Solid-State Hydrogen Fuel by PSII–Chitin Composite and Application to Biofuel Cell
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
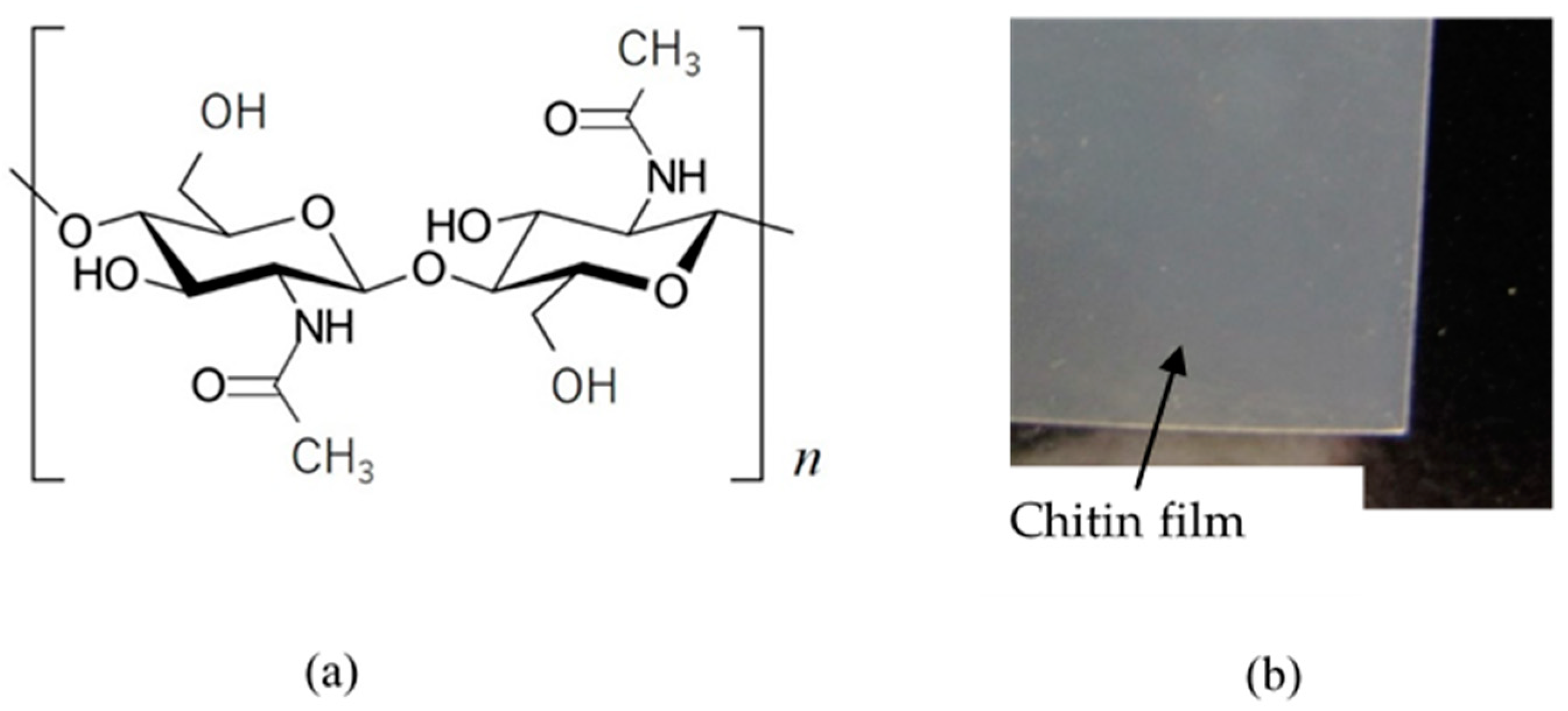
2.1. Bioelectrolyte “Chitin”
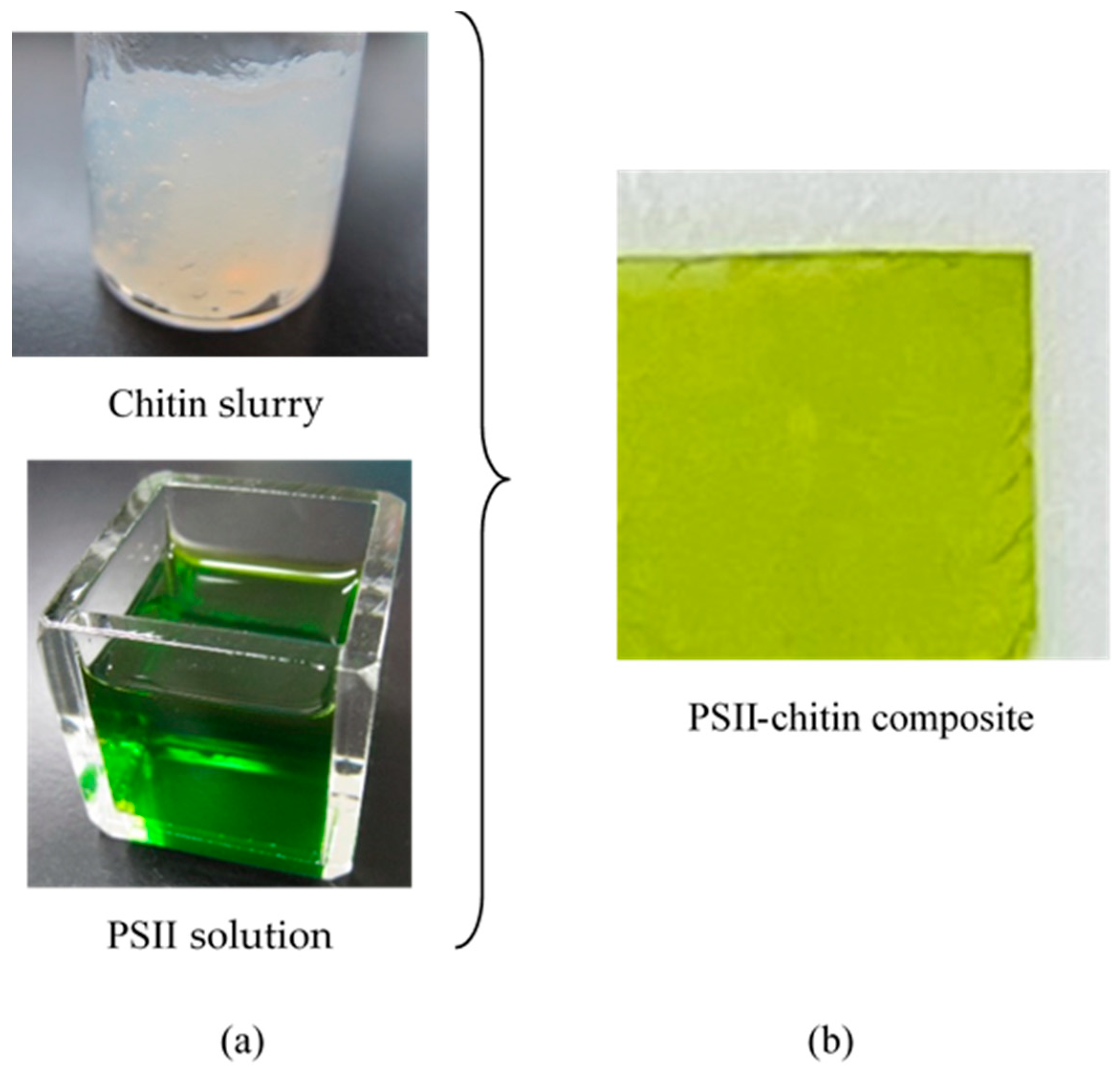
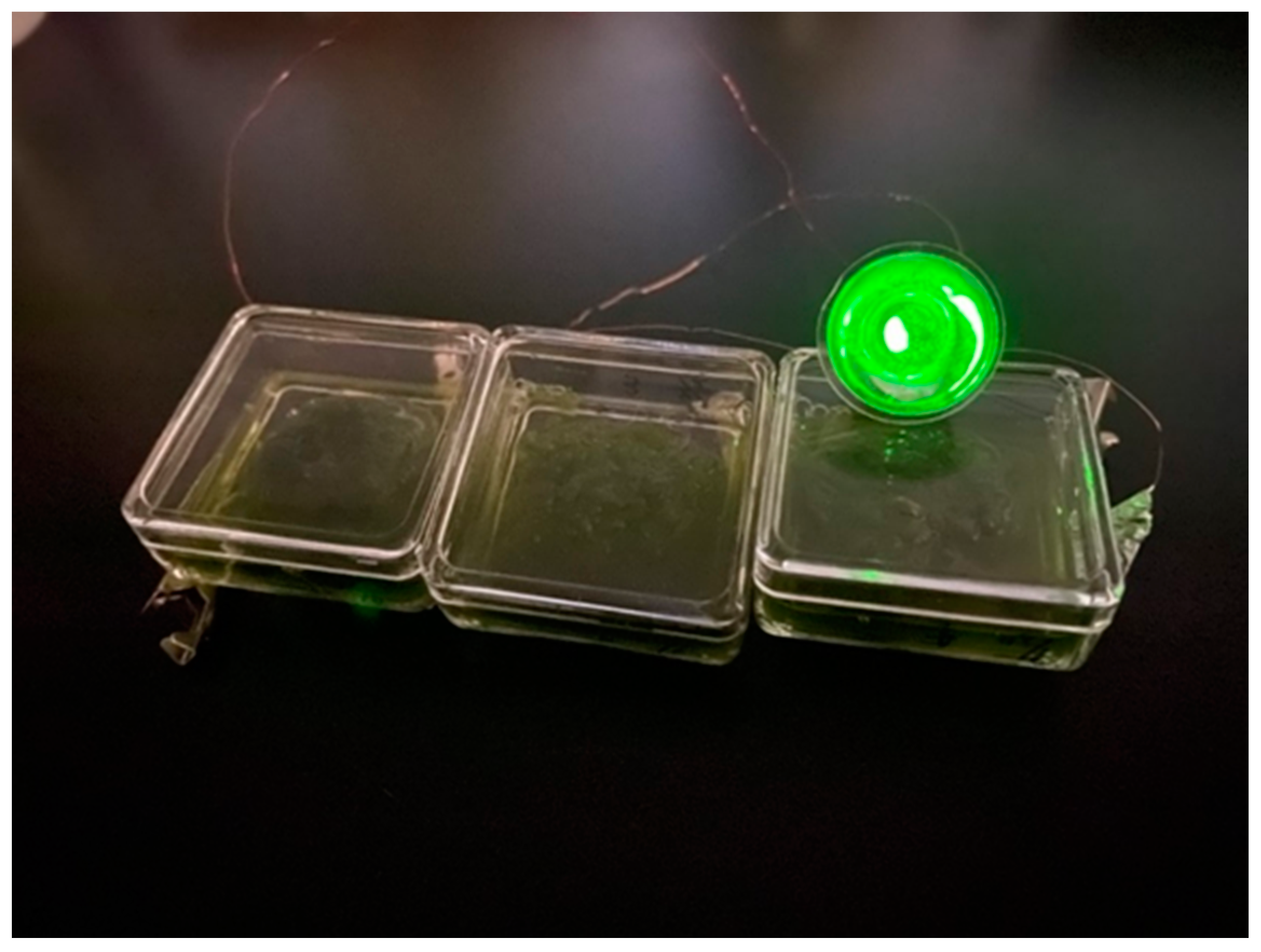
2.2. Preparation of PSII Containing Solution
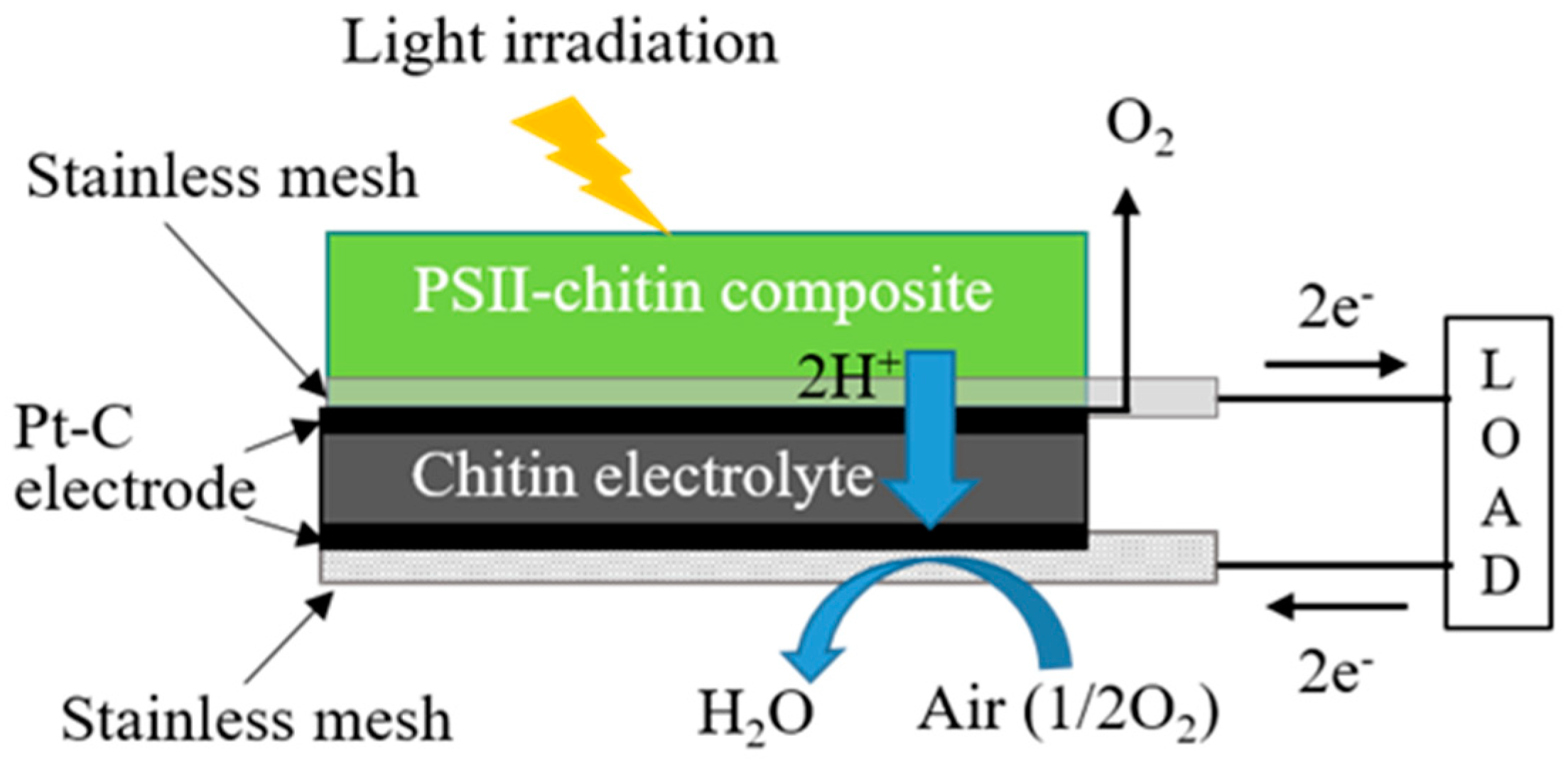
2.3. Preparation of Biofuel Cell Using Bioelectrolyte and Hydrogen Fuel Composed from the PSII–Chitin Composite
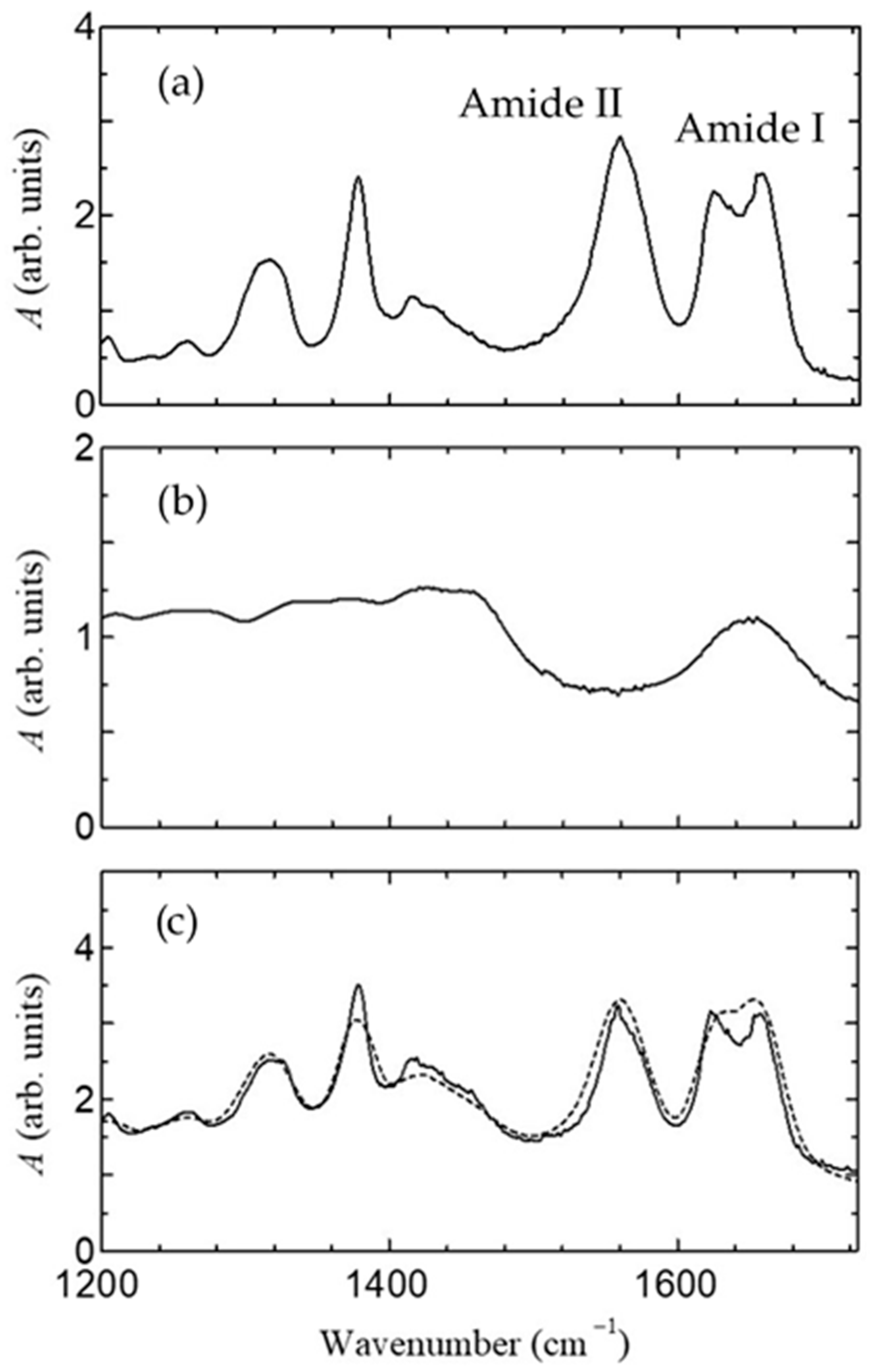
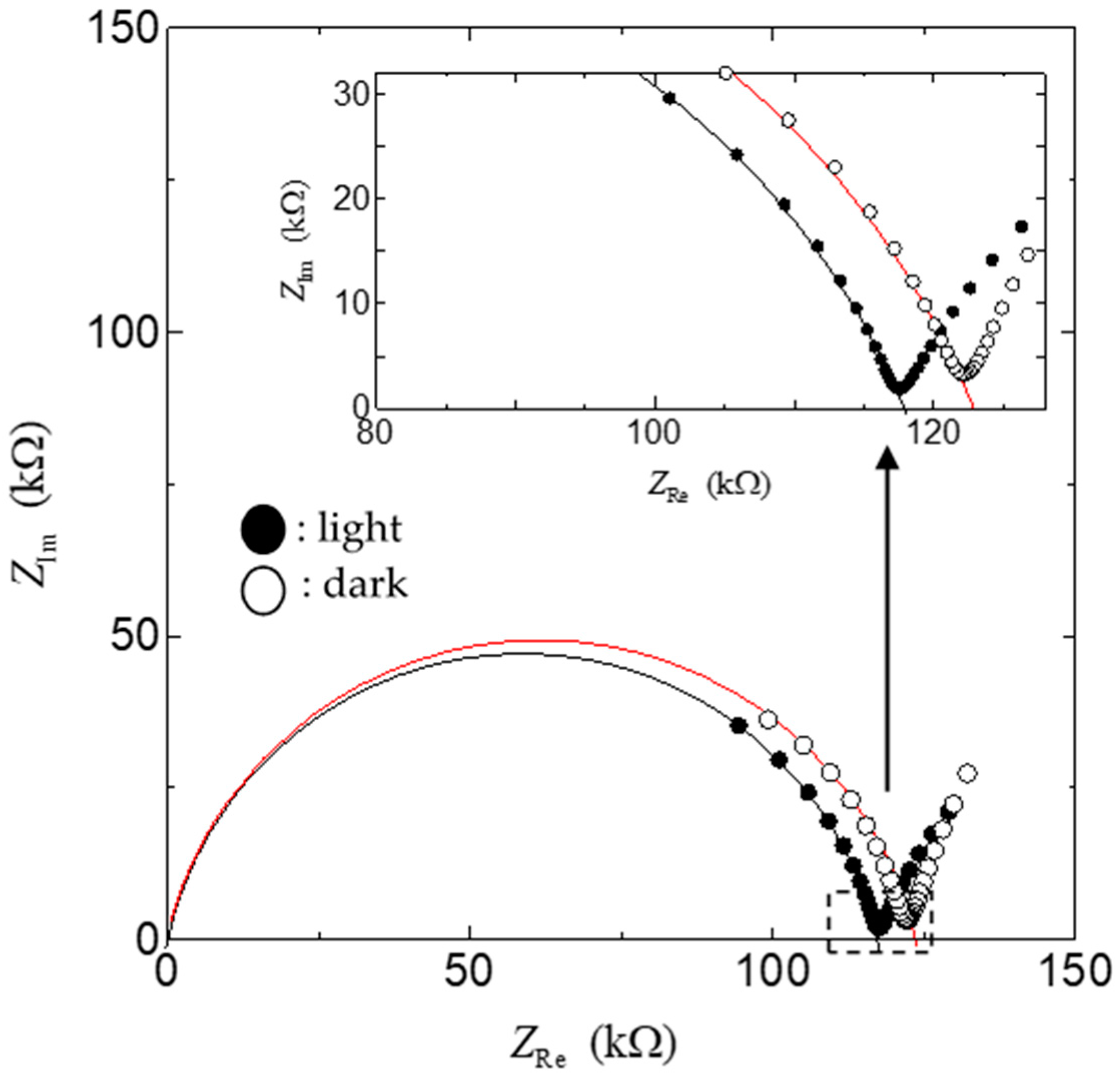
2.4. Measurement of FT-IR, Impedance, and Fuel Cell Characteristics
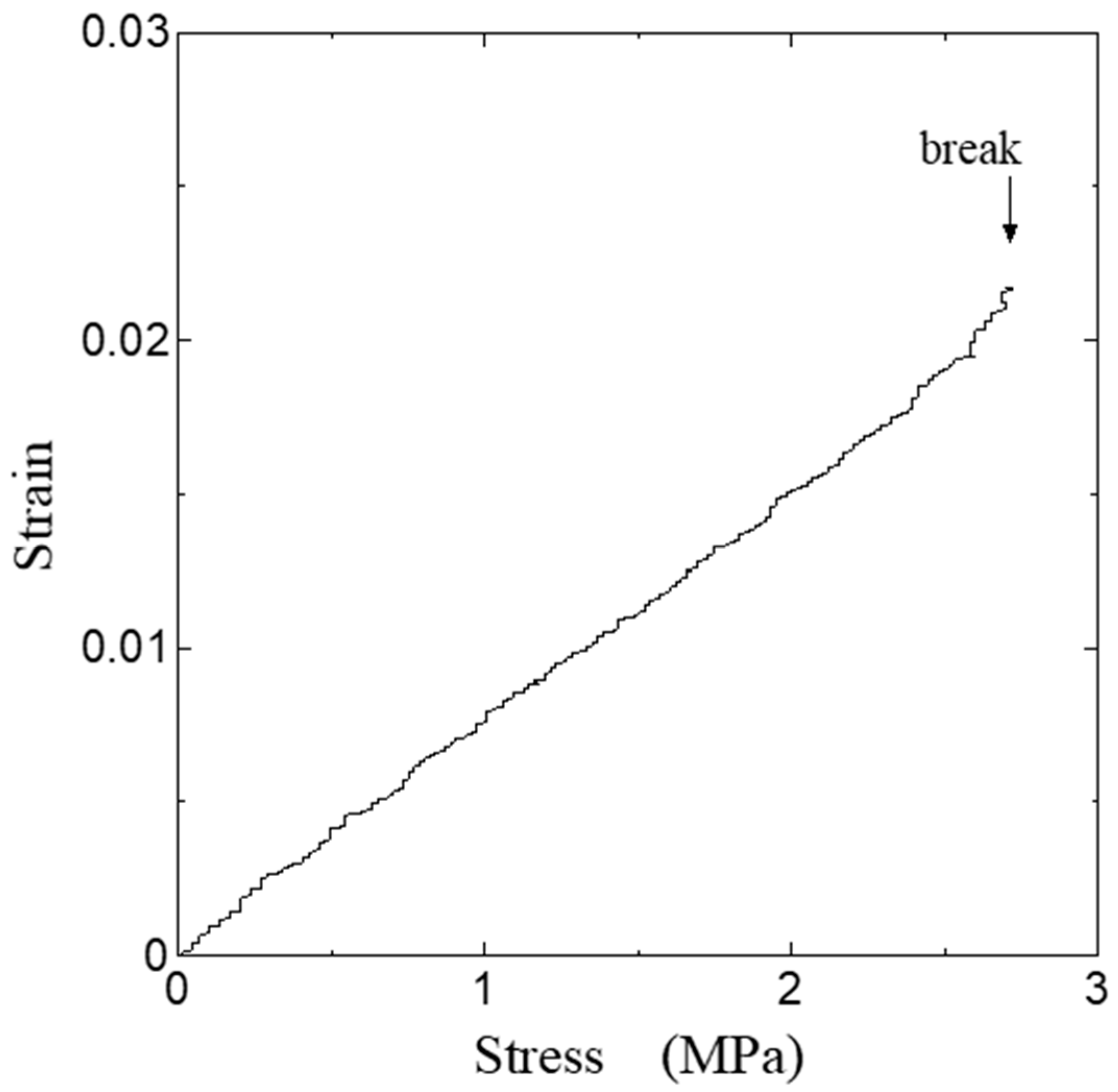
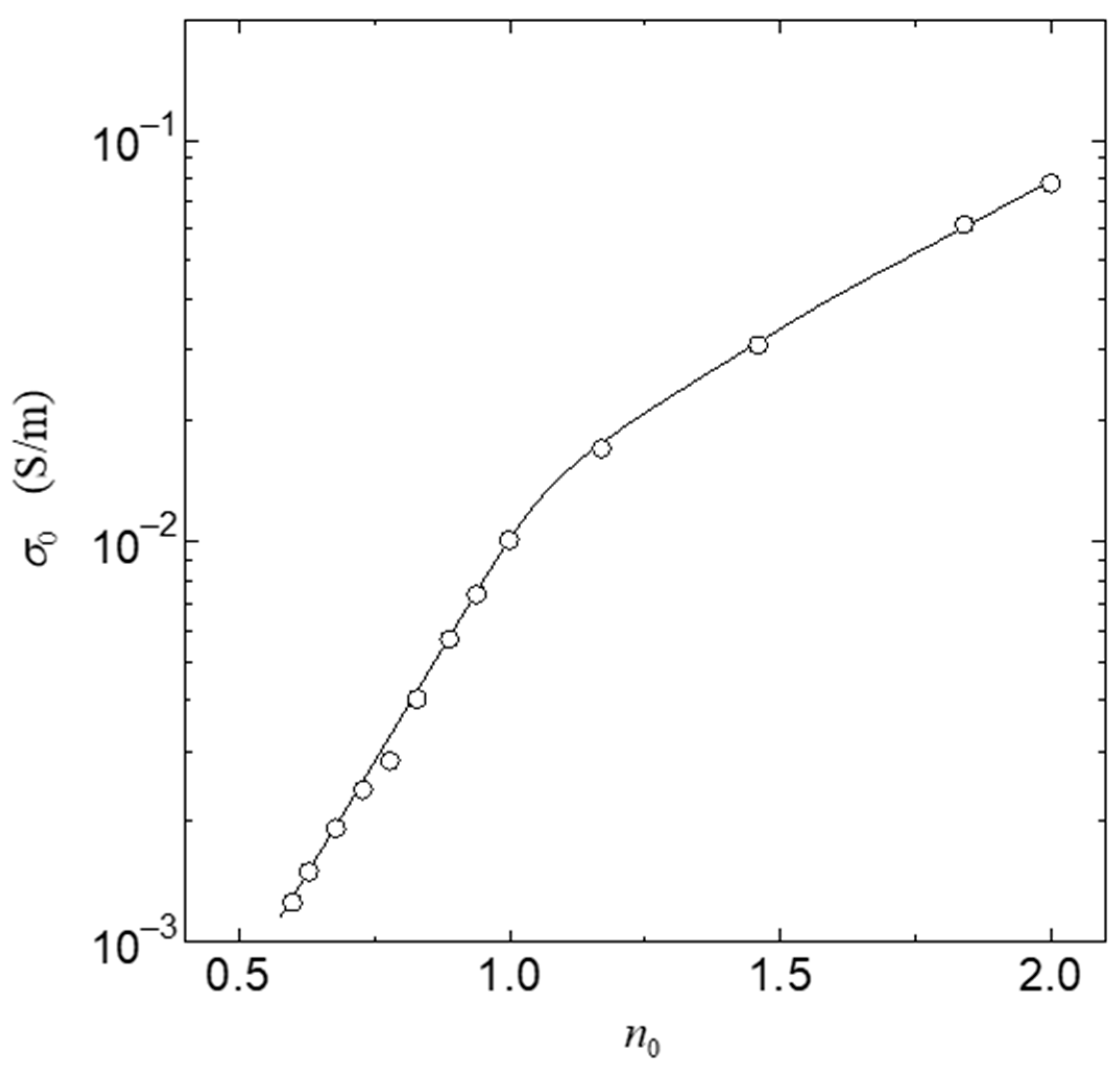
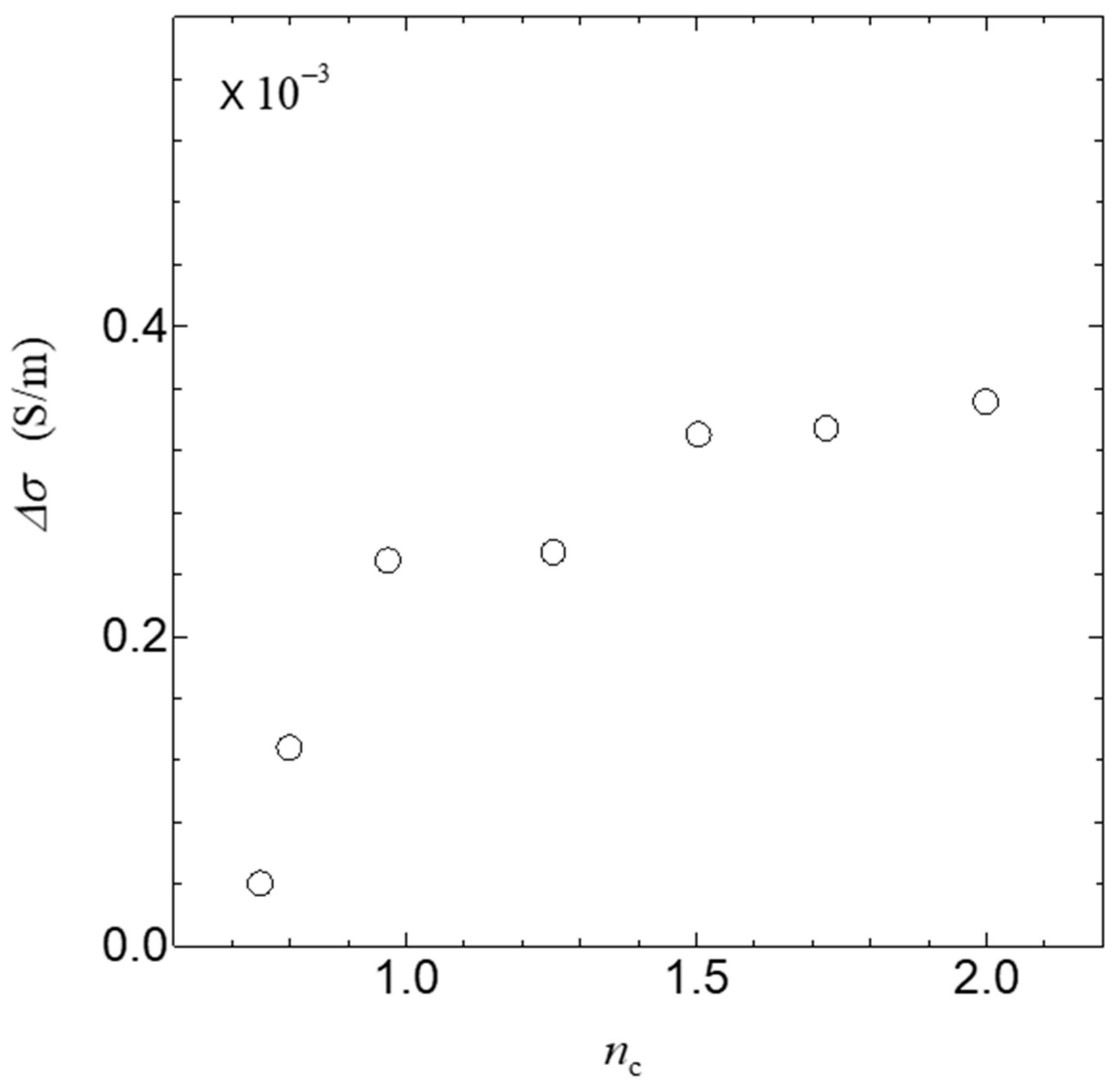
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrews, J.; Shabani, B. Where Does Hydrogen Fit in a Sustainable Energy Economy? Procedia Eng. 2012, 49, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viktorsson, L.; Heinonen, J.T.; Skulason, J.B.; Unnthorsson, R.A. Step towards the Hydrogen Economy–A Life Cycle Cost Analysis of a Hydrogen Refueling Station. Energies 2017, 10, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M.; Weeda, M. The Hydrogen Economy—Vision or reality? Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 7903–7919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulmier, T.; Fulcheri, L. Use of non-thermal plasma for hydrocarbon reforming. Chem. Eng. J. 2005, 106, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konieczny, A.; Mondal, K.; Wiltowski, T.; Dydo, P. Catalyst development for thermocatalytic decomposition of methane to hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaidis, P.; Poullikkas, A. A comparative overview of hydrogen processes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 67, 597–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M.; Balat, M. Political, economic and environmental impacts of biomass-based hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 3589–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holladay, J.D.; Hu, J.; King, D.L.; Wang, Y. An overview of hydrogen production technologies. Catal. Today 2009, 139, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norby, T. The Promise of Protonics. Nature 2001, 410, 877–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Kumasaka, G.; Saito, K.; Ikehata, S. Fabrication of solid-state fuel cell based on DNA film. Solid State Commun. 2005, 133, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Hatori, J.; Yoshida, Y.; Ikehata, S. Humidity Dependence of Proton Conductivity in DNA Film Studied by NMR and AC Conductivity. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 2014, 79, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, Y.; Hatori, J. Fuel Cell Based on Natural Sausage Casing. J. Biobased Mater. Bioenergy 2011, 5, 562–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Kawabata, T.; Hatori, J.; Oyama, H. Collagen-based fuel cell and its proton transfer. Mat. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matsuo, Y. Bio-Fuel Cell Based on Biopolymer Electrolyte. J. Fuel Cell Technol. 2014, 13, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Freier, E.; Wolf, S.; Gerwert, K. Proton transfer via a transient linear water-molecule chain in a membrane protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11435–11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ordinario, D.D.; Phan, L.; Wlkup IV, W.G.; Jocson, J.M.; Karshalev, E.; Hüsken, N.; Gorodetsky, A.A. Bulk protonic conductivity in a cephalopod structural protein. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 596–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, T.; Matsuo, Y. Chitin Based Fuel Cell and Its Proton Conductivity. Mat. Sci. Appl. 2018, 9, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kawabata, T.; Matsuo, Y. Role of acetyl group on proton conductivity in chitin system. J. Mater. 2019, 5, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhlaghi, N.; Najafpour-Darzi, G. A comprehensive review on biological. hydrogen production. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2020, 45, 22492–22512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wan, W. Effect of temperature on fermentative hydrogen production by mixed cultures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 5392–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Bai, Y.; Fan, Y.; Hou, H. Improved bio-hydrogen production from glucose by adding a specific methane inhibitor to microbial electrolysis cells with a double anode arrangement. J Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 16, 1389–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Ulrich, A.C.; Liu, Y. Coupling bioelectricity generation and oil sands tailings treatment using microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Liu, Y. Power generation and oil sands process-affected water treatment in microbial fuel cells. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 581–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batyrova, K.A.; Tsygankov, A.A.; Kosourov, S.N. Sustained hydrogen photo production by phosphorus-deprived Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cultures. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 8834–8839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sambusitia, C.; Bellucci, M.; Zabaniotou, A.; Beneduce, L.; Monlaua, F. Algae as promising feedstocks for fermentative biohydrogen production according to a biorefinery approach: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.M.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Guo, J.; Chang, W.S.; Nguyen, D.D.; Wang, J. Biohydrogen production from anaerobic digestion and its potential as renewable energy. Renew. Energy 2018, 129, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meher Kotay, S.; Das, D. Biohydrogen as a renewable energy resource prospects and potentials. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2008, 33, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagashima, H.; Asada, M.; Mino, H. Magnetic structure of manganese cluster in photosystem II investigated by electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys. Phys. 2018, 15, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, L. Why nature chose the Mn4CaO5 cluster as water-splitting catalyst in photosystem II: A new hypothesis for the mechanism of O–O bond formation. Dalton Trans. 2018, 41, 14381–14387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zouni, A.; Witt, H.-T.; Kern, J.; Fromme, P.; Krauss, N.; Saenger, W.; Orth, P. Crystal structure of photosystem II from Synechococcus elongatus at 3.8 Å resolution. Nature 2001, 409, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nugent, J.H.A.; Rich, A.M.; Evans, A.M. Photosynthetic water oxidation: Towards a mechanism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1503, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.P. Photosynthesis. Essays Biochem. 2016, 60, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ort, D.R.; Yocum, C.F. Light reactions of oxygenic photosynthesis. In Oxygenic Photosynthesis; Ort, D.R., Yocum, C.F., Eds.; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, J.-R.; Enami, I. Isolation of photosystem II. Low Temp. Sci. 2009, 67, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Miyao, M. Isolation of intact chloroplasts, thylakoids and photosystem II membranes from higher plants. Low Temp. Sci. 2009, 67, 197–203. [Google Scholar]
- Iwahashi, A.; Yamada, T.; Matsuo, Y.; Kawakami, H. Novel biofuel cell using hydrogen generation of photosynthesis. J. Funct. Biomater. 2020, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, T.; Kasai, Y.; Urayama, K.; Takizawa, T. Structure and mechanical properties of Nafion membranes. J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn. 2007, 56, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinaudo, M. Chitin and chitosan: Properties and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2006, 31, 603–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Miyake, T.; Rolandi, M. Grotthuss mechanisms: From proton transport in proton wires to bioprotonic devices. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2016, 28, 023001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, Y.; Iwahashi, A.; Matsuo, Y.; Kawakami, H. Solid-State Hydrogen Fuel by PSII–Chitin Composite and Application to Biofuel Cell. J. Compos. Sci. 2021, 5, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120317
Takahashi Y, Iwahashi A, Matsuo Y, Kawakami H. Solid-State Hydrogen Fuel by PSII–Chitin Composite and Application to Biofuel Cell. Journal of Composites Science. 2021; 5(12):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120317
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Yusuke, Akinari Iwahashi, Yasumitsu Matsuo, and Hinako Kawakami. 2021. "Solid-State Hydrogen Fuel by PSII–Chitin Composite and Application to Biofuel Cell" Journal of Composites Science 5, no. 12: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120317
APA StyleTakahashi, Y., Iwahashi, A., Matsuo, Y., & Kawakami, H. (2021). Solid-State Hydrogen Fuel by PSII–Chitin Composite and Application to Biofuel Cell. Journal of Composites Science, 5(12), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcs5120317




