Anti-EGFR Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Identifying, Tracking, and Overcoming Resistance
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The EGFR Pathway in Colorectal Cancer
Targeting the EGFR Pathway
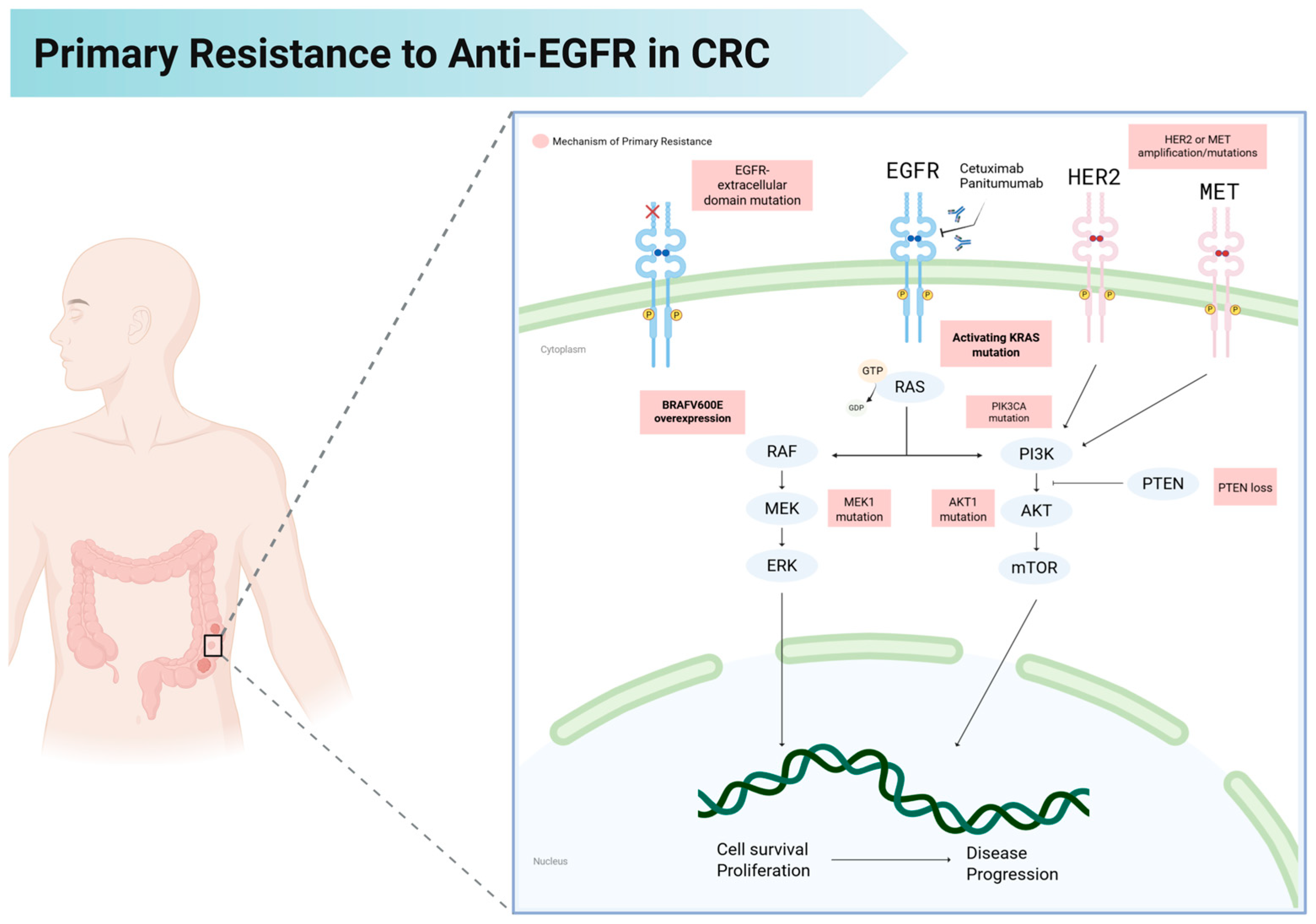
3. Mechanisms of Primary Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy
3.1. HER2 (ERBB2) Amplification and Mutations
3.2. PI3K Pathway Alterations (PIK3CA Mutations, PTEN Loss)
3.3. MET Amplification
3.4. MAP2K1 (MEK1) Mutations
3.5. AKT1 Mutations
3.6. Gene Fusions
| Mechanism of Primary Resistance | Prevalence | Clinical Impact in Patients Treated with Anti-EGFR Therapy (Effect Size, 95% CI) | Possible Strategies to Overcome Resistance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KRAS/NRAS activating mutations | 40% | OS: HR 1.06 (0.96–1.17) | Addition of anti-KRAS targeted therapy (e.g., Code BreaK 301 trial) | [61,109,110] |
| BRAF V600E mutations | 8–12% | OS: HR 0.91 (0.62–1.34); PFS: HR 0.88 (0.67–1.14); ORR: RR 1.31 (0.83–2.08) | Combined EGFR and BRAF inhibitors (e.g., BREAKWATER) | [47,111,112] |
| HER2 (ERBB2) amplification | 5–7% | PFS: HR 2.84 (1.44–5.60); ORR: OR 1.96 (1.10–3.48) | HER2-targeted therapy (e.g., HERACLES-B trial, TRIUMPH trial) | [71,72,75,113] |
| PIK3CA mutations/PTEN loss | 10–20% | PFS: WT HR 0.57 (0.38–0.87) †; mutant HR 0.70 (0.26–1.88) | Addition of PI3K or mTor inhibitors | [73,81,82,114,115] |
| MET amplification | 1–2% baseline; 22% after anti-EGFR | OS: HR 1.33 (1.06–1.59); PFS: HR 1.47 (1.03–1.91) ‡ | Dual EGFR/MET Inhibition (e.g., Tivantinib + Cetuximab) | [85,90,116,117] |
| MAP2K1 (MEK1) mutations | 1.8% (MSS, RAS/BRAF WT cohort) | Data remains limited to small case series/reports | Combined BRAF + EGFR + MEK1 inhibitiors | [118,119,120] |
| AKT1 mutations | <2% | Data remains limited to small case series/reports | AKT inhibitors | [94,121] |
| Oncogenic fusions (NTRK/RET/ALK/ROS1/FGFR3) | 1% | Data remains limited to small case series/reports | Fusion-targeted therapies (e.g., TRK, RET inhibitors) | [96] |
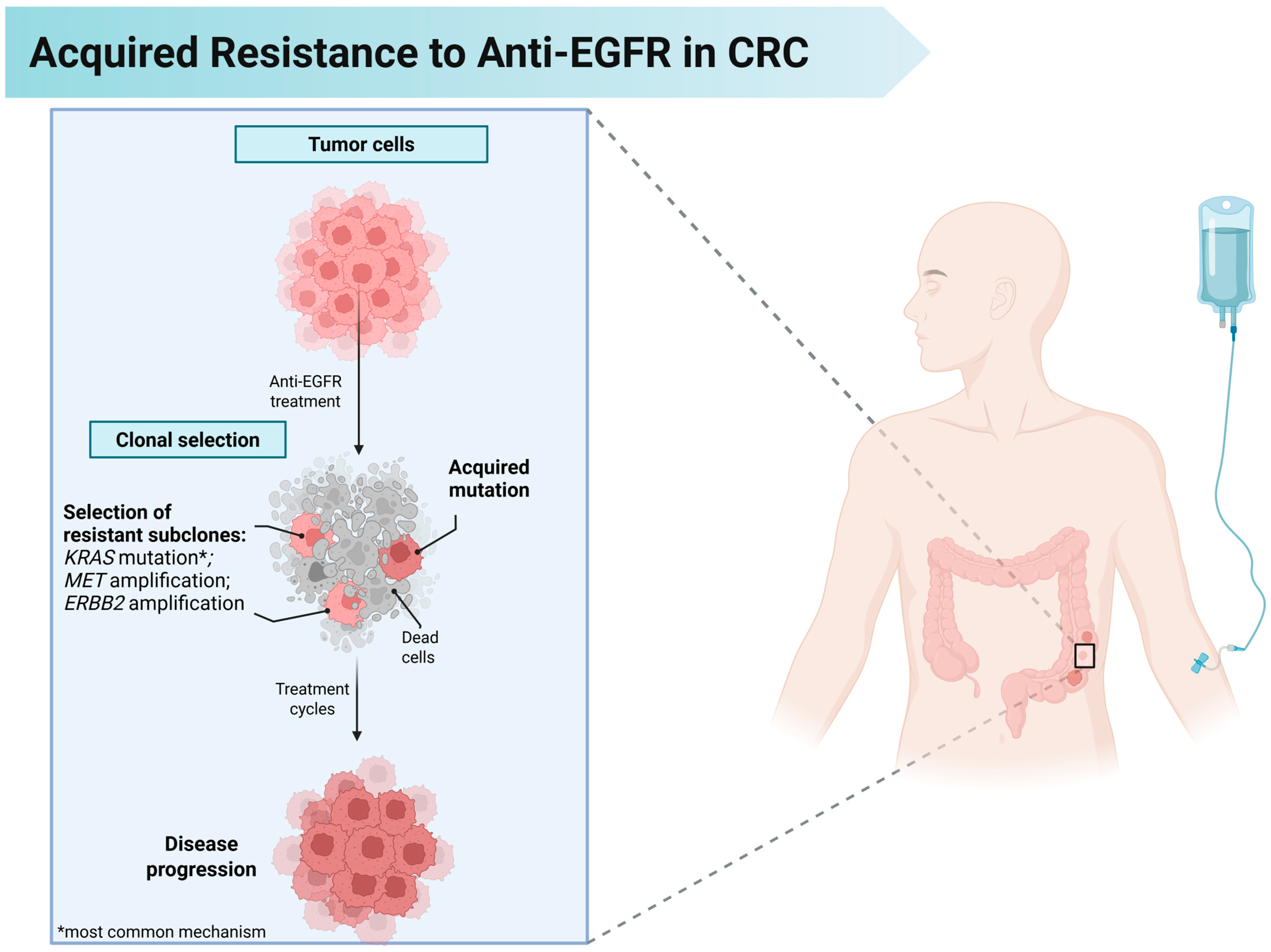
4. Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy
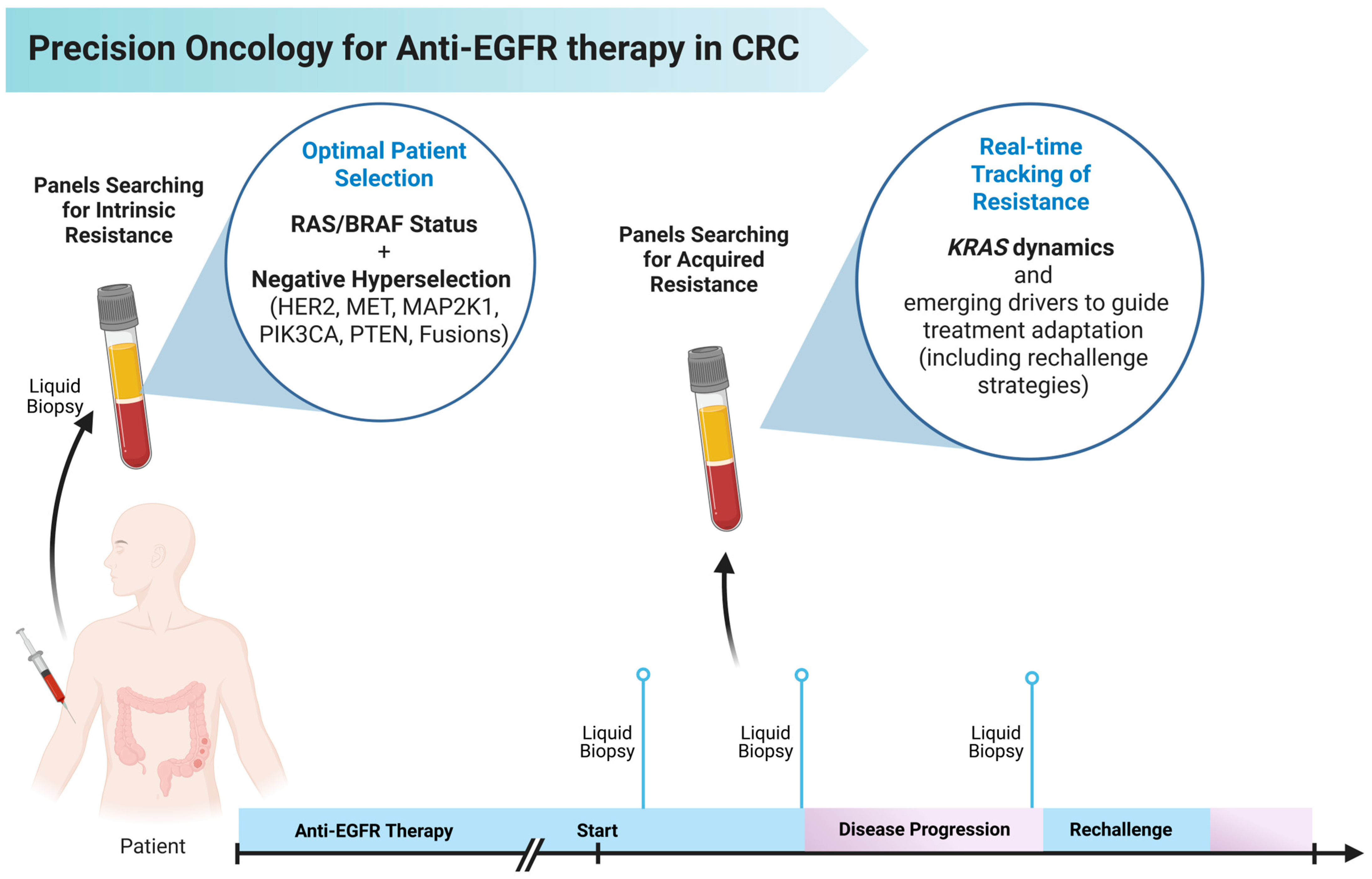
5. Hyperselection of Patients for Anti-EGFR Therapy
6. The Role of Circulating Tumor DNA in Tracking Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GBD 2019 Colorectal Cancer Collaborators. Global, regional, and national burden of colorectal cancer and its risk factors, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 627–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Wagle, N.S.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 233–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Jiang, C.; Morgan, E.; Zahwe, M.; Cao, Y.; Bray, F.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer incidence trends in younger versus older adults: An analysis of population-based cancer registry data. Lancet Oncol. 2025, 26, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szostek, J.; Serafin, M.; Mąka, M.; Jabłońska, B.; Mrowiec, S. Right-Sided Versus Left-Sided Colon Cancer-A 5-Year Single-Center Observational Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, W.; Wang, C.; Guo, T.; Yang, J.; Shao, Z.; Cai, G.; Cai, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Molecular Profiling Provides Clinical Insights into Targeted and Immunotherapies as Well as Colorectal Cancer Prognosis. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 414–428.E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Martini, G.; Ciardiello, D.; Tufo, S.D.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Ciardiello, F. Targeting the EGFR signalling pathway in metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 664–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, V.K.; Kennedy, E.B.; Baxter, N.N.; Benson, A.B.; Cercek, A.; Cho, M.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cremolini, C.; Davis, A.; Deming, D.A.; et al. Treatment of Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 678–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, A.; Adam, R.; Roselló, S.; Arnold, D.; Normanno, N.; Taïeb, J.; Seligmann, J.; De Baere, T.; Osterlund, P.; Yoshino, T.; et al. Metastatic colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 10–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, A.B.; Venook, A.P.; Adam, M.; Chang, G.; Chen, Y.-J.; Ciombor, K.K.; Cohen, S.A.; Cooper, H.S.; Deming, D.; Garrido-Laguna, I.; et al. Colon Cancer, Version 3.2024, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2024, 22, e240029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasi, P.M.; Afable, M.G.; Herting, C.; Lukanowski, M.; Jin, Z. Anti-EGFR Antibodies in the Management of Advanced Colorectal Cancer. Oncologist 2023, 28, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejpar, S.; Stintzing, S.; Ciardiello, F.; Tabernero, J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Beier, F.; Esser, R.; Lenz, H.-J.; Heinemann, V. Prognostic and Predictive Relevance of Primary Tumor Location in Patients with RAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Retrospective Analyses of the CRYSTAL and FIRE-3 Trials. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Lenz, H.-J.; Köhne, C.-H.; Heinemann, V.; Tejpar, S.; Melezínek, I.; Beier, F.; Stroh, C.; Rougier, P.; van Krieken, J.H.; et al. Fluorouracil, leucovorin, and irinotecan plus cetuximab treatment and RAS mutations in colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 692–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokemeyer, C.; Van Cutsem, E.; Rougier, P.; Ciardiello, F.; Heeger, S.; Schlichting, M.; Celik, I.; Köhne, C.-H. Addition of cetuximab to chemotherapy as first-line treatment for KRAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: Pooled analysis of the CRYSTAL and OPUS randomised clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 1466–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer: From heterogeneity to convergent evolution. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 1269–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, E.; Ciardiello, D.; Martini, G.; Troiani, T.; Cardone, C.; Vitiello, P.P.; Normanno, N.; Rachiglio, A.M.; Maiello, E.; Latiano, T.; et al. Implementing anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Challenges and future perspectives. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dienstmann, R.; Salazar, R.; Tabernero, J. Overcoming Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2015, 35, e149–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Bergamo, F.; Rossini, D.; Ghelardi, F.; De Grandis, M.C.; Germani, M.M.; Barsotti, G.; Formica, V.; Frassineti, G.L.; Boscolo, G.; et al. Negative hyperselection of elderly patients with RAS and BRAF wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer receiving initial panitumumab plus FOLFOX or 5-FU/LV. Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 195, 113396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, L.F.L.; Saldanha, E.F.; da Conceição, L.D.; Noronha, M.M.; da Silva, M.V.M.G.; Peixoto, R.D. ’Alpino Anti-EGFR Rechallenge in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and the Role of ctDNA: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2024, 56, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Geng, S.; Luo, H.; Wang, W.; Mo, Y.-Q.; Luo, Q.; Wang, L.; Song, G.-B.; Sheng, J.-P.; Xu, B. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer: Pathogenesis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe, M.L.; Marrocco, I.; Yarden, Y. EGFR in Cancer: Signaling Mechanisms, Drugs, and Acquired Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasinskas, A.M. EGFR Signaling in Colorectal Carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Int. 2011, 2011, 932932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, D.F.; Billadeau, D.D.; Jois, S.D. EGFR trafficking: Effect of dimerization, dynamics, and mutation. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1258371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, I.; Akita, R.; Vandlen, R.; Toomre, D.; Schlessinger, J.; Mellman, I. Spatial control of EGF receptor activation by reversible dimerization on living cells. Nature 2010, 464, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levantini, E.; Maroni, G.; Del Re, M.; Tenen, D.G. EGFR signaling pathway as therapeutic target in human cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 85, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, P.; Wang, Z. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Cell Proliferation Signaling Pathways. Cancers 2017, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koveitypour, Z.; Panahi, F.; Vakilian, M.; Peymani, M.; Seyed Forootan, F.; Nasr Esfahani, M.H.; Ghaedi, K. Signaling pathways involved in colorectal cancer progression. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Duarte, R.; Rebelo de Almeida, C.; Negrão, M.; Fernandes, A.; Borralho, P.; Sobral, D.; Gallego-Paez, L.M.; Machado, D.; Gramaça, J.; Vílchez, J.; et al. Predictive and Therapeutic Implications of a Novel PLCγ1/SHP2-Driven Mechanism of Cetuximab Resistance in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 1203–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesnelle, K.M.; Boehm, A.L.; Grandis, J.R. STAT-mediated EGFR signaling in cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 102, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, J.-P.; Lagorce, C.; Atlan, D.; Milano, G.; Domont, J.; Benamouzig, R.; Attar, A.; Benichou, J.; Martin, A.; Morere, J.-F.; et al. Impact of EGFR expression on colorectal cancer patient prognosis and survival. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, S.; Ciardiello, D.; Cioli, E.; Martinelli, E.; Troiani, T.; Giulia Zampino, M.; Fazio, N.; De Vita, F.; Ciardiello, F.; Martini, G. BRAFV600E mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: Current advances in personalized treatment and future perspectives. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2025, 134, 102905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaeger, R.; Corcoran, R.B. Targeting Alterations in the RAF-MEK Pathway. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, Y.; Diaz, L.A.; Schmidt-Kittler, O.; Cummins, J.M.; Delong, L.; Cheong, I.; Rago, C.; Huso, D.L.; Lengauer, C.; Kinzler, K.W.; et al. Mutant PIK3CA promotes cell growth and invasion of human cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhawer, M.; Goel, S.; Wilson, A.J.; Montagna, C.; Ling, Y.-H.; Byun, D.-S.; Nasser, S.; Arango, D.; Shin, J.; Klampfer, L.; et al. PIK3CA mutation/PTEN expression status predicts response of colon cancer cells to the epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cetuximab. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lièvre, A.; Ouine, B.; Canet, J.; Cartier, A.; Amar, Y.; Cacheux, W.; Mariani, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Selves, J.; Lecomte, T.; et al. Protein biomarkers predictive for response to anti-EGFR treatment in RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzzo, A.; Graziano, F.; Canestrari, E.; Magnani, M. Molecular predictors of efficacy to anti-EGFR agents in colorectal cancer patients. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2010, 10, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halder, S.; Basu, S.; Lall, S.P.; Ganti, A.K.; Batra, S.K.; Seshacharyulu, P. Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy: What’s new in 2023? Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2023, 27, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, J.; Dutta, S.; Upreti, V.V. Panitumumab: A Review of Clinical Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacology Properties After over a Decade of Experience in Patients with Solid Tumors. Adv. Ther. 2021, 38, 3712–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincenzi, B.; Schiavon, G.; Silletta, M.; Santini, D.; Tonini, G. The biological properties of cetuximab. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2008, 68, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurai, J.; Chikumi, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yamasaki, A.; Sako, T.; Touge, H.; Makino, H.; Takata, M.; Miyata, M.; et al. Antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity mediated by cetuximab against lung cancer cell lines. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracasso, P.M.; Burris, H.; Arquette, M.A.; Govindan, R.; Gao, F.; Wright, L.P.; Goodner, S.A.; Greco, F.A.; Jones, S.F.; Willcut, N.; et al. A phase 1 escalating single-dose and weekly fixed-dose study of cetuximab: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic rationale for dosing. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 986–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Weiner, L.M.; Belldegrun, A.S.; Crawford, J.; Tolcher, A.W.; Lockbaum, P.; Arends, R.H.; Navale, L.; Amado, R.G.; Schwab, G.; Figlin, R.A. Dose and schedule study of panitumumab monotherapy in patients with advanced solid malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltz, L.B.; Lenz, H.-J.; Kindler, H.L.; Hochster, H.S.; Wadler, S.; Hoff, P.M.; Kemeny, N.E.; Hollywood, E.M.; Gonen, M.; Quinones, M.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of cetuximab, bevacizumab, and irinotecan compared with cetuximab and bevacizumab alone in irinotecan-refractory colorectal cancer: The BOND-2 study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4557–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Lang, I.; Folprecht, G.; Nowacki, M.; Barone, C.; Shchepotin, I.; Maurel, J.; Cunningham, D.; Celik, I.; Kohne, C. Cetuximab plus FOLFIRI: Final data from the CRYSTAL study on the association of KRAS and BRAF biomarker status with treatment outcome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douillard, J.Y.; Siena, S.; Cassidy, J.; Tabernero, J.; Burkes, R.; Barugel, M.; Humblet, Y.; Bodoky, G.; Cunningham, D.; Jassem, J.; et al. Final results from PRIME: Randomized phase III study of panitumumab with FOLFOX4 for first-line treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1346–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, T.J.; Peeters, M.; Kim, T.W.; Li, J.; Cascinu, S.; Ruff, P.; Suresh, A.S.; Thomas, A.; Tjulandin, S.; Zhang, K.; et al. Panitumumab versus cetuximab in patients with chemotherapy-refractory wild-type KRAS exon 2 metastatic colorectal cancer (ASPECCT): A randomised, multicentre, open-label, non-inferiority phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Fiore, F.; Blanchard, F.; Charbonnier, F.; Le Pessot, F.; Lamy, A.; Galais, M.P.; Bastit, L.; Killian, A.; Sesboüé, R.; Tuech, J.J.; et al. Clinical relevance of KRAS mutation detection in metastatic colorectal cancer treated by Cetuximab plus chemotherapy. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowland, A.; Dias, M.M.; Wiese, M.D.; Kichenadasse, G.; McKinnon, R.A.; Karapetis, C.S.; Sorich, M.J. Meta-analysis comparing the efficacy of anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapy between KRAS G13D and other KRAS mutant metastatic colorectal cancer tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 55, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, C.; Liao, R.-Y.; Qiu, L.-X.; Wang, X.-W.; Ding, H.; Chen, Q. BRAF V600E mutation and resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 2219–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.; Muro, K.; Shitara, K.; Yamazaki, K.; Shiozawa, M.; Ohori, H.; Takashima, A.; Yokota, M.; Makiyama, A.; Akazawa, N.; et al. Panitumumab vs Bevacizumab Added to Standard First-Line Chemotherapy and Overall Survival Among Patients with RAS Wild-type, Left-Sided Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2023, 329, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holch, J.W.; Ricard, I.; Stintzing, S.; Modest, D.P.; Heinemann, V. The relevance of primary tumour location in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis of first-line clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 70, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baran, B.; Mert Ozupek, N.; Yerli Tetik, N.; Acar, E.; Bekcioglu, O.; Baskin, Y. Difference Between Left-Sided and Right-Sided Colorectal Cancer: A Focused Review of Literature. Gastroenterol. Res. 2018, 11, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Yoshino, T.; Van Cutsem, E.; Eng, C.; Kim, T.W.; Wasan, H.S.; Desai, J.; Ciardiello, F.; Yaeger, R.; Maughan, T.S.; et al. Encorafenib, cetuximab and chemotherapy in BRAF-mutant colorectal cancer: A randomized phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.; Anami, Y.; High, P.C.; Liang, Z.; Subramanian, S.; Ghosh, S.C.; AghaAmiri, S.; Guernsey-Biddle, C.; Tran, H.; Rowe, J.; et al. Antibody-Drug Conjugates Targeting the EGFR Ligand Epiregulin Elicit Robust Antitumor Activity in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, 973–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisheh, L.; Matis, S.; Taglieri, M.; Di Gregorio, L.; Benelli, R.; Poggi, A. EGFR-Targeted Antibody-Drug Conjugate to Different Aminobisphosphonates: Direct and Indirect Antitumor Effects on Colorectal Carcinoma Cells. Cancers 2024, 16, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopetz, S.; Boni, V.; Kato, K.; Raghav, K.P.S.; Pallis, A.; Habermehl, C.; Galipelli, S.; Courlet, P.; Rodriguez Rivera, I. First-in-human trial of M9140, an anti-CEACAM5 antibody drug conjugate (ADC) with exatecan payload, in patients (pts) with metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, L.; Parseghian, C.M.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.; Pan, H.; Gu, S.; Li, C.; et al. Abstract CT168: EMB-01, an EGFR/cMET bispecific antibody, in metastatic colorectal cancer: Results from an international phase Ib/II study. Cancer Res. 2025, 85, CT168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argiles, G.; Jungels, C.; Garcia-Carbonero, R.; Diez Garcia, M.; Bendell, J.C.; Tabernero, J.; Bekradda, M.; Lammerts van Bueren, J.; Bol, K.; Stalbovskaya, V.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation study of MCLA-158, a first-in-class bispecific antibody targeting EGFR and LGR5, in metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, H.-J.; Overman, M.J.; Van Cutsem, E.; Limon, M.L.; Wong, K.Y.M.; Hendlisz, A.; Aglietta, M.; Garcia-Alfonso, P.; Neyns, B.; Gelsomino, F.; et al. First-line (1L) nivolumab (NIVO) + ipilimumab (IPI) in patients (pts) with microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC): 64-month (mo) follow-up from CheckMate 142. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgadir, O.; Kuo, Y.-F.; Okorodudu, A.O.; Khan, M.F.; Cheng, Y.-W.; Dong, J. KRAS, NRAS, and BRAF Hot-Spot Mutations in Relation to Sidedness of Primary Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Diagnostics 2025, 15, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranđelović, I.; Nyíri, K.; Koppány, G.; Baranyi, M.; Tóvári, J.; Kigyós, A.; Tímár, J.; Vértessy, B.G.; Grolmusz, V. Gluing GAP to RAS Mutants: A New Approach to an Old Problem in Cancer Drug Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ríos-Hoyo, A.; Monzonís, X.; Vidal, J.; Linares, J.; Montagut, C. Unveiling acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer: A long and winding road. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1398419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.W.; Price, T.; Grasselli, J.; Strickler, J.H.; Masuishi, T.; Kwok, G.W.; Yalcin, S.; Obiozor, C.C.; Chan, E.; Gokani, P.; et al. A phase 3 study of first-line sotorasib, panitumumab, and FOLFIRI versus FOLFIRI with or without bevacizumab-awwb for patients with KRAS G12C–mutated metastatic colorectal cancer (CodeBreaK 301). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, TPS326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietrantonio, F.; Petrelli, F.; Coinu, A.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Borgonovo, K.; Maggi, C.; Cabiddu, M.; Iacovelli, R.; Bossi, I.; Lonati, V.; et al. Predictive role of BRAF mutations in patients with advanced colorectal cancer receiving cetuximab and panitumumab: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2015, 51, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, S.; Miller-Phillips, L.; Modest, D.P.; Fischer von Weikersthal, L.; Decker, T.; Kiani, A.; Vehling-Kaiser, U.; Al-Batran, S.-E.; Heintges, T.; Kahl, C.; et al. Impact of BRAF and RAS mutations on first-line efficacy of FOLFIRI plus cetuximab versus FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab: Analysis of the FIRE-3 (AIO KRK-0306) study. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 79, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stintzing, S.; Heinrich, K.; Tougeron, D.; Modest, D.P.; Schwaner, I.; Eucker, J.; Pihusch, R.; Stauch, M.; Kaiser, F.; Kahl, C.; et al. FOLFOXIRI Plus Cetuximab or Bevacizumab as First-Line Treatment of BRAFV600E-Mutant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: The Randomized Phase II FIRE-4.5 (AIO KRK0116) Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4143–4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzamiglio, M.; Soulabaille, A.; Lahlou, W.; Pilla, L.; Zaanan, A.; Taieb, J. Advances and challenges in targeted therapies for HER2-amplified colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2025, 222, 115471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alfonso, P.; Valladares-Ayerbes, M.; Muñoz Martín, A.J.; Morales Herrero, R.; Galvez Muñoz, E.; Prat-Llorens, G. State of the art of the molecular hyperselection to guide treatment with anti-EGFR antibodies in RAS WT mCRC: Implications for clinical practice and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2025, 25, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonesaka, K.; Zejnullahu, K.; Okamoto, I.; Satoh, T.; Cappuzzo, F.; Souglakos, J.; Ercan, D.; Rogers, A.; Roncalli, M.; Takeda, M.; et al. Activation of ERBB2 signaling causes resistance to the EGFR-directed therapeutic antibody cetuximab. Sci. Transl. Med. 2011, 3, 99ra86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Normanno, N. HER2 Signaling and Resistance to the Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody Cetuximab: A Further Step toward Personalized Medicine for Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 472–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, K.; Loree, J.M.; Morris, J.S.; Overman, M.J.; Yu, R.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Menter, D.; Korphaisarn, K.; Kee, B.; Muranyi, A.; et al. Validation of HER2 Amplification as a Predictive Biomarker for Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Antibody Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekaii-Saab, T.S.; Lach, K.; Hsu, L.-I.; Siadak, M.; Stecher, M.; Ward, J.; Beckerman, R.; Strickler, J.H. Impact of Anti-EGFR Therapies on HER2-Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis of Clinical Outcomes. Oncologist 2023, 28, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshino, T.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Raghav, K.; Masuishi, T.; Loupakis, F.; Kawakami, H.; Yamaguchi, K.; Nishina, T.; Wainberg, Z.; Elez, E.; et al. Final results of DESTINY-CRC01 investigating trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-expressing metastatic colorectal cancer. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Lonardi, S.; Martino, C.; Fenocchio, E.; Tosi, F.; Ghezzi, S.; Leone, F.; Bergamo, F.; Zagonel, V.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Pertuzumab and trastuzumab emtansine in patients with HER2-amplified metastatic colorectal cancer: The phase II HERACLES-B trial. ESMO Open 2020, 5, e000911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickler, J.H.; Cercek, A.; Siena, S.; André, T.; Ng, K.; Van Cutsem, E.; Wu, C.; Paulson, A.S.; Hubbard, J.M.; Coveler, A.L.; et al. Tucatinib plus trastuzumab for chemotherapy-refractory, HER2-positive, RAS wild-type unresectable or metastatic colorectal cancer (MOUNTAINEER): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meric-Bernstam, F.; Hurwitz, H.; Raghav, K.P.S.; McWilliams, R.R.; Fakih, M.; VanderWalde, A.; Swanton, C.; Kurzrock, R.; Burris, H.; Sweeney, C.; et al. Pertuzumab plus trastuzumab for HER2-amplified metastatic colorectal cancer (MyPathway): An updated report from a multicentre, open-label, phase 2a, multiple basket study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Okamoto, W.; Sawada, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Kato, K.; Taniguchi, H.; Kato, T.; Nishina, T.; Esaki, T.; Nomura, H.; et al. TRIUMPH Study: A multicenter Phase II study to evaluate efficacy and safety of combination therapy with trastuzumab and pertuzumab in patients with HER2-positive metastatic colorectal cancer (EPOC1602). Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, v207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Okamoto, W.; Kato, T.; Esaki, T.; Kato, K.; Komatsu, Y.; Yuki, S.; Masuishi, T.; Nishina, T.; Ebi, H.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA-guided treatment with pertuzumab plus trastuzumab for HER2-amplified metastatic colorectal cancer: A phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1899–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Michelini, F.; Shao, H.; Yeh, C.; Drago, J.Z.; Liu, D.; Rosiek, E.; Romin, Y.; Ghafourian, N.; Thyparambil, S.; et al. EGFR-directed antibodies promote HER2 ADC internalization and efficacy. Cell Rep. Med. 2024, 5, 101792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tang, R.; Jiang, L.; Jia, Y. The role of PIK3CA gene mutations in colorectal cancer and the selection of treatment strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1494802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, F.L.; Jorissen, R.N.; Lipton, L.; Mouradov, D.; Sakthianandeswaren, A.; Christie, M.; Li, S.; Tsui, C.; Tie, J.; Desai, J.; et al. PIK3CA and PTEN Gene and Exon Mutation-Specific Clinicopathologic and Molecular Associations in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Martini, M.; Molinari, F.; Veronese, S.; Nichelatti, M.; Artale, S.; Di Nicolantonio, F.; Saletti, P.; De Dosso, S.; Mazzucchelli, L.; et al. PIK3CA Mutations in Colorectal Cancer Are Associated with Clinical Resistance to EGFR-Targeted Monoclonal Antibodies. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1851–1857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent-Puig, P.; Cayre, A.; Manceau, G.; Buc, E.; Bachet, J.-B.; Lecomte, T.; Rougier, P.; Lievre, A.; Landi, B.; Boige, V.; et al. Analysis of PTEN, BRAF, and EGFR status in determining benefit from cetuximab therapy in wild-type KRAS metastatic colon cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 5924–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrone, F.; Lampis, A.; Orsenigo, M.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Gevorgyan, A.; Losa, M.; Frattini, M.; Riva, C.; Andreola, S.; Bajetta, E.; et al. PI3KCA/PTEN deregulation contributes to impaired responses to cetuximab in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Shi, J.; Feng, H.; Yu, Z.; Gao, Y. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers for anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody therapy in RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardelli, A.; Corso, S.; Bertotti, A.; Hobor, S.; Valtorta, E.; Siravegna, G.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Scala, E.; Cassingena, A.; Zecchin, D.; et al. Amplification of the MET receptor drives resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in colorectal cancer. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 658–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Religa, P.; Łazarczyk, M.; Mickael, M.-E.; Skiba, D.S. Misleading Interpretations of the MET Gene Acronym: Over 15 Years of Confusion in Scientific Publications and a Call for Reaffirming the Original Gene Nomenclature. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2025, 20, 1032–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, C.S.; Park, M.; Blair, D.G.; Tainsky, M.A.; Huebner, K.; Croce, C.M.; Vande Woude, G.F. Molecular cloning of a new transforming gene from a chemically transformed human cell line. Nature 1984, 311, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randon, G.; Maddalena, G.; Germani, M.M.; Pircher, C.C.; Manca, P.; Bergamo, F.; Giordano, M.; Sposetti, C.; Montagna, A.; Vetere, G.; et al. Negative Ultraselection of Patients with RAS/BRAF Wild-Type, Microsatellite-Stable Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Receiving Anti-EGFR-Based Therapy. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2022, 6, e2200037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, G.; Sun, X.; Ni, S.; Tan, C.; Xu, M.; Huang, D.; Ren, F.; Li, D.; Wei, P.; et al. MET amplification, expression, and exon 14 mutations in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 77, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghav, K.; Morris, V.; Tang, C.; Morelli, P.; Amin, H.M.; Chen, K.; Manyam, G.C.; Broom, B.; Overman, M.J.; Shaw, K.; et al. MET amplification in metastatic colorectal cancer: An acquired response to EGFR inhibition, not a de novo phenomenon. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 54627–54631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, C.; Bessudo, A.; Hart, L.L.; Severtsev, A.; Gladkov, O.; Müller, L.; Kopp, M.V.; Vladimirov, V.; Langdon, R.; Kotiv, B.; et al. A randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 study of tivantinib (ARQ 197) in combination with irinotecan and cetuximab in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer with wild-type KRAS who have received first-line systemic therapy. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, P.J.; Der, C.J. Targeting the Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the treatment of cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3291–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.-K.; Park, J.-I. MEK1/2 Inhibitors: Molecular Activity and Resistance Mechanisms. Semin. Oncol. 2015, 42, 849–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauri, G.; Patelli, G.; Gori, V.; Lauricella, C.; Mussolin, B.; Amatu, A.; Bencardino, K.; Tosi, F.; Bonazzina, E.; Bonoldi, E.; et al. Case Report: MAP2K1 K57N mutation is associated with primary resistance to anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies in metastatic colorectal cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 1030232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Chen, J.H.; Chao, S.X.; Pelka, K.; Giannakis, M.; Hess, J.; Burke, K.; Jorgji, V.; Sindurakar, P.; Braverman, J.; et al. Combined PD-1, BRAF and MEK inhibition in BRAFV600E colorectal cancer: A phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Jeong, E.G.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Mutational analysis of oncogenic AKT E17K mutation in common solid cancers and acute leukaemias. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 1533–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiphrakpam, P.D.; Rajappa, S.J.; Krishnan, M.; Batra, R.; Murthy, S.S.; Are, C. Colorectal cancer: Review of signaling pathways and associated therapeutic strategies. J. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 127, 1277–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hechtman, J.F.; Sadowska, J.; Huse, J.T.; Borsu, L.; Yaeger, R.; Shia, J.; Vakiani, E.; Ladanyi, M.; Arcila, M.E. AKT1 E17K in Colorectal Carcinoma Is Associated with BRAF V600E but Not MSI-H Status: A Clinicopathologic Comparison to PIK3CA Helical and Kinase Domain Mutants. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mayer, E.L.; Ren, Y.; Wagle, N.; Mahtani, R.; Ma, C.; DeMichele, A.; Cristofanilli, M.; Meisel, J.; Miller, K.D.; Abdou, Y.; et al. PACE: A Randomized Phase II Study of Fulvestrant, Palbociclib, and Avelumab After Progression on Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4/6 Inhibitor and Aromatase Inhibitor for Hormone Receptor–Positive/Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor–Negative Metastatic Breast Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 2050–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, K.; Lee, J.; Park, J.O.; Lim, H.Y.; Park, Y.S.; Kang, W.K.; Kim, S.T. The Impact of Cetuximab Plus AKT- or mTOR- Inhibitor in a Patient-Derived Colon Cancer Cell Model with Wild-Type RAS and PIK3CA Mutation. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2713–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; He, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Y. Ipatasertib, a novel Akt inhibitor, induces transcription factor FoxO3a and NF-κB directly regulates PUMA-dependent apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkomes, P.; Lunger, I.; Luetticke, A.; Oppermann, E.; Haetscher, N.; Serve, H.; Holzer, K.; Bechstein, W.O.; Rieger, M.A. Selective AKT Inhibition by MK-2206 Represses Colorectal Cancer-Initiating Stem Cells. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2849–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, A.S.F.; Gundestrup, A.K.; Kleif, J.; Thanon, T.; Bertelsen, C.A. Accuracy of preoperative staging with multidetector computed tomography in colon cancer. Color. Dis. 2021, 23, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, C.; Castanaro, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Ni, M.; Young, T.M.; Zhang, L.; Burova, E.; Thurston, G. FGFR3-TACC3 fusion proteins act as naturally occurring drivers of tumor resistance by functionally substituting for EGFR/ERK signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Laetsch, T.W.; Kummar, S.; DuBois, S.G.; Lassen, U.N.; Demetri, G.D.; Nathenson, M.; Doebele, R.C.; Farago, A.F.; Pappo, A.S.; et al. Efficacy of Larotrectinib in TRK Fusion-Positive Cancers in Adults and Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V.; Cassier, P.A.; Siena, S.; Garralda, E.; Paz-Ares, L.; Garrido, P.; Nadal, E.; Vuky, J.; Lopes, G.; Kalemkerian, G.P.; et al. Pan-cancer efficacy of pralsetinib in patients with RET fusion-positive solid tumors from the phase 1/2 ARROW trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratti, M.; Grizzi, G.; Passalacqua, R.; Lampis, A.; Cereatti, F.; Grassia, R.; Hahne, J.C. NTRK fusions in colorectal cancer: Clinical meaning and future perspective. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2021, 25, 677–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifton, K.; Rich, T.A.; Parseghian, C.; Raymond, V.M.; Dasari, A.; Pereira, A.A.L.; Willis, J.; Loree, J.M.; Bauer, T.M.; Chae, Y.K.; et al. Identification of Actionable Fusions as an Anti-EGFR Resistance Mechanism Using a Circulating Tumor DNA Assay. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, PO.19.00141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, V. Tissue-agnostic cancer therapies: Promise, reality, and the path forward. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loree, J.M.; Wang, Y.; Syed, M.A.; Sorokin, A.V.; Coker, O.; Xiu, J.; Weinberg, B.A.; Vanderwalde, A.M.; Tesfaye, A.; Raymond, V.M.; et al. Clinical and functional characterization of atypical KRAS/NRAS mutations in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 4587–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, J.; Ros, J.; Élez, E. The Evolving Treatment Landscape in BRAF-V600E–Mutated Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2022, 42, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elez, E.; Yoshino, T.; Shen, L.; Lonardi, S.; Cutsem, E.V.; Eng, C.; Kim, T.W.; Wasan, H.S.; Desai, J.; Ciardiello, F.; et al. Encorafenib, Cetuximab, and mFOLFOX6 in BRAF-Mutated Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2025, 392, 2425–2437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Tran, B.; Tie, J.; Markman, B.; Ananda, S.; Tebbutt, N.C.; Michael, M.; Link, E.; Wong, S.Q.; Chandrashekar, S.; et al. A Phase Ib/II Trial of Combined BRAF and EGFR Inhibition in BRAF V600E Positive Metastatic Colorectal Cancer and Other Cancers: The EVICT (Erlotinib and Vemurafenib In Combination Trial) Study. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodwin, R.; Jonker, D.; Chen, E.; Kennecke, H.; Cabanero, M.; Tsao, M.-S.; Vickers, M.; Bohemier, C.; Lim, H.; Ritter, H.; et al. A phase Ib study of a PI3Kinase inhibitor BKM120 in combination with panitumumab in patients with KRAS wild-type advanced colorectal cancer. Investig. New Drugs 2020, 38, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lou, S.; Lu, J.; Zheng, F.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, E.; Cui, S.; Zhao, H. Selective PI3Kδ inhibitor TYM-3-98 suppresses AKT/mTOR/SREBP1-mediated lipogenesis and promotes ferroptosis in KRAS-mutant colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, T.M.; Payne, S.N.; Pasch, C.A.; Yueh, A.E.; Van De Hey, D.R.; Korkos, D.P.; Clipson, L.; Maher, M.E.; Matkowskyj, K.A.; Newton, M.A.; et al. Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibition in Colorectal Cancers with APC and PIK3CA Mutations. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, X.-F.; Zou, J.; Luo, Z.-H. Prognostic value of c-Met in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 3706–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimassa, L.; Bozzarelli, S.; Pietrantonio, F.; Cordio, S.; Lonardi, S.; Toppo, L.; Zaniboni, A.; Bordonaro, R.; Di Bartolomeo, M.; Tomasello, G.; et al. Phase II Study of Tivantinib and Cetuximab in Patients with KRAS Wild-type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer with Acquired Resistance to EGFR Inhibitors and Emergence of MET Overexpression: Lesson Learned for Future Trials with EGFR/MET Dual Inhibition. Clin. Color. Cancer 2019, 18, 125–132.E2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.; Wang, C.; Guo, Y.; Valenzuela, V.; Wu, J.; Fakih, M. MAP2K1 Mutations in Advanced Colorectal Cancer Predict Poor Response to Anti-EGFR Therapy and to Vertical Targeting of MAPK Pathway. Clin. Color. Cancer 2021, 20, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankner, M.; Rousselle, E.; Petrecca, S.; Fabi, F.; Nowakowski, A.; Lazaratos, A.-M.; Rajadurai, C.V.; Stein, A.J.B.; Bian, D.; Tai, P.; et al. Clinical Activity of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Inhibitors in Patients with MAP2K1 (MEK1)-Mutated Metastatic Cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, e2400199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Lee, S.J.; Park, J.O.; Lim, H.Y.; Kang, W.K.; Park, Y.S.; Lee, J. The impact of cetuximab plus AKT- or mTOR- inhibitor in patient-derived colon cancer cell model with RAS wild type and PIK3CA mutation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, e15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Z.; Yu, X.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, X.; Sun, H. Colorectal cancer heterogeneity and targeted therapy: Clinical implications, challenges and solutions for treatment resistance. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 64, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siravegna, G.; Mussolin, B.; Buscarino, M.; Corti, G.; Cassingena, A.; Crisafulli, G.; Ponzetti, A.; Cremolini, C.; Amatu, A.; Lauricella, C.; et al. Clonal evolution and resistance to EGFR blockade in the blood of colorectal cancer patients. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Siena, S.; Tonini, G.; Bardelli, A.; Santini, D. Overcoming dynamic molecular heterogeneity in metastatic colorectal cancer: Multikinase inhibition with regorafenib and the case of rechallenge with anti-EGFR. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2016, 51, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niida, A.; Mimori, K.; Shibata, T.; Miyano, S. Modeling colorectal cancer evolution. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 66, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardiello, F.; Bianco, R.; Caputo, R.; Caputo, R.; Damiano, V.; Troiani, T.; Melisi, D.; De Vita, F.; De Placido, S.; Bianco, A.R.; et al. Antitumor activity of ZD6474, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in human cancer cells with acquired resistance to antiepidermal growth factor receptor therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 784–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagut, C.; Dalmases, A.; Bellosillo, B.; Crespo, M.; Pairet, S.; Iglesias, M.; Salido, M.; Gallen, M.; Marsters, S.; Tsai, S.P.; et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nat. Med. 2012, 18, 221–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, S.; Bellosillo, B.; Siravegna, G.; Martínez, A.; Cañadas, I.; Lazzari, L.; Ferruz, N.; Russo, M.; Misale, S.; González, I.; et al. Emergence of Multiple EGFR Extracellular Mutations during Cetuximab Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2157–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.; Kaltenbrun, E.; Anderson, G.R.; Stephens, S.J.; Arena, S.; Bardelli, A.; Counter, C.M.; Wood, K.C. Codon bias imposes a targetable limitation on KRAS-driven therapeutic resistance. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, L.A.; Williams, R.T.; Wu, J.; Kinde, I.; Hecht, J.R.; Berlin, J.; Allen, B.; Bozic, I.; Reiter, J.G.; Nowak, M.A.; et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature 2012, 486, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misale, S.; Yaeger, R.; Hobor, S.; Scala, E.; Janakiraman, M.; Liska, D.; Valtorta, E.; Schiavo, R.; Buscarino, M.; Siravegna, G.; et al. Emergence of KRAS mutations and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR therapy in colorectal cancer. Nature 2012, 486, 532–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Siravegna, G.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Corti, G.; Crisafulli, G.; Ahronian, L.G.; Mussolin, B.; Kwak, E.L.; Buscarino, M.; Lazzari, L.; et al. Tumor Heterogeneity and Lesion-Specific Response to Targeted Therapy in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Albéniz, X.; Alonso, V.; Escudero, P.; Méndez, M.; Gallego, J.; Rodríguez, J.R.; Salud, A.; Fernández-Plana, J.; Manzano, H.; Zanui, M.; et al. Prospective Biomarker Study in Advanced RAS Wild-Type Colorectal Cancer: POSIBA Trial (GEMCAD 10-02). Oncologist 2019, 24, e1115–e1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montagut, C.; Argilés, G.; Ciardiello, F.; Poulsen, T.T.; Dienstmann, R.; Kragh, M.; Kopetz, S.; Lindsted, T.; Ding, C.; Vidal, J.; et al. Efficacy of Sym004 in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer with Acquired Resistance to Anti-EGFR Therapy and Molecularly Selected by Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e175245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbiah, V.; Baik, C.; Kirkwood, J.M. Clinical Development of BRAF plus MEK Inhibitor Combinations. Trends Cancer 2020, 6, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, S.M.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.T.; Hur, J.Y.; Ebert, P.J.; Calley, J.N.; Wulur, I.H.; Gopalappa, T.; Wong, S.S.; Qian, H.-R.; et al. Genomic characterization of intrinsic and acquired resistance to cetuximab in colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, S.; Heitzer, E.; Ulz, P.; Lafer, I.; Lax, S.; Auer, M.; Pichler, M.; Gerger, A.; Eisner, F.; Hoefler, G.; et al. Changes in colorectal carcinoma genomes under anti-EGFR therapy identified by whole-genome plasma DNA sequencing. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolston, A.; Khan, K.; Spain, G.; Barber, L.J.; Griffiths, B.; Gonzalez-Exposito, R.; Hornsteiner, L.; Punta, M.; Patil, Y.; Newey, A.; et al. Genomic and Transcriptomic Determinants of Therapy Resistance and Immune Landscape Evolution during Anti-EGFR Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2019, 36, 35–50.E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, C.M.; Lau, R.; Sanchez, A.; Sun, R.X.; Fong, E.J.; Doche, M.E.; Chen, O.; Jusuf, A.; Lenz, H.-J.; Larson, B.; et al. Anti-EGFR Therapy Induces EGF Secretion by Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts to Confer Colorectal Cancer Chemoresistance. Cancers 2020, 12, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, Q.; Li, Q. Resistance to anti-EGFR therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer: Underlying mechanisms and reversal strategies. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.; Johnson, K.A.; Lippert, A.E.L.; Kraus, S.G.; Emmerich, P.B.; Pasch, C.A.; Zhang, W.; Matkowskyj, K.A.; LeBeau, A.M.; Deming, D.A. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Proteins as Potential Targets against Colorectal Cancers. Cancers 2024, 16, 3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Quazi, S.; Arora, S.; Osellame, L.D.; Burvenich, I.J.; Janes, P.W.; Scott, A.M. Cancer-associated fibroblasts as therapeutic targets for cancer: Advances, challenges, and future prospects. J. Biomed. Sci. 2025, 32, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaquero, J.; Pavy, A.; Gonzalez-Sanchez, E.; Meredith, M.; Arbelaiz, A.; Fouassier, L. Genetic alterations shaping tumor response to anti-EGFR therapies. Drug Resist. Updates 2022, 64, 100863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahler, A.; Kind, A.J.; Sers, C.; Mamlouk, S.; Müller, L.; Karthaus, M.; Fruehauf, S.; Graeven, U.; Fischer Von Weikersthal, L.; Sommerhäuser, G.; et al. Negative Hyperselection of Resistance Mutations for Panitumumab Maintenance in RAS Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer (PanaMa Phase II Trial, AIO KRK 0212). Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 30, 1256–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fucà, G.; Raimondi, A.; Prisciandaro, M.; Lonardi, S.; Cremolini, C.; Ratti, M.; Clavarezza, M.; Murialdo, R.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Smiroldo, V.; et al. Reinduction of an Anti-EGFR-based First-line Regimen in Patients with RAS Wild-type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Enrolled in the Valentino Study. Oncologist 2022, 27, e29–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitara, K.; Muro, K.; Watanabe, J.; Yamazaki, K.; Ohori, H.; Shiozawa, M.; Yasui, H.; Oki, E.; Sato, T.; Naito, T.; et al. Negative hyperselection of patients with RAS wild-type metastatic colorectal cancer for panitumumab: A biomarker study of the phase III PARADIGM trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morano, F.; Corallo, S.; Lonardi, S.; Raimondi, A.; Cremolini, C.; Rimassa, L.; Murialdo, R.; Zaniboni, A.; Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Tomasello, G.; et al. Negative Hyperselection of Patients with RAS and BRAF Wild-Type Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Who Received Panitumumab-Based Maintenance Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3099–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randon, G.; Pietrantonio, F. Towards Multiomics-Based Dissection of Anti-EGFR Sensitivity in Colorectal Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 4021–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.G.; Somer, R.A. Intratumor Heterogeneity: Novel Approaches for Resolving Genomic Architecture and Clonal Evolution. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assi, T.; Khoury, R.; Ibrahim, R.; Baz, M.; Ibrahim, T.; Le Cesne, A. Overview of the role of liquid biopsy in cancer management. Transl. Oncol. 2023, 34, 101702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrillo, A.; Salati, M.; Trapani, D.; Ghidini, M. Circulating Tumor DNA as a Biomarker for Outcomes Prediction in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Curr. Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larribère, L.; Martens, U.M. Advantages and Challenges of Using ctDNA NGS to Assess the Presence of Minimal Residual Disease (MRD) in Solid Tumors. Cancers 2021, 13, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, K.C.S.; Ramos, I.B.; Silva, J.M.C.; Barra, W.F.; Riggins, G.J.; Palande, V.; Pinho, C.T.; Frenkel-Morgenstern, M.; Santos, S.E.B.; Assumpcao, P.P.; et al. Current Perspectives on Circulating Tumor DNA, Precision Medicine, and Personalized Clinical Management of Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2020, 18, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, S.; Okamura, R.; Mareboina, M.; Lee, S.; Goodman, A.; Patel, S.P.; Fanta, P.T.; Schwab, R.B.; Vu, P.; Raymond, V.M.; et al. Revisiting Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Amplification as a Target for Anti-EGFR Therapy: Analysis of Cell-Free Circulating Tumor DNA in Patients with Advanced Malignancies. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2019, 3, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van ’t Erve, I.; Greuter, M.J.E.; Bolhuis, K.; Vessies, D.C.L.; Leal, A.; Vink, G.R.; van den Broek, D.; Velculescu, V.E.; Punt, C.J.A.; Meijer, G.A.; et al. Diagnostic Strategies toward Clinical Implementation of Liquid Biopsy RAS/BRAF Circulating Tumor DNA Analyses in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. J. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 22, 1430–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sartore-Bianchi, A.; Pietrantonio, F.; Lonardi, S.; Mussolin, B.; Rua, F.; Crisafulli, G.; Bartolini, A.; Fenocchio, E.; Amatu, A.; Manca, P.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA to guide rechallenge with panitumumab in metastatic colorectal cancer: The phase 2 CHRONOS trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1612–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite da Silva, L.F.; Saldanha, E.F.; de Menezes, J.S.A.; Halamy Pereira, L.; de Bragança Dos Santos, J.A.R.; Buonopane, I.R.; de Souza, E.M.; de Menezes, C.U.G.; Lopes, G. Plasma ctDNA kinetics as a predictor of systemic therapy response for advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncologist 2025, 30, oyae344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malla, M.; Loree, J.M.; Kasi, P.M.; Parikh, A.R. Using Circulating Tumor DNA in Colorectal Cancer: Current and Evolving Practices. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2846–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenza, C.; Saldanha, E.F.; Gong, Y.; De Placido, P.; Gritsch, D.; Ortiz, H.; Trapani, D.; Conforti, F.; Cremolini, C.; Peters, S.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA clearance as a predictive biomarker of pathologic complete response in patients with solid tumors treated with neoadjuvant immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 2025, 36, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napolitano, S.; Parikh, A.R.; Henry, J.; Parseghian, C.M.; Willis, J.; Raghav, K.P.; Morris, V.K.; Johnson, B.; Kee, B.K.; Dasari, A.N.; et al. Novel Clinical Tool to Estimate Risk of False-Negative KRAS Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA Testing. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2023, 7, e2300228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, L.; Belloum, Y.; Wikman, H.; Pantel, K. Clinical relevance of blood-based ctDNA analysis: Mutation detection and beyond. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, Y.; Taniguchi, H.; Ikeda, M.; Bando, H.; Kato, K.; Morizane, C.; Esaki, T.; Komatsu, Y.; Kawamoto, Y.; Takahashi, N.; et al. Clinical utility of circulating tumor DNA sequencing in advanced gastrointestinal cancer: SCRUM-Japan GI-SCREEN and GOZILA studies. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1859–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, P.S.; Chan, G.; Deming, D.A.; Chee, C.E. State-of-the-Art Management of Colorectal Cancer: Treatment Advances and Innovation. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2024, 44, e438466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medford, A.J.; Ellisen, L.W. Optimizing Access to Liquid Biopsy in the Present and Future Cancer Landscape. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, e2300609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Guo, B. RNA-based therapeutics for colorectal cancer: Updates and future directions. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 152, 104550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boustany, L.M.; LaPorte, S.L.; Wong, L.; White, C.; Vinod, V.; Shen, J.; Yu, W.; Koditek, D.; Winter, M.B.; Moore, S.J.; et al. A Probody T Cell-Engaging Bispecific Antibody Targeting EGFR and CD3 Inhibits Colon Cancer Growth with Limited Toxicity. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 4288–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Patient Population | Biomarkers Evaluated | Overall Response Rate (%) | Median PFS (Months) | Median OS (Months) | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PanaMa Trial [140] | mCRC, RAS WT | BRAF V600E/PIK3CA/AKT1/ALK/ERBB2/PTEN MUT and HER2/neu | 35.8% in hyperselected vs. 25% | 7.5 months in hyperselected vs. 4.4 months | 28.7 months in hyperselected vs. 22.2 months | Hyperselected patients had significantly better PFS and OS with panitumumab maintenance. |
| Valentino Study [144] | mCRC, RAS WT | HER2/MET PIK3CA/PTEN mutations | N/A | 10.5 months in hyperselected vs. 6.03 months | 33.3 months in hyperselected vs. 14.1 months | Reinduction with panitumumab was more effective in hyperselected patients. |
| PANDA Trial [145] | Elderly mCRC, RAS WT, BRAF WT | HER2/MET NTRK/ROS1/ALK/RET PIK3CA PTEN AKT1 MAP2K1 | 71% in hyperselected vs. 51% | 12.8 months in hyperselected vs. 7.6 months | 29.5 months in hyperselected vs. 20 months | Elderly hyperselected patients showed better PFS and OS with anti-EGFR therapy. |
| PRESSING2 Study [87] | mCRC, RAS WT, MSS, POLE WT | ERBB2/MET NTRKs/RET/ROS1/ALK AKT1/PTEN/PIK3CA | 79% in hyperselected vs. 56% | 12.8 months in hyperselected vs. 6.4 months | 49.9 months in hyperselected vs. 22.6 months | Ultraselected patients (without rare mutations) had significantly better survival outcomes. |
| PARADIGM Study [17] | mCRC, RAS WT | PTEN/EGFR HER2/MET ALK/RET/NTRK1 | N/A | N/A | 41.4 months in hyperselected vs. 18.7 | Exploratory analyses suggest that ctDNA is useful to identify gene alterations that predict resistance to EGFR inhibition. |
| Morano et al. [146] | mCRC, RAS/BRAF WT | ALK/ROS1/NTRKs/RET HER2/PIK3CAex.20/PTEN/AKT1 | 75.3% in hyperselected vs. 59.2% | 12.1 months in hyperselected vs. 7.7 | 68.1 months in hyperselected vs. 48.1 | Patients with right-sided tumors and those without hyperselected tumors had significantly poor outcomes in terms of overall ORR, PFS, and OS. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leite, L.F.; Noronha, M.M.; de Menezes, J.S.A.; da Conceição, L.D.; Almeida, L.F.C.; Cappellaro, A.P.; Belotto, M.; Biachi de Castria, T.; Peixoto, R.D.; Megid, T.B.C. Anti-EGFR Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Identifying, Tracking, and Overcoming Resistance. Cancers 2025, 17, 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172804
Leite LF, Noronha MM, de Menezes JSA, da Conceição LD, Almeida LFC, Cappellaro AP, Belotto M, Biachi de Castria T, Peixoto RD, Megid TBC. Anti-EGFR Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Identifying, Tracking, and Overcoming Resistance. Cancers. 2025; 17(17):2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172804
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeite, Luís Felipe, Mariana Macambira Noronha, Junior Samuel Alonso de Menezes, Lucas Diniz da Conceição, Luiz F. Costa Almeida, Anelise Poluboiarinov Cappellaro, Marcos Belotto, Tiago Biachi de Castria, Renata D’Alpino Peixoto, and Thais Baccili Cury Megid. 2025. "Anti-EGFR Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Identifying, Tracking, and Overcoming Resistance" Cancers 17, no. 17: 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172804
APA StyleLeite, L. F., Noronha, M. M., de Menezes, J. S. A., da Conceição, L. D., Almeida, L. F. C., Cappellaro, A. P., Belotto, M., Biachi de Castria, T., Peixoto, R. D., & Megid, T. B. C. (2025). Anti-EGFR Therapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: Identifying, Tracking, and Overcoming Resistance. Cancers, 17(17), 2804. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17172804








