Inflammaging and Cancer: A Challenge for the Mediterranean Diet
Abstract
:1. Inflammaging as a Major Component of Aging, Age-Related Diseases and Cancer
Inflammatory Sources for Cancer Development
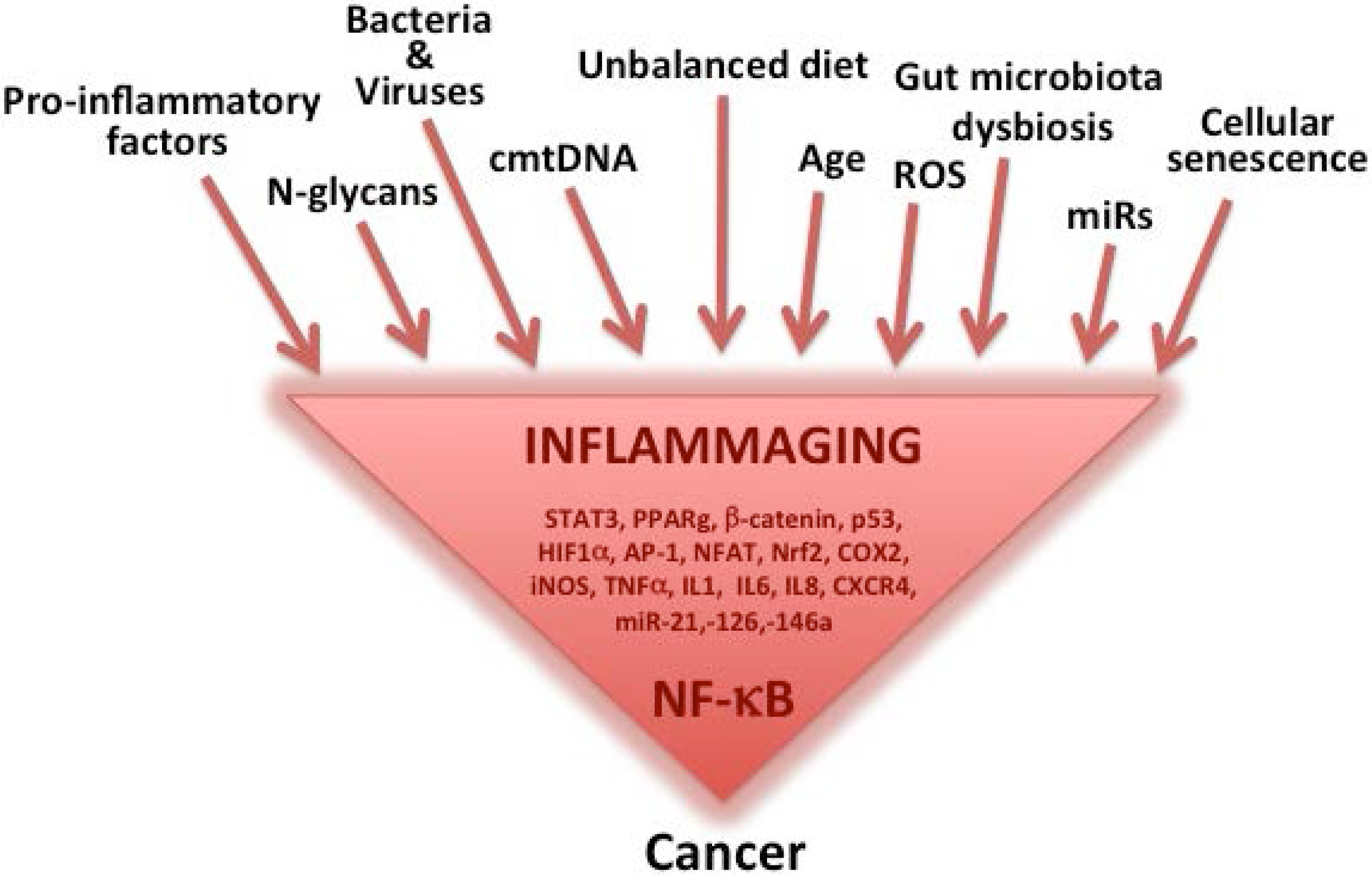
2. The Mediterranean Diet
2.1. The Mediterranean Diet: Definitions and Characteristics
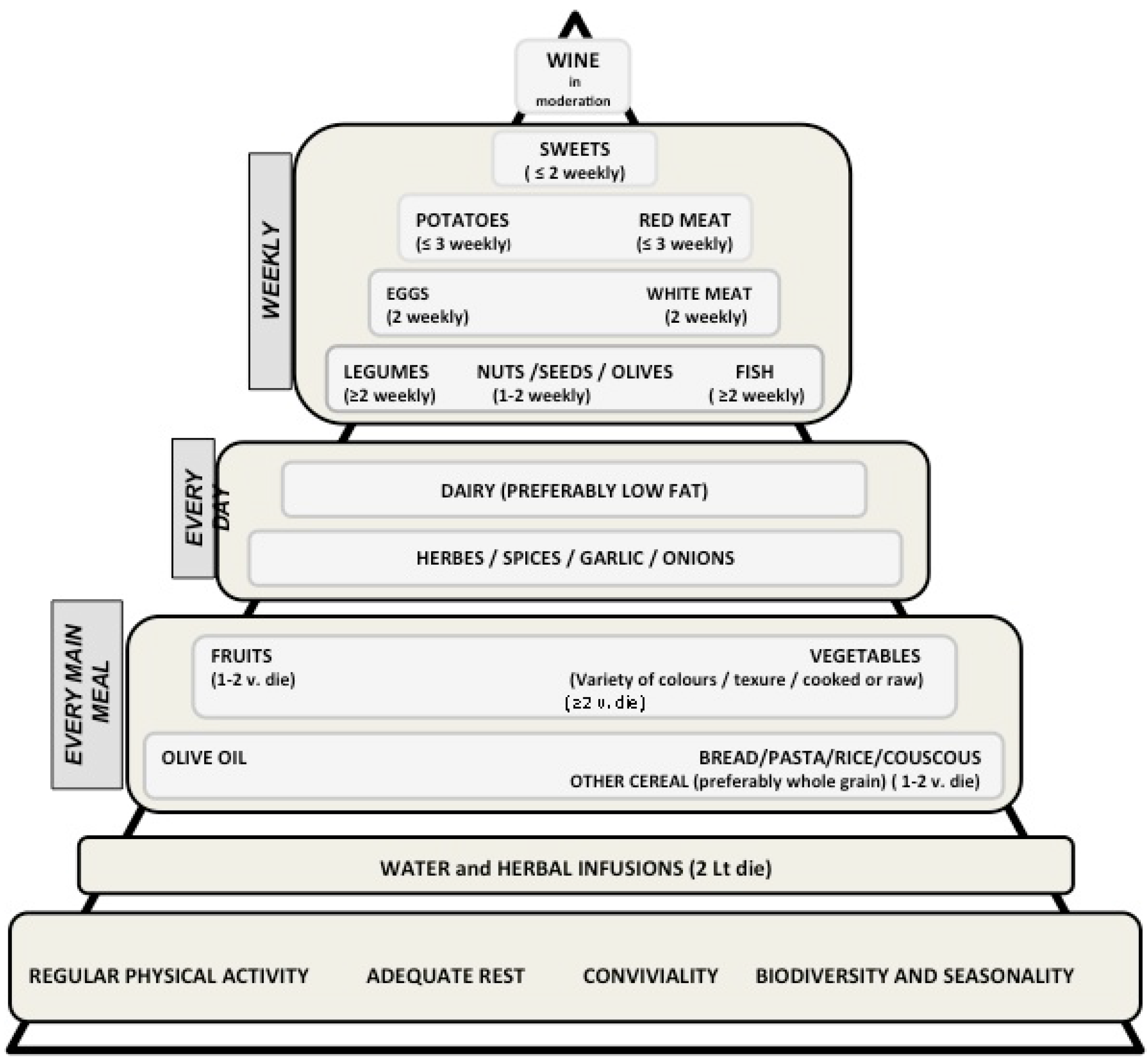
2.2. The Preventive Role of the Mediterranean Diet on Cancer
2.2.1. Epidemiological Studies
2.2.2. Chemoprotective Effects of Polyphenols on Inflammation and Cancer
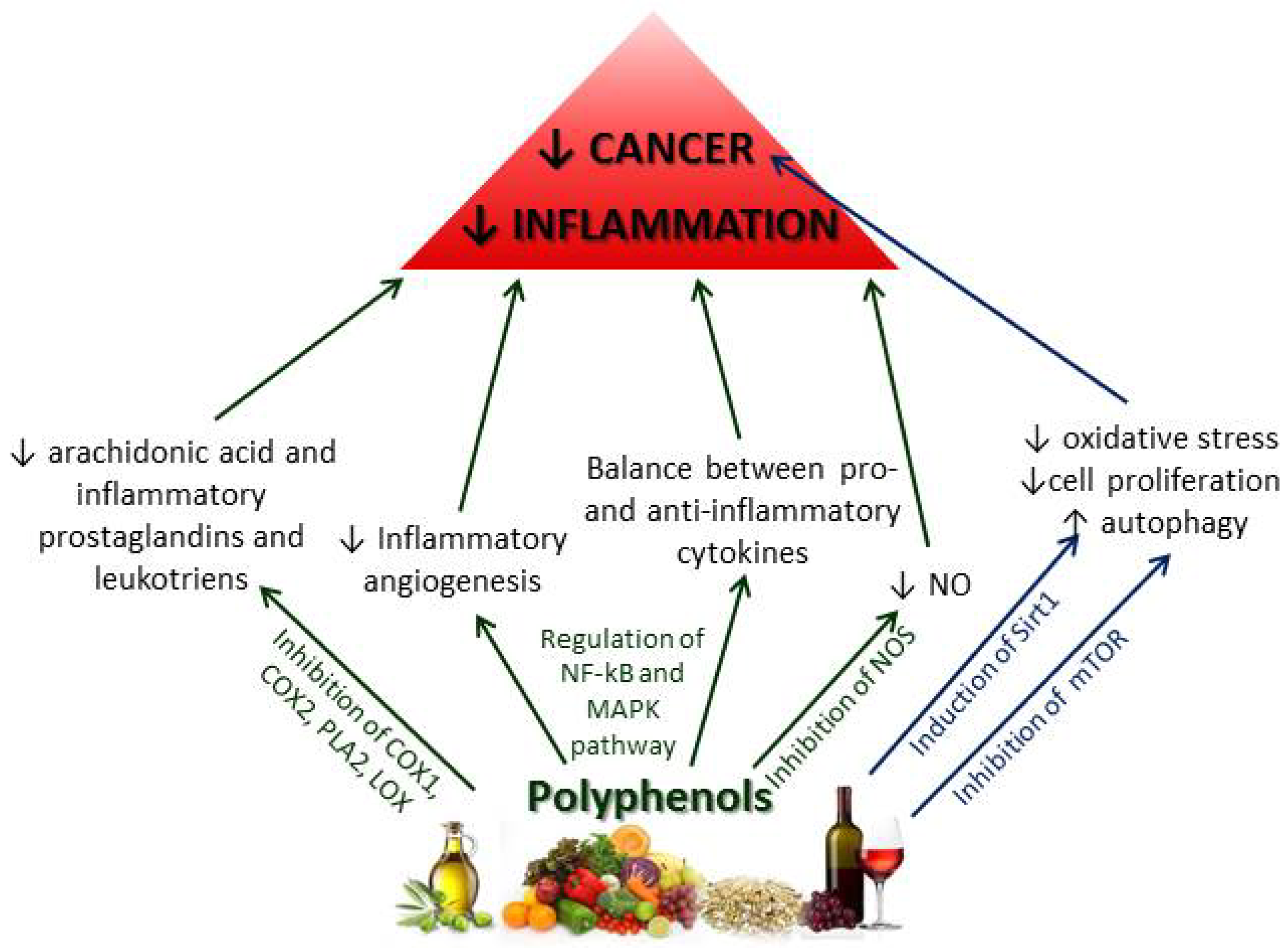
2.2.3. Other Mediterranean Diet Components and Their Effects on Inflammation and Cancer
2.3. The Mediterranean Diet Epigenetic Regulation: the Role of microRNAs
2.3.1. Fatty Acids
2.3.2. Vitamins
2.3.3. Phytochemicals
3. Gut Microbiota, Inflammation and Cancer
4. A Systems Biology Approach to Diet, Inflammation and Cancer
5. The Mediterranean Diet and Healthy Aging: the European Project NU-AGE Targeted on Inflammaging to Prevent Age-Related Diseases as a Whole
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Bonafè, M.; Valensin, S.; Olivieri, F.; de Luca, M.; Ottaviani, E.; de Benedictis, G. Inflamm-aging. An evolutionary perspective on immunosenescence. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 908, 244–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Campisi, J. Chronic inflammation (inflammaging) and its potential contribution to age-associated diseases. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.K.; Berger, S.L.; Brunet, A.; Campisi, J.; Cuervo, A.M.; Epel, E.S.; Franceschi, C.; Lithgow, G.J.; Morimoto, R.I.; Pessin, J.E.; et al. Geroscience: Linking aging to chronic disease. Cell 2014, 159, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, C. Inflammaging as a major characteristic of old people: Can it be prevented or cured? Nutr. Rev. 2007, 65, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschi, C.; Capri, M.; Monti, D.; Giunta, S.; Olivieri, F.; Sevini, F.; Panourgia, M.P.; Invidia, L.; Celani, L.; Scurti, M.; et al. Inflammaging and anti-inflammaging: A systemic perspective on aging and longevity emerged from studies in humans. Mech. Ageing. Dev. 2007, 128, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevenini, E.; Monti, D.; Franceschi, C. Inflammaging. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2013, 16, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedy, J. Galen on cancer and related diseases. Clio Med. 1975, 10, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trinchieri, G. Cancer and inflammation: An old intuition with rapidly evolving new concepts. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 30, 677–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Virchow, R. Cellular Pathology as Based upon Physiological and Pathological Histology; J.B. Lippincott: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1863. [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill, F.; Mantovani, A. Inflammation and cancer: Back to Virchow? Lancet 2001, 357, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The Hallmarks of Cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.L.; Tan, W.; Ricono, J.M.; Korchynskyi, O.; Zhang, M.; Gonias, S.L.; Cheresh, D.A.; Karin, M. Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKalpha controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin. Nature 2007, 446, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Balkwill, F. Cancer-related inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M. Nuclear factor-κB in cancer development and progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chia, W.K.; Ali, R.; Toh, H.C. Aspirin as adjuvant therapy for colorectal cancer—Reinterpreting paradigms. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, N.A.; Becht, E.; Remark, R.; Damotte, D.; Sautès-Fridman, C.; Fridman, W.H. The immune contexture of primary and metastatic human tumours. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 27, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.P.; Hofseth, L.J.; Harris, C.C. Radical causes of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 276–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colotta, F.; Allavena, P.; Sica, A.; Garlanda, C.; Mantovani, A. Cancer-related inflammation, the seventh hallmark of cancer: Links to genetic instability. Carcinogenesis 2009, 30, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grivennikov, S.I.; Greten, F.R.; Karin, M. Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell 2010, 140, 883–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Gehlot, P. Inflammation and cancer: How friendly is the relationship for cancer patients? Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2009, 9, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Multhoff, G.; Molls, M.; Radons, J. Chronic inflammation in cancer development. Front. Immunol. 2012, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lerma Barbaro, A.; Perletti, G.; Bonapace, I.M.; Monti, E. Inflammatory cues acting on the adult intestinal stem cells and the early onset of cancer (review). Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 959–968. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Salvioli, S.; Monti, D.; Lanzarini, C.; Conte, M.; Pirazzini, C.; Bacalini, M.G.; Garagnani, P.; Giuliani, C.; Fontanesi, E.; Ostan, R.; et al. Immune system, cell senescence, aging and longevity—inflamm-aging reappraised. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1675–1679. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonafè, M.; Storci, G.; Franceschi, C. Inflamm-aging of the stem cell niche: Breast cancer as a paradigmatic example: Breakdown of the multi-shell cytokine network fuels cancer in aged people. Bioessays 2012, 34, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diakos, C.I.; Charles, K.A.; McMillan, D.C.; Clarke, S.J. Cancer-related inflammation and treatment effectiveness. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 493–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevenini, E.; Caruso, C.; Candore, G.; Capri, M.; Nuzzo, D.; Duro, G.; Rizzo, C.; Colonna-Romano, G.; Lio, D.; di Carlo, D.; et al. Age-related inflammation: The contribution of different organs, tissues and systems. How to face it for therapeutic approaches. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Capri, M.; Salvioli, S.; Scurti, M.; Pini, E.; Monti, D.; Franceschi, C. Immunosenescence and immunogenetics of human longevity. Neuroimmunomodulation 2008, 15, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grignolio, A.; Franceschi, C. History of Research into Aging/Senescence; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wellen, K.E.; Fucho, R.; Gregor, M.F.; Furuhashi, M.; Morgan, C.; Lindstad, T.; Vaillancourt, E.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Saatcioglu, F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Coordinated regulation of nutrient and inflammatory responses by STAMP2 is essential for metabolic homeostasis. Cell 2007, 129, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erridge, C.; Attina, T.; Spickett, C.M.; Webb, D.J. A high-fat meal induces low-grade endotoxemia: Evidence of a novel mechanism of postprandial inflammation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1286–1292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Amar, J.; Iglesias, M.A.; Poggi, M.; Knauf, C.; Bastelica, D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Tuohy, K.M.; Chabo, C.; et al. Metabolic endotoxemia initiates obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregor, M.F.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 29, 415–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Martel, C.; Franceschi, S. Infections and cancer: Established associations and new hypotheses. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2009, 70, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Visser, K.E.; Eichten, A.; Coussens, L.M. Paradoxical roles of the immune system during cancer development. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Ouyang, W.; Huang, C. Inflammation, a key event in cancer development. Mol. Cancer Res. 2006, 4, 221–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macarthur, M.; Hold, G.L.; El-Omar, E.M. Inflammation and Cancer II. Role of chronic inflammation and cytokine polymorphisms in the pathogenesis of gastrointestinal malignancy. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 286, G515–G520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcomb, D.C. Inflammation and Cancer V. chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2004, 287, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baan, R.; Grosse, Y.; Straif, K.; Secretan, B.; El Ghissassi, F.; Bouvard, V. A review of human carcinogens Part F. Chemical agents and related occupations. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 1143–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, A.M. Mechanistic links between COPD and lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2013, 13, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askling, J.; Grunewald, J.; Eklund, A.; Hillerdal, G.; Ekbom, A. Increased risk for cancer following sarcoidosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 160, 1668–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calder, P.C.; Ahluwalia, N.; Brouns, F.; Buetler, T.; Clement, K.; Cunningham, K.; Esposito, K.; Jönsson, L.S.; Kolb, H.; Lansink, M.; et al. Dietary factors and low-grade inflammation in relation to overweight and obesity. Br. J. Nutr. 2011, 106, S5–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, A.; Gridley, G.; Svensson, M.; Nyrén, O.; McLaughlin, J.K.; Fraumeni, J.F.; Adam, H.O. A prospective study of obesity and cancer risk (Sweden). Cancer Causes Control 2001, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renehan, A.G.; Tyson, M.; Egger, M.; Heller, R.F.; Zwahlen, M. Body-mass index and incidence of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. Lancet 2008, 371, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basen-Engquist, K.; Chang, M. Obesity and cancer risk: Recent review and evidence. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 13, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karagozian, R.; Derdák, Z.; Baffy, G. Obesity-associated mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Metabolism 2014, 63, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.; Salvioli, S.; Franceschi, C. Oxidative stress and the ageing endocrine system. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2013, 9, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, S.; Gupta, S.C.; Chaturvedi, M.M.; Aggarwal, B.B. Oxidative stress, inflammation, and cancer: How are they linked? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1603–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A. Cancer: inflammation by remote control. Nature 2005, 435, 752–753. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.W.; Karin, M.A. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation, and cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoesel, B.; Schmid, J.A. The complexity of NF-κB signaling in inflammation and cancer. Mol. Cancer 2013, 2, 12–86. [Google Scholar]
- Tieri, P.; Termanini, A.; Bellavista, E.; Salvioli, S.; Capri, M.; Franceschi, C. Charting the NF-κB pathway interactome map. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Sung, B. NF-κB in cancer: A matter of life and death. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Mao, R.; Yang, J. NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer. Protein Cell 2013, 4, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freund, A.; Orjalo, A.V.; Desprez, P.Y.; Campisi, J. Inflammatory networks during cellular senescence: causes and consequences. Trends Mol. Med. 2010, 16, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Lazzarini, R.; Recchioni, R.; Marcheselli, F.; Rippo, M.R.; di Nuzzo, S.; Albertini, M.C.; Graciotti, L.; Babini, L.; Mariotti, S.; et al. MiR-146a as marker of senescence-associated pro-inflammatory status in cells involved in vascular remodelling. Age (Dordr) 2012, 35, 1157–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodier, F.; Campisi, J. Four faces of cellular senescence. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 192, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, O.A.; Redon, C.E.; Dickey, J.S.; Nakamura, A.J.; Bonner, W.M. Para-inflammation mediates systemic DNA damage in response to tumor growth. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2011, 4, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellavista, E.; Andreoli, F.; Parenti, M.D.; Martucci, M.; Santoro, A.; Salvioli, S.; Capri, M.; Baruzzi, A.; Del Rio, A.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Immunoproteasome in cancer and neuropathologies: a new therapeutic target? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 702–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellavista, E.; Martucci, M.; Vasuri, F.; Santoro, A.; Mishto, M.; Kloss, A.; Capizzi, E.; Degiovanni, A.; Lanzarini, C.; Remondini, D.; et al. Lifelong maintenance of composition, function and cellular/subcellulardistribution of proteasomes in human liver. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 141–142, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, R.I.; Cuervo, A.M. Proteostasis and the aging proteome in health and disease. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2014, 69, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keys, A.; Arvanis, C.; Blackburn, H. Seven Countries: A Multivariate Analysis of Death and Coronary Heart Disease; Harvard University Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutiérrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. PREDIMED Study Investigators. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonaccio, M.; di Castelnuovo, A.; de Curtis, A.; Costanzo, S.; Persichillo, M.; Donati, M.B.; Cerletti, C.; Iacoviello, L.; de Gaetano, G. Moli-sani Project Investigators. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with lower platelet and leukocyte counts: Results from the Moli-sani study. Blood 2014, 123, 3037–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Orfanos, P.; Norat, T.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, B.; Ocké, M.C.; Peeters, P.H.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Boeing, H.; Hoffmann, K.; Boffetta, P.; et al. Modified Mediterranean diet and survival: EPIC-elderly prospective cohort study. BMJ 2005, 330, 991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mente, A.; de Koning, L.; Shannon, H.S.; Anand, S.S. A systematic review of the evidence supporting a causal link between dietary factors and coronary heart disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misirli, G.; Benetou, V.; Lagiou, P.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D.; Trichopoulou, A. Relation of the traditional Mediterranean diet to cerebrovascular disease in a Mediterranean population. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 176, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetou, V.; Trichopoulou, A.; Orfanos, P.; Naska, A.; Lagiou, P.; Boffetta, P.; Trichopoulos, D.; Greek, E. Conformity to traditional Mediterranean diet and cancer incidence: The Greek EPIC cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 99, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couto, E.; Boffetta, P.; Lagiou, P.; Ferrari, P.; Buckland, G.; Overvad, K.; Dahm, C.C.; Tjonneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. Mediterranean dietary pattern and cancer risk in the EPIC cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand-Miller, J.; Dickinson, S.; Barclay, A.; Celermajer, D. The glycemic index and cardiovascular disease risk. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2007, 9, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirrahimi, A.; Chiavaroli, L.; Srichaikul, K.; Augustin, L.S.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Kendall, C.W.; Jenkins, D.J. The role of glycemic index and glycemic load in cardiovascular disease and its risk factors: A review of the recent literature. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2014, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, F.; Macchi, C.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Mediterranean diet and health. Biofactors 2013, 39, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vrese, M.; Schrezenmeir, J. Probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2008, 111, 1–66. [Google Scholar]
- De Lorgeril, M.; Salen, P. New insights into the health effects of dietary saturated and omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. BMC Med. 2012, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalogeropoulos, N.; Chiou, A.; Ioannou, M.S.; Karathanos, V.T. Nutritional evaluation and health promoting activities of nuts and seeds cultivated in Greece. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 64, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora-Ros, R.; Serafini, M.; Estruch, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; Arós, F.; Covas, M.I.; et al. PREDIMED Study Investigators. Mediterranean diet and non enzymatic antioxidant capacity in the PREDIMED study: Evidence for a mechanism of antioxidant tuning. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolomvotsou, A.I.; Rallidis, L.S.; Mountzouris, K.C.; Lekakis, J.; Koutelidakis, A.; Efstathiou, S.; Nana-Anastasiou, M.; Zampelas, A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and close dietetic supervision increase total dietary antioxidant intake and plasma antioxidant capacity in subjects with abdominal obesity. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Tong, T.Y.; Forouhi, N.G.; Khandelwal, S.; Prabhakaran, D.; Mozaffarian, D.; de Lorgeril, M. Definitions and potential health benefits of the Mediterranean diet: views from experts around the world. BMC Med. 2014, 12, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Kouris-Blazos, A.; Wahlqvist, M.L.; Gnardellis, C.; Lagiou, P.; Polychronopoulos, E.; Vassilakou, T.; Lipworth, L.; Trichopoulos, D. Diet and overall survival in elderly people. BMJ 1995, 311, 1457–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosire, C.; Stampfer, M.J.; Subar, A.F.; Park, Y.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Chiuve, S.E.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Reedy, J. Index-based dietary patterns and the risk of prostate cancer in the NIH-AARP diet and health study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 177, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrou, P.N.; Kipnis, V.; Thiébaut, A.C.; Reedy, J.; Subar, A.F.; Wirfält, E.; Flood, A.; Mouw, T.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Leitzmann, M.F.; et al. Mediterranean dietary pattern and prediction of all-cause mortality in a US population: results from the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwingshackl, L.; Hoffmann, G. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1884–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, G.; Biondi, A.; Galvano, F.; Mistretta, A.; Marventano, S.; Buscemi, S.; Drago, F.; Basile, F. Factors associated with colorectal cancer in the context of the Mediterranean diet: A case-control study. Nutr. Cancer 2014, 66, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnoli, C.; Grioni, S.; Sieri, S.; Palli, D.; Masala, G.; Sacerdote, C.; Vineis, P.; Tumino, R.; Giurdanella, M.C.; Pala, V.; et al. Italian Mediterranean Index and risk of colorectal cancer in the Italian section of the EPIC cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1404–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedy, J.; Mitrou, P.N.; Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Wirfält, E.; Flood, A.; Kipnis, V.; Leitzmann, M.; Mouw, T.; Hollenbeck, A.; Schatzkin, A.; et al. Index-based dietary patterns and risk of colorectal cancer: the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2008, 168, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenfield, S.A.; DuPre, N.; Richman, E.L.; Stampfer, M.J.; Chan, J.M.; Giovannucci, E.L. Mediterranean diet and prostate cancer risk and mortality in the health professionals follow-up study. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filomeno, M.; Bosetti, C.; Garavello, W.; Levi, F.; Galeone, C.; Negri, E.; la Vecchia, C. The role of a Mediterranean diet on the risk of oral and pharyngeal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosetti, C.; Gallus, S.; Trichopoulou, A.; Talamini, R.; Franceschi, S.; Negri, E.; la Vecchia, C. Influence of the Mediterranean diet on the risk of cancers of the upper aerodigestive tract. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2003, 12, 1091–1094. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samoli, E.; Lagiou, A.; Nikolopoulos, E.; Lagogiannis, G.; Barbouni, A.; Lefantzis, D.; Trichopoulos, D.; Brennan, P.; Lagiou, P. Mediterranean diet and upper aerodigestive tract cancer: the Greek segment of the Alcohol-Related Cancers and Genetic Susceptibility in Europe study. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 1369–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourouti, N.; Papavagelis, C.; Plytzanopoulou, P.; Kontogianni, M.; Vassilakou, T.; Malamos, N.; Linos, A.; Panagiotakos, D. Dietary patterns and breast cancer: A case-control study in women. Eur. J. Nutr. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- De la Torre-Carbot, K.; Chávez-Servín, J.L.; Jaúregui, O.; Castellote, A.I.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M.; Nurmi, T.; Poulsen, H.E.; Gaddi, A.V.; Kaikkonen, J.; Zunft, H.F.; et al. Elevated circulating LDL phenol levels in men who consumed virgin rather than refined olive oil are associated with less oxidation of plasma LDL. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camargo, A.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Cruz-Teno, C.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Perez-Martinez, P.; Gutierrez-Mariscal, F.M.; Lora-Aguilar, P.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; Fuentes-Jimenez, F.; et al. Expression of proinflammatory, proatherogenic genes is reduced by the Mediterranean diet in elderly people. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 500–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shisodia, S. Suppression of the nuclear factor-kappaB activation pathway by spice-derived phytochemicals: reasoning for seasoning. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2004, 1030, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, C.; Varì, R.; Scazzocchio, B.; Di Benedetto, R.; Filesi, C.; Masella, R. Polyphenols, intracellular signalling and inflammation. Ann. Ist. Super Sanita 2007, 43, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laughton, M.J.; Evans, P.J.; Moroney, M.A.; Hoult, J.R.; Halliwell, B. Inhibition of mammalian 5-lipoxygenase and cyclo-oxygenase by flavonoids and phenolic dietary additives. Relationship to antioxidant activity and to iron ion-reducing ability. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1991, 42, 1673–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrándiz, M.L.; Alcaraz, M.J. Anti-inflammatory activity and inhibition of arachidonic acid metabolism by flavonoids. Agents Actions 1991, 32, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.P.; Mani, I.; Iversen, L.; Ziboh, V.A. Effects of naturally-occurring flavonoids and biflavonoids on epidermal cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase from guinea-pigs. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 1998, 58, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chondrogianni, N.; Kapeta, S.; Chinou, I.; Vassilatou, K.; Papassideri, I.; Gonos, E.S. Anti-ageing and rejuvenating effects of quercetin. Exp. Gerontol. 2010, 45, 763–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scoditti, E.; Calabriso, N.; Massaro, M.; Pellegrino, M.; Storelli, C.; Martines, G.; de Caterina, R.; Carluccio, M.A. Mediterranean diet polyphenols reduce inflammatory angiogenesis through MMP-9 and COX-2 inhibition in human vascular endothelial cells: A potentially protective mechanism in atherosclerotic vascular disease and cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 527, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.C.; Huang, Y.T.; Tsai, S.H.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y.; Chen, C.F.; Lin, J.K. Suppression of inducible cyclooxygenase and inducible nitric oxide synthase by apigenin and related flavonoids in mouse macrophages. Carcinogenesis 1999, 20, 1945–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Cheon, B.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.P. Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.C.; Shen, S.C.; Lee, W.R.; Hou, W.C.; Yang, L.L.; Lee, T.J. Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and lipopolysaccharide induced inducible NOS and cyclooxygenase-2 gene expressions by rutin, quercetin, and quercetin pentaacetate in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Cell Biochem. 2001, 82, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miles, E.A.; Zoubouli, P.; Calder, P.C. Differential anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic compounds from extra virgin olive oil identified in human whole blood cultures. Nutrition 2005, 21, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calixto, J.B.; Campos, M.M.; Otuki, M.F.; Santos, A.R. Anti-inflammatory compounds of plant origin. Part II. modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and adhesion molecules. Plant. Med. 2004, 70, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comalada, M.; Ballester, I.; Bailón, E.; Sierra, S.; Xaus, J.; Gálvez, J.; de Medina, F.S.; Zarzuelo, A. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory markers in primary bone marrow-derived mouse macrophages by naturally occurring flavonoids: Analysis of the structure-activity relationship. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1010–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blonska, M.; Czuba, Z.P.; Krol, W. Effect of flavone derivatives on interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) mRNA expression and IL-1beta protein synthesis in stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Scand. J. Immunol. 2003, 57, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.; Mishra, M.; Ghosh, S.; Tewari, R.; Basu, A.; Seth, P.; Sen, E. Modulation of interleukin-1beta mediated inflammatory response in human astrocytes by flavonoids: Implications in neuroprotection. Brain Res. Bull. 2007, 73, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.D.; Choi, C.H.; Bark, H.; Son, H.Y.; Park, H.H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.W.; Park, E.K.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, S.H. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 5, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, I.; Biswas, S.K.; Kirkham, P.A. Regulation of inflammation and redox signaling by dietary polyphenols. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1439–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benvenuto, M.; Fantini, M.; Masuelli, L.; de Smaele, E.; Zazzeroni, F.; Tresoldi, I.; Calabrese, G.; Galvano, F.; Modesti, A.; Bei, R. Inhibition of ErbB receptors, Hedgehog and NF-kappaB signaling by polyphenols in cancer. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2013, 18, 1290–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.C.; Chow, M.P.; Huang, W.C.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, Y.J. Flavonoids inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in respiratory epithelial cells through activator protein-1 and nuclear factor-kappaB: Structure-activity relationships. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 66, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.M.; Wu, C.H.; Yen, G.C. Effects of flavonoids on the expression of the pro-inflammatory response in human monocytes induced by ligation of the receptor for AGEs. Mol. Nutr. Food. Res. 2006, 50, 1129–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallauf, K.; Giller, K.; Huebbe, P.; Rimbach, G. Nutrition and healthy ageing: Calorie restriction or polyphenol-rich “MediterrAsian” diet? Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 707421. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bruning, A. Inhibition of mTOR signaling by quercetin in cancer treatment and prevention. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2013, 13, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galli, M.; van Gool, F.; Leo, O. Sirtuins and inflammation: friends or foes? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 81, 569–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horio, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Kuno, A.; Kunimoto, R. Cellular and molecular effects of sirtuins in health and disease. Clin. Sci. (Lond) 2011, 121, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, F.; Hoberg, J.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Keller, M.D.; Jones, D.R.; Frye, R.A.; Mayo, M.W. Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 2369–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, T.L.; Michishita, E.; Adler, A.S.; Damian, M.; Berber, E.; Lin, M.; McCord, R.A.; Ongaigui, K.C.; Boxer, L.D.; Chang, H.Y.; et al. SIRT6 links histone H3 lysine 9 deacetylation to NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression and organismal life span. Cell 2009, 136, 62–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhazzazi, T.Y.; Kamarajan, P.; Verdin, E.; Kapila, Y.L. Sirtuin-3 (SIRT3) and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gool, F.; Galli, M.; Gueydan, C.; Kruys, V.; Prevot, P.P.; Bedalov, A.; Mostoslavsky, R.; Alt, F.W.; de Smedt, T.; Leo, O. Intracellular NAD levels regulate tumor necrosis factor protein synthesis in a sirtuin-dependent manner. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parbin, S.; Kar, S.; Shilpi, A.; Sengupta, D.; Deb, M.; Rath, S.K.; Patra, S.K. Histone deacetylases: A saga of perturbed acetylation homeostasis in cancer. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 11–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, N.Y.; Surh, Y.J. Janus-faced role of SIRT1 in tumorigenesis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2012, 1271, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayram, B.; Ozcelik, B.; Grimm, S.; Roeder, T.; Schrader, C.; Ernst, I.M.; Wagner, A.E.; Grune, T.; Frank, J.; Rimbach, G. A diet rich in olive oil phenolics in the heart of SAMP8 mice by induction of Nrf2-dependent gene expression. Rejuvenation Res. 2012, 15, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menendez, J.A.; Joven, J.; Aragonès, G.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Beltrán-Debón, R.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Camps, J.; Corominas-Faja, B.; Cufí, S.; Fernández-Arroyo, S.; et al. Xenohormetic and anti-aging activity of secoiridoid polyphenols present in extra virgin olive oil: A new family of gerosuppressant agents. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 555–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popat, R.; Plesner, T.; Davies, F.; Cook, G.; Cook, M.; Elliott, P.; Jacobson, E.; Gumbleton, T.; Oakervee, H.; Cavenagh, J. A phase 2 study of SRT501 (resveratrol) with bortezomib for patients with relapsed and or refractory multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 714–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohn, T. Dietary factors affecting polyphenol bioavailability. Nutr. Rev. 2014, 72, 429–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holzapfel, N.P.; Holzapfel, B.M.; Champ, S.; Feldthusen, J.; Clements, J.; Hutmacher, D.W. The potential role of lycopene for the prevention and therapy of prostate cancer: from molecular mechanisms to clinical evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14620–14646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjelakovic, G.; Nikolova, D.; Gluud, C. Antioxidant supplements and mortality. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2014, 17, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Hébert, J.R.; Li, W.; Bertone-Johnson, E.R.; Olendzki, B.; Pagoto, S.L.; Tinker, L.; Rosal, M.C.; Ockene, I.S.; Ockene, J.K.; et al. Association between dietary fiber and markers of systemic inflammation in the Women’s Health Initiative Observational Study. Nutrition 2008, 24, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Griffith, J.A.; Chasan-Taber, L.; Olendzki, B.C.; Jackson, E.; Stanek, E.J., 3rd; Li, W.; Pagoto, S.L.; Hafner, A.R.; Ockene, I.S. Association between dietary fiber and serum C-reactive protein. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chuang, S.C.; Vermeulen, R.; Sharabiani, M.T.; Sacerdote, C.; Fatemeh, S.H.; Berrino, F.; Krogh, V.; Palli, D.; Panico, S.; Tumino, R.; et al. The intake of grain fibers modulates cytokine levels in blood. Biomarkers 2011, 16, 504–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.S.; Hirose, Y.; Cohen, L.A.; Simi, B.; Cooma, I.; Rao, C.V. Preventive potential of wheat bran fractions against experimental colon carcinogenesis: implications for human colon cancer prevention. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 4792–4797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guigoz, Y.; Rochat, F.; Perruisseau-Carrier, G.; Rochat, I.; Schiffrin, E.J. Effects of oligosaccharide on the faecal flora and nonspecific immune system in elderly people. Nutr. Res. 2002, 22, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarczyk, M.M.; Miller, M.J.; Freund, G.G. The health benefits of dietary fiber: Beyond the usual suspects of type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and colon cancer. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1058–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durko, L.; Malecka-Panas, E. Lifestyle Modifications and Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Colorectal. Cancer Rep. 2014, 10, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toner, C.D. Communicating clinical research to reduce cancer risk through diet: Walnuts as a case example. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2014, 8, 347–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urpi-Sarda, M.; Casas, R.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Romero-Mamani, E.S.; Valderas-Martínez, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.I.; Toledo, E.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Llorach, R.; et al. The Mediterranean diet pattern and its main components are associated with lower plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor receptor 60 in patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, R.E.; Flatt, S.W.; Newman, V.A.; Natarajan, L.; Rock, C.L.; Thomson, C.A.; Caan, B.J.; Parker, B.A.; Pierce, J.P. Marine fatty acid intake is associated with breast cancer prognosis. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapkin, R.S.; Kim, W.; Lupton, J.R.; McMurray, D.N. Dietary docosahexaenoic and eicosapentaenoic acid: emerging mediators of inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2009, 81, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarelli, R.L.; Pierre, F.; Corpet, D.E. Processed meat and colorectal cancer: A review of epidemiologic and experimental evidence. Nutr. Cancer 2008, 60, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myles, I.A. Fast food fever: reviewing the impacts of the Western diet on immunity. Nutr. J. 2014, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Spazzafumo, L.; Santini, G.; Lazzarini, R.; Albertini, M.C.; Rippo, M.R.; Galeazzi, R.; Abbatecola, A.M.; Marcheselli, F.; Monti, D.; et al. Age-related differences in the expression of circulating microRNAs: miR-21 as a new circulating marker of inflammaging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2012, 133, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esquela-Kerscher, A.; Slack, F.J. Oncomirs—microRNAs with a role in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R.I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzur, G.; Israel, A.; Levy, A.; Benjamin, H.; Meiri, E.; Shufaro, Y.; Meir, K.; Khvalevsky, E.; Spector, Y.; Rojansky, N.; et al. Comprehensive gene and microRNA expression profiling reveals a role for microRNAs in human liver development. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e7511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.P.; Harris, C.C. Inflammation and cancer: an ancient link with novel potentials. Int. J. Cancer 2007, 121, 2373–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olivieri, F.; Rippo, M.R.; Monsurrò, V.; Salvioli, S.; Capri, M.; Procopio, A.D.; Franceschi, C. MicroRNAs linking inflamm-aging, cellular senescence and cancer. Ageing Res. Rev. 2013, 12, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piepoli, A.; Tavano, F.; Copetti, M.; Mazza, T.; Palumbo, O.; Panza, A.; di Mola, F.F.; Pazienza, V.; Mazzoccoli, G.; Biscaglia, G.; et al. miRNA expression profiles identify drivers in colorectal and pancreatic cancers. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Govindan, R.; Wang, L.; Liu, P.Y.; Goodgame, B.; Wen, W.; Sezhiyan, A.; Pfeifer, J.; Li, Y.F.; Hua, X.; et al. MicroRNA profiling and prediction of recurrence/relapse-free survival in stage I lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Wang, H.; Fisher, W.E.; Lin, P.H.; Yao, Q.; Chen, C. Profiling of 95 microRNAs in pancreatic cancer cell lines and surgical specimens by real-time PCR analysis. World. J. Surg. 2009, 33, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenech, M.; El-Sohemy, A.; Cahill, L.; Ferguson, L.R.; French, T.A.; Tai, E.S.; Milner, J.; Koh, W.P.; Xie, L.; Zucker, M.; et al. Nutrigenetics and nutrigenomics: Viewpoints on the current status and applications in nutrition research and practice. J. Nutrigenet. Nutrigenomics 2011, 4, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.L.; Chapkin, R.S.; Lupton, J.R. Fish oil blocks azoxymethane-induced rat colon tumorigenesis by increasing cell differentiation and apoptosis rather than decreasing cell proliferation. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davidson, L.A.; Wang, N.; Ivanov, I.; Goldsby, J.; Lupton, J.R.; Chapkin, R.S. Identification of actively translated mRNA transcripts in a rat model of early-stage colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev. Res. 2009, 2, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachroo, P.; Ivanov, I.; Davidson, L.A.; Chowdhary, B.P.; Lupton, J.R.; Chapkin, R.S. Classification of diet-modulated gene signatures at the colon cancer initiation and progression stages. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 5, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turk, H.F.; Barhoumi, R.; Chapkin, R.S. Alteration of EGFR spatiotemporal dynamics suppresses signal transduction. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimri, M.; Bommi, P.V.; Sahasrabuddhe, A.A.; Khandekar, J.D.; Dimri, G.P. Dietary omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids suppress expression of EZH2 in breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2010, 31, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leaver, H.A.; Wharton, S.B.; Bell, H.S.; Leaver-Yap, I.M.; Whittle, I.R. Highly unsaturated fatty acid induced tumour regression in glioma pharmacodynamics and bioavailability of gamma linolenic acid in an implantation glioma model: effects on tumour biomass, apoptosis and neuronal tissue histology. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2002, 67, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B.S.; Burill, C.; Rigotty, J. Effect of diets high in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids on initiation and postinitiation stages of colon carcinogenesis. Cancer Res 1991, 51, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Whelan, J.; McEntee, M.F. Dietary (n-6) PUFA and intestinal tumorigenesis. J Nutr. 2004, 134, 3421–3426. [Google Scholar]
- Vinciguerra, M.; Sgroi, A.; Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Buhler, L.H.; Foti, M. Unsaturated fatty acids inhibit the expression of tumor suppressor phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) via microRNA-21 up-regulation in hepatocytes. Hepatology 2009, 49, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodin, R.A.; Meng, S.; Archer, S.; Tang, R. Cellular growth state differentially regulates enterocyte gene expression in butyrate-treated HT-29 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1996, 7, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinnebusch, B.F.; Meng, S.; Wu, J.T.; Archer, S.Y.; Hodin, R.A. The effects of short-chain fatty acids on human colon cancer cell phenotype are associated with histone hyperacetylation. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chirakkal, H.; Leech, S.H.; Brookes, K.E.; Prais, A.L.; Waby, J.S.; Corfe, B.M. Upregulation of BAK by butyrate in the colon is associated with increased Sp3 binding. Oncogene 2006, 25, 7192–7200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comalada, M.; Bailón, E.; de Haro, O.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Xaus, J.; Zarzuelo, A.; Gálvez, J. The effects of short-chain fatty acids on colon epithelial proliferation and survival depend on the cellular phenotype. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 132, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Dong, T.S.; Dalal, S.R.; Wu, F.; Bissonnette, M.; Kwon, J.H.; Chang, E.B. The microbe-derived short chain fatty acid butyrate targets miRNA-dependent p21 gene expression in human colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, M.S.; Schwartz, S.L.; Zhao, C.; Davidson, L.A.; Zhou, B.; Lupton, J.R.; Ivanov, I.; Chapkin, R.S. Integrated microRNA and mRNA expression profiling in a rat colon carcinogenesis model: Effect of a chemo-protective diet. Physiol. Genomics 2011, 43, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zuo, L.; Xu, C.; Shen, T.; Pan, H.; Zhang, Z. Apoptosis and differentiation induced by sodium selenite combined with all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in NB4 cells. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 2002, 23, 628–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Terao, M.; Fratelli, M.; Kurosaki, M.; Zanetti, A.; Guarnaccia, V.; Paroni, G.; Tsykin, A.; Lupi, M.; Gianni, M.; Goodall, G.J.; et al. Induction of miR-21 by retinoic acid in estrogen receptor-positive breast carcinoma cells: Biological correlates and molecular targets. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 4027–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Gocek, E.; Liu, C.G.; Studzinski, G.P. MicroRNAs181 regulate the expression of p27Kip1 in human myeloid leukemia cells induced to differentiate by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arts, I.C.; Hollman, P.C. Polyphenols and disease risk in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 317–325. [Google Scholar]
- Scalbert, A.; Manach, C.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Dietary polyphenols and the prevention of diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 45, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroeter, H.; Heiss, C.; Balzer, J.; Kleinbongard, P.; Keen, C.L.; Hollenberg, N.K.; Sies, H.; Kwik-Uribe, C.; Schmitz, H.H.; Kelm, M. Epicatechin mediates beneficial effects of flavanol-rich cocoa on vascular function in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 1024–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spencer, J.P.; Abd El Mohsen, M.M.; Minihane, A.M.; Mathers, J.C. Biomarkers of the intake of dietary polyphenols: strengths, limitations and application in nutrition research. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Joven, J.; Espinel, E.; Rull, A.; Aragonès, G.; Rodríguez-Gallego, E.; Camps, J.; Micol, V.; Herranz-López, M.; Menéndez, J.A.; Borrás, I.; et al. Plant-derived polyphenols regulate expression of miRNA paralogs miR-103/107 and miR-122 and prevent diet-induced fatty liver disease in hyperlipidemic mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Estrov, Z.; Ji, Y.; Coombes, K.R.; Harris, D.H.; Kurzrock, R. Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) alters the expression profiles of microRNAs in human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 464–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, B.; Ali, S.; Kong, D.; Sarkar, S.H.; Wang, Z.; Banerjee, S.; Aboukameel, A.; Padhye, S.; Philip, P.A.; Sarkar, F.H. Anti-tumor activity of a novel compound-CDF is mediated by regulating miR-21, miR-200, and PTEN in pancreatic cancer. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Candela, M.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; Franceschi, C.; Brigidi, P. Aging of the human metaorganism: the microbial counterpart. Age (Dordr) 2012, 34, 247–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claesson, M.J.; Cusack, S.; O’Sullivan, O.; Greene-Diniz, R.; de Weerd, H.; Flannery, E.; Marchesi, J.R.; Falush, D.; Dinan, T.; Fitzgerald, G.; et al. Composition, variability, and temporal stability of the intestinal microbiota of the elderly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4586–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckburg, P.B.; Bik, E.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Purdom, E.; Dethlefsen, L.; Sargent, M.; Gill, S.R.; Nelson, K.E.; Relman, D.A. Diversity of the human intestinal microbial flora. Science 2005, 308, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Brigidi, P.; O’Toole, P.W.; de Vos, W.M. Maintenance of a healthy trajectory of the intestinal microbiome during aging: A dietary approach. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, R.N.; Anokhin, A.P.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeffery, I.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Diet-microbiota interactions and their implications for healthy living. Nutrients 2013, 5, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claesson, M.J.; Jeffery, I.B.; Conde, S.; Power, S.E.; O’Connor, E.M.; Cusack, S.; Harris, H.M.; Coakley, M.; Lakshminarayanan, B.; O’Sullivan, O.; et al. Gut microbiota composition correlates with diet and health in the elderly. Nature 2012, 488, 178–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ridaura, V.K.; Faith, J.J.; Rey, F.E.; Knight, R.; Gordon, J.I. The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: A metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 2009, 1, 6ra14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäckhed, F.; Ley, R.E.; Sonnenburg, J.L.; Peterson, D.A.; Gordon, J.I. Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 2005, 307, 1915–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duncan, S.H.; Belenguer, A.; Holtrop, G.; Johnstone, A.M.; Flint, H.J.; Lobley, G.E. Reduced dietary intake of carbohydrates by obese subjects results in decreased concentrations of butyrate and butyrate-producing bacteria in feces. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, E.; Nylund, L.; Candela, M.; Ostan, R.; Bucci, L.; Pini, E.; Nikkïla, J.M.; Monti, D.; Satokari, R.; Franceschi, C.; et al. Through aging, and beyond: gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, P.; Ferlay, J. Mortality and survival in breast and colorectal cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 424–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mladenova, D.; Kohonen-Corish, M.R. Review: Mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease: insights into the mechanisms of inflammation-associated colorectal cancer. In Vivo 2012, 26, 627–646. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikolaki, S.; Tsiamis, G. Microbial diversity in the era of omic technologies. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 958719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjalsma, H.; Boleij, A.; Marchesi, J.R.; Dutilh, B.E. A bacterial driver-passenger model for colorectal cancer: beyond the usual suspects. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Wang, T.C. Cancer. Bacteria deliver a genotoxic hit. Science 2012, 338, 52–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wishart, D.S.; Knox, C.; Guo, A.C.; Eisner, R.; Young, N.; Gautam, B.; Hau, D.D.; Psychogios, N.; Dong, E.; Bouatra, S.; et al. HMDB: A knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucl. Acids Res. 2009, 37, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahy, E.; Subramaniam, S.; Murphy, R.C.; Nishijima, M.; Raetz, C.R.; Shimizu, T.; Spener, F.; van Meer, G.; Wakelam, M.J.; Dennis, E.A. Update of the LIPID MAPS comprehensive classification system for lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayavekhin, N.; Homan, E.; Saghatelian, A. Exploring disease through metabolomics. ACS Chem. Biol. 2010, 5, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieger, C.; Geistlinger, L.; Altmaier, E.; Hrabé de Angelis, M.; Kronenberg, F.; Meitinger, T.; Mewes, H.W.; Wichmann, H.-E.; Weinberger, K.M.; Adamski, J.; et al. Genetics meets metabolomics: A genome-wide association study of metabolite profiles in human serum. PLoS Genet 2008, 4, e1000282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chadeau-Hyam, M.; Ebbels, T.M.; Brown, I.J.; Chan, Q.; Stamler, J.; Huang, C.C.; Daviglus, M.L.; Ueshima, H.; Zhao, L.; Holmes, E.; et al. Metabolic profiling and the metabolome-wide association study: significance level for biomarker identification. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 4620–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Elliott, P. The metabolome-wide association study: A new look at human disease risk factors. J Proteome Res 2008, 7, 3637–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bictash, M.; Ebbels, T.M.; Chan, Q.; Loo, R.L.; Yap, I.K.; Brown, I.J.; de Iorio, M.; Daviglus, M.L.; Holmes, E.; Stamler, J.; et al. Opening up the “Black Box”: Metabolic phenotyping and metabolome-wide association studies in epidemiology. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2010, 63, 970–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, E.; MacNeil, L.T.; Ritter, A.D.; Yilmaz, L.S.; Rosebrock, A.P.; Caudy, A.A.; Walhout, A.J. Interspecies systems biology uncovers metabolites affecting C. elegans gene expression and life history traits. Cell 2014, 156, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nookaew, I.; Gabrielsson, B.G.; Holmäng, A.; Sandberg, A.S.; Nielsen, J. Identifying molecular effects of diet through systems biology: Influence of herring diet on sterol metabolism and protein turnover in mice. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, J.L.; Shockcor, J.P. Metabolic profiles of cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratlin, J.L.; Serkova, N.J.; Eckhardt, S.G. Clinical applications of metabolomics in oncology: A review. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tieri, P.; de la Fuente, A.; Termanini, A.; Franceschi, C. Integrating Omics data for signaling pathways, interactome reconstruction, and functional analysis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2011, 719, 415–433. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, A.; Poisson, L.M.; Rajendiran, T.M.; Khan, A.P.; Cao, Q.; Yu, J.; Laxman, B.; Mehra, R.; Lonigro, R.J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metabolomic profiles delineate potential role for sarcosine in prostate cancer progression. Nature 2009, 457, 910–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, N.K.H.; de Meij, T.G.; Oort, F.A.; Ben Larbi, I.; Mulder, C.J.; van Bodegraven, A.A.; van der Schee, M.P. The Scent of Colorectal Cancer: Detection by Volatile Organic Compound Analysis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floegel, A.; Wientzek, A.; Bachlechner, U.; Jacobs, S.; Drogan, D.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Krumsiek, J.; Schulze, M.B.; Pischon, T.; et al. Linking diet, physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness and obesity to serum metabolite networks: findings from a population-based study. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2014, 38, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurostat. Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/help/new-eurostat-website (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- The European Project NU-AGE (FP7,n° 266486; 2011–2016). Available online: http://www.nu-age.eu (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- Santoro, A.; Pini, E.; Scurti, M.; Palmas, G.; Berendsen, A.; Brzozowska, A.; Pietruszka, B.; Szczecinska, A.; Cano, N.; Meunier, N.; et al. The NU-AGE Consortium. Combating inflammaging through a Mediterranean whole diet approach: the NU-AGE project’s conceptual framework and design. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berendsen, A.; Santoro, A.; Pini, E.; Cevenini Ostan, R.; Pietruszka, B.; Rolf, K.; Cano, N.; Caille, A.; Lyon-Belgy, N.; Fairweather-Tait, S.; et al. A randomized trial on the effect of a full dietary intervention on ageing in European elderly people: Design of the NU-AGE dietary intervention study. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2013, 134, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calçada, D.; Vianello, D.; Giampieri, E.; Sala, C.; Castellani, G.; de Graaf, A.; Kremer, B.; van Ommen, B.; Feskens, E.; Santoro, A.; et al. The role of low-grade inflammation and metabolic flexibility in aging and nutritional modulation thereof: a systems biology approach. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mediterranean diet and inflammaging in the elderly: The European project NU-AGE. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2014, 136–137. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, V. Microbiome: Cultural differences. Nature 2012, 492, S14–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ostan, R.; Lanzarini, C.; Pini, E.; Scurti, M.; Vianello, D.; Bertarelli, C.; Fabbri, C.; Izzi, M.; Palmas, G.; Biondi, F.; et al. Inflammaging and Cancer: A Challenge for the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients 2015, 7, 2589-2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7042589
Ostan R, Lanzarini C, Pini E, Scurti M, Vianello D, Bertarelli C, Fabbri C, Izzi M, Palmas G, Biondi F, et al. Inflammaging and Cancer: A Challenge for the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients. 2015; 7(4):2589-2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7042589
Chicago/Turabian StyleOstan, Rita, Catia Lanzarini, Elisa Pini, Maria Scurti, Dario Vianello, Claudia Bertarelli, Cristina Fabbri, Massimo Izzi, Giustina Palmas, Fiammetta Biondi, and et al. 2015. "Inflammaging and Cancer: A Challenge for the Mediterranean Diet" Nutrients 7, no. 4: 2589-2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7042589
APA StyleOstan, R., Lanzarini, C., Pini, E., Scurti, M., Vianello, D., Bertarelli, C., Fabbri, C., Izzi, M., Palmas, G., Biondi, F., Martucci, M., Bellavista, E., Salvioli, S., Capri, M., Franceschi, C., & Santoro, A. (2015). Inflammaging and Cancer: A Challenge for the Mediterranean Diet. Nutrients, 7(4), 2589-2621. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7042589




