Elevated Serum TNF-α/IL-1β Levels and Under-Nutrition Predict Early Mortality and Hospital Stay Burden in Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Patient Selection and Group Allocation
2.3. Data Collection and Variable Definitions
2.4. Laboratory Procedures
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Patient Demographics
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Findings
4.2. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADA | Adenosinedeaminase |
| ACE | Angiotensin-convertingenzyme |
| AUROC | Area under the receiver-operating-characteristic curve |
| BCG | Bacille Calmette–Guérin(vaccine) |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| COPD | Chronicobstructive pulmonary disease |
| COVID-19 | Coronavirus disease 2019 |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CXCL | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand |
| ECDC | European Centres for Disease Prevention and Control |
| EPTB | Extrapulmonary tuberculosis |
| EU | European Union |
| GBD | Global Burden of Disease study |
| HDT | Host-directed therapy |
| HIV | Human immunodeficiency virus |
| ICH | International Conference on Harmonisation |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-gamma |
| IL-1α | Interleukin-1-alpha |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1-beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 |
| IL-10 | Interleukin-10 |
| IRB | Institutional review board |
| IRR | Incidence-rate ratio |
| IQR | Inter-quartile range |
| LOS | Length of stay |
| MDR-TB | Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis |
| MGIT | Mycobacteria Growth Indicator Tube (culture system) |
| miR | Micro-RNA |
| MMP-9 | Matrixmetalloproteinase-9 |
| NLR | Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte rratio |
| NTP | (Romanian) National Tuberculosis Control Programme |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PBMC | Peripheral-blood mononuclear cell |
| pSWE | Point shear-wave elastography |
| ROC | Receiver-operating-characteristic curve |
| R2 | Coefficient of determination |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| STROBE | Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
| Th1 | Type-1 helper T-cell response |
| TNF-α | Tumour-necrosis-factor-alpha |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Review of the National Tuberculosis Programme in Romania. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/149036/Review%20of%20the%20national%20tuberculosis%20programme%20in%20Romania.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y#:~:text=ABSTRACT,DK-2100%20Copenhagen%20Ø%2C%20Denmark (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. WHO Regional Office for Europe. Tuberculosis Surveillance and Monitoring in Europe 2023—2021 Data; ECDC: Stockholm, Sweden, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, H.; Ruan, X.; Li, W.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, Y. Global, regional, and national burden of tuberculosis and attributable risk factors for 204 countries and territories, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the GBD 2021 study. BMC Public Health 2024, 24, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. The End TB Strategy. In WHO/HTM/TB/2015.19; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Peng, P. Global, regional, and national mortality of tuberculosis attributable to alcohol and tobacco from 1990 to 2019. J. Glob. Health 2024, 14, 04023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Dumitrescu, A.; Baiceanu, D.; Popa, C.; Dragomir, A.; Mahler, B.; Hoelscher, M.; Lange, C.; Heyckendorf, J.; Rachow, A.; et al. Impact of drug-resistant tuberculosis on socio-economic status and quality of life in Bucharest. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2024, 43, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margineanu, I.; Butnaru, T.; Lam, M.; Baiceanu, D.; Dragomir, R.; Arbore, A.S.; Mahler, B.; Munteanu, I.; Mihaltan, F.; Akkerman, O.; et al. Tuberculosis impacts multiple aspects of quality of life in Romanian patients. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2024, 29, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaushik, S.R.; Sahu, S.; Guha, H.; Saha, S.; Das, R.; Kupa, R.-U.; Kapfo, W.; Deka, T.; Basumatary, R.; Thong, A.; et al. Low circulatory Fe and Se levels with a higher IL-6/IL-10 ratio provide nutritional immunity in tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 985538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandiarajan, A.N.; Kumar, N.P.; Selvaraj, N.; Ahamed, S.F.; Viswanathan, V.; Thiruvengadam, K.; Hissar, S.; Shanmugam, S.; Bethunaickan, R.; Nott, S.; et al. Distinct TB-antigen stimulated cytokine profiles predict unfavourable outcomes. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1392256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankrah, J.N.O.; Gyilbagr, F.; Vicar, E.K.; Frimpong, E.A.B.; Alhassan, R.B.; Baako, I.S.; Boakye, A.N.; Akwetey, S.A.; Karikari, A.B.; Sorvor, F.K.B.; et al. T-cell exhaustion and inflammatory markers in PBMCs predict tuberculosis treatment outcome. Cytokine 2024, 182, 156708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.-P.; Hong, J.-C.; Jiang, Z.-J.; Pan, Y.-Y.; Liu, X.-F.; Wang, J.-M.; Fan, R.-J.; Yang, B.-H.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Fan, Q.-C.; et al. Systemic and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for tuberculous meningitis identification. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0224623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.; Pan, H.; Fei, Z.; Zhang, T. Clinical value of serum miRNA-206 in pulmonary tuberculosis. J. Infect. Chemother. 2025, 31, 102589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, J.V.; Bongaerts, B.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Risso, A.; Guo, Y.; Silva, L.P.; Boeckmann, M.; Schlesinger, S.; Damen, J.A.; Richter, B.; et al. Undernutrition as a risk factor for tuberculosis disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 6, CD015890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, J.V.; Bongaerts, B.; Metzendorf, M.-I.; Risso, A.; Guo, Y.; Silva, L.P.; Boeckmann, M.; Schlesinger, S.; Damen, J.A.; Richter, B.; et al. Diabetes as a risk factor for tuberculosis disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2024, 8, CD016013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pipitò, L.; Colomba, C.; Mancuso, A.; Catania, B.; Cuccia, A.; Sergio, M.; Iaria, C.; Cascio, A. Hospitalizations for tuberculosis in Sicily (2009–2021): Predictors of mortality. J. Infect. Public Health 2023, 16, 1518–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, P.; Yimit, Y.; Cai, X.; Aimaiti, A.; Sheng, W.; Mamat, M.; Nijiati, M. Machine-learning prediction of prolonged length of stay after surgery for tuberculosis spondylitis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, M.; Liu, L.; Li, A.; Lu, H. Predictive machine-learning models for anticipating loss to follow-up in tuberculosis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naicker, N.; Rodel, H.; Perumal, R.; Ganga, Y.; Bernstein, M.; Benede, N.; Karim, S.A.; Padayacthi, N.; Sigal, A.; Naidoo, K. Metformin increases cell viability and regulates pro-inflammatory response to M. tuberculosis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 3629–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeken, V.A.C.M.; Qi, C.; Mourits, V.P.; de Bree, L.C.J.; Moorlag, S.J.C.F.M.; Sonawane, V.; Lemmers, H.; Dijkstra, H.; Joosten, L.A.B.; van Laarhoven, A.; et al. Plasma metabolome predicts trained-immunity responses after BCG vaccination. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliori, G.B.; Sotgiu, G.; Rosales-Klintz, S.; Centis, R.; D’AMbrosio, L.; Abubakar, I.; Bothamley, G.; Caminero, J.A.; Cirillo, D.M.; Dara, M.; et al. ERS/ECDC Statement: European Union standards for tuberculosis care, 2017 update. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirzaei, A.; Mahmoudi, H. Evaluation of TNF-α cytokine production in patients with tuberculosis compared to healthy people. GMS Hyg. Infect. Control. 2018, 13, Doc09. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, T.; Hong, J.; Huang, C.; Yang, P.; Liao, S.; Chang, K. Increased TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 levels in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid with upregulation of their mRNA in macrophages from active pulmonary tuberculosis. Tuber. Lung Dis. 1999, 79, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devalraju, K.P.; Neela, V.S.K.; Chintala, S.; Krovvidi, S.S.; Valluri, V.L. Transforming Growth Factor-β suppresses interleukin-2 and IL-1β production in HIV-tuberculosis co-infection. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2019, 39, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.-L.; Perng, W.-C.; Huang, C.-H.; Yang, C.-Y.; Wu, C.-P.; Chen, J.-H. Association of reduced TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-1β but increased IL-10 expression with improved chest radiography in pulmonary tuberculosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2010, 17, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, J.E.; Fernandez-Vilaseca, M.; Elkington, P.T.G.; Horncastle, D.E.; Graeber, M.B.; Friedland, J.S. IFN-γ synergizes with IL-1β to up-regulate MMP-9 secretion in a cellular model of CNS tuberculosis. FASEB J. 2007, 21, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Sim, Y.S.; Ryu, Y.J.; Chang, J.H.; Shim, S.S.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.H. High blood neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio associated with poor outcomes in miliary tuberculosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Hou, H.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, X. Association between indices of peripheral blood inflammation and cavitary pulmonary tuberculosis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2024, 17, 5133–5142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Zhou, H.; Shu, L.; Wang, R.; Zhao, C. Clinical application of NRS-2002 in nutritional risk screening of tuberculosis inpatients. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2021, 10, 5322–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, Y.C.; Dourado, A.L.L.; de Oliveira, P.V.; de Oliveira Rezende, A.; de Souza Sales, A.C.; de Sousa, G.P.; de Araújo Pereira, E.; Sousa, E.L.C.; Lindoso, M.C.C.M.; Júnior, R.D.M.R.; et al. Nutritional factors and food and nutrition insecurity in patients with tuberculosis. Nutrients 2025, 17, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daliu, P.; Bogdan, I.; Rosca, O.; Licker, M.; Stanga, L.C.; Hogea, E.; Vaduva, D.B.; Muntean, D. Fungal Pulmonary Coinfections in COVID-19: Microbiological Assessment, Inflammatory Profiles, and Clinical Outcomes. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chan, M.S.; Moore, Z.; Patton, D.; McNamara, D.; O’Connor, T.; Avsar, P. A systematic review of patient risk factors for complications following stoma formation among adults undergoing colorectal surgery. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2023, 38, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanga, L.C.; Vaduva, D.M.B.; Grigoras, M.L.; Nussbaum, L.A.; Gurgus, D.; Strat, L.; Zamfir, A.S.; Poroch, V.; Folescu, R. Nosocomial Infections Distribution and Impact in Medical Units. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 2265–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacob, M.S.; Kundnani, N.R.; Sharma, A.; Meche, V.; Ciobotaru, P.; Bedreag, O.; Sandesc, D.; Dragan, S.R.; Papurica, M.; Stanga, L.C. Multifactorial Risk Stratification in Patients with Heart Failure, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Atrial Fibrillation: A Comprehensive Analysis. Life 2025, 15, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Denti, F.C.; Guerra, E.; Caroppo, F.; Abruzzese, P.; Alessi, F.; Barone, F.; Bernardino, P.; Bergamini, M.; Bernardo, M.C.; Bosio, G.; et al. Outcomes of a Risk-Stratified Protocol for Preventing Peristomal Skin Complications in Patients with an Ostomy: A Cohort Study. Nurs. Rep. 2025, 15, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]

| Variable | TB (n = 80) | Controls (n = 40) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 50.1 ± 14.8 | 46.6 ± 8.4 | 0.096 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 63 (78.8) | 15 (37.5) | <0.001 |
| Variable | n (%) |
|---|---|
| Current smoker | 59 (76.6) |
| Chronic alcohol use | 23 (29.9) |
| Occasional alcohol use | 5 (6.5) |
| Known household TB contact | 13 (16.9) |
| ≥1 prior COVID-19 episode | 24 (31.2) |
| Currently employed | 35 (45.5) |
| Symptomatic at presentation | 77 (96.3) |
| Symptom duration | |
| <4 weeks | 33 (41.3) |
| 4–12 weeks | 23 (28.7) |
| >12 weeks | 21 (26.2) |
| BMI category | |
| Underweight (<18.5 kg·m−2) | 22 (27.5) |
| Normal (18.5–24.9) | 47 (58.7) |
| Overweight (≥25) | 11 (13.8) |
| ≥1 comorbidity | 25 (31.2) |
| Single comorbidity | 17 (21.2) |
| ≥2 comorbidities | 8 (10.0) |
| Median length of stay, days (IQR) | 29 (23–34) |
| Marker | TB Median (IQR) pg/mL | Control Median (IQR) pg/mL | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | 4.84 (3.11–8.41) | 4.14 (2.31–12.87) | 0.527 |
| IL-1α | 3.57 (1.62–9.19) | 4.12 (0.68–16.40) | 0.599 |
| IL-1β | 5.34 (3.93–16.35) | 3.67 (2.48–8.31) | 0.008 |
| TNF-α | 24.11 (18.42–43.15) | 16.21 (8.02–43.15) | 0.009 |
| NLR | 4.01 (2.44–7.28) | 2.78 (1.93–4.05) | 0.071 |
| Marker | Survivors (n = 76) Median (IQR) | Non-Survivors (n = 4) Median (IQR) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | 4.84 (3.02–8.32) | 8.66 (4.67–19.26) | 0.22 |
| IL-1α | 3.57 (1.62–8.37) | 9.09 (1.89–26.41) | 0.74 |
| IL-1β | 3.56 (2.43–8.13) | 18.07 (4.94–46.03) | 0.079 |
| TNF-α | 23.20 (18.19–37.54) | 71.43 (48.69–140.22) | 0.037 |
| NLR | 3.70 (1.95–5.55) | 7.84 (2.55–9.41) | 0.002 |
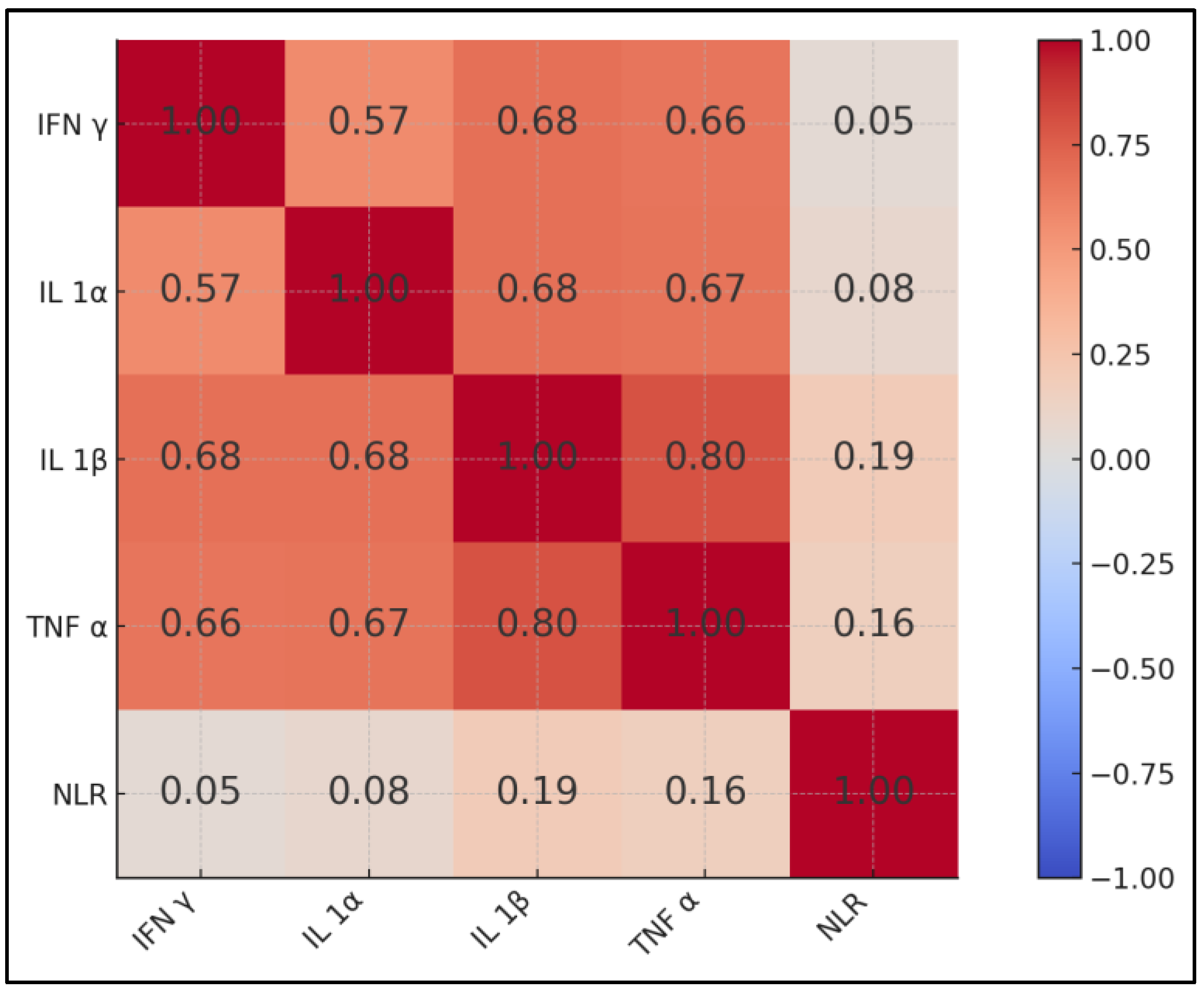
| Variables | IFN-γ | IL-1α | IL-1β | TNF-α | NLR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ | 1 | ρ = 0.57 * | 0.68 * | 0.66 * | 0.05 |
| IL-1α | 0.57 * | 1 | 0.68 * | 0.67 * | 0.08 |
| IL-1β | 0.68 * | 0.68 * | 1 | 0.80 * | 0.19 |
| TNF-α | 0.66 * | 0.67 * | 0.80 * | 1 | 0.16 |
| NLR | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.19 | 0.16 | 1 |
| Subgroup | n | Median LOS (Days) | Comparator n | Median LOS | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Smoking vs. non-smoking | 59 | 28 | 18 | 31 | 0.41 |
| ≥1 comorbidity vs. none | 25 | 28 | 52 | 29 | 0.69 |
| BMI categories | 0.03 † | ||||
| Underweight | 22 | 27 | — | — | |
| Normal | 47 | 30 | — | — | |
| Overweight | 8 | 23 | — | — |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanciu, I.-V.; Fildan, A.-P.; Ilie, A.C.; Oancea, C.; Stanga, L.; Tudorache, E.; Bratosin, F.; Rosca, O.; Bogdan, I.; Tofolean, D.-E.; et al. Elevated Serum TNF-α/IL-1β Levels and Under-Nutrition Predict Early Mortality and Hospital Stay Burden in Pulmonary Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155327
Stanciu I-V, Fildan A-P, Ilie AC, Oancea C, Stanga L, Tudorache E, Bratosin F, Rosca O, Bogdan I, Tofolean D-E, et al. Elevated Serum TNF-α/IL-1β Levels and Under-Nutrition Predict Early Mortality and Hospital Stay Burden in Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2025; 14(15):5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155327
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanciu, Ionut-Valentin, Ariadna-Petronela Fildan, Adrian Cosmin Ilie, Cristian Oancea, Livia Stanga, Emanuela Tudorache, Felix Bratosin, Ovidiu Rosca, Iulia Bogdan, Doina-Ecaterina Tofolean, and et al. 2025. "Elevated Serum TNF-α/IL-1β Levels and Under-Nutrition Predict Early Mortality and Hospital Stay Burden in Pulmonary Tuberculosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 14, no. 15: 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155327
APA StyleStanciu, I.-V., Fildan, A.-P., Ilie, A. C., Oancea, C., Stanga, L., Tudorache, E., Bratosin, F., Rosca, O., Bogdan, I., Tofolean, D.-E., Preotesoiu, I., Zamfir, V., & Dantes, E. (2025). Elevated Serum TNF-α/IL-1β Levels and Under-Nutrition Predict Early Mortality and Hospital Stay Burden in Pulmonary Tuberculosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 14(15), 5327. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm14155327







