The Effects of Heat Stress on Dairy Cows
A special issue of Dairy (ISSN 2624-862X). This special issue belongs to the section "Dairy Animal Nutrition and Welfare".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 15 August 2026 | Viewed by 566
Special Issue Editors
Interests: dairy animal health; dairy cows; heat stress mitigation; milk quality; ruminant production and nutrition
Interests: dairy cattle production; nutrition; health and reproduction; heat stress mitigation; milk quality; ruminal microbiota
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
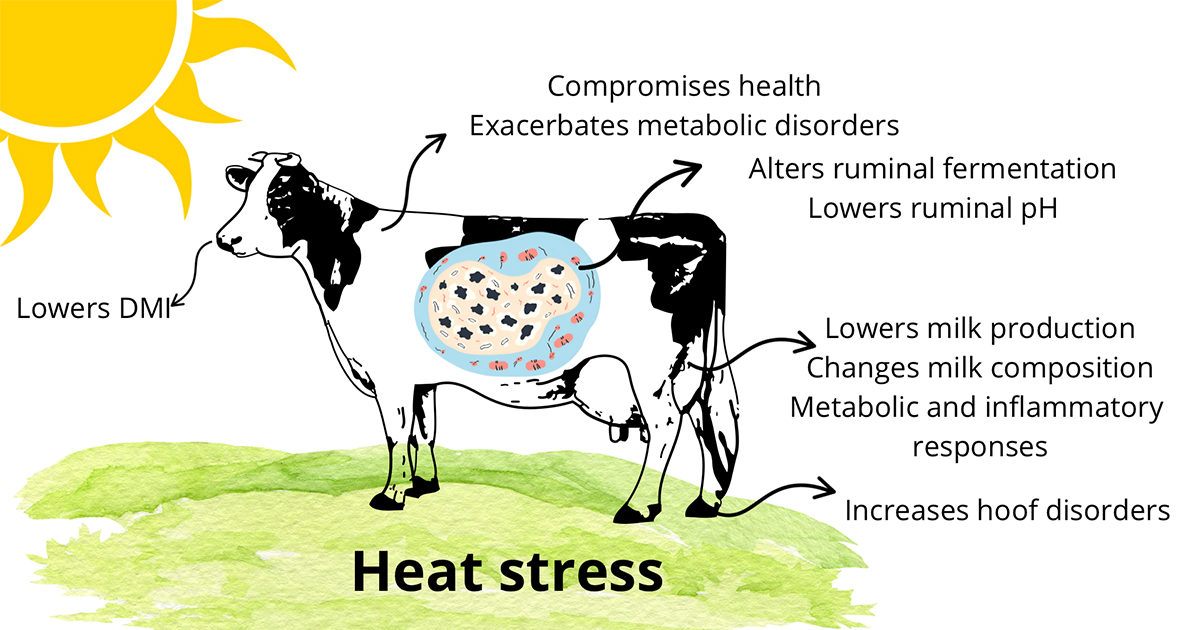
Extreme heat reduces feed intake due to thermoregulation mechanisms that limit ruminal heat production. The issues of limited water and low-quality feed worsen these challenges. Feeding shifts to nighttime grazing and slower digestion may improve nutrient absorption, but this is often offset by heat stress and water restriction. Heat stress also alters ruminal fermentation, lowering pH even when dry matter intake remains stable. In addition, the effects of heat stress in dairy cows have been reported as a reduction in dry matter intake and milk production, changes in milk composition and the milk fatty acid profile, systemic and mammary gland metabolic and inflammatory responses.
Creating an adequate environment for dairy cows has become increasingly essential, especially during the summer in tropical countries. Given climate change, the effects of heat stress on animals have intensified, making investigations into strategies to mitigate its impact on milk production even more relevant. Its effects can compromise the health of dairy cows at various stages, being more severe during the transition period. During this phase, heat stress exacerbates metabolic disorders such as ketosis and milk fever and increases the incidence of retained placenta, abomasal displacement, mastitis, and hoof disorders. Consequently, there is a negative impact on milk production and, most importantly, the quality of the milk produced by these animals.
We seek articles on heat stress in animals, particularly linked to water deprivation or infrequent intake in arid regions. This Special Issue will publish original articles that have not been previously published in other journals and that can significantly contribute to the advancement of science in the field of heat stress in dairy cattle. The primary focus will be on the impacts of heat stress on animal health, reproduction, and, most importantly, milk production and quality.
Prof. Dr. Geraldo Tadeu Dos Santos
Dr. Camila Soares Cunha
Guest Editors
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Dairy is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1400 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- dairy cows
- heat stress
- milk production
- health
- incidence of retained placenta
- mastitis
- metabolic disorders
- quality of the milk produced
- physiological thermal stress
- reproductive performance
- temperature and humidity index
- transition period
- immunity
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






