Local Fungi Promote Plant Growth by Positively Affecting Rhizosphere Metabolites to Drive Beneficial Microbial Assembly
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Strains
2.2. Preparation of Strain Fermentation Broth
2.3. Test Plants
2.4. Substrate and Mixing Materials
2.5. Overview of Experimental Field and Experimental Design
2.5.1. Overview of Experimental Area
2.5.2. Design of Experimental Plots and Sowing
2.6. Field Management
2.7. Sample Collection and Processing
2.7.1. Plant Sample Collection
2.7.2. Rhizosphere Soil Collection and Processing
2.8. Forage Phenotype and Biochemical Measurement
2.9. Rhizosphere Soil Physical and Chemical Properties and Enzyme Activity Measurement
2.10. Root and Rhizosphere Soil Microbiome Analysis
2.11. Determination of Rhizosphere Soil Metabolites
2.12. Data Analysis
3. Results
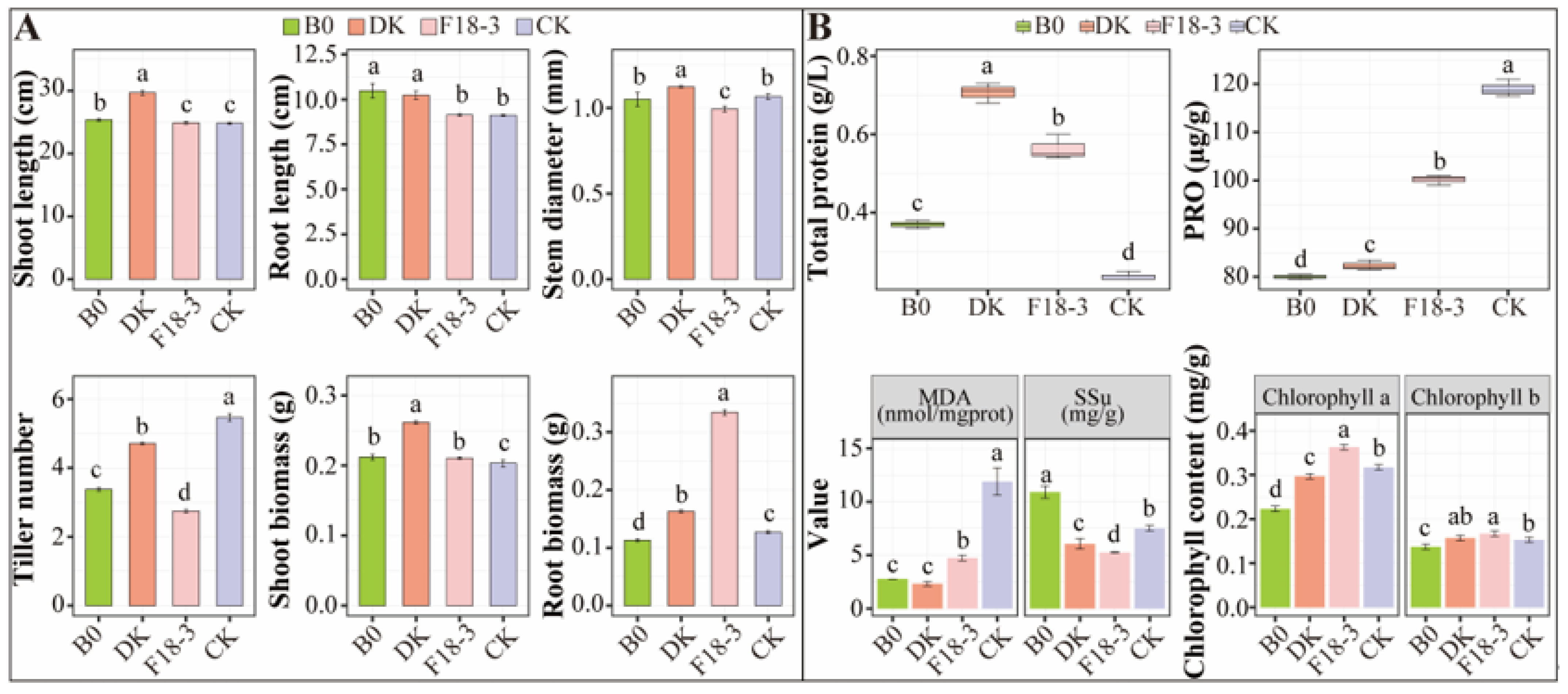
3.1. Effects of Strain Treatments on Plant Growth and Physicochemical Factors of Rhizosphere Soil
3.2. Strain Treatments Differentially Shapes the Endophytic and Rhizosphere Microbial Community Structures of Plants
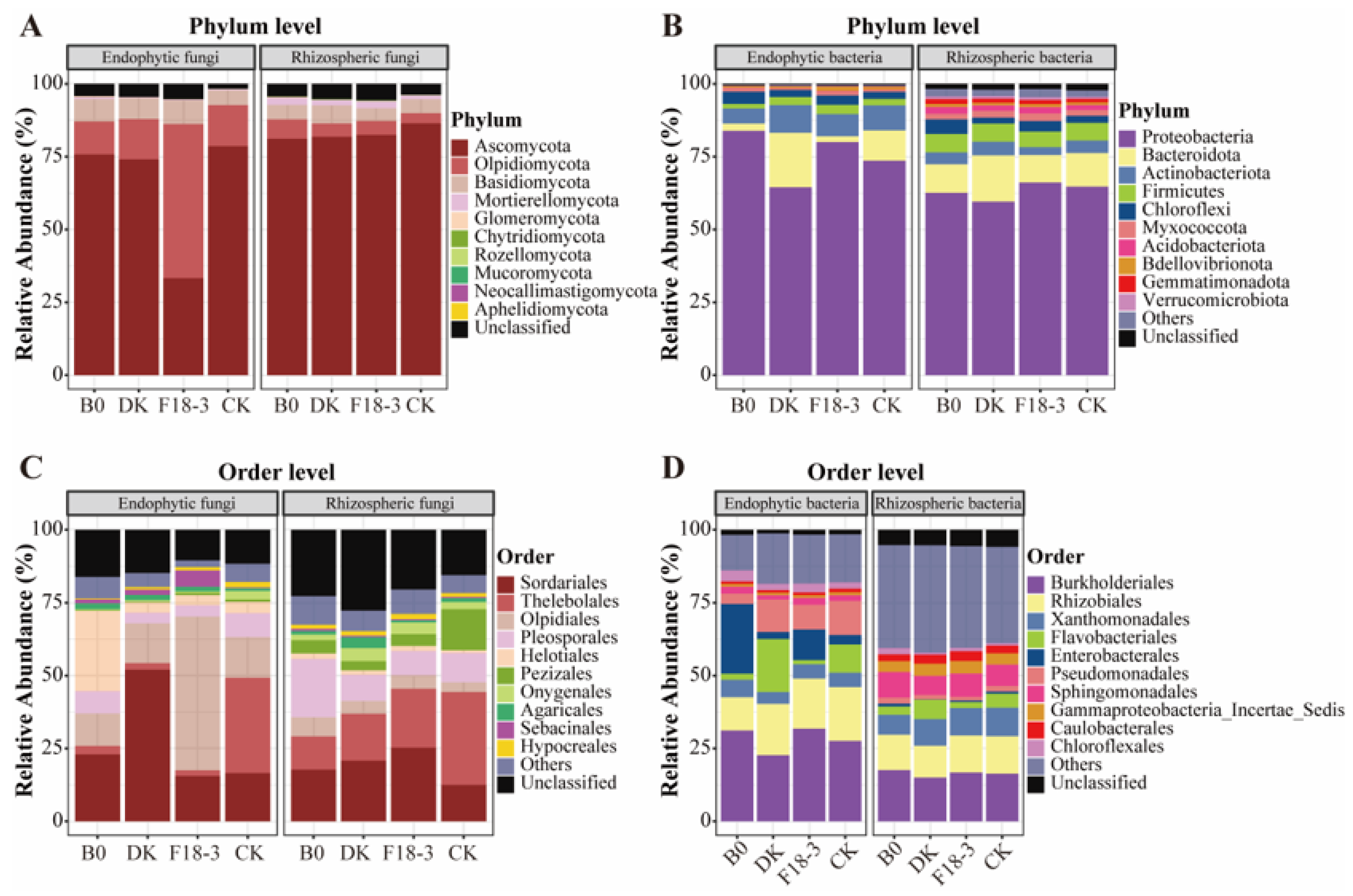
3.2.1. Overview of Microbial Community Composition
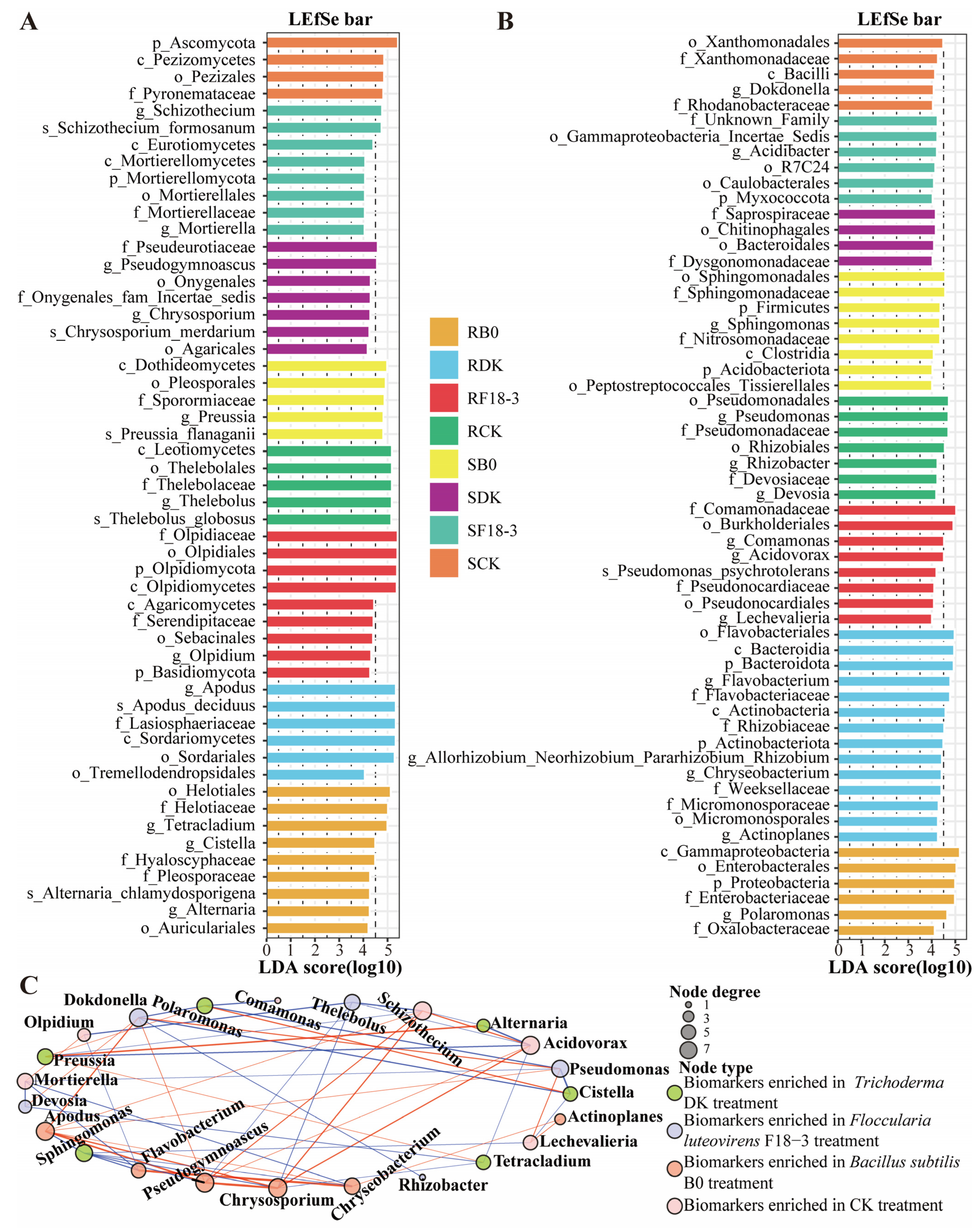
3.2.2. Differential Characteristics of Microbial Community Structure
3.3. Strain Treatments Drive the Assembly of Endophytic and Rhizosphere Microbial Communities in Plants
3.4. Microbial Groups Potentially Related to Strain Regulation
3.5. Influence of Strain Treatment on Metabolism of Plant Rhizosphere Soil
3.6. Rhizosphere Metabolites Drive the Assembly of Microorganisms Associated with Plant Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Metabolites Regulate Plant Growth and Stress Resistance
4.2. Metabolite–Microbe Synergy Drives Plant Growth
4.3. Synergistic Interactions Among Microorganisms Drive Plant Growth
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feng, Y.; Wang, J.; Bai, Z.; Reading, L. Effects of surface coal mining and land reclamation on soil properties: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 191, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Fang, X.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhao, F. Influence of mining and vegetation restoration on soil properties in the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlanyo, A.S.; Li, J. Evaluating the environmental and economic impact of mining for post-mined land restoration and land-use: A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 279, 111623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, H.; Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.L.; Gong, N. Heavy metal pollution diagnosis and ecological risk assessment of the surrounding soils of coal waste pile at Naluo Coal Mine, Liupanshui, Guizhou. Int. J. Min. Reclam. Environ. 2016, 30, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, X.; Hou, L.; Shao, A. Impact of the coal mining on the spatial distribution of potentially toxic metals in farmland tillage soil. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Nie, X.; Zhao, T.; Liu, X. The impact of coal pollution on soil microbial diversity and community structure. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2025, 25, 1706–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruijn, F.J. Biological nitrogen fixation. In Principles of Plant-Microbe Interactions: Microbes for Sustainable Agriculture; Lugtenberg, B., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 215–224. [Google Scholar]
- Maheshwari, D.K.; Dheeman, S.; Agarwal, M. Phytohormone producing PGPR for sustainable agriculture. In Bacterial Metabolites in Sustainable Agroecosystem; Maheshwari, D.K., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 159–182. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, A.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jia, B. Beneficial microorganisms: Regulating growth and defense for plant welfare. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2025, 23, 986–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladipo, O.G.; Awotoye, O.O.; Olayinka, A.; Ezeokoli, O.T.; Maboeta, M.S.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Heavy metal tolerance potential of Aspergillus strains isolated from mining sites. Bioremediation J. 2016, 20, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Bu, H.; Feng, Q.; Wassie, M.; Amee, M.; Jiang, Y.; Bi, Y.; Hu, L.; Chen, L. Identification of Cd-resistant microorganisms from heavy metal-contaminated soil and its potential in promoting the growth and Cd accumulation of bermudagrass. Environ. Res. 2021, 200, 111730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, B.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, H.; Zhao, Z.; Li, T. Diversity and functional roles of root-associated endophytic fungi in two dominant pioneer trees reclaimed from a metal mine slag heap in Southwest China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowles, T.M.; Barrios-Masias, F.H.; Carlisle, E.A.; Cavagnaro, T.R.; Jackson, L.E. Effects of arbuscular mycorrhizae on tomato yield, nutrient uptake, water relations, and soil carbon dynamics under deficit irrigation in field conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Song, J.; Xin, X.; Xie, X.; Zhao, B. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal 14-3-3 proteins are involved in arbuscule formation and responses to abiotic stresses during AM symbiosis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebisa, L.A. Associations of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) for enhancements in soil fertility and promotion of plant growth: A Review. Adv. Biosci. Bioeng. 2024, 12, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.J.; Chen, X.P.; Li, Z.L. Mechanism and application of plant growth-promoting bacteria in heavy metal bioremediation. Environ. Sci. China 2022, 43, 4911–4922. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, M.C.S.; Rahul, V.D.; Uppar, P.; Madhuri, M.L.; Tripathy, B.; Vyas, R.D.V.; Swami, D.V.; Raju, S.S. Enhancing the phytoremediation of heavy metals by plant growth promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR) consortium: A Narrative Review. J. Basic. Microbiol. 2024, 65, e2400529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Lu, Y.; Tan, Z.; Wu, H.; Bian, X.; Qi, Z.; Zhang, L. Application of a composite microbial agent in the restoration of ecologically damaged areas in typical coal mines in Northwest China. Microbiol. China 2024, 51, 1391–1404. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.; Xiao, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Deng, Y. Effect of AM fungi on soil remediation and improvement of abandoned ionic rare earth mining area. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 132–141. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.; Huan, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, L. Long-term observation of field application of reclaimed mine substrates by ryegrass-AMF-sludge combination: Key factors of organic carbon accumulation. J. Environ. Eng. 2023, 149, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wang, Y.; Qi, C.; Li, J. Effects of endophytic fungi seed soaking on growth and root endophytic fungal communities of Avena sativa. Acta Prataculturae Sin. 2025, 34, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Xie, Z.; Dai, D.; Mao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, X. Correlation between mycelial growth and microstructure of Floccularia luteovirens. J. Qinghai Univ. 2022, 40, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, J. The Study on Change of Palaeoenvironment in Muli Permafrost Aera of Tianjun County of Qinghai Province Since Mid-Last Glacial Age. Master’s Thesis, China University of Geosciences, Beijing, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, D. Plant and field sampling. In Application of Sampling and Detection Methods in Agricultural Plant Biotechnology; Shillito, R., Shan, G., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2022; pp. 177–189. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Hu, Y.; Hu, A.; Niu, B.; Yang, X.; Jiao, H.; Xu, R.; Song, L.; Zhang, G. Shifts in the dynamic mechanisms of soil organic matter transformation with nitrogen addition: From a soil carbon/nitrogen-driven mechanism to a microbe-driven mechanism. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Luo, Y. Variation in antioxidant enzyme activities of two strawberry cultivars with short-term low temperature stress. World J. Agric. Sci. 2008, 4, 458–462. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, Q.; Wang, W.; Yang, Y.; Hu, J.; Bian, C.; Jin, L.; Li, G.; Xiong, X. Rhizosphere microbial diversity and community dynamics during potato cultivation. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2020, 98, 103176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Shi, L.; Chen, Y. The great potential for phytoremediation of abandoned tailings pond using ectomycorrhizal Pinus sylvestris. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibetta, S.; Schena, L.; Abdelfattah, A.; Pangallo, S.; Cacciola, S.O. Selection and experimental evaluation of universal primers to study the fungal microbiome of higher plants. Phytobiomes J. 2018, 2, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckers, B.; Op De Beeck, M.; Thijs, S.; Truyens, S.; Weyens, N.; Boerjan, W.; Vangronsveld, J. Performance of 16s rDNA primer pairs in the study of rhizosphere and endosphere bacterial microbiomes in metabarcoding studies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magoč, T.; Salzberg, S.L. FLASH: Fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2957–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokulich, N.A.; Subramanian, S.; Faith, J.J.; Gevers, D.; Gordon, J.I.; Knight, R.; Mills, D.A.; Caporaso, J.G. Quality-filtering vastly improves diversity estimates from Illumina amplicon sequencing. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. UPARSE: Highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ondov, B.D.; Bergman, N.H.; Phillippy, A.M. Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. ggplot2. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Boutros, P.C. VennDiagram: A package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, J.R.; Lex, A.; Gehlenborg, N. UpSetR: An R package for the visualization of intersecting sets and their properties. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2938–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R. Vegan: Community Ecology Package, R Package Version 1; 2010. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, S.; Parfrey, L.W.; Doebeli, M. Decoupling function and taxonomy in the global ocean microbiome. Science 2016, 353, 1272–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.A.; Want, E.J.; O’Maille, G.; Abagyan, R.; Siuzdak, G. XCMS: Processing mass spectrometry data for metabolite profiling using nonlinear peak alignment, matching, and identification. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevenot, E.A. ropls: PCA, PLS (-DA) and OPLS (-DA) for Multivariate Analysis and Feature Selection of Omics Data, R Package Version 1.0. 2016. Available online: https://bioconductor.org/packages/ropls/ (accessed on 11 June 2025).
- Wang, F.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Wu, C.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, L.; Yang, J.; Cai, P.; Chen, J.; Ge, T. Combating wheat yellow mosaic virus through microbial interactions and hormone pathway modulations. Microbiome 2024, 12, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Portal-Gonzalez, N.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, H.; Portieles, R.; Borras-Hidalgo, O.; He, W.; Santos-Bermudez, R. Metabolome-driven microbiome assembly determining the health of ginger crop (Zingiber officinale L. Roscoe) against rhizome rot. Microbiome 2024, 12, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, L.; Song, Y.; Mackelprang, R.; Zhang, D.; Qin, S.; Chen, L.; Wu, L.; Peng, Y.; Yang, Y. Metagenomic insights into microbial community structure and metabolism in alpine permafrost on the Tibetan Plateau. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinsabaugh, R.L.; Follstad Shah, J.J. Ecoenzymatic stoichiometry and ecological theory. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 43, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Ma, W.; Wu, J.; Gong, Y.; Xu, G. Vegetation degradation impacts soil nutrients and enzyme activities in wet meadow on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, R.; Sharma, M.P.; Prakash, A.; Ramesh, A.; Bhattacharjya, S.; Patra, A.K.; Manna, M.C.; Kurganova, I.; Kuzyakov, Y. Glycoproteins of arbuscular mycorrhiza for soil carbon sequestration: Review of mechanisms and controls. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, S.; Gangola, S.; Jaggi, V.; Sahgal, M. Functional characterization and molecular fingerprinting of potential phosphate solubilizing bacterial candidates from Shisham rhizosphere. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 7003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.; Li, T.; von Sperber, C.; Ge, L.; Cao, C.; Zhai, Z.; Bu, Z.; Wang, M. Low molecular weight organic acids mobilize soil organic phosphorus for enzymatic hydrolysis in a temperate montane peatland. Biogeochemistry 2025, 168, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Ai, W.; Wen, S.; Yang, X.; Liu, X. Mechanism, influencing factors and practical application of organic acids in improving soil phytate bioavailability. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2023, 29, 2150–2171. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yan, D. Effects of External Application of α-Ketoglutarate on Growth, Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus Accumulation and Their Stoichiometric Relationships in Kosteletzkya virginica under Salt Stress. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2023, 25, 170–177. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, S. Research progress of azelaic acid in plants. Plant Physiol. J. 2022, 58, 483–491. [Google Scholar]
- Shibl, A.A.; Ochsenkühn, M.A.; Mohamed, A.R.; Isaac, A.; Coe, L.S.Y.; Yun, Y.; Skrzypek, G.; Raina, J.B.; Seymour, J.R.; Afzal, A.J.; et al. Molecular mechanisms of microbiome modulation by the eukaryotic secondary metabolite azelaic acid. Elife 2024, 12, 88525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korenblum, E.; Dong, Y.; Szymanski, J.; Panda, S.; Jozwiak, A.; Massalha, H.; Meir, S.; Rogachev, I.; Aharoni, A. Rhizosphere microbiome mediates systemic root metabolite exudation by root-to-root signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 3874–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Gong, J.; Luo, S.; Zuo, Y.; Shen, Y. Role of Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid in Plant Defense Response. Metabolites 2023, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, S.; Iqbal, R.K.; Ashraf, H.; Rasool, M.A.; Ansari, M.J.; Alarfaj, A.A.; Alharbi, S.A. Mitigating effect of γ-aminobutyric acid and gibberellic acid on tomato plant cultivated in Pb-polluted soil. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhu, S.; Pan, W.; Wu, L.; Hu, Z. The bioavailability of soil amino acids and the regulation mechanism by environmental factors: A review. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2020, 26, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar]
- Kawade, K.; Tabeta, H.; Ferjani, A.; Hirai, M.Y. The Roles of Functional Amino Acids in Plant Growth and Development. Plant Cell Physiol. 2023, 64, 1482–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Bassler, B.L. Bacterial quorum sensing in complex and dynamically changing environments. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadotani, N.; Akagi, A.; Takatsuji, H.; Miwa, T.; Igarashi, D. Exogenous proteinogenic amino acids induce systemic resistance in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, A.; Reichelt, M.; Furch, A.; Mithöfer, A.; Oelmüller, R. Cellooligomer/CELLOOLIGOMER RECEPTOR KINASE1 signaling exhibits crosstalk with PAMP-triggered immune responses and sugar metabolism in Arabidopsis roots. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, J.; Wen, T.; Zhao, M.; Li, R.; Goossens, P.; Huang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Vivanco, J.M.; Kowalchuk, G.A.; et al. Root exudates drive the soil-borne legacy of aboveground pathogen infection. Microbiome 2018, 6, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.F.; Yang, L.; Yan, Z.X.; Jiang, B.B.; Li, S.; Huang, H.C.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhu, S.S.; Yang, M. Ginsenosides in root exudates of Panax notoginseng drive the change of soil microbiota through carbon source different utilization. Plant Soil 2020, 455, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Tang, H.; Guo, J.; Pan, C.; Wang, R.; Wu, Y.; Yu, Y. Root Exudates’ Roles and Analytical Techniques Progress. Soils 2023, 55, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- van Meer, G.; Voelker, D.R.; Feigenson, G.W. Membrane lipids: Where they are and how they behave. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, R.A.; Nwangburuka, C.C.; Oboirien, B.O. Origins, roles and fate of organic acids in soils: A review. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2017, 108, 393–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, K.P.; Kumar, A.; Sakthivel, K.; Reddy, B.; Kumar, M.; Patel, A.; Sheoran, N.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Prakash, G.; Rathour, R.; et al. Deciphering core phyllomicrobiome assemblage on rice genotypes grown in contrasting agroclimatic zones: Implications for phyllomicrobiome engineering against blast disease. Environ. Microbiome 2022, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, H.; Jia, M.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Ali, G.; Mao, L.; Zhang, J.; Fan, T.; et al. Key decomposers of straw depending on tillage and fertilization. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 358, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, S.; Kong, H.J.; Park, J.; Seo, Y.S. Comparative genomic analysis of Chryseobacterium species: Deep insights into plant-growth-promoting and halotolerant capacities. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 001108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; She, M.; Li, H.; Jing, S.; Jiang, H.; Gao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Fu, J. Growth Promotion Mechanisms of flavobacterium succinicans and Their Physiological Regulation on the Growth and Stress Tolerance in Lolium perenne. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2021, 29, 1704–1711. [Google Scholar]
- Hagagy, N.; AbdElgawad, H. The potential of Actinoplanes spp. for alleviating the oxidative stress induced by thallium toxicity in wheat plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 213, 108853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Ma, W.; Zheng, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, K.; Tong, Y.; Huang, G.; et al. Benzoic acid facilitates ANF in monocot crops by recruiting nitrogen-fixing Paraburkholderia. ISME J. 2024, 18, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Zhang, S.; Shen, W.; Zhu, W.; Noor, I.; Liu, J.; Li, G. Benzoic acid plays a part in rhizosphere microbial composition of peach seedlings grown in replanted soil. Rhizosphere 2021, 19, 100364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudrappa, T.; Czymmek, K.J.; Paré, P.W.; Bais, H.P. Root-secreted malic acid recruits beneficial soil bacteria. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Li, Z.; Deng, Z.; Xie, C.; Gu, Y.; Lei, P.; Wang, R.; Li, S.; Xu, H. Effects of malic acid and syringic acid from tomato root exudates on soil bacterial community structure and potential function. Jiangsu J. Agric. Sci. 2022, 38, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Santolini, M.; Barabási, A.L. Predicting perturbation patterns from the topology of biological networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E6375–E6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barea, J.M.; Pozo, M.J.; Azcón, R.; Azcón-Aguilar, C. Microbial co-operation in the rhizosphere. J. Exp. Bot. 2005, 56, 1761–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebotar, V.K.; Asis, C.A.; Akao, S. Production of growth-promoting substances and high colonization ability of rhizobacteria enhance the nitrogen fixation of soybean when coinoculated with Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2001, 34, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D. Advances in Studies on the Interaction between PGPR and Rhizobium. Adv. Microbiol. 2022, 11, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, C.R. The role of antibiosis in biocontrol. In Trichoderma and Gliocladium: Enzymes, Biological Control, and Commercial Applications, 2nd ed.; Harman, G.E., Kubicek, C.P., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 1998; pp. 173–184. [Google Scholar]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, D.; Xie, Z.; Guo, J.; Wang, B.; Peng, Q.; Yang, J.; Deng, B.; Gao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fa, X.; et al. Local Fungi Promote Plant Growth by Positively Affecting Rhizosphere Metabolites to Drive Beneficial Microbial Assembly. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081752
Dong D, Xie Z, Guo J, Wang B, Peng Q, Yang J, Deng B, Gao Y, Guo Y, Fa X, et al. Local Fungi Promote Plant Growth by Positively Affecting Rhizosphere Metabolites to Drive Beneficial Microbial Assembly. Microorganisms. 2025; 13(8):1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081752
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Deyu, Zhanling Xie, Jing Guo, Bao Wang, Qingqing Peng, Jiabao Yang, Baojie Deng, Yuan Gao, Yuting Guo, Xueting Fa, and et al. 2025. "Local Fungi Promote Plant Growth by Positively Affecting Rhizosphere Metabolites to Drive Beneficial Microbial Assembly" Microorganisms 13, no. 8: 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081752
APA StyleDong, D., Xie, Z., Guo, J., Wang, B., Peng, Q., Yang, J., Deng, B., Gao, Y., Guo, Y., Fa, X., & Yu, J. (2025). Local Fungi Promote Plant Growth by Positively Affecting Rhizosphere Metabolites to Drive Beneficial Microbial Assembly. Microorganisms, 13(8), 1752. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms13081752





