Comprehensive Atlas of the Myelin Basic Protein Interaction Landscape
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
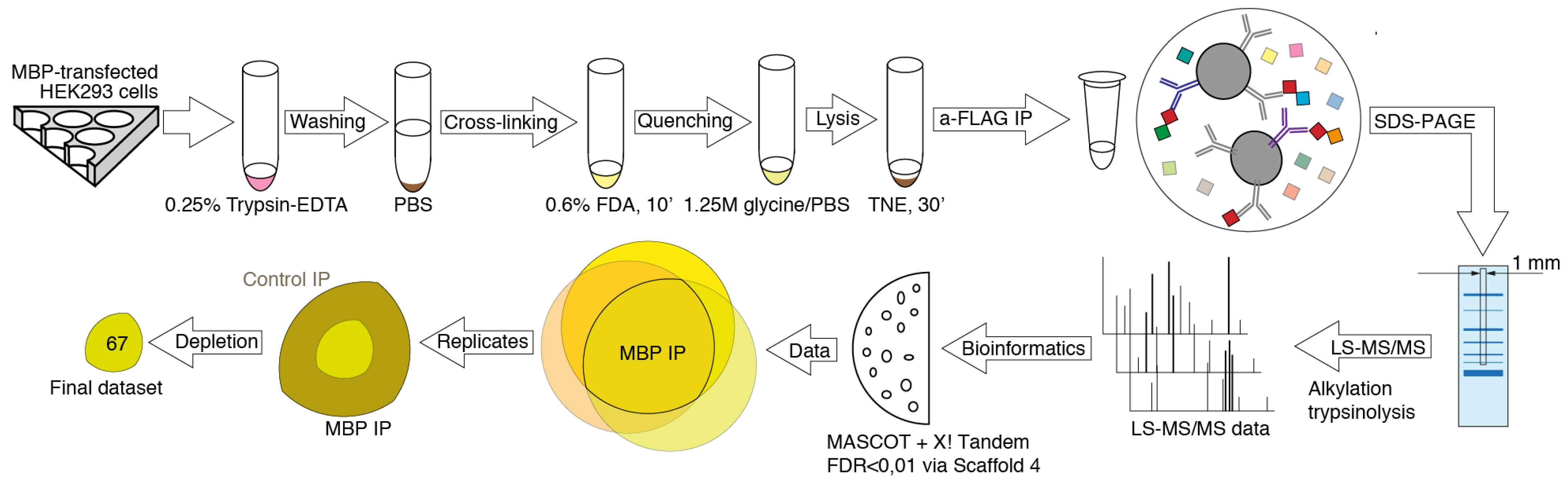
2.1. Cells and Transfection
2.2. Formaldehyde Cross-Linking
2.3. Immunoprecipitation
2.4. Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamins, J.A.; Morell, P. Proteins of Myelin and Their Metabolism. Neurochem. Res. 1978, 3, 137–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbay, B.; Fournier, M.; Sallafranque, M.L.; Muller, S.; Boiron, F.; Heape, A.; Cassagne, C.; Bonnet, J. Po, MBP, Histone, and DNA Levels in Sciatic Nerve. Neurochem. Pathol. 1988, 8, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krigbaum, W.R.; Hsu, T.S. Molecular Conformation of Bovine A1 Basic Protein, a Coiling Macromolecule in Aqueous Solution. Biochemistry 1975, 14, 2542–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polverini, E.; Fasano, A.; Zito, F.; Riccio, P.; Cavatorta, P. Conformation of Bovine Myelin Basic Protein Purified with Bound Lipids. Eur. Biophys. J. EBJ 1999, 28, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harauz, G.; Ishiyama, N.; Hill, C.M.D.; Bates, I.R.; Libich, D.S.; Farès, C. Myelin Basic Protein-Diverse Conformational States of an Intrinsically Unstructured Protein and Its Roles in Myelin Assembly and Multiple Sclerosis. Micron 2004, 35, 503–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harauz, G.; Libich, D. The Classic Basic Protein of Myelin—Conserved Structural Motifs and the Dynamic Molecular Barcode Involved in Membrane Adhesion and Protein-Protein Interactions. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2009, 10, 196–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, S.; Snaidero, N.; Pähler, G.; Frey, S.; Sánchez, P.; Zweckstetter, M.; Janshoff, A.; Schneider, A.; Weil, M.-T.; Schaap, I.A.T.; et al. Myelin Membrane Assembly Is Driven by a Phase Transition of Myelin Basic Proteins Into a Cohesive Protein Meshwork. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, J.M. Myelin Basic Protein: A Multifunctional Protein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2006, 63, 1945–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, J.M.; Yip, P.M.; Rangaraj, G.; Jo, E. Effect of Posttranslational Modifications to Myelin Basic Protein on Its Ability to Aggregate Acidic Lipid Vesicles. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 5065–5071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, I.R.; Boggs, J.M.; Feix, J.B.; Harauz, G. Membrane-Anchoring and Charge Effects in the Interaction of Myelin Basic Protein with Lipid Bilayers Studied by Site-Directed Spin Labeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 29041–29047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, C.M.D.; Harauz, G. Charge Effects Modulate Actin Assembly by Classic Myelin Basic Protein Isoforms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 329, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homchaudhuri, L.; Polverini, E.; Gao, W.; Harauz, G.; Boggs, J.M. Influence of Membrane Surface Charge and Post-Translational Modifications to Myelin Basic Protein on Its Ability to Tether the Fyn-SH3 Domain to a Membrane in Vitro. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 2385–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogurov, A.; Kudriaeva, A.; Kuzina, E.; Smirnov, I.; Bobik, T.; Ponomarenko, N.; Kravtsova-Ivantsiv, Y.; Ciechanover, A.; Gabibov, A. Multiple Sclerosis Autoantigen Myelin Basic Protein Escapes Control by Ubiquitination during Proteasomal Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 17758–17766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudriaeva, A.; Kuzina, E.S.; Zubenko, O.; Smirnov, I.V.; Belogurov, A. Charge-Mediated Proteasome Targeting. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 6852–6866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutton, J.D.; Winston, R.; Rodman, T.C. Multiple Sclerosis: Etiological Mechanisms and Future Directions. Exp. Biol. Med. 2004, 229, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sospedra, M.; Martin, R. Immunology of Multiple Sclerosis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 23, 683–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogurov, A.A.; Kurkova, I.N.; Friboulet, A.; Thomas, D.; Misikov, V.K.; Zakharova, M.Y.; Suchkov, S.V.; Kotov, S.V.; Alehin, A.I.; Avalle, B.; et al. Recognition and Degradation of Myelin Basic Protein Peptides by Serum Autoantibodies: Novel Biomarker for Multiple Sclerosis. J. Immunol. 1950 2008, 180, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponomarenko, N.A.; Durova, O.M.; Vorobiev, I.I.; Belogurov, A.A.; Kurkova, I.N.; Petrenko, A.G.; Telegin, G.B.; Suchkov, S.V.; Kiselev, S.L.; Lagarkova, M.A.; et al. Autoantibodies to Myelin Basic Protein Catalyze Site-Specific Degradation of Their Antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, N.A.; Durova, O.M.; Vorobiev, I.I.; Belogurov, A.A.; Telegin, G.B.; Suchkov, S.V.; Misikov, V.K.; Morse, H.C.; Gabibov, A.G. Catalytic Activity of Autoantibodies toward Myelin Basic Protein Correlates with the Scores on the Multiple Sclerosis Expanded Disability Status Scale. Immunol. Lett. 2006, 103, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzina, E.S.; Chernolovskaya, E.L.; Kudriaeva, A.A.; Zenkova, M.A.; Knorre, V.D.; Surina, E.A.; Ponomarenko, N.A.; Bobik, T.V.; Smirnov, I.V.; Bacheva, A.V.; et al. Immunoproteasome Enhances Intracellular Proteolysis of Myelin Basic Protein. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 453, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Mastronardi, F.G.; Wood, D.D.; Lubman, D.M.; Zand, R.; Moscarello, M.A. Multiple Sclerosis: An Important Role for Post-Translational Modifications of Myelin Basic Protein in Pathogenesis. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2003, 2, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzina, E.S.; Kudriaeva, A.A.; Glagoleva, I.S.; Knorre, V.D.; Gabibov, A.G.; Belogurov, A.A. Deimination of the Myelin Basic Protein Decelerates Its Proteasome-Mediated Metabolism. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 469, 277–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harauz, G.; Musse, A.A. A Tale of Two Citrullines—Structural and Functional Aspects of Myelin Basic Protein Deimination in Health and Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2007, 32, 137–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Neugebauer, U.; Bürck, J.; Myllykoski, M.; Baumgärtel, P.; Popp, J.; Kursula, P. Charge Isomers of Myelin Basic Protein: Structure and Interactions with Membranes, Nucleotide Analogues, and Calmodulin. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzina, E.; Kudriaeva, A.; Smirnov, I.; Dubina, M.V.; Gabibov, A.; Belogurov, A. Glatiramer Acetate and Nanny Proteins Restrict Access of the Multiple Sclerosis Autoantigen Myelin Basic Protein to the 26S Proteasome. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 926394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belogurov, A.; Kuzina, E.; Kudriaeva, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Kovalchuk, S.; Surina, Y.; Smirnov, I.; Lomakin, Y.; Bacheva, A.; Stepanov, A.; et al. Ubiquitin-Independent Proteosomal Degradation of Myelin Basic Protein Contributes to Development of Neurodegenerative Autoimmunity. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, A.; Tomas, H.; Havli, J.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. In-Gel Digestion for Mass Spectrometric Characterization of Proteins and Proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2856–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalchuk, S.I.; Jensen, O.N.; Rogowska-Wrzesinska, A. FlashPack: Fast and Simple Preparation of Ultrahigh-Performance Capillary Columns for LC-MS. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2019, 18, 383–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Riverol, Y.; Csordas, A.; Bai, J.; Bernal-Llinares, M.; Hewapathirana, S.; Kundu, D.J.; Inuganti, A.; Griss, J.; Mayer, G.; Eisenacher, M.; et al. The PRIDE Database and Related Tools and Resources in 2019: Improving Support for Quantification Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D442–D450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsch, E.W.; Bandeira, N.; Sharma, V.; Perez-Riverol, Y.; Carver, J.J.; Kundu, D.J.; García-Seisdedos, D.; Jarnuczak, A.F.; Hewapathirana, S.; Pullman, B.S.; et al. The ProteomeXchange Consortium in 2020: Enabling “big Data” Approaches in Proteomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D1145–D1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, B.W.; Toews, J.; Kast, J. Utility of Formaldehyde Cross-Linking and Mass Spectrometry in the Study of Protein–Protein Interactions. J. Mass Spectrom. 2008, 43, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klockenbusch, C.; Kast, J. Optimization of Formaldehyde Cross-Linking for Protein Interaction Analysis of Non-Tagged Integrin β 1. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colman, D.R.; Kreibich, G.; Frey, A.B.; Sabatini, D.D. Synthesis and Incorporation of Myelin Polypeptides into CNS Myelin. J. Cell Biol. 1982, 95, 598–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ainger, K.; Avossa, D.; Morgan, F.; Hill, S.J.; Barry, C.; Barbarese, E.; Carson, J.H. Transport and Localization of Exogenous Myelin Basic Protein MRNA Microinjected into Oligodendrocytes. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, J.H.; Worboys, K.; Ainger, K.; Barbarese, E. Translocation of Myelin Basic Protein MRNA in Oligodendrocytes Requires Microtubules and Kinesin. Cell Motil. Cytoskelet. 1997, 38, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, C.; Kramer, E.-M.; Cardine, A.-M.; Schraven, B.; Brandt, R.; Trotter, J. Process Outgrowth of Oligodendrocytes Is Promoted by Interaction of Fyn Kinase with the Cytoskeletal Protein Tau. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, C.; Bauer, N.M.; Schäfer, I.; White, R. Making Myelin Basic Protein-from MRNA Transport to Localized Translation. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Nastou, K.C.; Lyon, D.; Kirsch, R.; Pyysalo, S.; Doncheva, N.T.; Legeay, M.; Fang, T.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING Database in 2021: Customizable Protein-Protein Networks, and Functional Characterization of User-Uploaded Gene/Measurement Sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D605–D612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Gable, A.L.; Lyon, D.; Junge, A.; Wyder, S.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Simonovic, M.; Doncheva, N.T.; Morris, J.H.; Bork, P.; et al. STRING V11: Protein-Protein Association Networks with Increased Coverage, Supporting Functional Discovery in Genome-Wide Experimental Datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D607–D613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granneman, S.; Petfalski, E.; Swiatkowska, A.; Tollervey, D. Cracking Pre-40S Ribosomal Subunit Structure by Systematic Analyses of RNA-Protein Cross-Linking. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2026–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valgardsdottir, R.; Brede, G.; Eide, L.G.; Frengen, E.; Prydz, H. Cloning and Characterization of MDDX28, a Putative Dead-Box Helicase with Mitochondrial and Nuclear Localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 32056–32063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.-T.; Barrientos, A. The Human Mitochondrial DEAD-Box Protein DDX28 Resides in RNA Granules and Functions in Mitoribosome Assembly. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 854–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonicka, H.; Shoubridge, E.A. Mitochondrial RNA Granules Are Centers for Posttranscriptional RNA Processing and Ribosome Biogenesis. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 920–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, R.; Yamamoto, M.; Ueki, T.; Yoshioka, N.; Tanaka, K.; Morisaki, H.; Seiwa, C.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kawano, H.; Tsuruo, Y.; et al. A DEAD-Box RNA Helicase Ddx54 Protein in Oligodendrocytes Is Indispensable for Myelination in the Central Nervous System. J. Neurosci. Res. 2013, 91, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoch-Kraft, P.; White, R.; Tenzer, S.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; Trotter, J.; Gonsior, C. Dual Role of the RNA Helicase DDX5 in Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Myelin Basic Protein in Oligodendrocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs204750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatsuta, T.; Model, K.; Langer, T. Formation of Membrane-Bound Ring Complexes by Prohibitins in Mitochondria. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 248–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poitelon, Y.; Bogni, S.; Matafora, V.; Della-Flora Nunes, G.; Hurley, E.; Ghidinelli, M.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Taveggia, C.; Silvestri, N.; Bachi, A.; et al. Spatial Mapping of Juxtacrine Axo-Glial Interactions Identifies Novel Molecules in Peripheral Myelination. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della-Flora Nunes, G.; Wilson, E.R.; Marziali, L.N.; Hurley, E.; Silvestri, N.; He, B.; O’Malley, B.W.; Beirowski, B.; Poitelon, Y.; Wrabetz, L.; et al. Prohibitin 1 Is Essential to Preserve Mitochondria and Myelin Integrity in Schwann Cells. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Myers, M.P.; Buratti, E.; Baralle, F.E. Characterizing TDP-43 Interaction with Its RNA Targets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 5062–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollervey, J.R.; Curk, T.; Rogelj, B.; Briese, M.; Cereda, M.; Kayikci, M.; König, J.; Hortobágyi, T.; Nishimura, A.L.; Zupunski, V.; et al. Characterizing the RNA Targets and Position-Dependent Splicing Regulation by TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Conicella, A.E.; Schmidt, H.B.; Martin, E.W.; Rhoads, S.N.; Reeb, A.N.; Nourse, A.; Ramirez Montero, D.; Ryan, V.H.; Rohatgi, R.; et al. A Single N-Terminal Phosphomimic Disrupts TDP-43 Polymerization, Phase Separation, and RNA Splicing. EMBO J. 2018, 37, e97452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohan, Z.; Matej, R.; Rusina, R.; Kovacs, G.G. Oligodendroglial Response in the Spinal Cord in TDP-43 Proteinopathy with Motor Neuron Involvement. Neurodegener. Dis. 2014, 14, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, K.; Sonobe, Y.; Ghadge, G.; Pytel, P.; Lépine, P.; Pernin, F.; Cui, Q.-L.; Antel, J.P.; Zandee, S.; Prat, A.; et al. RNA-Binding Protein Altered Expression and Mislocalization in MS. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, e704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.-J.; Agrawal, I.; Vainshtein, A.; Ho, W.Y.; Xin, W.; Tucker-Kellogg, G.; Susuki, K.; Peles, E.; Ling, S.-C.; Chan, J.R. TDP-43 Maximizes Nerve Conduction Velocity by Repressing a Cryptic Exon for Paranodal Junction Assembly in Schwann Cells. eLife 2021, 10, e64456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Herbert, A.; Rich, A.; Samuel, C.E. Double-Stranded RNA-Specific Adenosine Deaminase: Nucleic Acid Binding Properties. Methods 1998, 15, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacem, N.; Kavo, A.; Zerad, L.; Richard, L.; Mathis, S.; Kapur, R.P.; Parisot, M.; Amiel, J.; Dufour, S.; de la Grange, P.; et al. ADAR1 Mediated Regulation of Neural Crest Derived Melanocytes and Schwann Cell Development. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, K.S.; Kidd, G.J.; Carson, J.H.; Smith, R. HnRNP A2 Selectively Binds the Cytoplasmic Transport Sequence of Myelin Basic Protein MRNA. Biochemistry 1998, 37, 7021–7029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggipinto, M.; Rabiner, C.; Kidd, G.J.; Hawkins, A.J.; Smith, R.; Barbarese, E. Increased Expression of the MBP MRNA Binding Protein HnRNP A2 during Oligodendrocyte Differentiation. J. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 75, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, C.S.; Göritz, C.; Nord, Y.; Hermanson, O.; López-Iglesias, C.; Visa, N.; Castelo-Branco, G.; Percipalle, P. In Cultured Oligodendrocytes the A/B-Type HnRNP CBF-A Accompanies MBP MRNA Bound to MRNA Trafficking Sequences. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 3008–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Gonsior, C.; Bauer, N.M.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; Luhmann, H.J.; Trotter, J. Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein (HnRNP) F Is a Novel Component of Oligodendroglial RNA Transport Granules Contributing to Regulation of Myelin Basic Protein (MBP) Synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1742–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin-Tricaud, C.; Rutishauser, U.; Tricaud, N. P120 Catenin Is Required for Thickening of Schwann Cell Myelin. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2007, 35, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadis, P.Z.; Moon, S.Y.; Thoreson, M.A.; Mariner, D.J.; Crawford, H.C.; Zheng, Y.; Reynolds, A.B. Inhibition of RhoA by P120 Catenin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 2, 637–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosheva, I.; Shtutman, M.; Elbaum, M.; Bershadsky, A.D. P120 Catenin Affects Cell Motility via Modulation of Activity of Rho-Family GTPases: A Link between Cell-Cell Contact Formation and Regulation of Cell Locomotion. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noren, N.K.; Liu, B.P.; Burridge, K.; Kreft, B. P120 Catenin Regulates the Actin Cytoskeleton via Rho Family GTPases. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 150, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggs, J.M.; Homchaudhuri, L.; Ranagaraj, G.; Liu, Y.; Smith, G.S.; Harauz, G. Interaction of Myelin Basic Protein with Cytoskeletal and Signaling Proteins in Cultured Primary Oligodendrocytes and N19 Oligodendroglial Cells. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperber, B.R.; Boyle-Walsh, É.A.; Engleka, M.J.; Gadue, P.; Peterson, A.C.; Stein, P.L.; Scherer, S.S.; McMorris, F.A. A Unique Role for Fyn in CNS Myelination. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; White, R. From Axon–Glial Signalling to Myelination: The Integrating Role of Oligodendroglial Fyn Kinase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peckham, H.; Giuffrida, L.; Wood, R.; Gonsalvez, D.; Ferner, A.; Kilpatrick, T.J.; Murray, S.S.; Xiao, J. Fyn Is an Intermediate Kinase That BDNF Utilizes to Promote Oligodendrocyte Myelination. Glia 2016, 64, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Ku, L.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Y. Developmental Abnormalities of Myelin Basic Protein Expression in Fyn Knock-out Brain Reveal a Role of Fyn in Posttranscriptional Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.; Gonsior, C.; Krämer-Albers, E.-M.; Stöhr, N.; Hüttelmaier, S.; Trotter, J. Activation of Oligodendroglial Fyn Kinase Enhances Translation of MRNAs Transported in HnRNP A2–Dependent RNA Granules. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 181, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouaouina, M.; Harburger, D.S.; Calderwood, D.A. Talin and Signaling through Integrins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 757, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderwood, D.A.; Ginsberg, M.H. Talin Forges the Links between Integrins and Actin. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 694–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Critchley, D.R. Biochemical and Structural Properties of the Integrin-Associated Cytoskeletal Protein Talin. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2009, 38, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapholz, B.; Brown, N.H. Talin—The Master of Integrin Adhesions. J. Cell Sci. 2017, 130, 2435–2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, M.; Legate, K.R.; Zent, R.; Fässler, R. The Tail of Integrins, Talin, and Kindlins. Science 2009, 324, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Lian, G.; Lenkinski, R.; De Grand, A.; Vaid, R.R.; Bryce, T.; Stasenko, M.; Boskey, A.; Walsh, C.; Sheen, V. Filamin B Mutations Cause Chondrocyte Defects in Skeletal Development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 1661–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Han, S.W.; McKeel, D.W.; Goate, A.; Wu, J.Y. Interaction of Presenilins with the Filamin Family of Actin-Binding Proteins. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaheri, A.; Carpén, O.; Heiska, L.; Helander, T.S.; Jääskeläinen, J.; Majander-Nordenswan, P.; Sainio, M.; Timonen, T.; Turunen, O. The Ezrin Protein Family: Membrane-Cytoskeleton Interactions and Disease Associations. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, H.; Yang, Y.; Shi, Y. Ezrin Interacts with L-Periaxin by the “Head to Head and Tail to Tail” Mode and Influences the Location of L-Periaxin in Schwann Cell RSC96. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2020, 1864, 129520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendez-Vasquez, C.V.; Rios, J.C.; Zanazzi, G.; Lambert, S.; Bretscher, A.; Salzer, J.L. Nodes of Ranvier Form in Association with Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin (ERM)-Positive Schwann Cell Processes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 1235–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perretti, M.; D’Acquisto, F. Annexin A1 and Glucocorticoids as Effectors of the Resolution of Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Martinez, M.T.; Porte, F.; Liautard, J.P.; Sri Widada, J. Effects of Profilin-Annexin I Association on Some Properties of Both Profilin and Annexin I: Modification of the Inhibitory Activity of Profilin on Actin Polymerization and Inhibition of the Self-Association of Annexin I and Its Interactions with Liposomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1997, 1339, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Probst-Cousin, S.; Kowolik, D.; Kuchelmeister, K.; Kayser, C.; Neundörfer, B.; Heuss, D. Expression of Annexin-1 in Multiple Sclerosis Plaques. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2002, 28, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huitinga, I.; Bauer, J.; Strijbos, P.J.; Rothwell, N.J.; Dijkstra, C.D.; Tilders, F.J. Effect of Annexin-1 on Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) in the Rat. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 111, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, J.S.; Minagar, A.; Harper, M.; Robinson-Jackson, S.; Jennings, M.; Smith, S.J. Proteomic Analysis of Human Cerebral Endothelial Cells Activated by Multiple Sclerosis Serum and IFNβ-1b. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2007, 32, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketomi, M.; Kinoshita, N.; Kimura, K.; Kitada, M.; Noda, T.; Asou, H.; Nakamura, T.; Ide, C. Nogo-A Expression in Mature Oligodendrocytes of Rat Spinal Cord in Association with Specific Molecules. Neurosci. Lett. 2002, 332, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Salehi, A.H.; Roux, P.P.; Kubu, C.J.; Zeindler, C.; Bhakar, A.; Tannis, L.-L.; Verdi, J.M.; Barker, P.A. NRAGE, A Novel MAGE Protein, Interacts with the P75 Neurotrophin Receptor and Facilitates Nerve Growth Factor–Dependent Apoptosis. Neuron 2000, 27, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgaya, J.M. The Neurotrophin Receptor P75NTR as a Positive Modulator of Myelination. Science 2002, 298, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.K.; Potts, P.R. A Comprehensive Guide to the MAGE Family of Ubiquitin Ligases. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 1114–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wüst, H.M.; Wegener, A.; Fröb, F.; Hartwig, A.C.; Wegwitz, F.; Kari, V.; Schimmel, M.; Tamm, E.R.; Johnsen, S.A.; Wegner, M.; et al. Egr2-Guided Histone H2B Monoubiquitination Is Required for Peripheral Nervous System Myelination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 8959–8976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.; Miehe, M.; Laufer, S.; Johnsen, S.A. The H2B Ubiquitin-Protein Ligase RNF40 Is Required for Somatic Cell Reprogramming. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpiuk, O.; Najafova, Z.; Kramer, F.; Hennion, M.; Galonska, C.; König, A.; Snaidero, N.; Vogel, T.; Shchebet, A.; Begus-Nahrmann, Y.; et al. The Histone H2B Monoubiquitination Regulatory Pathway Is Required for Differentiation of Multipotent Stem Cells. Mol. Cell 2012, 46, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, R.J.; Lazzarini, R.A.; Colman, D.R.; Friedrich, V.L. Cytoplasmic and Nuclear Localization of Myelin Basic Proteins Reveals Heterogeneity among Oligodendrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 1996, 46, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clausell, J.; Happel, N.; Hale, T.K.; Doenecke, D.; Beato, M. Histone H1 Subtypes Differentially Modulate Chromatin Condensation without Preventing ATP-Dependent Remodeling by SWI/SNF or NURF. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e0007243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, P.; Munroe, D.; Prawitt, D.; Chu, L.L.; Bric, E.; Kim, J.; Reid, L.H.; Davies, C.; Nakagama, H.; Loebbert, R.; et al. Functional Characterization of Human Nucleosome Assembly Protein-2 (NAP1L4) Suggests a Role as a Histone Chaperone. Genomics 1997, 44, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serlidaki, D.; van Waarde, M.A.W.H.; Rohland, L.; Wentink, A.S.; Dekker, S.L.; Kamphuis, M.J.; Boertien, J.M.; Brunsting, J.F.; Nillegoda, N.B.; Bukau, B.; et al. Functional Diversity between HSP70 Paralogs Caused by Variable Interactions with Specific Co-Chaperones. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 7301–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquino, D.A.; Peng, D.; Lopez, C.; Farooq, M. The Constitutive Heat Shock Protein-70 Is Required for Optimal Expression of Myelin Basic Protein during Differentiation of Oligodendrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 1998, 23, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, D.J.; Rodríguez, J.A.; Bañuelos, S. Nucleophosmin, a Multifunctional Nucleolar Organizer with a Role in DNA Repair. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2020, 1868, 140532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frottin, F.; Schueder, F.; Tiwary, S.; Gupta, R.; Körner, R.; Schlichthaerle, T.; Cox, J.; Jungmann, R.; Hartl, F.U.; Hipp, M.S. The Nucleolus Functions as a Phase-Separated Protein Quality Control Compartment. Science 2019, 365, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrea, D.M.; Cika, J.A.; Stanley, C.B.; Nourse, A.; Onuchic, P.L.; Banerjee, P.R.; Phillips, A.H.; Park, C.-G.; Deniz, A.A.; Kriwacki, R.W. Self-Interaction of NPM1 Modulates Multiple Mechanisms of Liquid–Liquid Phase Separation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.-X.; Nguemaha, V.; Mazarakos, K.; Qin, S. Why Do Disordered and Structured Proteins Behave Differently in Phase Separation? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rekulapally, P.; Suresh, S.N. Nucleolus: A Protein Quality Control Compartment. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 993–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

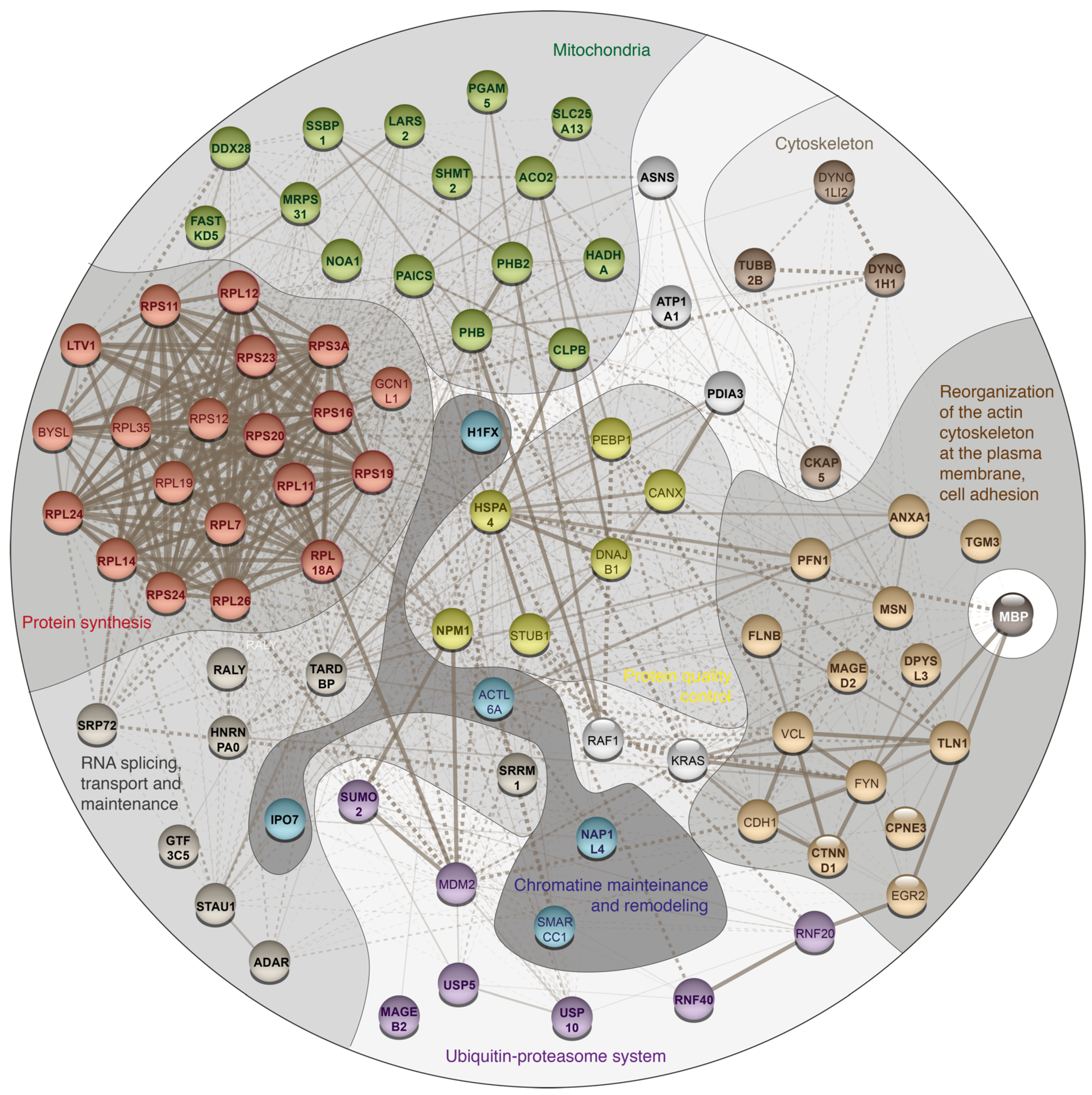
| Protein Name | Gene Name | PSMs for MBP Experiment | PSMs for Control Experiment | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Protein synthesis | |||||||
| 40S ribosomal protein S16 | RPS16 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S19 | RPS19 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S20 | RPS20 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S23 | RPS23 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L11 | RPL11 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L12 | RPL12 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L18a | RPL18A | 0 | 3 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Protein LTV1 homolog | LTV1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ribosomal protein L7, isoform CRA_a | RPL7 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S24 | RPS24 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S11 | RPS11 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L26 | RPL26 | 0 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| 40S ribosomal protein S3a | RPS3A | 3 | 2 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L24 | RPL24 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 60S ribosomal protein L14 | RPL14 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Mitochondria | |||||||
| 28S ribosomal protein S31, mitochondrial | MRPS31 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Aconitate hydratase, mitochondrial | ACO2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| cDNA FLJ46863 fis, clone UTERU3011558 | NOA1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| FAST kinase domain-containing protein 5, mitochondrial | FASTKD5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Isoform 2 of Caseinolytic peptidase B protein homolog | CLPB | 0 | 2 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Prohibitin (Fragment) | PHB1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Prohibitin-2 | PHB2 | 5 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, mitochondrial (Fragment) | SSBP1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Solute carrier family 25, member 13 (Citrin) variant (Fragment) | SLC25A13 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX28 | DDX28 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Enoyl-CoA hydratase | HADHA | 3 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Probable leucine--tRNA ligase, mitochondrial | LARS2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| AIR carboxylase (Fragment) | PAICS | 2 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Serine hydroxymethyltransferase | SHMT2 | 5 | 3 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 7 |
| Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase PGAM5, mitochondrial | PGAM5 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| mRNA splicing, transport and maintenance | |||||||
| cDNA FLJ77421, highly similar to Homo sapiens autoantigen p542 mRNA | RALY | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Isoform 2 of General transcription factor 3C polypeptide 5 | GTF3C5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Serine/arginine repetitive matrix 1 isoform 2 (Fragment) | SRRM1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A0 | HNRNPA0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Signal recognition particle subunit SRP72 | SRP72 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| cDNA FLJ75871, highly similar to Homo sapiens staufen, RNA binding protein (STAU), transcript variant T3, mRNA | STAU1 | 0 | 5 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| RNA-specific adenosine deaminase | ADAR | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| TAR DNA-binding protein 43 | TARDBP | 4 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Reorganization of the cytoskeleton and intercellular adhesion | |||||||
| Annexin A1 | ANXA1 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Catenin delta-1 | CTNND1 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Copine III, isoform CRA_a | CPNE3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Filamin B, beta (Actin binding protein 278), isoform CRA_a | FLNB | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Moesin | MSN | 2 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| cDNA FLJ56823, highly similar to Protein-glutamine gamma-glutamyltransferase E | TGM3 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Profilin-1 | PFN1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Talin-1 | TLN1 | 3 | 4 | 16 | 0 | 1 | 5 |
| Testicular secretory protein Li 7 | DPYSL3 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Cytoskeleton and intracellular traffic | |||||||
| Cytoskeleton-associated protein 5 | CKAP5 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Cytoplasmic dynein 1 heavy chain 1 | DYNC1H1 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Tubulin beta chain | TUBB2B | 0 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Ubiquitin-proteasome system related | |||||||
| cDNA, FLJ93871, highly similar to Homo sapiens melanoma antigen, family B, 2 (MAGEB2), mRNA | MAGEB2 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| E3 ubiquitin protein ligase | RNF40 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Small ubiquitin-related modifier | SUMO2 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase | USP10 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Melanoma antigen family D, 2, isoform CRA_a | MAGED2 | 0 | 2 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase | USP5 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Quality control proteins | |||||||
| Heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 | HSPA4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Nucleophosmin (Fragment) | NPM1 | 11 | 3 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| Chromatin mainteinance and remodeling | |||||||
| Nucleosome assembly protein 1-like 4, isoform CRA_b | NAP1L4 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Histone H1.10 | H1-10 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Importin-7 | IPO7 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Unassigned to the specific group proteins | |||||||
| Asparagine synthetase [glutamine-hydrolyzing] | ASNS | 0 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Protein disulfide-isomerase A3 (Fragment) | PDIA3 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha (Fragment) | ATP1A1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| BAF53A protein | BAF53A | 2 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor interacting complex protein | PRIC295 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smirnova, E.V.; Rakitina, T.V.; Ziganshin, R.H.; Arapidi, G.P.; Saratov, G.A.; Kudriaeva, A.A.; Belogurov, A.A. Comprehensive Atlas of the Myelin Basic Protein Interaction Landscape. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111628
Smirnova EV, Rakitina TV, Ziganshin RH, Arapidi GP, Saratov GA, Kudriaeva AA, Belogurov AA. Comprehensive Atlas of the Myelin Basic Protein Interaction Landscape. Biomolecules. 2021; 11(11):1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111628
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmirnova, Evgeniya V., Tatiana V. Rakitina, Rustam H. Ziganshin, Georgij P. Arapidi, George A. Saratov, Anna A. Kudriaeva, and Alexey A. Belogurov. 2021. "Comprehensive Atlas of the Myelin Basic Protein Interaction Landscape" Biomolecules 11, no. 11: 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111628
APA StyleSmirnova, E. V., Rakitina, T. V., Ziganshin, R. H., Arapidi, G. P., Saratov, G. A., Kudriaeva, A. A., & Belogurov, A. A. (2021). Comprehensive Atlas of the Myelin Basic Protein Interaction Landscape. Biomolecules, 11(11), 1628. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom11111628






