Identification and Characterization of Troponin T Associated with Development, Metabolism and Reproduction in Tribolium castaneum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis
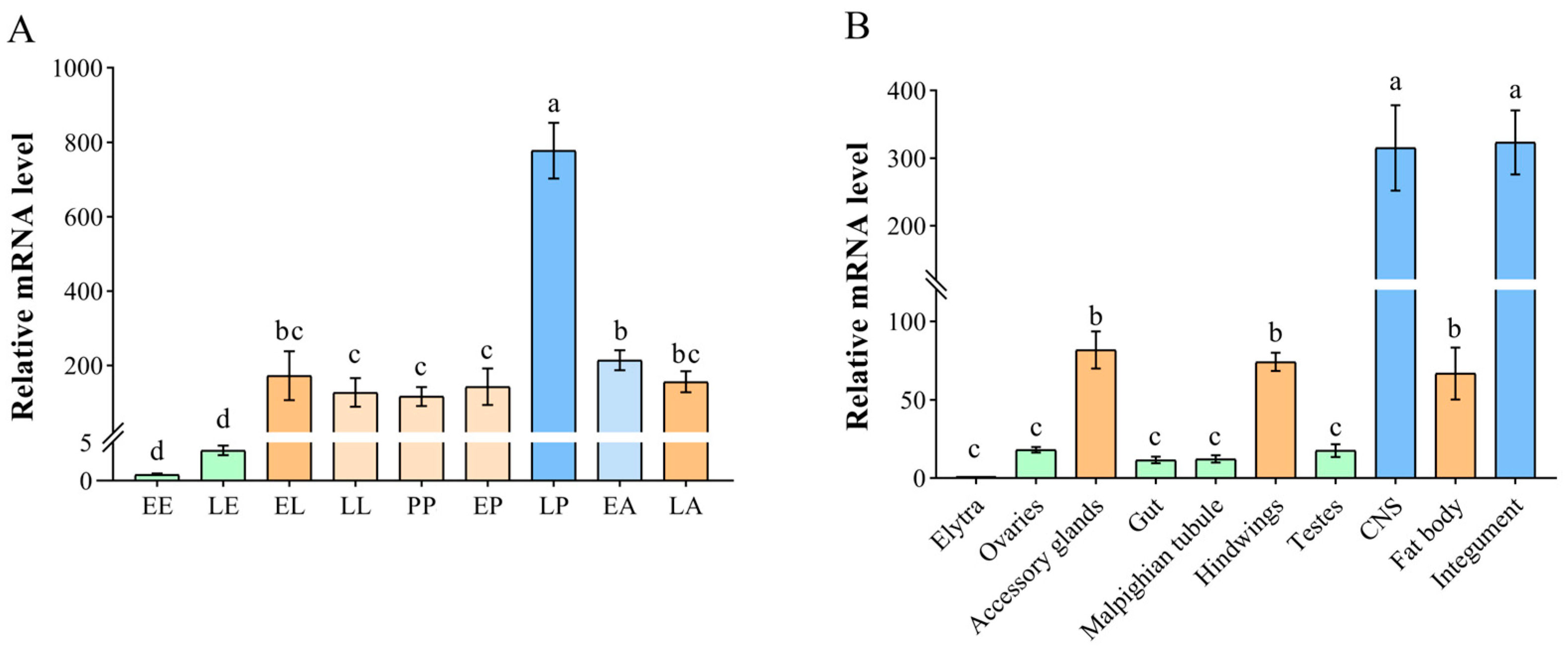
2.2. Temporal and Spatial Expression Patterns of TnT
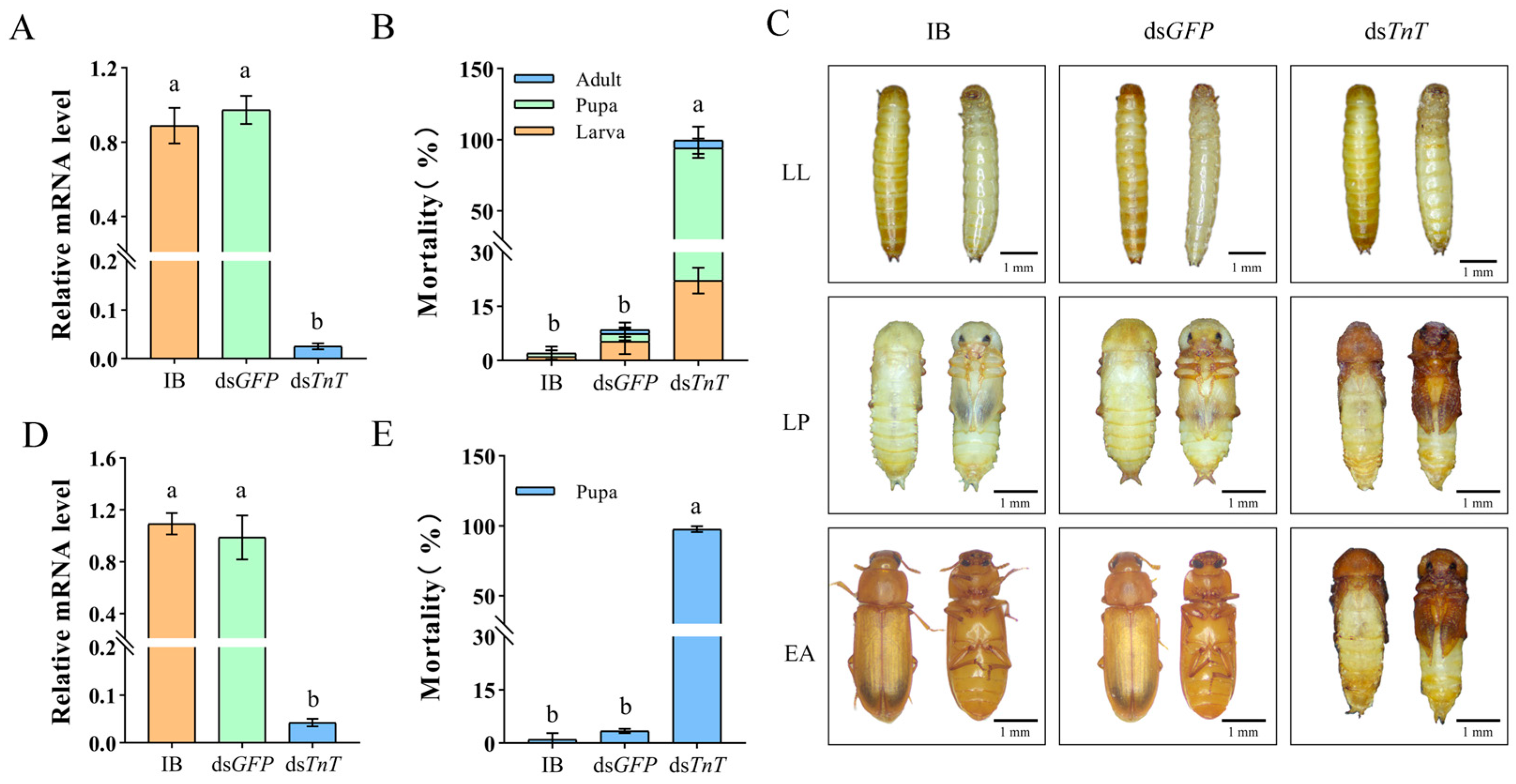
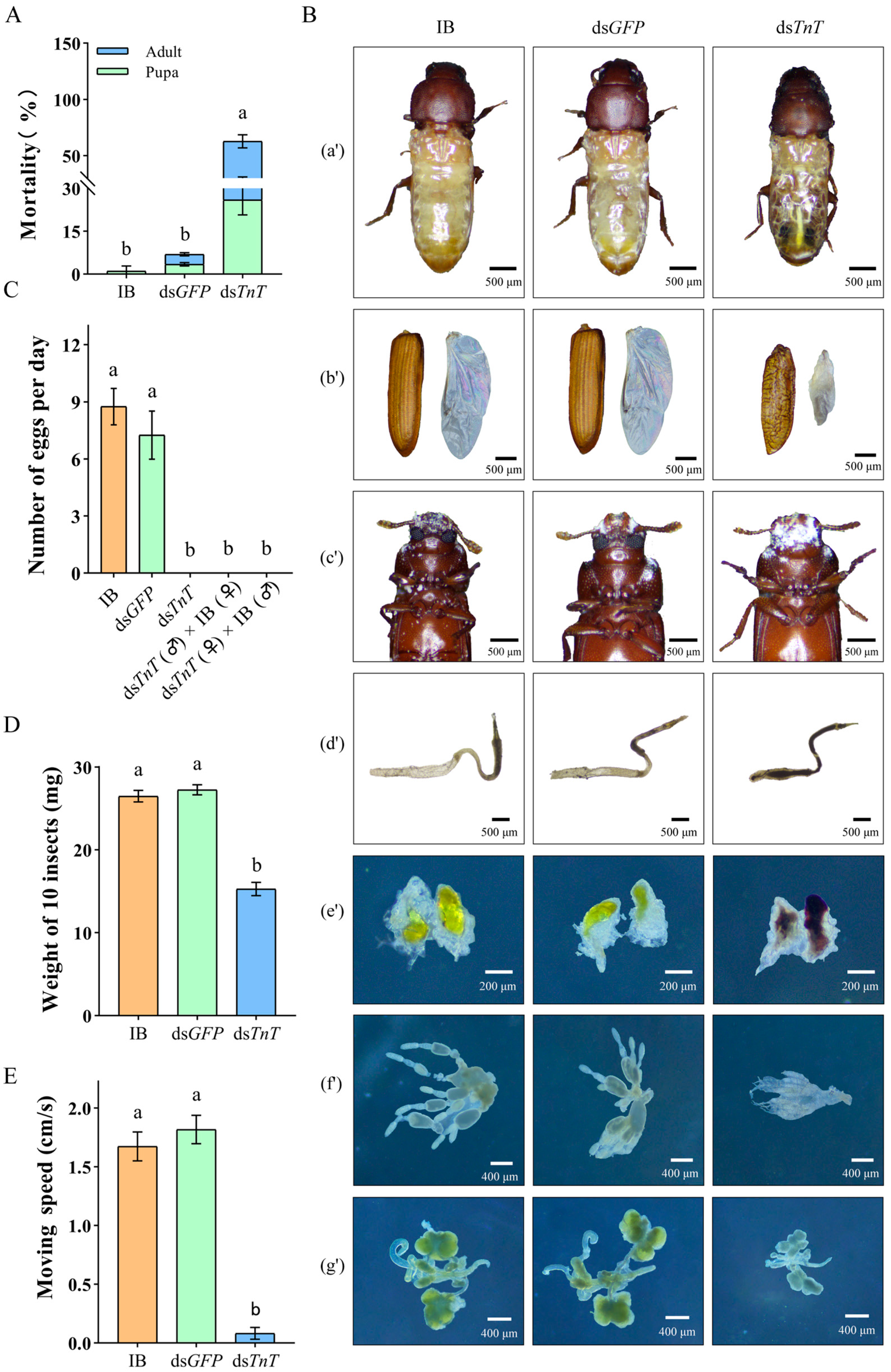
2.3. RNAi Phenotypes of TnT in T. castaneum
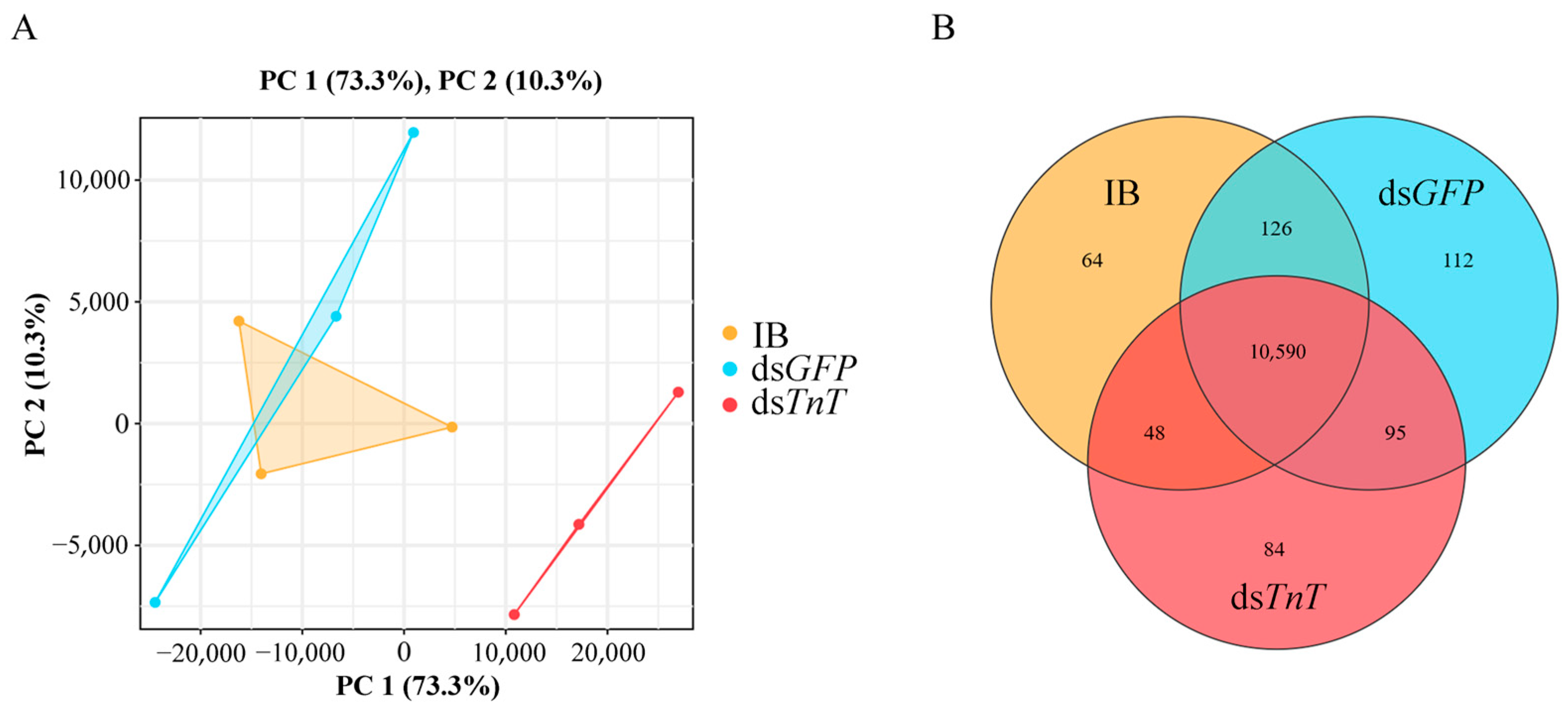
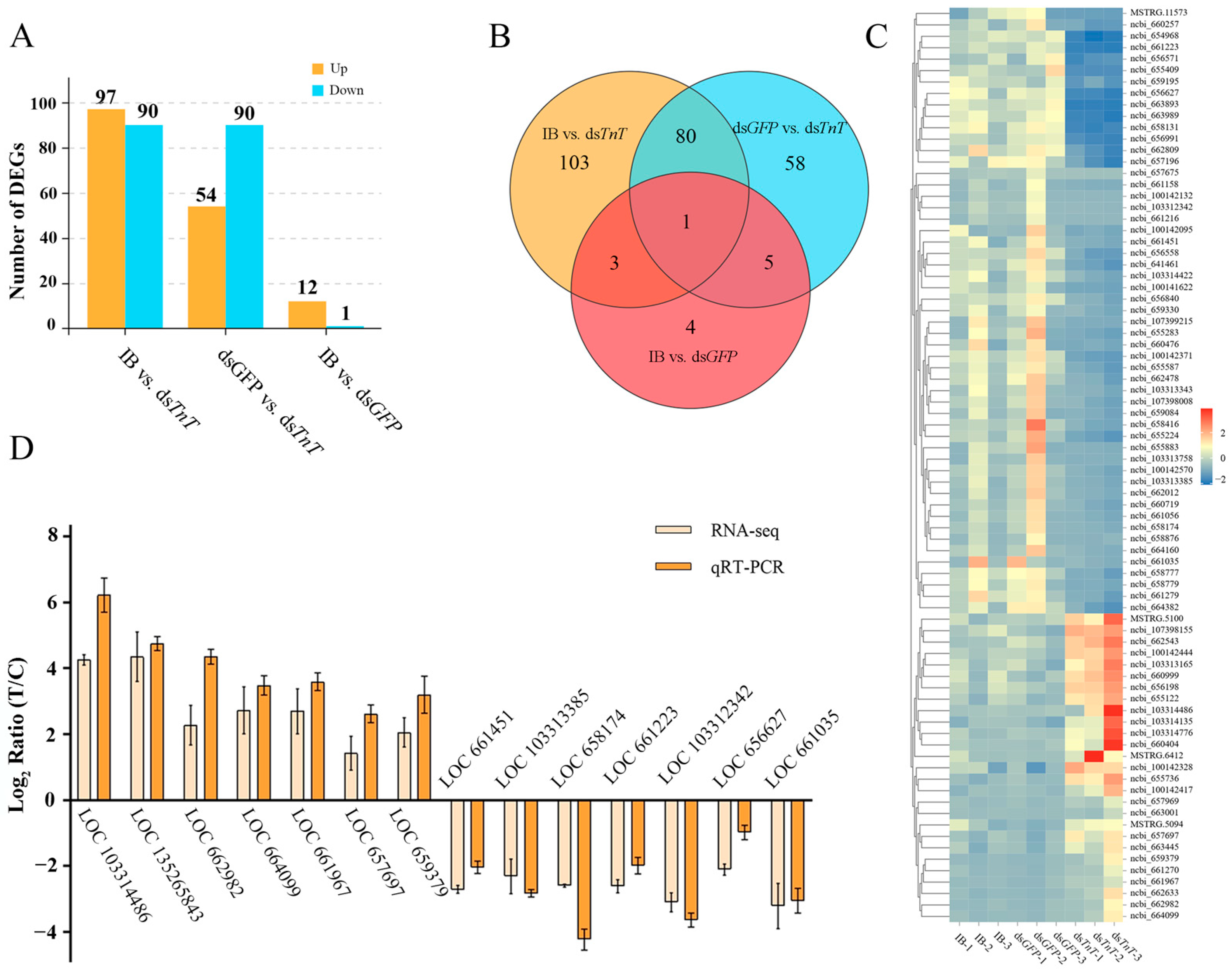
2.4. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
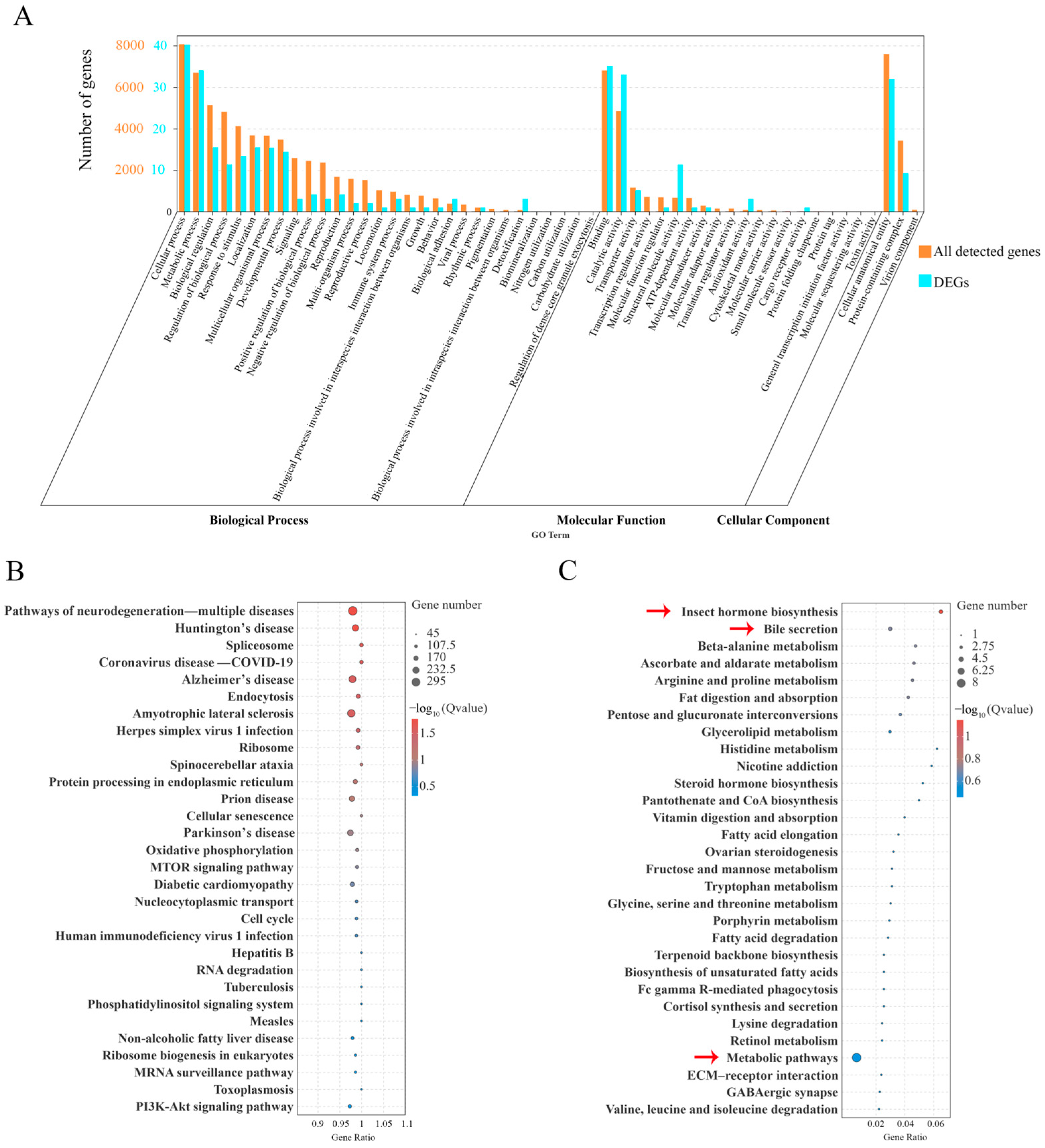
2.5. GO Classification and KEGG Analysis of All Detected Genes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Insects
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.4. RNA Interference (RNAi)
4.5. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
4.6. Bioinformatics and Data Analysis
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barnes, D.E.; Hwang, H.; Ono, K.; Lu, H.; Ono, S. Molecular evolution of troponin I and a role of its N-terminal extension in nematode locomotion. Cytoskeleton 2016, 73, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohtsuki, I. Calcium ion regulation of muscle contraction: The regulatory role of troponin T. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1999, 190, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Bethea, J.P.; Hetzel-Ebben, H.L.; Landim-Vieira, M.; Mayper, R.J.; Williams, R.L.; Kessler, L.E.; Ruiz, A.M.; Gargiulo, K.; Rose, J.S.M.; et al. Mandibular muscle troponin of the Florida carpenter ant Camponotus floridanus: Extending our insights into invertebrate Ca(2+) regulation. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2021, 42, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, T.; Thongam, U.; Jin, J.P. Invertebrate troponin: Insights into the evolution and regulation of striated muscle contraction. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 666, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, T.; Sujkowski, A.; Cobb, T.; Wessells, R.J.; Jin, J.P. The glutamic acid-rich-long C-terminal extension of troponin T has a critical role in insect muscle functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3794–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Jin, J.P. TNNT1, TNNT2, and TNNT3: Isoform genes, regulation, and structure-function relationships. Gene 2016, 582, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.C.; Gaze, D.C.; Collinson, P.O.; Marber, M.S. Cardiac troponins: From myocardial infarction to chronic disease. Cardiovasc. Res. 2017, 113, 1708–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdulhaq, U.N.; Daana, M.; Dor, T.; Fellig, Y.; Eylon, S.; Schuelke, M.; Shaag, A.; Elpeleg, O.; Edvardson, S. Nemaline body myopathy caused by a novel mutation in troponin T1 (TNNT1). Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S.B.; Shah, H.; O’Sullivan, J.; Anderson, B.; Bhaskar, S.; Williams, S.; Al-Sheqaih, N.; Mueed Bidchol, A.; Banka, S.; Newman, W.G.; et al. Exome Sequencing Identifies a Dominant TNNT3 Mutation in a Large Family with Distal Arthrogryposis. Mol. Syndromol. 2014, 5, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, F.; Nakada, K.; Yonemura, I.; Hirabayashi, T.; Miyazaki, J.I. Tissue-specific distribution of breast-muscle-type and leg-muscle-type troponin T isoforms in birds. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1999, 1426, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.Z.; Chen, X.; Hossain, M.M.; Jin, J.P. Toad heart utilizes exclusively slow skeletal muscle troponin T: An evolutionary adaptation with potential functional benefits. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 29753–29764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullard, B.; Pastore, A. Regulating the contraction of insect flight muscle. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2011, 32, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nongthomba, U.; Ansari, M.; Thimmaiya, D.; Stark, M.; Sparrow, J. Aberrant splicing of an alternative exon in the Drosophila troponin-T gene affects flight muscle development. Genetics 2007, 177, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marden, J.H.; Fitzhugh, G.H.; Girgenrath, M.; Wolf, M.R.; Girgenrath, S. Alternative splicing, muscle contraction and intraspecific variation: Associations between troponin T transcripts, Ca(2+) sensitivity and the force and power output of dragonfly flight muscles during oscillatory contraction. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 3457–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Cui, Y.; Lu, H.; Chen, X.; Li, Q.; Ye, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhu, S. Myofilaments promote wing expansion and maintain genitalia morphology in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Insect Mol. Biol. 2023, 32, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilder, R.J.; Stewart, H. Parasitic gut infection in Libellula pulchella causes functional and molecular resemblance of dragonfly flight muscle to skeletal muscle of obese vertebrates. J. Exp. Biol. 2019, 222, jeb188508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marden, J.H.; Fescemyer, H.W.; Saastamoinen, M.; MacFarland, S.P.; Vera, J.C.; Frilander, M.J.; Hanski, I. Weight and nutrition affect pre-mRNA splicing of a muscle gene associated with performance, energetics and life history. J. Exp. Biol. 2008, 211, 3653–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, M.N.; Naqqash, M.N.; Rezk, A.A.; Mehmood, K.; Bakhsh, A.; Elshafie, H.; Al-Khayri, J.M. Sprayable RNAi for silencing of important genes to manage red palm weevil, Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0308613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Liao, Y.; Yang, B.; Wang, G. RNAi-mediated pest control targeting the Troponin I (wupA) gene in sweet potato weevil, Cylas formicarius. Insect Sci. 2024, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishilevich, E.; Bowling, A.J.; Frey, M.L.F.; Wang, P.H.; Lo, W.; Rangasamy, M.; Worden, S.E.; Pence, H.E.; Gandra, P.; Whitlock, S.L.; et al. RNAi targeting of rootworm Troponin I transcripts confers root protection in maize. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2019, 104, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoe, J.; Rascón, A.A., Jr.; Kunz, S.; Miesfeld, R.L. Molecular genetic analysis of midgut serine proteases in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2009, 39, 903–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavener, D.R.; MacIntyre, R.J. Biphasic expression and function of glucose dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 6286–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunieda, T.; Fujiyuki, T.; Kucharski, R.; Foret, S.; Ament, S.A.; Toth, A.L.; Ohashi, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Kamikouchi, A.; Kage, E.; et al. Carbohydrate metabolism genes and pathways in insects: Insights from the honey bee genome. Insect Mol. Biol. 2006, 15, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Wu, Y.; You, L.L.; Xu, B.; Ge, L.Q.; Yang, G.Q.; Wu, J.C. Jinggangmycin-suppressed reproduction in the small brown planthopper (SBPH), Laodelphax striatellus (Fallen), is mediated by glucose dehydrogenase (GDH). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 139, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Shen, Y.H.; Yang, W.J.; Cao, Y.F.; Xiang, Z.H.; Zhang, Z. Expansion of the silkworm GMC oxidoreductase genes is associated with immunity. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, M.A.; Buechler, S.A.; Arnold, R.J.; Sformo, T.; Barnes, B.M.; Duman, J.G. Elucidating the biochemical overwintering adaptations of Larval Cucujus clavipes puniceus, a nonmodel organism, via high throughput proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 4634–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemoine, A.; Mathelin, J.; Braquart-Varnier, C.; Everaerts, C.; Delachambre, J. A functional analysis of ACP-20, an adult-specific cuticular protein gene from the beetle Tenebrio: Role of an intronic sequence in transcriptional activation during the late metamorphic period. Insect Mol. Biol. 2004, 13, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, T.L.; Krchma, L.J.; Ahmad, S.A.; Kramer, K.J. Pupal cuticle proteins of Manduca sexta: Characterization and profiles during sclerotization. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 30, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, J.G.; Nouzova, M.; Navare, A.; Noriega, F.G. NADP+-dependent farnesol dehydrogenase, a corpora allata enzyme involved in juvenile hormone synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21091–21096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Perez, C.; Nouzova, M.; Clifton, M.E.; Garcia, E.M.; LeBlanc, E.; Noriega, F.G. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 converts farnesal into farnesoic acid in the Corpora allata of mosquitoes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 43, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, F.O.; Leyria, J.; Nouzova, M.; Fruttero, L.L.; Noriega, F.G.; Canavoso, L.E. Juvenile hormone mediates lipid storage in the oocytes of Dipetalogaster maxima. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 133, 103499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.X.; Yan, Q.; Liu, T.W.; Wang, J.X.; Zhao, X.F. Lipases are differentially regulated by hormones to maintain free fatty acid homeostasis for insect brain development. BMC Biol. 2024, 22, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera-Pérez, C.; Clifton, M.E.; Noriega, F.G.; Jindra, M. Juvenile Hormone Regulation and Action. In Advances in Invertebrate (Neuro) Endocrinology; Apple Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Nunes, C.; Sucena, É.; Koyama, T. Endocrine regulation of immunity in insects. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 3928–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, U.; Ferber, M.; Hustert, R. Maturation of muscle properties and its hormonal control in an adult insect. J. Exp. Biol. 2001, 204, 3531–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretscher, H.; O’Connor, M.B. The Role of Muscle in Insect Energy Homeostasis. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 580687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Hu, X.X.; Zhai, M.F.; Yu, X.J.; Song, X.W.; Gao, S.S.; Wu, W.; Li, B. Characterization and functional analysis of hsp18.3 gene in the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Insect Sci. 2019, 26, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, B.; Farsad-Akhtar, N.; Mardi, A.; Baghbani, E.; Bornedeli, S.; Asadi, M.; Shanehbandi, D. lncRNA PVT1 silencing inhibits gastric cancer cells’ progression via enhancing chemosensitivity to paclitaxel. Gene 2025, 932, 148900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tungjitwitayakul, J.; Suwannakhon, N.; Tatun, N. The impact of UV-C radiation on the sugar metabolism of the red flour beetle Tribolium castaneum Herbst (Coleoptera; Tenebrionidae). Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2024, 100, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mannino, M.C.; Davyt-Colo, B.; Huarte-Bonnet, C.; Diambra, L.; Pedrini, N. Transcriptomic landscape of the interaction between the entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana and its tolerant host Tribolium castaneum revealed by dual RNA-seq. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, L.L.; Li, W.Z.; Jin, L.; Li, G.Q. Rnai-based functional analysis of bursicon genes related to cuticle pigmentation in a ladybird beetle. J. Insect Physiol. 2024, 158, 104696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhai, Y.; Zheng, H. Deciphering the cellular heterogeneity of the insect brain with single-cell RNA sequencing. Insect Sci. 2024, 31, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene ID | Log2 Ratio (TnT/IB) | Log2 Ratio (TnT/GFP) | Regulation | Protein | Phenotype After RNAi of DEGs in Tribolium castaneum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOC659195 | −1.18 | −1.12 | Down | troponin C | 50.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC641461 | −1.2 | −1.23 | Down | L-ascorbate oxidase-like protein | 100.0% lethality (1) 60.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC658777 | −1.39 | −1.41 | Down | progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 3 | 90.0% lethality (1) |
| LOC664382 | −1.48 | −1.61 | Down | pro-resilin | 60.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC660257 | −1.51 | −1.56 | Down | elongation of very-long-chain fatty acid protein | 100.0% lethality (1) 100.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC655409 | −1.74 | −1.85 | Down | actin, muscle | 100.0% lethality (1) 100.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC657196 | −1.79 | −1.85 | Down | protein lethal (2) essential for life | 50.0% lethality (1) 30.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC658131 | −1.98 | −2.78 | Down | DNA ligase 1 | 30.0% lethality (1); 30.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC656558 | −1.80 | −1.91 | Down | collagen alpha-1(V) chain | 40.0% lethality (1); 40.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC655283 | −2.06 | −1.90 | Down | fatty acyl-CoA reductase wat | 50% lethality (1) |
| LOC658876 | −2.25 | −2.19 | Down | splicing factor 3A subunit 2 | 90.0% lethality (1); 60.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC655587 | −2.30 | −2.44 | Down | peroxidase | 50.0% lethality (1); 30.0% lethality (2); |
| LOC656840 | −2.39 | −2.68 | Down | pupal cuticle protein 20 | 80% lethality (1) |
| LOC661451 | −2.43 | −2.16 | Down | cytochrome P450 CYP314A1 | no/almost no eggs (1) |
| LOC103313385 | −2.48 | −2.58 | Down | general odorant-binding protein 70 | 60.0% lethality (1) 50.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC661279 | −2.63 | −2.12 | Down | aldehyde dehydrogenase family 3 member B1 | 40% lethality (2) |
| LOC661223 | −2.60 | −2.67 | Down | 46 kDa FK506-binding nuclear protein | 60% lethality (2) |
| LOC103312342 | −3.16 | −3.23 | Down | adult-specific cuticular protein ACP-20 | 20.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC660476 | −3.61 | −3.15 | Down | histidine-rich glycoprotein | 50.0% lethality (1); head and thorax and abdomen segment random not present |
| LOC655883 | −3.96 | −4.25 | Down | Osi2 DUF1676 domain-containing protein | 40.0% lethality (1) 40.0% lethality (2) |
| LOC103313758 | −5.36 | −5.11 | Down | cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C | 40.0% lethality (1); irregular larval musculature pattern (1) |
| LOC107399215 | −6.28 | −5.82 | Down | larval cuticle protein A2B-like | 40.0% lethality (2) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Li, M.; Sun, R.; Xie, J. Identification and Characterization of Troponin T Associated with Development, Metabolism and Reproduction in Tribolium castaneum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062786
Li W, Sun Y, Liang Y, Wang Y, Fan Y, Li M, Sun R, Xie J. Identification and Characterization of Troponin T Associated with Development, Metabolism and Reproduction in Tribolium castaneum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062786
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenzhuo, Yaning Sun, Yuanye Liang, Yifan Wang, Yongmei Fan, Mengmeng Li, Ranfeng Sun, and Jia Xie. 2025. "Identification and Characterization of Troponin T Associated with Development, Metabolism and Reproduction in Tribolium castaneum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062786
APA StyleLi, W., Sun, Y., Liang, Y., Wang, Y., Fan, Y., Li, M., Sun, R., & Xie, J. (2025). Identification and Characterization of Troponin T Associated with Development, Metabolism and Reproduction in Tribolium castaneum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2786. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062786






