Evidence for Pituitary Repression of the Human Growth Hormone-Related Placental Lactogen Genes and a Role for P Sequences
Abstract
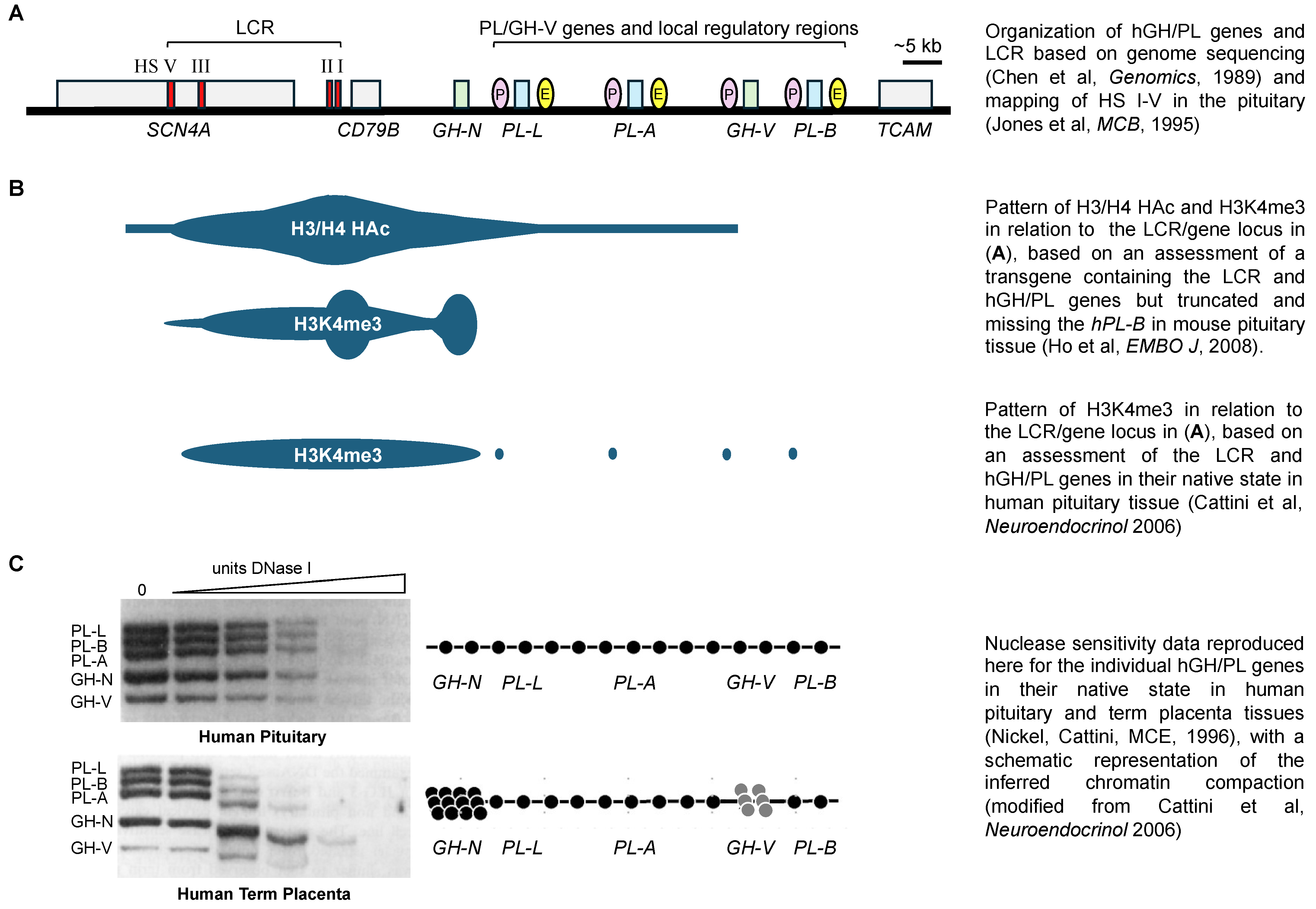
:1. The Human Growth Hormone and Placental Lactogen Genes
2. The hGH/PL Gene Cluster and the Role of Pit-1
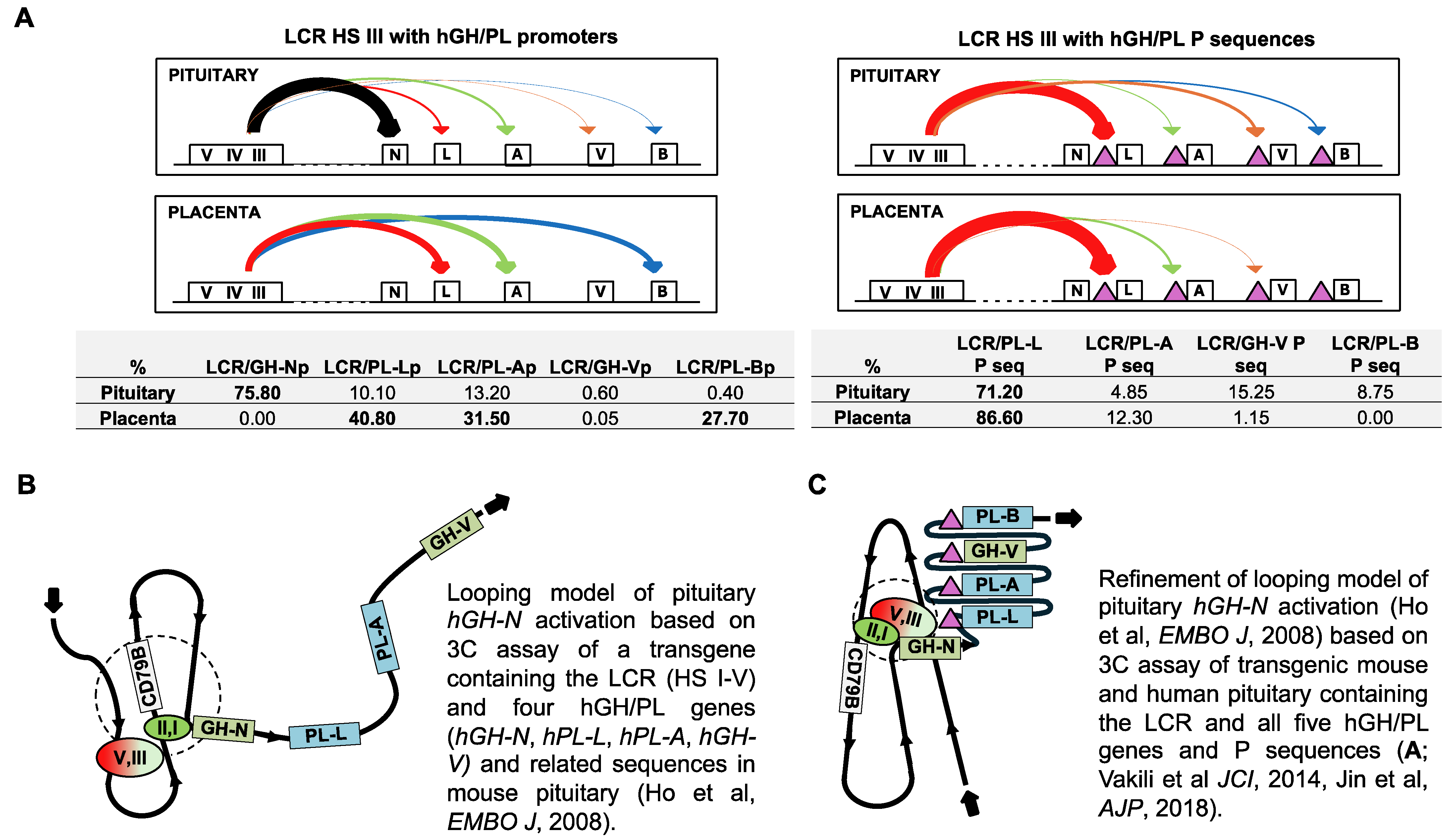
3. LCR and hGH/PL Gene-Related Sequence Interactions in Pituitary Expression
4. HS I/II and HS III Interactions with hGH-N Are a Feature of Efficient Pituitary Expression
5. P Sequences Bind Transcription Factors with Repressor Function in Human Pituitary Tissue
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barsh, G.S.; Seeburg, P.H.; Gelinas, R.E. The human growth hormone gene family: Structure and evolution of the chromosomal locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983, 11, 3939–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, E.Y.; Liao, Y.C.; Smith, D.H.; Barrera-Saldana, H.A.; Gelinas, R.E.; Seeburg, P.H. The human growth hormone locus: Nucleotide sequence, biology, and evolution. Genomics 1989, 4, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.H.; Grumbach, M.M.; Kaplan, S.L.; Josimovich, J.B.; Friesen, H.; Catt, K.J. Human chorionic somato-mammotropin (HCS), proposed terminology for designation of a placental hormone. Experientia 1968, 24, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newbern, D.; Freemark, M. Placental hormones and the control of maternal metabolism and fetal growth. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2011, 18, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWilliams, D.; Boime, I. Cytological localization of placental lactogen messenger ribonucleic acid in syncytiotrophoblast layers of human placenta. Endocrinology 1980, 107, 761–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horseman, N.D.; Gregerson, K.A. Chapter 6—Prolactin. In Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric, 7th ed.; Jameson, L.J., De Groot, L.J., de Kretser, D.M., Giudice, L.C., Grossman, A.B., Melmed, S., Potts, J.T., Weir, G.C., Eds.; W. B. Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016; pp. 91–103. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Surabhi, R.M.; Fresnoza, A.; Lytras, A.; Cattini, P.A. A role for A/T-rich sequences and Pit-1/GHF-1 in a distal enhancer located in the human growth hormone locus control region with preferential pituitary activity in culture and transgenic mice. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shewchuk, B.M.; Asa, S.L.; Cooke, N.E.; Liebhaber, S.A. Pit-1 binding sites at the somatotrope-specific DNase I hypersensitive sites I, II of the human growth hormone locus control region are essential for in vivo hGH-N gene activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35725–35733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Hoya, M.; Vila, V.; Jimenez, O.; Castrillo, J.L. Anterior pituitary development and Pit-1/GHF-1 transcription factor. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 1998, 54, 1059–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Cattini, P.A. Appearance of the pituitary factor Pit-1 increases chromatin remodeling at hypersensitive site III in the human GH locus. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 45, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattini, P.A.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Detillieux, K.A. Regulation of the human growth hormone gene family: Possible role for Pit-1 in early stages of pituitary-specific expression and repression. Neuroendocrinology 2006, 83, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, B.E.; Nachtigal, M.W.; Bock, M.E.; Cattini, P.A. Differential binding of rat pituitary-specific nuclear factors to the 5′-flanking region of pituitary and placental members of the human growth hormone gene family. Mol. Cell Biochem. 1991, 106, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickel, B.E.; Cattini, P.A. Nuclease sensitivity of the human growth hormone-chorionic somatomammotropin locus in pituitary and placenta suggest different mechanisms for tissue-specific regulation. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 1996, 118, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Norquay, L.D.; Yang, X.; Gregoire, S.; Cattini, P.A. Binding of AP-2 and ETS-domain family members is associated with enhancer activity in the hypersensitive site III region of the human growth hormone/chorionic somatomammotropin locus. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 574–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elefant, F.; Cooke, N.E.; Liebhaber, S.A. Targeted recruitment of histone acetyltransferase activity to a locus control region. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 13827–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Oomah, K.; Cattini, P.A. Enhancer-blocking activity is associated with hypersensitive site V sequences in the human growth hormone locus control region. DNA Cell Biol. 2011, 30, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Cooke, N.E.; Liebhaber, S.A. Tissue specific CTCF occupancy and boundary function at the human growth hormone locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 4906–4921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, B.K.; Monks, B.R.; Liebhaber, S.A.; Cooke, N.E. The human growth hormone gene is regulated by a multicomponent locus control region. Mol. Cell Biol. 1995, 15, 7010–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norquay, L.D.; Yang, X.; Jin, Y.; Detillieux, K.A.; Cattini, P.A. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-3alpha binding at P sequences of the human growth hormone locus is associated with pituitary repressor function. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.W.; Wu, K.; Eberhardt, N.L. Human placental TEF-5 transactivates the human chorionic somatomammotropin gene enhancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 879–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elefant, F.; Su, Y.; Liebhaber, S.A.; Cooke, N.E. Patterns of histone acetylation suggest dual pathways for gene activation by a bifunctional locus control region. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 6814–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytras, A.; Detillieux, K.; Cattini, P.A. Identification of functional CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein and Ets protein binding sites in the human chorionic somatomammotropin enhancer sequences. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquemin, P.; Oury, C.; Peers, B.; Morin, A.; Belayew, A.; Martial, J.A. Characterization of a single strong tissue-specific enhancer downstream from the three human genes encoding placental lactogen. Mol. Cell Biol. 1994, 14, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walker, W.H.; Fitzpatrick, S.L.; Saunders, G.F. Human placental lactogen transcriptional enhancer. Tissue specificity and binding with specific proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 12940–12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, H.; Jin, Y.; Menticoglou, S.; Cattini, P.A. CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) and downstream human placental growth hormone genes are targets for dysregulation in pregnancies complicated by maternal obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 22849–22861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattini, P.A.; Jin, Y.; Jarmasz, J.S.; Noorjahan, N.; Bock, M.E. Obesity and regulation of human placental lactogen production in pregnancy. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2020, 32, e12859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroiwa, Y.; Kaneko-Ishino, T.; Kagitani, F.; Kohda, T.; Li, L.L.; Tada, M.; Suzuki, R.; Yokoyama, M.; Shiroishi, T.; Wakana, S.; et al. Peg3 imprinted gene on proximal chromosome 7 encodes for a zinc finger protein. Nat. Genet. 1996, 12, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Ye, A.; Kim, J. DNA-Binding Motif of the Imprinted Transcription Factor PEG3. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, A.; Gubbiotti, M.A.; Iozzo, R.V. Decorin-inducible Peg3 Evokes Beclin 1-mediated Autophagy and Thrombospondin 1-mediated Angiostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 5055–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sojoodi, M.; Stradiot, L.; Tanaka, K.; Heremans, Y.; Leuckx, G.; Besson, V.; Staels, W.; Van de Casteele, M.; Marazzi, G.; Sassoon, D.; et al. The zinc finger transcription factor PW1/PEG3 restrains murine beta cell cycling. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiaville, M.M.; Huang, J.M.; Kim, H.; Ekram, M.B.; Roh, T.Y.; Kim, J. DNA-binding motif and target genes of the imprinted transcription factor PEG3. Gene 2013, 512, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Ishikawa, G.; Luo, S.S.; Mishima, T.; Goto, T.; Robinson, J.M.; Matsubara, S.; Takeshita, T.; Kataoka, H.; Takizawa, T. The cytotrophoblast layer of human chorionic villi becomes thinner but maintains its structural integrity during gestation. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 76, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayhew, T.M. Turnover of human villous trophoblast in normal pregnancy: What do we know and what do we need to know? Placenta 2014, 35, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.; Dang, Y.L.; Wang, H.; Lin, H.Y.; Zhu, C.; Ge, H.; Cross, J.C.; et al. Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the diversity of trophoblast subtypes and patterns of differentiation in the human placenta. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 819–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiby, S.E.; Lough, M.; Keverne, E.B.; Surani, M.A.; Loke, Y.W.; King, A. Paternal monoallelic expression of PEG3 in the human placenta. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Vakili, H.; Liu, S.Y.; Menticoglou, S.; Bock, M.E.; Cattini, P.A. Chromosomal architecture and placental expression of the human growth hormone gene family are targeted by pre-pregnancy maternal obesity. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 315, E435–E445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, A.P.; Liebhaber, S.A.; Cooke, N.E. Epigenetic modifications at the human growth hormone locus predict distinct roles for histone acetylation and methylation in placental gene activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 18, 1018–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.; Elefant, F.; Cooke, N.; Liebhaber, S. A defined locus control region determinant links chromatin domain acetylation with long-range gene activation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 291–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, M.; Nomoto, K.; Nakazato, S. Gene structure of rat testicular cell adhesion molecule 1 (TCAM-1), and its physical linkage to genes coding for the growth hormone and BAF60b, a component of SWI/SNF complexes. Gene 1999, 226, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surabhi, R.M.; Bose, S.; Kuschak, B.C.; Cattini, P.A. Physical linkage of the human growth hormone gene family and the thyroid hormone receptor interacting protein-1 gene on chromosome 17. Gene 1998, 212, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surabhi, R.M.; Daly, L.D.; Cattini, P.A. Evidence for evolutionary conservation of a physical linkage between the human BAF60b, a subunit of SWI/SNF complex, and thyroid hormone receptor interacting protein-1 genes on chromosome 17. Genome 1999, 42, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.; Tadevosyan, A.; Liebhaber, S.A.; Cooke, N.E. The juxtaposition of a promoter with a locus control region transcriptional domain activates gene expression. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; McNicol, I.; Cattini, P.A. A locus control region generates distinct active placental lactogen and inactive growth hormone gene domains in term placenta that are disrupted with maternal obesity. Placenta 2025, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemaigre, F.P.; Peers, B.; Lafontaine, D.A.; Mathy-Hartert, M.; Rousseau, G.G.; Belayew, A.; Martial, J.A. Pituitary-specific factor binding to the human prolactin, growth hormone, and placental lactogen genes. DNA 1989, 8, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nachtigal, M.W.; Nickel, B.E.; Klassen, M.E.; Zhang, W.G.; Eberhardt, N.L.; Cattini, P.A. Human chorionic somatomammotropin and growth hormone gene expression in rat pituitary tumour cells is dependent on proximal promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989, 17, 4327–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenfeld, G. Chromatin as an essential part of the transcriptional mechanism. Nature 1992, 355, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesch, B.J.; Page, D.C. Poised chromatin in the mammalian germ line. Development 2014, 141, 3619–3626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.; Nightingale, F.; Zhu, Y.; MacGregor-Chatwin, C.; Zhang, P. Structure of native chromatin fibres revealed by Cryo-ET in situ. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeshima, K.; Ide, S.; Babokhov, M. Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2019, 58, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.T.; Oh, S.; Ro, D.H.; Yoo, H.; Kwon, Y.W. The Key Role of DNA Methylation and Histone Acetylation in Epigenetics of Atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2020, 9, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.; Lau, P. Epigenetic regulation by histone methylation and histone variants. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igolkina, A.A.; Zinkevich, A.; Karandasheva, K.O.; Popov, A.A.; Selifanova, M.V.; Nikolaeva, D.; Tkachev, V.; Penzar, D.; Nikitin, D.M.; Buzdin, A. H3K4me3, H3K9ac, H3K27ac, H3K27me3 and H3K9me3 Histone Tags Suggest Distinct Regulatory Evolution of Open and Condensed Chromatin Landmarks. Cells 2019, 8, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.C.; Cooke, N.E.; Liebhaber, S.A. Long-range looping of a locus control region drives tissue-specific chromatin packing within a multigene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 4651–4664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, E.; Bock, M.E.; Cattini, P.A. Expression of Placental Members of the Human Growth Hormone Gene Family Is Increased in Response to Sequential Inhibition of DNA Methylation and Histone Deacetylation. Biores Open Access 2015, 4, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, H.; Jin, Y.; Cattini, P.A. Energy homeostasis targets chromosomal reconfiguration of the human GH1 locus. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5002–5012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigal, M.W.; Nickel, B.E.; Cattini, P.A. Pituitary-specific repression of placental members of the human growth hormone gene family. A possible mechanism for locus regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 8473–8479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norquay, L.D.; Yang, X.; Sheppard, P.; Gregoire, S.; Dodd, J.G.; Reith, W.; Cattini, P.A. RFX1 and NF-1 Associate with P Sequences of the Human Growth Hormone Locus in Pituitary Chromatin. Mol. Endocrinol. 2003, 17, 1027–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surabhi, R.M. Studies on the Role of the Distal Sequences Involved in the Expression of the Human Growth Hormone/Chorionic Somatomammotropin Gene Family. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Physiology, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. A Study of the Role of Transcription Factors and Chromatin Remodeling in the Activation/Repression of the Human Growth Hormone/Chorionic Somatomammotropin Genes. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Physiology, University of Manitoba, Winnipeg, MB, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, S.Y.; Fresnoza, A.; Detillieux, K.A.; Duckworth, M.L.; Cattini, P.A. Differential placental hormone gene expression during pregnancy in a transgenic mouse containing the human growth hormone/chorionic somatomammotropin locus. Placenta 2009, 30, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norquay, L.D.; Jin, Y.; Surabhi, R.M.; Gietz, R.D.; Tanese, N.; Cattini, P.A. A member of the nuclear factor-1 family is involved in the pituitary repression of the human placental growth hormone genes. Biochem. J. 2001, 354, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaestner, K.H. The hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (HNF3 or FOXA) family in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 11, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfrum, C.; Besser, D.; Luca, E.; Stoffel, M. Insulin regulates the activity of forkhead transcription factor Hnf-3beta/Foxa-2 by Akt-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear/cytosolic localization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11624–11629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, L.A.; Lin, F.R.; Cuesta, I.; Friedman, D.; Jarnik, M.; Zaret, K.S. Opening of compacted chromatin by early developmental transcription factors HNF3 (FoxA) and GATA-4. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brun, M.; Jain, S.; Monckton, E.A.; Godbout, R. Nuclear Factor I Represses the Notch Effector HEY1 in Glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Uno, J.K.; Inouye, M.; Collins, J.F.; Ghishan, F.K. NF1 transcriptional factor(s) is required for basal promoter activation of the human intestinal NaPi-IIb cotransporter gene. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2005, 288, G175–G181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernadt, C.T.; Nowling, T.; Wiebe, M.S.; Rizzino, A. NF-Y behaves as a bifunctional transcription factor that can stimulate or repress the FGF-4 promoter in an enhancer-dependent manner. Gene Expr. 2005, 12, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schang, A.L.; Granger, A.; Querat, B.; Bleux, C.; Cohen-Tannoudji, J.; Laverriere, J.N. GATA2-induced silencing and LIM-homeodomain protein-induced activation are mediated by a bi-functional response element in the rat GnRH receptor gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 2013, 27, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cattini, P.A.; Jin, Y. Evidence for Pituitary Repression of the Human Growth Hormone-Related Placental Lactogen Genes and a Role for P Sequences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094421
Cattini PA, Jin Y. Evidence for Pituitary Repression of the Human Growth Hormone-Related Placental Lactogen Genes and a Role for P Sequences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094421
Chicago/Turabian StyleCattini, Peter A., and Yan Jin. 2025. "Evidence for Pituitary Repression of the Human Growth Hormone-Related Placental Lactogen Genes and a Role for P Sequences" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094421
APA StyleCattini, P. A., & Jin, Y. (2025). Evidence for Pituitary Repression of the Human Growth Hormone-Related Placental Lactogen Genes and a Role for P Sequences. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094421





