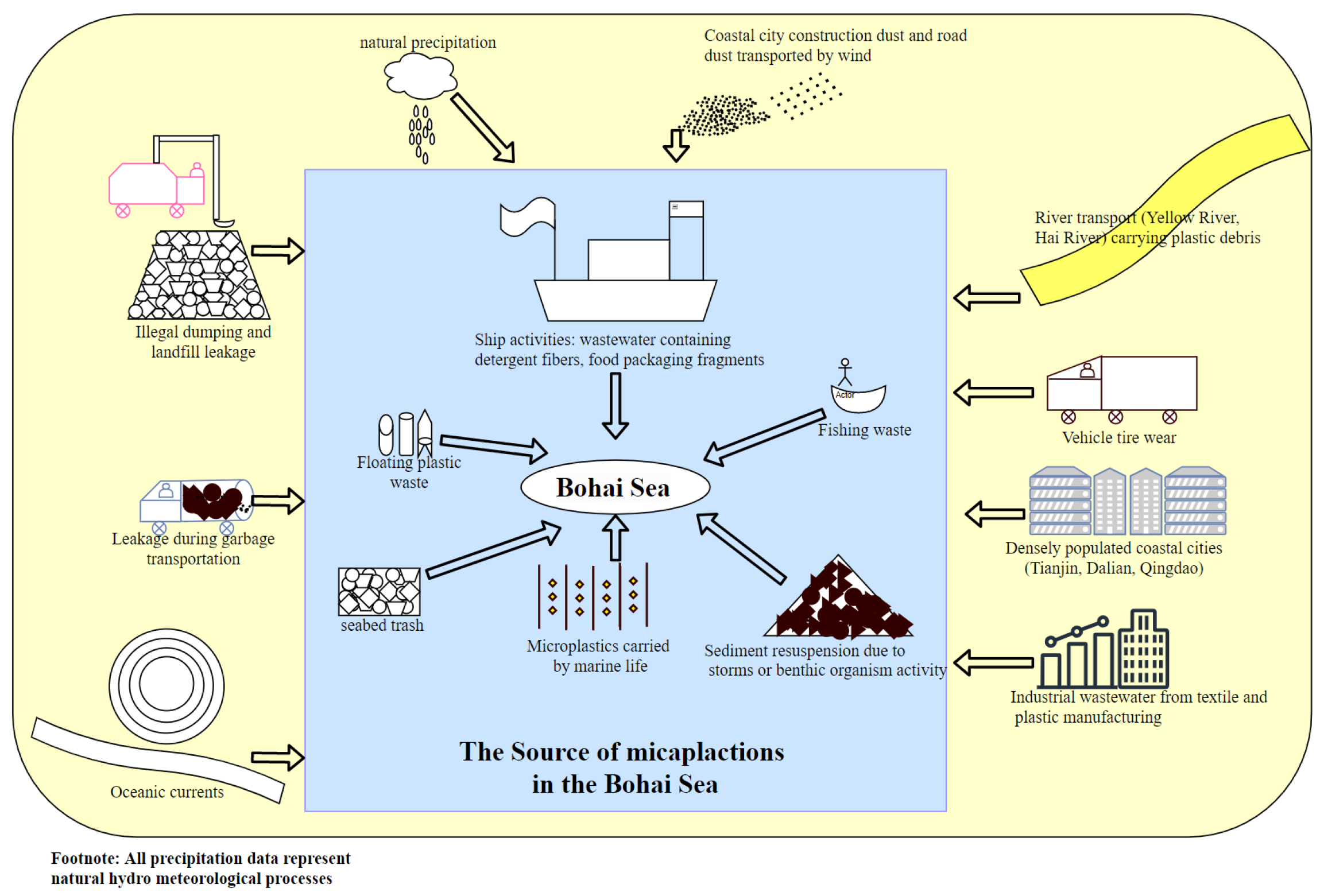
3. Sources of Microplastics in Bohai Sea Aquatic Organisms
3.1. Land-Based Inputs
3.2. Marine Sources
3.3. Natural Driving Factors
4. Microplastic Pollution in Aquatic Organisms of the Bohai Sea
4.1. Concentration Distribution Characteristics of Microplastics in the Bohai Sea
4.2. Microplastic Accumulation in Aquatic Organisms
4.3. The Morphology and Migration Mechanisms of Microplastics in Bohai Sea Aquatic Organisms
5. Microplastic Ecological Risks to Bohai Sea Aquatic Organisms
5.1. Biological Accumulation Effects
5.2. Toxic Effects of Microplastics
5.3. Ecosystem Cascade Effect
| Impact | Value or Trend | Correlation | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| The photosynthetic efficiency of phytoplankton was reduced | 12–18% | Energy flow path was interrupted, primary productivity was reduced | [9,22] |
| The primary productivity of the Bohai Sea was reduced | Approximately 150,000 tons of carbon per year | Accounted for 6–8% of the total amount | [14,80] |
| The resource amount of Fenneropenaeus chinensis in the Bohai Sea was reduced | 92% (1990–2020) | Microplastic concentration was positively correlated with juvenile mortality (r = 0.76, p < 0.01) | [82] |
| The competitive advantage of tolerant species was significant | Biomass of polychaetes (e.g., Pygospio elegans) increased by 40–60%, while the density of sensitive species (e.g., Manila clam) decreased by 55–70% | - | [83] |
| The diversity of benthic organisms was reduced | Shannon diversity index decreased from 3.2 to 2.1 | It was significantly negatively correlated with microplastic abundance in sediments (R2 = 0.68) | [29,31] |
5.4. Human Health Exposure Risk
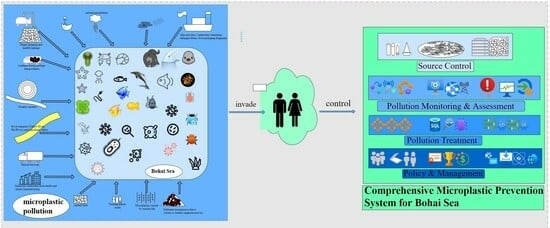
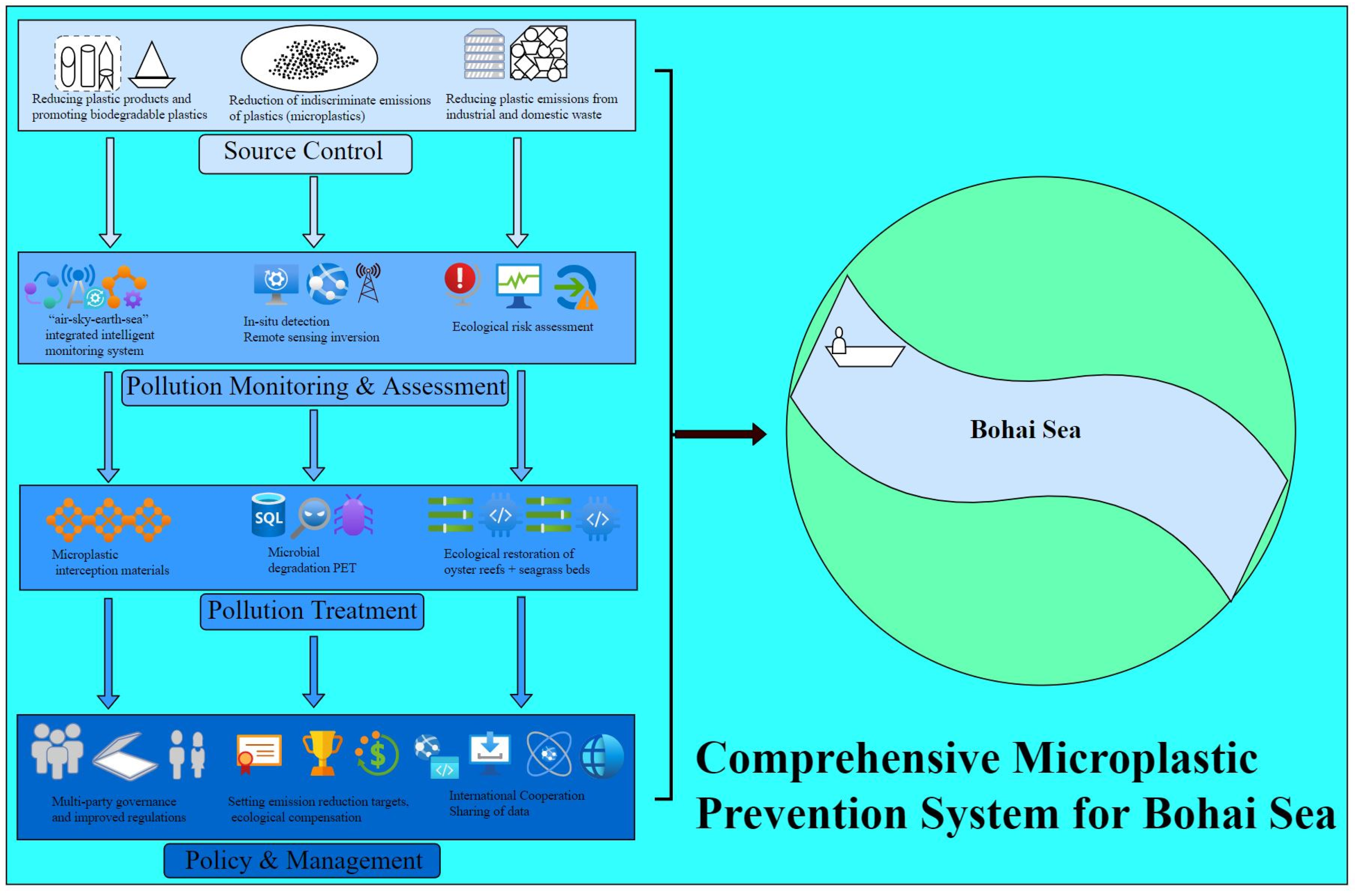
6. Construction of a Comprehensive Prevention and Control System for Microplastic Pollution in the Bohai Sea
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Yang, J.; Xing, Y.; Ling, W.; Liu, K.; Yang, Q.; Ma, H.; Pei, Z.; Wu, T.; et al. The fate of microplastic pollution in the Changjiang River estuary: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 425, 138970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liang, T.; Liu, X.S. Characteristics, distribution patterns and sources of atmospheric microplastics in the Bohai and Yellow Seas, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 17106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, T.T.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Microplastic pollution in Pearl River Networks: Characteristic, potential sources, and migration pathways. Water Res. 2025, 276, 123261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, P.P.; Xiao, J.E.; Liu, H.T.; Niu, Z.G.; Ma, Y.N.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Ma, Y. An inversion model of microplastics abundance based on satellite remote sensing: A case study in the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kong, L.; Li, Z.; Su, Q.; Qu, L.; Wang, X.; Han, J.; Han, J.; Wu, L.; Zhang, N. Distribution characteristics and ecological risk analysis of microplastics in sediments and effluents related to offshore oil and gas activities in the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 206, 116731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Su, Q.Y.; Wei, H.H.; Lin, L.; Huang, L.L. Microplastics in the seawater of the Beibu Gulf, the Northern South China Sea: Occurrence, sources, and ecological risk. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024, 43, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, D.; Loganathan, S.; Sathiyamoorthy, M.; Azamathulla, H.M. Microplastic pollution—A rising threat along an urban lake in the Vellore district of Tamil Nadu, India: Abundance and risk exposure. Water Qual. Res. J. 2025, 60, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.D.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhao, S.; Yan, X.L.; Guo, S.; Liu, Y.L.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J. Long-term pollution status of microplastics in sediment of a typical mariculture area. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Li, J.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Du, S.Y.; Liu, S.T.; Jiao, S.P.; Niu, F.; Tu, J.; Zong, Y.; Wang, X. Microplastics distribution, ecological risk and outflows of rivers in the Bohai rim region of China—A flux model considering small and medium-sized rivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 953, 176035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Wang, X.D.; Jiang, H.Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Zhao, J.M.; Teng, J.; Wang, Q. Vertical distribution of microplastics in sediment columns along the coastline of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhu, X.P.; Shan, E.C.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, C.F.; Sun, W.; Wang, Q. The physiological response of the clam Ruditapes philippinarum and scallop Chlamys farreri to varied concentrations of microplastics exposure. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 200, 116151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.L.; Sun, C.F.; Wang, X.D.; Hou, C.W.; Teng, J.; Zhao, J.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Q. The pollution characteristics and risk assessment of microplastics in mollusks collected from the Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.K.; Ma, L.K.; Qiu, K.C.; Feng, Z.H.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhong, Z.; Cheng, F.; Zhai, T.; Zeng, J.; Huang, W. Characterization and risk assessment of microplastics in laver from the Yueqing Bay. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 193, 106258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, Y.T.; Ge, Y.W.; Wang, R.L.; Xu, W.Q.; Liu, C.H.; Guo, Z.X.; Wang, S.; Jia, H.; Li, Y. Occurrence and migration patterns of microplastics in different tidal zones of tourist beaches: A case study in the Bohai Bay, North China. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.F.; Yang, L.N.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Ma, G.S. Internal and external microplastic exposure in young adults: A pilot study involving 26 college students in Changsha, China. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.L.; Li, W.T.; Xu, C.H.; Qin, Q.S.; Fan, W.J.; Li, X.H.; Zhao, D. Adsorption mechanism of cefradine on three microplastics: A combined molecular dynamics simulation and density functional theory calculation study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jiang, F.H.; Li, J.X.; Cao, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, F.T.; Wang, S.; Sun, C. Interlinked water and sediment microplastics in the Laizhou Bay of China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2024. 43, 446–458. [CrossRef]
- Mai, L.; Bao, L.J.; Shi, L.; Liu, L.; Zeng, E. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons affiliated with microplastics in surface waters of Bohai and Huanghai Seas, China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 834–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelmans, A.A.; Belay, B.M.G.; Mintenig, S.M.; Nor, N.; Redondo-Hasselerharm, P.; Ruijter, V. Towards a rational and efficient risk assessment for microplastics. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Chen, T.; Qian, Z.; Chen, Z. The temporal and spatial distribution and surface morphology of atmospheric microplastics around the Bohai Sea. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2020, 40, 1401–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Li, X.; Hu, W.J.; Yu, S.B.; Li, X.; Lei, L.S.; Yang, F.; Luo, Y. Landscape and risk assessment of microplastic contamination in farmed oysters and seawater along the coastline of China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 470, 134169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wolanski, E.; Dai, Z.; Lambrechts, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, H. Trapping of plastics in semi-enclosed seas: Insights from the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2018, 137, 509–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechselberger, C. From Cradle to Grave: Microplastics—A Dangerous Legacy for Future Generations. Environments 2024, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, K.; Ito, M.; Hano, T.; Ohkubo, N. Estimation of the uptake of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons desorbed from polyethylene microplastics in the digestive tract of the red seabream (Pagrus major) and mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 209, 117216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandsma, S.H.; Vethaak, A.D.; Leslie, H.A.; Vethaak, A.D. Microplastics en route: Field measurements in the Dutch river delta and Amsterdam canals, wastewater treatment plants, North Sea sediments and biota. Environ. Int. 2017, 101, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.Z.; Wang, T.; Li, J.D.; Liu, X.H.; Zhu, Q. Simulation of seasonal transport of microplastics and influencing factors in the China Seas based on the ROMS model. Water Res. 2023, 244, 120493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.L.; Li, J.X.; Hu, J.; Li, X.G.; Sun, C.J. A review of microplastics in China marine waters. J. Ocean. Univ. China 2023, 22, 1326–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Mei, X.; Mi, B.; Yang, H.; Han, Z.-Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lü, W.-C. Current status and cause analysis of microplastic pollution in sea areas in China. China Geol. 2022, 5, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.Y.; Kong, L.N.; Wang, X.M.; Li, Y.X.; Cheng, J.Y.; Han, J.B.; Chen, H.; Zhang, N. Distribution and characteristics of microplastics in sediment at representative dredged material ocean dumping sites, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 193, 115201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Y.; Tian, H.T.; Lv, J.T.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, G.B. Influence of microplastics on the photodegradation of perfluorooctane sulfonamide (FOSA). J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 127, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.H.; Zhang, A.G.; Teng, J.; Yang, X.L.; Yuan, X.T.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X. Pollution characteristics and ecological risk of microplastic in sediments of liaodong bay from the northern Bohai Sea in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 187, 114505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pervez, R.; Lai, Y.S.; Song, Y.J.; Li, X.X.; Lai, Z.P. Impact of microplastic pollution on coastal ecosystems using comprehensive beach quality indices. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 194, 115304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, P.Y.; Zhao, Y.Q.; Zuo, C.X.; Cai, Y.M.; Shen, C.; Ji, B.; Wei, T. The unheeded inherent connections and overlap between microplastics and poly- and perfluoroalkyl substances: A comprehensive review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 878, 163028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.Q.; Lang, M.F.; Wu, R.R.; Zhang, Z.M.; Guo, X.T. A review of the distribution, characteristics and environmental fate of microplastics in different environments of China. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2023, 261, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.B.; Banik, P.; Nur, A.A.; Choudhury, T.R.; Liba, S.I.; Albeshr, M.F.; Yu, J.; Arai, T. Microplastics in fish culture ponds: Abundance, characterization, and contamination risk assessment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1251158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Meng, X.W.; Bao, T.; Liu, B.; Wang, Q.; Jin, J.; Wu, K. Spatial-temporal distribution and ecological risk assessment of microplastics in the Shiwuli River. Water 2023, 15, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Liu, S.S.; Li, Y.; Ouyang, W.; He, M.C.; Liu, X.T.; Lin, C. A review of sources, status, and risks of microplastics in the largest semi-enclosed sea of China, the Bohai Sea. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Lin, Y.; Booth, A.M.; Song, X.K.; Cui, Y.Z.; Xia, B.; Gu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, F.; Cai, M. Fate, source and mass budget of sedimentary microplastics in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Han, L.H.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Jones, K.; Xu, E.G. Missing relationship between meso- and microplastics in adjacent soils and sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 424, 127234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhao, Y.J.; Shan, E.C. Observational and model studies on transport and inventory of microplastics from a leak accident on the beaches of Yantai. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.C.; Zou, X.Q.; Yuan, F.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, C.L.; Fan, Q.Y.; Fu, G.; Yu, W. Can microplastics in offshore waters reflect plastic emissions from coastal regions? Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.C.; Zhao, J.M.; Teng, J.; Ren, J.Y.; Zheng, P.F.; Zhu, X.P.; Liu, Y.; Sun, X.; Yuan, S.; Wang, Q. Seasonal change of microplastics uptake in the pacific oysters Crassostrea gigas cultured in the Yellow Sea and Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, S.Q.; Wu, L.B.; Yang, Y.J.; Yu, X.X.; Liu, Q.X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Vertical distribution and river-sea transport of microplastics with tidal fluctuation in a subtropical estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.X.; Huang, R.Q.; Hu, L.L.; Zhang, C.F.; Xu, X.R.; Song, L.; Wang, Z.; Pan, X.; Christakos, G.; Wu, J. Microplastics distribution in different habitats of Ximen Island and the trapping effect of blue carbon habitats on microplastics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 181, 113912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Yang, F.; Kazmi, S.; Zhao, Y.N.; Chen, M.; Wang, J. A review of microplastic pollution in seawater, sediments and organisms of the chinese coastal and marginal seas. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.H.; Wei, H.H.; Huang, W.; Wu, X.X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Q.F. Occurrence of microplastic pollution in the Beibu Gulf, the Northern South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 821008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Guan, C.Y.; Han, J.; Chai, M.W.; Li, R.L. Microplastics in China Sea: Analysis, status, source, and fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 803, 149887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, M.L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Fan, S.Y.; Zheng, R.Y.; Yu, X. Impacts of terrestrial input on the distribution characteristics of microplastics in the east china sea characterized by chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.L.; Zhen, Y.; Wei, L.L.; Dai, Y.F.; Wang, X.Y.; Tong, S.H.; Zhao, L. Microplastic pollution in finless porpoises and their habitats along the Fujian coast of the east China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1050957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.H.; Zhao, J.; Sun, C.X.; Li, D.Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.Y.; Yue, T.; Xing, B. Interaction and combined toxicity of microplastics and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances in aquatic environment. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wan, L.; Cai, W.Q.; Tang, J.; Wu, Z.J.; Zhang, K.D. Species-specific microplastic enrichment characteristics of scleractinian corals from reef environment: Insights from an in-situ study at the Xisha Islands. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 815, 152845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Wang, Z.Z.; Peng, X.Z.; Su, Y.Y.; Fu, P.C.; Ge, C.J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, L.; Yu, H.; Peng, L. Occurrence and spatial distribution of microplastics, and their correlation with petroleum in coastal waters of Hainan Island, China. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 294, 118636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, K.; Muthuramalingam, S. Global sources, abundance, size, and distribution of microplastics in marine sediments-a critical review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2022, 264, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sethulekshmi, S.; Shriwastav, A. Abundance, morphology, and spatio-temporal variation of microplastics at the beaches of Mumbai, India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2022, 56, 107702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.Y.; Ren, Z.F.; Xu, X.Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L.; Qiu, H.; Cao, X. Oil spills enhanced dispersion and transport of microplastics in sea water and sand at coastal beachheads. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambandam, M.; Dhineka, K.; Sivadas, S.K.; Kaviarasan, T.; Begum, M.; Hoehn, D.; Sivyer, D.; Mishra, P.; Murthy, M. Occurrence, characterization, and source delineation of microplastics in the coastal waters and shelf sediments of the central east coast of India, Bay of Bengal. Chemosphere 2022, 303, 135135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, J.J.; Zhu, X.P.; Sun, C.F.; Teng, J.; Chen, L.M.; Shan, E.; Zhao, J. Microplastics in fish meals: An exposure route for aquaculture animals. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 807, 151049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropin, N.Y.; Rakhmatullina, S.N.; Vorobiev, E.D.; Vorobiev, D.S.; Frank, Y.A. Microplastic Content in the Gastrointestinal Tract of Some Fish Species of Lake Kubenskoe (Vologda Oblast). Inland. Water Biol. 2024, 17, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Yadav, O.; Sarkar, A.; Achari, G.; Slobodnik, J. Environmental exposure to microplastics: A scoping review on potential human health effects and knowledge gaps. BLDE Univ. J. Health Sci. 2020, 5, S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.L.; Wang, Y.Y.; Wang, S.W.; Xie, J.; Han, Q.; Chen, M.Q. Comparing the effects of polystyrene microplastics exposure on reproduction and fertility in male and female mice. Toxicology 2022, 465, 153059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Yoo, K. Microplastic contamination and microbial colonization in coastal area of Busan City, Korea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1030476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhineka, K.; Sambandam, M.; Sivadas, S.K.; Kaviarasan, T.; Pradhan, U.; Begum, M.; Mishra, P.; Murthy, M. Characterization and seasonal distribution of microplastics in the nearshore sediments of the south-east coast of India, Bay of Bengal. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2022, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.P.; Chen, L.L.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Y.R.; Ma, Y.; Chau, H.S.; Tao, D.; Wu, C.; Li, C.T.; Lam, P.K.S. Microplastic occurrence in the Northern South China Sea, a case for pre and post cyclone analysis. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Tu, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.B.; Vogts, A.; Plewe, S.; Pan, X.; Luo, Y.; Waniek, J. Biofilm enhances the copper (ii) adsorption on microplastic surfaces in coastal seawater: Simultaneous evidence from visualization and quantification. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 853, 158217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedik, K.; Eryasar, A.R.; Ozturk, R.C.; Mutlu, E.; Karaoglu, K.; Sahin, A.; Ozvarol, Y. The broad-scale microplastic distribution in surface water and sediments along northeastern mediterranean shoreline. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.J.; Lao, Q.B.; Liu, M.Y.; Huang, P.; Chen, B.; Zhou, X.; Chen, P.; Chen, K.; Song, Z.; Cai, M. Impact of intensive mariculture activities on microplastic pollution in a typical semi-enclosed bay: Zhanjiang Bay. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 176, 113402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Yuan, H.; Tang, J.; Cai, X.F.; Yang, B. Preliminary investigation of microplastics in the production process of sea salt sourced from the Bohai Sea, China, using an optimised and consistent approach. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2021, 38, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.L.; Cao, L.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.H.; Dou, S.Z. Assessment of plastic pollution in the Bohai Sea: Abundance, distribution, morphological characteristics and chemical components. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, M.; Hano, T.; Kono, K.; Ohkubo, N. Desorption of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from polyethylene microplastics in two morphologically different digestive tracts of marine teleosts: Gastric red seabream (Pagrus major) and agastric mummichog (Fundulus heteroclitus). Environ. Pollut. 2022, 308, 119589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.F.; Wang, G.Y.; Yang, Y.Y.; Zhu, W.M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ouyang, Z.Z.; Guo, X. The occurrence and effect of altitude on microplastics distribution in agricultural soils of Qinghai Province, northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.P.; Ran, W.; Teng, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Hou, C.W.; Zhao, J.M.; Qi, X.T.; Wang, Q. Microplastic pollution in nearshore sediment from the Bohai Sea coastline. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 107, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Tu, C.; Yang, J.; Fu, C.C.; Li, Y.; Waniek, J.J. Trapping of microplastics in halocline and turbidity layers of the semi-enclosed Baltic Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 761566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Li, B.J.; Yu, W.W.; Zou, X.Q. Microplastic pollution and quantitative source apportionment in the Jiangsu coastal area, china. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 166, 112237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Xu, X.P.; Yue, B.Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.Z.; Xu, X.M.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. A novel thermoanalytical method for quantifying microplastics in marine sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 144316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Yu, Y.Y.; Wu, H.W.; Wu, W.N.; Wang, L.; An, L.H.; Cai, W. Microplastics in spotted seal cubs (Phoca largha): Digestion after ingestion? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.Z.; Cui, T.F.; Wu, H.W.; Leblanc, G.A.; Wang, F.F.; An, L.H. A proposed nomenclature for microplastic contaminants. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 172, 112960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.X.; Wang, W.M.; Liu, H.; Xu, X.H.; Xia, J.H. A review on the occurrence, distribution, characteristics, and analysis methods of microplastic pollution in ecosystems. Env. Pollut. Bioavail 2021, 33, 227–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reineccius, J.; Bresien, J.; Waniek, J.J. Separation of microplastics from mass-limited samples by an effective adsorption technique. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 788, 147881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, X.P.; Hou, C.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Teng, J.; Zhang, C.; Tan, H.; Shan, E.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhao, J.M. Microplastic uptake in commercial fishes from the Bohai Sea, China. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qun, L.; Xiujuan, S.; Jun, W.; Zhongyi, L.I.; Amp, T.Y. Changes in Chinese Shrimp (Fenneropenaeus chinensis) Carrying Capacity of the Bohai Sea. Prog. Fish. Sci. 2018, 39, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.F.; Wu, H.W.; Wu, W.N.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.L.; An, L.H.; Xu, Q.J. Microplastic characteristics in organisms of different trophic levels from Liaohe Estuary, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 789, 148027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; You, J.A.; Li, Y.J.; Zhang, J.D.; He, Y.; Breider, F.; Tao, S.; Liu, W.X. Insights into the horizontal and vertical profiles of microplastics in a river emptying into the sea affected by intensive anthropogenic activities in Northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 779, 146589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhu, X.P.; Shan, E.C.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Q. Toxic effects of exposure to microplastics with environmentally relevant shapes and concentrations: Accumulation, energy metabolism and tissue damage in oyster Crassostrea gigas. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Saha, M.; Rathore, C.; Suneel, V.; Ray, D.; Naik, A.; Unnikrishnan, K.; Dhivya, M.; Daga, K. Spatial and seasonal variation of microplastics and possible sources in the estuarine system from central west coast of India. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhu, X.P.; Shan, E.C.; Wang, Q. Oxidative stress biomarkers, physiological responses and proteomic profiling in oyster (Crassostrea gigas) exposed to microplastics with irregular-shaped pe and pet microplastic. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.H.; Sun, X.J. Research status of microplastics pollution in abiotic environment in china. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Advances in Energy, Environment and Chemical Engineering (AEECE), Jinan, China, 19–21 June 2020; IOP: Philadelphia, PA, USA; pp. 1–5.
- Li, J.J.; Huang, W.; Xu, Y.J.; Jin, A.M.; Zhang, D.D.; Zhang, C.F. Microplastics in sediment cores as indicators of temporal trends in microplastic pollution in andong salt marsh, Hangzhou Bay, China. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2020, 35, 101149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Zhang, S.F.; Zhao, Q.; Qu, L.; Ma, D.Y.; Wang, J.Y. Spatio-temporal distribution of plastic and microplastic debris in the surface water of the Bohai Sea, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 158, 111343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.D.; Cai, C.Y.; He, Y.; Chen, L.Y.; Xiong, X.; Huang, H.J.; Tao, S.; Liu, W.X. Occurrence and characteristics of microplastics in the haihe river: An investigation of a seagoing river flowing through a megacity in northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, S.; Razis, A.; Shaari, K.; Amal, M.; Saad, M.Z.; Isa, N.M.; Nazarudin, M.F.; Zulkifli, S.Z.; Sutra, J.; Ibrahim, M. Microplastics pollution as an invisible potential threat to food safety and security, policy challenges and the way forward. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Hou, C.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Wu, X.F.; Wang, Y.J.; Yi, Y.J. The flowing of microplastics was accelerated under the influence of artificial flood generated by hydropower station. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 255, 120174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, D.D.; Chen, C.M.; Qi, H.Y.; Fan, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.Z.; Peng, L.C.; Li, B. Occurrences and distribution of microplastic pollution and the control measures in China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 153, 110963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, J.; Zhao, J.M.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, B.; Koelmans, A.A.; Wu, D.; Gao, M.; Sun, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. A systems analysis of microplastic pollution in Laizhou Bay, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 745, 140815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fok, L.; Lam, T.; Li, H.X.; Xu, X.R. A meta-analysis of methodologies adopted by microplastic studies in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 135371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ling, W.; Hou, C.; Yang, J.; Xing, Y.; Lu, Q.; Wu, T.; Gao, Z. Global Distribution Characteristics and Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics in Aquatic Organisms Based on Meta-Analysis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 491, 137977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Watershed Type | Surface Water Concentration (Particles/m3) | Concentration in Bottom Waters (Particles/m3) | Main Microplastic Types | Main Particle Size Range (mm) | Main Sources | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estuary | 5–15 | 3–10 | Fibrous (40–60%), fragmented (20–30%) | 0.1–5 | Riverine inputs, vessel activity, wastewater treatment plant tailwater discharges | [42] |
| Harbor | 5–15 | 3–10 | Fibrous (40–60%), fragmented (20–30%) | 0.1–3 | Vessel activity, industrial discharges, shoreline litter inputs | [43] |
| Mariculture area | 3–10 | 2–6 | Fibrous (50%), Fragmented (30%) | 0.5–3 | Aging of aquaculture facilities, release of plastic debris | [44] |
| Offshore area | 0.5–2 | 0.5–3 | Granular (30%), Fragmented (20%) | 0.5–3 | Atmospheric deposition, ocean circulation transport | [45] |
| Summer | 3–10 | 2–6 | Fibrous (40%), Fragmented (30%) | 0.1–5 | Increased surface runoff inputs, enhanced tourism activities | [46] |
| Winter | 1–5 | 3–8 | Fibrous (50%), Fragmented (40%) | <1 | Enhanced microplastic deposition, increased sediment abundance | [47] |
| Bohai Bay | 3–8 | 2–5 | Fiber Class (40%), Fragment Class (30%) | 0.1–5 | Strong mixing of water bodies, significant PE, PP plastic pollution | [48] |
| Deep water (>30 m) | 0.5–1.5 | 2–5 | Fragment Class (50–70%) | <1 | Sedimentation of saline stratum, long-term degradation of historical plastic debris | [49] |
| Biological Category | Intake Pathway | Body Microplastic Content (Particles/Individual) | Main Microplastic Types | Main Distribution Sites of Microplastics | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Demersal fish | Ingestion of benthic organisms | 3–8 | Fragments | Digestive tract, liver | [51] |
| Pelagic fish | Misuse of microplastics in surface waters | 1–3 | Fibers | Digestive tract, muscle | [52] |
| Small yellow croaker | Accidental ingestion or food chain transfer | - | - | Liver (detection rate 5–10%) | [53,54] |
| Cultured oyster | Filter feeding | 5–15 | Fiber class (>70%) | Digestive tract | [55] |
| Wild oyster | Filter feeding | 2–5 | Fiber class (>70%) | Digestive tract | [56] |
| Plankton | Misuse of microplastics | 1–3 | Pellet class, Fiber class | Digestive tract | [57] |
| Microplastic Type | Main Source | Morphological Characteristics | Host Organisms | Migration Type | Driving Force | Migration-Transformation Mechanism | Research Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Textile fibers, fishing nets | Length of 0.5–5 mm, highly flexible, easily entangled in the digestive tract | Pelagic fish (Spanish mackerel, mackerel), bivalves (oysters, mussels) | Horizontal migration | Tidal action | Nearshore microplastics were resuspended and deposited repeatedly, forming pollution retention zones | Nearshore pollution accumulation was enhanced | [2,6,59] |
| Fragment Type | Degraded plastic packaging, industrial plastic waste | Sharp edges, easily caused tissue damage | Demersal fish (eel, flounder), filter-feeding organisms (bivalves, zooplankton) | Horizontal migration | Circulation transport | Microplastics were transported from northern Bohai Bay to central Bohai by the Liaodong coastal current, while the Lubei coastal current carried them southward to the Yellow Sea | Microplastics were transported across regions | [37,60] |
| Pellet Type | Industrial plastic raw materials, personal care microbeads | Diameter < 1 mm, easily ingested by plankton | Zooplankton (copepods, cladocerans), filter-feeding bivalves (mussels, scallops) | Vertical sinking | Biological pump | Microplastics were ingested by plankton and settled into deep water via fecal pellets | 80% of microplastics were transferred through the biological pump | [61,62,63] |
| Pellet Type | Industrial plastic raw materials, personal care microbeads | Diameter < 1 mm, easily ingested by plankton | Zooplankton (copepods, cladocerans), filter-feeding bivalves (mussels, scallops) | Vertical sinking | Flocculation effect | Microplastics aggregated with organic matter, accelerating their sinking to the seabed | The sinking rate increased by two to three times | [64,65,66] |
| Category | Example Species | Ingestion Pathway | Microplastic Content | Main Particle Size | Tissue Distribution Characteristics | Biomagnification Effect | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filter-feeding organisms | Crassostrea gigas, Ruditapes philippinarum | Water filtration | 5–15 particles/individual | - | Predominantly in the digestive tract (>90%) | - | [16,67] |
| Predatory organisms | Larimichthys polyactis, Paralichthys olivaceus | Ingestion of contaminated prey | 2–8 particles/individual | <1 mm | 15–30% were detected in the liver and gills | - | [68,69,70,71] |
| Benthic-feeding organisms | Apostichopus japonicus | Sediment ingestion | 3–5 particles/g gut content | 80% were fibers | Accumulated in the digestive tract | - | [72] |
| Zooplankton | Copepods | Accidental ingestion | 0.5–2 particles/individual | 50–200 μm | Found in the digestive tract | 2.6–3.8 | [14,72] |
| Primary consumers | Atheriniformes | Feeding on zooplankton | 3–5 particles/individual | - | Found in the digestive tract | 2.6–3.8 | [22,43,73] |
| Top predators | Scomberomorus niphonius | Feeding on primary consumers | 8–15 particles/individual | - | Found in the digestive tract | 2.6–3.8 | [74] |
| Cross-organ migration | Danio rerio | Nanoplastic penetration into the circulatory system | - | 100 nm | Oxidative stress response in liver cells | - | [75] |
| Mammals | Seals | Ingestion of contaminated prey | - | - | Over 90% accumulated in the intestine | - | [76] |
| Toxicity Category | Mechanism | Example Species | Effects Observed | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Physical Damage | Mechanical obstruction | Fish (Lateolabrax japonicus) | Reduced feeding efficiency by 20–40% due to digestive tract blockage | [73] |
| Mechanical obstruction | Juvenile Lateolabrax japonicus | Survival rate decreased by 35% compared to the control group | [49,75] | |
| Tissue abrasion | Fish gill epithelial cells | Sharp-edged microplastics caused epithelial scratches, disrupting osmoregulation | [34,76] | |
| Tissue abrasion exposure | Mytilus edulis (Mussels) | Hemolymph pH decreased by 0.3–0.5 units due to microplastic | [77,78] | |
| Chemical Synergistic Toxicity | Pollutant carrier | - | Microplastics had a surface area of 1.2–3.5 m2/g, adsorbing PAHs at 0.8–2.3 μg/g | [79] |
| Pollutant carrier | - | Lead and cadmium concentrations on Bohai Sea microplastics were 45–120 mg/kg and 8–25 mg/kg, 2–4 times higher than background sediments | [17,32] | |
| Endocrine disruption | Paralichthys olivaceus (Flounder) | BPA-adsorbed polyethylene microplastics increased plasma estradiol levels by 180%, reducing gonadal development index by 22% | [6,79] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Li, H.; Ling, W.; Li, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, P. Sources, Status, and Potential Risks of Microplastics in Marine Organisms of the Bohai Sea: A Systematic Review. Toxics 2025, 13, 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050400
Yang J, Li H, Ling W, Li Y, Zhang K, Zhang P. Sources, Status, and Potential Risks of Microplastics in Marine Organisms of the Bohai Sea: A Systematic Review. Toxics. 2025; 13(5):400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050400
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jian, Hongxia Li, Wei Ling, Yifei Li, Kangkang Zhang, and Pu Zhang. 2025. "Sources, Status, and Potential Risks of Microplastics in Marine Organisms of the Bohai Sea: A Systematic Review" Toxics 13, no. 5: 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050400
APA StyleYang, J., Li, H., Ling, W., Li, Y., Zhang, K., & Zhang, P. (2025). Sources, Status, and Potential Risks of Microplastics in Marine Organisms of the Bohai Sea: A Systematic Review. Toxics, 13(5), 400. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13050400