Vitamin D and Its Role in Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Vitamin D Synthesis and Metabolic Pathways
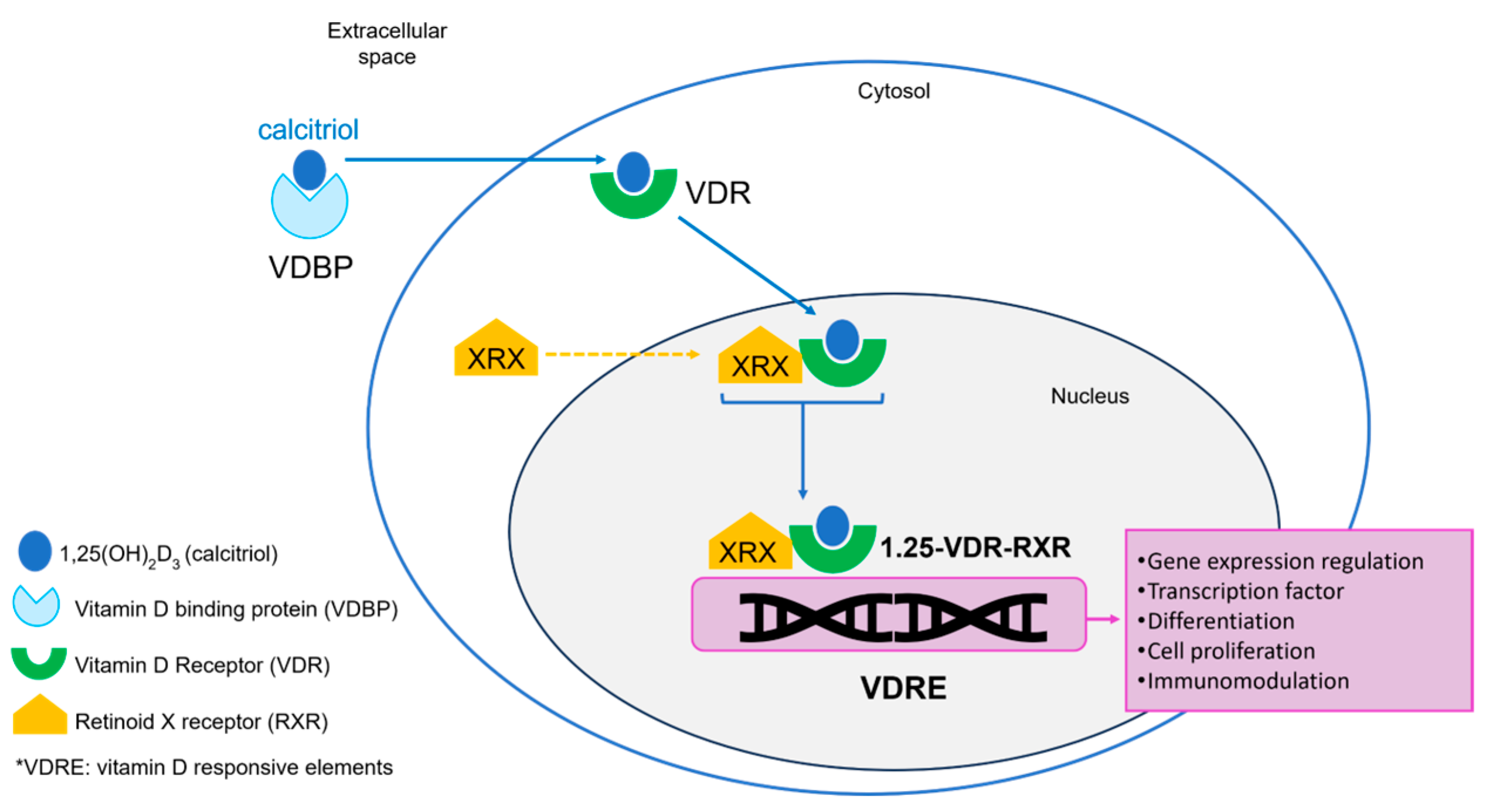
3. Vitamin D Receptor (VDR) and Immune Activation
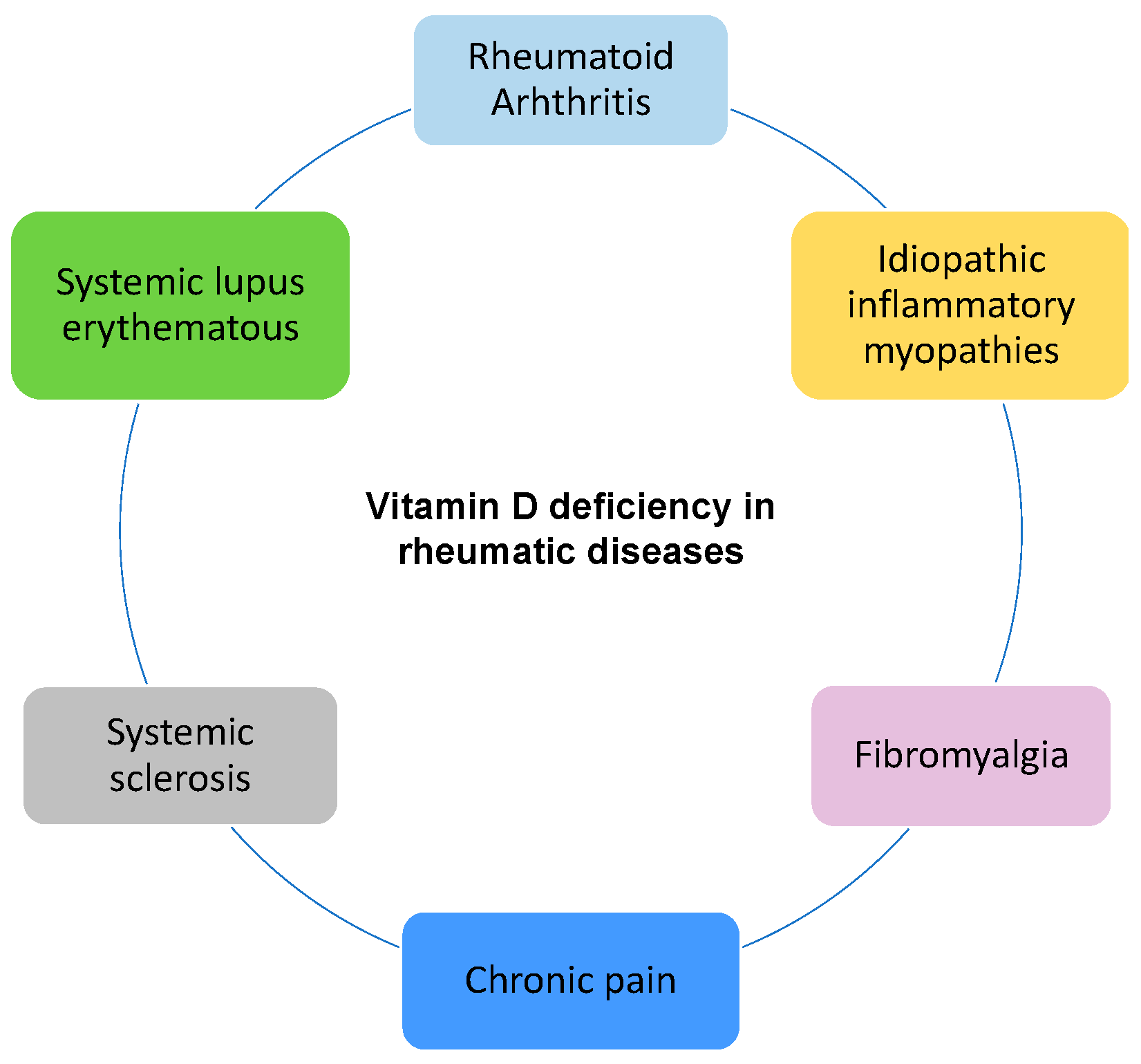
4. Vitamin D in Rheumatic Diseases
4.1. Rheumatoid Arthritis
4.2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
4.3. Systemic Sclerosis
4.4. Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies
4.5. Fibromyalgia and Chronic Pain
5. Discussion and Final Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vidal, M.; Lane, N.E. The importance of vitamin D. Rheumatol. Orthop. Med. 2020, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.F.; Vidal, M.; Lane, N.E.; Keen, R.; Alba, R. Doses and Schemes for Correcting Vitamin D Deficiency: An Update. Food Nutr. J. 2024, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, R.F.; Liu, P.T.; Modlin, R.L.; Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Impact of Vitamin D on Immune Function: Lessons Learned from Genome-Wide Analysis. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gombart, A.F.; Borregaard, N.; Koeffler, H.P. Human Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide (CAMP) Gene Is a Direct Target of the Vitamin D Receptor and Is Strongly Up-Regulated in Myeloid Cells by 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Otsa, K.; Laas, K.; Yprus, M.; Lehtme, R.; Secchi, M.E.; Seriolo, B. Circannual Vitamin D Serum Levels and Disease Activity in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Northern Versus Southern Europe. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2006, 24, 702–704. [Google Scholar]
- Kamen, D.L.; Tangpricha, V. Vitamin D and Molecular Actions on the Immune System: Modulation of Innate and Autoimmunity. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 88, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, T.; Hosoi, T.; Tanaka, E.; Nakajima, A.; Taniguchi, A.; Momohara, S.; Yamanaka, H. Prevalence of and Factors Associated with Vitamin D Deficiency in 4,793 Japanese Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2013, 32, 1081–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, S.Y.; Cai, H.Y.; Wang, P.; Lv, T.T.; Liu, L.N.; Mao, Y.M.; Zhao, C.-N.; Wu, Q.; Dan, Y.-L.; Sam, N.B.; et al. Association between Circulating 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalfenberg, G.K. A Review of the Critical Role of Vitamin D in the Functioning of the Immune System and the Clinical Implications of Vitamin D Deficiency. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouillon, R.; Schuit, F.; Antonio, L.; Rastinejad, F. Vitamin D Binding Protein: A Historic Overview. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D.; Schwartz, J. Vitamin D Binding Protein, Total and Free Vitamin D Levels in Different Physiological and Pathophysiological Conditions. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, P.J.; Gysemans, C.; Verstuyf, A.; Mathieu, C. Vitamin D’s Effect on Immune Function. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, Y.O.K.O.; Castillo, L.; DeLuca, H.F. The 24-Hydroxylation of 1, 25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3. J. Biol. Chem. 1977, 252, 1421–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldurthy, V.; Wei, R.; Campbell, M.; Lupicki, K.; Dhawan, P.; Christakos, S. 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 24-Hydroxylase: A Key Regulator of 1,25(OH)2D3 Catabolism and Calcium Homeostasis. Vitam. Horm. 2016, 100, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voltan, G.; Cannito, M.; Ferrarese, M.; Ceccato, F.; Camozzi, V. Vitamin D: An Overview of Gene Regulation, Ranging from Metabolism to Genomic Effects. Genes 2023, 14, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, H.K.; Shrestha, S.; Rokka, K.; Shakya, R. Vitamin D, Calcium, Parathyroid Hormone, and Sex Steroids in Bone Health and Effects of Aging. J. Osteoporos. 2020, 2020, 9324505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D: Production, Metabolism and Mechanisms of Action. In Endotext; Feingold, K.R., Ahmed, S.F., Anawalt, B., Blackman, M.R., Boyce, A., Chrousos, G., Corpas, E., de Herder, W.W., Dhatariya, K., Dungan, K., et al., Eds.; MDText.com, Inc.: South Dartmouth, MA, USA, 2000; Updated 31 December 2021. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK278935 (accessed on 1 April 2025).
- Lehmann, B.; Meurer, M. Extrarenal Sites of Calcitriol Synthesis: The Particular Role of the Skin. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2003, 164, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewison, M.; Zehnder, D.; Bland, R.; Stewart, P.M. 1alpha-Hydroxylase and the Action of Vitamin D. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2000, 25, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, D.; Bland, R.; Williams, M.C.; McNinch, R.W.; Howie, A.J.; Stewart, P.M.; Hewison, M. Extrarenal Expression of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-Hydroxylase. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikle, D.D.; Patzek, S.; Wang, Y. Physiologic and Pathophysiologic Roles of Extra Renal CYP27B1: Case Report and Review. Bone Rep. 2018, 8, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.H. Vitamin D Metabolism and Signaling in the Immune System. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2012, 13, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kongsbak, M.; Levring, T.B.; Geisler, C.; Von Essen, M.R. The Vitamin D Receptor and T Cell Function. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronato Solari, S.; Laguens Calabrese, G.; Di Girolamo Massimi, V.T. Acción de la Vitamina D3 en el Sistema Inmune. Rev. Cubana Hematol. Inmunol. Hemoter. 2005, 21, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Medrano, M.; Carrillo-Cruz, E.; Montero, I.; Perez-Simon, J.A. Vitamin D: Effect on Haematopoiesis and Immune System and Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.C.; Martini, L.A.; Rogero, M.M. Current Perspectives on Vitamin D, Immune System, and Chronic Diseases. Nutrition 2011, 27, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azrielant, S.; Shoenfeld, Y. Vitamin D and the Immune System. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2017, 19, 510–511. [Google Scholar]
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D Metabolism and Function in the Skin. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 347, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantorna, M.T.; Arora, J. Two Lineages of Immune Cells That Differentially Express the Vitamin D Receptor. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 228, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamasauskiene, L.; Golubickaite, I.; Ugenskiene, R.; Sjakste, N.; Paramonova, N.; Wu, L.S.H.; Sitkauskiene, B. Vitamin D Receptor Gene Polymorphisms in Atopy. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2021, 9, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khafaei, M.; Sadeghi Hajiabadi, M.; Abdolmaleki, A. Role of 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol in Immunological and Molecular Pathways Involved in Multiple Sclerosis. Cent. Asian J. Med. Pharm. Sci. Innov. 2021, 1, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kongsbak-Wismann, M.; Rode, A.K.O.; Hansen, M.M.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Geisler, C. Vitamin D Up-Regulates the Vitamin D Receptor by Protecting It from Proteasomal Degradation. In Handbook of Immunosenescence; Fulop, T., Franceschi, C., Hirokawa, K., Pawelec, G., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, J.A.; Qasem, A.; Naser, S.A. Cathelicidin Mediates an Anti-Inflammatory Role of Active Vitamin D (Calcitriol) during M. paratuberculosis Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 875772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Quiroz, J.; García-Becerra, R.; Santos-Martínez, N.; Avila, E.; Larrea, F.; Díaz, L. Calcitriol Stimulates Gene Expression of Cathelicidin Antimicrobial Peptide in Breast Cancer Cells with Different Phenotype. J. Biomed. Sci. 2016, 23, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Christakos, S. Mechanisms Underlying the Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by Vitamin D. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8251–8260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewison, M. Vitamin D and the Immune System: New Perspectives on an Old Theme. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2010, 39, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Liu, D.; Deng, F. The Role of Vitamin D in Immune System and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Inflamm. Res. 2022, 15, 3167–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sîrbe, C.; Rednic, S.; Grama, A.; Pop, T.L. An Update on the Effects of Vitamin D on the Immune System and Autoimmune Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peelen, E.; Knippenberg, S.; Muris, A.H.; Thewissen, M.; Smolders, J.; Tervaert, J.W.C.; Damoiseaux, J. Effects of Vitamin D on the Peripheral Adaptive Immune System: A Review. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, P.H.; Gorman, S.; Finlay-Jones, J.J. Modulation of the Immune System by UV Radiation: More Than Just the Effects of Vitamin D? Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 584–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanlier, N.; Guney-Coskun, M. Vitamin D, the Immune System, and Its Relationship with Diseases. Egypt. Pediatr. Assoc. Gaz. 2022, 70, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, T.; Kikuta, J.; Ishii, M. The Effects of Vitamin D on Immune System and Inflammatory Diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeke, F.; van Etten, E.; Gysemans, C.; Overbergh, L.; Mathieu, C. Vitamin D Signaling in Immune-Mediated Disorders: Evolving Insights and Therapeutic Opportunities. Mol. Aspects Med. 2008, 29, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; June, R.R.; Zheng, S.G. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis via Suppression of Th17 Cells Through miR-124 Mediated Inhibition of IL-6 Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabral-Pacheco, G.A.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Castruita-De la Rosa, C.; Ramirez-Acuña, J.M.; Perez-Romero, B.A.; Guerrero-Rodriguez, J.F.; Martinez-Avila, N.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. The Roles of Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Human Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulik, Ł.; Łęgosz, P.; Motyl, G. Matrix metalloproteinases in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis: A state of the art review. Reumatologia 2023, 61, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugarte-Berzal, E.; Vandooren, J.; Bailón, E.; Opdenakker, G.; García-Pardo, A. Inhibition of MMP-9-Dependent Degradation of Gelatin, but Not Other MMP-9 Substrates, by the MMP-9 Hemopexin Domain Blades 1 and 4. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11751–11760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetlow, L.C.; Woolley, D.E. The Effects of 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 on Matrix Metalloproteinase and Prostaglandin E2 Production by Cells of the Rheumatoid Lesion. Arthritis Res. Ther. 1999, 1, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stojanovic, S.K.; Stamenkovic, B.N.; Cvetkovic, J.M.; Zivkovic, V.G.; Apostolovic, M.R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Level in Synovial Fluid—Association with Joint Destruction in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis. Medicina 2023, 59, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; McKelvey, K.; Shen, K.; Minhas, N.; March, L.; Park, S.-Y.; Christopher, J.; Jackson, C.J. Endogenous MMP-9 and not MMP-2 promotes rheumatoid synovial fibroblast survival, inflammation and cartilage degradation. Rheumatology 2014, 53, 2270–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timms, P.M.; Mannan, N.; Hitman, G.A.; Noonan, K.; Mills, P.G.; Syndercombe-Court, D.; Aganna, E.; Price, C.P.; Boucher, B.J. Circulating MMP9, Vitamin D and Variation in the TIMP-1 Response with VDR Genotype: Mechanisms for Inflammatory Damage in Chronic Disorders? QJM 2002, 95, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldırım, Y.A.; Ozturk, A.; Doğruel, F.; Saraçoğlu, H.; Yazıcı, C. Serum Vitamin D Concentration Is Inversely Associated with Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 Level in Periodontal Diseases. J. Periodontol. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busa, P.; Huang, N.; Kuthati, Y.; Wong, C.S. Vitamin D Reduces Pain and Cartilage Destruction in Knee Osteoarthritis Animals through Inhibiting the Matrix Metalloprotease (MMPs) Expression. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, H.V.T.; Nguyen, Y.T.; Kim, N.; Lee, H.J. Vitamin A, D, E, and K as Matrix Metalloproteinase-2/9 Regulators That Affect Expression and Enzymatic Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostoglou-Athanassiou, I.; Athanassiou, P.; Lyraki, A.; Raftakis, I.; Antoniadis, C. Vitamin D and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 3, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Liu, J.; Davies, M.L.; Chen, W. Serum Vitamin D Level and Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity: Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutolo, M.; Vojinovic, J.; Tincani, A.; Soldano, S.; Andreoli, L.; Dall’Ara, F.; Sulli, A. THU0116 European Multicentre Pilot Survey to Assess Vitamin D and Clinical Status in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, A51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Wang, J. Effect of Vitamin D on the Recurrence Rate of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 10, 1812–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buondonno, I.; Rovera, G.; Sassi, F.; Rigoni, M.M.; Lomater, C.; Parisi, S.; Pellerito, R.A.; Isaia, G.C.; d’Amelio, P. Vitamin D and Immunomodulation in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, K.; Danda, D. Supplementation of 1, 25 Dihydroxy Vitamin D3 in Patients with Treatment Naive Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 14, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenngam, N. Vitamin D and Rheumatic Diseases: A Review of Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malakooti, S.K.; Siddiqui, H.; Wilson, B.; Bej, T.; O’Mara, M.; Desotelle, A.; Lange, A.; Shive, C.L.; Singer, N.G.; McComsey, G.A.; et al. Higher Vitamin D Levels Before Methotrexate Therapy Initiation Are Associated with Lower Subsequent Mortality in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamen, D.L.; Cooper, G.S.; Bouali, H.; Shaftman, S.R.; Hollis, B.W.; Gilkeson, G.S. Vitamin D Deficiency in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Autoimmun. Rev. 2006, 5, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borba, V.Z.C.; Vieira, J.G.H.; Kasamatsu, T.; Radominski, S.C.; Sato, E.I.; Lazaretti-Castro, M. Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Osteoporos. Int. 2009, 20, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.M.; Wu, L.J.; Luo, C.N.; Shi, Y.M.; Wu, X. Relationship of Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. Yi Xue Ban = J. Peking Univ. Health Sci. 2021, 53, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attar, S.M.; Siddiqui, A.M. Vitamin D Deficiency in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Oman Med. J. 2013, 28, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, S.; Marynych, L.; Malovana, T.; Denyshchych, L. Vitamin D Level in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Its Relationship to Disease Course and Bone Mineral Density. Lupus Sci. Med. 2023, 10, e000968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaconu, A.D.; Ostafie, I.; Ceasovschih, A.; Șorodoc, V.; Lionte, C.; Ancuța, C.; Șorodoc, L. Role of Vitamin D in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Literature Review. J. Immunol. Res. 2021, 2021, 9782994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal-Bekar, N.E.; İşlekel, G.H.; Köken-Avşar, A.; Yarkan-Tuğsal, H.; Tuna, G.; Zengin, B.; Birlik, A.M. Vitamin D Attenuates Elevated Oxidative DNA Damage in Scleroderma Patients with Organ Involvement: A Prospective Study. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 229, 106273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzi, M.; Gallina, E.; Manfredi, G.F.; Patrucco, F.; Acquaviva, A.; Colangelo, D.; Pirisi, M.; Bellan, M. Vitamin D in Systemic Sclerosis: A Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groseanu, L.; Bojinca, V.; Gudu, T.; Saulescu, I.; Predeteanu, D.; Balanescu, A.; Berghea, F.; Opris, D.; Borangiu, A.; Constantinescu, C.; et al. Low Vitamin D Status in Systemic Sclerosis and the Impact on Disease Phenotype. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2016, 3, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.B.; Gandhi, N.; Clarke, J.; McMahan, Z. Gastrointestinal Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: An Update. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 24, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Sun, M.H.; Chen, F.; Li, J.R. Vitamin D Levels in Systemic Sclerosis Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2017, 11, 3119–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caramaschi, P.; Dalla Gassa, A.; Ruzzenente, O.; Volpe, A.; Ravagnani, V.; Tinazzi, I.; Barausse, G.; Bambara, L.M.; Biasi, D. Very Low Levels of Vitamin D in Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Clin. Rheumatol. 2010, 29, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhaouadi, T.; Riahi, A.; Ben Abdallah, T.; Gorgi, Y.; Sfar, I. Vitamin D association with systemic sclerosis and its clinical features: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.; Hax, V.; Monticielo, O.; Macedo, T.F.; Barreto, R.K.M.; Marcondes, N.A.; Chakr, R. Dualities of the Vitamin D in Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Literature Review. Adv. Rheumatol. 2021, 61, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, A.; Zhou, S.; Liu, C.; Hu, Z.; Xie, C.; Zheng, X.; Luo, X. Vitamin D Levels in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Postgrad. Med. 2024, 136, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azali, P.; Helmers, S.B.; Kockum, I.; Olsson, T.; Alfredsson, L.; Charles, P.J.; Aulin, K.P.; Lundberg, I.E. Low Serum Levels of Vitamin D in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agoncillo, M.; Yu, J.; Gunton, J.E. The Role of Vitamin D in Skeletal Muscle Repair and Regeneration in Animal Models and Humans: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iolascon, G.; Moretti, A.; Paoletta, M.; Liguori, S.; Di Munno, O. Muscle Regeneration and Function in Sports: A Focus on Vitamin D. Medicina 2021, 57, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysa, E.; Gotelli, E.; Campitiello, R.; Paolino, S.; Pizzorni, C.; Casabella, A.; Sulli, A.; Smith, V.; Cutolo, M. Vitamin D and Muscle Status in Inflammatory and Autoimmune Rheumatic Diseases: An Update. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Eisa, E.S.; Alghadir, A.H.; Gabr, S.A. Correlation between Vitamin D Levels and Muscle Fatigue Risk Factors Based on Physical Activity in Healthy Older Adults. Clin. Interv. Aging 2016, 11, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, L.F.; Messina, O.; Rodríguez, T.; Vidal, M.; Pineda, C.; Morales, R.; Collado, A. Refractory Fibromyalgia. Clin. Rheumatol. 2021, 40, 3853–3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal Neira, L.F.; Morales Olazabal, R.; Cueva Tovar, K.; Vidal Wilman, M.; Pasapera Alban, N.; Rojas Vilca, J. Serum Levels of Vitamin D in Women Treated at Rheumatology Services in Lima. Int. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 14, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- von Känel, R.; Müller-Hartmannsgruber, V.; Kokinogenis, G.; Egloff, N. Vitamin D and Central Hypersensitivity in Patients with Chronic Pain. Pain Med. 2014, 15, 1609–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendelman, O.; Itzhaki, D.; Makarov, S.; Bennun, M.; Amital, H. A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study Adding High Dose Vitamin D to Analgesic Regimens in Patients with Musculoskeletal Pain. Lupus 2015, 24, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipton, E.A.; Shipton, E.E. Vitamin D and Pain: Vitamin D and Its Role in the Aetiology and Maintenance of Chronic Pain States and Associated Comorbidities. Pain Res. Treat. 2015, 2015, 904967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianella, F.; Hsia, C.C.; Sakhaee, K. The Role of Vitamin D in Sarcoidosis. Faculty Rev. 2020, 9, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daryabor, G.; Gholijani, N.; Kahmini, F.R. A Review of the Critical Role of Vitamin D Axis on the Immune System. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2023, 132, 104866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D: A D-Lightful Health Perspective. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66 (Suppl. S2), S182–S194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
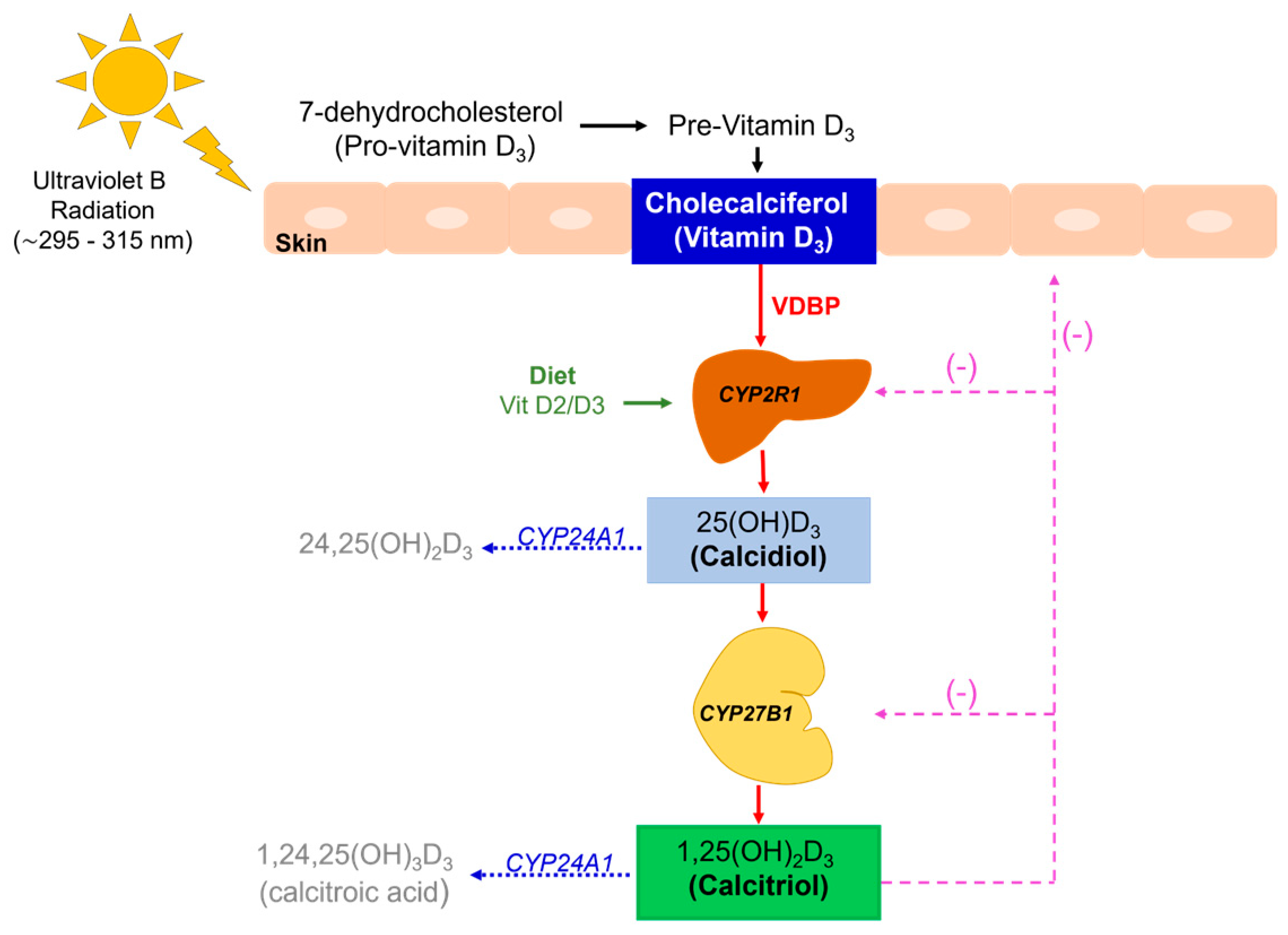

| Cholecalciferol (vitamin D3) | Fat-soluble molecule produced in the skin after UV light exposure. It is a non-hydroxylated form of vitamin D3 |
| 25-hydroxylase enzyme (CYP2R1) | Hepatic enzyme that hydroxylates cholecalciferol into calcidiol |
| 25OHD (calcidiol, calcifediol) 25OHD3 if animal origin 25OHD2 if vegetable origin | Hepatic molecule obtained after the first hydroxylation of cholecalciferol in the liver |
| 1-α-hydroxylase enzyme (CYP27B1) | Renal enzyme that hydroxylates calcidiol into calcitriol |
| 1,25(OH)2D (calcitriol) 1,25(OH)2D3 if animal origin 1,25(OH)2D2 if vegetable origin | Active form of vitamin D produced after renal hydroxylation |
| 25(OH)D-24-α-hydroxylase 24-hydroxylase 1,25(OH)2-D-24-hydroxylase (CYP24A1) | Catabolic enzyme that degrades metabolites of vitamin D into soluble calcitroic acid for rapid renal excretion |
| 1α-hydroxy-23-carboxy-24,25,26,27- tetranorvitamin D3 (calcitroic acid) | Inactive product result of the catabolism of calcitriol; it is soluble in water and excreted in bile |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vidal, M.; Lane, N.E. Vitamin D and Its Role in Rheumatic Diseases. Metabolites 2025, 15, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040259
Vidal M, Lane NE. Vitamin D and Its Role in Rheumatic Diseases. Metabolites. 2025; 15(4):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040259
Chicago/Turabian StyleVidal, Maritza, and Nancy E. Lane. 2025. "Vitamin D and Its Role in Rheumatic Diseases" Metabolites 15, no. 4: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040259
APA StyleVidal, M., & Lane, N. E. (2025). Vitamin D and Its Role in Rheumatic Diseases. Metabolites, 15(4), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo15040259