Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
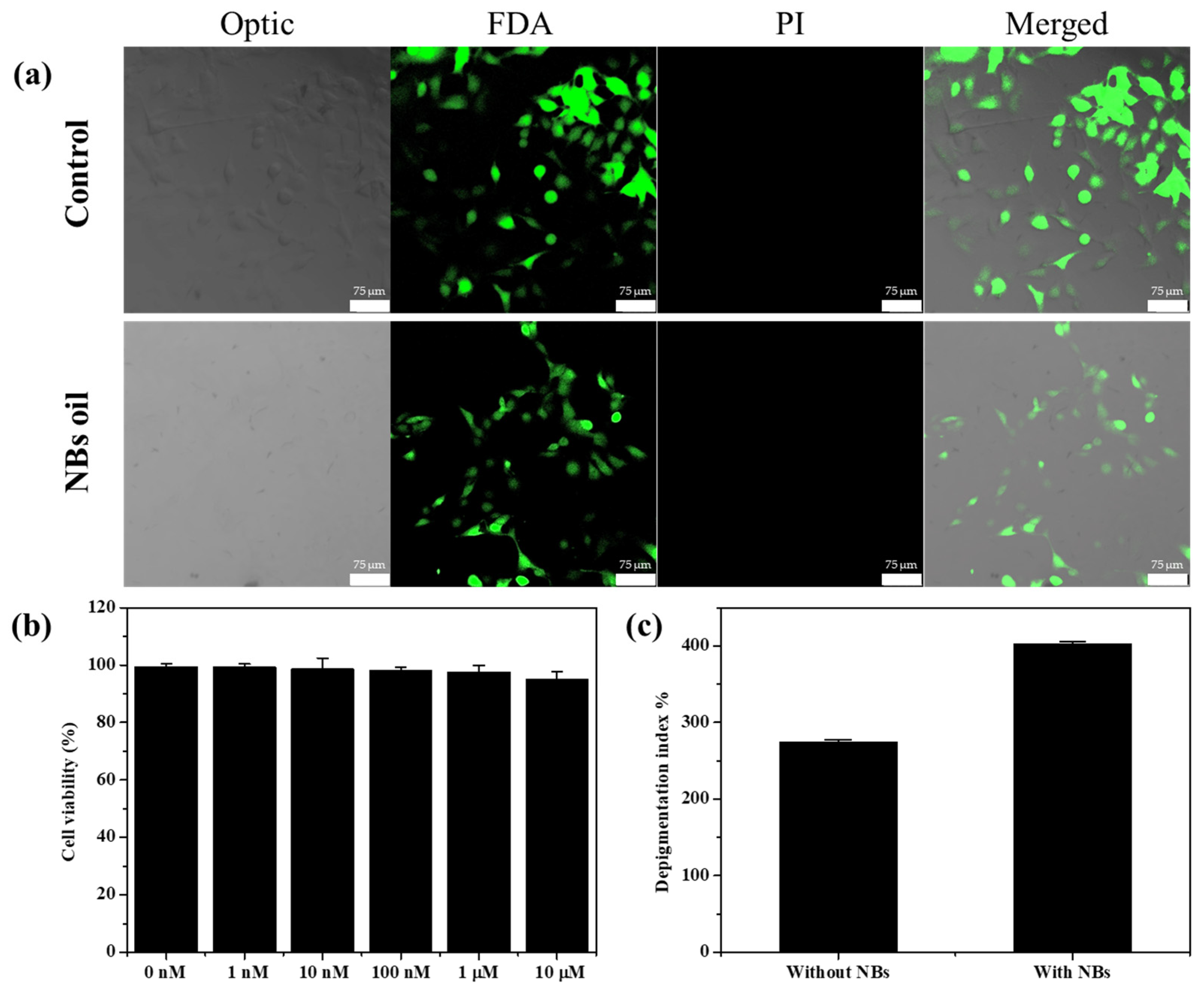
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, B.; Cho, H.-E.; Moon, S.H.; Ahn, H.-J.; Bae, S.; Cho, H.-D.; An, S. Transdermal delivery systems in cosmetics. Biomed. Dermatol. 2020, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro, L.; Lai, F.; Offerta, A.; Sarpietro, M.G.; Micicchè, L.; Maccioni, A.M.; Valenti, D.; Fadda, A.M. From nanoemulsions to nanostructured lipid carriers: A relevant development in dermal delivery of drugs and cosmetics. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torin Huzil, J.; Sivaloganathan, S.; Kohandel, M.; Foldvari, M. Drug delivery through the skin: Molecular simulations of barrier lipids to design more effective noninvasive dermal and transdermal delivery systems for small molecules, biologics, and cosmetics. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2011, 3, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Shabbir, M.; Shahid, N. The Structure of Skin and Transdermal Drug Delivery System—A Review. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2015, 8, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. Potential of Nanoparticles as Permeation Enhancers and Targeted Delivery Options for Skin: Advantages and Disadvantages. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 3271–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwah, H.; Garg, T.; Goyal, A.K.; Rath, G. Permeation enhancer strategies in transdermal drug delivery. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 564–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okyar, A.; Ozsoy, Y.; Gungor, S. Novel Formulation Approaches for Dermal and Transdermal Delivery of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. In Rheumatoid Arthritis; Intech: Rijeka, The Croatia, 2012; pp. 25–48. [Google Scholar]
- Hardman, M.J.; Sisi, P.; Banbury, D.N.; Byrne, C. Patterned acquisition of skin barrier function during development. Development 1998, 125, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, T.J. Skin barrier function and allergic risk. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 399–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keservani, R.K.; Bandopadhyay, S.; Bandyopadhyay, N.; Sharma, A.K. Design and fabrication of transdermal/skin drug-delivery system. In Drug Delivery Systems; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 131–178. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.G.; Baek, E.J.; Davaa, E.; Nho, Y.C.; Lim, Y.M.; Park, J.S.; Gwon, H.J.; Huh, K.M.; Park, J.S. Topical treatment of the buccal mucosa and wounded skin in rats with a triamcinolone acetonide-loaded hydrogel prepared using an electron beam. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 447, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Ethosomes: New prospects in transdermal delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2003, 20, 63–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, K.; Zulfakar, M.H. Recent advances in gel technologies for topical and transdermal drug delivery. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2014, 40, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vintiloiu, A.; Leroux, J.C. Organogels and their use in drug delivery—A review. J. Control. Release 2008, 125, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; He, H. A review of cosmetic skin delivery. J. Cosmet. Derm. 2021, 20, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Hirao, M.; Hashimoto, J.; Kawato, Y.; Kaneshiro, S.; Morimoto, T.; Koizumi, K.; Yoshikawa, H. Oxygen and air nanobubble water solution promote the growth of plants, fishes, and mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Aluthgun Hewage, S.; Batagoda, J.H. Stability of Nanobubbles. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nirmalkar, N.; Pacek, A.W.; Barigou, M. On the Existence and Stability of Bulk Nanobubbles. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10964–10973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Fan, Y.; Howard, M.D.; Vaughan, J.C.; Zhang, B. Imaging nanobubble nucleation and hydrogen spillover during electrocatalytic water splitting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 5878–5883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpitschka, S.; Dietrich, E.; Seddon, J.R.; Zandvliet, H.J.; Lohse, D.; Riegler, H. Nonintrusive optical visualization of surface nanobubbles. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 066102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshoridze, S.I.; Levin, Y.K. Thermodynamic Analysis of the Stability of Nanobubbles in Water. Nanosci. Technol. Int. J. 2019, 10, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ma, X.; Eisener, J.; Pfeiffer, P.; Ohl, C.D.; Sun, C. How bulk nanobubbles are stable over a wide range of temperatures. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2021, 596, 184–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhou, L.; Gao, Y. Can bulk nanobubbles be stabilized by electrostatic interaction? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2021, 23, 16501–16505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandan, R.; Banerjee, R. Pro-apoptotic liposomes-nanobubble conjugate synergistic with paclitaxel: A platform for ultrasound responsive image-guided drug delivery. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, C.; Gulati, S.; Fioravanti, G.; Stewart, P.L.; Exner, A.A. Cryo-EM Visualization of Lipid and Polymer-Stabilized Perfluorocarbon Gas Nanobubbles—A Step Towards Nanobubble Mediated Drug Delivery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, A.; Banerjee, R. Nanobubble Liposome Complexes for Diagnostic Imaging and Ultrasound-Triggered Drug Delivery in Cancers: A Theranostic Approach. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 15567–15580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotchie, A.; Zhang, X.H. Response of interfacial nanobubbles to ultrasound irradiation. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Alheshibri, M. The effect of ultrasound on bulk and surface nanobubbles: A review of the current status. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2021, 76, 105629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, M.H.; Chen, W.; Li, C.H.; Fang, C.Y.; Chang, Y.C.; Wei, D.H.; Liu, R.S.; Hsiao, M. An Advanced In Situ Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Ultrasonic Theranostics Nanocomposite Platform: Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier and Improving the Suppression of Glioblastoma Using Iron-Platinum Nanoparticles in Nanobubbles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 26759–26769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Sun, X.; Duan, F.; Yao, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, J.; Nie, L. Instant Ultrasound-Evoked Precise Nanobubble Explosion and Deep Photodynamic Therapy for Tumors Guided by Molecular Imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 21097–21107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teirlinck, E.; Xiong, R.; Brans, T.; Forier, K.; Fraire, J.; Van Acker, H.; Matthijs, N.; De Rycke, R.; De Smedt, S.C.; Coenye, T.; et al. Laser-induced vapour nanobubbles improve drug diffusion and efficiency in bacterial biofilms. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellow, C.; O’relly, M.A.; Hynynen, k.; Zheng, G.; Goertz, D.E. Simultaneous intravital optical and acoustic monitoring of ultrasound-triggered nanobubble generation and extravasation. Nano Lett. 2020, 20, 4512–4519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goliaei, A.; Adhikari, U.; Berkowitz, M.L. Opening of the blood-brain barrier tight junction due to shock wave induced bubble collapse: A molecular dynamics simulation study. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; De Leon, A.C.; Perera, R.; Abenojar, E.; Gopalakrishnan, R.; Basilion, J.P.; Wang, X.; Exner, A.A. Molecular imaging of orthotopic prostate cancer with nanobubble ultrasound contrast agents targeted to PSMA. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Perera, R.; Kolios, M.C.; Wijkstra, H.; Exner, A.A.; Mischi, M.; Turco, S. The unique second wave phenomenon in contrast enhanced ultrasound imaging with nanobubbles. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-H.; Cho, C.H.; Jung, Y.G. Nano Bubble Generator. Korean Patent 10-2382940, 22 March 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-H. Apparatus for Producing Nano-Bubble Water. Korean Patent 10-2379024, 18 December 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinardell, M.; Mitjans, M. Alternative Methods to Animal Testing for the Safety Evaluation of Cosmetic Ingredients: An Overview. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franz, T.J. Percutaneous absorption on the relevance of in vitro data. J. Investig. Derm. 1975, 64, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.J.; Yoon, J.-H.; Kang, N.G.; Park, S.G.; Jeong, S.H. Diffusion properties of different compounds across various synthetic membranes using Franz-type diffusion cells. J. Pharm. Investig. 2012, 42, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.E.; Kim, S.; Kim, B.H. In vitro skin absorption tests of three types of parabens using a Franz diffusion cell. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2017, 27, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Amaro, M.I.; Healy, A.M.; Cabral, L.M.; de Sousa, V.P. Comparative evaluation of rivastigmine permeation from a transdermal system in the Franz cell using synthetic membranes and pig ear skin with in vivo-in vitro correlation. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 512, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supe, S.; Takudage, P. Methods for evaluating penetration of drug into the skin: A review. Skin Res. Technol. 2021, 27, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, J.; Jung, E.; Huh, S.; Park, J.O.; Lee, J.W.; Byun, S.Y.; Park, D. Mechanisms of depigmentation by alpha-bisabolol. J. Derm. Sci. 2008, 52, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jun, H.; Jung, E.; Ha, J.; Park, D. Whitening effect of alpha-bisabolol in Asian women subjects. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2010, 32, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, H.J.; Jang, I.; Hyun, K.S.; Jung, S.K.; Hong, G.H.; Jeong, H.A.; Oh, S.G. Preparation of alpha-bisabolol and phenylethyl resorcinol/TiO2 hybrid composites for potential applications in cosmetics. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, S.; Lim, G.J.; Lee, J.Y. Quantitative analysis of melanin content in a three-dimensional melanoma cell culture. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Time (Hour) | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 24 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration with NBs (mM) | 0.124 | 0.279 | 0.501 | 1.223 | 2.099 | 2.526 | 3.003 |
| Concentration without NBs (mM) | 0.115 | 0.151 | 0.289 | 0.832 | 1.340 | 1.723 | 2.062 |
| Comparison (With NBs/Without NBs) | 1.1 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.5 | 1.5 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.; Shin, S.; Shukla, N.; Kim, K.; Park, M.-H. Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193286
Park Y, Shin S, Shukla N, Kim K, Park M-H. Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics. Nanomaterials. 2022; 12(19):3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193286
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Yuri, Soyeon Shin, Nutan Shukla, Kibeom Kim, and Myoung-Hwan Park. 2022. "Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics" Nanomaterials 12, no. 19: 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193286
APA StylePark, Y., Shin, S., Shukla, N., Kim, K., & Park, M.-H. (2022). Effects of Nanobubbles in Dermal Delivery of Drugs and Cosmetics. Nanomaterials, 12(19), 3286. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12193286









