Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Endothelial Integrity and Alleviate Emotional Impairments in a Diabetic Mouse Model via Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
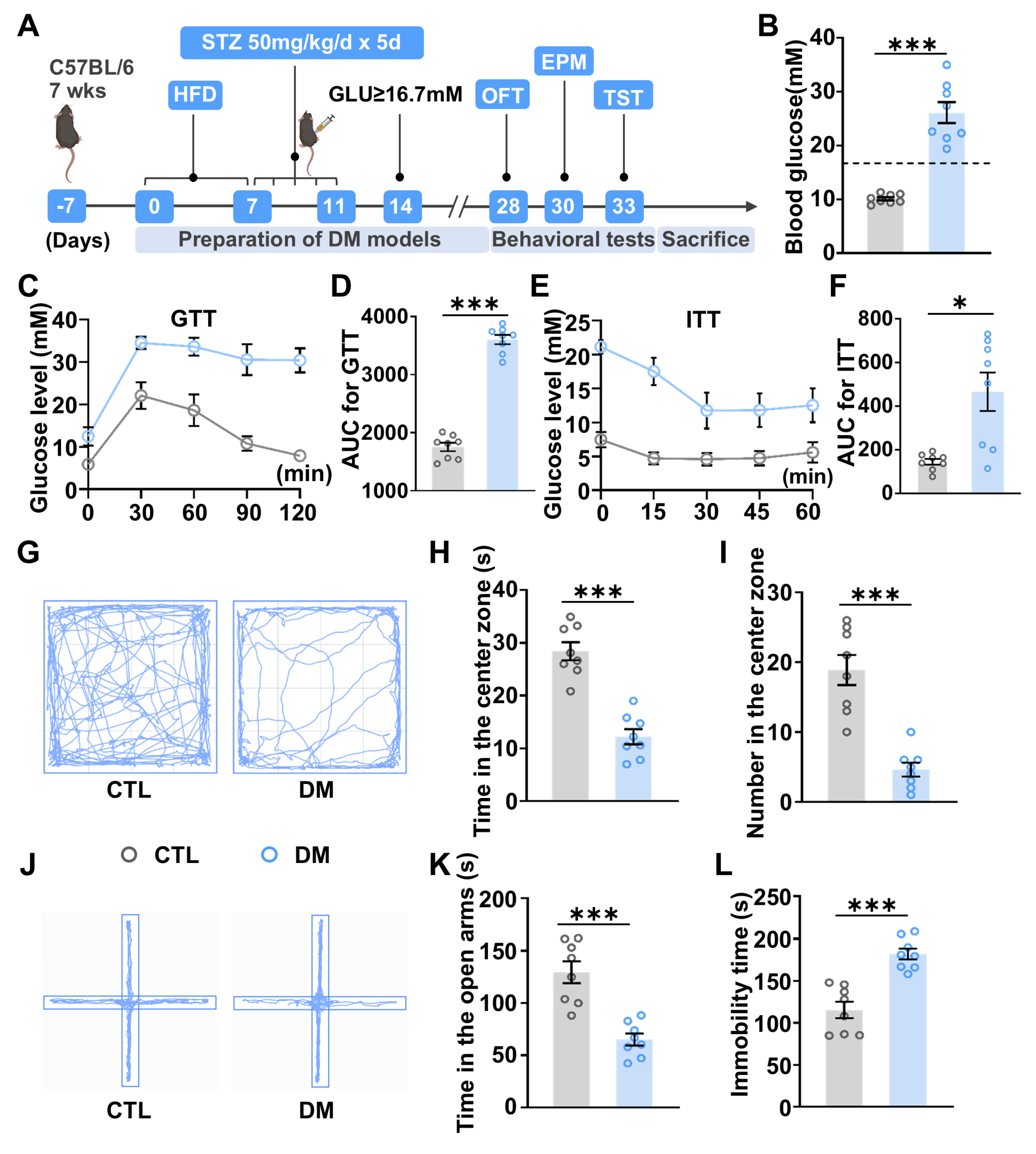
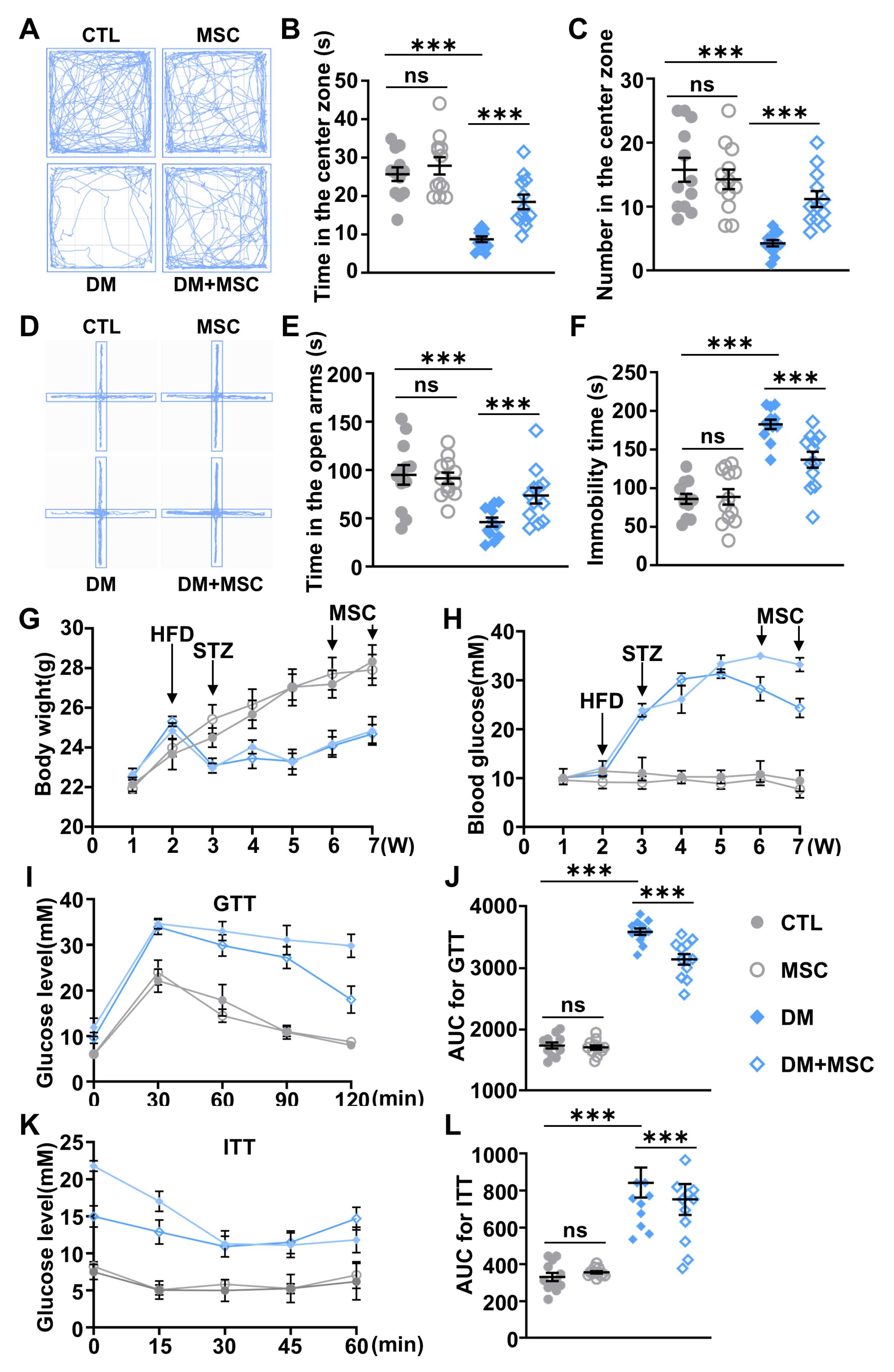
2.1. Diabetic Mice Exhibit Anxiety- and Depressive-like Behaviors
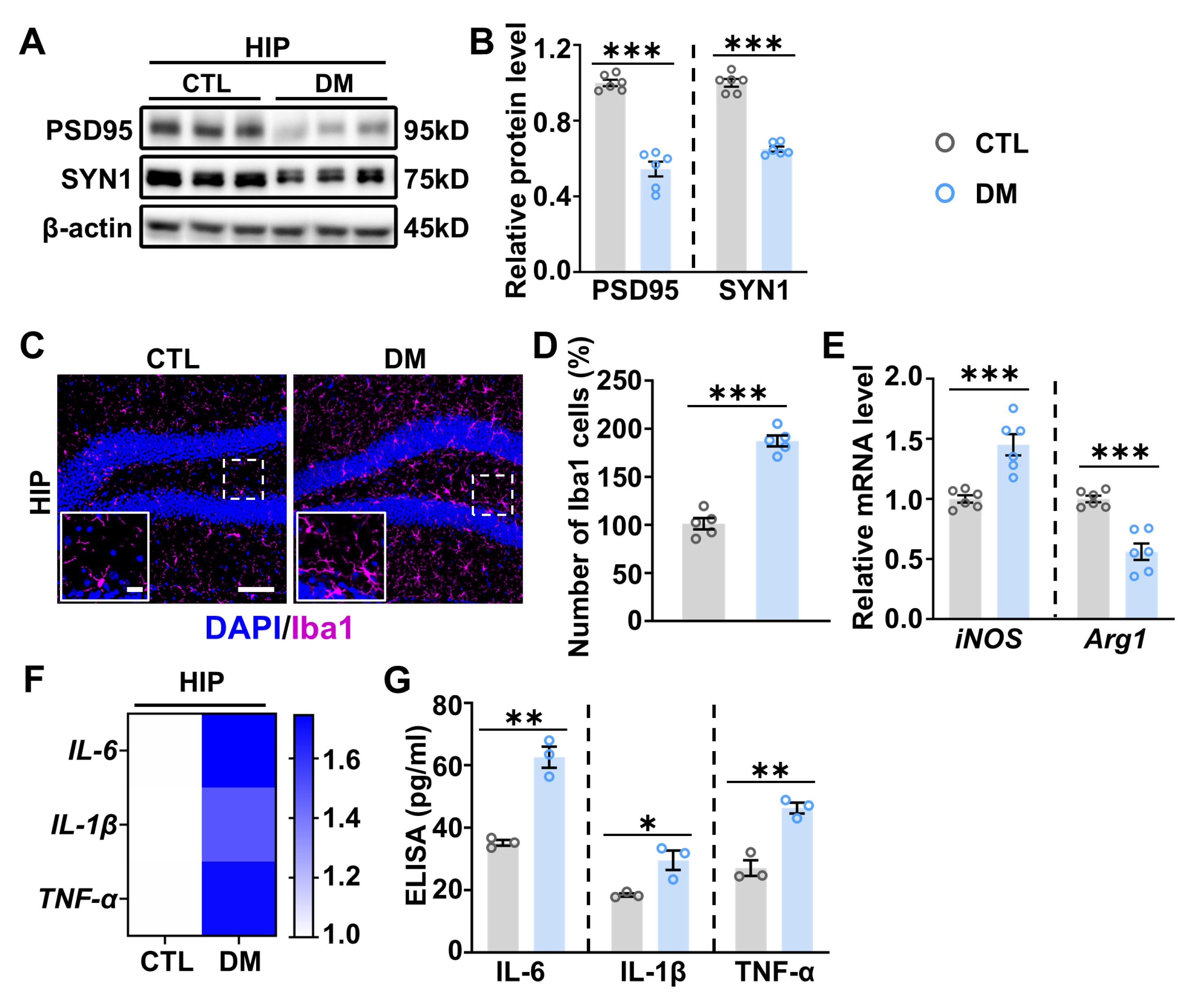
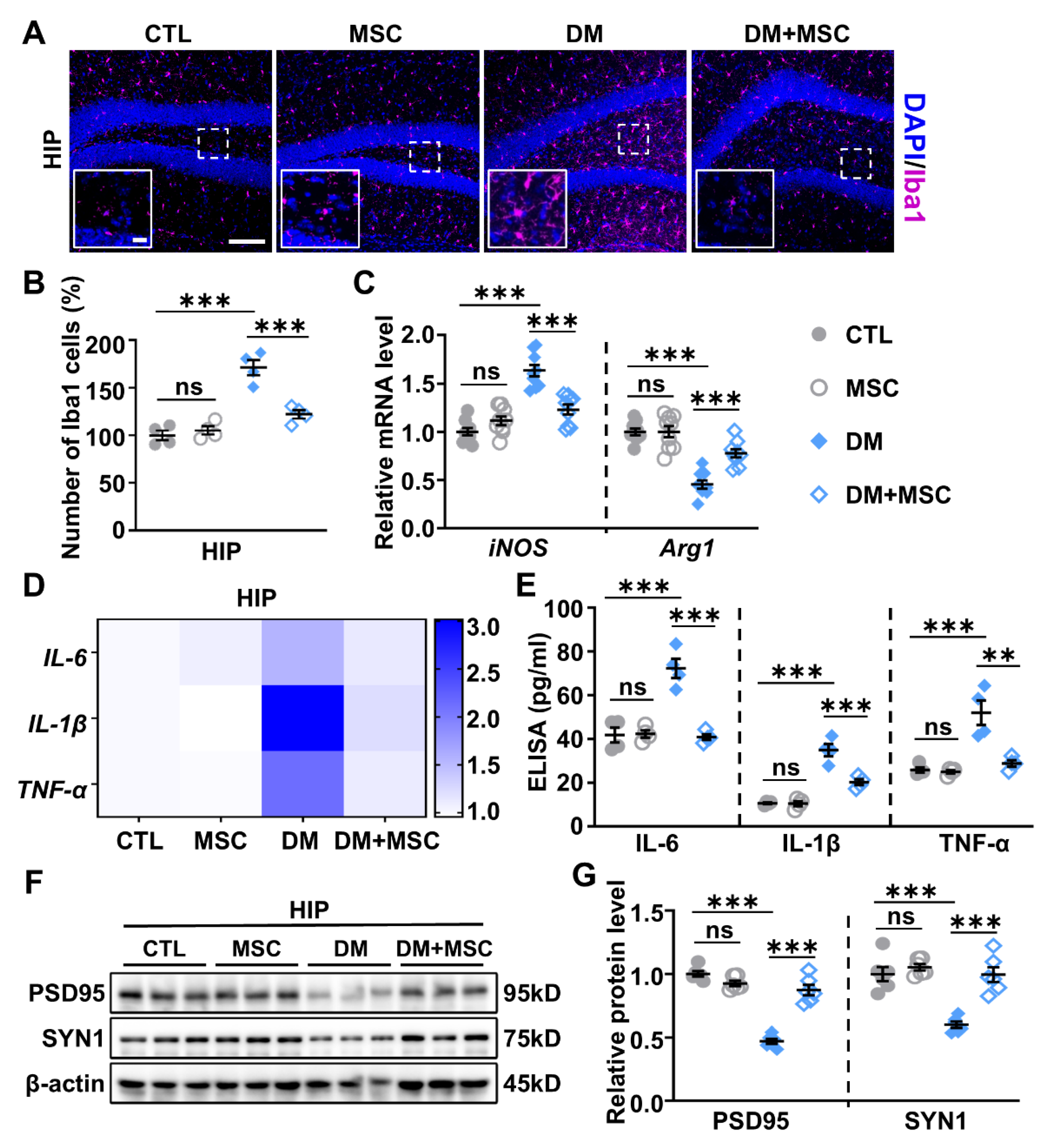
2.2. Increased Neuroinflammation in the Hippocampus of DM Mice
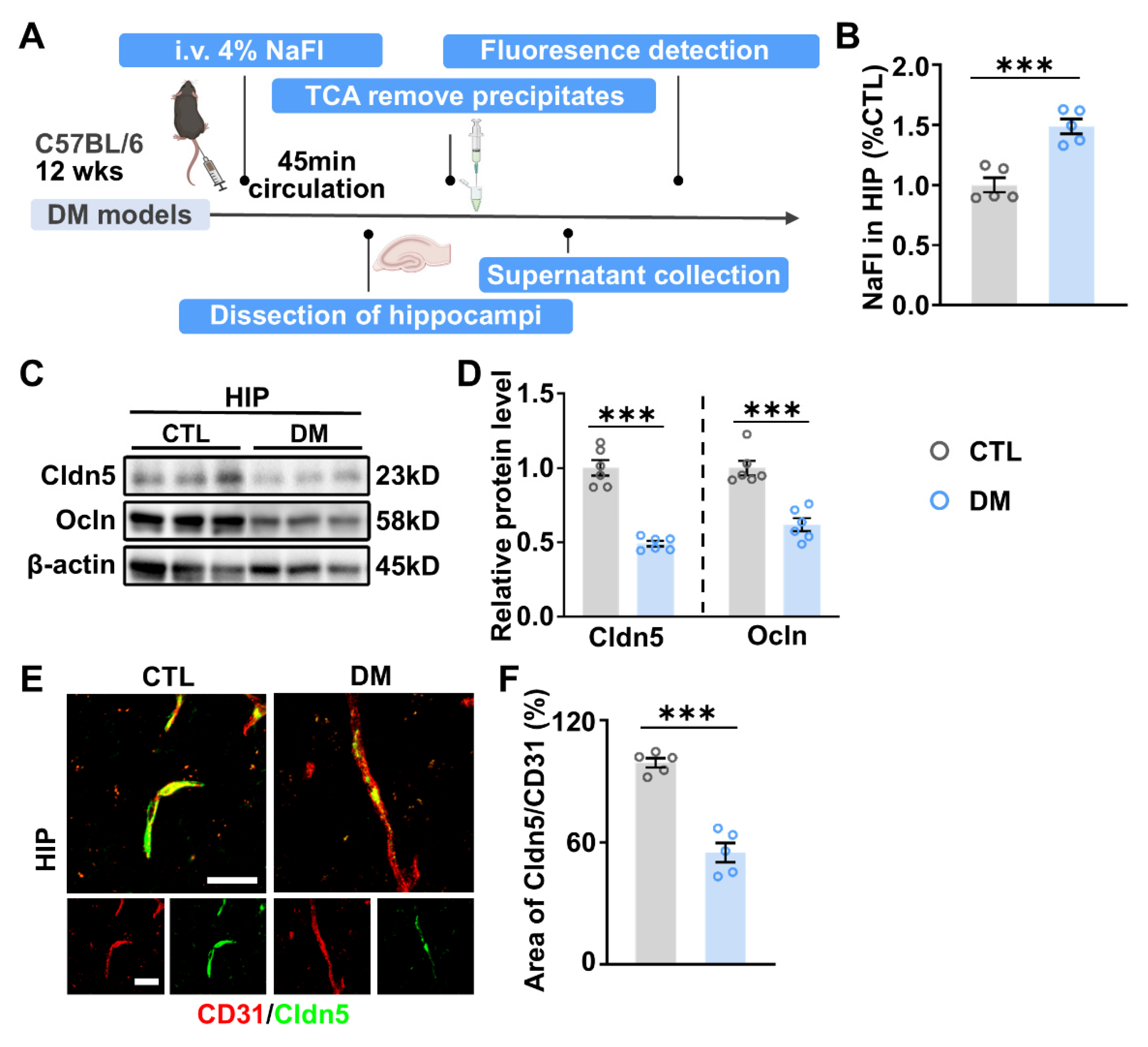
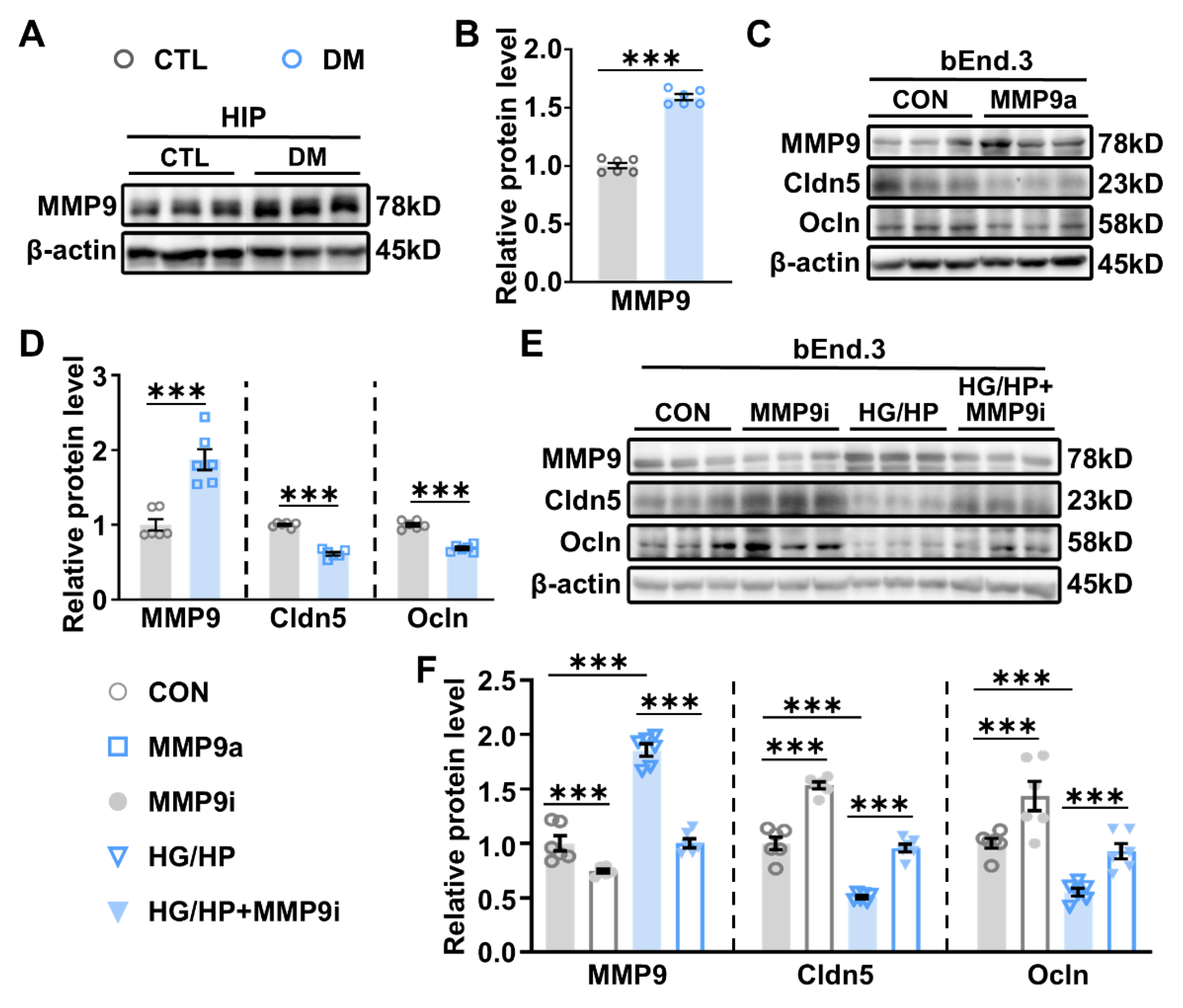
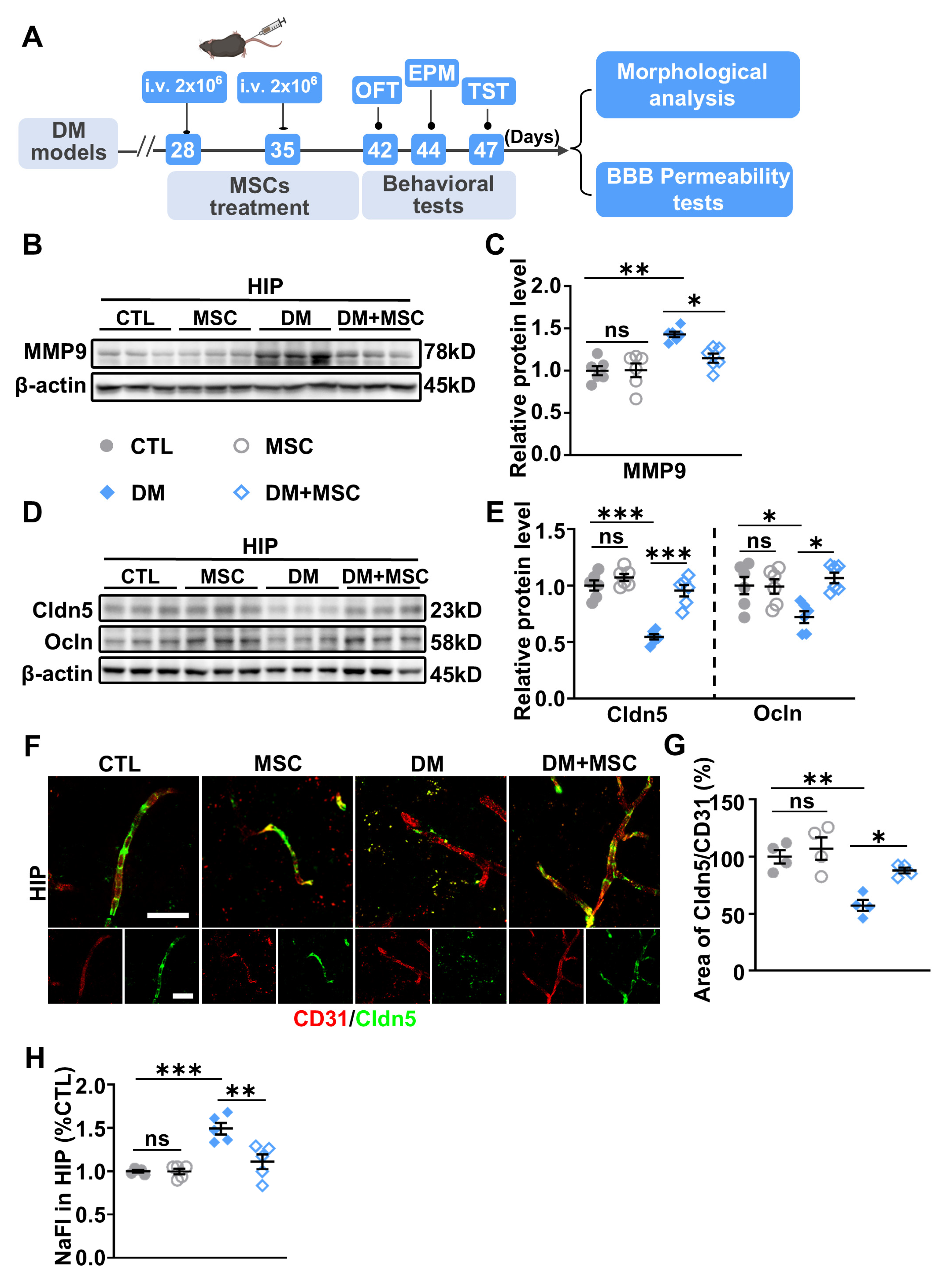
2.3. Impaired BBB Permeability and Enhanced MMP-9 Expression in the HIP of DM Mice
2.4. MSCs Suppress MMP-9 Expression and Restore BBB Integrity in the DM Hippocampus
2.5. MSCs Attenuate Neuroinflammation in the HIP of DM Mice
2.6. MSC Application Alleviated Emotional Deficits and Hyperglycemia in DM Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of MSC Culture
4.2. Endothelial Culture and Treatment
4.3. Preparation of the DM Mouse Models
4.4. Intravenous Injections of MSC
4.5. Behavioral Tests
4.6. In Vivo BBB Permeability Assay
4.7. Immunofluorescent Staining
4.8. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.9. Western Blot
4.10. Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lancet, T. Diabetes: A Defining Disease of the 21st Century. Lancet 2023, 401, 2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, E.; Lim, S.; Lamptey, R.; Webb, D.R.; Davies, M.J. Type 2 Diabetes. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2022, 400, 1803–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sloten, T.T.; Sedaghat, S.; Carnethon, M.R.; Launer, L.J.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Cerebral Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes: Stroke, Cognitive Dysfunction, and Depression. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.Y.; Cheung, C.M.G.; Larsen, M.; Sharma, S.; Simó, R. Diabetic Retinopathy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2016, 2, 16012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, H.-J.; Huber, T.B.; Isermann, B.; Schiffer, M. CKD in Diabetes: Diabetic Kidney Disease versus Nondiabetic Kidney Disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biessels, G.J.; Despa, F. Cognitive Decline and Dementia in Diabetes Mellitus: Mechanisms and Clinical Implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerskov, M.; Vorum, H.V.; Larsen, T.B.L.; Skjoeth, F.S. Retinal Artery Occlusion as Indicator of Stroke in Diabetes. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, ehac544.1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Nowell, J.; Edison, P. Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Alzheimer’s Disease -related Pathology Preceding Cognitive Impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, e092534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInerney, A.M.; Lindekilde, N.; Nouwen, A.; Schmitz, N.; Deschênes, S.S. Diabetes Distress, Depressive Symptoms, and Anxiety Symptoms in People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Network Analysis Approach to Understanding Comorbidity. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 1715–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, M.V.; De Paula, J.J.; Ávila, R.; Pires, L.R.; Cintra, M.T.; Dias, R.F.; Bicalho, M.A. Association of Depression and Diabetes Mellitus with Processing Speed, Inhibitory Control and Cognitive Flexibility in Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 16, e043892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, Z.; Zhou, L.; Xing, C.; Wen, Y.; Du, H. The Blood-Brain Barrier, a Key Bridge to Treat Neurodegenerative Diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 91, 102070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.V.; Vekaria, H.J.; Hartz, A.M.S.; Bauer, B.; Hubbard, W.B. Oxidative Stress Alters Mitochondrial Homeostasis in Isolated Brain Capillaries. Fluids Barriers CNS 2024, 21, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongelli-Sabino, B.M.; Canuto, L.P.; Collares-Buzato, C.B. Acute and Chronic Exposure to High Levels of Glucose Modulates Tight Junction-Associated Epithelial Barrier Function in a Renal Tubular Cell Line. Life Sci. 2017, 188, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebner, S.; Dijkhuizen, R.M.; Reiss, Y.; Plate, K.H.; Agalliu, D.; Constantin, G. Functional Morphology of the Blood-Brain Barrier in Health and Disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 311–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, A.; Lee, T.; Juo, S.H.; Yang, D. Hyperglycemia Increases the Production of Amyloid Beta-Peptide Leading to Decreased Endothelial Tight Junction. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2016, 22, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, J.; Hou, S.; Hu, G.; Ma, H.; Gong, Q.; Kan, X.; Ran, X.; Cao, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. The Inflammatory Environment Mediated by a High-Fat Diet Inhibited the Development of Mammary Glands and Destroyed the Tight Junction in Pregnant Mice. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 8193–8201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jatana, S.; Abbadi, A.; West, G.A.; Ponti, A.K.; Braga-Neto, M.B.; Smith, J.L.; Marino-Melendez, A.; Willard, B.; Nagy, L.E.; Motte, C.D.L. Hyperglycemic Environments Directly Compromise Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Function in an Organoid Model and Hyaluronan (~35 kDa) Protects via a Layilin Dependent Mechanism. Matrix Biol. 2024, 133, 116–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosas-Martínez, L.; Rodríguez-Muñoz, R.; Namorado-Tonix, M.D.C.; Missirlis, F.; Del Valle-Mondragón, L.; Sánchez-Mendoza, A.; Reyes-Sánchez, J.L.; Cervantes-Pérez, L.G. Hyperglycemic Levels in Early Stage of Diabetic Nephropathy Affect Differentially Renal Expression of Claudins-2 and -5 by Oxidative Stress. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 119003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Duan, H.; Feng, J.; Xiang, J.; Feng, L.; Liu, D.; Chen, X.; Jing, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.; et al. Soluble CD146, a Cerebrospinal Fluid Marker for Neuroinflammation, Promotes Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction. Theranostics 2020, 10, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.B.; Tozer, D.J.; Loubière, L.; Harshfield, E.L.; Hong, Y.T.; Fryer, T.D.; Williams, G.B.; Graves, M.J.; Aigbirhio, F.I.; O’Brien, J.T.; et al. MINocyclinE to Reduce Inflammation and Blood-brain Barrier Leakage in Small Vessel diseAse (MINERVA): A Phase II, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Experimental Medicine Trial. Alzheimers Dement. 2024, 20, 3852–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, F.; Dohgu, S.; Matsumoto, J.; Takahashi, H.; Machida, T.; Wakigawa, T.; Harada, E.; Miyaji, H.; Koga, M.; Nishioku, T.; et al. Brain Pericytes among Cells Constituting the Blood-Brain Barrier Are Highly Sensitive to Tumor Necrosis Factor-α, Releasing Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 and Migrating in Vitro. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhao, B.; Wu, Q.; Gong, Y.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liang, X.; Zhang, Q. Gastrodin Alleviates Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy by Regulating Energy Homeostasis via Activating AMPK and Inhibiting MMP9. Phytomedicine 2024, 135, 156033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Maggi, L.; Scianni, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Giustetto, M.; Ferreira, T.A.; Guiducci, E.; Dumas, L.; et al. Synaptic Pruning by Microglia Is Necessary for Normal Brain Development. Science 2011, 333, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, S.; Anderzhanova, E.A.; Bajaj, T.; Wiechmann, S.; Dethloff, F.; Weckmann, K.; Heinz, D.E.; Ebert, T.; Hartmann, J.; Geiger, T.M.; et al. Stress-Primed Secretory Autophagy Promotes Extracellular BDNF Maturation by Enhancing MMP9 Secretion. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Kim, J.; Williams, R.; Sandhir, R.; Gregory, E.; Brooks, W.M.; Berman, N.E.J. Effects of Aging on Blood Brain Barrier and Matrix Metalloproteases Following Controlled Cortical Impact in Mice. Exp. Neurol. 2012, 234, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aid, S.; Silva, A.C.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Choi, S.H.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Bosetti, F. Cyclooxygenase-1 and -2 Differentially Modulate Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption through Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wu, C.; Korpos, E.; Zhang, X.; Agrawal, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Faber, C.; Schäfers, M.; Körner, H.; Opdenakker, G.; et al. Focal MMP-2 and MMP-9 Activity at the Blood-Brain Barrier Promotes Chemokine-Induced Leukocyte Migration. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 1040–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerwien, H.; Hermann, S.; Zhang, X.; Korpos, E.; Song, J.; Kopka, K.; Faust, A.; Wenning, C.; Gross, C.C.; Honold, L.; et al. Imaging Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity in Multiple Sclerosis as a Specific Marker of Leukocyte Penetration of the Blood-Brain Barrier. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 364ra152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Duinkerken, E.; Moreno, A.B.; Eto, F.N.; Lotufo, P.; Barreto, S.M.; Giatti, L.; Viana, M.C.; Nunes, M.A.; Chor, D.; Griep, R.H. Biopsychosocial Factors Associated with a Current Depressive Episode in Diabetes: The ELSA-Brasil Study. Diabet. Med. J. Br. Diabet. Assoc. 2020, 37, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanelli, G.; Raschi, E.; Hafez, G.; Matura, S.; Schiweck, C.; Poluzzi, E.; Lunghi, C. The Interface of Depression and Diabetes: Treatment Considerations. Transl. Psychiatry 2025, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamura-Inoue, T.; He, H. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Their Advantages and Potential Clinical Utility. World J. Stem Cells 2014, 6, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeinhom, A.; Fadallah, S.A.; Mahmoud, M. Human Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cell Based-Therapy in Diabetes Mellitus: Experimental and Clinical Perspectives. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Chen, Z.; Lai, X.; Yin, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, L. Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived HIF-1α-Overexpressed Extracellular Vesicles Ameliorate Hypoxia-Induced Pancreatic β Cell Apoptosis and Senescence through Activating YTHDF1-Mediated Protective Autophagy. Bioorganic Chem. 2022, 129, 106194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monfrini, M.; Donzelli, E.; Rodriguez-Menendez, V.; Ballarini, E.; Carozzi, V.A.; Chiorazzi, A.; Meregalli, C.; Canta, A.; Oggioni, N.; Crippa, L.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for the Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 288, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Yang, L. Therapeutic Potential: The Role of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Diverse Sources and Their Derived Exosomes in Diabetic Nephropathy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 175, 116672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Huang, W.; Yi, J.; Deng, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Shi, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, T.; Chen, X.; et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Alleviate Depressive and Anxiety-like Behaviors via a Lung Vagal-to-Brain Axis in Male Mice. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, S.; Jiang, L.; Yao, L.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, S.; Hong, M.; Zheng, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Depressive Disorder via Inhibiting the Inflammatory Polarization of Microglia. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2024, 179, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Liu, D.; Guo, Z.; Han, P.; Ma, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, R.; He, J. Physicochemical Properties, Structural Characterization, and Antidiabetic Activity of Selenylated Low Molecular Weight Apple Pectin in HFD/STZ-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Mice. Carbohydr. Polym. 2025, 348, 122790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S.; Aghajanian, G.K.; Sanacora, G.; Krystal, J.H. Synaptic Plasticity and Depression: New Insights from Stress and Rapid-Acting Antidepressants. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 238–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tao, W. Current Perspectives on Microglia-Neuron Communication in the Central Nervous System: Direct and Indirect Modes of Interaction. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 66, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-E.; Kim, M.; Kim, S.; Lee, R.; Ujihara, Y.; Marquez-Wilkins, E.M.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Yang, E.; Kim, H.; Lee, C.; et al. Endothelial SHANK3 Regulates Tight Junctions in the Neonatal Mouse Blood-Brain Barrier through β-Catenin Signaling. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Chen, Z.-X.; Cen, J.; Shen, H.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Chen, S. MMP-2 and MMP-9 Secreted by Leukemic Cells Increase the Permeability of Blood-Brain Barrier by Disrupting Tight Junction Proteins in Central Nervous System Leukemia. Blood 2010, 116, 2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, I. The Blood–Brain Barrier in Systemic Infection and Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 2489–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandjinou, M.; Sheehy, O.; Bérard, A. Antidepressant Use during Pregnancy and the Risk of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Nested Case-Control Study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; An, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wan, X.; Zhao, X.; Yang, X.; Tian, J.; Song, X. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Diabetes-Exacerbated Atherosclerosis via AMPK/mTOR Pathway-Mediated Autophagy-Related Macrophage Polarization. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2025, 24, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almutairi, M.M.A.; Gong, C.; Xu, Y.G.; Chang, Y.; Shi, H. Factors Controlling Permeability of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 57–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, C.; Pfau, M.L.; Hodes, G.E.; Kana, V.; Wang, V.X.; Bouchard, S.; Takahashi, A.; Flanigan, M.E.; Aleyasin, H.; LeClair, K.B.; et al. Social Stress Induces Neurovascular Pathology Promoting Depression. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1752–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zenaro, E.; Piacentino, G.; Constantin, G. The Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2017, 107, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, V.E.; Weber, M.T.; Xiao, R.; Cullen, D.K.; Meaney, D.F.; Stewart, W.; Smith, D.H. Mechanical Disruption of the Blood–Brain Barrier Following Experimental Concussion. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 135, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Han, L.; Wang, Y.; Deng, D.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, L.; Chen, X. Prolonged Anesthesia Induces Neuroinflammation and Complement-Mediated Microglial Synaptic Elimination Involved in Neurocognitive Dysfunction and Anxiety-like Behaviors. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rexrode, L.E.; Hartley, J.; Showmaker, K.C.; Challagundla, L.; Vandewege, M.W.; Martin, B.E.; Blair, E.; Bollavarapu, R.; Antonyraj, R.B.; Hilton, K.; et al. Molecular Profiling of the Hippocampus of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 1968–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Passos, I.C.; Mwangi, B.; Amaral-Silva, H.; Tannous, J.; Wu, M.-J.; Zunta-Soares, G.B.; Soares, J.C. Hippocampal Subfield Volumes in Mood Disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavalali, E.T.; Monteggia, L.M. Targeting Homeostatic Synaptic Plasticity for Treatment of Mood Disorders. Neuron 2020, 106, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Wu, Y.; Du, F.; Shi, S.; Duan, Y.; Chen, A.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Single-Cell Raman Spectroscopy as a Vovel Platform for Unveiling the Heterogeneity of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Talanta 2025, 292, 127933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Na, T.; Zhang, K.; Yang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wei, L.; Xu, L.; Yan, X.; Liu, W.; Liu, G.; et al. GMP-Grade Microcarrier and Automated Closed Industrial Scale Cell Production Platform for Culture of MSCs. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2022, 16, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, L.; Tao, Q.; Wu, Y.; Wang, N.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Shi, A.; Zhou, X.; Yu, S.; et al. Synthesis of SPIO Nanoparticles and the Subsequent Applications in Stem Cell Labeling for Parkinson’s Disease. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ji, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Peng, H.; Wang, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, J. The Different Molecular Code in Generation of Dopaminergic Neurons from Astrocytes and Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, W.; Riopel, M.; Bandyopadhyay, G.; Dong, Y.; Birmingham, A.; Seo, J.B.; Ofrecio, J.M.; Wollam, J.; Hernandez-Carretero, A.; Fu, W.; et al. Adipose Tissue Macrophage-Derived Exosomal miRNAs Can Modulate in Vivo and in Vitro Insulin Sensitivity. Cell 2017, 171, 372–384.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, H.; Liu, J.; Guo, Y.; Mu, Y.; Shen, J.; Cheng, Y.; Fu, X.; Han, W. Infusion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorates Hyperglycemia in Type 2 Diabetic Rats. Diabetes 2012, 61, 1616–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, R.; Pan, J.; Tang, X.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Ma, W. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Ameliorate Depression by Regulating Jmjd3 and Microglia Polarization in Myocardial Infarction Mice. Psychopharmacology 2021, 238, 2973–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraeuter, A.-K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Open Field Test for Measuring Locomotor Activity and Anxiety-like Behavior. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2019, 1916, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, Y.; Niu, Y.; Wan, B.; Lu, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, L. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 Signal Mediates M1-Type Microglia and Accelerates High-Altitude-Induced Forgetting. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1189348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshizaki, K.; Asai, M.; Hara, T. High-Fat Diet Enhances Working Memory in the Y-Maze Test in Male C57BL/6J Mice with Less Anxiety in the Elevated plus Maze Test. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Z.-F.; Zhou, X.-L.; Zhang, X.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.-M.; Guo, Q.-L.; Ji, G.; Wu, G.-F.; Wang, N.-N.; Yang, H.; et al. Beclin-1-Mediated Autophagy May Be Involved in the Elderly Cognitive and Affective Disorders in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice. Transl. Neurodegener. 2016, 5, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Duan, Y.; Ni, P.; Zhang, J.; Yu, S. Cerebral-Organoid-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Oxidative Stress and Promote LMX1A-Dependent Dopaminergic Differentiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Names | Primer Sequences (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| iNOS | forward: TTCACCCAGTTGTGCATCGACCTA |
| reverse: AACTCCAATCTCGGTGCCCATGTA | |
| Arg1 | forward: TTGGCAAGGTGATGGAAGAGACCT |
| reverse: CGAAGCAAGCCAAGGTTAAAGCCA | |
| IL-6 | forward: TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC |
| reverse: TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | |
| IL-1β | forward: GCAACTGTTCCTGAACTCAACT |
| reverse: ATCTTTTGGGGTCCGTCAACT | |
| TNF-α | forward: GCCACCACGCTCTTCTGTCT |
| reverse: TGAGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAAC | |
| β-actin | forward: TGCTGACAGAGGCACCACTGAA |
| reverse: CAGTTGTACGTCCAGAGGCATAG |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, A.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, S.; Du, F.; Peng, H.; Zeng, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Shi, S.; Li, S.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Endothelial Integrity and Alleviate Emotional Impairments in a Diabetic Mouse Model via Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073355
Chen A, Duan Y, Zhou S, Du F, Peng H, Zeng D, Wang J, Wu Y, Shi S, Li S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Endothelial Integrity and Alleviate Emotional Impairments in a Diabetic Mouse Model via Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073355
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Aoying, Yuhan Duan, Shaocong Zhou, Fangzhou Du, Huiyu Peng, Dongao Zeng, Jingwen Wang, Yue Wu, Shuaiguang Shi, Shikai Li, and et al. 2025. "Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Endothelial Integrity and Alleviate Emotional Impairments in a Diabetic Mouse Model via Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073355
APA StyleChen, A., Duan, Y., Zhou, S., Du, F., Peng, H., Zeng, D., Wang, J., Wu, Y., Shi, S., Li, S., Yu, S., & Zhang, J. (2025). Mesenchymal Stem Cells Restore Endothelial Integrity and Alleviate Emotional Impairments in a Diabetic Mouse Model via Inhibition of MMP-9 Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073355







