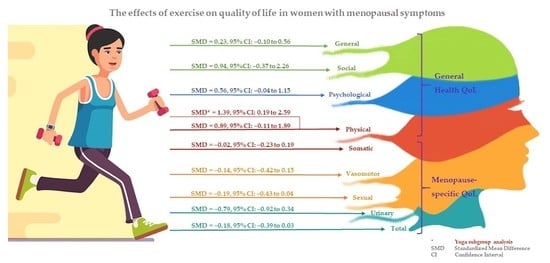
Exercise and Quality of Life in Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Share and Cite
Nguyen, T.M.; Do, T.T.T.; Tran, T.N.; Kim, J.H. Exercise and Quality of Life in Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197049
Nguyen TM, Do TTT, Tran TN, Kim JH. Exercise and Quality of Life in Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(19):7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197049
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Thi Mai, Thi Thanh Toan Do, Tho Nhi Tran, and Jin Hee Kim. 2020. "Exercise and Quality of Life in Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 19: 7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197049
APA StyleNguyen, T. M., Do, T. T. T., Tran, T. N., & Kim, J. H. (2020). Exercise and Quality of Life in Women with Menopausal Symptoms: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(19), 7049. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17197049