Investigating How Genomic Contexts Impact IS5 Transposition Within the Escherichia coli Genome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. E. coli Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. Construction of IS5 Deletion Mutants
2.3. Deletion or Blockage of the nmpC Promoter (PnmpC)
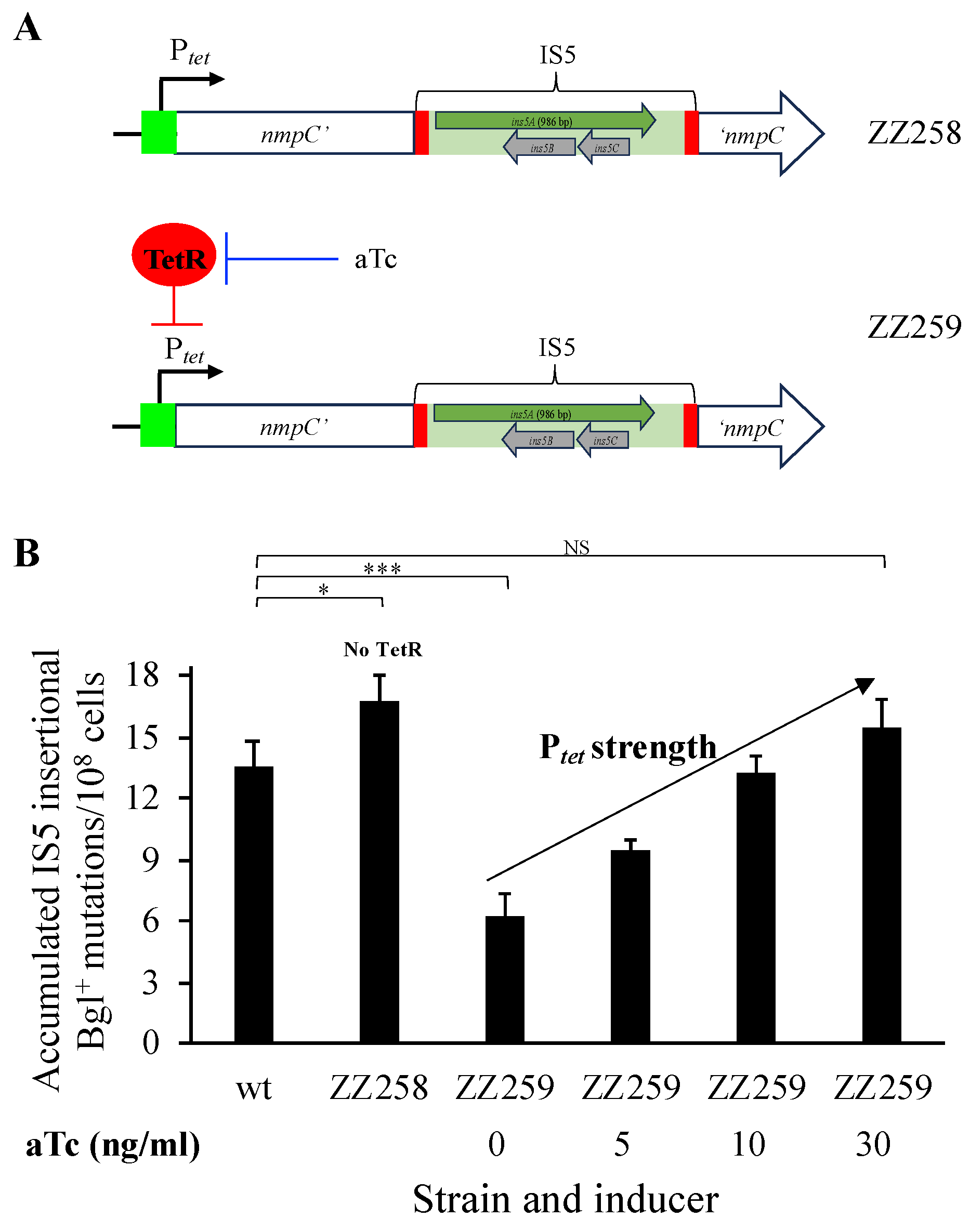
2.4. Construction of Ptet Substitution for PnmpC on the Chromosome
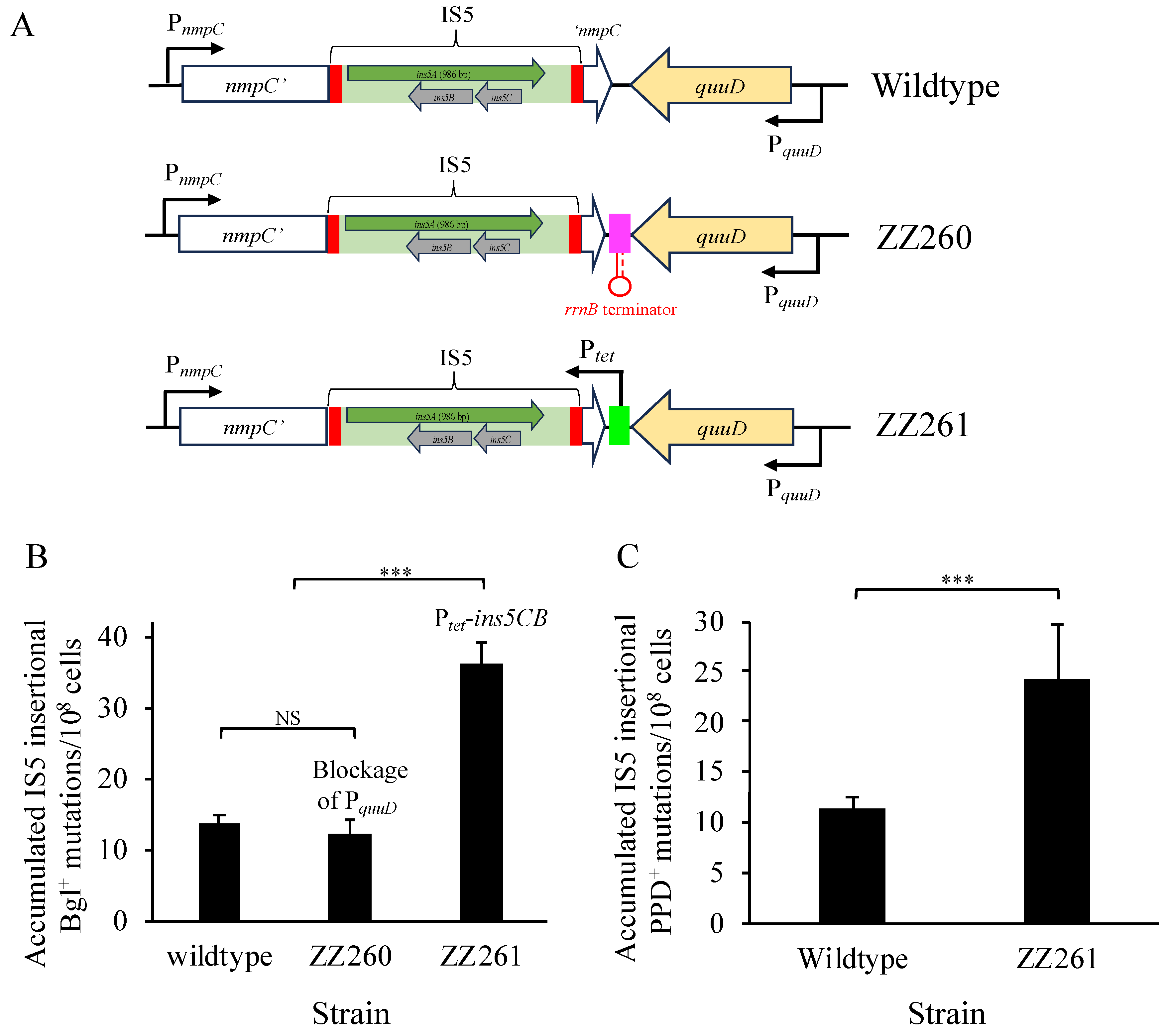
2.5. Insertion of a Terminator or Ptet Downstream of nmpC
2.6. Construction of Ptet Driving ins5A at the intS Locus
2.7. β-Glucoside Growth Mutation (Bgl+) Assay
2.8. Swarming Mutation Assay
2.9. Propanediol Growth (PPD+) Mutation Assay
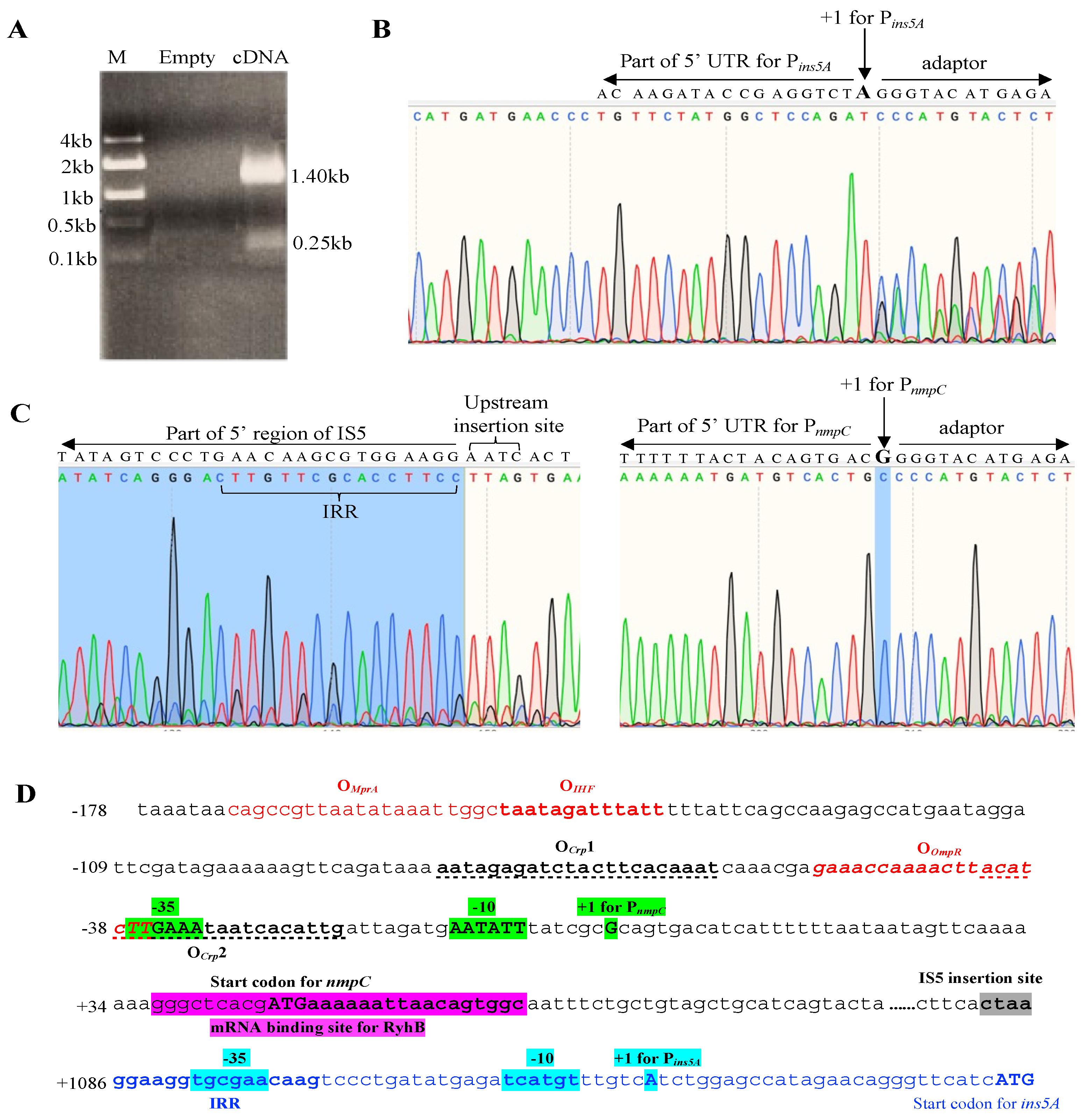
2.10. TSS Determination Using a SMARTer® RACE 5′/3′ Kit
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
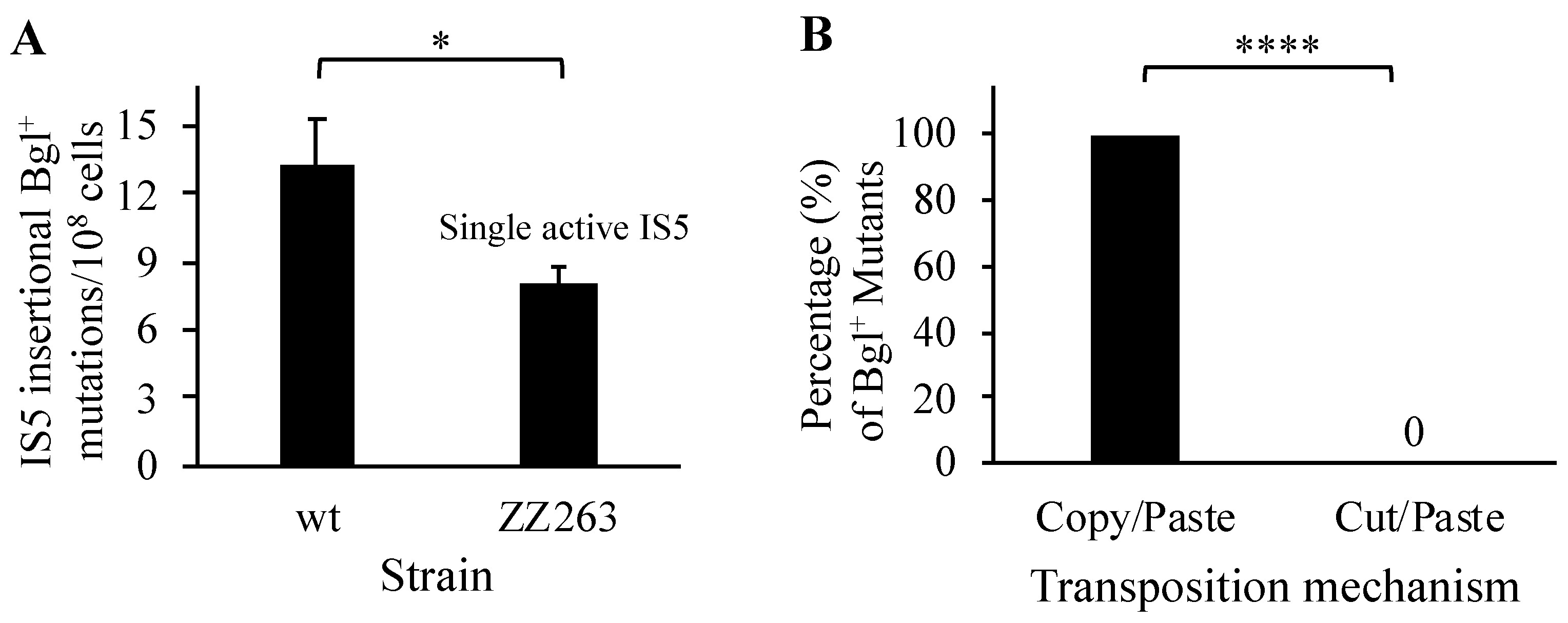
3.1. Two Copies of IS5 with Point Mutations Are Incapable of Transposition
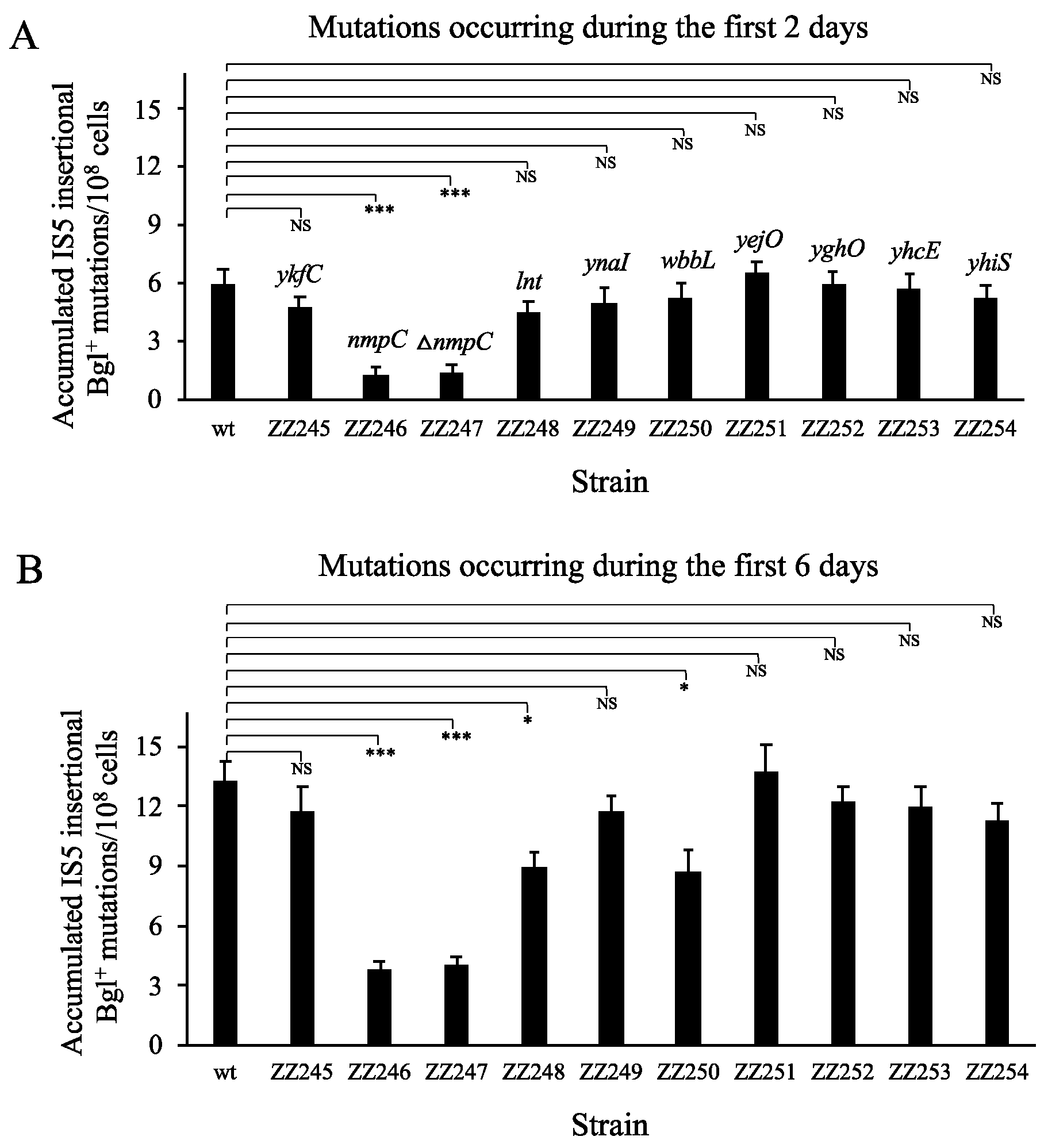
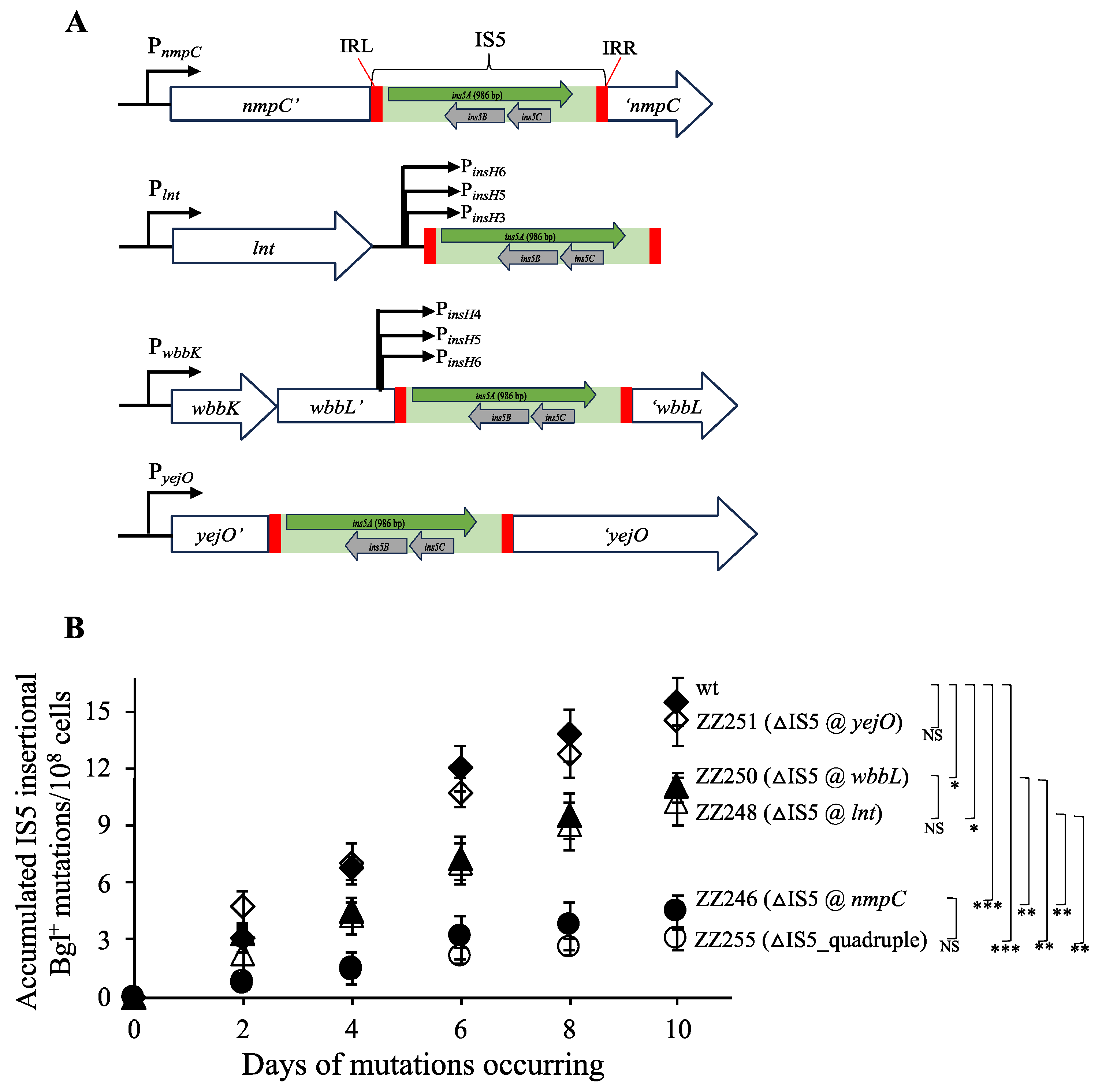
3.2. IS5 at nmpC Plays a Major Role in IS5 Insertion Upstream of the Bgl Operon
3.3. IS5 at nmpC is Important for Other IS5-Targeted Gene Mutations
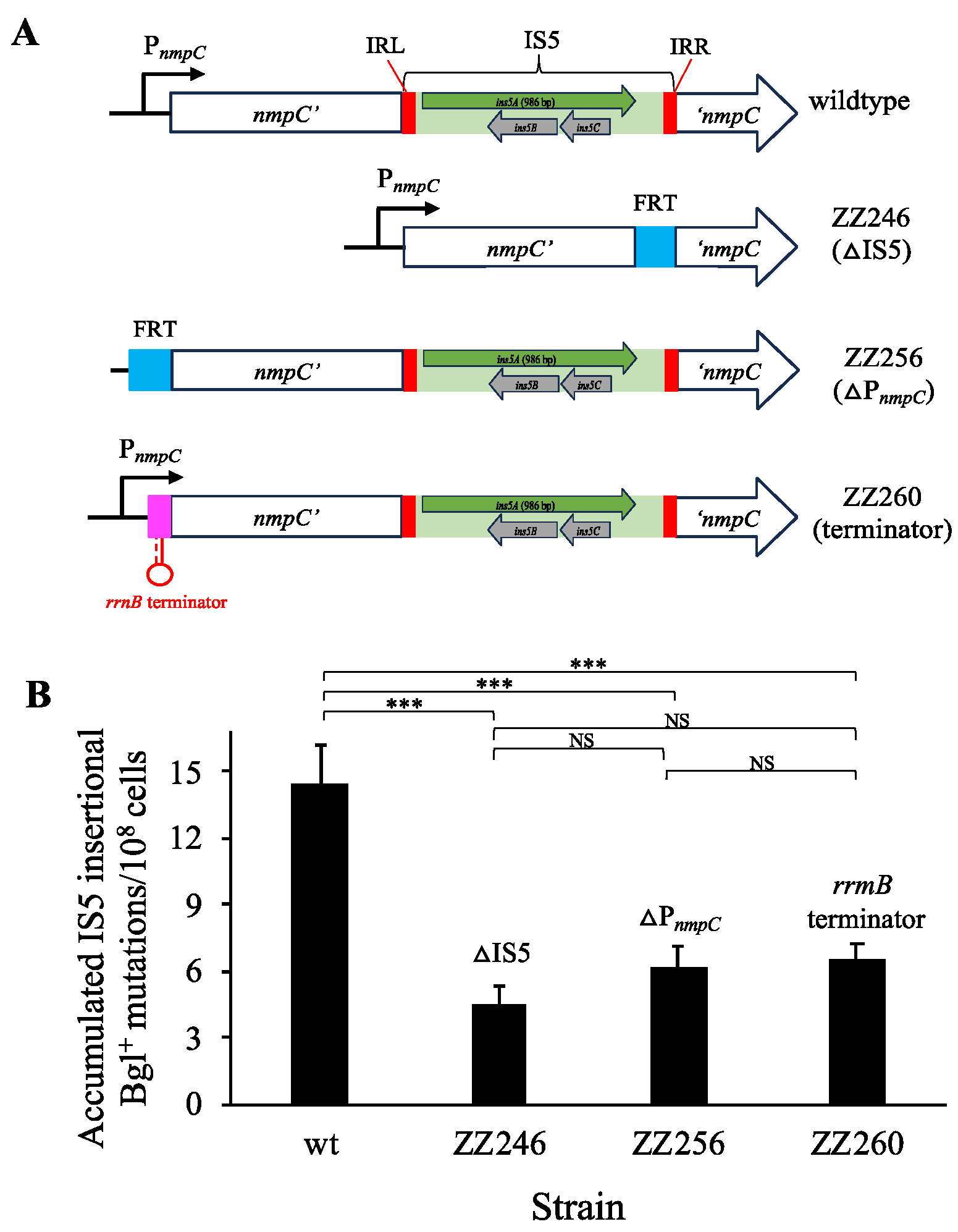
3.4. nmpC Promoter Is Critical for the Overall IS5 Transposition Rate
3.5. IS5 at the nmpC Locus is the Only Element That Efficiently Transcribes ins5A
3.6. IS5 Transposition Activity Is Proportional to the Strength of the Promoter Upstream of nmpC
3.7. Increased Expression of ins5A at the intS Locus Does Not Promote IS5 Transposition
3.8. Blockage of the Downstream Genomic Region Near nmpC Has Little Effect on IS5 Transposition, But Increased ins5CB Expression Enhances It
3.9. “Copy/Paste” Is the Dominant Mechanism for IS5 Transposition
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siguier, P.; Filee, J.; Chandler, M. Insertion sequences in prokaryotic genomes. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 526–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykhuizen, D.E.; Sawyer, S.A.; Green, L.; Miller, R.D.; Hartl, D.L. Joint distribution of insertion elements IS4 and IS5 in natural isolates of Escherichia coli. Genetics 1985, 111, 219–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, S.A.; Dykhuizen, D.E.; DuBose, R.F.; Green, L.; Mutangadura-Mhlanga, T.; Wolczyk, D.F.; Hartl, D.L. Distribution and abundance of insertion sequences among natural isolates of Escherichia coli. Genetics 1987, 115, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahillon, J.; Leonard, C.; Chandler, M. IS elements as constituents of bacterial genomes. Res. Microbiol. 1999, 150, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naas, T.; Blot, M.; Fitch, W.M.; Arber, W. Dynamics of IS-related genetic rearrangements in resting Escherichia coli K-12. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1995, 12, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeside, C.; Gaffe, J.; Deatherage, D.E.; Tenaillon, O.; Briska, A.M.; Ptashkin, R.N.; Cruveiller, S.; Medigue, C.; Lenski, R.E.; Barrick, J.E.; et al. Large chromosomal rearrangements during a long-term evolution experiment with Escherichia coli. mBio 2014, 5, e01377-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Doak, T.G.; Popodi, E.; Foster, P.L.; Tang, H. Insertion sequence-caused large-scale rearrangements in the genome of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 7109–7119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jespersen, M.G.; Hayes, A.J.; Tong, S.Y.C.; Davies, M.R. Insertion sequence elements and unique symmetrical genomic regions mediate chromosomal inversions in Streptococcus pyogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, 13128–13137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.A.; Plague, G.R. Genomic changes following host restriction in bacteria. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2004, 14, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touchon, M.; Rocha, E.P. Causes of insertion sequences abundance in prokaryotic genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 969–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plague, G.R.; Dunbar, H.E.; Tran, P.L.; Moran, N.A. Extensive proliferation of transposable elements in heritable bacterial symbionts. J. Bacteriol. 2008, 190, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glansdorff, N.; Charlier, D.; Zafarullah, M. Activation of gene expression by IS2 and IS3. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1981, 45 Pt 1, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubert, D.; Naas, T.; Heritier, C.; Poirel, L.; Nordmann, P. Functional characterization of IS1999, an IS4 family element involved in mobilization and expression of beta-lactam resistance genes. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 6506–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siguier, P.; Gourbeyre, E.; Chandler, M. Bacterial insertion sequences: Their genomic impact and diversity. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partridge, S.R.; Kwong, S.M.; Firth, N.; Jensen, S.O. Mobile Genetic Elements Associated with Antimicrobial Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipszyc, A.; Szuplewska, M.; Bartosik, D. How Do Transposable Elements Activate Expression of Transcriptionally Silent Antibiotic Resistance Genes? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, M. The behavior of mobile genetic elements (MGEs) in different environments. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2017, 81, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blattner, F.R.; Fiandt, M.; Hass, K.K.; Twose, P.A.; Szybalski, W. Deletions and insertions in the immunity region of coliphage lambda: Revised measurement of the promoter-startpoint distance. Virology 1974, 62, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, L.; Miller, R.D.; Dykhuizen, D.E.; Hartl, D.L. Distribution of DNA insertion element IS5 in natural isolates of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engler, J.A.; van Bree, M.P. The nucleotide sequence and protein-coding capability of the transposable element IS5. Gene 1981, 14, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoner, B.; Kahn, M. The nucleotide sequence of IS5 from Escherichia coli. Gene 1981, 14, 165–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rak, B.; Lusky, M.; Hable, M. Expression of two proteins from overlapping and oppositely oriented genes on transposable DNA insertion element IS5. Nature 1982, 297, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, S.; Kato, M.; Kohara, Y.; Mizuno, T. Insertion sequence IS5 contains a sharply curved DNA structure at its terminus. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1988, 214, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yen, M.R.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Precise excision of IS5 from the intergenic region between the fucPIK and the fucAO operons and mutational control of fucPIK operon expression in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umeda, M.; Ohtsubo, E. Mapping of insertion element IS5 in the Escherichia coli K-12 chromosome. Chromosomal rearrangements mediated by IS5. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 213, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, F.; Matteau, D.; Baby, V.; Rodrigue, S. Complete Genome Sequence of Escherichia coli BW25113. Genome Announc. 2014, 2, e01038-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Inouye, M. Inactivation of the Serratia marcescens gene for the lipoprotein in Escherichia coli by insertion sequences, IS1 and IS5; sequence analysis of junction points. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1981, 183, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteway, J.; Koziarz, P.; Veall, J.; Sandhu, N.; Kumar, P.; Hoecher, B.; Lambert, I.B. Oxygen-insensitive nitroreductases: Analysis of the roles of nfsA and nfsB in development of resistance to 5-nitrofuran derivatives in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1998, 180, 5529–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesslinger, C.; Sawers, G. The tdcE gene in Escherichia coli strain W3110 is separated from the rest of the tdc operon by insertion of IS5 elements. DNA Seq. 1998, 9, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawers, R.G. Expression of fnr is constrained by an upstream IS5 insertion in certain Escherichia coli K-12 strains. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2609–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, A.E.; Felton, J.; Wright, A. Insertion of DNA activates the cryptic bgl operon in E. coli K12. Nature 1981, 293, 625–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnetz, K.; Rak, B. IS5: A mobile enhancer of transcription in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Chakrabarti, T.; Lin, E.C. Constitutive activation of L-fucose genes by an unlinked mutation in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 159, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.M.; Lu, Z.; Lin, E.C. Constitutive activation of the fucAO operon and silencing of the divergently transcribed fucPIK operon by an IS5 element in Escherichia coli mutants selected for growth on L-1,2-propanediol. J. Bacteriol. 1989, 171, 6097–6105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, C.S.; Pruss, B.M.; Matsumura, P. Increased motility of Escherichia coli by insertion sequence element integration into the regulatory region of the flhD operon. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 7529–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Saier, M.H., Jr. A mechanism of transposon-mediated directed mutation. Mol. Microbiol. 2009, 74, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, D.; Breier, A.M.; Higgins, N.P. Microarray analysis of transposition targets in Escherichia coli: The impact of transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9780–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humayun, M.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Butcher, A.M.; Moshayedi, A.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Hopping into a hot seat: Role of DNA structural features on IS5-mediated gene activation and inactivation under stress. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0180156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.; Legood, S.; Wheat, R.L.; Forrest, D.; Sharma, P.; Haycocks, J.R.J.; Grainger, D.C. H-NS is a bacterial transposon capture protein. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopkowski, P.W.; Zhang, Z.; Saier, M.H., Jr. The effect of DNA-binding proteins on insertion sequence element transposition upstream of the bgl operon in Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1388522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, K.; Tran, D.; Saier, M. Insertion Sequence (IS) Element-Mediated Activating Mutations of the Cryptic Aromatic beta-Glucoside Utilization (BglGFB) Operon Are Promoted by the Anti-Terminator Protein (BglG) in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wood, T.K. IS5 inserts upstream of the master motility operon flhDC in a quasi-Lamarckian way. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Kukita, C.; Humayun, M.Z.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Environment-directed activation of the Escherichia coli flhDC operon by transposons. Microbiology (Reading) 2017, 163, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawers, R.G. Transcript analysis of Escherichia coli K-12 insertion element IS5. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 244, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datsenko, K.A.; Wanner, B.L. One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6640–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klumpp, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hwa, T. Growth rate-dependent global effects on gene expression in bacteria. Cell 2009, 139, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, E.; Zhang, Z.; Kuhlman, T.; Hwa, T. Quantitative characteristics of gene regulation by small RNA. PLoS Biol. 2007, 5, e229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, J.; Foster, P.L. Adaptive reversion of a frameshift mutation in Escherichia coli. Genetics 1991, 128, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Huo, J.; Velo, J.; Zhou, H.; Flaherty, A.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Comprehensive Characterization of fucAO Operon Activation in Escherichia coli. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta, A.M.; Collado-Vides, J. Sigma70 promoters in Escherichia coli: Specific transcription in dense regions of overlapping promoter-like signals. J. Mol. Biol. 2003, 333, 261–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blasband, A.J.; Marcotte, W.R., Jr.; Schnaitman, C.A. Structure of the lc and nmpC outer membrane porin protein genes of lambdoid bacteriophage. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 12723–12732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coll, J.L.; Heyde, M.; Portalier, R. Expression of the nmpC gene of Escherichia coli K-12 is modulated by external pH. Identification of cis-acting regulatory sequences involved in this regulation. Mol. Microbiol. 1994, 12, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueguen, E.; Rousseau, P.; Duval-Valentin, G.; Chandler, M. The transpososome: Control of transposition at the level of catalysis. Trends Microbiol. 2005, 13, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindahl, M.S.; Crockford, G.W.; Hancock, R.E. Outer membrane protein NmpC of Escherichia coli: Pore-forming properties in black lipid bilayers. J. Bacteriol. 1984, 159, 1053–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugsley, A.P.; Schnaitman, C.A. Identification of three genes controlling production of new outer membrane pore proteins in Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 1978, 135, 1118–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbyshire, K.M.; Kramer, M.; Grindley, N.D. Role of instability in the cis action of the insertion sequence IS903 transposase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4048–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derbyshire, K.M.; Grindley, N.D. Cis preference of the IS903 transposase is mediated by a combination of transposase instability and inefficient translation. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 21, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rak, B.; von Reutern, M. Insertion element IS5 contains a third gene. EMBO J. 1984, 3, 807–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.C.; Reznikoff, W.S. Role of the IS50 R proteins in the promotion and control of Tn5 transposition. J. Mol. Biol. 1984, 177, 645–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerbib, D.; Polard, P.; Escoubas, J.M.; Galas, D.; Chandler, M. The regulatory role of the IS1-encoded InsA protein in transposition. Mol. Microbiol. 1990, 4, 471–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.T.; Hwang, J.H.; Lee, L.C.; Lee, C.H.; Li, P.L.; Hsieh, Y.C. Functional analysis of the 14 kDa protein of insertion sequence 2. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 236, 503–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval-Valentin, G.; Normand, C.; Khemici, V.; Marty, B.; Chandler, M. Transient promoter formation: A new feedback mechanism for regulation of IS911 transposition. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 5802–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datta, A.R.; Rosner, J.L. Reduced transposition in rho mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 888–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galas, D.J.; Chandler, M. Bacterial insertion sequences. In Mobile DNA; Berg, D.E., Howe, M.M., Eds.; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1989; pp. 109–162. [Google Scholar]
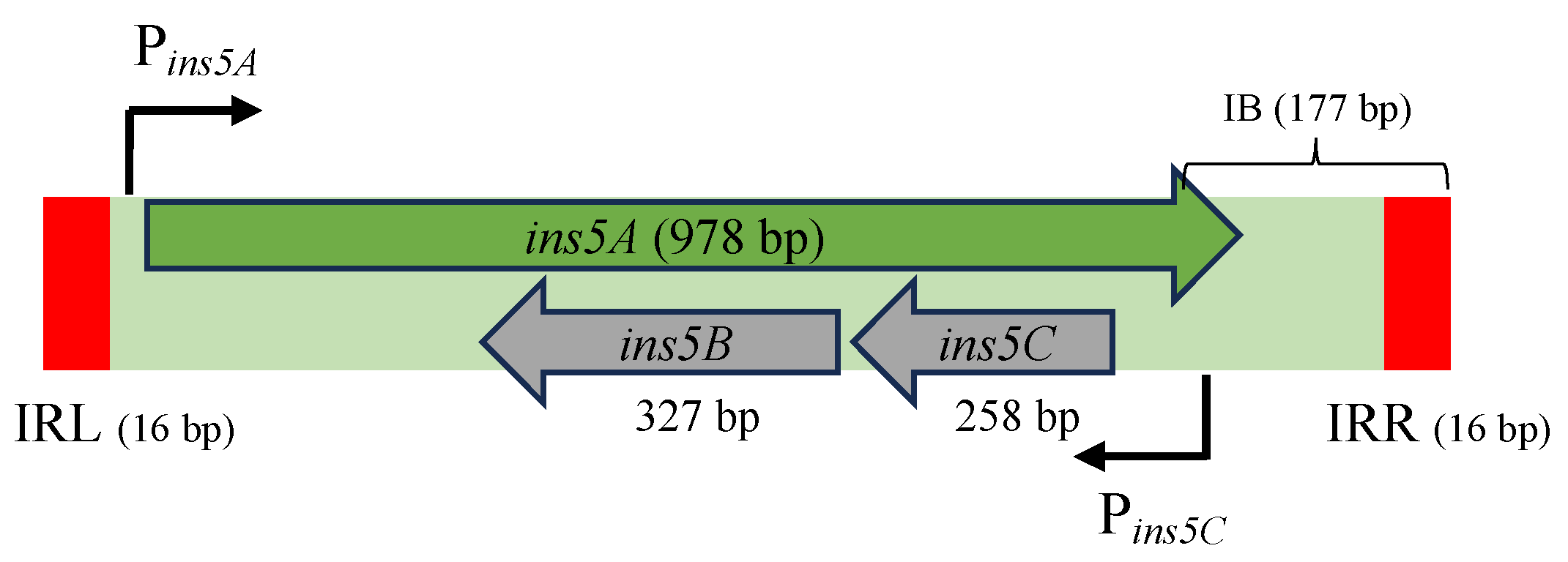


| Copy | Coordinates * (Kb) | Target Genes ** | Orientation *** | Similarity to IS5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 269.8/270.8 | ykfC | Reverse | 100% |
| 2 | 570.2/571.2 | nmpC | Direct | 100% |
| 3 | 683.5/684.5 | gltI/lnt | Direct | 100% |
| 4 | 1390.3/1391.3 | ynaI/ynaJ | Reverse | 100% |
| 5 | 1422.0/1423.0 | lomR | Reverse | 91.5% |
| 6 | 2059.8/2060.8 | cobU/yoeG | Reverse | 99.6% |
| 7 | 2095.4/2096.4 | wbbL | Direct | 100% |
| 8 | 2282.5/2283.6 | yejO | Direct | 100% |
| 9 | 3123.5/3124.5 | yghO | Reverse | 100% |
| 10 | 3359.1/3360.1 | yhcE | Reverse | 100% |
| 11 | 3635.4/3646.6 | yhiS | Reverse | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Onstead, J.; Zhang, Z.; Huo, J.; Ord, J.W.; Smith, S.; Saier, M.H., Jr. Investigating How Genomic Contexts Impact IS5 Transposition Within the Escherichia coli Genome. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122600
Onstead J, Zhang Z, Huo J, Ord JW, Smith S, Saier MH Jr. Investigating How Genomic Contexts Impact IS5 Transposition Within the Escherichia coli Genome. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122600
Chicago/Turabian StyleOnstead, Jonathan, Zhongge Zhang, Jialu Huo, Jack W. Ord, Sofia Smith, and Milton H. Saier, Jr. 2024. "Investigating How Genomic Contexts Impact IS5 Transposition Within the Escherichia coli Genome" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122600
APA StyleOnstead, J., Zhang, Z., Huo, J., Ord, J. W., Smith, S., & Saier, M. H., Jr. (2024). Investigating How Genomic Contexts Impact IS5 Transposition Within the Escherichia coli Genome. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2600. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122600






