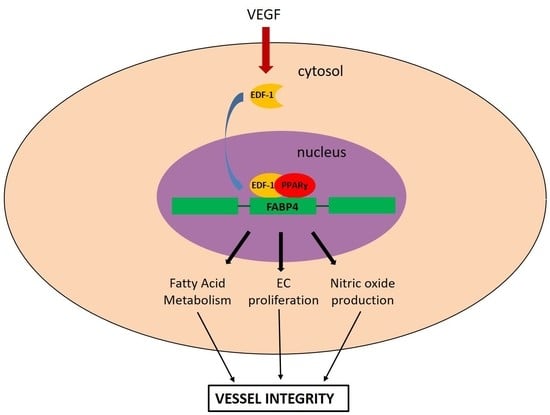
The Contribution of EDF1 to PPARγ Transcriptional Activation in VEGF-Treated Human Endothelial Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
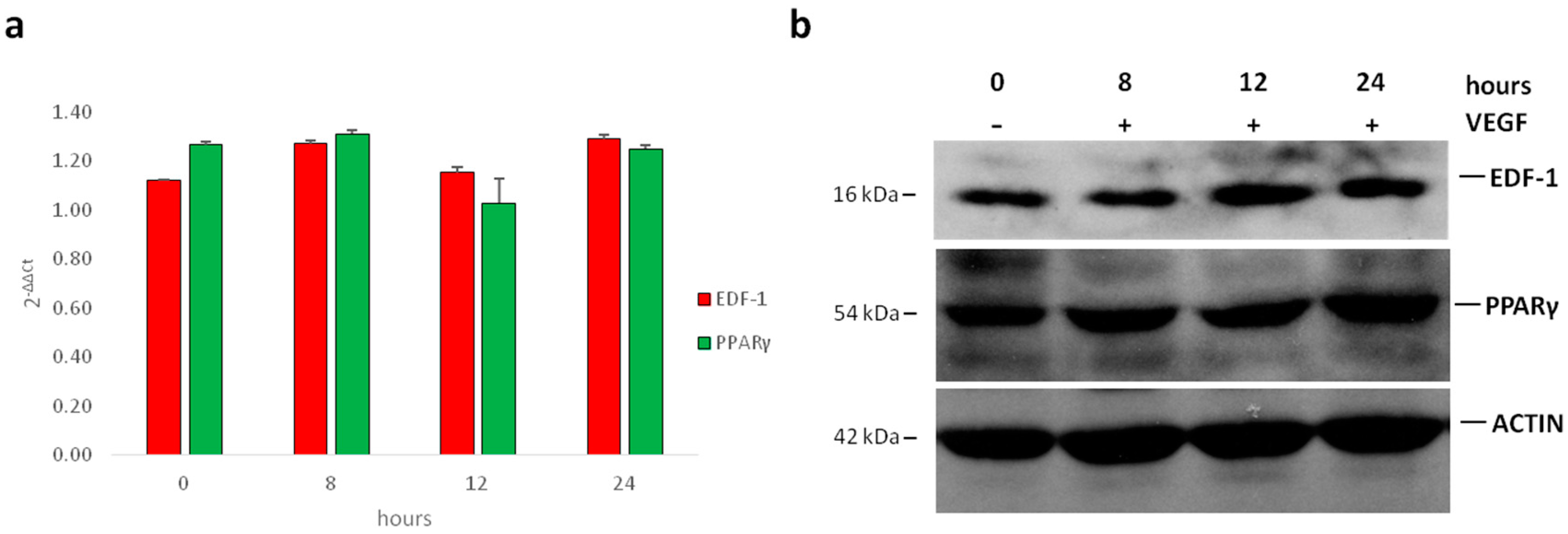
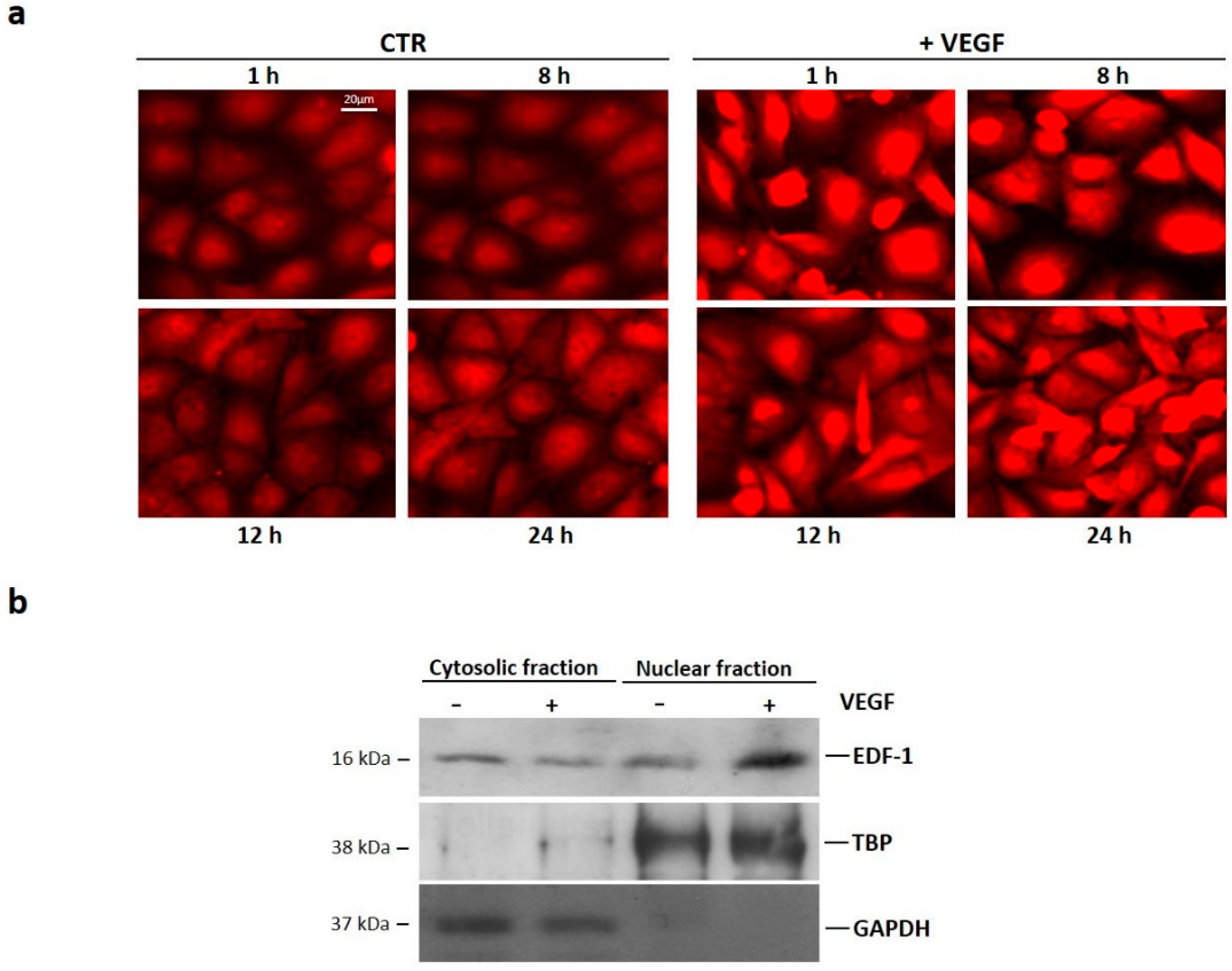
2.1. Translocation of EDF1 to the Nucleus in Response to VEGF
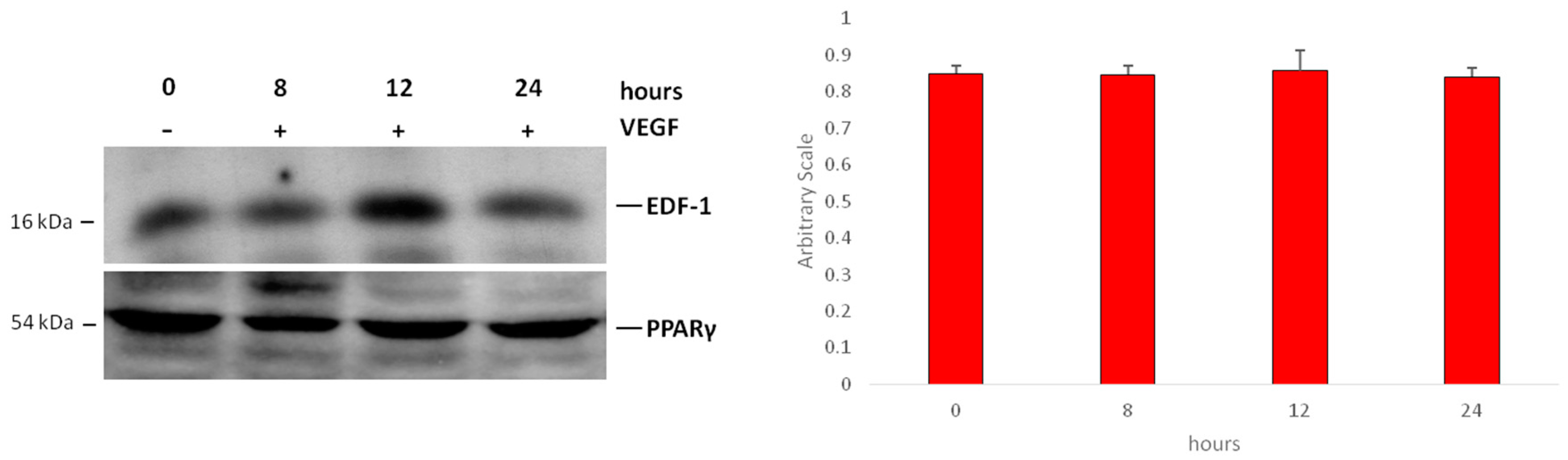
2.2. Interaction between EDF1 and PPARγ in HUVEC
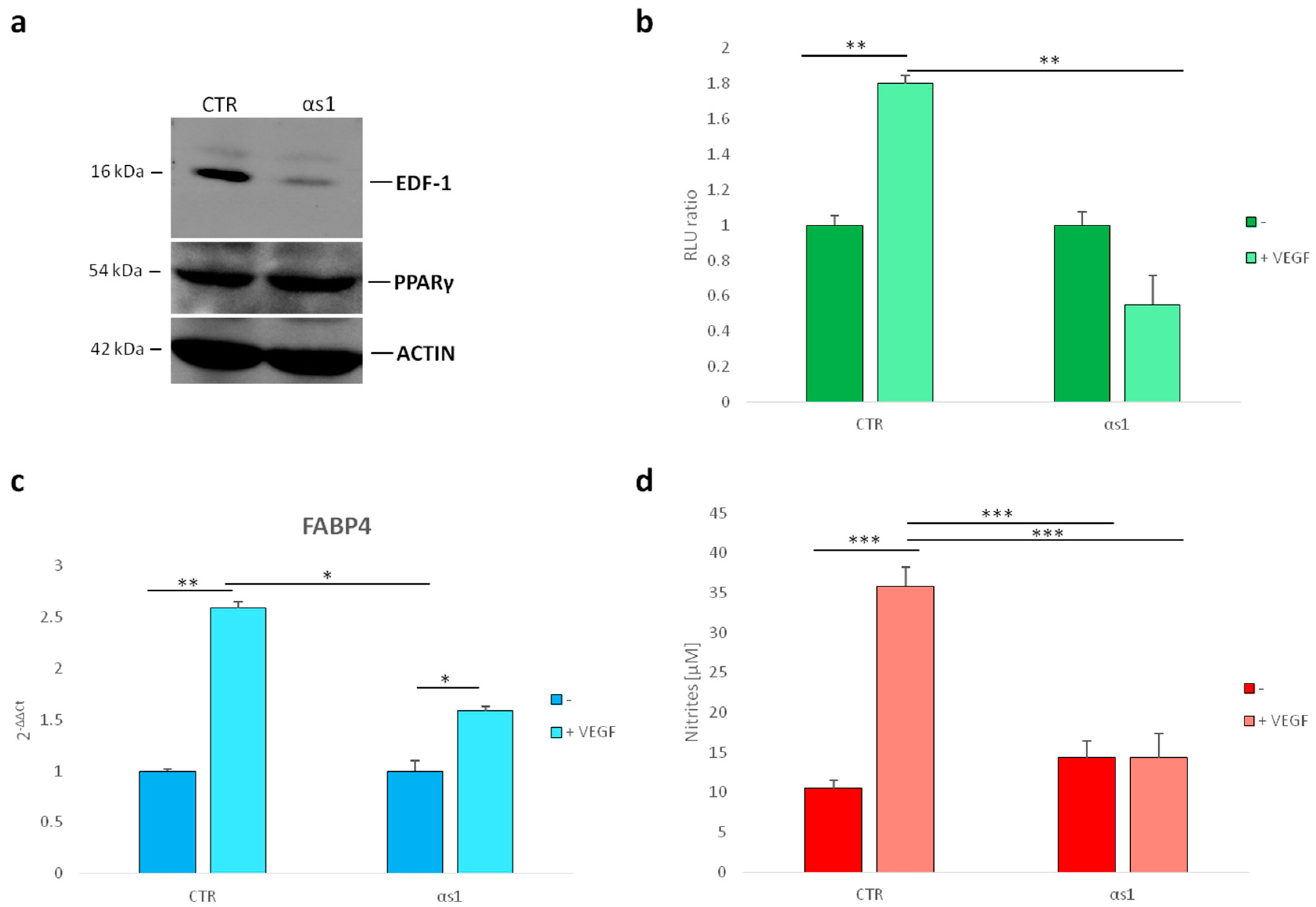
2.3. Effect of Silencing EDF1 in VEGF-Induced PPARγ Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation
4.3. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.4. Reporter Gene Assay
4.5. Real-Time-PCR
4.6. NO Release
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| EDF | Endothelial Differentiation-related factor |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ |
| EC | Endothelial cells |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
References
- Duan, S.Z.; Usher, M.G.; Mortensen, R.M. Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor—Mediated Effects in the Vasculature. Circ. Res. 2008, 102, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, A.; Schwarz, E.J.; Dimaculangan, D.D.; Lazar, M.A. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) γ: Adipose predominant expression and induction early in adipocyte differentiation. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 798–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadian, M.; Suh, J.M.; Hah, N.; Liddle, C.; Atkins, A.R.; Downes, M.; Evans, R.M. PPARgamma signaling and metabolism: The good, the bad and the future. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, T.; Takakuwa, R.; Marchand, S.; Dentz, E.; Bornert, J.M.; Messaddeq, N.; Wendling, O.; Mark, M.; Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W.; et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ is required in mature white and brown adipocytes for their survival in the mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4543–4547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaru, T.; Steger, D.J.; Lefterova, M.I.; Schupp, M.; Lazar, M.A. Adipocyte specific expression of murine resistin is mediated by synergism between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ and CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 6116–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaki, M.; Matsuda, M.; Maeda, N.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Makishima, M.; Shimomura, I. Induction of adiponectin, a fat-derived antidiabetic and antiatherogenic factor, by nuclear receptors. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halabi, C.M.; Beyer, A.M.; de Lange, W.J.; Keen, H.L.; Baumbach, G.L.; Faraci, F.M.; Sigmund, C.D. Interference with PPARγ Function in Smooth Muscle Causes Vascular Dysfunction and Hypertension. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotlinowski, J.; Jozkowicz, A. PPAR Gamma and Angiogenesis: Endothelial Cells Perspective. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, 8492353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinhenz, J.M.; Kleinhenz, D.J.; You, S.; Ritzenthaler, J.D.; Hansen, J.M.; Archer, D.R.; Sutliff, R.L.; Hart, C.M. Disruption of endothelial peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ reduces vascular nitric oxide production. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2009, 297, H1647–H1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Ishibashi, S.; Perrey, S.; Osuga, J.; Gotoda, T.; Kitamine, T.; Tamura, Y.; Okazaki, H.; Yahagi, N.; Iizuka, Y.; et al. Troglitazone inhibits atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-knockout mice: Pleiotropic effects on CD36 expression and HDL. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2001, 21, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charbonnel, B.; Dormandy, J.; Erdmann, E.; Massi-Benedetti, M.; Skene, A.; PROactive Study Group. The prospective pioglitazone clinical trial in macrovascular events (PROactive): Can pioglitazone reduce cardiovascular events in diabetes? Study design and baseline characteristics of 5238 patients. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dougherty, E.J.; Danner, R.L. PPARγ signaling and emerging opportunities for improved therapeutics. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 111, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, M.G.; Lunyak, V.V.; Glass, C.K. Sensors and signals: A coactivator/corepressor/epigenetic code for integrating signal-dependent programs of transcriptional response. Genes Dev. 2005, 20, 1405–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brendel, C.; Gelman, L.; Auwerx, J. Multiprotein bridging factor-1 (MBF-1) is a cofactor for nuclear receptors that regulate lipid metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2002, 16, 1367–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidi, M.; Mariotti, M.; Maier, J.A. Transcriptional coactivator EDF-1 is required for PPARgamma-stimulated adipogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takemaru, K.; Li, F.Q.; Ueda, H.; Hirose, S. Multiprotein bridging factor 1 (MBF1) is an evolutionarily conserved transcriptional coactivator that connects a regulatory factor and TATA element-binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 7251–7256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busk, P.K.; Wulf-Andersen, L.; Strøm, C.C.; Enevoldsen, M.; Thirstrup, K.; Haunsø, S.; Sheikh, S.P. Multiprotein bridging factor 1 cooperates with c-Jun and is necessary for cardiac hypertrophy in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2003, 286, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.X.; Jindra, M.; Ueda, H.; Hiromi, Y.; Hirose, S. Drosophila MBF1 is a co-activator for Tracheae Defective and contributes to the formation of tracheal and nervous systems. Development 2003, 130, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragoni, I.; Mariotti, M.; Consalez, G.G.; Soria, M.R.; Maier, J.A. EDF-1, a novel gene product down-regulated in human endothelial cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31119–31124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, E.; Mariotti, M.; De Benedictis, L.; Maier, J.A. The dual role of endothelial differentiation-related factor-1 in the cytosol and nucleus: Modulation by protein kinase A. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 1069–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bautch, V.L. VEGF-Directed Blood Vessel Patterning: From Cells to Organism. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariotti, M.; De Benedictis, L.; Avon, E.; Maier, J.A.M. Interaction between endothelial differentiation-related factor-1 and calmodulin in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 24047–24051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leidi, M.; Mariotti, M.; Maier, J.A. EDF-1 contributes to the regulation of nitric oxide release in VEGF-treated human endothelial cells. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 89, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castiglioni, S.; Cazzaniga, A.; Maier, J.A. Potential interplay between NFκB and PPARγ in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells cultured in low magnesium. Magnes. Res. 2014, 27, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Shimamoto, K.; Miura, T. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4): Pathophysiological Insights and Potent Clinical Biomarker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2015, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmasri, H.; Ghelfi, E.; Yu, C.W.; Traphagen, S.; Cernadas, M.; Cao, H.; Shi, G.P.; Plutzky, J.; Sahin, M.; Hotamisligil, G.; et al. Endothelial cell-fatty acid binding protein 4 promotes angiogenesis: Role of stem cell factor/c-kit pathway. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magri, C.J.; Gatt, N.; Xuereb, R.G.; Fava, S. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ and the endothelium: Implications in cardiovascular disease. Expert Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2011, 9, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragonès, G.; Saavedra, P.; Heras, M.; Cabré, A.; Girona, J.; Masana, L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 impairs the insulin-dependent nitric oxide pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheibi, S.; Jeddi, S.; Kashfi, K.; Ghasemi, A. Regulation of vascular tone homeostasis by NO and H2S: Implications in hypertension. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 149, 42–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Jo, S.A.; Jo, I. Nitric oxide production and regulation of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by prolonged treatment with troglitazone: Evidence for involvement of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma-dependent and PPARgamma-independent signaling pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2499–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cazzaniga, A.; Locatelli, L.; Castiglioni, S.; Maier, J. The Contribution of EDF1 to PPARγ Transcriptional Activation in VEGF-Treated Human Endothelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071830
Cazzaniga A, Locatelli L, Castiglioni S, Maier J. The Contribution of EDF1 to PPARγ Transcriptional Activation in VEGF-Treated Human Endothelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071830
Chicago/Turabian StyleCazzaniga, Alessandra, Laura Locatelli, Sara Castiglioni, and Jeanette Maier. 2018. "The Contribution of EDF1 to PPARγ Transcriptional Activation in VEGF-Treated Human Endothelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071830
APA StyleCazzaniga, A., Locatelli, L., Castiglioni, S., & Maier, J. (2018). The Contribution of EDF1 to PPARγ Transcriptional Activation in VEGF-Treated Human Endothelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 1830. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071830