Mercury and Arctic Char Gill Microbiota Correlation in Canadian Arctic Communities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistics
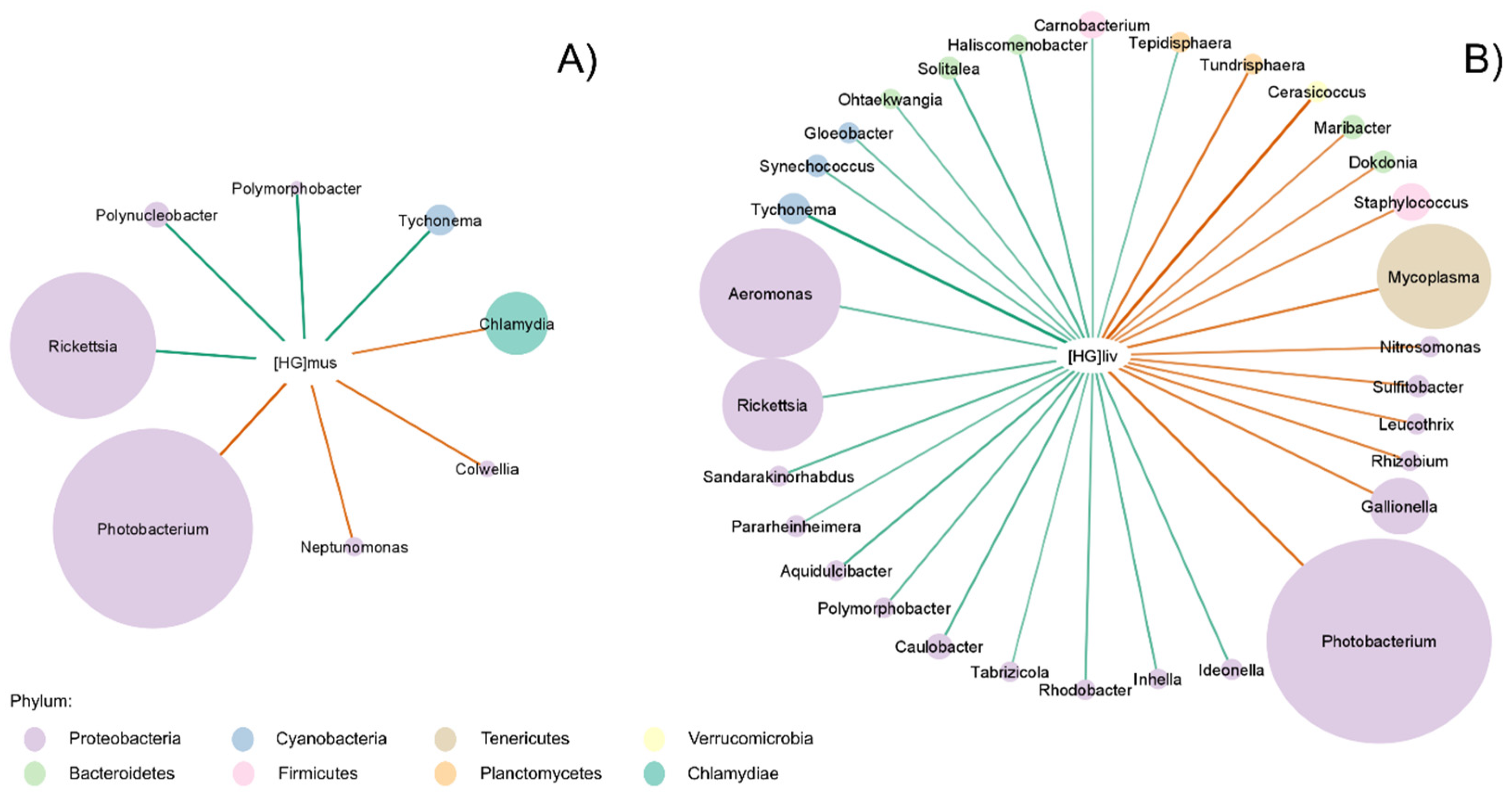
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Higher Mercury Concentrations at the Highest Latitude
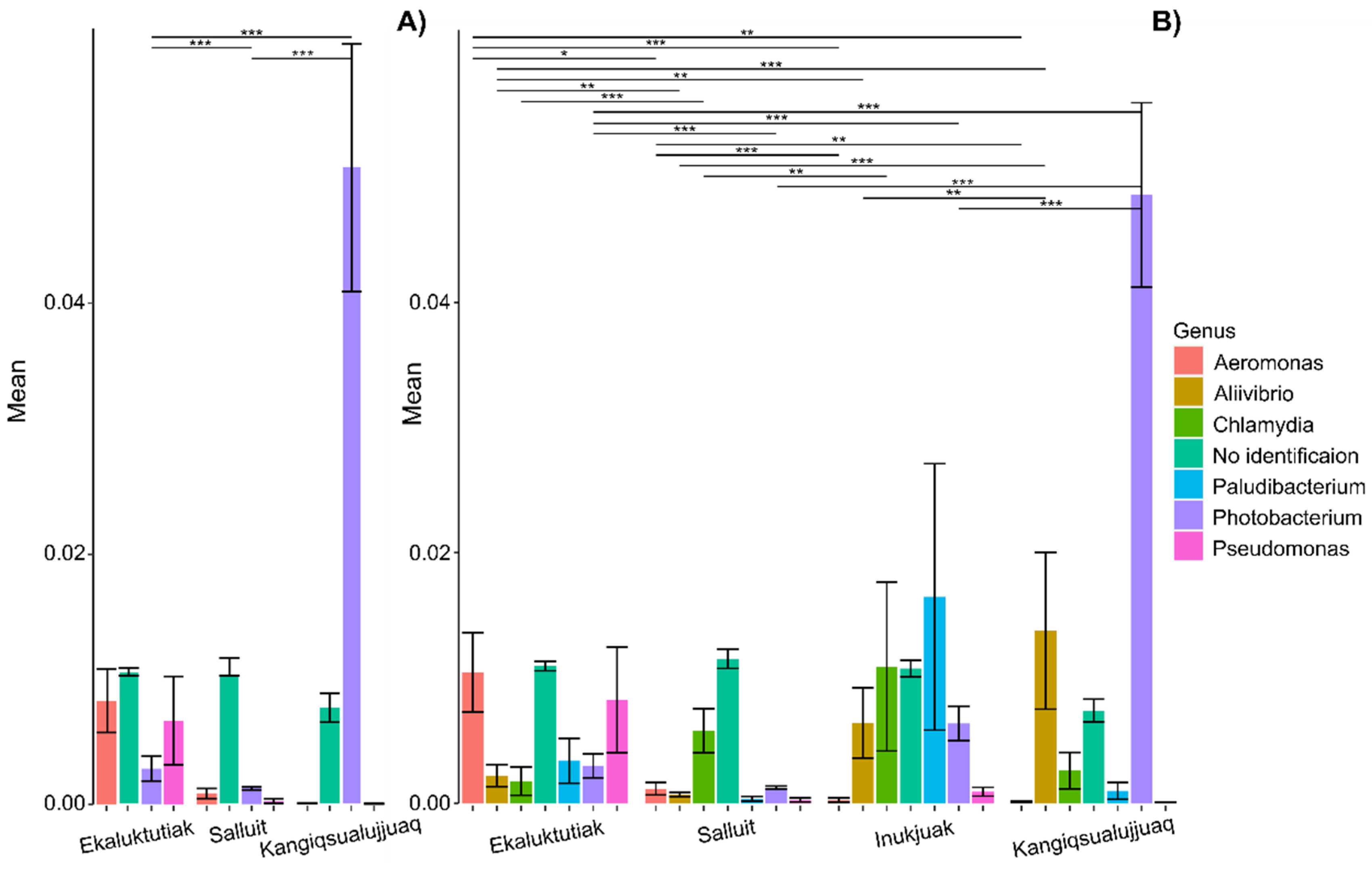
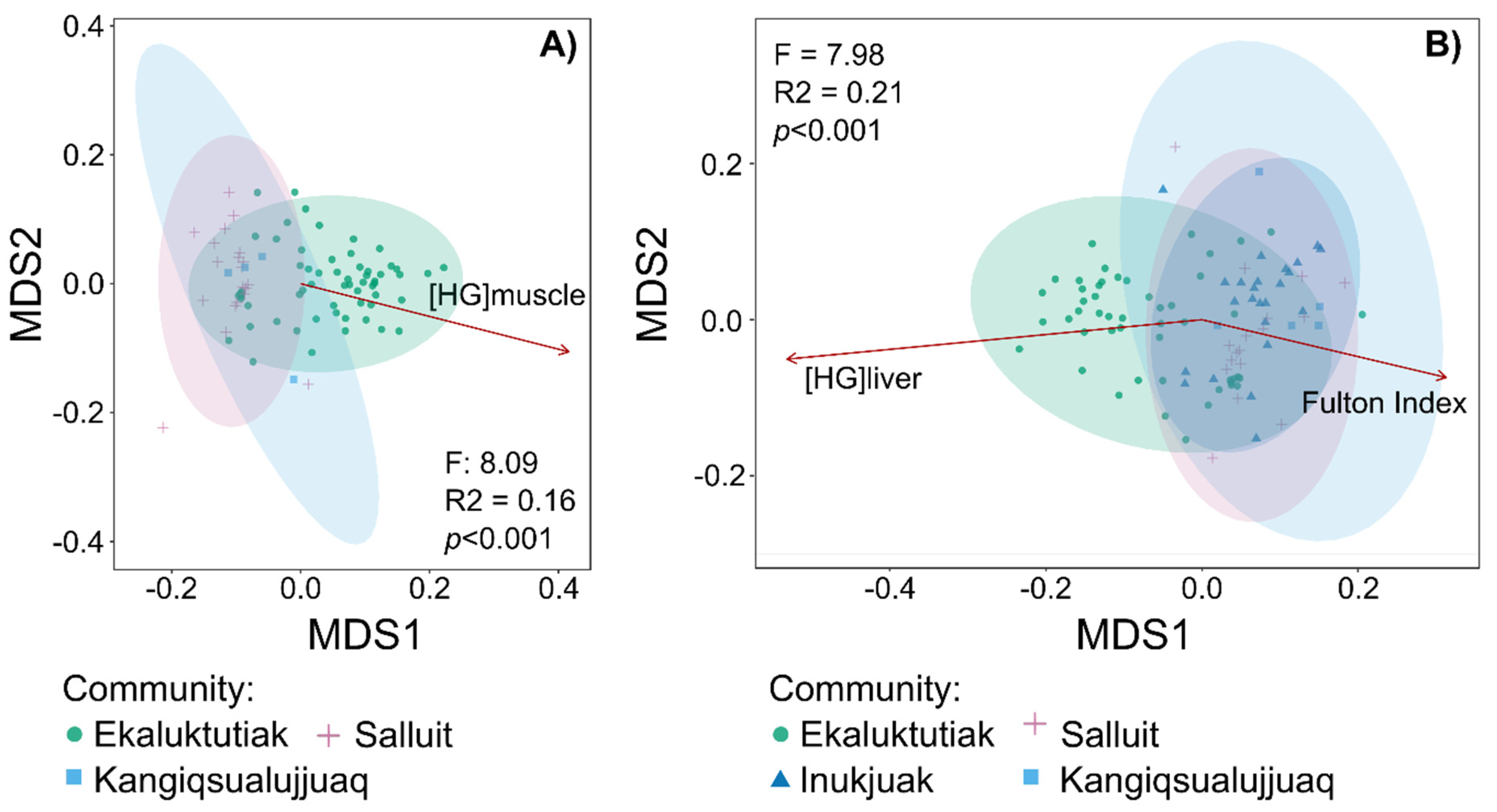
4.2. Correlation Between Mercury Concentrations and Arctic Char Gill Microbiota
4.3. Mercury Transformation Role of Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falardeau, M.; Bennett, E.M.; Else, B.; Fisk, A.; Mundy, C.J.; Choy, E.S.; Ahmed, M.M.M.; Harris, L.N.; Moore, J.-S. Biophysical Indicators and Indigenous and Local Knowledge Reveal Climatic and Ecological Shifts with Implications for Arctic Char Fisheries. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2022, 74, 102469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobling, M.; Jørgensen, E.H.; Arnesen, A.M.; Ringø, E. Feeding, Growth and Environmental Requirements of Arctic Charr: A Review of Aquaculture Potential. Aquac. Int. 1993, 1, 20–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roux, M.J.; Tallman, R.F.; Lewis, C.W. Small-Scale Arctic Charr Salvelinus alpinus Fisheries in Canada’s Nunavut: Management Challenges and Options. J. Fish. Biol. 2011, 79, 1625–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J. The Arctic Charr, Salvelinus alpinus. In Charrs: Salmonid Fishes of the Genus Salvelinus; Junk: The Hague, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 15–98. [Google Scholar]
- Power, M.; Reist, J.D.; Dempson, J.B. Fish in High-Latitude Arctic Lakes. In Polar Lakes and Rivers: Limnology of Arctic and Antarctic Aquatic Ecosystems; Vincent, W.F., Laybourn-Parry, J., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2008; pp. 249–268. ISBN 978-0-19-170750-6. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, E.B. The Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus) “Complex” in North America Revisited. Hydrobiologia 2016, 783, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Wiener, J.G.; Eckley, C.S.; Willacker, J.J.; Evers, D.C.; Marvin-DiPasquale, M.; Obrist, D.; Fleck, J.A.; Aiken, G.R.; Lepak, J.M.; et al. Mercury in Western North America: A Synthesis of Environmental Contamination, Fluxes, Bioaccumulation, and Risk to Fish and Wildlife. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnan, Y.; Le Dantec, T.; Moore, C.W.; Edwards, G.C.; Obrist, D. New Constraints on Terrestrial Surface–Atmosphere Fluxes of Gaseous Elemental Mercury Using a Global Database. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 507–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selin, N.E. Global Biogeochemical Cycling of Mercury: A Review. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2009, 34, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, C.T.; Mason, R.P.; Chan, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Pirrone, N. Mercury as a Global Pollutant: Sources, Pathways, and Effects. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 4967–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shindell, D.T.; Chin, M.; Dentener, F.; Doherty, R.M.; Faluvegi, G.; Fiore, A.M.; Hess, P.; Koch, D.M.; MacKenzie, I.A.; Sanderson, M.G.; et al. A Multi-Model Assessment of Pollution Transport to the Arctic. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 5353–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engstrom, D.R. Fish Respond When the Mercury Rises. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16394–16395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu-Kim, H.; Kucharzyk, K.H.; Zhang, T.; Deshusses, M.A. Mechanisms Regulating Mercury Bioavailability for Methylating Microorganisms in the Aquatic Environment: A Critical Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 2441–2456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, J.M.; Johs, A.; Podar, M.; Bridou, R.; Hurt, R.A.; Smith, S.D.; Tomanicek, S.J.; Qian, Y.; Brown, S.D.; Brandt, C.C.; et al. The Genetic Basis for Bacterial Mercury Methylation. Science 2013, 339, 1332–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergler, D.; Anderson, H.A.; Chan, L.H.M.; Mahaffey, K.R.; Murray, M.; Sakamoto, M.; Stern, A.H. Methylmercury Exposure and Health Effects in Humans: A Worldwide Concern. Ambio 2007, 36, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, N.; Abass, K.; Dietz, R.; Krümmel, E.; Rautio, A.; Weihe, P. The Impact of Mercury Contamination on Human Health in the Arctic: A State of the Science Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandheinrich, M.B.; Wiener, J.G. Methylmercury in Freshwater Fish | 5 | v2 | Recent Advances in Assessi. Available online: https://www.taylorfrancis.com/chapters/oa-edit/10.1201/b10598-5/methylmercury-freshwater-fish-mark-sandheinrich-james-wiener (accessed on 20 October 2023).
- Dillon, T.; Beckvar, N.; Kern, J. Residue-Based Mercury Dose–Response in Fish: An Analysis Using Lethality-Equivalent Test Endpoints. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada Health Canada’s Maximum Levels for Chemical Contaminants in Foods. Government of Canada. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-safety/chemical-contaminants/maximum-levels-chemical-contaminants-foods.html (accessed on 5 October 2023).
- Olivia-Ribeiro, C.A. Distribution Kinetics of Dietary Methylmercury in the Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus) | Environmental Science & Technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, W.-X. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Model for Inorganic and Methylmercury in a Marine Fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10173–10181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seco, J.; Xavier, J.C.; Bustamante, P.; Coelho, J.P.; Saunders, R.A.; Ferreira, N.; Fielding, S.; Pardal, M.A.; Stowasser, G.; Viana, T.; et al. Main Drivers of Mercury Levels in Southern Ocean Lantern Fish Myctophidae. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 264, 114711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Nabavi, S.M.B.; Parsa, Y. Bioaccumulation of Trace Mercury in Trophic Levels of Benthic, Benthopelagic, Pelagic Fish Species, and Sea Birds from Arvand River, Iran. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2013, 156, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suhendrayatna, S.; Arahman, N.; Sipahutar, L.W.; Rinidar, R.; Elvitriana, E. Toxicity and Organ Distribution of Mercury in Freshwater Fish (Oreochromis niloticus) after Exposure to Water Contaminated Mercury (HgII). Toxics 2019, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassaninezhad, L.; Safahieh, A.; Salamat, N.; Savari, A.; Majd, N.E. Assessment of Gill Pathological Responses in the Tropical Fish Yellowfin Seabream of Persian Gulf under Mercury Exposure. Toxicol. Rep. 2014, 1, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poleksić, V.; Mitrović-Tutundžić, V. Fish Gills as a Monitor of Sublethal and Chronic Effects of Pollution. In Sublethal and Chronic Effects of Pollutants on Freshwater Fish; Fishing News Books: Oxford, UK, 1994; pp. 339–352. [Google Scholar]
- Lemire, J.A.; Harrison, J.J.; Turner, R.J. Antimicrobial Activity of Metals: Mechanisms, Molecular Targets and Applications. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 371–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.F.; Element, G.; van Coeverden de Groot, P.; Engel, K.; Neufeld, J.D.; Shah, V.; Walker, V.K. Anadromous Arctic Char Microbiomes: Bioprospecting in the High Arctic. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacchi, L.; Lowrey, L.; Musharrafieh, R.; Crossey, K.; Larragoite, E.T.; Salinas, I. Effects of Transportation Stress and Addition of Salt to Transport Water on the Skin Mucosal Homeostasis of Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2015, 435, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Moullac, G.; Soyez, C.; Saulnier, D.; Ansquer, D.; Avarre, J.C.; Levy, P. Effect of Hypoxic Stress on the Immune Response and the Resistance to Vibriosis of the shrimpPenaeus Stylirostris. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 1998, 8, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, S.; Bernatchez, L.; Audet, C.; Derôme, N. Network Analysis Highlights Complex Interactions between Pathogen, Host and Commensal Microbiota. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e84772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easy, R.H.; Ross, N.W. Changes in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Epidermal Mucus Protein Composition Profiles Following Infection with Sea Lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2009, 4, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estensoro, I.; Jung-Schroers, V.; Álvarez-Pellitero, P.; Steinhagen, D.; Sitjà-Bobadilla, A. Effects of Enteromyxum Leei (Myxozoa) Infection on Gilthead Sea Bream (Sparus aurata) (Teleostei) Intestinal Mucus: Glycoprotein Profile and Bacterial Adhesion. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 567–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Leadbeater, S.; Garcia, C.; Sylvain, F.-E.; Custodio, M.; Ang, K.P.; Powell, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Elliot, J.; et al. Parasitism Perturbs the Mucosal Microbiome of Atlantic Salmon. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 43465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, K.M.; Patel, S.; Robinson, A.J.; Bu, L.; Jarungsriapisit, J.; Moore, L.J.; Salinas, I. Salmonid Alphavirus Infection Causes Skin Dysbiosis in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Post-Smolts. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Marel, M.; Caspari, N.; Neuhaus, H.; Meyer, W.; Enss, M.-L.; Steinhagen, D. Changes in Skin Mucus of Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio L., after Exposure to Water with a High Bacterial Load. J. Fish. Dis. 2010, 33, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, N.; Sylvain, F.-E.; Holland, A.; Luis Val, A.; Derome, N. Gut Microbiota of an Amazonian Fish in a Heterogeneous Riverscape: Integrating Genotype, Environment, and Parasitic Infections. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e02755-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoole, D.; Lewis, J.W.; Schuwerack, P.M.M.; Chakravarthy, C.; Shrive, A.K.; Greenhough, T.J.; Cartwright, J.R. Inflammatory Interactions in Fish Exposed to Pollutants and Parasites: A Role for Apoptosis and C Reactive Protein. Parasitology 2003, 126, S71–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankevičiūtė, M.; Sauliutė, G.; Makaras, T.; Čapukoitienė, B.; Vansevičiūtė, G.; Markovskaja, S. Biomarker Responses in Perch (Perca fluviatilis) under Multiple Stress: Parasite Co-Infection and Multicomponent Metal Mixture Exposure. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaib, B.; Seghouani, H.; Ijaz, U.Z.; Derome, N. Community Recovery Dynamics in Yellow Perch Microbiome after Gradual and Constant Metallic Perturbations. Microbiome 2020, 8, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheaib, B.; Seghouani, H.; Llewellyn, M.; Vandal-Lenghan, K.; Mercier, P.-L.; Derome, N. The Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens) Microbiome Revealed Resistance to Colonisation Mostly Associated with Neutralism Driven by Rare Taxa under Cadmium Disturbance. Anim. Microbiome 2021, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, B.; Austin, D.A. Bacterial Fish Pathogens: Disease of Farmed and Wild Fish, 6th ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-32674-0. [Google Scholar]
- Dillon, R.; Charnley, K. Mutualism between the Desert Locust Schistocerca Gregaria and Its Gut Microbiota. Res. Microbiol. 2002, 153, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylvain, F.; Leroux, N.; Normandeau, É.; Custodio, J.; Mercier, P.-L.; Bouslama, S.; Holland, A.; Barroso, D.; Val Adalberto, L.; Derome, N. Important Role of Endogenous Microbial Symbionts of Fish Gills in the Challenging but Highly Biodiverse Amazonian Blackwaters. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberdi, A.; Aizpurua, O.; Bohmann, K.; Zepeda-Mendoza, M.L.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Do Vertebrate Gut Metagenomes Confer Rapid Ecological Adaptation? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2016, 31, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Lin, X.; Tam, N.; Ho, J.C.H.; Wong, M.K.-S.; Gu, J.; Chan, T.F.; Tse, W.K.F. Osmotic Stress Induces Gut Microbiota Community Shift in Fish. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3784–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, K.P.; Zhu, P.; Boncan, D.A.T.; Yang, L.; Leung, C.C.T.; Ho, J.C.H.; Lin, X.; Chan, T.F.; Kong, R.Y.C.; Tse, W.K.F. Integrated Omics Approaches Revealed the Osmotic Stress-Responsive Genes and Microbiota in Gill of Marine Medaka. mSystems 2022, 7, e00047-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podar, M.; Gilmour, C.C.; Brandt, C.C.; Soren, A.; Brown, S.D.; Crable, B.R.; Palumbo, A.V.; Somenahally, A.C.; Elias, D.A. Global Prevalence and Distribution of Genes and Microorganisms Involved in Mercury Methylation. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayath, C.A.; Ibala Zamba, A.; Goma-Tchimbakala, J.; Mamonékéné, V.; Mombo Makanga, G.M.; Lebonguy, A.A.; Nguimbi, E. Microbiota Landscape of Gut System of Guppy Fish (Poecilia reticulata) Plays an Outstanding Role in Adaptation Mechanisms. Int. J. Microbiol. 2019, 2019, e3590584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakade, A.; Sharma, M.; Salama, E.-S.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, L.; Xing, X.; Yue, J.; Song, Z.; Nan, L.; Yujun, S.; et al. Heavy Metals (HMs) Pollution in the Aquatic Environment: Role of Probiotics and Gut Microbiota in HMs Remediation. Environ. Res. 2023, 223, 115186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.; Sunyer, J.O.; Salinas, I. The Mucosal Immune System of Fish: The Evolution of Tolerating Commensals While Fighting Pathogens. Fish. Shellfish. Immunol. 2013, 35, 1729–1739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppang, E.O.; Kvellestad, A.; Fischer, U. Fish Mucosal Immunity: Gill. In Mucosal Health in Aquaculture; Beck, B.H., Peatman, E., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 93–133. ISBN 978-0-12-417186-2. [Google Scholar]
- Element, G.; Engel, K.; Neufeld, J.D.; Casselman, J.M.; van Coeverden de Groot, P.; Greer, C.W.; Walker, V.K. Seasonal Habitat Drives Intestinal Microbiome Composition in Anadromous Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus). Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3112–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, E.F.; Juurakko, C.L.; Engel, K.; Neufeld, J.D.; Casselman, J.M.; Greer, C.W.; Walker, V.K. Environmental Impacts on Skin Microbiomes of Sympatric High Arctic Salmonids. Fishes 2023, 8, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amill, F.; Gauthier, J.; Rautio, M.; Derome, N. Characterization of Gill Bacterial Microbiota in Wild Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus) across Lakes, Rivers, and Bays in the Canadian Arctic Ecosystems. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e02943-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potvin, M.; Rautio, M.; Lovejoy, C. Freshwater Microbial Eukaryotic Core Communities, Open-Water and Under-Ice Specialists in Southern Victoria Island Lakes (Ekaluktutiak, NU, Canada). Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 786094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Froese, R. Cube Law, Condition Factor and Weight–Length Relationships: History, Meta-Analysis and Recommendations. J. Appl. Ichthyol. 2006, 22, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eagles-Smith, C.A.; Ackerman, J.T.; Willacker, J.J.; Tate, M.T.; Lutz, M.A.; Fleck, J.; Stewart, R.; Wiener, J.G.; Evers, D.C.; Lepak, J.M.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Mercury Concentrations in Freshwater Fish across the Western United States and Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1171–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An R Package for Reproducible Interactive Analysis and Graphics of Microbiome Census Data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kassambara, A. Ggpubr: “ggplot2” Based Publication Ready Plots. 2023. Available online: https://rpkgs.datanovia.com/ggpubr/ (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Use R! Springer: New York, NY, USA; Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-24277-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; Averick, M.; Bryan, J.; Chang, W.; McGowan, L.; François, R.; Grolemund, G.; Hayes, A.; Henry, L.; Hester, J.; et al. Welcome to the Tidyverse. J. Open Source Softw. 2019, 4, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.; O’Hara, R.; Simpson, G.; Solymos, P.; Stevenes, M.; Wagner, H. Vegan: Community Ecology Package; R Package Version 2.5-7. 2020. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/346579465_vegan_community_ecology_package_version_25-7_November_2020 (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C.I. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel Test in the Face of Heterogeneous Dispersions: What Null Hypothesis Are You Testing? Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, F.E. Hmisc: Harrell Miscellaneous; R Package Version 4.7-0. 2022. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/Hmisc/index.html (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inkscape Project Inkscape Project. Available online: http://citebay.com/how-to-cite/inkscape/ (accessed on 21 October 2023).
- Dittman, J.A.; Driscoll, C.T. Factors Influencing Changes in Mercury Concentrations in Lake Water and Yellow Perch (Perca Flavescens) in Adirondack Lakes. Biogeochemistry 2009, 93, 179–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, H.K.; Kidd, K.A. Mercury Concentrations in Arctic Food Fishes Reflect the Presence of Anadromous Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus), Species, and Life History. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3286–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastwood, S.; Couture, P. Seasonal Variations in Condition and Liver Metal Concentrations of Yellow Perch (Perca Flavescens) from a Metal-Contaminated Environment. Aquat. Toxicol. 2002, 58, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyniuk, M.A.C.; Couture, P.; Tran, L.; Beaupré, L.; Power, M. Seasonal Variation of Total Mercury and Condition Indices of Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus) in Northern Québec, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 738, 139450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckvar, N.; Dillon, T.M.; Read, L.B. Approaches for Linking Whole-Body Fish Tissue Residues of Mercury or DDT to Biological Effects Thresholds. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2005, 24, 2094–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Ribeiro, C.A.; Belger, L.; Pelletier, É.; Rouleau, C. Histopathological Evidence of Inorganic Mercury and Methyl Mercury Toxicity in the Arctic Charr (Salvelinus alpinus). Environ. Res. 2002, 90, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barst, B.D.; Rosabal, M.; Campbell, P.G.C.; Muir, D.G.C.; Wang, X.; Köck, G.; Drevnick, P.E. Subcellular Distribution of Trace Elements and Liver Histology of Landlocked Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus) Sampled along a Mercury Contamination Gradient. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiener, J.G.; Sandheinrich, M.B.; Bhavsar, S.P.; Bohr, J.R.; Evers, D.C.; Monson, B.A.; Schrank, C.S. Toxicological Significance of Mercury in Yellow Perch in the Laurentian Great Lakes Region. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 161, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chételat, J.; Amyot, M.; Arp, P.; Blais, J.M.; Depew, D.; Emmerton, C.A.; Evans, M.; Gamberg, M.; Gantner, N.; Girard, C.; et al. Mercury in Freshwater Ecosystems of the Canadian Arctic: Recent Advances on Its Cycling and Fate. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509–510, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barst, B.D.; Drevnick, P.E.; Muir, D.C.G.; Gantner, N.; Power, M.; Köck, G.; Chéhab, N.; Swanson, H.; Rigét, F.; Basu, N. Screening-level Risk Assessment of Methylmercury for Non-anadromous Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2019, 38, 489–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, D.C.G. Spatial Trends and Historical Deposition of Mercury in Eastern and Northern Canada Inferred from Lake Sediment Cores. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4802–4809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gantner, N.; Muir, D.C.; Power, M.; Iqaluk, D.; Reist, J.D.; Babaluk, J.A.; Meili, M.; Borg, H.; Hammar, J.; Michaud, W.; et al. Mercury Concentrations in Landlocked Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus) from the Canadian Arctic. Part II: Influence of Lake Biotic and Abiotic Characteristics on Geographic Trends in 27 Populations. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2010, 29, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, D.M.; Nislow, K.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Folt, C.L. Rapid, Efficient Growth Reduces Mercury Concentrations in Stream-Dwelling Atlantic Salmon. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2010, 139, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rypel, A.L. Mercury Concentrations in Lentic Fish Populations Related to Ecosystem and Watershed Characteristics. AMBIO 2010, 39, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacMillan, G.A.; Girard, C.; Chételat, J.; Laurion, I.; Amyot, M. High Methylmercury in Arctic and Subarctic Ponds Is Related to Nutrient Levels in the Warming Eastern Canadian Arctic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 7743–7753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Environment and Climate Change Canada NPRI Substance Overview: Mercury. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/national-pollutant-release-inventory/tools-resources-data/mercury.html (accessed on 6 October 2023).
- Hudelson, K.E.; Muir, D.C.G.; Drevnick, P.E.; Köck, G.; Iqaluk, D.; Wang, X.; Kirk, J.L.; Barst, B.D.; Grgicak-Mannion, A.; Shearon, R.; et al. Temporal Trends, Lake-to-Lake Variation, and Climate Effects on Arctic Char (Salvelinus alpinus) Mercury Concentrations from Six High Arctic Lakes in Nunavut, Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 801–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streets, D.G.; Horowitz, H.M.; Jacob, D.J.; Lu, Z.; Levin, L.; ter Schure, A.F.H.; Sunderland, E.M. Total Mercury Released to the Environment by Human Activities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 5969–5977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehnherr, I.; St. Louis, V.L.; Kirk, J.L. Methylmercury Cycling in High Arctic Wetland Ponds: Controls on Sedimentary Production. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 10523–10531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrie, J.; Wang, F.; Sanei, H.; Macdonald, R.W.; Outridge, P.M.; Stern, G.A. Increasing Contaminant Burdens in an Arctic Fish, Burbot (Lota Lota), in a Warming Climate. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.S.; Muir, D.C.G. Temporal Trends and Spatial Variations of Mercury in Sea-Run Arctic Char From Cambridge Bay. Nunavut. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 6331–6340. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, A.D.; Wilson, S.J.; Fryer, R.J.; Thomas, P.J.; Hudelson, K.; Andreasen, B.; Blévin, P.; Bustamante, P.; Chastel, O.; Christensen, G.; et al. Temporal Trends of Mercury in Arctic Biota: 10 More Years of Progress in Arctic Monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 839, 155803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, H.K. Comparison of Mercury Concentrations in Landlocked, Resident, and Sea-run Fish (Salvelinus spp.) from Nunavut, Canada. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérin-Lajoie, J.; Herrmann, T.M.; MacMillan, G.A.; Hébert-Houle, É.; Monfette, M.; Rowell, J.A.; Soucie, T.A.; Snowball, H.; Townley, E.; Lévesque, E.; et al. IMALIRIJIIT: A Community-Based Environmental Monitoring Program in the George River Watershed, Nunavik, Canada. Ecoscience 2018, 25, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houde, M.; Krümmel, E.M.; Mustonen, T.; Brammer, J.; Brown, T.M.; Chételat, J.; Dahl, P.E.; Dietz, R.; Evans, M.; Gamberg, M.; et al. Contributions and Perspectives of Indigenous Peoples to the Study of Mercury in the Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 841, 156566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemire, M.; Kwan, M.; Laouan-Sidi, A.E.; Muckle, G.; Pirkle, C.; Ayotte, P.; Dewailly, E. Local Country Food Sources of Methylmercury, Selenium and Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Nunavik, Northern Quebec. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509–510, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.S.; Muir, D.C.G.; Keating, J.; Wang, X. Anadromous Char as an Alternate Food Choice to Marine Animals: A Synthesis of Hg Concentrations, Population Features and Other Influencing Factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509–510, 175–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.M.; Venables, B.; Roberts, A. Effects of Dietary Methylmercury on the Dopaminergic System of Adult Fathead Minnows and Their Offspring. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2017, 36, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.M.; Soulen, B.K.; Overturf, C.L.; Drevnick, P.E.; Roberts, A.P. Embryotoxicity of Maternally Transferred Methylmercury to Fathead Minnows (Pimephales promelas). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 1436–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefansson, E.S.; Heyes, A.; Rowe, C.L. Tracing Maternal Transfer of Methylmercury in the Sheepshead Minnow (Cyprinodon variegatus) with an Enriched Mercury Stable Isotope. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 1957–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBofsky, A.R.; Klingler, R.H.; Mora-Zamorano, F.X.; Walz, M.; Shepherd, B.; Larson, J.K.; Anderson, D.; Yang, L.; Goetz, F.; Basu, N.; et al. Female Reproductive Impacts of Dietary Methylmercury in Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens) and Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 2018, 195, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Zamorano, F.X.; Klingler, R.; Basu, N.; Head, J.; Murphy, C.A.; Binkowski, F.P.; Larson, J.K.; Carvan, M.J.I. Developmental Methylmercury Exposure Affects Swimming Behavior and Foraging Efficiency of Yellow Perch (Perca flavescens) Larvae. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 4870–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y. Gut Microbiota-Mediated Ferroptosis Contributes to Mercury Exposure-Induced Brain Injury in Common Carp. Metallomics 2022, 14, mfab072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Yang, Q.; Song, Y.; Cheng, B.; Ai, X. Effect of Copper Sulphate Exposure on the Oxidative Stress, Gill Transcriptome and External Microbiota of Yellow Catfish, Pelteobagrus Fulvidraco. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-L.; Li, S.; Qin, C.-B.; Zhu, Z.-X.; Hu, W.-P.; Yang, L.-P.; Lu, R.-H.; Li, W.-J.; Nie, G.-X. Intestinal Microbiota and Lipid Metabolism Responses in the Common Carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) Following Copper Exposure. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 160, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves Pessoa, R.B.; de Oliveira, W.F.; Marques, D.S.C.; dos Santos Correia, M.T.; de Carvalho, E.V.M.M.; Coelho, L.C.B.B. The Genus Aeromonas: A General Approach. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 130, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Sánchez, V.; Latif-Eugenín, F.; Soriano-Vargas, E.; Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.J.; Aguilera-Arreola, M.G.; Castro-Escarpulli, G. Re-Identification of Aeromonas Isolates from Rainbow Trout and Incidence of Class 1 Integron and β-Lactamase Genes. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 172, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Kamila, B.; Barman, S.; Joshi, S.R.; Mandal, T.; Halder, G. Interlining Cr(VI) Remediation Mechanism by a Novel Bacterium Pseudomonas Brenneri Isolated from Coalmine Wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Elala, N.; Abdelsalam, M.; Marouf, S.; Setta, A. Comparative Analysis of Virulence Genes, Antibiotic Resistance and gyrB-Based Phylogeny of Motile Aeromonas Species Isolates from Nile Tilapia and Domestic Fowl. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaz-Hidalgo, R.; Figueras, M.J. Aeromonas spp. Whole Genomes and Virulence Factors Implicated in Fish Disease. J. Fish. Dis. 2013, 36, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bruijn, I. Exploring Fish Microbial Communities to Mitigate Emerging Diseases in Aquaculture. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2018, 94, fix161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; Boutin, S.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Derome, N. Teleost Microbiomes: The State of the Art in Their Characterization, Manipulation and Importance in Aquaculture and Fisheries. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, X.; Zhu, J.; Rensing, C.; Liu, Y.; Gao, S.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q.; Liu, Y.-R. Recent Advances in Exploring the Heavy Metal(Loid) Resistant Microbiome. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Widenfalk, A.; Bertilsson, S.; Sundh, I.; Goedkoop, W. Effects of Pesticides on Community Composition and Activity of Sediment Microbes—Responses at Various Levels of Microbial Community Organization. Environ. Pollut. 2008, 152, 576–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, D.; McDonald, J.L.; Hosken, D.J. What Do You Mean, ‘Resilient’? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holling, C.S. Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 1973, 4, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, S.; Köhler, G. Intestinal Microbiome and Metal Toxicity. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2020, 19, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilmour, C.C.; Podar, M.; Bullock, A.L.; Graham, A.M.; Brown, S.D.; Somenahally, A.C.; Johs, A.; Hurt, R.A., Jr.; Bailey, K.L.; Elias, D.A. Mercury Methylation by Novel Microorganisms from New Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 11810–11820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capo, E.; Feng, C.; Bravo, A.G.; Bertilsson, S.; Soerensen, A.L.; Pinhassi, J.; Buck, M.; Karlsson, C.; Hawkes, J.; Björn, E. Expression Levels of hgcAB Genes and Mercury Availability Jointly Explain Methylmercury Formation in Stratified Brackish Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13119–13130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Xu, X.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, X. The Alteration of Gut Microbiome Community Play an Important Role in Mercury Biotransformation in Largemouth Bass. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothenberg, S.E.; Keiser, S.; Ajami, N.J.; Wong, M.C.; Gesell, J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Johs, A. The Role of Gut Microbiota in Fetal Methylmercury Exposure: Insights from a Pilot Study. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 242, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shams, S.; Capelli, C.; Cerasino, L.; Ballot, A.; Dietrich, D.R.; Sivonen, K.; Salmaso, N. Anatoxin-a Producing Tychonema (Cyanobacteria) in European Waterbodies. Water Res. 2015, 69, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, E.N.; Surette, M.G.; Kidd, K.A. Altered Microbiomes of Aquatic Macroinvertebrates and Riparian Spiders Downstream of Municipal Wastewater Effluents. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, M.; Daugaard, U.; Choffat, Y.; Zheng, X.; Petchey, O.L. Predicting the Effects of Multiple Global Change Drivers on Microbial Communities Remains Challenging. Glob. Change Biol. 2022, 28, 5575–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Jeon, C.O. Solitalea Longa Sp. Nov., Isolated from Freshwater and Emended Description of the Genus Solitalea. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2826–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weon, H.-Y.; Kim, B.-Y.; Lee, C.-M.; Hong, S.-B.; Jeon, Y.-A.; Koo, B.-S.; Kwon, S.-W. Solitalea koreensis gen. nov., sp. nov. and the reclassification of [Flexibacter] canadensis as Solitalea canadensis comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2009, 59 Pt 8, 1969–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, H.; Gallo, S.; Badger, P.; Hillwig, M. Changes in Microbial Communities of a Passive Coal Mine Drainage Bioremediation System. Can. J. Microbiol. 2019, 65, 775–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Jiang, H. Aquidulcibacter paucihalophilus gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel member of family Caulobacteraceae isolated from cyanobacterial aggregates in a eutrophic lake. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 110, 1169–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Brodie, E.L.; Suzuki, Y.; McAdams, H.H.; Andersen, G.L. Whole-Genome Transcriptional Analysis of Heavy Metal Stresses in Caulobacter Crescentus. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 8437–8449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, E.; Sun, L.; Ding, X.; Sun, D.; Liu, J.; Wang, W. Complete Genome Sequence of Caulobacter Flavus RHGG3T, a Type Species of the Genus Caulobacter with Plant Growth-Promoting Traits and Heavy Metal Resistance. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuda, W.; Chino, Y.; Araki, S.; Kondo, Y.; Imanaka, H.; Kanai, T.; Atomi, H.; Imanaka, T. Polymorphobacter Multimanifer Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., a Polymorphic Bacterium Isolated from Antarctic White Rock. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 2034–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köhler, J.M.; Kalensee, F.; Cao, J.; Günther, P.M. Hadesarchaea and Other Extremophile Bacteria from Ancient Mining Areas of the East Harz Region (Germany) Suggest an Ecological Long-Term Memory of Soil. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elghazaly, M.M.; Ghoneim, A.Z. The Antioxidant Defense Responses of Sea Cucumber Holothuria Polii Against Rickettsia-like Organism (RLOs) Infection and Heavy Metal Pollution in Alexandria Coast. J. Biosci. Appl. Res. 2017, 3, 80–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkay, T.; Gu, B. Demethylation─The Other Side of the Mercury Methylation Coin: A Critical Review. ACS Environ. Au 2022, 2, 77–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, X.; Zhao, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.-F. Intestinal Methylation and Demethylation of Mercury. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2019, 102, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monachese, M.; Burton, J.P.; Reid, G. Bioremediation and Tolerance of Humans to Heavy Metals through Microbial Processes: A Potential Role for Probiotics? Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 6397–6404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braune, B.; Chételat, J.; Amyot, M.; Brown, T.; Clayden, M.; Evans, M.; Fisk, A.; Gaden, A.; Girard, C.; Hare, A.; et al. Mercury in the Marine Environment of the Canadian Arctic: Review of Recent Findings. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509–510, 67–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, M.S.; McGinnity, P.; Dionne, M.; Letourneau, J.; Thonier, F.; Carvalho, G.R.; Creer, S.; Derome, N. The Biogeography of the Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar) Gut Microbiome. ISME J. 2016, 10, 1280–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Sun, G.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Intestinal Microbiota of Healthy and Unhealthy Atlantic Salmon Salmo salar L. in a Recirculating Aquaculture System. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 414–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, B.; Ping, Z.; Mahmood, Q.; Lin, Q.; Pervez, A.; Irshad, M.; Bilal, M.; Bhatti, Z.A.; Shaheen, S. Assessment of Combined Toxicity of Heavy Metals from Industrial Wastewaters on Photobacterium Phosphoreum T3S. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigneron, A.; Cruaud, P.; Aubé, J.; Guyoneaud, R.; Goñi-Urriza, M. Transcriptomic Evidence for Versatile Metabolic Activities of Mercury Cycling Microorganisms in Brackish Microbial Mats. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2021, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.-T.; Liu, Y.; Tan, S.; Wang, W.-X.; Wang, X. The Role of Intestinal Microbiota of the Marine Fish (Acanthopagrus Latus) in Mercury Biotransformation. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 277, 116768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Tan, S.; Pan, K.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, X. Effects of Diet Composition on Gut Microbiome and Mercury Biotransformation in the Gobyfish. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorokhova, E.; Soerensen, A.L.; Motwani, N.H. Mercury-Methylating Bacteria Are Associated with Copepods: A Proof-of-Principle Survey in the Baltic Sea. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0230310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, F.; Leroux, N.; Normandeau, É.; Holland, A.; Bouslama, S.; Mercier, P.-L.; Luis Val, A.; Derome, N. Genomic and Environmental Factors Shape the Active Gill Bacterial Community of an Amazonian Teleost Holobiont. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e02064-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeremiason, J.; Engstrom, D.R.; Swain, E.B.; Nater, E.A.; Johnson, B.M.; Almendinger, J.E.; Monson, B.A.; Kolka, R.K. Sulfate Addition Increases Methylmercury Production in an Experimental Wetland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 3800–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
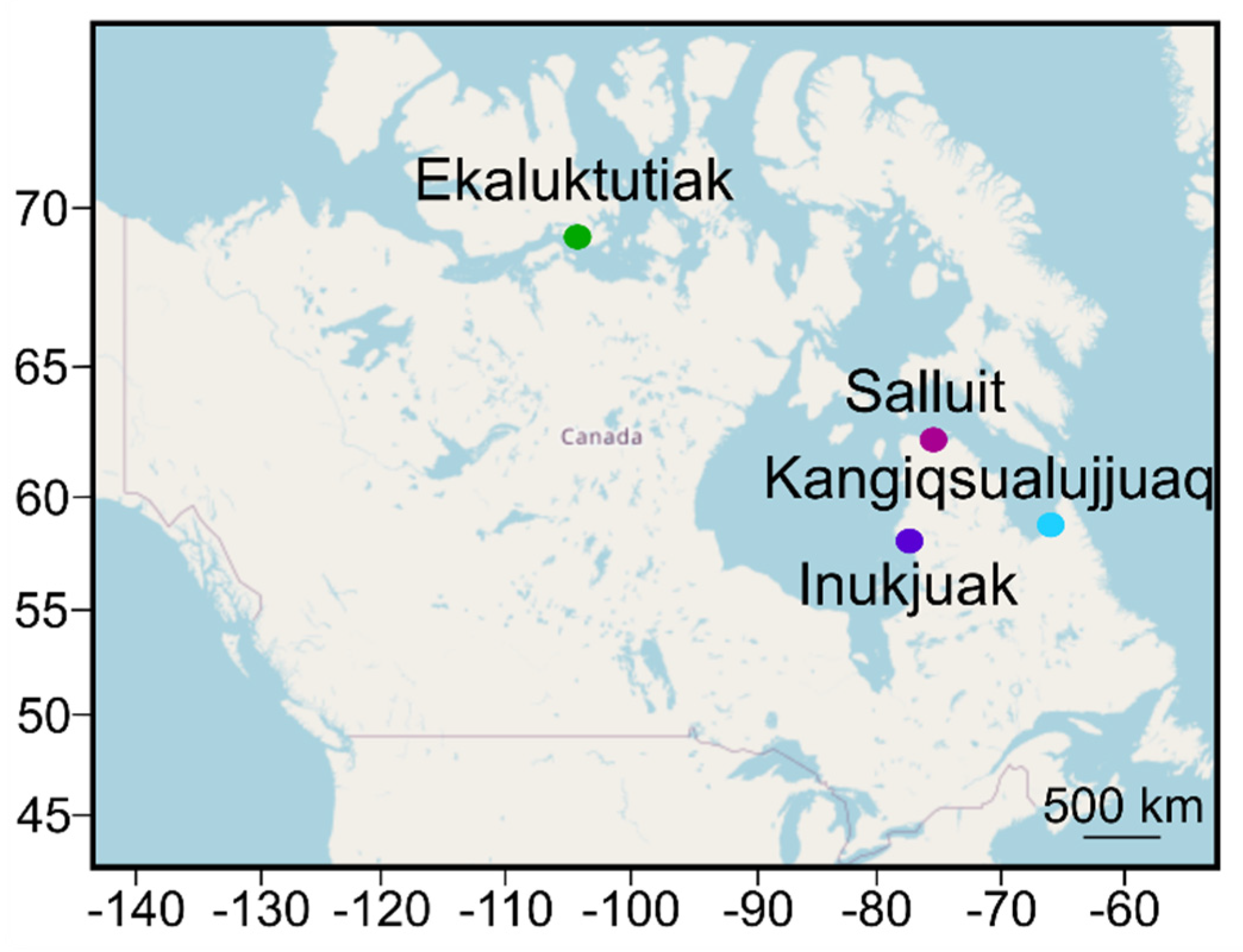
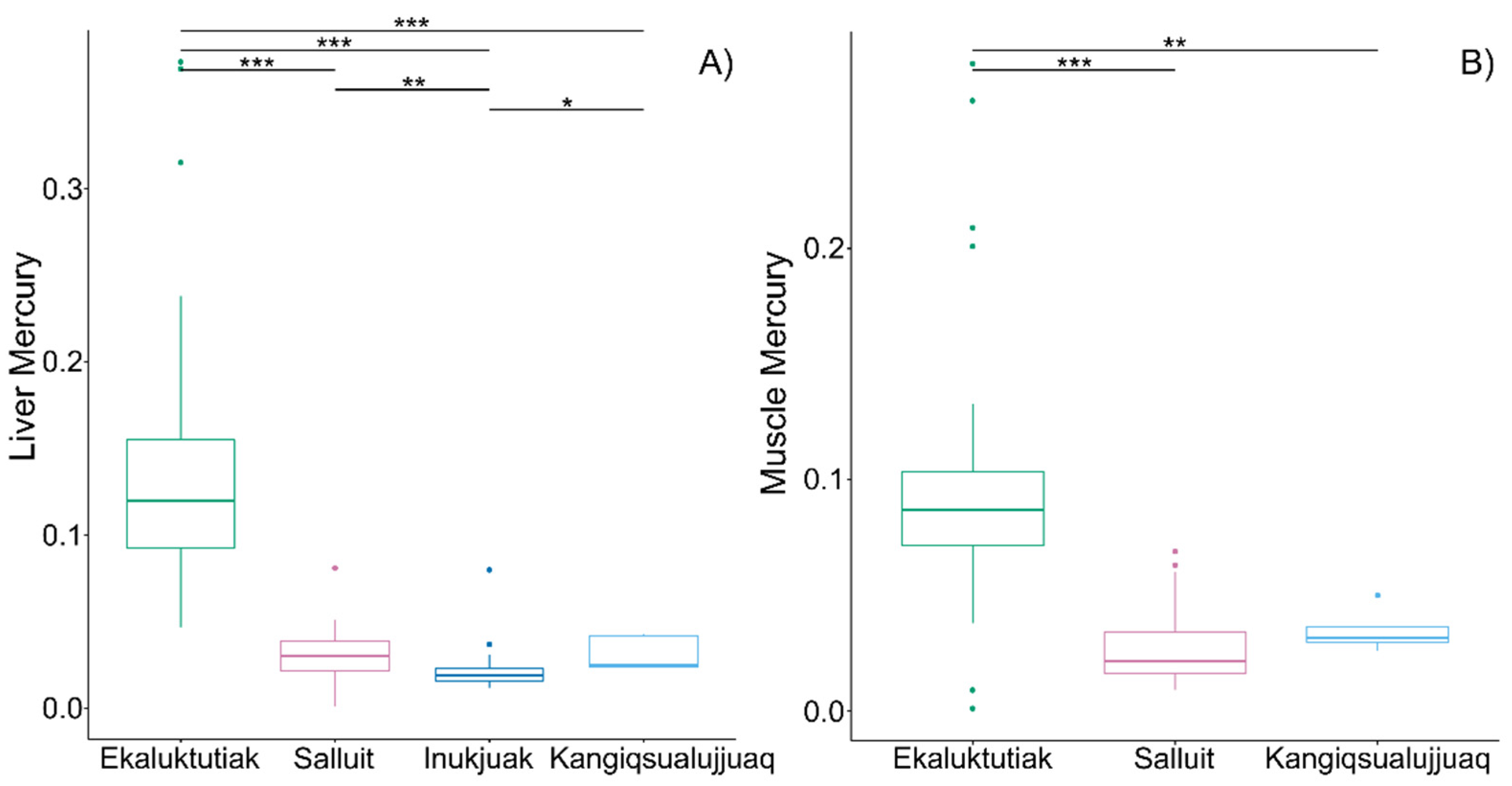
| Communities | Region | Nliver | Nmuscle | Stat | Fulton Index | [Hg] Liver | [Hg] Muscle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ekaluktutiak | Victoria Island, Kitikmeot (Nunavut) | 51 | 63 | Mean ± SD | 1.0 ± 0.3 a | 0.14 ± 0.08 bc | 0.09 ± 0.05 ef |
| Min | 0.2 | 0.05 | 0.001 | ||||
| Max | 1.6 | 0.37 | 0.28 | ||||
| Salluit | Hudson Strait, Kativik (Nunavik) | 18 | 22 | Mean ± SD | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 0.03 ± 0.02 b | 0.03 ± 0.02 e |
| Min | 0.8 | 0.001 | 0.01 | ||||
| Max | 1.4 | 0.08 | 0.07 | ||||
| Inukjuak | Hudson Bay South, Kativik (Nunavik) | 25 | NA | Mean ± SD | 1.2 ± 0.1 a | 0.02 ± 0.01 bd | NA |
| Min | 0.9 | 0.01 | NA | ||||
| Max | 1.3 | 0.08 | NA | ||||
| Kangiqsualujjuaq | Ungava Bay, Kativik (Nunavik) | 5 | 4 | Mean ± SD | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.03 ± 0.01 cd | 0.03 ± 0.01 f |
| Min | 0.9 | 0.02 | 0.03 | ||||
| Max | 1.3 | 0.04 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amill, F.; Couture, P.; Derome, N. Mercury and Arctic Char Gill Microbiota Correlation in Canadian Arctic Communities. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122449
Amill F, Couture P, Derome N. Mercury and Arctic Char Gill Microbiota Correlation in Canadian Arctic Communities. Microorganisms. 2024; 12(12):2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122449
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmill, Flora, Patrice Couture, and Nicolas Derome. 2024. "Mercury and Arctic Char Gill Microbiota Correlation in Canadian Arctic Communities" Microorganisms 12, no. 12: 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122449
APA StyleAmill, F., Couture, P., & Derome, N. (2024). Mercury and Arctic Char Gill Microbiota Correlation in Canadian Arctic Communities. Microorganisms, 12(12), 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms12122449






