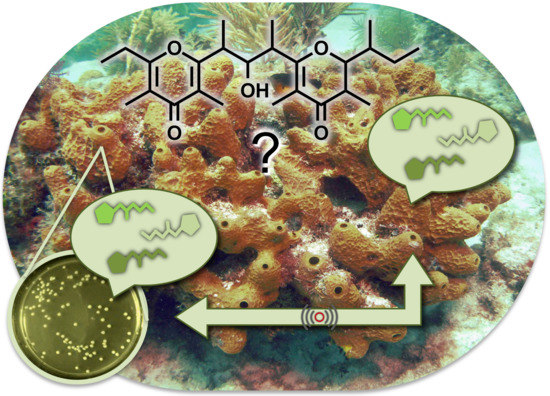
Isolation of Smenopyrone, a Bis-γ-Pyrone Polypropionate from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea
Abstract
1. Introduction
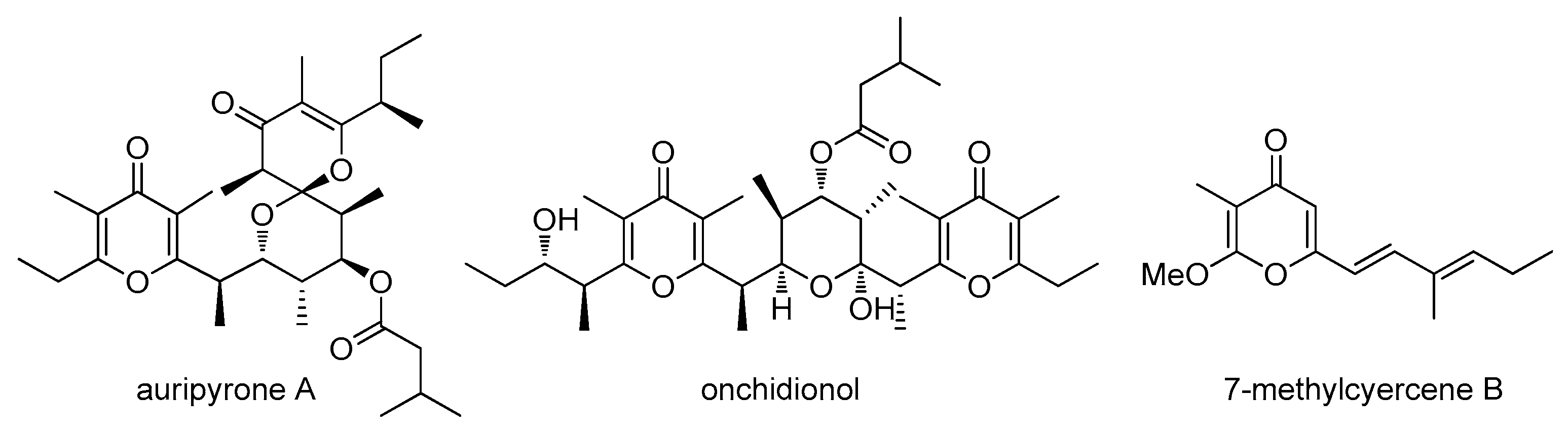
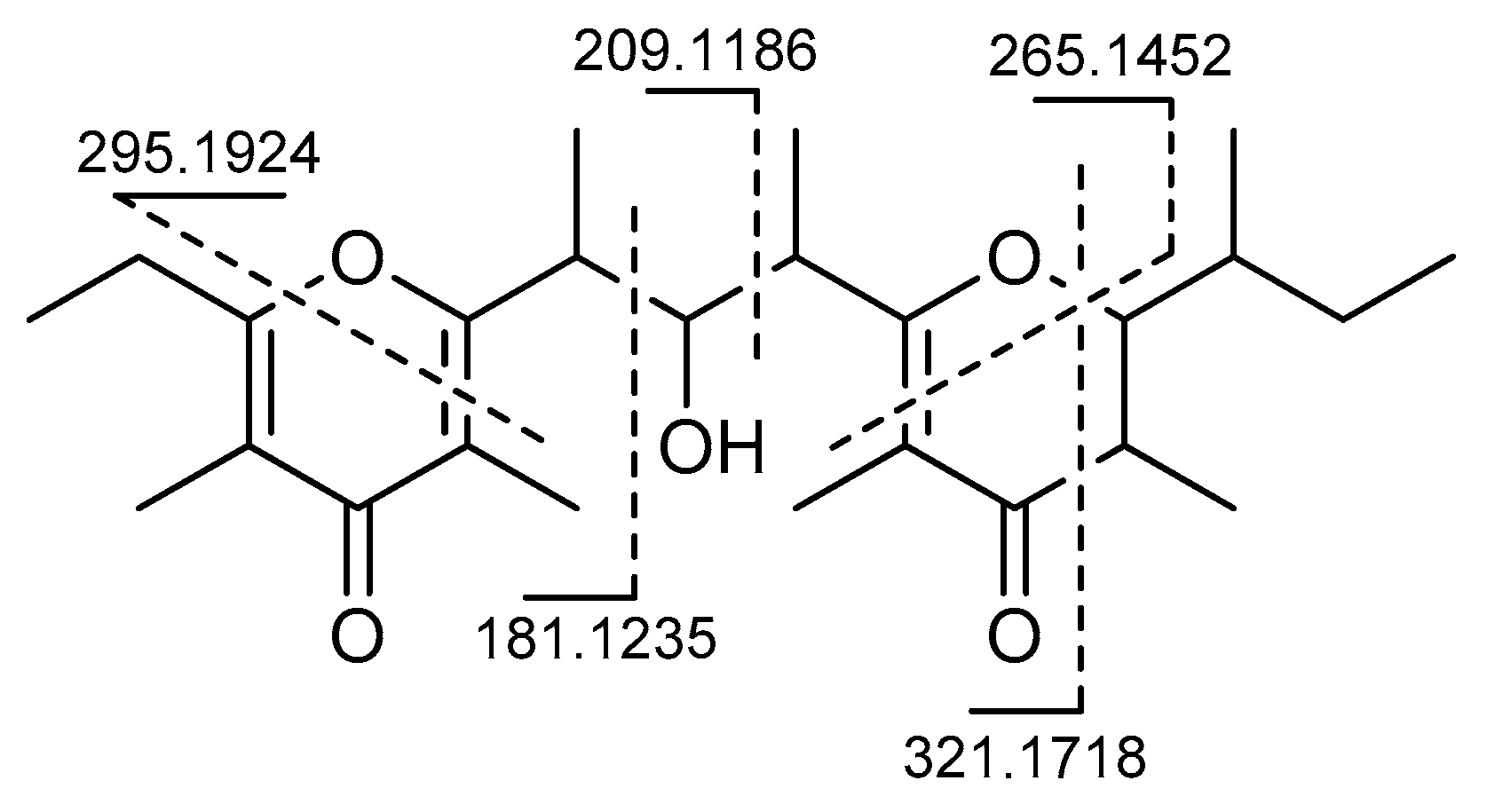
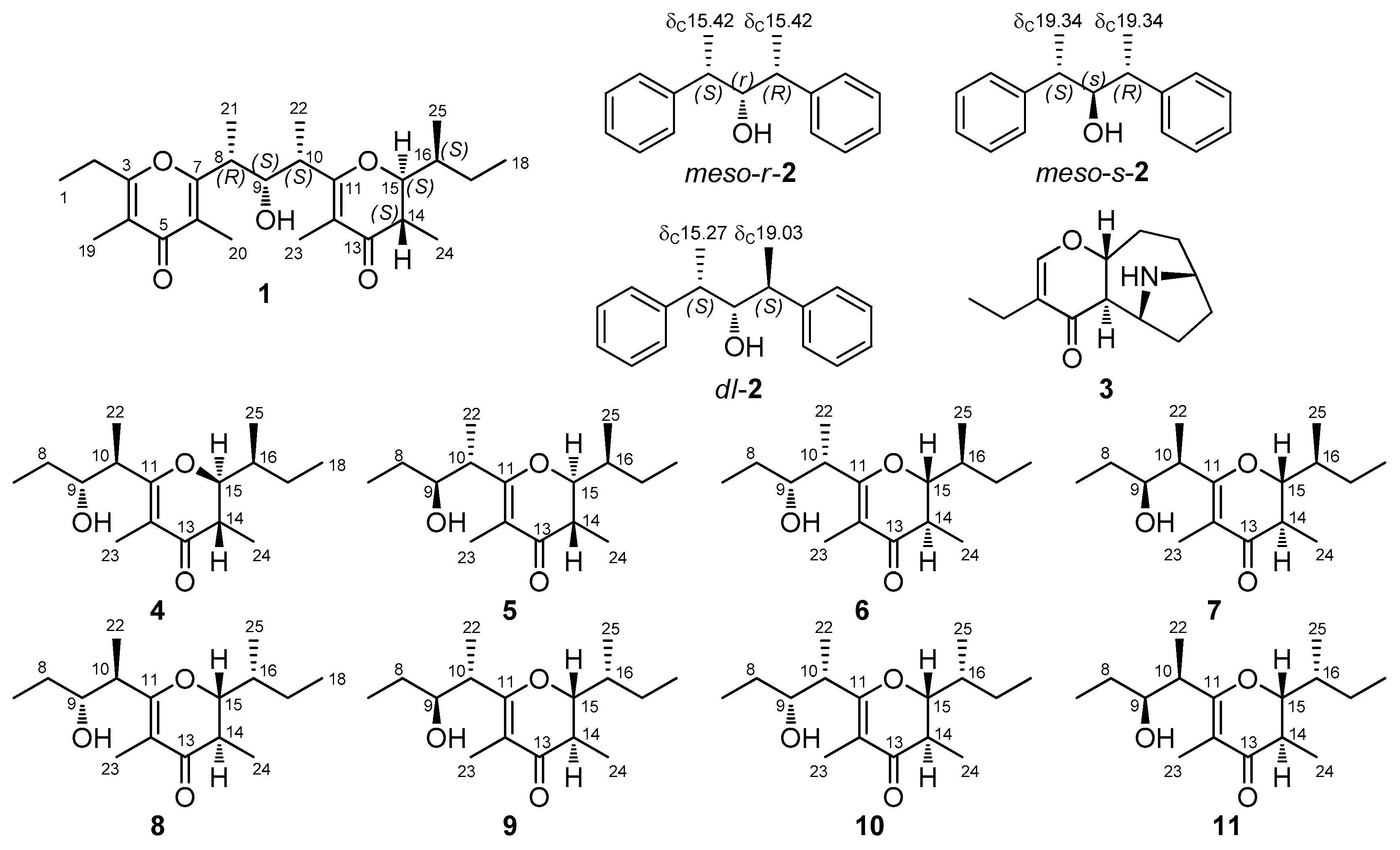
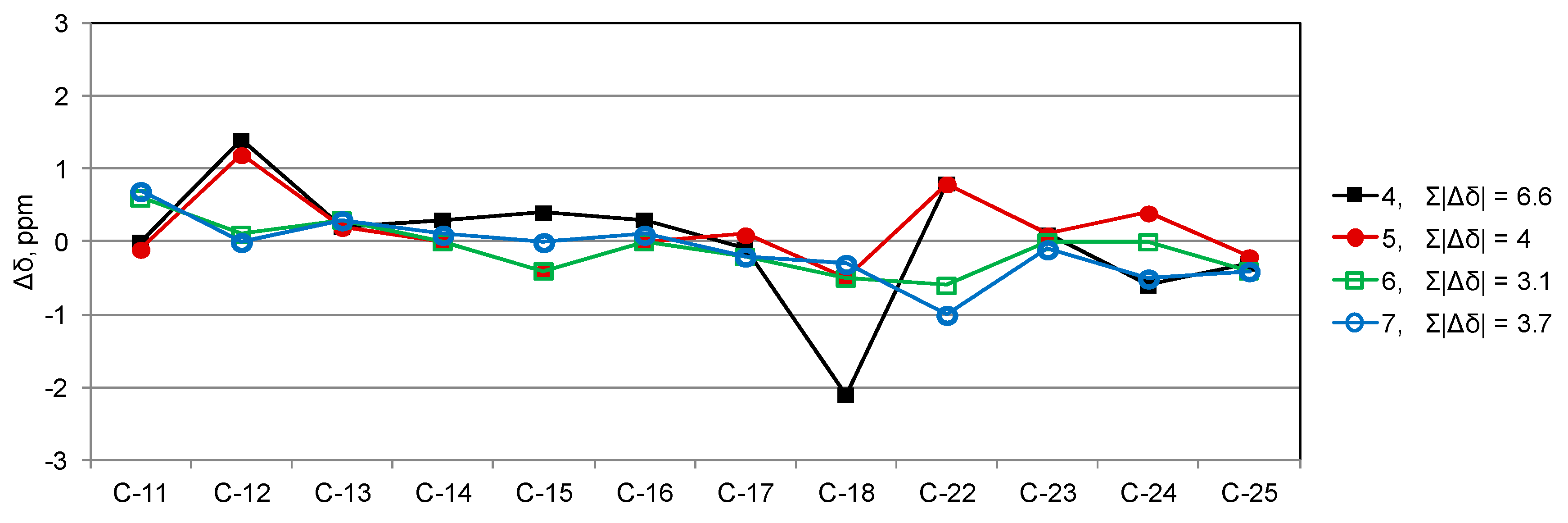
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. General Experimental Procedure
4.2. Collections, Extraction, and Isolation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilk, W.; Waldmann, H.; Kaiser, M. γ-Pyrone natural products—A privileged compound class provided by nature. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 2304–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, J.R. Marine Invertebrate Chemical Defenses. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies-Coleman, M.T.; Garson, M.J. Marine polypropionates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 1998, 15, 477–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.; Ciavatta, M.L.; Wang, J.R.; Cirillo, I.; Mathieu, V.; Kiss, R.; Mollo, E.; Guo, Y.W.; Gavagnin, M. Extending the Record of Bis-γ-pyrone Polypropionates from Marine Pulmonate Mollusks. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 2065–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.F.; Li, X.L.; Yao, L.G.; Li, J.; Gavagnin, M.; Guo, Y.W. Marine bis-γ-pyrone polypropionates of onchidione family and their effects on the XBP1 gene expression. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2018, 28, 1093–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suenaga, K.; Kigoshi, H.; Yamada, K. Auripyrones A and B, cytotoxic polypropionates from the sea hare Dolabella auricularia: Isolation and structures. Tetrahedron Lett. 1996, 37, 5151–5154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Petit, G.R.; Hamel, E. Dolastatin 10, a powerful cytostatic peptide derived from a marine animal: Inhibition of tubulin polymerization mediated through the vinca alkaloid binding domain. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1990, 39, 1941–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Ectyoceramide, the First Natural Hexofuranosylceramide from the Marine Sponge Ectyoplasia ferox. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 8, 1433–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; D’Esposito, M.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Basilico, N.; Parapini, S.; Taramelli, D. Damicoside from Axinella damicornis: The influence of a glycosylated galactose 4-OH group on the immunostimulatory activity of α-galactoglycosphingolipids. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 7411–7417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Imperatore, C.; Mangoni, A. Glycolipids from sponges. Part 17. Clathrosides and Isoclathrosides, Unique Glycolipids from the Caribbean Sponge Agelas clathrodes. J. Nat. Prod. 2006, 69, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamoral-Theys, D.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Kiss, R.; Costantino, V. Evaluation of the antiproliferative activity of diterpene isonitriles from the sponge Pseudoaxinella flava in apoptosis-sensitive and apoptosis-resistant cancer cell lines. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 2299–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Della Sala, G.; Teta, R.; Caso, A.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Pawlik, J.R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Chlorinated Thiazole-Containing Polyketide-Peptides from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia conulosa: Structure Elucidation on Microgram Scale. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 16, 2871–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caso, A.; Mangoni, A.; Piccialli, G.; Costantino, V.; Piccialli, V. Studies toward the Synthesis of Smenamide A, an Antiproliferative Metabolite from Smenospongia aurea: Total Synthesis of ent-Smenamide A and 16-epi-Smenamide A. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 1477–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caso, A.; Laurenzana, I.; Lamorte, D.; Trino, S.; Esposito, G.; Piccialli, V.; Costantino, V. Smenamide A Analogues. Synthesis and Biological Activity on Multiple Myeloma Cells. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlik, J.R. Thechemical ecology of sponges on Caribbeanreefs: Natural products shape natural systems. Bioscience 2011, 61, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantino, V.; Fattorusso, E.; Mangoni, A.; Perinu, C.; Teta, R.; Panza, E.; Ianaro, A. Tedarenes A and B: Structural and stereochemical analysis of two new strained cyclic diarylheptanoids from the marine sponge Tedania ignis. J. Org. Chem. 2012, 77, 6377–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangoni, A. Strategies for Structural Assignment of Marine Natural Products Through Advanced NMR-based Techniques. In Handbook of Marine Natural Products; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 518–546. [Google Scholar]
- Manker, D.C.; Faulkner, D.J.; Xe, C.F.; Clardy, J. Metabolites of Siphonaria maura from Costa Rica. J. Org. Chem. 1986, 51, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crossman, J.S.; Perkins, M.V. Total Synthesis and Structural Elucidation of (−)-Maurenone. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwink, L.; Knochel, P. Enantioselective Preparation of C2-Symmetrical Ferrocenyl Ligands for Asymmetric Catalysis. Chem. Eur. J. 1998, 4, 950–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takada, N.; Iwatsuki, M.; Suenaga, K.; Uemura, D. Pinnamine, an alkaloidal marine toxin, isolated from Pinna muricata. Tetrahedron Lett. 2000, 41, 6425–6428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutignano, A.; Villani, G.; Fontana, A. One metabolite, two pathways: Convergence of polypropionate biosynthesis in fungi and marine molluscs. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 992–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Torres, J.P.; Ammon, M.A.; Marett, L.; Teichert, R.W.; Reilly, C.A.; Kwan, J.C.; Hughen, R.W.; Flores, M.; Tianero, M.D.; et al. A bacterial source for mollusk pyrone polyketides. Chem. Biol. 2013, 20, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hentschel, U.; Usher, K.M.; Taylor, M.W. Marine sponges as microbial fermenters. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2006, 55, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, M.; Imperatore, C.; Grozdanov, L.; Costantino, V.; Mangoni, A.; Hentschel, U.; Fattorusso, E. Cellular localisation of secondary metabolites isolated from the Caribbean sponge Plakortis simplex. Mar. Biol. 2007, 151, 1365–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, A.L.; Peraud, O.; Kasanah, N.; Sims, J.W.; Kothalawala, N.; Anderson, M.A.; Abbas, S.H.; Rao, K.V.; Jupally, V.R.; Kelly, M.; et al. An analysis of the sponge Acanthostrongylophora igens’ microbiome yields an actinomycete that produces the natural product manzamine A. Front. Mar. Sci. 2014, 1, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Mai, L.H.; Longeon, A.; Teta, R.; Meijer, L.; Van Soest, R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Chloromethylhalicyclamine B, a Marine-Derived Protein Kinase CK1δ/ε Inhibitor. J. Nat. Prod. 2016, 79, 2953–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, J.F.; Venturi, V. A novel widespread interkingdom signaling circuit. Trends Plant Sci. 2013, 18, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardères, J.; Taupin, L.; Saidin, J.B.; Dufour, A.; Le Pennec, G. N-acyl homoserine lactone production by bacteria within the sponge Suberites domuncula (Olivi, 1972) (Porifera, Demospongiae). Mar. Biol. 2012, 159, 1685–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardères, J.; Henry, J.; Bernay, B.; Ritter, A.; Zatylny-Gaudin, C.; Wiens, M.; Müller, W.E.; Le Pennec, G. Cellular Effects of Bacterial N-3-Oxo-Dodecanoyl-L-Homoserine Lactone on the Sponge Suberites domuncula (Olivi, 1792): Insights into an Intimate Inter-Kingdom Dialogue. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantino, V.; Della Sala, G.; Saurav, K.; Teta, R.; Bar-Shalom, R.; Mangoni, A.; Steindler, L. Plakofuranolactone as a Quorum Quenching Agent from the Indonesian Sponge Plakortis cf. lita. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachmann, A.O.; Brameyer, S.; Kresovic, D.; Hitkova, I.; Kopp, Y.; Manske, C.; Schubert, K.; Bode, H.B.; Heermann, R. Pyrones as bacterial signaling molecules. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2013, 9, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Glukhov, E.; Gerwick, L.; Gerwick, W.H.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Combined LC−MS/MS and Molecular Networking Approach Reveals New Cyanotoxins from the 2014 Cyanobacterial Bloom in Green Lake, Seattle. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 14301–14310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, G.; Teta, R.; Miceli, R.; Ceccarelli, L.S.; Della Sala, G.; Camerlingo, R.; Irollo, E.; Mangoni, A.; Pirozzi, G.; Costantino, V. Isolation and Assessment of the in Vitro Anti-Tumor Activity of Smenothiazole A and B, Chlorinated Thiazole-Containing Peptide/Polyketides from the Caribbean Sponge, Smenospongia aurea. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teta, R.; Irollo, E.; Della Sala, G.; Pirozzi, G.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Smenamides A and B, Chlorinated Peptide/Polyketide Hybrids Containing a Dolapyrrolidinone Unit from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea. Evaluation of Their Role as Leads in Antitumor Drug Research. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 4451–4463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
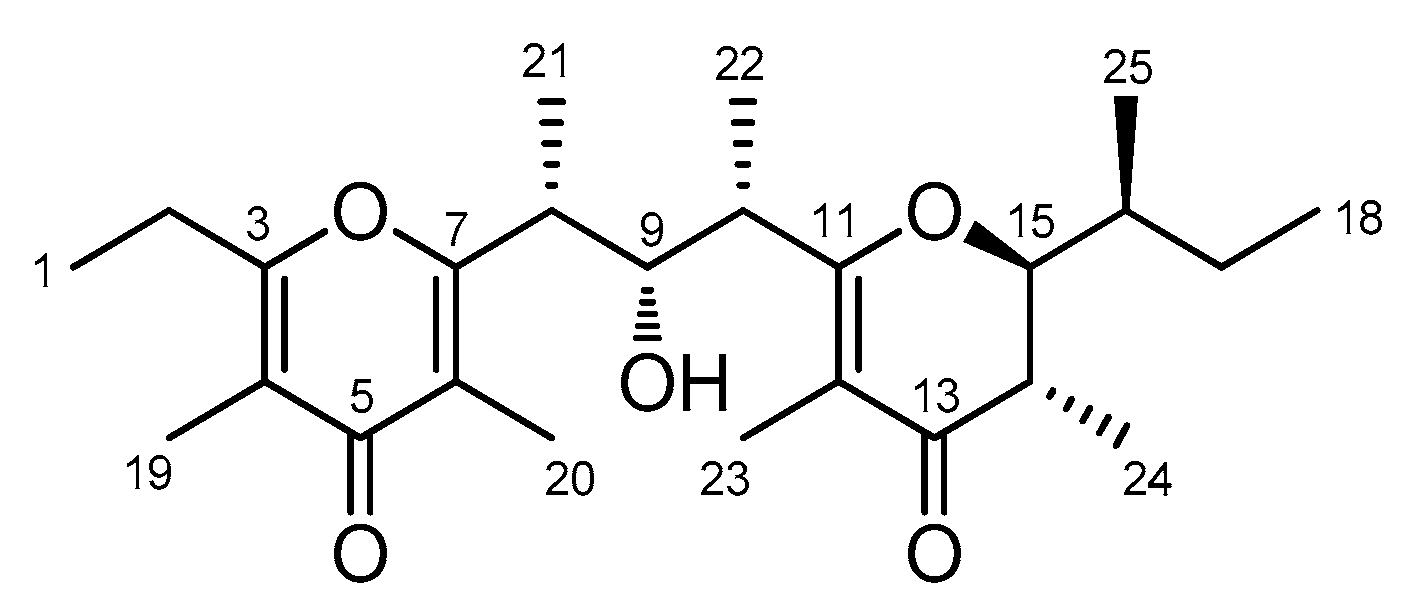
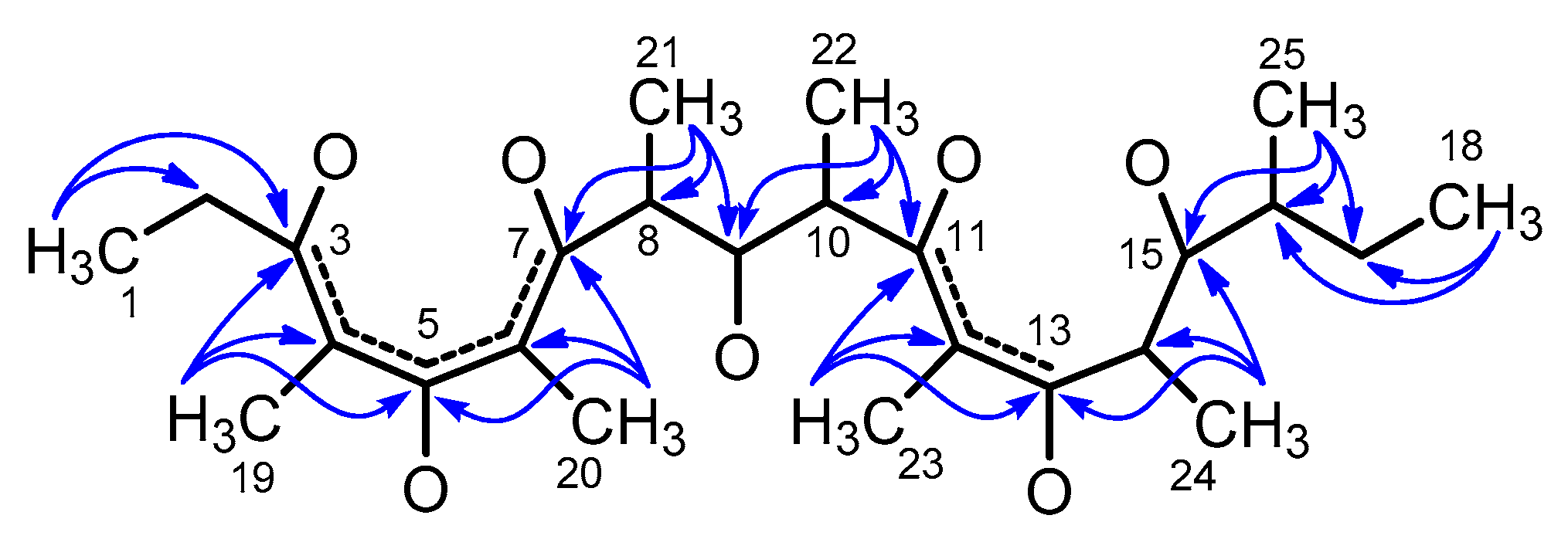
| Position | δC, Type | δH, Mult (J in Hz) | HMBC a | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 11.7 (CH3) | 1.25 (t, 7.5) | 2, 3 | |
| 2 | 25.7 (CH2) | a,b | 2.71 (m) | 1, 3 |
| 3 | 167.5 (C) | - | ||
| 4 | 119.0 (C) | - | ||
| 5 | 182.0 (C) | - | ||
| 6 | 120.3 (C) | - | ||
| 7 | 167.7 (C) | - | ||
| 8 | 41.7 (CH) | 3.15 (quintet, 7.1) | 9, 21 | |
| 9 | 75.6 (CH) | 4.02 (t, 7.1) | 7, 8, 21, 22 | |
| 10 | 41.5 (CH) | 2.93 (quintet, 7.0) | 9, 11, 22 | |
| 11 | 175.6 (C) | - | ||
| 12 | 109.2 (C) | - | ||
| 13 | 197.9 (C) | - | ||
| 14 | 41.5 (CH) | 2.53 (dq, 12.8, 6.9) | 13, 15, 24 | |
| 15 | 88.0 (CH) | 3.84 (dd, 12.8, 3.0) | ||
| 16 | 36.6 (CH) | 1.78 (m) | ||
| 17 | 23.0 (CH2) | a | 1.64 (m) | |
| b | 1.29 (m) | |||
| 18 | 12.1 (CH3) | 0.98 (t, 7.5) | 16, 17 | |
| 19 | 9.6 (CH3) | 1.93 (s) | 3, 4, 5 | |
| 20 | 10.1 (CH3) | 1.91 (s) | 5, 6, 7 | |
| 21 | 15.5 (CH3) | 1.28 (d, 7.1) | 7, 8, 9 | |
| 22 | 14.1 (CH3) | 1.26 (d, 6.9) | 9, 10, 11 | |
| 23 | 9.4 (CH3) | 1.63 (s) | 11, 12, 13 | |
| 24 | 10.7 (CH3) | 1.06 (d, 6.9) | 13, 14, 15 | |
| 25 | 16.6 (CH3) | 1.11 (d, 6.9) | 15, 16, 17 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esposito, G.; Teta, R.; Della Sala, G.; Pawlik, J.R.; Mangoni, A.; Costantino, V. Isolation of Smenopyrone, a Bis-γ-Pyrone Polypropionate from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080285
Esposito G, Teta R, Della Sala G, Pawlik JR, Mangoni A, Costantino V. Isolation of Smenopyrone, a Bis-γ-Pyrone Polypropionate from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea. Marine Drugs. 2018; 16(8):285. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080285
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsposito, Germana, Roberta Teta, Gerardo Della Sala, Joseph R. Pawlik, Alfonso Mangoni, and Valeria Costantino. 2018. "Isolation of Smenopyrone, a Bis-γ-Pyrone Polypropionate from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea" Marine Drugs 16, no. 8: 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080285
APA StyleEsposito, G., Teta, R., Della Sala, G., Pawlik, J. R., Mangoni, A., & Costantino, V. (2018). Isolation of Smenopyrone, a Bis-γ-Pyrone Polypropionate from the Caribbean Sponge Smenospongia aurea. Marine Drugs, 16(8), 285. https://doi.org/10.3390/md16080285