Efficacy of a Multi-component m-Health Weight-loss Intervention in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Trial Design
2.1.1. Intervention
2.1.2. Measures
2.2. Statistical Analyses
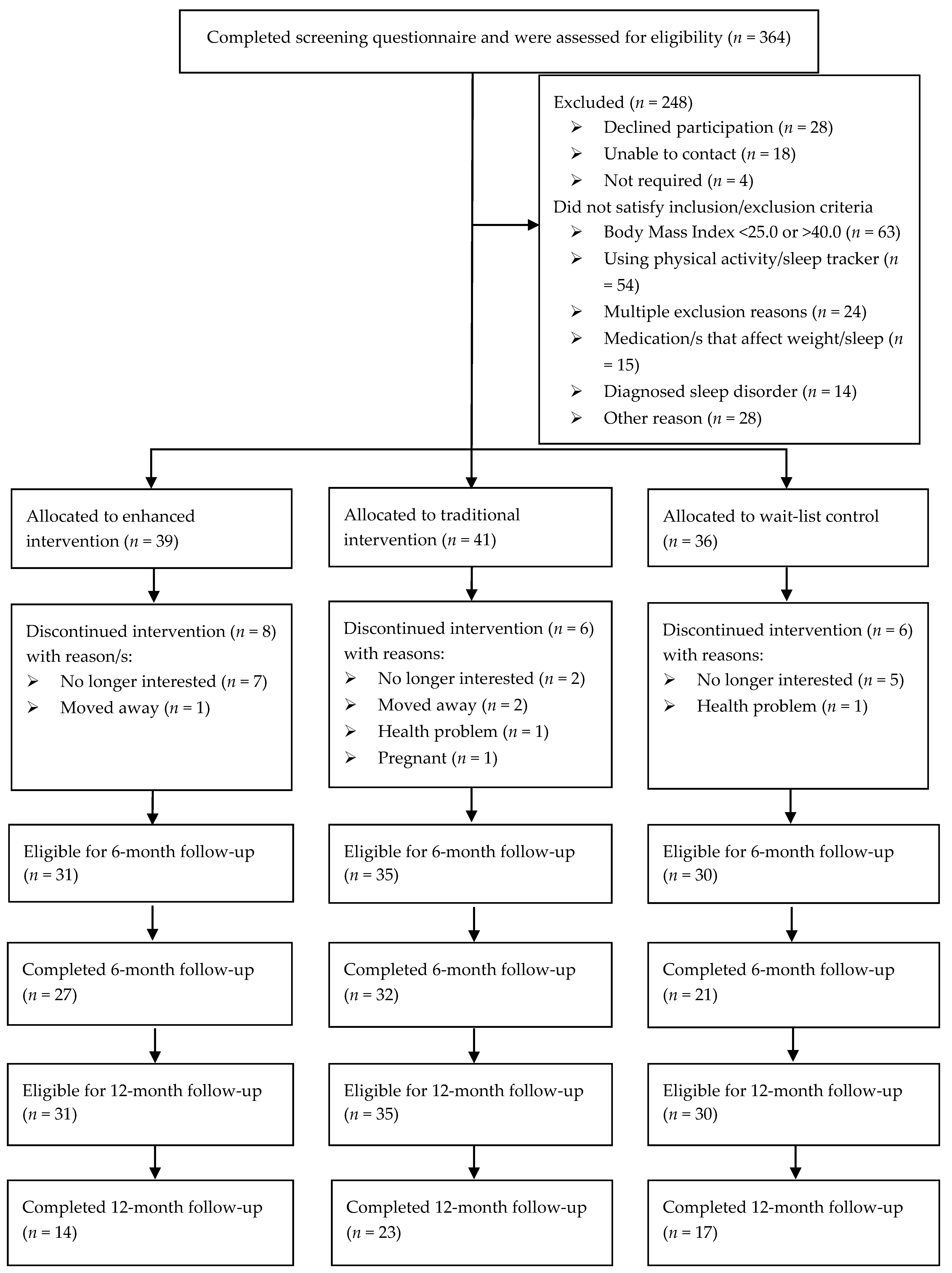
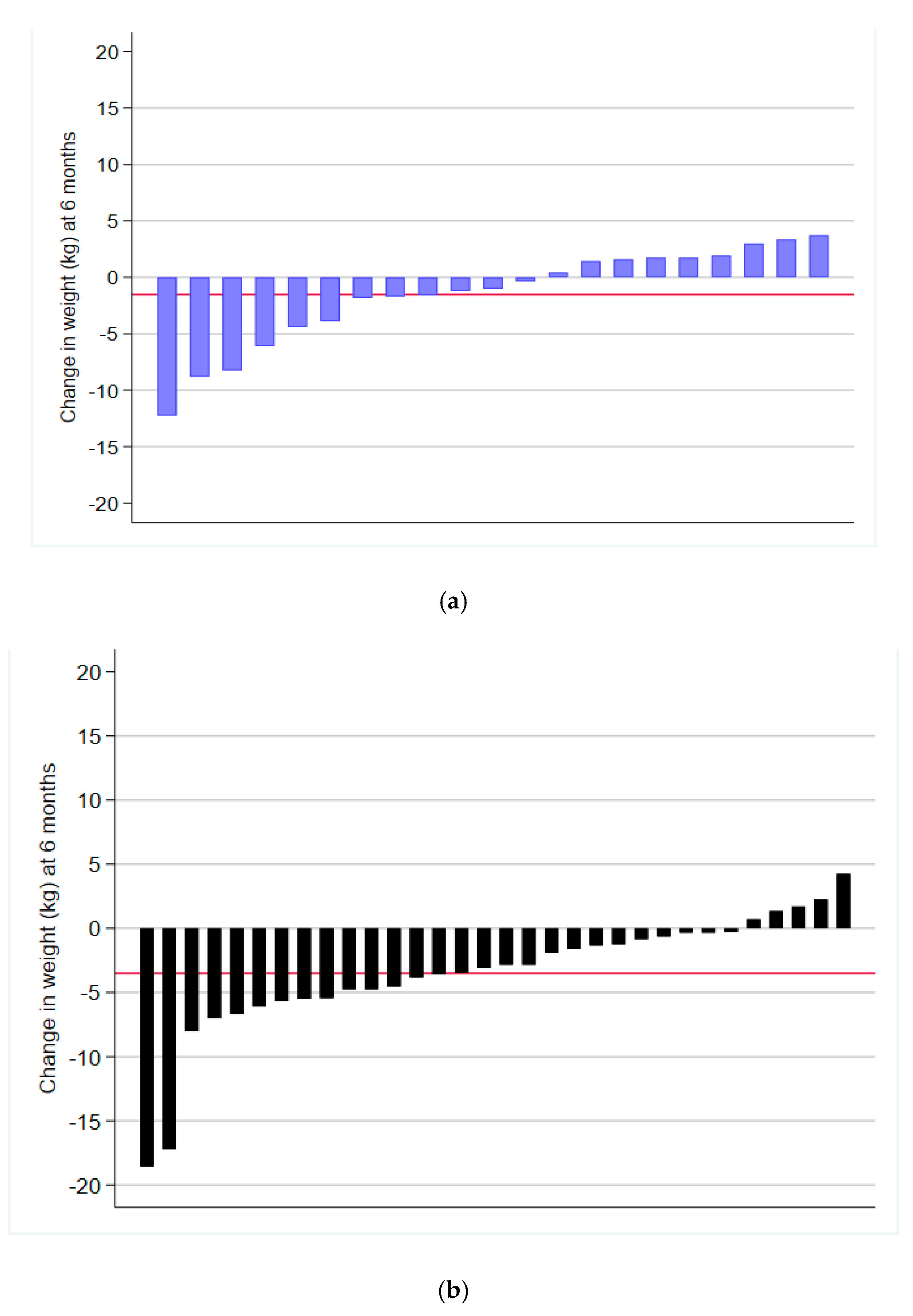
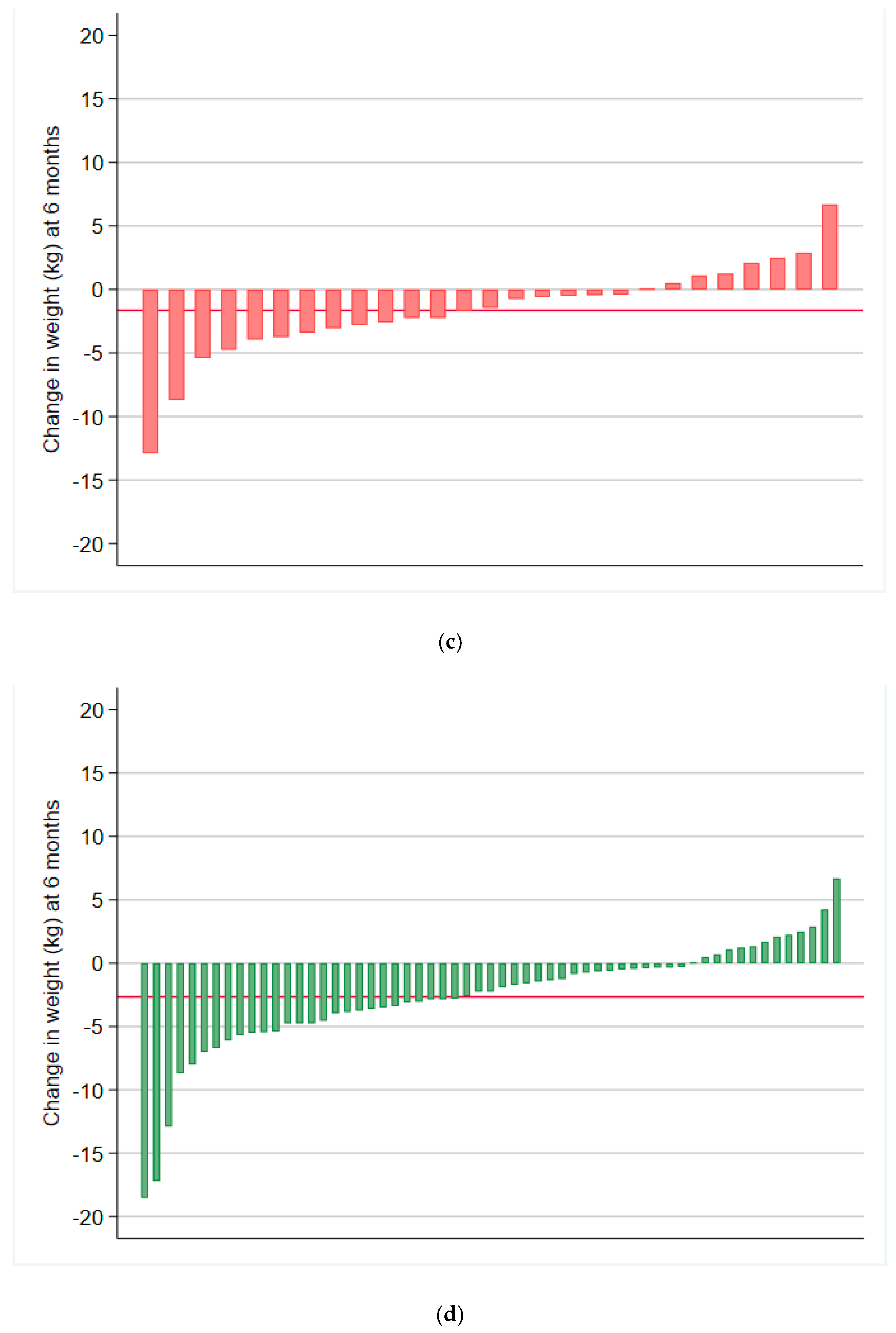
3. Results
3.1. Weight and Behavioural Outcomes
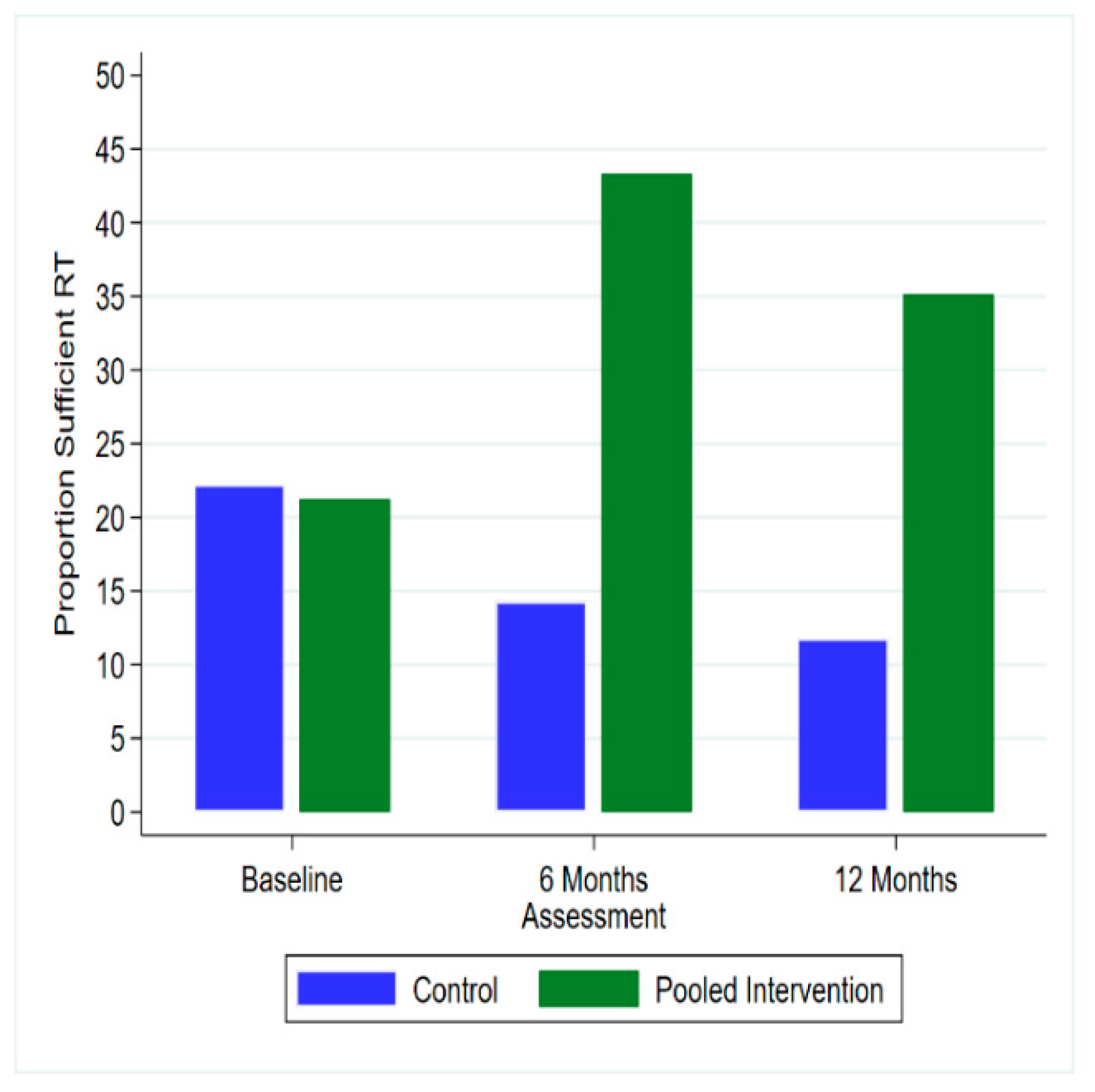
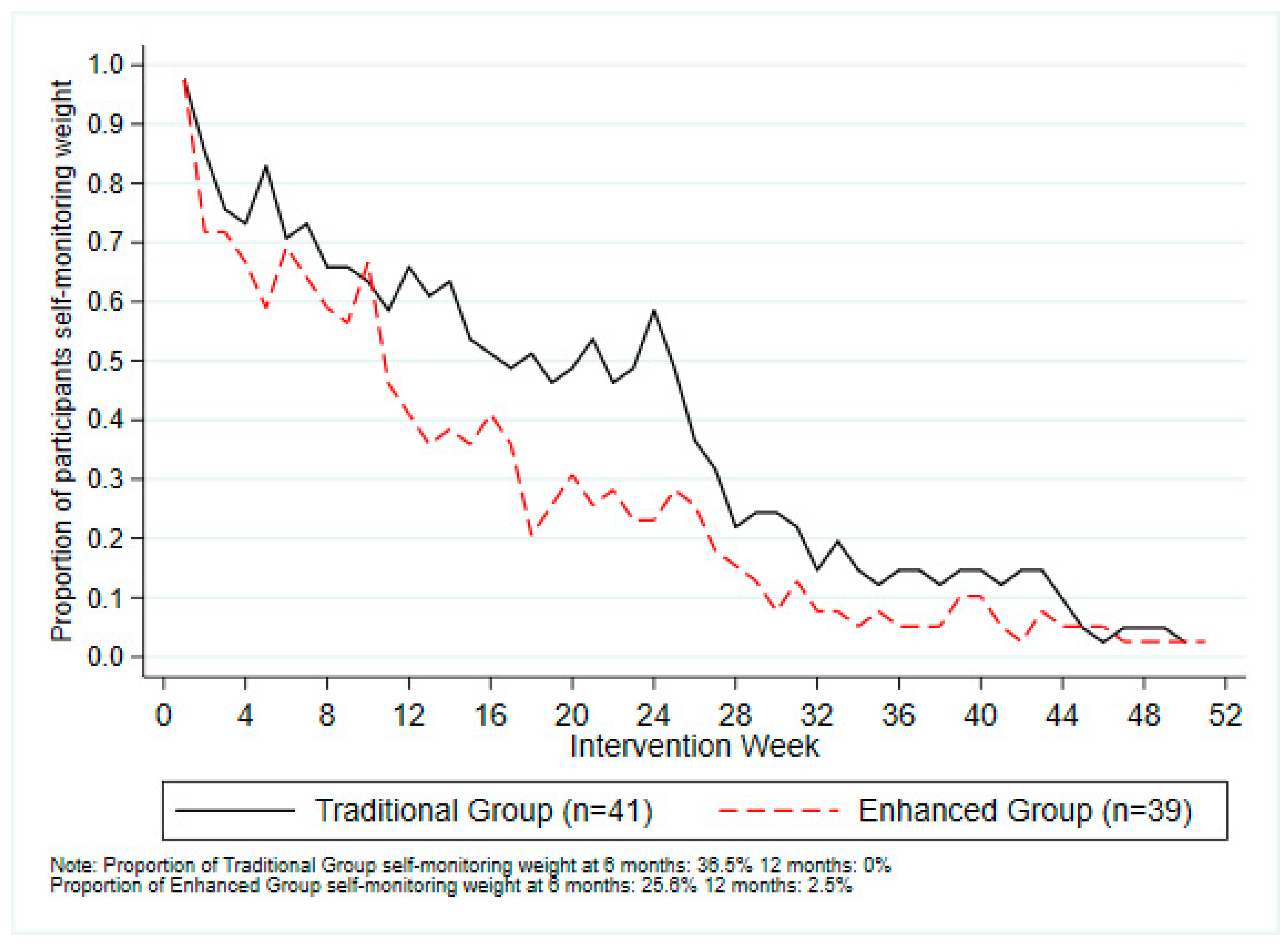
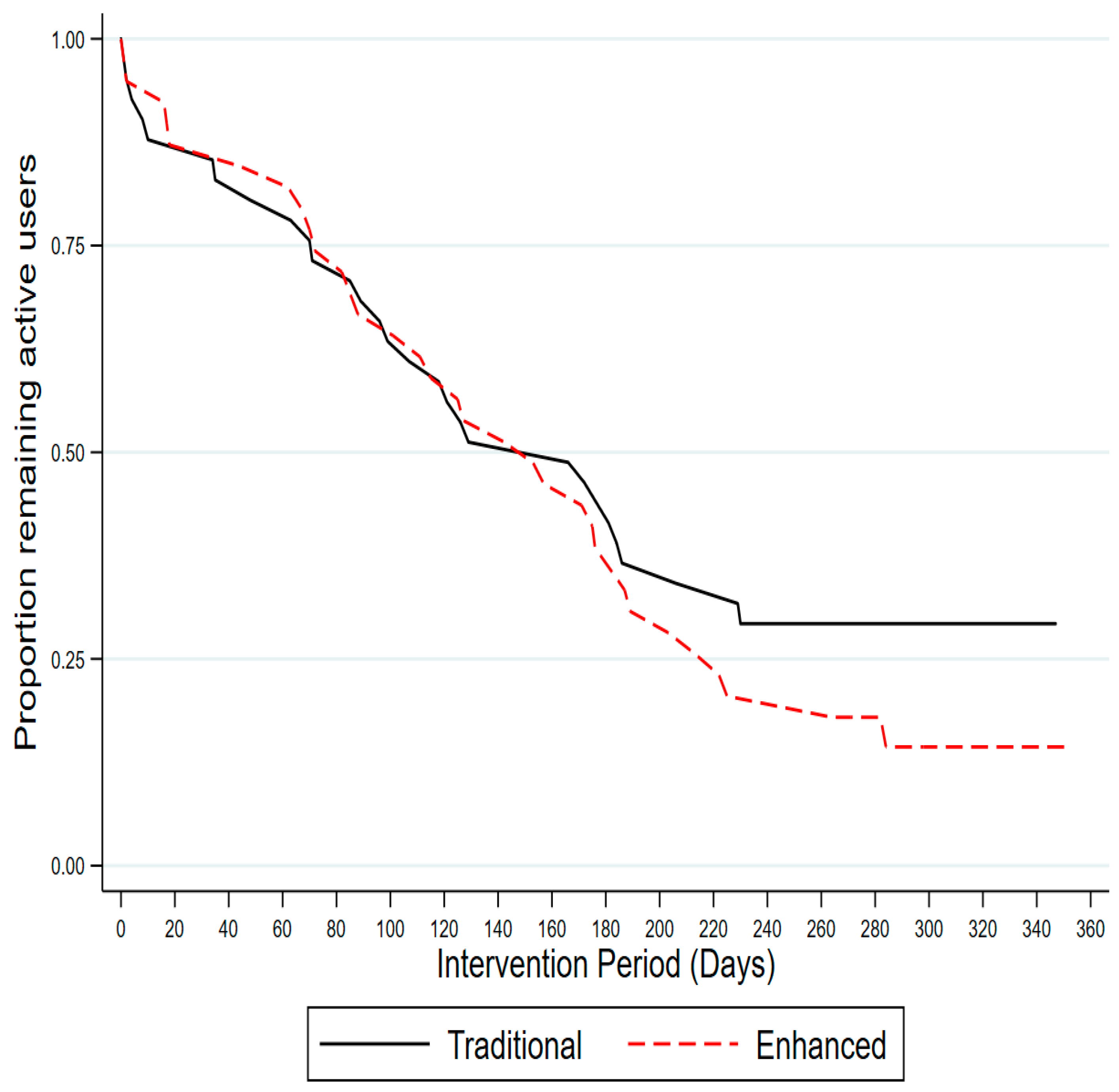
3.2. Usage Outcomes
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jensen, M.D.; Ryan, D.H.; Apovian, C.M.; Ard, J.D.; Comuzzie, A.G.; Donato, K.A.; Hu, F.B.; Hubbard, V.S.; Jakicic, J.M.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults. A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation 2014, 129, S102–S138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Health and Medical Research Council. Summary Guide for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Primary Care; National Health and Medical Research Council: Melbourne, Australia, 2013.
- Hutchesson, M.J.; Rollo, M.E.; Krukowski, R.; Ells, L.; Harvey, J.; Morgan, P.J.; Callister, R.; Plotnikoff, R.; Collins, C.E. eHealth interventions for the prevention and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 376–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguiar, E.J.; Morgan, P.J.; Collins, C.E.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Callister, R. Efficacy of interventions that include diet, aerobic and resistance training components for type 2 diabetes prevention: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, E.E.; Bourguet, C.C.; Palmieri, P.A.; Scott, E.D.; Matthews, B.A.; Dudley, P.; Chipman, K.J. The better weight-better sleep study: A pilot intervention in primary care. Am. J. Health Behav. 2012, 36, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, M.J.; Brown, W.J.; Burrows, T.L.; Collins, C.E.; Fenton, S.; Glozier, N.; Kolt, G.S.; Morgan, P.J.; Hensley, M.; Holliday, E.G.; et al. Examining the efficacy of a multicomponent m-Health physical activity, diet and sleep intervention for weight loss in overweight and obese adults: Randomised controlled trial protocol. BMJ Open 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Tremblay, A. Insufficient Sleep as a Contributor to Weight Gain: An Update. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2012, 1, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oftedal, S.; Vandelanotte, C.; Duncan, M.J. Patterns of Diet, Physical Activity, Sitting and Sleep Are Associated with Socio-Demographic, Behavioural, and Health-Risk Indicators in Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buysse, D.J. Sleep health: Can we define It? does it matter? Sleep 2014, 37, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kline, C.E. The bidirectional relationship between exercise and sleep: Implications for exercise adherence and sleep improvement. Am. J. Lifestyle Med. 2014, 8, 375–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayward, A.T.; Burton, N.W.; Brown, W.J.; Holliday, E.G.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Duncan, M.J. Associations between Changes in Activity and Sleep Quality and Duration over Two Years. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Khatib, H.K.; Harding, S.V.; Darzi, J.; Pot, G.K. The effects of partial sleep deprivation on energy balance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 71, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capers, P.L.; Fobian, A.D.; Kaiser, K.A.; Borah, R.; Allison, D.B. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the impact of sleep duration on adiposity and components of energy balance. Obes. Rev. 2015, 16, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenton, S.; Burrows, T.; Skinner, J.A.; Duncan, M.J. The influence of sleep health on dietary intake: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet 2020, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Thomson, C.A.; Morrow, K.L.; Flatt, S.W.; Wertheim, B.C.; Perfect, M.M.; Ravia, J.J.; Sherwood, N.E.; Karanja, N.; Rock, C.L. Relationship Between Sleep Quality and Quantity and Weight Loss in Women Participating in a Weight-Loss Intervention Trial. Obesity 2012, 20, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janney, C.A.; Kilbourne, A.M.; Germain, A.; Lai, Z.; Hoerster, K.D.; Goodrich, D.E.; Klingaman, E.A.; Verchinina, L.; Richardson, C.R. The Influence of Sleep Disordered Breathing on Weight Loss in a National Weight Management Program. Sleep 2016, 39, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Bureau of Statistics. 4364.0.55.001-National Health Survey: First Results, 2014–2015; Australian Bureau of Statistics: Canberra, Australia, 2015.
- Schoeppe, S.; Alley, S.; Van Lippevelde, W.; Bray, N.A.; Williams, S.L.; Duncan, M.J.; Vandelanotte, C. Efficacy of interventions that use apps to improve diet, physical activity and sedentary behaviour: A systematic review. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2016, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanhalli, A.; Saxena, M.; Wadhwa, B. Combined interventions for physical activity, sleep, and diet using smartphone apps: A scoping literature review. Int. J. Med. Inform. 2019, 123, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-H.; Hwang, J.; Choi, Y.-K. Effect of Mobile Health on Obese Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthc Inf. Res. 2019, 25, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, B.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Rayward, A.T.; Oldmeadow, C.; Vandelanotte, C.; Brown, W.J.; Duncan, M.J. Efficacy of an m-Health Physical Activity and Sleep Health Intervention for Adults: A Randomized Waitlist-Controlled Trial. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 57, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayward, A.T.; Murawski, B.; Duncan, M.J.; Holliday, E.G.; Vandelanotte, C.; Brown, W.J.; Plotnikoff, R.C. Efficacy of an m-Health Physical Activity and Sleep Intervention to Improve Sleep Quality in Middle-Aged Adults: The Refresh Study Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Behav. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, C.; Michie, S. A taxonomy of behavior change techniques used in interventions. Health Psychol. 2008, 27, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandura, A. The primacy of self-regulation in health promotion. Appl. Psychol. 2005, 54, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkin, B.; Webb, T.L.; Chang, B.P.I.; Prestwich, A.; Conner, M.; Kellar, I.; Benn, Y.; Sheeran, P. Does monitoring goal progress promote goal attainment? A meta-analysis of the experimental evidence. Psychol. Bull. 2016, 142, 198–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, C.E.; Boggess, M.M.; Watson, J.F.; Guest, M.; Duncanson, K.; Pezdirc, K.; Rollo, M.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Burrows, T.L. Reproducibility and comparative validity of a food frequency questionnaire for Australian adults. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 33, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, T.L.; Hutchesson, M.J.; Rollo, M.E.; Boggess, M.M.; Guest, M.; Collins, C.E. Fruit and vegetable intake assessed by food frequency questionnaire and plasma carotenoids: A validation study in adults. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3240–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council. Australian Dietary Guidelines. Available online: https://www.eatforhealth.gov.au/guidelines (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Australian Government National Health and Medical Research Council. Australian Guide to Healthy Eating 2017. Available online: https://www.eatforhealth.gov.au/guidelines/australian-guide-healthy-eating (accessed on 23 April 2020).
- Frankenfield, D.; Roth-Yousey, L.; Compher, C. Comparison of predictive equations for resting metabolic rate in healthy nonobese and obese adults: A systematic review. J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 2005, 105, 775–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.L.; Rollo, M.E.; Schumacher, T.; Collins, C.E. Diet Quality Scores of Australian Adults Who Have Completed the Healthy Eating Quiz. Nutrients 2017, 9, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabia, S.; van Hees, V.T.; Shipley, M.J.; Trenell, M.I.; Hagger-Johnson, G.; Elbaz, A.; Kivimaki, M.; Singh-Manoux, A. Association between questionnaire- and accelerometer-assessed physical activity: The role of sociodemographic factors. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, V.T.; Fang, Z.; Langford, J.; Assah, F.; Mohammad, A.; da Silva, I.C.; Trenell, M.I.; White, T.; Wareham, N.J.; Brage, S. Autocalibration of accelerometer data for free-living physical activity assessment using local gravity and temperature: An evaluation on four continents. J. Appl. Physiol. 2014, 117, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, V.T.; Gorzelniak, L.; Dean León, E.C.; Eder, M.; Pias, M.; Taherian, S.; Ekelund, U.; Renström, F.; Franks, P.W.; Horsch, A.; et al. Separating Movement and Gravity Components in an Acceleration Signal and Implications for the Assessment of Human Daily Physical Activity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hees, V.T.; Sabia, S.; Anderson, K.N.; Denton, S.J.; Oliver, J.; Catt, M.; Abell, J.G.; Kivimaki, M.; Trenell, M.I.; Singh-Manoux, A. A Novel, Open Access Method to Assess Sleep Duration Using a Wrist-Worn Accelerometer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowlands, A.V.; Mirkes, E.M.; Yates, T.; Clemes, S.; Davies, M.; Khunti, K.; Edwardson, C.L. Accelerometer-assessed Physical Activity in Epidemiology: Are Monitors Equivalent? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, W.J.; Bauman, A.; Chey, T.; Trost, S.; Mummery, K. Comparison of surveys used to measure physical activity. Aust. N. Z. J. Public Health 2004, 28, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, W.J.; Bauman, A.; Trost, S.; Mummery, W.K.; Owen, N. Test-retest reliability of four physical activity measures used in population surveys. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2004, 7, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. The Active Australia Survey: A Guide and Manual for Implementation, Analysis and Reporting; AIHW: Canberra, Aistralia, 2003.
- Chau, J.Y.; van der Ploeg, H.P.; Dunn, S.; Kurko, J.; Bauman, A.E. A tool for measuring workers′ sitting time by domain: The Workforce Sitting Questionnaire. Br. J. Sports Med. 2011, 45, 1216–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buysse, D.J.; Reynolds, C.F., 3rd; Monk, T.H.; Berman, S.R.; Kupfer, D.J. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989, 28, 193–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, C.M.; Belleville, G.; Bélanger, L.; Ivers, H. The Insomnia Severity Index: Psychometric Indicators to Detect Insomnia Cases and Evaluate Treatment Response. Sleep 2011, 34, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monk, T.H.; Buysse, D.J.; Kennedy, K.S.; Pods, J.M.; DeGrazia, J.M.; Miewald, J.M. Measuring sleep habits without using a diary: The sleep timing questionnaire. Sleep 2003, 26, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, M.J.; Kline, C.E.; Rebar, A.L.; Vandelanotte, C.; Short, C.E. Greater bed- and wake-time variability is associated with less healthy lifestyle behaviors: A cross-sectional study. J. Public Health 2016, 24, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooke, J. SUS: A “Quick and Dirty” Usability Scale; Jordan, P.W., Thomas, B., Weerdmeester, B.A., McClelland, A.L., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Adan, A.; Almirall, H. Horne & Östberg morningness-eveningness questionnaire: A reduced scale. Personal. Individ. Differ. 1991, 12, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelminski, I.; Petros, T.V.; Plaud, J.J.; Ferraro, F.R. Psychometric properties of the reduced Horne and Ostberg questionnaire. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2000, 29, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waters, L.; George, A.S.; Chey, T.; Bauman, A. Weight change in control group participants in behavioural weight loss interventions: A systematic review and meta-regression study. BMC Med Res. Methodol. 2012, 12, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatakis, E.; Lee, I.M.; Bennie, J.; Freeston, J.; Hamer, M.; O’Donovan, G.; Ding, D.; Bauman, A.; Mavros, Y. Does Strength-Promoting Exercise Confer Unique Health Benefits? A Pooled Analysis of Data on 11 Population Cohorts With All-Cause, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Mortality Endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perlis, M.L.; Jungquist, C.; Smith, M.T.; Posner, D. Cognitive Behavioral Treatment of Insomnia: A Session-by-Session Guide; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murawski, B.; Wade, L.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; Lubans, D.R.; Duncan, M.J. A systematic review and meta-analysis of cognitive and behavioral interventions to improve sleep health in adults without sleep disorders. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 40, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacevic, A.; Mavros, Y.; Heisz, J.J.; Fiatarone Singh, M.A. The effect of resistance exercise on sleep: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med. Rev. 2018, 39, 52–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Wijndaele, K.; Sharp, S.J.; Strain, T.; Pearce, M.; White, T.; Wareham, N.; Brage, S. Specific physical activities, sedentary behaviours and sleep as long-term predictors of accelerometer-measured physical activity in 91,648 adults: A prospective cohort study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burrows, T.; Fenton, S.; Duncan, M. Diet and sleep health: A scoping review of intervention studies in adults. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. Off. J. Br. Diet. Assoc. 2020, 33, 308–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandelanotte, C.; Müller, A.M.; Short, C.E.; Hingle, M.; Nathan, N.; Williams, S.L.; Lopez, M.L.; Parekh, S.; Maher, C.A. Past, Present, and Future of eHealth and mHealth Research to Improve Physical Activity and Dietary Behaviors. J. Nutr. Educ. Behav. 2016, 48, 219–228.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donkin, L.; Hickie, I.B.; Christensen, H.; Naismith, S.L.; Neal, B.; Cockayne, N.L.; Glozier, N. Rethinking the Dose-Response Relationship Between Usage and Outcome in an Online Intervention for Depression: Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 2013, 15, e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, M.J.; Collins, C.E.; Morgan, P.J. Dropout, nonusage attrition, and pretreatment predictors of nonusage attrition in a commercial Web-based weight loss program. J. Med. Internet Res. 2010, 12, e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, E.; Freund, M.; Booth, A.; Duncan, M.J.; Johnson, N.; Short, C.E.; Wolfenden, L.; Stacey, F.G.; Kay-Lambkin, F.; Vandelanotte, C. Comparative efficacy of simultaneous versus sequential multiple health behavior change interventions among adults: A systematic review of randomised trials. Prev. Med. 2016, 89, 211–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mc Sharry, J.; Olander, E.K.; French, D.P. Do single and multiple behavior change interventions contain different behavior change techniques? Health Psychol. 2015, 34, 960–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.; Senay, I.; Durantini, M.; Sánchez, F.; Hennessy, M.; Spring, B.; Albarracín, D. When it comes to lifestyle recommendations, more is sometimes less: A meta-analysis of theoretical assumptions underlying the effectiveness of interventions promoting multiple behavior domain change. Psychol. Bull. 2015, 141, 474–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, M.S.; Aubert, S.; Barnes, J.D.; Saunders, T.J.; Carson, V.; Latimer-Cheung, A.E.; Chastin, S.F.M.; Altenburg, T.M.; Chinapaw, M.J.M. Sedentary Behavior Research Network (SBRN)–Terminology Consensus Project process and outcome. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2017, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Pooled Intervention | Enhanced | Traditional | Control | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N = 80 | N = 39 | N = 41 | N = 36 | N = 116 | |
| M (SD), N (%) | M (SD), N (%) | M (SD), N (%) | M (SD), N (%) | M (SD), N (%) | |
| Age (years) | 46.3 (9.8) | 47.2 (9.4) | 45.4 (10.2) | 40.5 (10.7) | 44.5 (10.4) |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 57 (71.3%) | 27 (69.2%) | 30 (73.2%) | 25 (69.4%) | 82 (70.7%) |
| Male | 23 (28.7%) | 12 (30.8%) | 11 (26.8%) | 11 (30.6%) | 34 (29.3%) |
| Years Education | 17.1 (2.9) | 17.3 (3.0) | 16.9 (2.7) | 14.8 (2.7) | 16.4 (3.0) |
| Marital Status | |||||
| Married/Defacto | 63 (78.8%) | 30 (76.9%) | 33 (80.5%) | 29 (80.6%) | 92 (79.3%) |
| Not Married | 17 (21.3%) | 9 (23.1%) | 8 (19.5%) | 7 (19.4%) | 24 (20.7%) |
| Employment | |||||
| Full time | 43 (53.8%) | 21 (53.8%) | 22 (53.7%) | 19 (52.8%) | 62 (53.4%) |
| Part time/casual | 26 (32.5%) | 11 (28.2%) | 15 (36.6%) | 13 (36.1%) | 39 (33.6%) |
| Retired | 6 (7.5%) | 3 (7.7%) | 3 (7.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 6 (5.2%) |
| Other | 5 (6.3%) | 4 (10.3%) | 1 (2.4%) | 4 (11.1%) | 9 (7.8%) |
| Weight (kg) | 89.8 (13.4) | 90.8 (13.1) | 88.9 (13.8) | 92.5 (16.1) | 90.7 (14.3) |
| Measured BMI | 31.7 (3.9) | 31.9 (4.0) | 31.4 (3.8) | 31.9 (3.9) | 31.7 (3.9) |
| Measured BMI Categories | |||||
| BMI 25.0–29.9 | 25 (31.3%) | 11 (28.2%) | 14 (34.1%) | 10 (27.8%) | 35 (30.2%) |
| BMI 30.0–40.0 | 55 (68.8%) | 28 (71.8%) | 27 (65.9%) | 26 (72.2%) | 81 (69.8%) |
| Waist Circ. (cm) | 99.6 (10.8) | 99.5 (12.5) | 99.6 (9.0) | 99.7 (11.7) | 99.6 (11.0) |
| HbA1c | 5.5 (0.6) | 5.5 (0.4) | 5.5 (0.7) | 5.3 (0.3) | 5.4 (0.5) |
| Self-reported MVPA (mins.wk) | 346.4 (316.3) | 341.5 (270.6) | 351.0 (357.7) | 238.1 (239.2) | 312.8 (297.8) |
| Resistance Training Freq. (d.wk) | |||||
| 0–1 Session | 63 (78.8%) | 32 (82.1%) | 31 (75.6%) | 28 (77.8%) | 91 (78.4%) |
| 2+ Session | 17 (21.3%) | 7 (17.9%) | 10 (24.4%) | 8 (22.2%) | 25 (21.6%) |
| MVPA (mins.d) ‡ | 56.4 (33.3) | 56.6 (34.0) | 56.3 (33.0) | 49.2 (24.2) | 54.4 (31.1) |
| Light Intensity Activity (mins.d) ‡ | 197.8 (76.4) | 199.8 (74.3) | 196.1 (79.1) | 188.0 (66.0) | 195.1 (73.5) |
| Daily Sitting Time (mins.d) | 703.0 (205.5) | 667.4 (194.5) | 736.8 (212.2) | 678.1 (183.6) | 695.3 (198.5) |
| Sedentary Time (mins.d) ‡ | 617.7 (121.7) | 606.0 (143.5) | 629.7 (94.8) | 584.0 (180.7) | 607.4 (142.3) |
| Energy Intake (kj.d) | 9921.6 (3274.0) | 9422.1 (3518.6) | 10,396.9 (2989.0) | 9152.6 (2810.3) | 9683.0 (3145.6) |
| Total diet quality (ARFS 0–73) | 36.3 (8.4) | 36.5 (9.0) | 36.0 (8.0) | 33.3 (10.0) | 35.4 (9.0) |
| PSQI Global Score | 7.1 (3.0) | 7.3 (2.8) | 7.0 (3.1) | 6.7 (3.0) | 7.0 (3.0) |
| PSQI Sleep Quality Classification | |||||
| Good Quality Sleep | 18 (22.5%) | 7 (17.9%) | 11 (26.8%) | 8 (22.2%) | 26 (22.4%) |
| Poor Quality Sleep | 62 (77.5%) | 32 (82.1%) | 30 (73.2%) | 28 (77.8%) | 90 (77.6%) |
| Insomnia Severity Index | 9.2 (4.9) | 9.9 (4.6) | 8.5 (5.2) | 7.6 (4.8) | 8.7 (4.9) |
| PSQI Sleep Duration (hrs.d) | 6.8 (1.0) | 6.7 (1.1) | 6.8 (1.0) | 6.8 (0.9) | 6.8 (1.0) |
| Sleep Duration (hrs.d) ‡ | 6.4 (0.9) | 6.4 (0.9) | 6.4 (0.9) | 6.7 (0.7) | 6.5 (0.9) |
| Bed time Variability | 3.4 (1.7) | 3.5 (1.8) | 3.2 (1.6) | 3.0 (1.4) | 3.3 (1.6) |
| Wake time Variability | 2.4 (1.3) | 2.3 (1.3) | 2.6 (1.4) | 2.4 (1.3) | 2.4 (1.3) |
| Nightly Awakenings ‡ | 2.6 (1.6) | 2.8 (1.8) | 2.3 (1.3) | 1.6 (1.4) | 2.3 (1.6) |
| DASS-Depression | 6.2 (6.3) | 5.8 (4.9) | 6.5 (7.4) | 8.4 (7.9) | 6.9 (6.9) |
| DASS-Anxiety | 4.5 (4.9) | 4.2 (4.5) | 4.7 (5.2) | 5.1 (5.8) | 4.7 (5.2) |
| DASS-Stress | 10.8 (6.4) | 10.8 (6.1) | 10.8 (6.8) | 10.9 (6.8) | 10.8 (6.5) |
| Outcome | Control | Pooled Intervention | Group Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M (95% CI) | M (95% CI) | ||
| Weight (kg) | |||
| 6 Months | 87.67 (85.58, 89.75) | 86.75 (85.45, 88.04) | −0.92 (−3.33, 1.48) |
| 12 Months | 87.21 (85.00, 89.43) | 87.21 (85.74, 88.69) | −0.00 (−2.62, 2.62) |
| Waist Circ. (cm) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 97.14 (94.91, 99.37) | 96.52 (95.14, 97.90) | −0.62 (−3.18, 1.95) |
| 12 Months | 95.45 (93.10, 97.80) | 96.04 (94.49, 97.59) | 0.59 (−2.17, 3.36) |
| HbA1c | |||
| 6 Months | 5.44 (5.31, 5.57) | 5.45 (5.37, 5.53) | 0.01 (−0.15, 0.16) |
| 12 Months | 5.32 (5.17, 5.46) | 5.28 (5.18, 5.37) | −0.04 (−0.21, 0.13) |
| Self-report MVPA (mins.wk) † | |||
| 6 Months | 415.19 (294.31, 536.06) | 469.48 (374.56, 564.40) | 54.29 (−86.96, 195.54) |
| 12 Months | 415.53 (182.85, 648.21) | 442.30 (329.19, 555.40) | 26.77 (−225.90, 279.43) |
| MVPA (mins.d) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 67.35 (55.01, 79.70) | 69.98 (61.54, 78.42) | 2.63 (−12.22,17.48) |
| 12 Months | 66.76 (56.37, 77.15) | 73.54 (61.56, 85.53) | 6.78 (−9.19,22.76) |
| Light Intensity Activity (mins.d) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 224.57 (200.90, 248.24) | 224.03 (206.60, 241.45) | −0.54 (−29.45, 28.37) |
| 12 Months | 219.20 (197.49, 240.92) | 222.49 (197.50, 247.47) | 3.28 (−30.64, 37.20) |
| Daily Sitting Time (mins.d) | |||
| 6 Months | 682.86 (601.06, 764.66) | 652.30 (602.49, 702.11) | −30.56 (−123.65, 62.53) |
| 12 Months | 568.56 (483.50, 653.61) | 568.66 (518.92, 618.40) | 0.10 (−100.25, 100.46) |
| Sedentary Time (mins.d) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 633.66 (592.52, 674.80) | 661.33 (627.06, 695.60) | 27.67 (−30.40, 85.74) |
| 12 Months | 649.40 (597.45, 701.35) | 617.38 (576.14, 658.62) | −32.02 (−99.47, 35.43) |
| Energy Intake (kj.d) | |||
| 6 Months | 9117.77 (8256.43, 9979.11) | 8080.74 (7557.45, 8604.03) | −1037.03 (−2028.84, −45.22) |
| 12 Months | 9105.88 (8169.46, 10042.29) | 8192.52 (7567.82, 8817.21) | −913.36 (−2030.75, 204.04) |
| PSQI Global Score † | |||
| 6 Months | 6.76 (5.50, 8.02) | 5.96 (5.24, 6.68) | −0.80 (−2.26, 0.67) |
| 12 Months | 5.96 (4.66, 7.26) | 5.30 (4.35, 6.25) | −0.66 (−2.27, 0.95) |
| Insomnia Severity Index | |||
| 6 Months | 8.03 (6.33, 9.74) | 6.43 (5.41, 7.46) | −1.60 (−3.56, 0.36) |
| 12 Months | 8.16 (6.31, 10.00) | 5.56 (4.33, 6.80) | −2.59 (−4.79, −0.39) |
| Bed time Variability † | |||
| 6 Months | 2.78 (2.18, 3.39) | 3.16 (2.76, 3.56) | 0.38 (−0.35, 1.11) |
| 12 Months | 3.36 (2.65, 4.06) | 3.02 (2.57, 3.46) | −0.34 (−1.18, 0.50) |
| Wake time Variability ¥ | |||
| 6 Months | 2.03 (1.56, 2.50) | 2.44 (2.13, 2.75) | 0.18 (−0.08, 0.44) |
| 12 Months | 2.49 (1.93, 3.04) | 2.16 (1.82, 2.51) | −0.14 (−0.41, 0.13) |
| Nightly Awakenings ‡ | |||
| 6 Months | 2.28 (1.74, 2.83) | 2.18 (1.85, 2.51) | −0.10 (−0.74, 0.53) |
| 12 Months | 1.97 (1.27, 2.67) | 2.10 (1.65, 2.56) | 0.13 (−0.71, 0.98) |
| DASS-Depression † | |||
| 6 Months | 6.44 (4.88, 8.01) | 4.96 (3.70, 6.23) | −1.48 (−3.54, 0.58) |
| 12 Months | 3.12 (1.32, 4.91) | 4.84 (3.48, 6.20) | 1.72 (−0.61, 4.05) |
| DASS-Anxiety | |||
| 6 Months | 3.41 (2.10, 4.72) | 3.19 (2.40, 3.99) | −0.21 (−1.71, 1.29) |
| 12 Months | 3.13 (1.75, 4.51) | 2.68 (1.79, 3.58) | −0.44 (−2.07, 1.18) |
| DASS-Stress | |||
| 6 Months | 9.96 (7.76, 12.17) | 8.93 (7.60, 10.26) | −1.03 (−3.56, 1.50) |
| 12 Months | 9.34 (6.95, 11.73) | 8.20 (6.61, 9.79) | −1.14 (−3.98, 1.71) |
| Outcome | Traditional | Enhanced | Group Difference (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| M (95% CI) | M (95% CI) | ||
| Weight (kg) | |||
| 6 Months | 85.37 (83.71, 87.04) | 87.28 (85.46, 89.10) | 1.91 (−0.50, 4.31) |
| 12 Months | 86.34 (84.54, 88.14) | 87.19 (85.06, 89.32) | 0.85 (−1.89, 3.59) |
| Waist Circ. (cm) | |||
| 6 Months | 95.12 (93.41, 96.84) | 97.81 (95.93, 99.69) | 2.69 (0.20, 5.18) |
| 12 Months | 95.42 (93.57, 97.27) | 96.17 (93.96, 98.39) | 0.75 (−2.08, 3.59) |
| HbA1c | |||
| 6 Months | 5.46 (5.35, 5.57) | 5.45 (5.33, 5.57) | −0.01 (−0.17, 0.15) |
| 12 Months | 5.36 (5.23, 5.48) | 5.18 (5.02, 5.33) | −0.18 (−0.38, 0.02) |
| Self-report MVPA (mins.wk) † | |||
| 6 Months | 555.61 (433.42, 677.79) | 404.16 (260.54, 547.78) | −151.45 (−330.31, 27.41) |
| 12 Months | 532.45 (380.27, 684.63) | 365.56 (219.20, 511.91) | −166.90 (−374.08, 40.29) |
| MVPA (mins.d) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 76.28 (60.97, 91.58) | 61.54 (50.82, 72.26) | −14.74 (−37.03, 7.56) |
| 12 Months | 76.66 (58.12, 95.19) | 70.43 (51.69, 89.18) | −6.22 (−35.66, 23.22) |
| Light Intensity Activity (mins.d) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 224.97 (197.83, 252.10) | 209.09 (184.21, 233.96) | −15.88 (−56.55, 24.79) |
| 12 Months | 222.45 (184.93, 259.97) | 208.14 (175.34, 240.95) | −14.31 (−68.62, 40.00) |
| Daily Sitting Time (mins.d) | |||
| 6 Months | 677.99 (615.46, 740.53) | 652.09 (583.53, 720.65) | −25.90 (−116.44, 64.64) |
| 12 Months | 549.21 (487.68, 610.74) | 618.45 (530.56, 706.35) | 69.24 (−39.00, 177.48) |
| Sedentary Time (mins.d) ‡,† | |||
| 6 Months | 648.89 (612.76, 685.01) | 688.27 (635.49, 741.06) | 39.38 (−21.99, 100.76) |
| 12 Months | 594.00 (549.77, 638.24) | 699.66 (635.44, 763.87) | 105.66 (30.83, 180.48) |
| Energy Intake (kj.d) | |||
| 6 Months | 8189.80 (7487.54, 8892.07) | 8305.46 (7520.13, 9090.79) | 115.65 (−939.39, 1170.70) |
| 12 Months | 8603.07 (7798.02, 9408.12) | 7878.94 (6838.57, 8919.31) | −724.13 (−2053.96, 605.70) |
| PSQI Global Score † | |||
| 6 Months | 6.14 (5.22, 7.06) | 5.78 (4.62, 6.94) | −0.36 (−1.86, 1.14) |
| 12 Months | 5.34 (4.00, 6.67) | 5.31 (4.13, 6.49) | −0.03 (−1.79, 1.74) |
| Insomnia Severity Index | |||
| 6 Months | 6.27 (4.89, 7.66) | 6.89 (5.33, 8.45) | 0.62 (−1.44, 2.67) |
| 12 Months | 5.86 (4.31, 7.40) | 5.19 (3.26, 7.13) | −0.66 (−3.12, 1.80) |
| Bed Time Variability | |||
| 6 Months | 3.43 (2.79, 4.06) | 2.83 (2.41, 3.25) | −0.60 (−1.37, 0.18) |
| 12 Months | 3.45 (2.80, 4.11) | 2.38 (1.97, 2.78) | −1.08 (−1.86,−0.29) |
| Wake time Variability ¥ | |||
| 6 Months | 2.49 (2.07, 2.91) | 2.39 (1.92, 2.85) | −0.04 (−0.29, 0.21) |
| 12 Months | 2.22 (1.80, 2.64) | 2.09 (1.54, 2.64) | −0.06 (−0.38, 0.26) |
| Nightly Awakenings ‡ | |||
| 6 Months | 2.36 (1.91, 2.81) | 2.38 (1.89, 2.86) | 0.02 (−0.63, 0.67) |
| 12 Months | 2.48 (1.92, 3.04) | 1.83 (1.03, 2.63) | −0.65 (−1.62, 0.32) |
| DASS-Depression † | |||
| 6 Months | 4.61 (3.30, 5.92) | 5.02 (2.74, 7.30) | 0.41 (−2.25, 3.07) |
| 12 Months | 5.18 (3.47, 6.89) | 3.82 (1.87, 5.77) | −1.36 (−4.04, 1.32) |
| DASS-Anxiety | |||
| 6 Months | 3.35 (2.32, 4.39) | 3.27 (2.11, 4.43) | −0.08 (−1.60, 1.43) |
| 12 Months | 3.40 (2.28, 4.52) | 1.86 (0.49, 3.24) | −1.54 (−3.29, 0.21) |
| DASS-Stress | |||
| 6 Months | 10.04 (8.29, 11.78) | 8.02 (6.08, 9.96) | −2.02 (−4.58, 0.54) |
| 12 Months | 9.31 (7.30, 11.32) | 7.10 (4.51, 9.70) | −2.21 (−5.48, 1.05) |
| Outcome | Traditional | Enhanced | Total | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Mean | SD | Min | Max | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max | N | Mean | SD | Min | Max | p-Value | |
| Total Entries † | 41 | 156.5 | 102.8 | 0 | 342 | 39 | 140.4 | 83.3 | 1 | 353 | 80 | 148.7 | 93.6 | 0 | 353 | 0.440 |
| Physical Activity Entries ‡ | 41 | 152.5 | 102.1 | 0 | 340 | 39 | 122.5 | 77.9 | 0 | 344 | 80 | 137.9 | 91.8 | 0 | 344 | 0.140 |
| Food Entries | 41 | 126.9 | 101.8 | 0 | 337 | 39 | 83.2 | 68.4 | 0 | 313 | 80 | 105.6 | 89.3 | 0 | 337 | 0.030 |
| Sleep Entries | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 39 | 119.7 | 83.7 | 0 | 352 | 39 | 119.7 | 83.7 | 0 | 352 | N/A |
| Body Weight Entries | 41 | 62.2 | 81.9 | 0 | 327 | 39 | 38.2 | 59.5 | 0 | 349 | 80 | 50.5 | 72.4 | 0 | 349 | 0.140 |
| Separate Physical Activity Behaviours | ||||||||||||||||
| Fitbit MVPA Entries | 41 | 151.0 | 100.9 | 0 | 339 | 39 | 121.5 | 78.0 | 0 | 344 | 80 | 136.6 | 91.1 | 0 | 344 | 0.150 |
| Daily Steps Entries | 41 | 127.0 | 93.9 | 0 | 333 | 39 | 77.1 | 62.5 | 0 | 283 | 80 | 102.7 | 83.5 | 0 | 333 | <0.001 |
| Resistance Training Entries | 41 | 127.2 | 96.5 | 0 | 331 | 39 | 68.5 | 62.4 | 0 | 274 | 80 | 98.6 | 86.4 | 0 | 331 | <0.001 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duncan, M.J.; Fenton, S.; Brown, W.J.; Collins, C.E.; Glozier, N.; Kolt, G.S.; Holliday, E.G.; Morgan, P.J.; Murawski, B.; Plotnikoff, R.C.; et al. Efficacy of a Multi-component m-Health Weight-loss Intervention in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176200
Duncan MJ, Fenton S, Brown WJ, Collins CE, Glozier N, Kolt GS, Holliday EG, Morgan PJ, Murawski B, Plotnikoff RC, et al. Efficacy of a Multi-component m-Health Weight-loss Intervention in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2020; 17(17):6200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176200
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuncan, Mitch J., Sasha Fenton, Wendy J. Brown, Clare E. Collins, Nicholas Glozier, Gregory S. Kolt, Elizabeth G. Holliday, Philip J. Morgan, Beatrice Murawski, Ronald C. Plotnikoff, and et al. 2020. "Efficacy of a Multi-component m-Health Weight-loss Intervention in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial" International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 17, no. 17: 6200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176200
APA StyleDuncan, M. J., Fenton, S., Brown, W. J., Collins, C. E., Glozier, N., Kolt, G. S., Holliday, E. G., Morgan, P. J., Murawski, B., Plotnikoff, R. C., Rayward, A. T., Stamatakis, E., Vandelanotte, C., & Burrows, T. L. (2020). Efficacy of a Multi-component m-Health Weight-loss Intervention in Overweight and Obese Adults: A Randomised Controlled Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17(17), 6200. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17176200








