Unambiguous Determination of Benzo[a]pyrene and Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene in HPLC Fractions via Room-Temperature Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrices
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
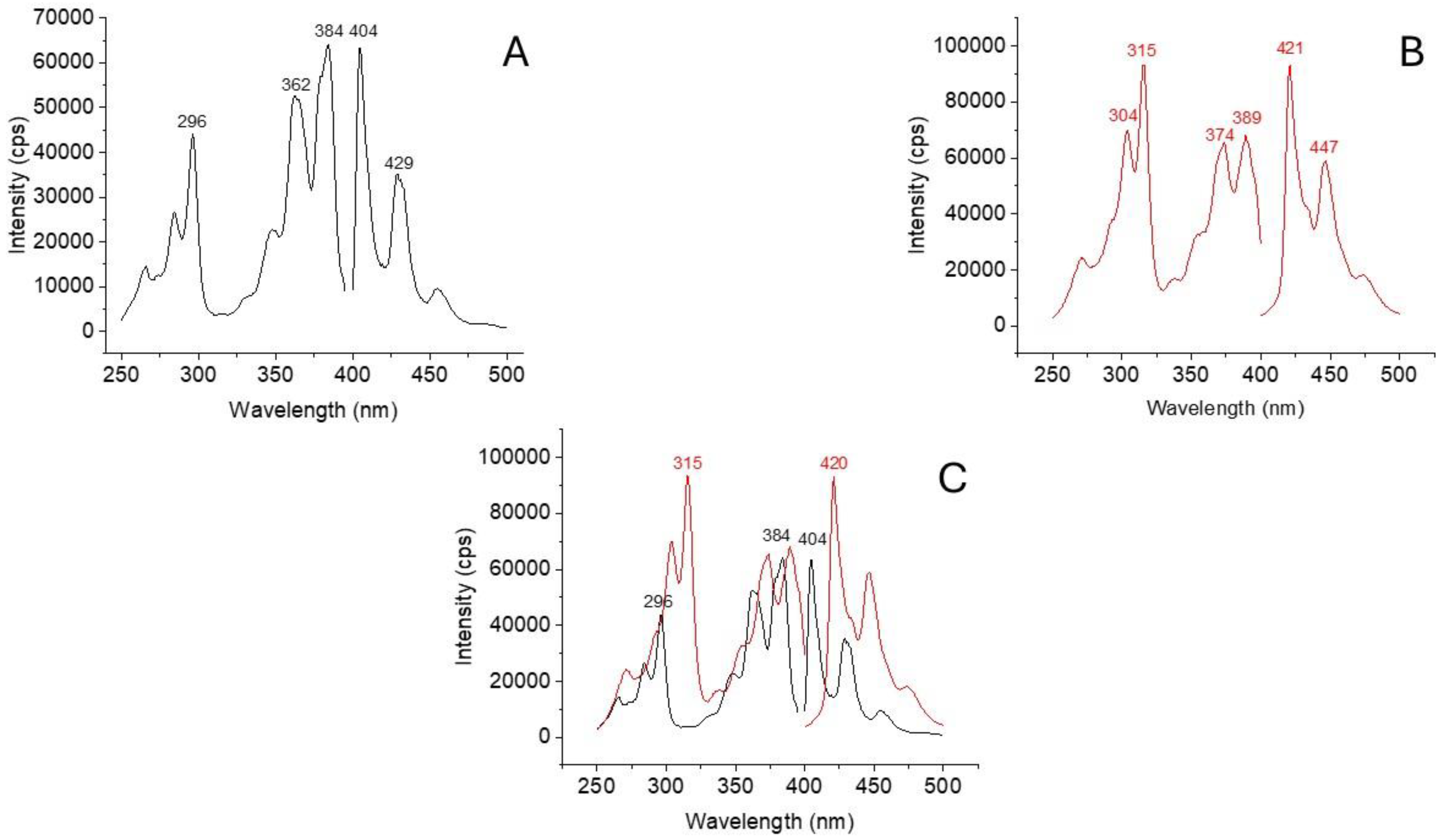
2.1. Room Temperature Excitation and Fluorescence Spectra of BaP and DBalP
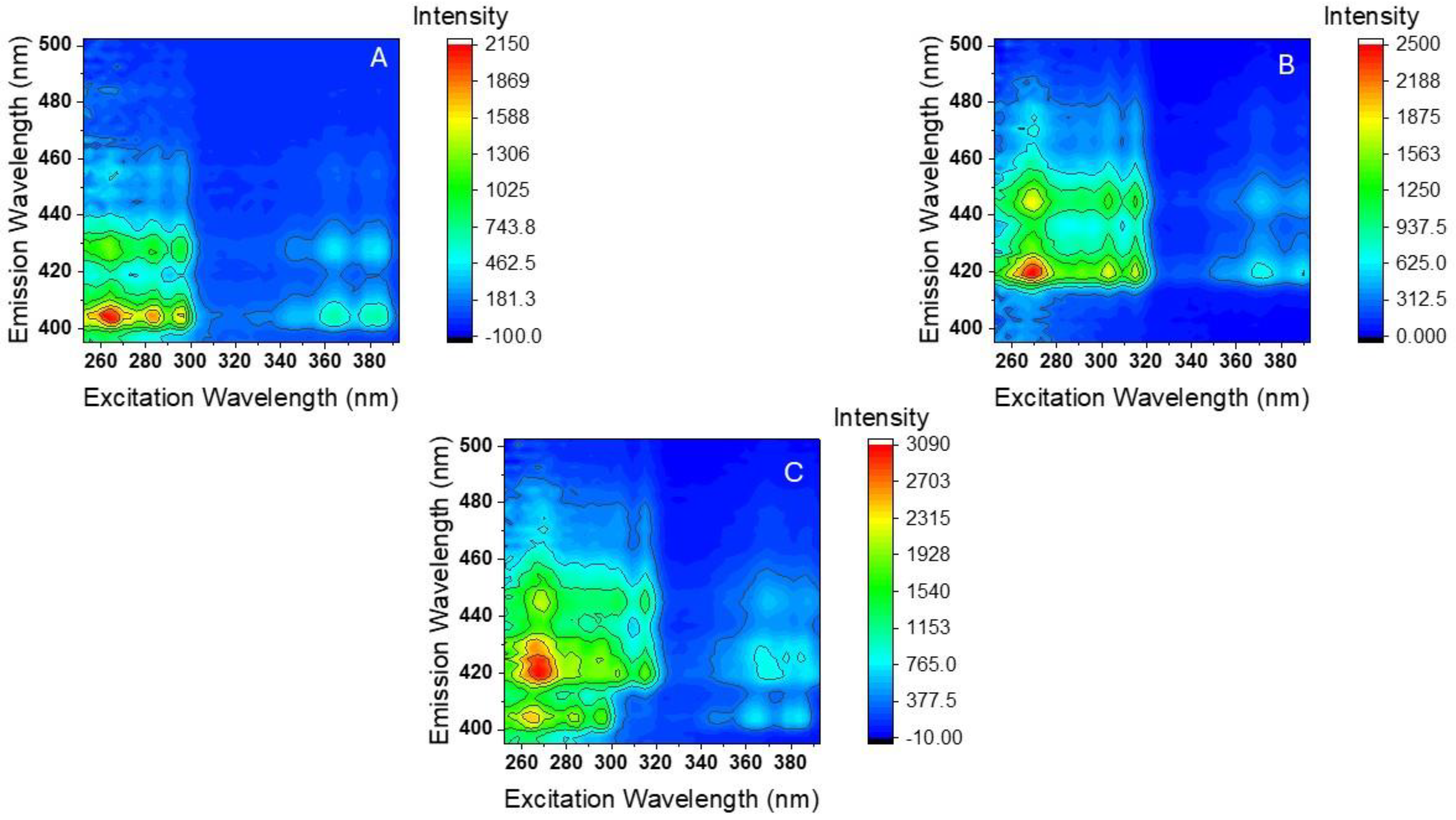
2.2. Room-Temperature Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrices (RTF-EEMs) of BaP and DBalP
2.3. RTF-EEMs’ Analytical Figures of Merit for the Analysis of BaP and DBalP in Acetonitrile
2.4. Calibration and Validation Sets for PARAFAC Analysis
2.5. HPLC–EEM Analysis of Tobacco Smoke Condensate
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Preparation of Calibration and Validation Sets for PARAFAC Analysis
3.3. Collection of Tobacco Smoke Condensate
3.4. HPLC–EEM Analysis of Tobacco Smoke Condensate
3.5. Instrumentation
3.6. Software for Data Analysis with PARAFAC
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, K.P.; Jankowiak, R.; Small, G.J. High-performance liquid chromatography interfaced with fluorescence line-narrowing spectroscopy for on-line analysis. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wise, S.A.; Rodgers, R.P.; Reddy, C.M.; Nelson, R.K.; Kujawinski, E.B.; Wade, T.L.; Campiglia, A.D.; Lieu, Z. Advances in Chemical Analysis of Oil Spills Since the Deepwater Horizon Disaster. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2022, 53, 1638–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.Y.; Gao, S.T.; Zhu, Z.J.; Zeng, X.Y.; Liang, Y.; Yu, Z.Q.; Peng, P.A. Two-dimensional gas chromatography coupled to isotope ratio mass spectrometry for determining high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in sediments. J. Chromatogr. A 2023, 1693, 463879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans Chemical Agents and Related Occupations. Lyon (FR): International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, No. 100F BENZO[a]PYRENE, 2012. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK304415/ (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Cavalieri, E.L.; Higginbotham, S.; Rogan, E.G. Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene—The Most Potent Carcinogenic Aromatic Hydrocarbon. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd. 1994, 6, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, B.; Luch, A.; Bravo, C.F.; Atkin, J.; Steppan, L.B.; Pereira, C.; Kerkvliet, N.I.; Baird, W.M. Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene induced DNA adduct formation in lung tissue in vivo. Cancer Lett. 2005, 227, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, G.K.; Gupta, R.C.; Vadhanam, M.V. Effect of phytochemical intervention on dibenzo[a,l]pyrene-induced DNA adduct formation. Mutat. Res./Fundam. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2015, 774, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalczyk, K.; Roszak, J.; Sobanska, Z.; Stepnik, M. Review of mechanisms of genotoxic action of dibenzo[def,p]chrysene (formerly dibenzo[a,l]pyrene). Toxin Rev. 2023, 42, 460–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comas, A.; Santana, A.; Campiglia, A.D. On the co-elution of benzo[a]pyrene and dibenzo[a,l]pyrene in chromatographic fractions and their unambiguous determination in tobacco extracts via laser-excited time resolved Shpol’skii spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2023, 15, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elcoroaaristizabal, S.; de Juan, A.; Garcia, A.J.; Durana, N.; Alonso, L. Comparison of second-order multivariate methods for screening and determination of PAHs by total fluorescence spectroscopy. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2014, 132, 63–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadvand, M.; Sereshti, H.; Parastar, H. Chemometric-based determination of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aqueous samples using ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction combined to gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1413, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.W.; Zhang, S.H.; Wu, B.C.; Chen, W.; Wang, J.B.; Liu, Y. A green chemometrics-assisted fluorimetric detection method for the direct and simultaneous determination of six polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in oil-field wastewaters. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 200, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, S.K.; Mishra, A.K. Identification of pyrene in complex sample matrix using time-resolved fluorescence measurement coupled with PARAFAC analysis. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2019, 383, 111991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catena, S.; Sanllorente, S.; Sarabia, L.A.; Boggia, R.; Turrini, F.; Ortiz, M.C. Unequivocal identification and quantification of PAHs content in ternary synthetic mixtures and in smoked tuna by means of excitation-emission fluorescence spectroscopy coupled with PARAFAC. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 10456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, K.C.; Barreto, M.C.; Siqueira, A.S.; Freitas AC, P.; Oliveira, L.G.; Bastos ME, P.A.; Rocha ME, P.; Silva, L.A.; Fragoso, W.D. Oil spill in northeastern Brazil: Application of fluorescence spectroscopy and PARAFAC in the analysis of oil-related compounds. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 129154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seopela, M.P.; Powers, L.C.; Clark, C.; Heyes, A.; Gonsior, M. Combined fluorescent measurements, parallel factor analysis and GC-mass spectrometry in evaluating the photodegradation of PAHS in freshwater systems. Chemosphere 2021, 269, 129386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, A.S.; Almeida, L.F.; Fragoso, W.D. Determination of anthracene, phenanthrene, and fluorene in tap water and sediment samples by fluorescence spectroscopy on nylon membranes and second-order calibration. Talanta 2023, 253, 124002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearn, B.A.; Ding, Y.S.; Watson, C.H.; Johnson, T.L.; Zewdie, G.; Jeong-Im, J.H.; Walters, M.J.; Holman, M.R.; Rochester, C.G. Multi-year Study of PAHs in Mainstream Cigarette Smoke. Tob. Regul. Sci. 2018, 4, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazzi, P.; Hardy, E.M.; Appenzeller, B.M.R. Biomonitoring of children exposure to urban pollution and environmental tobacco smoke with hair analysis—A pilot study on children living in Paris and Yeu Island, France. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 665, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adesina, O.A.; Olowolafe, T.I.; Igbafe, A. Levels of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon from mainstream smoke of tobacco products and its risks assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 5, 100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhardt, T.; Scherer, M.; Scherer, G.; Pluym, N.; Weber, T.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Time trend of exposure to secondhand tobacco smoke and polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons between 1995 and 2019 in Germany—Showcases for successful European legislation. Environ. Res. 2023, 216 Pt 2, 114638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.N.; Miller, J.C.; Miller, R.D. Statistics and Chemometrics for Analytical Chemistry, 7th ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.R.; Stedmon, C.A.; Graeber, D.; Bro, R. Fluorescence spectroscopy and multi-way techniques. PARAFAC. Anal. Methods 2013, 5, 6557–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, T.; Dong, B. Characterizing dissolved organic matter in Taihu Lake with PARAFAC and SOM method. Water Sci. Technol. 2022, 85, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinç, E.; Ertekin, Z.C.; Ünal, N. Three-way analysis of pH-UV absorbance dataset for the determination of paracetamol and its pKa value in presence of excipients. Spectrochim. Acta Part A 2020, 230, 118049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, A. Analytical Figures of Merit in Univariate, Multivariate, and Multiway Calibration: What Have We Learned? What Do We Still Need to Learn? J. Chemom. 2024, 38, e3613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, A.C.; Escandar, G.M. Recent Advances in Multiway Analytical Figures of Merit. Data Handl. Sci. Technol. 2024, 33, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goicoechea, H.C.; Yu, S.; Moore AF, T.; Campiglia, A.D. Four-way modeling of 4.2 K time-resolved excitation emission fluorescence data for the quantitation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in soil samples. Talanta 2012, 101, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SRM 3222; Collection of Tobacco Smoke Condensate (SRM 3222 Cigarette Tobacco Filler). National Standards of Technology. Chemical Sciences Division, Material Measurement Laboratory, NIST: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2017.
- Bro, R. PARAFAC Tutorial and applications. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 1997, 38, 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappini, F.A.; Munoz de la Pena, A.; Goicoechea, H.C.; Olivieri, A.C. An upgrade of MVC2, a MATLAB graphical user interface for second-order multivariate calibration: Beyond trilinear models. Chemometr. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2023, 237, 104814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| λexc/λem 1 | LOD 2 (ng/mL) | LOQ 3 (ng/mL) | LDR 4 (ng/mL) | R 5 | % RSD 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BaP | 384/404 | 4.7 | 16 | 16–104 | 0.9995 | 0.6 |
| DBalP | 315/421 | 32 | 107 | 107–500 | 0.9988 | 4.2 |
| Sample | BaP (ng/mL) | DBalP (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28.9 | 164.6 |
| 2 | 91.1 | 164.6 |
| 3 | 28.9 | 442.4 |
| 4 | 91.1 | 442.4 |
| 5 | 16.0 | 303.5 |
| 6 | 104.0 | 303.5 |
| 7 | 60.0 | 107.0 |
| 8 | 60.0 | 500.0 |
| 9 | 60.0 | 303.5 |
| 10 | 0.0 | 303.5 |
| 11 | 60.0 | 0.0 |
| Sample | BaP (ng/mL) | DBalP (ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal 1 | Predicted 2 | Nominal 1 | Predicted 2 | |
| 1 | 39.5 | 37.8 | 159.8 | 165.0 |
| 2 | 85.5 | 87.9 | 159.8 | 156.9 |
| 3 | 39.5 | 40.9 | 400.2 | 382.9 |
| 4 | 85.5 | 89.9 | 400.2 | 431.5 |
| 5 | 30.0 | 32.6 | 280.0 | 267.2 |
| 6 | 95.0 | 87.9 | 280.0 | 277.2 |
| 7 | 62.5 | 64.1 | 110.0 | 117.2 |
| 8 | 62.5 | 65.7 | 450.0 | 428.4 |
| 9 | 62.5 | 64.3 | 280.0 | 286.9 |
| Sample | BaP (ng/mL) | DBalP (ng/mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominal 1 | Predicted 2 | Nominal 1 | Predicted 2 | |
| 1 | 0.0 | – | 0.0 | – |
| 2 | 85.5 | 88.4 | 0.0 | – |
| 3 | 0.0 | – | 400.2 | 387.2 |
| 4 | 39.5 | 38.3 | 159.8 | 162.1 |
| 5 | 85.5 | 87.9 | 400.2 | 406.1 |
| Average Recovery (%) | – | 100.9 | – | 99.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Knecht, G.T.; Nauth, S.D.; Alvarado, J.C.G.; Santana, A.M.; Goicoechea, H.C.; Campiglia, A.D. Unambiguous Determination of Benzo[a]pyrene and Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene in HPLC Fractions via Room-Temperature Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrices. Molecules 2025, 30, 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071550
Knecht GT, Nauth SD, Alvarado JCG, Santana AM, Goicoechea HC, Campiglia AD. Unambiguous Determination of Benzo[a]pyrene and Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene in HPLC Fractions via Room-Temperature Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrices. Molecules. 2025; 30(7):1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071550
Chicago/Turabian StyleKnecht, George T., Stephanie D. Nauth, Juan C. Gomez Alvarado, Anthony M. Santana, Hector C. Goicoechea, and Andres D. Campiglia. 2025. "Unambiguous Determination of Benzo[a]pyrene and Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene in HPLC Fractions via Room-Temperature Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrices" Molecules 30, no. 7: 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071550
APA StyleKnecht, G. T., Nauth, S. D., Alvarado, J. C. G., Santana, A. M., Goicoechea, H. C., & Campiglia, A. D. (2025). Unambiguous Determination of Benzo[a]pyrene and Dibenzo[a,l]pyrene in HPLC Fractions via Room-Temperature Fluorescence Excitation–Emission Matrices. Molecules, 30(7), 1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30071550









