Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- 75% (w/w) E. crassipes (33.75 g) and 25% of iron (III) chloride (11.25 g) (EC1)
- 85% (w/w) E. crassipes (38.25 g) and 15% of iron (III) chloride (6.75 g) (EC2)
- 95% (w/w) E. crassipes (42.75 g) and 5% of iron (III) chloride (2.25 g) (EC3)
3. Results
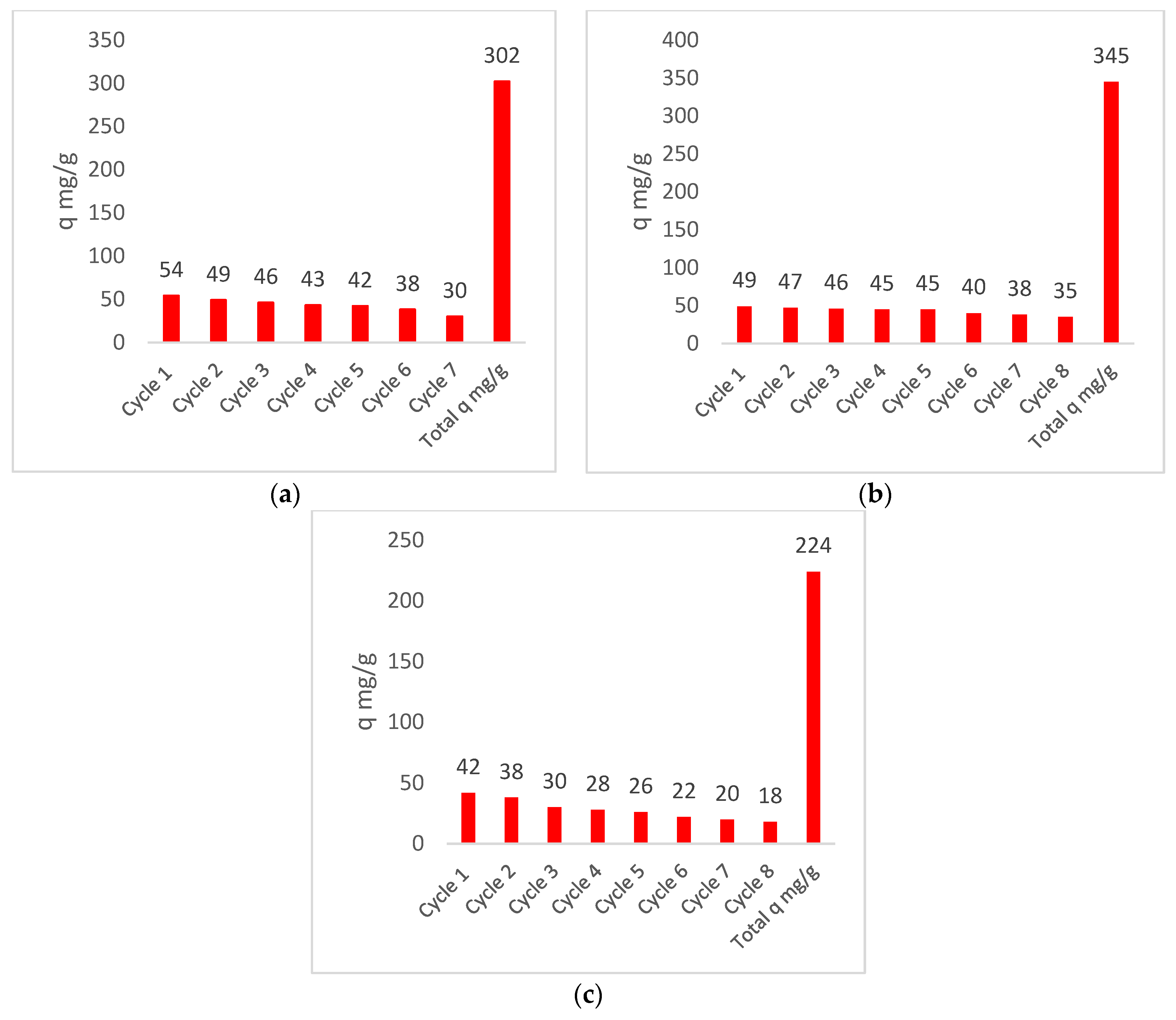
| Biomass | Elutions | Kf (cm/min) | Volume Goal (L) | Time Break (min) | (1/s) | Equation–Isotherm | qm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (1) | 1 | 0.6 | 4.4 | 480 | 0.017 | Langmuir | 54 |
| 2 | 0.58 | 4.2 | 460 | 0.018 | Langmuir | 49 | |
| 3 | 0.57 | 3.9 | 440 | 0.019 | Langmuir | 46 | |
| 4 | 0.55 | 3.7 | 400 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 43 | |
| 5 | 0.45 | 3.4 | 370 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 42 | |
| 6 | 0.43 | 3.0 | 350 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 38 | |
| 7 | 0.42 | 2.4 | 280 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 30 | |
| Total qm | 302 | ||||||
| EC (2) | 1 | 0.51 | 4.1 | 458 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 49 |
| 2 | 0.50 | 4.0 | 450 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 47 | |
| 3 | 0.45 | 3.5 | 410 | 0.022 | Langmuir | 46 | |
| 4 | 0.44 | 3.4 | 390 | 0.022 | Freundlich | 45 | |
| 5 | 0.39 | 3.3 | 370 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 45 | |
| 6 | 0.38 | 3.3 | 350 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 40 | |
| 7 | 0.37 | 3.0 | 280 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 38 | |
| 8 | 0.35 | 2.8 | 260 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 35 | |
| Total qm | 345 | ||||||
| EC (3) | 1 | 0.50 | 3.7 | 450 | 0.022 | Langmuir | 42 |
| 2 | 0.49 | 3.2 | 440 | 0.023 | Langmuir | 38 | |
| 3 | 0.48 | 3.0 | 380 | 0.023 | Langmuir | 30 | |
| 4 | 0.45 | 2.7 | 360 | 0.024 | Freundlich | 28 | |
| 5 | 0.44 | 2.2 | 280 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 26 | |
| 6 | 0.40 | 1.9 | 240 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 22 | |
| 7 | 0.40 | 1.5 | 220 | 0.021 | Langmuir | 20 | |
| 8 | 0.39 | 1.5 | 170 | 0.020 | Langmuir | 18 | |
| Total qm | 224 |
| Research | Biomass | Contaminat | qm mg/g | Cicles of Elutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [66] | Microcrystalline Cellulose core | Cu (II) | 423 | 5 |
| [67] | Aminated Cellulose | Pb (II) | 609 | 5 |
| [68] | Sugarcane Bagasse | Pb (II) | 333 | 3 |
| [69] | Polyacrylicacid/carboxymethyl cellulose/activated carbon | Cu (II) | 193 | 3 |
| [70] | Supramolecular cellulose-based | Co (II) | 158 | 4 |
| [71] | Chitosan/Cellulose-Fe(III) | Cr (VI) | 391 | 6 |
| [72] | β–cyclodextrin modified magnetic cellulose | Pb (II) | 200 | 3 |
| [73] | carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel | Cu (II) | 293 | 4 |
| [74] | cellulose-derived poly(amidoxime) | Cr (III) | 202 | 3 |
| [75] | Cellulose-ZIF hybrid | Pb (II) | 354 | 4 |
| [76] | Biomass-based aerogel | Cu (II) | 380 | 5 |
| [77] | Alginate-polyvinyl alcohol | Cr (VI) | 86 | 4 |
| [78] | Cellulose Crassipes xantate | Cr (VI) | 59 | 4 |
| [79] | Salvinia molesta | Cr (VI) | 33 | - |
| [80] | (Eichhornia crassipes) roots | Pb (II) | 40 | 2 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paul, A.; Dey, S.; Ram, D.K.; Das, A.P. Hexavalent chromium pollution and its sustainable management through bioremediation. Geomicrobiol. J. 2024, 41, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, K.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Lin, L.; Feng, H.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, Z. Screening of cadmium-chromium-tolerant strains and synergistic remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil using king grass combined with highly efficient microbial strains. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sable, H.; Singh, V.; Kumar, V.; Roy, A.; Pandit, S.; Kaur, K.; Rustagi, S.; Malik, S. Toxicological and bioremediation profiling of nonessential heavy metals (mercury, chromium, cadmium, aluminium) and their impact on human health: A review. Toxicol. Anal. Clin. 2024, 36, 205–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, T.P.; Samdani, M.S.; Jhanani, G.K.; Sathiyamoorthi, E.; Lee, J. Metal accumulation and genetic adaptation of Oryza sativa to Cadmiun and Chromium heavy metal stress: A hydroponic and RAPD analyses. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Development of a treatment for water contaminated with Cr (VI) using cellulose xanthogenate from E. crassipes on a pilot scale. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Aguilar, A.M.L. Designing, Modeling and Developing Scale Models for the Treatment of Water Contaminated with Cr (VI) through Bacterial Cellulose Biomass. Water 2024, 16, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and development of a biotreatment of E. crassipes for the decontamination of water with Chromium (VI). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, T.; Shah, G.M.; Zeb, B.S.; Gul, I.; Bibi, S.; Hussain, Z.; Irshad, M. Phytoremediation potential and vegetation assessment of plant species growing on multi-metals contaminated coal mining site. Environ. Res. Commun. 2024, 6, 055006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Dong, X.; Fan, Y.; Deng, C.; Yang, D.; Chen, R.; Chai, W. Performance of coal slime-based silicon fertilizer in simulating lead-contaminated soil: Heavy metal solidification and multi-nutrient release characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 478, 135453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniagua-López, M.; García-Robles, H.; Aguilar-Garrido, A.; Romero-Freire, A.; Lorite, J.; Sierra-Aragón, M. Vegetation establishment in soils polluted by heavy metal (loid) s after assisted natural remediation. Plant Soil 2024, 497, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.A.B. The Design of a Process for Adsorbing and Eluting Chromium (VI) Using Fixed-Bed Columns of E. crassipes with Sodium Tripolyphosphate (TPP). Water 2024, 16, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño Sayago, U.F. Diseño y evaluación de un biosistema de tratamiento a escala piloto de aguas de curtiembres a través de la Eichhornia crassipes. Rev. Colomb. Biotecnol. 2016, 18, 74–81. [Google Scholar]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Castro, Y.P.; Rivera, L.R.C.; Mariaca, A.G. Estimation of equilibrium times and maximum capacity of adsorption of heavy metals by E. crassipes (review). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayago, U.F.C. The design of a sustainable industrial wastewater treatment system and the generation of biohydrogen from E. crassipes. Polymers 2024, 16, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.S.; Meitei, M.D.; Upadhyay, K.K.; Chanda, R.; Mawi, R.; Singh, N.S.; Brearley, F.Q.; Tripathi, S.K. Bioremediation of Toxic Metals Using Aquatic Macrophytes: Challenges and Opportunities. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2024, 52, e202400273. [Google Scholar]
- Zeb, B.S.; Mahmood, Q.; Irshad, M.; Zafar, H.; Wang, R. Sustainable treatment of combined industrial wastewater: Synergistic phytoremediation with Eichhornia crassipes, Pistia stratiotes, and Arundo donax in biofilm wetlands. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2024, 27, 128–134. [Google Scholar]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Gómez-Caicedo, M.I.; Mercado Suárez, Á.L. Design of a sustainable system for wastewater treatment and generation of biofuels based on the biomass of the aquatic plant Eichhornia crassipes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11068. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, J.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, P.; Kumar, P. Kinetics and prediction modeling of heavy metal phytoremediation from glass industry effluent by water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 5481–5492. [Google Scholar]
- Lima, H.D.P.; Asencios, Y.J. Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms (natural or carbonized) as biosorbent to remove pollutants in water. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 750. [Google Scholar]
- Tabrez, S.; Zughaibi, T.A.; Javed, M. Water quality index, Labeo rohita, and Eichhornia crassipes: Suitable bio-indicators of river water pollution. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 75–82. [Google Scholar]
- Carreño Sayago, U.F.; Piñeros Castro, Y.; Conde Rivera, L.R. Design of a fixed-bed column with vegetal biomass and its recycling for Cr (VI) treatment. Recycling 2022, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zawahry, M.M.; Abdelghaffar, F.; Abdelghaffar, R.A.; Hassabo, A.G. Equilibrium and kinetic models on the adsorption of Reactive Black 5 from aqueous solution using Eichhornia crassipes/chitosan composite. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 136, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaballah, M.S.; Ismail, K.; Aboagye, D.; Ismail, M.M.; Sobhi, M.; Stefanakis, A.I. Effect of design and operational parameters on nutrients and heavy metal removal in pilot floating treatment wetlands with Eichhornia crassipes treating polluted lake water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 25664–25678. [Google Scholar]
- Koley, A.; Bray, D.; Banerjee, S.; Sarhar, S.; Thahur, R.G.; Hazra, A.K.; Mandal, N.C.; Chaudhury, S.; Ross, A.B.; Camargo-Valero, M.A.; et al. Water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) a sustainable strategy for heavy metals removal from contaminated waterbodies. In Bioremediation of Toxic Metal(loid)s; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 95–114. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, H.L.; Erdem, H.; Sahin, M.; Erdem, M. Iron-incorporated activated carbon synthesis from biomass mixture for enhanced arsenic adsorption. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.X.; Yan, L.; Zhou, X.H.; Huang, S.T.; Liang, J.Y.; Zhang, W.X.; Guo, Z.W.; Guo, P.R.; Qian, W.; Kong, L.J.; et al. Simultaneous adsorption of Cr (VI) and phenol by biochar-based iron oxide composites in water: Performance, kinetics and mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125930. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Wang, W.; Liang, F.; Zhang, W.X. Heavy metal removal using nanoscale zero-valent iron (nZVI): Theory and application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 322, 163–171. [Google Scholar]
- Abdul-Raheim, A.R.M.; El-Saeed Shimaa, M.; Farag, R.K.; Abdel-Raouf Manar, E.; Reem, K.F.; Abdel-Raouf Manar, E. Low cost biosorbents based on modified starch iron oxide nanocomposites for selective removal of some heavy metals from aqueous solutions. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2016, 7, 402–409. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Yang, H.; Na, Z.; Lin, K. A novel biodegradable arsenic adsorbent by immobilization of iron oxyhydroxide (FeOOH) on the root powder of long-root Eichhornia crassipes. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 258–266. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.; Kim, T.K.; Zoh, K.D. Removal mechanism of heavy metal (Cu, Ni, Zn, and Cr) in the presence of cyanide during electrocoagulation using Fe and Al electrodes. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 33, 101109. [Google Scholar]
- Worch, E. Adsorption Technology in Water Treatment: Fundamentals, Processes, and Modeling; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136732. [Google Scholar]
- Inglezakis, V.J.; Fyrillas, M.M.; Stylianou, M.A. Two-phase homogeneous diffusion model for the fixed bed sorption of heavy metals on natural zeolites. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 266, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavand, M.; Asasian, N.; Soleimani, M.; Kaghazchi, T.; Bardestani, R. Film-pore-[concentration-dependent] surface diffusion model for heavy metal ions adsorption: Single and multi-component systems. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauletto, P.S.; Dotto, G.L.; Salau, N.P.G. Diffusion mechanisms and effect of adsorbent geometry on heavy metal adsorption. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 157, 182–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Feng, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, R.; Ju, J.; Liu, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B. Adsorption of heavy metal ions by iron tailings: Behavior, mechanism, evaluation and new perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmegeed, A.F.; Sayed, M.; Abbas, M.; Moniem, S.M.A.; Farag, R.S.; Sayed, A.Z.; Naga, S.M. Hydroxyapatite-magnetite nanocomposites: Synthesis and superior adsorption properties for lead ion removal, with insights into intraparticle diffusion, kinetic modeling, and phase dependency. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 36074–36087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofomaja, A.E.; Naidoo, E.B.; Pholosi, A. Intraparticle diffusion of Cr (VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: A comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S. Afr. J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 32, 39–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.; Hu, T.; Zhai, Y.; Qin, H.; Aliyeva, J.; Zhang, H. Fungal cell with artificial metal container for heavy metals biosorption: Equilibrium, kinetics study and mechanisms analysis. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, A.; Abushaikha, A.; Allen, S.J.; McKay, G. Ion exchange homogeneous surface diffusion modelling by binary site resin for the removal of nickel ions from wastewater in fixed beds. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 358, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, G.; Gómez, E.; Miguel, B.; Hidalgo, A.M.; Gómez, M.; Murcia, M.D.; Guzmán, M.A. Feasibility of adsorption kinetic models to study carrier-mediated transport of heavy metal ions in emulsion liquid membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, W.N.W.; Syah, M.I.A.I.; Abd Muhet, N.H.; Bakar, N.H.A.; Yusop, H.M.; Samah, N.A. Adsorption behavior of heavy metal ions by hybrid inulin-TEOS for water treatment. Civ. Eng. J. 2022, 8, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Development of a wastewater treatment system contaminated with Cr (VI) through vegetable biomass modified with TIO2. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 6521–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C. Design and Development of a Pilot-Scale Industrial Wastewater Treatment System with Plant Biomass and EDTA. Water 2023, 15, 3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros Ballesteros, V. Recent advances in the treatment of industrial wastewater from different celluloses in continuous systems. Polymers 2023, 15, 3996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Jeon, E.K.; Baek, K. Role of reducing agent in extraction of arsenic and heavy metals from soils by use of EDTA. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, G.; He, Q.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, W.; Qian, T.; Wu, Q. Effect of mixed chelators of EDTA, GLDA, and citric acid on bioavailability of residual heavy metals in soils and soil properties. Chemosphere 2018, 209, 776–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Dai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Gao, Q.; Dai, Y.; Xia, F.; Zhang, X. EDTA-based adsorbents for the removal of metal ions in wastewater. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 434, 213809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, G.; Wang, T. Effective removal of the heavy metal-organic complex Cu-EDTA from water by catalytic persulfate oxidation: Performance and mechanisms. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 314, 128119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, R.R.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.G.; Hong, S.M.; Sawant, S.Y.; Lee, S.M. Efficient removal of hazardous lead, cadmium, and arsenic from aqueous environment by iron oxide modified clay-activated carbon composite beads. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 162, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Tsang, E.P. Biosynthesized iron nanoparticles in aqueous extracts of Eichhornia crassipes and its mechanism in the hexavalent chromium removal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 399, 322–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benítez, L.T.; Tovar, C.T.; Bolívar, W.M.; Ortiz, Á.V. Estudio de modificación química y física de biomasa (Citrus sinensis y Musa paradisiaca) para la adsorción de metales pesados en solución. Rev. Luna Azul 2014, 39, 124–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañizares-Villanueva, R.O. Biosorción de metales pesados mediante el uso de biomasa microbiana. Rev. Latinoam. Microbiol.-Mex. 2000, 42, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Shim, Y.S.; Kim, Y.K.; Kong, S.H.; Rhee, S.W.; Lee, W.K. The adsorption characteristics of heavy metals by various particle sizes of MSWI bottom ash. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Júnior, W.N.; Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Competitive fixed-bed biosorption of Ag (I) and Cu (II) ions on Sargassum filipendula seaweed waste. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 36, 101294. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Shi, N.; Pan, W.P. Insight into mass transfer mechanism and equilibrium modeling of heavy metals adsorption on hierarchically porous biochar. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 287, 120558. [Google Scholar]
- Abiodun, O.A.O.; Oluwaseun, O.; Oladayo, O.K.; Abayomi, O.; George, A.A.; Opatola, E.; Orah, R.F.; Isukuru, E.J.; Ede, I.C.; Oluwayomi, O.T.; et al. Remediation of heavy metals using biomass-based adsorbents: Adsorption kinetics and isotherm models. Clean Technol. 2023, 5, 934–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wedler, C.; Span, R. A pore-structure dependent kinetic adsorption model for consideration in char conversion–Adsorption kinetics of CO2 on biomass chars. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2021, 231, 116281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Aguilar, A.M.L. Bacterial Cellulose-Derived Sorbents for Cr (VI) Remediation: Adsorption, Elution, and Reuse. Polymers 2024, 16, 2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreño-Sayago, U.F. Development of microspheres using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) for treatment of contaminated water with Cr (VI). Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 4735–4746. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Kumar, S.; Panghal, V. Adsorption of chromium (Cr6+) on dead biomass of Salvinia molesta (Kariba weed) and Typha latifolia (broadleaf cattail): Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic study. Appl. Water Sci. 2021, 11, 149. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, A.C.D.; do Amaral Sobrinho, N.M.B.; dos Santos, F.S.; dos Santos, A.M.; Pereira, A.C.C.; Lima, E.S.A. Biosorption of toxic metals by water lettuce (Pistia stratiotes) biomass. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2017, 228, 156. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Zhan, J.; Chen, B.; Meng, X.; Pan, X. Removal of Pb, Zn, Cu, and Cd by two types of Eichhornia crassipes. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2016, 33, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Kang, Y.; Ma, H.; Dong, J.; Wang, Y.; Kuang, S. Efficient removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions using Mn-doped FeOOH: Performance and mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2023, 231, 116161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Min, X.; Ke, Y.; Lin, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Peng, N.; Yan, X.; Luo, S.; Wu, J.; et al. Recent progress in understanding the mechanism of heavy metals retention by iron (oxyhydr) oxides. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarak, M.F.; Zayed, A.M.; Ahmed, H.A. Carbon/carborundum@ microcrystalline cellulose core shell nano-composite: Synthesis, characterization and application for heavy metals adsorption from aqueous solutions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 182, 114896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nawah, J.Y.; El-Khouly, A.S. Characterization and Adsorption Behavior of Newly Synthesized Aminated Cellulose with Jeffamine EDR148 Towards Ni (II), Cu (II), and Pb (II) Heavy Metal Ions. Polymers 2025, 17, 255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xie, Z.; Wen, J.; Tang, T.; Jiang, L.; Hu, G.; Li, M. Synthesis of Cellulose–Poly (Acrylic Acid) Using Sugarcane Bagasse Extracted Cellulose Fibres for the Removal of Heavy Metal Ions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, X.; Xie, H.; Li, X.; Hao, C. Polyacrylic acid/carboxymethyl cellulose/activated carbon composite hydrogel for removal of heavy metal ion and cationic dye. Cellulose 2022, 29, 483–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Shao, G.; Qin, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Liz, Z.; Fu, Y. Supramolecular cellulose-based heavy metal adsorbent for efficient and accurate removal of cobalt (II) for water treatment. React. Funct. Polym. 2024, 194, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.M.; Hossain, M.S.; Khalil, N.A.; Zulkifli, M.; Arafath, M.A.; Shaharun, M.S.; Ayub, R.; Yahaya, A.N.; Ismail, N. Adsorptive elimination of heavy metals from aqueous solution using magnetic chitosan/cellulose-Fe (III) composite as a bio-sorbent. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Wu, Z.; Tian, X.; An, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Deng, F.; Meng, X.; Qu, J. Concurrent elimination and stepwise recovery of Pb (II) and bisphenol A from water using β–cyclodextrin modified magnetic cellulose: Adsorption performance and mechanism investigation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Deng, H.; Wang, W.; Hu, L.; Ye, S.; Fu, J.; Zhang, S. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Cu (II) by red mud/polyacrylic acid/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogel. Arab. J. Chem. 2025, 18, 106067. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.; Qu, T.; Irshad, M.K.; Shang, J. Simultaneous removal of Cd (II) and As (III) from co-contaminated aqueous solution by α-FeOOH modified biochar. Biochar 2020, 2, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhamid, H.N.; Sultan, S.; Mathew, A.P. Binder-free Three-dimensional (3D) printing of Cellulose-ZIF8 (CelloZIF-8) for water treatment and carbon dioxide (CO2) adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 468, 143567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ke, Y.; Shang, Q.; Yang, X.; Wang, D.; Liao, G. Fabrication of multifunctional biomass-based aerogel with 3D hierarchical porous structure from waste reed for the synergetic adsorption of dyes and heavy metal ions. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138934. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Zou, K.; Yuan, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, B.; Qing, T.P.; Feng, B. A biomass resource strategy for alginate-polyvinyl alcohol double network hydrogels and their adsorption to heavy metals. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 301, 122050. [Google Scholar]
- Durairaj, S. Sorption capacity of Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) Solms for zinc removal from electroplating industry wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 30849–30866. [Google Scholar]
- Fubara, A.G.; Uche, C.C.; Nwoko, C.O.; Tony-Njoku, R.F.; Ojiaku, A.A.; Edo, F.A. Assessment of the effectiveness of water hyacinth (E. crassipes) in the biosorption of heavy metals from Aluminium extruding company effluents. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2022, 26, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Jahangiri, F.M.; Moutushi, H.T.; Moniruzzaman, M.; Hoque, S.; Hossain, M.E. Removal of lead from aqueous solutions and wastewaters using water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) roots. Water Pract. Technol. 2021, 16, 404–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.M.; Ahn, C.W.; Hahn, B.D.; Choi, J.J.; Kim, Y.D.; Lim, S.K.; Jung, K.; Park, Y.-C.; Choi, J.H. Easy approach to realize low cost and high cell capacity in sodium nickel-iron chloride battery. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 168, 442–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kavand, M.; Fakoor, E.; Mahzoon, S.; Soleimani, M. An improved film–pore–surface diffusion model in the fixed-bed column adsorption for heavy metal ions: Single and multi-component systems. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 113, 330–342. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Wang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.J.; Daroch, M.; Liu, K.K. A highly efficient adsorbent adapting to low pH condition for Pb (II) sequestration from aqueous solution–marine diatom: Laboratory and pilot scale tests. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128321. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Lei, C.; Yan, B.; Li, L.L. Analysis of heavy metals fixation and associated energy consumption during sewage sludge combustion: Bench scale and pilot test. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolali, A.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, J.; Liang, S.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Liu, Y. Application of a breakthrough biosorbent for removing heavy metals from synthetic and real wastewaters in a lab-scale continuous fixed-bed column. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 229, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Nguyen, B.Q.; Duong, T.T.; Bui, A.T.; Nguyen, H.T.; Cao, H.T.; Mai, N.T.; Nguyen, K.M.; Pham, T.T.; Kim, K.W. Pilot-scale removal of arsenic and heavy metals from mining wastewater using adsorption combined with constructed wetland. Minerals 2019, 9, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juela, D.; Vera, M.; Cruzat, C.; Astudillo, A.; Vanegas, E. A new approach for scaling up fixed-bed adsorption columns for aqueous systems: A case of antibiotic removal on natural adsorbent. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2022, 159, 953–963. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.; Ranjan, M.R. Heavy metal removal from wastewater using low cost adsorbents. J. Bioremediat. Biodegrad. 2015, 6, 315. [Google Scholar]
- Malik, D.S.; Jain, C.K.; Yadav, A.K. Removal of heavy metals from emerging cellulosic low-cost adsorbents: A review. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2113–2136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Lan, J.; Bo, C.; Gong, B.; Ou, J. Adsorption of heavy metal onto biomass-derived activated carbon. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 4275–4302. [Google Scholar]
- Anastopoulos, I.; Ighalo, J.O.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Triantafyllidis, K.S.; Pashalidis, I.; Kalderis, D. Sunflower-biomass derived adsorbents for toxic/heavy metals removal from (waste) water. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 117540. [Google Scholar]
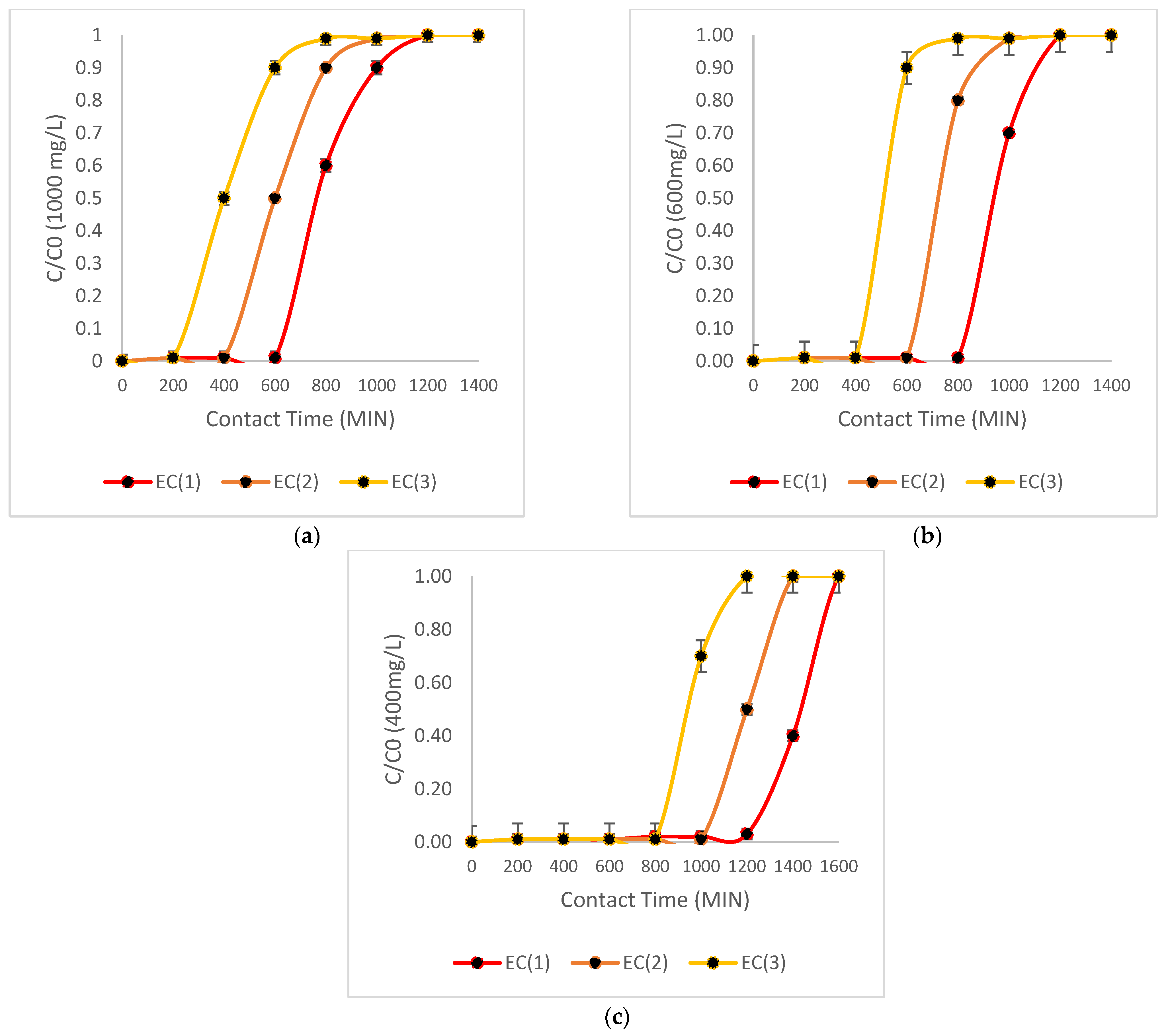
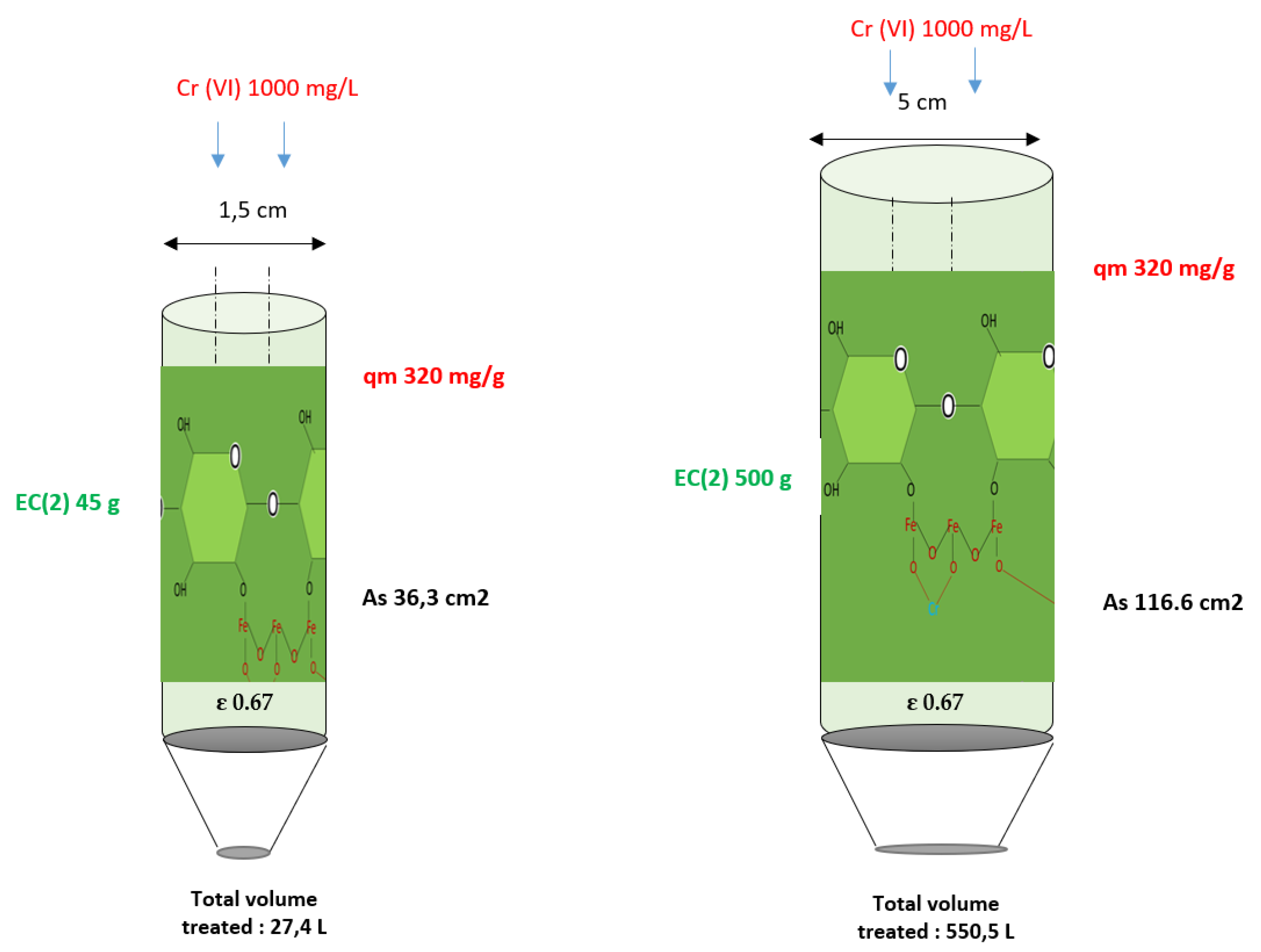
| Biomass | As cm2 | (cm/min) | Volume Goal (L) | Time Break (min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (1) | 36.3 | 0.6 | 4.4 | 480 |
| EC (2) | 36.3 | 0.50 | 3.9 | 420 |
| EC (3) | 36.3 | 0.45 | 3.4 | 390 |
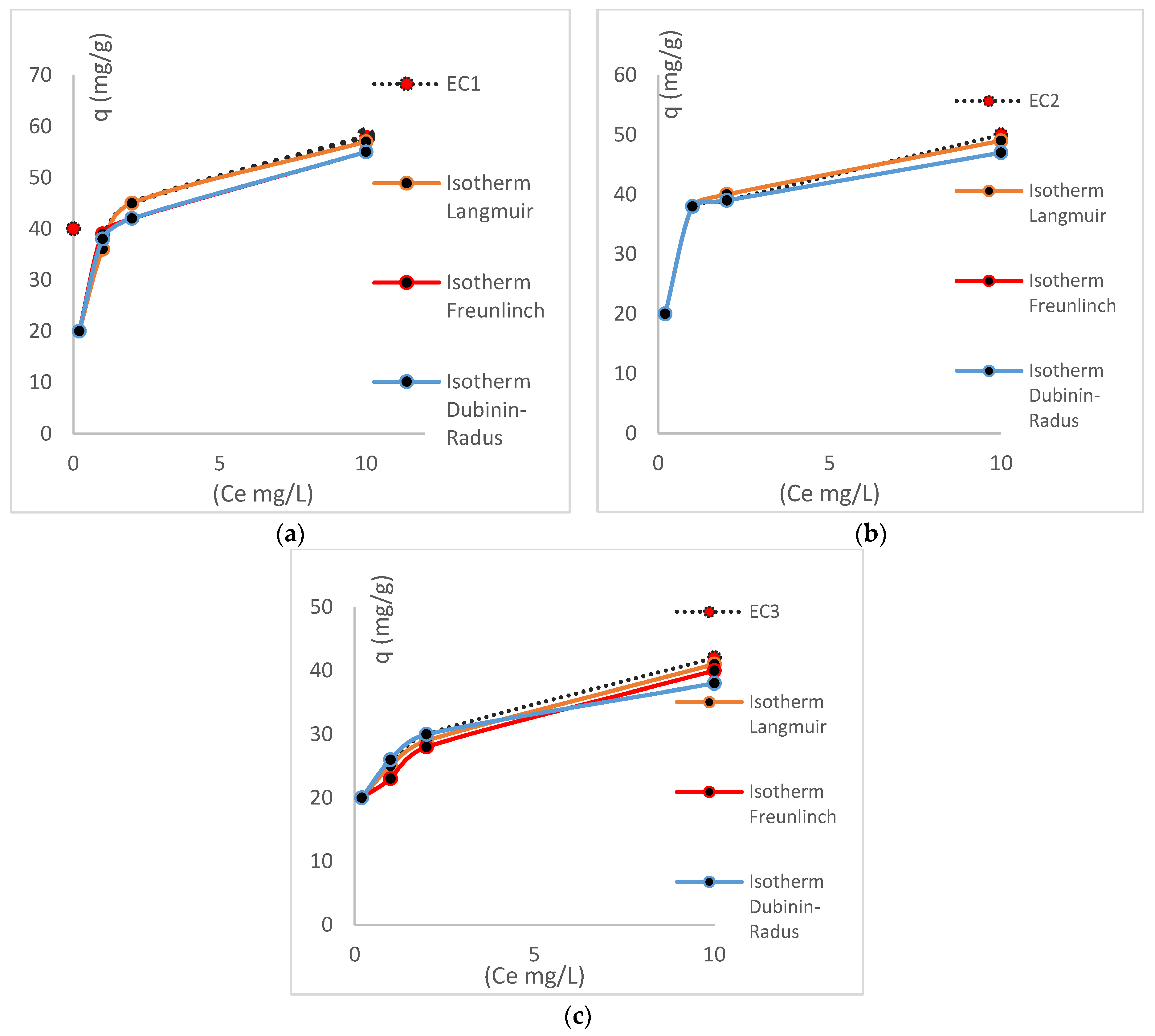
| Isotherm | Parameters | R2 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC (1) | Langmuir | B = 0.6; qm; 58 | 0.99 |
| Freundlich | K = 0.17 | 0.91 | |
| Dubinin Radus | B = 0.017; qm 55 | 0.89 | |
| Isotherm | Parameters | R2 | |
| EC (2) | Langmuir | B = 0.5; qm; 50 | 0.99 |
| Freundlich | K = 0,11 | 0.92 | |
| Dubinin Radus | B = 0.018; qm 49 | 0.95 | |
| Isotherm | Parameters | R2 | |
| EC (3) | Langmuir | B = 0.4; qm; 42 | 0.98 |
| Freundlich | K = 0.10 | 0.96 | |
| Dubinin Radus | B = 0.019; qm 40 | 0.90 |
| Biomass | (1/s) | Equation–Isotherm | qm |
|---|---|---|---|
| EC (1) | 0.016 | Langmuir | 58 |
| EC (2) | 0.017 | Langmuir | 50 |
| EC (3) | 0.019 | Langmuir | 42 |
| Cost | EC1 | EC2 | EC3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity total (g Cr/kg material) | 302 | 345 | 224 |
| Cost (USD) 1 Kg material | 3.25 | 3.0 | 2.15 |
| g Cr/(USD) | 92.92 | 116.9 | 104.18 |
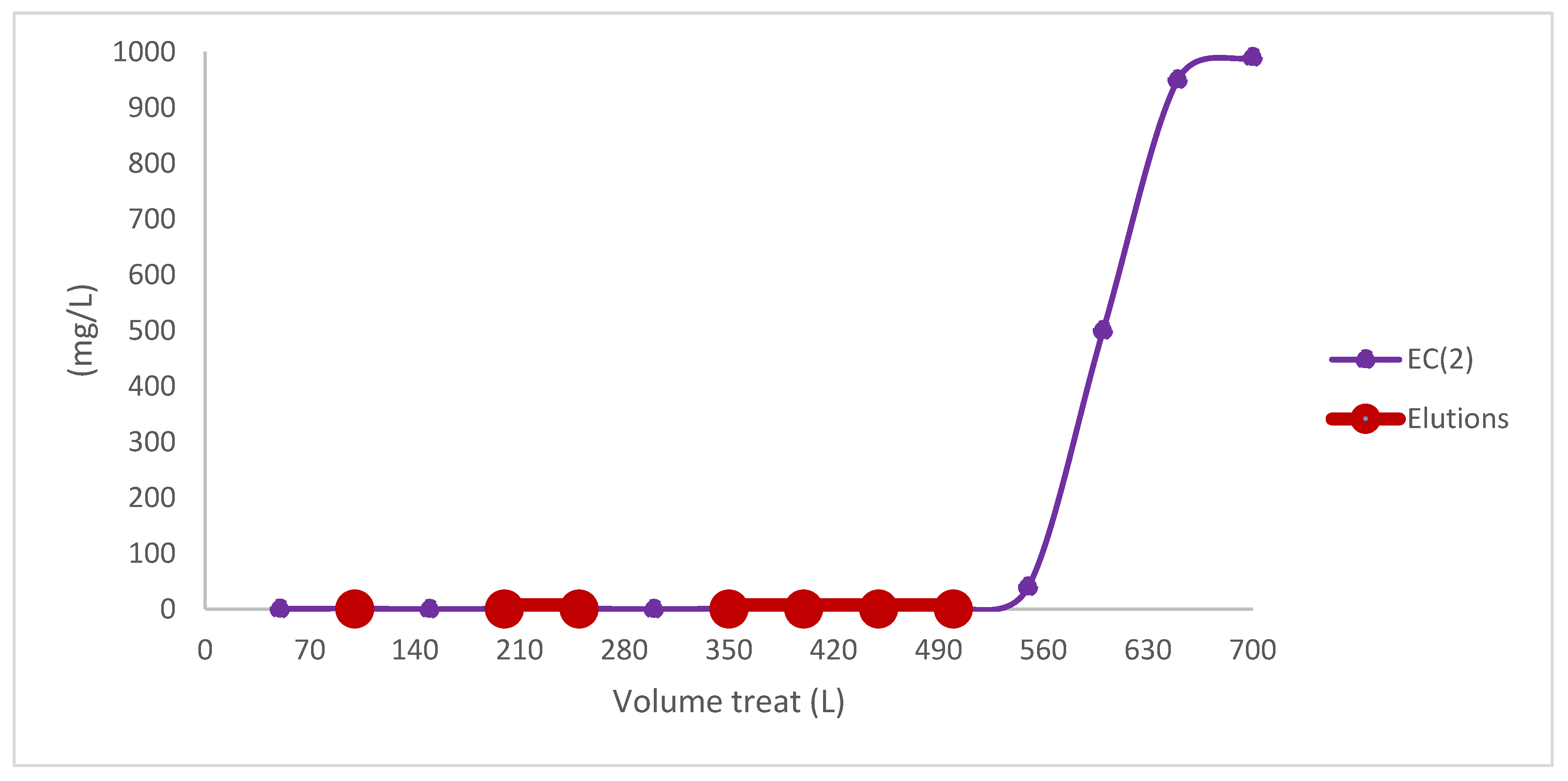
| M (g) | Volume Mass (Vb) | Density of Biomass | As Cm2 | Caudal mL/min | Volume Treat (L) | Elutions | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC (2) | 45 | 55 | 0.85 | 61.5 | 20 | 27.4 | 8 |
| Scalling | 500 | 583 | 0.85 | 116.6 | 200 | 550.5 | 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayago, U.F.C.; Ballesteros, V.B.; Lozano, A.M. Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride. Toxics 2025, 13, 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030230
Sayago UFC, Ballesteros VB, Lozano AM. Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride. Toxics. 2025; 13(3):230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030230
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayago, Uriel Fernando Carreño, Vladimir Ballesteros Ballesteros, and Angelica María Lozano. 2025. "Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride" Toxics 13, no. 3: 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030230
APA StyleSayago, U. F. C., Ballesteros, V. B., & Lozano, A. M. (2025). Development of a Treatment System of Water with Cr (VI) Through Models Using E. crassipes Biomass with Iron Chloride. Toxics, 13(3), 230. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics13030230








