Quantum-Chemical Prediction of Molecular and Electronic Structure of Carbon-Nitrogen Chemical Compound with Unusual Ratio Atoms: C(N20)
Abstract
1. Introduction

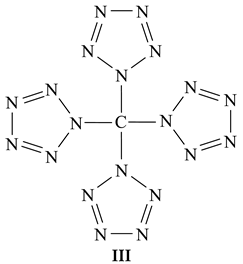
2. Results and Discussion
3. Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ringer, A.L.; Sherrill, C.D.; King, R.A.; Crawford, T.D. Low-lying singlet excited states of isocyanogen. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2008, 106, 1137–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brotherton, T.K.; Lynn, J.W. The Synthesis and Chemistry of Cyanogen. Chem. Revs. 1959, 59, 841–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bircumshaw, L.L.; Tayler, F.M.; Whiffen, D.H. Paracyanogen: Its formation and properties. Part I. J. Chem. Soc. 1954, 931–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, E.C. The Ammono Carbonic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1922, 44, 486–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Cohen, M.L. Prediction of new low compressibility solids. Science 1989, 245, 841–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakov, O.F.; Blinov, L.N.; Arif, M.; Pozdnyakov, A.O.; Filippov, S.N.; Semencha, A.V. Mass spectrometry of carbon nitride C3N4. Tech. Phys. Lett. 2005, 31, 1001–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Blinov, L.N.; Lappalainen, R.; Filippov, S.N. Preparation of powdered carbon nitride C3N4. Glass Phys. Chem. 2004, 30, 573–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.-B.; Lv, Q.; Zhu, H.-S. Carbon nitride prepared by solvothermal method. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 1070–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.R.; Gillan, E.G. From Triazines to Heptazines: Deciphering the Local Structure of Amorphous Nitrogen-Rich Carbon Nitride Materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 7373–7379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansor, N.; Belen Jorge, A.; Corà, F.; Gibbs, C.; Jervis, R.; McMillan, P.F.; Wang, X.; Brett, D.J.L. Graphitic Carbon Nitride Supported Catalysts for Polymer Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 6831–6838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, F.; Callear, S.K.; Carins, G.M.; Irvine, J.T.S. Structural Investigation of Graphitic Carbon Nitride via XRD and Neutron Diffraction. Chem. Mater. 2015, 27, 2612–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsunskii, B.L.; Pepekin, V.I. On the way to carbon nitride. Russ. Chem. Rev. 1997, 66, 901–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, A.; Fischer, A.; Goettmann, F.; Antonietti, M.; Müller, J.-O.; Schlögl, R.; Carlsson, J.M. Graphitic carbon nitride materials: Variation of structure and morphology and their use as metal-free catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 4893–4908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, W.-J.; Tan, L.-L.; Ng, Y.H.; Yong, S.-T.; Chai, S.-P. Graphitic Carbon Nitride (g-C3N4)-Based Photocatalysts for Artificial Photosynthesis and Environmental Remediation: Are We a Step Closer To Achieving Sustainability? Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 7159–7329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, B.; Sun, H.; Wang, S. Engineered Graphitic Carbon Nitride-Based Photocatalysts for Visible-Light-Driven Water Splitting: A Review. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 6504–6526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuber, B.; Hirsch, A. A new route to nitrogen heterofullerenes and the first synthesis of (C69N)2. Chem. Commun. 1996, 1421–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banert, K.; Joo, Y.-H.; Ruffer, T.; Walfort, B.; Lang, H. The Exciting Chemistry of Tetraazidomethane. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1168–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachkov, D.V.; Mikhailov, O.V. A new chemical compound with an unusual ratio of number of carbon and nitrogen atoms–C(N12): Quantum-chemical modelling. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 35974–35981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forquet, V.; Miró Sabaté, C.; Chermette, H.; Jacob, G.; Labarthe, É.; Delalu, H.; Darwich, C. Energetic Properties of Rocket Propellants Evaluated through the Computational Determination of Heats of Formation of Nitrogen-Rich Compounds. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhenain, A.; Darwich, C.; Miró Sabaté, C.; Le, D.-M.; Bougrine, A.-J.; Delalu, H.; Lacôte, E.; Payen, L.; Guitton, J.; Labarthe, E.; et al. (E)-1,1,4,4-Tetramethyl-2-tetrazene (TMTZ): A Prospective Alternative to Hydrazines in Rocket Propulsion. Chem. Eur. J. 2017, 23, 9897–9907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yungman, V.S. (Ed.) Thermal Constants of Substances; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Becke, A.D. Density-functional exchange-energy approximation with correct asymptotic behavior. Phys. Rev. A 1988, 38, 3098–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdew, J.P.; Burke, K.; Wang, Y. Generalized gradient approximation for the exchange-correlation hole of a many-electron system. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 16533–16539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, M.G.; Bushmarinov, I.S.; Sun, J.; Perdew, J.P.; Lyssenko, K.A. Density functional theory is straying from the path toward the exact functional. Science 2017, 355, 49–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chachkov, D.V.; Mikhailov, O.V. Structure of (5656)macrotetracyclic chelates in the ternary systems M(II)-ethanedithioamide-acetone (M = Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu, Zn) according to DFT calculations. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 58, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chachkov, D.V.; Mikhailov, O.V. Quantum-chemical calculation of molecular structures of (5656)macrotetracyclic 3d-metal complexes self-assembled inquaternary systems M(II) ion-ethanedithioamide-formaldehyde-ammonia by the density functional theory method. Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 59, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhailov, O.V.; Chachkov, D.V. DFT Quantum-Chemical Modeling Molecular Structures of Cobalt Macrocyclic Complexes with Porphyrazine or Its Benzo-Derivatives and Two Oxygen Acido Ligands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Truhlar, D.G. The M06 suite of density functionals for main group thermochemistry, thermochemical kinetics, noncovalent interactions, excited states, and transition elements: Two new functionals and systematic testing of four M06-class functionals and 12 other functionals. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2008, 120, 215–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F. Accurate Coulomb-fitting basis sets for H to Rn. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2006, 8, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision A.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, C.; Plesset, M.S. Note on an approximation treatment for many-electron systems. Phys. Rev. 1934, 46, 0618–0622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head-Gordon, M.; Pople, J.A.; Frisch, M.J. MP2 energy evaluation by direct methods. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1988, 153, 503–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pople, J.A.; Seeger, R.; Krishnan, R. Variational Configuration Interaction Methods and Comparison with Perturbation Theory. Int. J. Quant. Chem. 1977, S11, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinhold, F.; Landis, C.R.; Glendening, E.D. What is NBO analysis and how is it useful? Int. Revs. Phys. Chem. 2016, 35, 399–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochterski, J.W. Thermochemistry in Gaussian; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
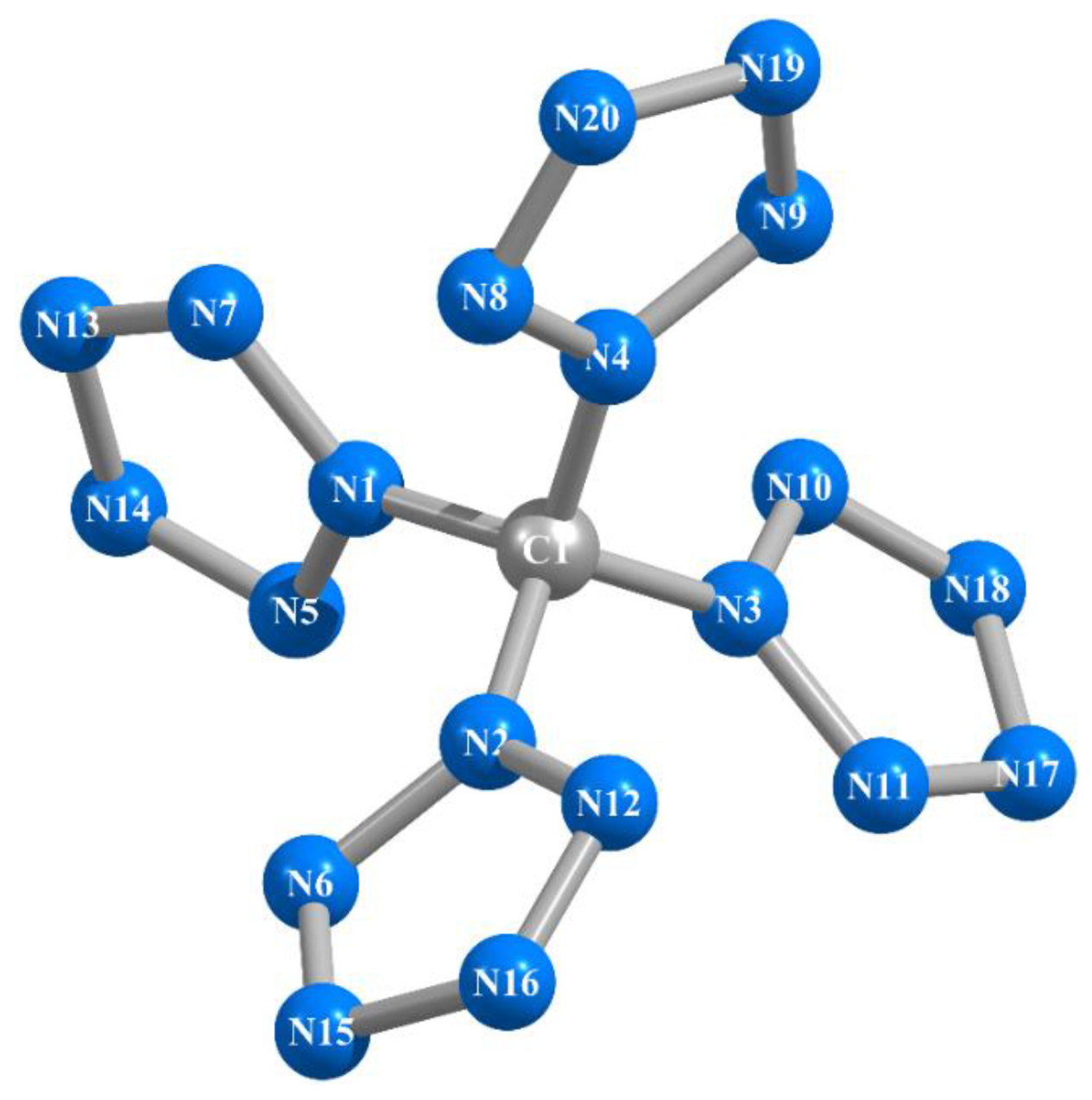
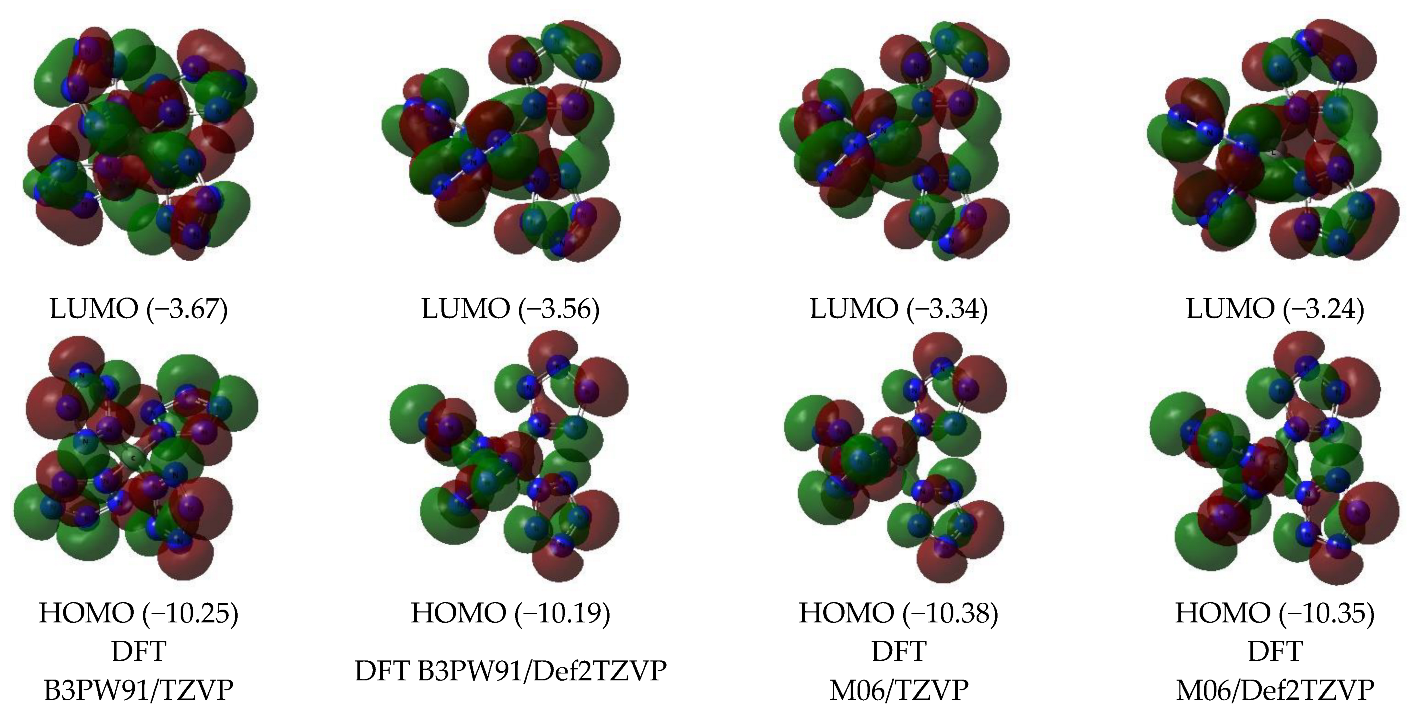
| Structural Parameter | Calculated by | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DFT B3PW91/ TZVP | DFT B3PW91/ Def2TZVP | DFT M06/ TZVP | DFT M06/ Def2TZVP | MP2/ TZVP | MP3/ TZVP | |
| Bond lengths | ||||||
| C–N bond lengths, pm | ||||||
| C1N1 | 144.9 | 145.0 | 144.4 | 144.5 | 144.1 | 144.4 |
| C1N2 | 144.9 | 145.0 | 144.4 | 144.5 | 144.1 | 144.4 |
| C1N3 | 144.9 | 145.0 | 144.4 | 144.5 | 144.1 | 144.4 |
| C1N4 | 144.9 | 145.0 | 144.4 | 144.5 | 144.1 | 144.4 |
| N–N bond lengths, pm | ||||||
| N1N5 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.4 | 132.8 |
| N5N14 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.5 |
| N14N13 | 136.0 | 136.5 | 136.5 | 136.2 | 135.3 | 136.5 |
| N13N7 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.6 |
| N7N1 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.5 | 132.8 |
| N2N6 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.5 | 132.8 |
| N6N15 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.5 |
| N15N16 | 136.0 | 136.5 | 136.5 | 136.2 | 135.3 | 136.5 |
| N16N12 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.6 |
| N12N2 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.4 | 132.8 |
| N3N10 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.4 | 132.8 |
| N10N18 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.5 |
| N18N17 | 136.0 | 136.5 | 136.5 | 136.2 | 135.3 | 136.5 |
| N17N11 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.6 |
| N11N3 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.5 | 132.8 |
| N4N8 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.4 | 132.8 |
| N8N20 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.5 |
| N20N19 | 136.0 | 136.5 | 136.5 | 136.2 | 135.3 | 136.5 |
| N19N9 | 127.5 | 127.5 | 127.0 | 127.0 | 131.2 | 127.6 |
| N9N4 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.1 | 132.7 | 133.5 | 132.8 |
| Bond angles | ||||||
| Bond angles in the 5-numbered ring (N1N5N14N13N7), deg | ||||||
| N1N5N14 | 104.6 | 104.7 | 104.7 | 104.8 | 103.4 | 104.5 |
| N5N14N13 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.3 | 109.2 | 109.6 | 109.3 |
| N14N13N7 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.8 | 109.3 |
| N13N7N1 | 104.5 | 104.6 | 104.6 | 104.8 | 103.3 | 104.5 |
| N7N1N5 | 112.1 | 112.0 | 112.0 | 111.9 | 113.9 | 112.4 |
| Bond angles sum (BAS1), deg | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 |
| Bond angles in the 5-numbered ring (N2N6N15N16N12), deg | ||||||
| N2N6N15 | 104.5 | 104.6 | 104.6 | 104.8 | 103.3 | 104.5 |
| N6N15N16 | 109.5 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.8 | 109.3 |
| N15N16N12 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.3 | 109.2 | 109.6 | 109.3 |
| N16N12N2 | 104.5 | 104.7 | 104.7 | 104.8 | 103.4 | 104.5 |
| N12N2N6 | 112.1 | 112.0 | 112.0 | 111.9 | 113.9 | 112.4 |
| Bond angles sum (BAS2), deg | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 |
| Bond angles in the 5-numbered ring (N3N10N18N17N11), deg | ||||||
| N3N10N18 | 104.6 | 104.7 | 104.7 | 104.8 | 103.4 | 104.5 |
| N10N18N17 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.3 | 109.2 | 109.6 | 109.3 |
| N18N17N11 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.8 | 109.3 |
| N17N11N3 | 104.5 | 104.6 | 104.6 | 104.8 | 103.3 | 104.5 |
| N11N3N10 | 112.1 | 112.0 | 112.0 | 111.9 | 113.9 | 112.4 |
| Bond angles sum (BAS3), deg | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 |
| Bond angles in the 5-numbered ring (N4N8N20N19N9), deg | ||||||
| N4N8N20 | 104.6 | 104.7 | 104.7 | 104.8 | 103.4 | 104.5 |
| N8N20N19 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.3 | 109.2 | 109.6 | 109.3 |
| N20N19N9 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.4 | 109.3 | 109.8 | 109.3 |
| N19N9N4 | 104.5 | 104.6 | 104.6 | 104.8 | 103.3 | 104.5 |
| N9N4N8 | 112.1 | 112.0 | 112.0 | 111.9 | 113.9 | 112.4 |
| Bond angles sum (BAS4), deg | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 | 540.0 |
| (NCN) bond angles between carbon and two nitrogen atoms, deg | ||||||
| N1C1N2 | 110.1 | 110.2 | 110.0 | 110.1 | 110.1 | 108.1 |
| N1C1N3 | 110.1 | 110.2 | 110.0 | 110.1 | 110.1 | 108.1 |
| N1C1N4 | 110.1 | 110.2 | 110.0 | 110.1 | 110.1 | 110.2 |
| N2C1N3 | 110.1 | 110.2 | 110.0 | 110.1 | 110.1 | 110.2 |
| N2C1N4 | 108.2 | 108.0 | 108.3 | 108.2 | 108.2 | 108.1 |
| N3C1N4 | 108.2 | 108.0 | 108.3 | 108.2 | 108.2 | 110.2 |
| Calculation Method | Effective Charge on Atom, in Elementary Charge Units | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | N1, N2, N3, N4 | N5, N8, N10, N12 | N6, N7, N9, N11 | N13, N15, N17, N19 | N14, N16, N18, N20 | |
| B3PW91/TZVP | +0.55 | −0.06 | −0.00 | −0.01 | −0.03 | −0.03 |
| B3PW91/Def2TZVP | +0.56 | −0.06 | −0.00 | −0.01 | −0.03 | −0.03 |
| M06/TZVP | +0.57 | −0.07 | +0.00 | −0.00 | −0.03 | −0.03 |
| M06/Def2TZVP | +0.59 | −0.07 | +0.00 | −0.01 | −0.03 | −0.03 |
| MP2/TZVP | +0.68 | −0.12 | +0.02 | +0.02 | −0.04 | −0.04 |
| MP3/TZVP | +0.68 | −0.13 | +0.02 | +0.02 | −0.04 | −0.04 |
| Calculation Method | ∆fH0, kJ/mol | S0, J/mol∙K | ∆fG0, kJ/mol |
|---|---|---|---|
| B3PW91/TZVP | 2213.5 | 551.5 | 2616.0 |
| G4 | 2052.1 | 559.8 | 2452.2 |
| Calculation Method | Reaction | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1) | (2) | (3) * | (4) * | |||||
| ∆rH0, kJ | ∆rS0, J∙K−1 | ∆rH0, kJ | ∆rS0, J∙K−1 | ∆rH0, kJ | ∆rS0, J∙K−1 | ∆rH0, kJ | ∆rS0, J∙K−1 | |
| B3PW91/ TZVP | −2288.3 | 1347.1 | −1196.4 | 1520.2 | −1913.2 | 1368.0 | −1911.4 | 1364.6 |
| G4 | −2459.0 | 1378.5 | −1344.5 | 1513.0 | −2061.2 | 1360.8 | −2059.4 | 1357.4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikhailov, O.V.; Chachkov, D.V. Quantum-Chemical Prediction of Molecular and Electronic Structure of Carbon-Nitrogen Chemical Compound with Unusual Ratio Atoms: C(N20). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065172
Mikhailov OV, Chachkov DV. Quantum-Chemical Prediction of Molecular and Electronic Structure of Carbon-Nitrogen Chemical Compound with Unusual Ratio Atoms: C(N20). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2023; 24(6):5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065172
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikhailov, Oleg V., and Denis V. Chachkov. 2023. "Quantum-Chemical Prediction of Molecular and Electronic Structure of Carbon-Nitrogen Chemical Compound with Unusual Ratio Atoms: C(N20)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 24, no. 6: 5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065172
APA StyleMikhailov, O. V., & Chachkov, D. V. (2023). Quantum-Chemical Prediction of Molecular and Electronic Structure of Carbon-Nitrogen Chemical Compound with Unusual Ratio Atoms: C(N20). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 24(6), 5172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24065172







