From Genes to Disease: Reassessing LOXHD1 and AGBL1’s Contribution to Fuchs’ Dystrophy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Design
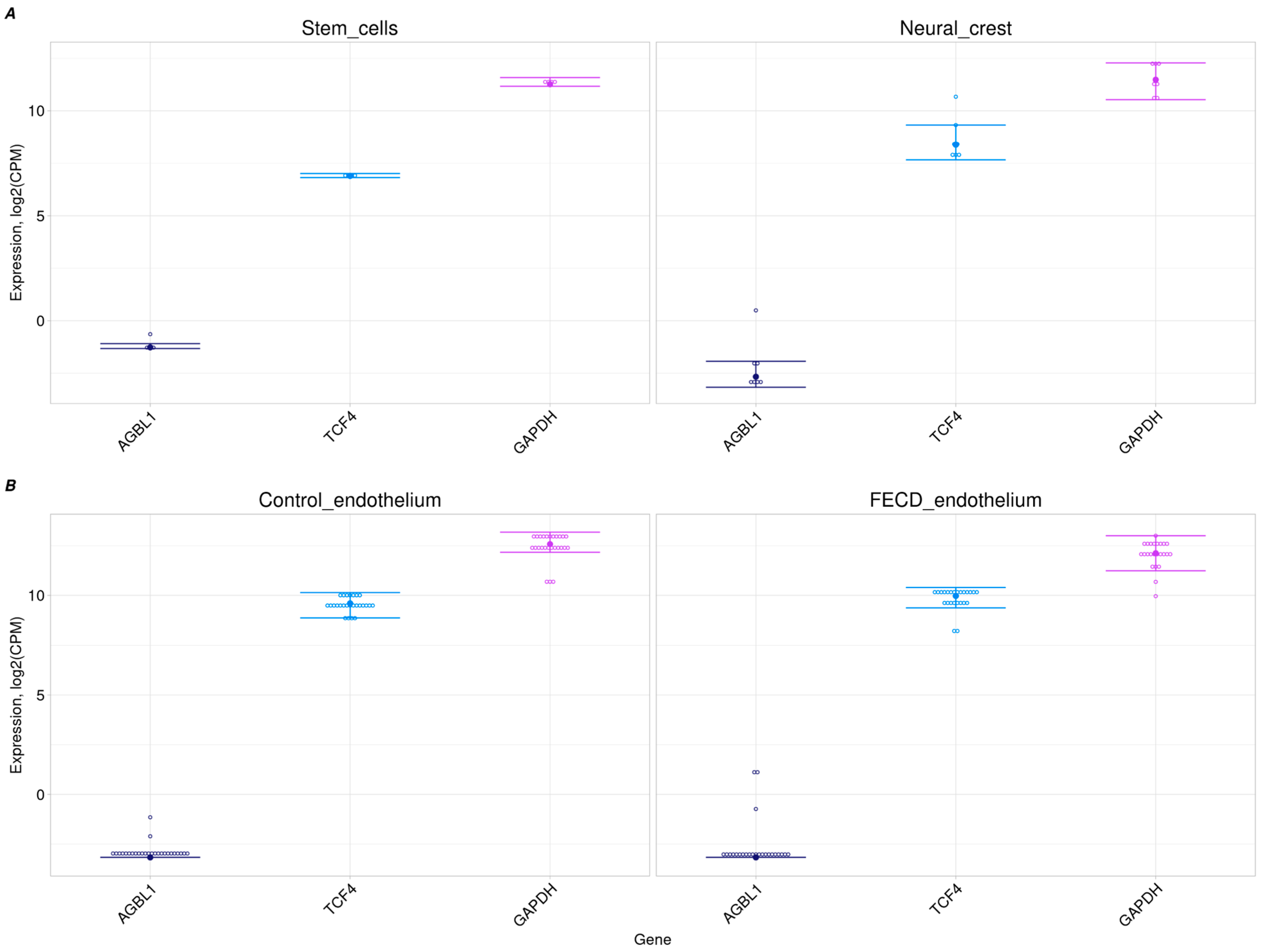
2.2. No AGBL1 Expression in Progenitor Cells and Corneal Endothelium
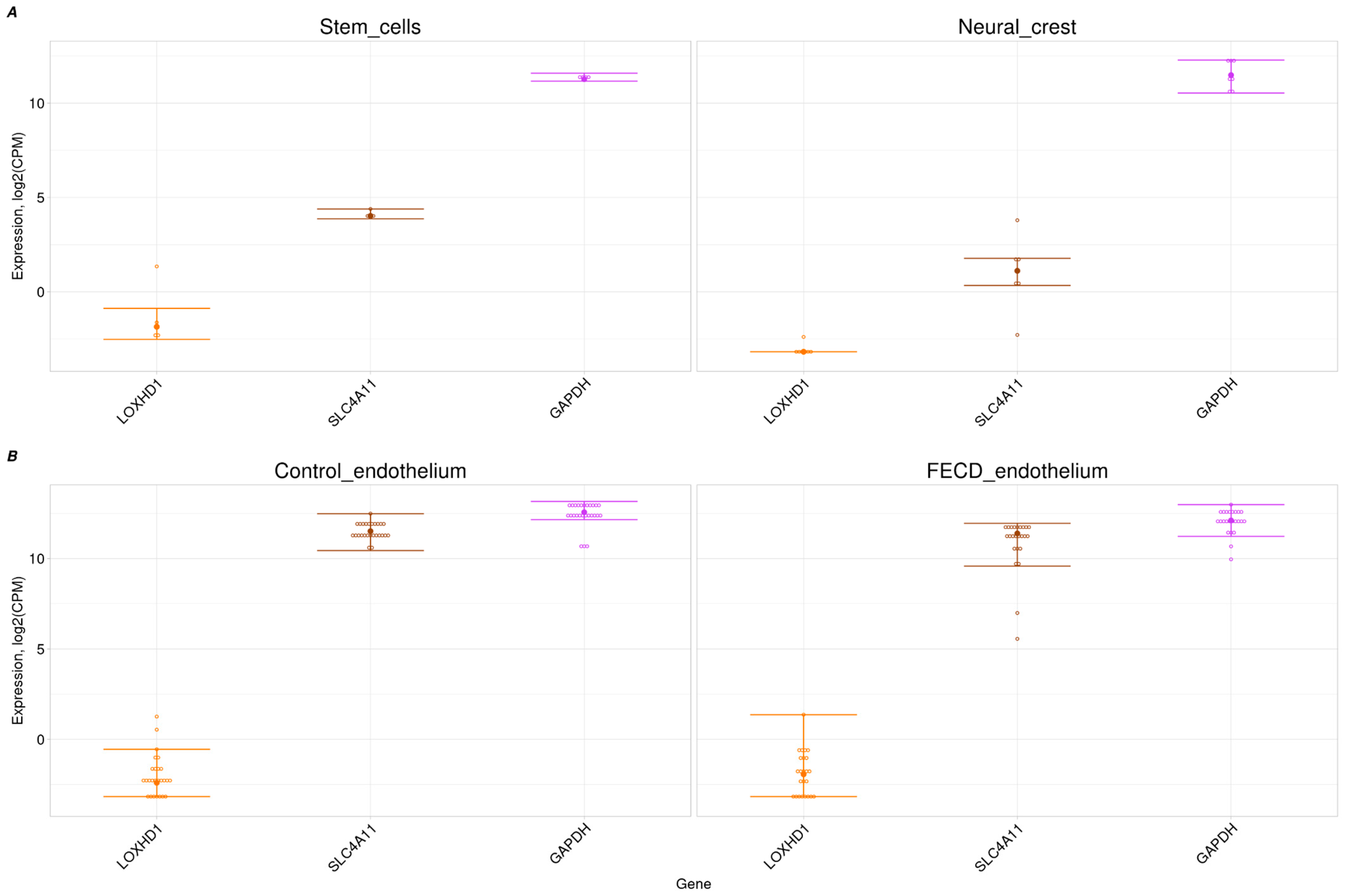
2.3. Trace Expression of LOXHD1 in Corneal Endothelium and Its Progenitors
2.4. Candidate Variants Found Among In-House Cohorts
2.5. No FECD Signs Among AGBL1 Candidate Variant Carriers
2.6. No FECD Signs Among LOXHD1 Candidate Variant Carriers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Datasets for RNA-Seq Analysis
4.2. RNA-Seq Analysis
4.3. List of Candidate Variants in the LOXHD1 and AGBL1 Genes
4.4. Evaluation of the Correlation of the FECD Phenotype with the Carriage of the Candidate Variants
4.4.1. Search Strategy for Carriers of AGBL1 and LOXHD1 Gene Variants
4.4.2. Cohorts for Search for Variant Carriers
4.5. Biological Samples and DNA Extraction
4.6. Genotyping
4.7. Validation of Variants and Analysis of TCF4 Repeat Expansion
4.8. Ophthalmic Examination of Participants
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, S.E.; Bourne, W.M. Fuchs’ Dystrophy. Cornea 1988, 7, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aiello, F.; Gallo Afflitto, G.; Ceccarelli, F.; Cesareo, M.; Nucci, C. Global Prevalence of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy (FECD) in Adult Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 2022, 3091695. [Google Scholar]
- Gottsch, J.D.; Sundin, O.H.; Liu, S.H.; Jun, A.S.; Broman, K.W.; Stark, W.J.; Vito, E.C.; Narang, A.K.; Thompson, J.M.; Magovern, M. Inheritance of a Novel COL8A2 Mutation Defines a Distinct Early-Onset Subtype of Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 1934–1939. [Google Scholar]
- Krachmer, J.H.; Purcell, J.J.; Young, C.W.; Bucher, K.D. Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy: A Study of 64 Families. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1978, 96, 2036–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; McGhee, C.N.; Patel, D.V. The Molecular Basis of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2019, 23, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magovern, M.; Beauchamp, G.R.; McTigue, J.W.; Fine, B.S.; Baumiller, R.C. Inheritance of Fuchs’ Combined Dystrophy. Ophthalmology 1979, 86, 1897–1920. [Google Scholar]
- Gottsch, J.D.; Bowers, A.L.; Margulies, E.H.; Seitzman, G.D.; Kim, S.W.; Saha, S.; Jun, A.S.; Stark, W.J.; Liu, S.H. Serial Analysis of Gene Expression in the Corneal Endothelium of Fuchs’ Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 594–599. [Google Scholar]
- Wieben, E.D.; Aleff, R.A.; Tosakulwong, N.; Butz, M.L.; Highsmith, W.E.; Edwards, A.O.; Baratz, K.H. A Common Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion Within the Transcription Factor 4 (TCF4, E2-2) Gene Predicts Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e49083. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, S.; Munier, F.L.; Yardley, J.; Hart-Holden, N.; Perveen, R.; Cousin, P.; Sutphin, J.E.; Noble, B.; Batterbury, M.; Kielty, C.; et al. Missense Mutations in COL8A2, the Gene Encoding the 2 Chain of Type VIII Collagen, Cause Two Forms of Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2001, 10, 2415–2423. [Google Scholar]
- Riazuddin, S.A.; Zaghloul, N.A.; Al-Saif, A.; Davey, L.; Diplas, B.H.; Meadows, D.N.; Eghrari, A.O.; Minear, M.A.; Li, Y.-J.; Klintworth, G.K.; et al. Missense Mutations in Tcf8 Cause Late-Onset Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy and Interact with FCD4 on Chromosome 9p. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 86, 45–53. [Google Scholar]
- Riazuddin, S.A.; Vasanth, S.; Katsanis, N.; Gottsch, J.D. Mutations in AGBL1 Cause Dominant Late-Onset Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy and Alter Protein-Protein Interaction with TCF4. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 93, 758–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riazuddin, S.A.; Parker, D.S.; McGlumphy, E.J.; Oh, E.C.; Iliff, B.W.; Schmedt, T.; Jurkunas, U.; Schleif, R.; Katsanis, N.; Gottsch, J.D. Mutations in LOXHD1, a Recessive-Deafness Locus, Cause Dominant Late-Onset Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 90, 533–539. [Google Scholar]
- Mootha, V.V.; Gong, X.; Ku, H.-C.; Xing, C. Association and Familial Segregation of CTG18. 1 Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion of TCF4 Gene in Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 33–42. [Google Scholar]
- Okumura, N.; Hayashi, R.; Nakano, M.; Tashiro, K.; Yoshii, K.; Aleff, R.; Butz, M.; Highsmith, E.W.; Wieben, E.D.; Fautsch, M.P.; et al. Association of rs613872 and Trinucleotide Repeat Expansion in the TCF4 Gene of German Patients with Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Cornea 2019, 38, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Skorodumova, L.O.; Belodedova, A.V.; Antonova, O.P.; Sharova, E.I.; Akopian, T.A.; Selezneva, O.V.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Malyugin, B.E. CTG18. 1 Expansion Is the Best Classifier of Late-Onset Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy Among 10 Biomarkers in a Cohort from the European Part of Russia. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 4748–4754. [Google Scholar]
- Vithana, E.N.; Morgan, P.E.; Ramprasad, V.; Tan, D.T.; Yong, V.H.; Venkataraman, D.; Venkatraman, A.; Yam, G.H.; Nagasamy, S.; Law, R.W.; et al. SLC4A11 Mutations in Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2008, 17, 656–666. [Google Scholar]
- Riazuddin, S.A.; Vithana, E.N.; Seet, L.-F.; Liu, Y.; Al-Saif, A.; Koh, L.W.; Heng, Y.M.; Aung, T.; Meadows, D.N.; Eghrari, A.O.; et al. Missense Mutations in the Sodium Borate Cotransporter SLC4A11 Cause Late-Onset Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Soumittra, N.; Loganathan, S.K.; Madhavan, D.; Ramprasad, V.L.; Arokiasamy, T.; Sumathi, S.; Karthiyayini, T.; Rachapalli, S.R.; Kumaramanickavel, G.; Casey, J.R.; et al. Biosynthetic and Functional Defects in Newly Identified SLC4A11 Mutants and Absence of COL8A2 Mutations in Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. J. Hum. Genet. 2014, 59, 444–453. [Google Scholar]
- Aldave, A.J.; Yellore, V.S.; Yu, F.; Bourla, N.; Sonmez, B.; Salem, A.K.; Rayner, S.A.; Sampat, K.M.; Krafchak, C.M.; Richards, J.E. Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy Is Associated with TCF8 Gene Mutations and Abdominal Hernia. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2007, 143, 2549–2556. [Google Scholar]
- Krafchak, C.M.; Pawar, H.; Moroi, S.E.; Sugar, A.; Lichter, P.R.; Mackey, D.A.; Mian, S.; Nairus, T.; Elner, V.; Schteingart, M.T.; et al. Mutations in Tcf8 Cause Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy and Ectopic Expression of Col4a3 by Corneal Endothelial Cells. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 77, 694–708. [Google Scholar]
- Liskova, P.; Tuft, S.J.; Gwilliam, R.; Ebenezer, N.D.; Jirsova, K.; Prescott, Q.; Martincova, R.; Pretorius, M.; Sinclair, N.; Boase, D.L.; et al. Novel Mutations in the ZEB1 Gene Identified in Czech and British Patients with Posterior Polymorphous Corneal Dystrophy. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tsedilina, T.R.; Sharova, E.; Iakovets, V.; Skorodumova, L.O. Systematic Review of SLC4A11, ZEB1, LOXHD1, and AGBL1 Variants in the Development of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1153122. [Google Scholar]
- Wieben, E.D.; Aleff, R.A.; Tang, X.; Kalari, K.R.; Maguire, L.J.; Patel, S.V.; Baratz, K.H.; Fautsch, M.P. Gene Expression in the Corneal Endothelium of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy Patients with and Without Expansion of a Trinucleotide Repeat in TCF4. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200005. [Google Scholar]
- Frausto, R.F.; Wang, C.; Aldave, A.J. Transcriptome Analysis of the Human Corneal Endothelium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 7821–7830. [Google Scholar]
- Frausto, R.F.; Le, D.J.; Aldave, A.J. Transcriptomic Analysis of Cultured Corneal Endothelial Cells as a Validation for Their Use in Cell Replacement Therapy. Cell Transplant. 2016, 25, 1159–1176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tone, S.O.; Kocaba, V.; Böhm, M.; Wylegala, A.; White, T.L.; Jurkunas, U.V. Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: The Vicious Cycle of Fuchs’ Pathogenesis. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 80, 100863. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, T.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, P. Genetic Mutations and Molecular Mechanisms of Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Eye Vis. 2021, 8, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Fautsch, M.P.; Wieben, E.D.; Baratz, K.H.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Sadan, A.N.; Hafford-Tear, N.J.; Tuft, S.J.; Davidson, A.E. TCF4-Mediated Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: Insights into a Common Trinucleotide Repeat-Associated Disease. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 81, 100883. [Google Scholar]
- Kannabiran, C.; Chaurasia, S.; Ramappa, M.; Mootha, V.V. Update on the Genetics of Corneal Endothelial Dystrophies. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2022, 70, 2239–2248. [Google Scholar]
- Nikitina, A.S.; Belodedova, A.V.; Malyugin, B.E.; Sharova, E.I.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Larin, A.K.; Veselovsky, V.A.; Antonova, O.P.; Skorodumova, L.O. Dataset on Transcriptome Profiling of Corneal Endothelium from Patients with Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy. Data Brief 2019, 25, 104047. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, Y.; Hu, J.; Liang, H.; Kanchwala, M.; Xing, C.; Beebe, W.; Bowman, C.B.; Gong, X.; Corey, D.R.; Mootha, V.V. Analyzing Pre-Symptomatic Tissue to Gain Insights into the Molecular and Mechanistic Origins of Late-Onset Degenerative Trinucleotide Repeat Disease. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 6740–6758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patel, S.P.; Parker, M.D. SLC4A11 and the Pathophysiology of Congenital Hereditary Endothelial Dystrophy. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 475392. [Google Scholar]
- Rogowski, K.; Van Dijk, J.; Magiera, M.M.; Bosc, C.; Deloulme, J.-C.; Bosson, A.; Peris, L.; Gold, N.D.; Lacroix, B.; Grau, M.B.; et al. A Family of Protein-Deglutamylating Enzymes Associated with Neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 143, 564–578. [Google Scholar]
- Amberger, J.S.; Bocchini, C.A.; Scott, A.F.; Hamosh, A. OMIM. Org: Leveraging Knowledge Across Phenotype–Gene Relationships. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D1038–D1043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grillet, N.; Schwander, M.; Hildebrand, M.S.; Sczaniecka, A.; Kolatkar, A.; Velasco, J.; Webster, J.A.; Kahrizi, K.; Najmabadi, H.; Kimberling, W.J.; et al. Mutations in LOXHD1, an Evolutionarily Conserved Stereociliary Protein, Disrupt Hair Cell Function in Mice and Cause Progressive Hearing Loss in Humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 328–337. [Google Scholar]
- Trouillet, A.; Miller, K.K.; George, S.S.; Wang, P.; Ali, N.E.; Ricci, A.; Grillet, N. LOXHD1 Mutations Cause Mechanotransduction Defects in Cochlear Hair Cells. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 3331–3343. [Google Scholar]
- Wesdorp, M.; Schreur, V.; Beynon, A.J.; Oostrik, J.; van de Kamp, J.M.; Elting, M.W.; van den Boogaard, M.-J.; Feenstra, I.; Admiraal, R.J.; Kunst, H.P.; et al. Further Audiovestibular Characterization of Dfnb77, Caused by Deleterious Variants in LOXHD1, and Investigation into the Involvement of Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy. Clin. Genet. 2018, 94, 221–231. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Scheibinger, M.; Ellwanger, D.C.; Krey, J.F.; Choi, D.; Kelly, R.T.; Heller, S.; Barr-Gillespie, P.G. Single-Cell Proteomics Reveals Changes in Expression During Hair-Cell Development. eLife 2019, 8, e50777. [Google Scholar]
- Chng, Z.; Peh, G.S.; Herath, W.B.; Cheng, T.Y.; Ang, H.-P.; Toh, K.-P.; Robson, P.; Mehta, J.S.; Colman, A. High Throughput Gene Expression Analysis Identifies Reliable Expression Markers of Human Corneal Endothelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67546. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Khan, S.Y.; Kabir, F.; Gottsch, J.D.; Riazuddin, S.A. Comparative Transcriptome Analysis of hESC-and iPSC-Derived Corneal Endothelial Cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2018, 176, 252–257. [Google Scholar]
- Altamirano, F.; Ortiz-Morales, G.; O’Connor-Cordova, M.A.; Sancén-Herrera, J.P.; Zavala, J.; Valdez-Garcia, J.E. Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy: An Updated Review. Int. Ophthalmol. 2024, 44, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howaldt, A.; Clahsen, T.; Mestanoglu, M.; Odenthal, M.; Tahmaz, V.; Cursiefen, C.; Matthaei, M. Pathogenese Der Fuchs’-Endotheldystrophie, Die Fibrilläre Schicht und Individualisierte Therapie. Die Ophthalmol. 2024, 121, 787–795. [Google Scholar]
- Desir, J.; Moya, G.; Reish, O.; Van Regemorter, N.; Deconinck, H.; David, K.L.; Meire, F.M.; Abramowicz, M.J. Borate Transporter SLC4A11 Mutations Cause Both Harboyan Syndrome and Non-Syndromic Corneal Endothelial Dystrophy. J. Med. Genet. 2007, 44, 322–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liskova, P.; Dudakova, L.; Tesar, V.; Bednarova, V.; Kidorova, J.; Jirsova, K.; Davidson, A.E.; Hardcastle, A.J. Detailed Assessment of Renal Function in a Proband with Harboyan Syndrome Caused by a Novel Homozygous SLC4A11 Nonsense Mutation. Ophthalmic Res. 2015, 53, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, B.S.; Ansar, S.; Arokiasamy, T.; Sudhir, R.R.; Umashankar, V.; Rajagopal, R.; Soumittra, N. Analysis of Candidate Genes ZEB1 and LOXHD1 in Late-Onset Fuchs’ Endothelial Corneal Dystrophy in an Indian Cohort. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 443–449. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Wu, D.; Li, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, H.; Hong, J.; Xu, J. Novel Mutations Associated with Various Types of Corneal Dystrophies in a Han Chinese Population. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Fuku, N.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Tanaka, M.; Miyachi, M.; Murakami, H.; Mitchell, B.D.; Morrison, E.; Ahmetov, I.; Generozov, E.; et al. Multi-phase, multi-ethnic GWAS uncovers putative loci in predisposition to elite sprint and power performance, health and disease. Biol. Sport 2025, 42, 141–159. [Google Scholar]
- Zoega, G.M.; Fujisawa, A.; Sasaki, H.; Kubota, A.; Sasaki, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Jonasson, F. Prevalence and risk factors for cornea guttata in the Reykjavik Eye Study. Ophthalmology 2006, 113, 565–569. [Google Scholar]
- Eghrari, A.O.; McGlumphy, E.J.; Iliff, B.W.; Wang, J.; Emmert, D.; Riazuddin, S.A.; Katsanis, N.; Gottsch, J.D. Prevalence and Severity of Fuchs’ Corneal Dystrophy in Tangier Island. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 153, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, K.; Kojima, M.; Sasaki, H.; Shui, Y.-B.; Chew, S.J.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ono, M.; Morikawa, Y.; Sasaki, K. Prevalence of Primary Cornea Guttata and Morphology of Corneal Endothelium in Aging Japanese and Singaporean Subjects. Ophthalmic Res. 2002, 34, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Higa, A.; Sakai, H.; Sawaguchi, S.; Iwase, A.; Tomidokoro, A.; Amano, S.; Araie, M. Prevalence of and Risk Factors for Cornea Guttata in a Population-Based Study in a Southwestern Island of Japan: The Kumejima Study. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2011, 129, 332. [Google Scholar]
- Lorenzetti, D.; Uotila, M.; Parikh, N.; Kaufman, H. Central Cornea Guttata: Incidence in the General Population. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1967, 64, 1155–1158. [Google Scholar]
- Goar, E.L. Dystrophy of the Corneal Endothelium (Cornea Guttata), with Report of a Histologic Examination. Trans. Am. Ophthalmol. Soc. 1933, 31, 48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Afshari, N.A.; Igo, R.P., Jr.; Morris, N.J.; Stambolian, D.; Sharma, S.; Pulagam, V.L.; Dunn, S.; Stamler, J.F.; Truitt, B.J.; Rimmler, J.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies three novel loci in Fuchs endothelial corneal dystrophy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundin, O.H.; Jun, A.S.; Broman, K.W.; Liu, S.H.; Sheehan, S.E.; Vito, E.C.; Stark, W.J.; Gottsch, J.D. Linkage of late-onset Fuchs corneal dystrophy to a novel locus at 13pTel-13q12. 13. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Riazuddin, A.S.; Eghrari, A.O.; Al-Saif, A.; Davey, L.; Meadows, D.N.; Katsanis, N.; Gottsch, J.D. Linkage of a mild late-onset phenotype of Fuchs corneal dystrophy to a novel locus at 5q33.1–q35.2. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 5667–5671. [Google Scholar]
- Stebbins, M.J.; Gastfriend, B.D.; Canfield, S.G.; Lee, M.-S.; Richards, D.; Faubion, M.G.; Li, W.-J.; Daneman, R.; Palecek, S.P.; Shusta, E.V. Human Pluripotent Stem Cell–Derived Brain Pericyte–Like Cells Induce Blood-Brain Barrier Properties. Sci. Adv. 2019, 5, eaau7375. [Google Scholar]
- Saeki, T.; Yoshimatsu, S.; Ishikawa, M.; Hon, C.-C.; Koya, I.; Shibata, S.; Hosoya, M.; Saegusa, C.; Ogawa, K.; Shin, J.W.; et al. Critical Roles of FGF, RA, and WNT Signalling in the Development of the Human Otic Placode and Subsequent Lineages in a Dish. Regen. Ther. 2022, 20, 165–186. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, M.E.; McClendon, J.; Long, H.K.; Sorayya, A.; Van Nostrand, J.L.; Wysocka, J.; Attardi, L.D. The Spatiotemporal Pattern and Intensity of P53 Activation During Embryogenesis Dictates Phenotypic Diversity in P53-Driven Developmental Syndromes. Dev. Cell 2019, 50, 212. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, M.A.; Zhang, S.; Sengupta, S.; Ma, H.; Bell, G.W.; Horton, B.; Sharma, B.; George, R.E.; Spranger, S.; Jaenisch, R. Formation of Human Neuroblastoma in Mouse-Human Neural Crest Chimeras. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 579–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 11 January 2022).
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize Analysis Results for Multiple Tools and Samples in a Single Report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt Removes Adapter Sequences from High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. EMBnet. J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patro, R.; Duggal, G.; Love, M.I.; Irizarry, R.A.; Kingsford, C. Salmon Provides Fast and Bias-Aware Quantification of Transcript Expression. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 417–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: A Bioconductor Package for Differential Expression Analysis of Digital Gene Expression Data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R. 2021. Available online: http://www.rstudio.com/ (accessed on 10 January 2022).
- Wickham, H. ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–189. [Google Scholar]
- Karczewski, K.J.; Francioli, L.C.; Tiao, G.; Cummings, B.B.; Alföldi, J.; Wang, Q.; Collins, R.L.; Laricchia, K.M.; Ganna, A.; Birnbaum, D.P.; et al. The Mutational Constraint Spectrum Quantified from Variation in 141,456 Humans. Nature 2020, 581, 434–443. [Google Scholar]
- Barbitoff, Y.A.; Khmelkova, D.N.; Pomerantseva, E.A.; Slepchenkov, A.V.; Zubashenko, N.A.; Mironova, I.V.; Kaimonov, V.S.; Polev, D.E.; Tsay, V.V.; Glotov, A.S.; et al. Expanding the Russian Allele Frequency Reference via Cross-Laboratory Data Integration: Insights from 7452 Exome Samples. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2024, 11, nwae326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, P.J.; Wagstaff, J.F.; Fokkema, I.F.; Cutting, G.R.; Rehm, H.L.; Davies, A.C.; den Dunnen, J.T.; Gretton, L.J.; Dalgleish, R. Standardizing Variant Naming in Literature with VariantValidator to Increase Diagnostic Rates. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 2284–2286. [Google Scholar]
- Ilina, E.N. (Research Institute for Systems Biology and Medicine, Moscow, Russia). Collection of control group samples for omics studies. Personal communication, 2016. (Biomedical study). [Google Scholar]
- Semenova, E.A.; Zempo, H.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Kumagai, H.; Larin, A.K.; Sultanov, R.I.; Babalyan, K.A.; Zhelankin, A.V.; Tobina, T.; Shiose, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies CDKN1A as a Novel Locus Associated with Muscle Fiber Composition. Cells 2022, 11, 3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene | dbSNP ID | HGVS Description of Candidate Variants | Allele Frequency in Cohort 1 (n = 50) | Allele Frequency in Cohort 2 (n = 171) | Allele Frequency in gnomAD (v2.1.1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOXHD1 | rs148468627 | NC_000018.10:g.46477695C>T | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.002227 (420/188598) |
| LOXHD1 | rs764897088 | NC_000018.10:g.46483630G>T | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.000006386 (1/156588) |
| LOXHD1 | ND | NC_000018.10:g.46485062C>G | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | ND |
| LOXHD1 | rs201994383 | NC_000018.10:g.46507646G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.0002981 (56/187842) |
| LOXHD1 | rs775871086 | NC_000018.10:g.46509757T>A | 0 (0/100)) | 0 (0/342) | 0.0002582 (49/189802) |
| LOXHD1 | rs200242497 | NC_000018.10:g.46509805C>T | 0 (0/100) | 0.00292 (1/342) | 0.0007381 (140/189686) |
| LOXHD1 | rs372241056 | NC_000018.10:g.46521131A>G | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.0004314 (81/187742) |
| LOXHD1 | rs200792636 | NC_000018.10:g.46541815G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.0002001 (36/189872) |
| LOXHD1 | rs564297037 | NC_000018.10:g.46566335G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.00005664 (9/158890) |
| LOXHD1 | rs376539851 | NC_000018.10:g.46566443G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.0005068 (95/187466) |
| LOXHD1 | rs141932807 | NC_000018.10:g.46577732C>T | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.001258 (238/189162) |
| LOXHD1 | rs540100675 | NC_000018.10:g.46579680G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.00009475 (18/189970) |
| LOXHD1 | rs113444922 | NC_000018.10:g.46591948G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.00007337 (14/190808) |
| LOXHD1 | rs192376005 | NC_000018.10:g.46592017G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0.00585 (2/342) | 0.002651 (509/192004) |
| LOXHD1 | rs566553343 | NC_000018.10:g.46639658G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.00003192 (6/187960) |
| LOXHD1 | rs2039074525 | NC_000018.10:g.46649158C>T | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | ND |
| LOXHD1 | rs980201296 | NC_000018.10:g.46649241A>C | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.00001269 (2/157626) |
| AGBL1 | rs185919705 | NC_000015.10:g.86674435C>T | 0.01000 (1/100) | 0.00292 (1/342) | 0.001753 (486/277246) |
| AGBL1 | rs377248005 | NC_000015.10:g.86397372G>A | 0 (0/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.0002209 (60/271636) |
| AGBL1 | rs181958589 | NC_000015.10:g.86674322G>C | 0.01000 (1/100) | 0 (0/342) | 0.001130 (312/276112) |
| Participant | Candidate Variant Carriage | Age, Years | Ophthalmic Examination Results | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| proband | carrier | >50 | no FECD | causality rejected |
| >50 | FECD | causality not rejected | ||
| <50 | no FECD | inconclusive | ||
| <50 | FECD | causality not rejected | ||
| first-degree relative | carrier | >50 | no FECD | causality rejected |
| >50 | FECD | causality not rejected | ||
| non carrier | >50 | no FECD | inconclusive | |
| >50 | FECD | inconclusive |
| Participant ID | Relation | Proband ID | Sex | Age | AGBL1 | LOXHD1 | CTG18.1 Genotype (Repeats Number in Each Allele) | Ophthalmic Examination | FECD Diagnosis (Krachmer Grade) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs185919705 | rs181958589 | rs192376005 | rs200242497 | ||||||||
| CTRL_001 | proband | CTRL_001/RF17-173 | male | 51 | T/C (het) | ref hom (14/26) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| CTRL_001.2 | mother | CTRL_001 | female | 80 | T/C (het) | ref hom (11/14) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| CTRL_001.3 | father | CTRL_001 | male | 78 | C/C (ref hom) | ref hom (11/26) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| CTRL_048 | proband | CTRL_048 | female | 48 | C/G (het) | ref hom (11/11) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| CTRL_048.4 | sister | CTRL_048 | female | 50 | C/G (het) | ref hom (11/31) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| RF17-023 | proband | RF17_023 | male | 50 | A/G (het) | ref hom (22/27) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| RF17-063 | proband | RF17_063 | male | 37 | A/G (het) | ref hom (11/14) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| RF17-063.2 | mother | RF17-063 | female | 59 | A/A (ref hom) | ref hom (14/17) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| RF17-063.3 | father | RF17-063 | male | 61 | A/G (het) | ref hom (11/34) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| RF17-172 | proband | RF17_172 | male | 30 | T/C (het) | ref hom (14/15) | no | ND | |||
| RF17-172.2 | mother | RF17_172 | female | 53 | C/C (ref hom) | ref hom (11/15) | yes | no/(0) | |||
| RF17-172.3 | father | RF17_172 | male | 58 | T/C (het) | ref hom (14/24) | yes | no/(0) | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsedilina, T.R.; Sharova, E.I.; Kanygina, A.V.; Malyugin, B.E.; Antonova, O.P.; Belodedova, A.V.; Tkachenko, I.S.; Gelyastanov, A.M.; Zolotarev, A.V.; Klokov, A.V.; et al. From Genes to Disease: Reassessing LOXHD1 and AGBL1’s Contribution to Fuchs’ Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073343
Tsedilina TR, Sharova EI, Kanygina AV, Malyugin BE, Antonova OP, Belodedova AV, Tkachenko IS, Gelyastanov AM, Zolotarev AV, Klokov AV, et al. From Genes to Disease: Reassessing LOXHD1 and AGBL1’s Contribution to Fuchs’ Dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073343
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsedilina, Tatiana Romanovna, Elena Ivanovna Sharova, Alexandra Vasilevna Kanygina, Boris Eduardovich Malyugin, Olga Pavlovna Antonova, Alexandra Vladimirovna Belodedova, Ivan Sergeevich Tkachenko, Aslan Mukhtarovich Gelyastanov, Andrey Vladimirovich Zolotarev, Aleksey Vladimirovich Klokov, and et al. 2025. "From Genes to Disease: Reassessing LOXHD1 and AGBL1’s Contribution to Fuchs’ Dystrophy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073343
APA StyleTsedilina, T. R., Sharova, E. I., Kanygina, A. V., Malyugin, B. E., Antonova, O. P., Belodedova, A. V., Tkachenko, I. S., Gelyastanov, A. M., Zolotarev, A. V., Klokov, A. V., Murashev, A. O., Fedyushkina, I. V., Generozov, E. V., & Skorodumova, L. O. (2025). From Genes to Disease: Reassessing LOXHD1 and AGBL1’s Contribution to Fuchs’ Dystrophy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3343. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073343








