Interaction Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and an Obesity Genetic Risk Score on Adiposity and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: The HELENA Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
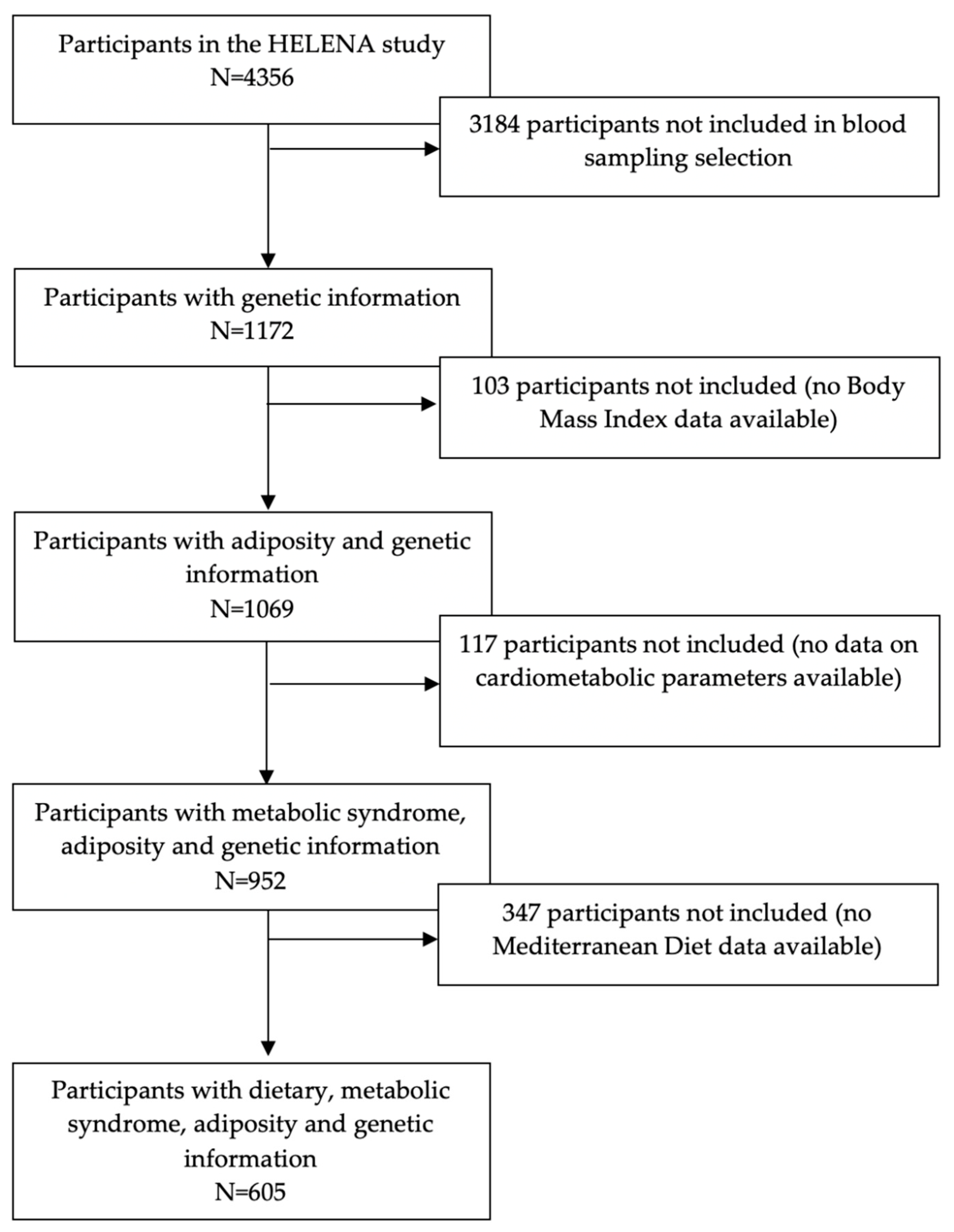
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Population
2.2. Physical Examination, Adiposity Measurements and Cardiometabolic Risk Score
2.3. Dietary Intake Assessment and Mediterranean Diet Score
2.4. Genomic Information and Genetic Risk Score
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Characteristics of the Study Sample
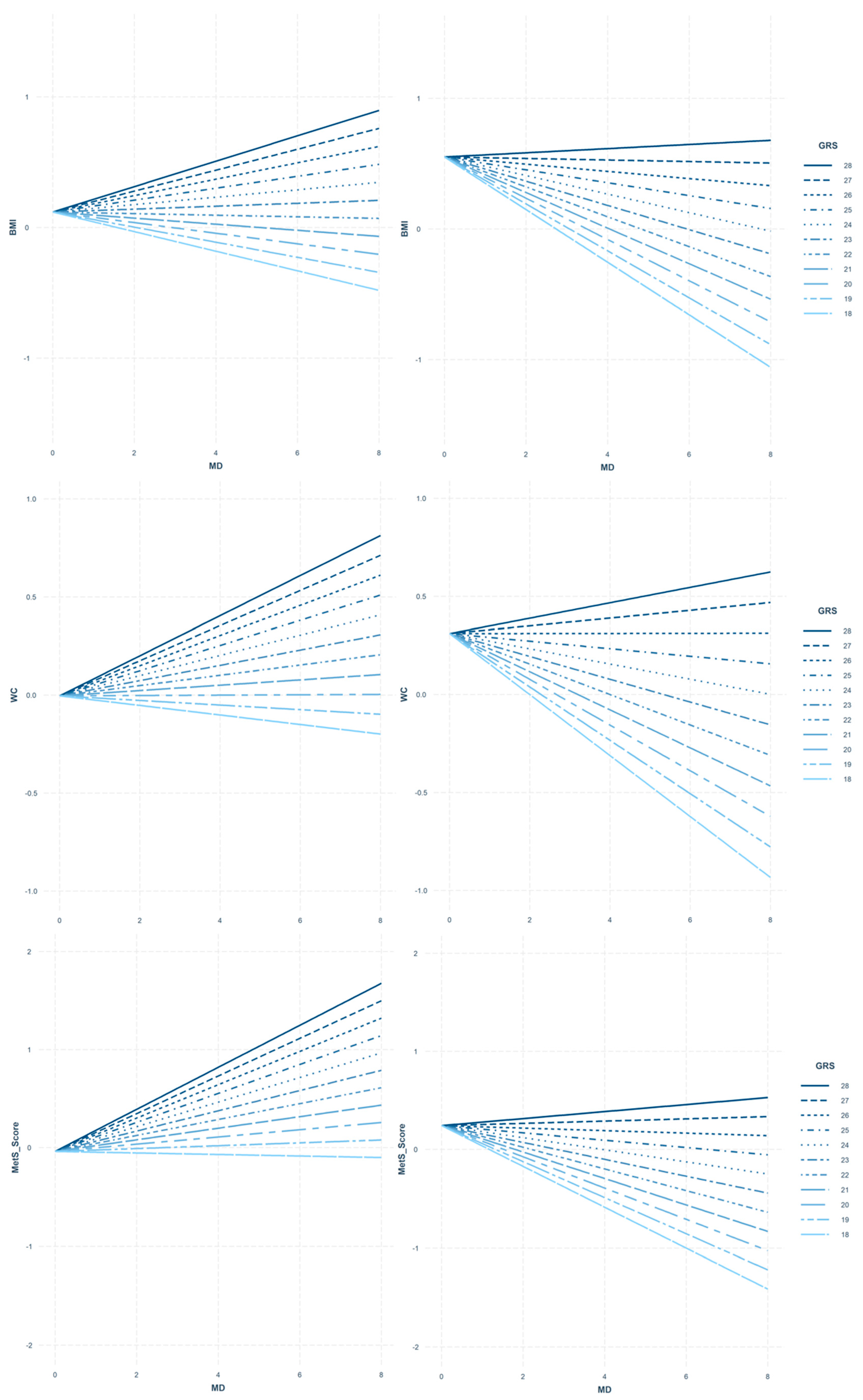
3.2. Interaction between MD and Obesity-GRS on Adiposity/Cardiometabolic Variables
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, S0140–S6736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca-Gómez, L.; Abdeen, Z.A.; Hamid, Z.A.; Abu-Rmeileh, N.M.; Acosta-Cazares, B.; Acuin, C.; Adams, R.J.; Aekplakorn, W.; Afsana, K.; Aguilar-Salinas, C.A.; et al. Worldwide trends in body-mass index, underweight, overweight, and obesity from 1975 to 2016: A pooled analysis of 2416 population-based measurement studies in 128·9 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2017, 390, 2627–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spinelli, A.; Buoncristiano, M.; Kovacs, V.; Yngve, A.; Spiroski, I.; Obreja, G.; Starc, G.; Pérez, N.; Rito, A.; Kunešová, M.; et al. Prevalence of Severe Obesity among Primary School Children in 21 European Countries. Obes. Facts 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steene-Johannessen, J.; Kolle, E.; Anderssen, S.; Andersen, L. Cardiovascular disease risk factors in a population-based sample of Norwegian children and adolescents. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Investig. 2009, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmet, P.A.; Alberti, K.G.M.; Kaufman, F.; Tajima, N.; Silink, M.; Arslanian, S.; Wong, G.; Bennett, P.; Shaw, J.; Caprio, S. The metabolic syndrome in children and adolescents—An IDF consensus report. Pediatric Diabetes 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendo-Urteaga, T.; De Moraes, A.C.F.; Collese, T.S.; Manios, Y.; Hagströmer, M.; Sjöström, M.; Kafatos, A.; Widhalm, K.; Vanhelst, J.; Marcos, A.; et al. The combined effect of physical activity and sedentary behaviors on a clustered cardio-metabolic risk score: The Helena study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristi-Montero, C.; Chillón, P.; Labayen, I.; Casajus, J.A.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Vanhelst, J.; Manios, Y.; Moreno, L.A.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R. Cardiometabolic risk through an integrative classification combining physical activity and sedentary behavior in European adolescents: HELENA study. J. Sport Health Sci. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognon, G.; Hebestreit, A.; Lanfer, A.; Moreno, L.; Pala, V.; Siani, A.; Tornaritis, M.; De Henauw, S.; Veidebaum, T.; Molnár, D.; et al. Mediterranean diet, overweight and body composition in children from eight European countries: Cross-sectional and prospective results from the IDEFICS study. NMCD 2014, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notario-Barandiaran, L.; Valera-Gran, D.; Gonzalez-Palacios, S.; Garcia-de-la-Hera, M.; Fernández-Barrés, S.; Pereda-Pereda, E.; Fernández-Somoano, A.; Guxens, M.; Iñiguez, C.; Romaguera, D.; et al. High adherence to a mediterranean diet at age 4 reduces overweight, obesity and abdominal obesity incidence in children at the age of 8. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velázquez-López, L.; Santiago-Díaz, G.; Nava-Hernández, J.; Muñoz-Torres, A.V.; Medina-Bravo, P.; Torres-Tamayo, M. Mediterranean-style diet reduces metabolic syndrome components in obese children and adolescents with obesity. BMC Pediatrics 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Liang, L.; Fu, J.-F.; Wang, C.-L.; Ling, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Interactions between obesity-related copy number variants and dietary behaviors in childhood obesity. Nutrients 2015, 7, 3054–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koochakpoor, G.; Hosseini-Esfahani, F.; Daneshpour, M.S.; Hosseini, S.A.; Mirmiran, P. Effect of interactions of polymorphisms in the Melanocortin-4 receptor gene with dietary factors on the risk of obesity and Type 2 diabetes: A systematic review. Diabet. Med. 2016, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotta, L.; Mokrosiński, J.; Mendes de Oliveira, E.; Li, C.; Sharp, S.; Luan, J.; Brouwers, B.; Ayinampudi, V.; Bowker, N.; Kerrison, N.; et al. Human Gain-of-Function MC4R Variants Show Signaling Bias and Protect against Obesity. Cell 2019, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lv, D.; Zhang, D.-D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, L.; Fu, J.-F.; Xiong, F.; Liu, G.-L.; Gong, C.-X.; Luo, F.-H.; et al. Genetic variations in SEC16B, MC4R, MAP2K5 and KCTD15 were associated with childhood obesity and interacted with dietary behaviors in Chinese school-age population. Gene 2015, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, A.; Aulchenko, Y.; Elefante, S.; Borsboom, G.; Steyerberg, E.; Van Duijn, C. Predictive testing for complex diseases using multiple genes: Fact or fiction? Genet. Med. 2006, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seyednasrollah, F.; Mäkelä, J.; Pitkänen, N.; Juonala, M.; Hutri-Kähönen, N.; Lehtimäki, T.; Viikari, J.; Kelly, T.; Li, C.; Bazzano, L.; et al. Prediction of Adulthood Obesity Using Genetic and Childhood Clinical Risk Factors in the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Viljakainen, H.; Dahlström, E.; Figueiredo, R.; Sandholm, N.; Rounge, T.; Weiderpass, E. Genetic risk score predicts risk for overweight and obesity in Finnish preadolescents. Clin. Obes. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, L.A.; Gottrand, F.; Huybrechts, I.; Ruiz, J.R.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; DeHenauw, S. Nutrition and lifestyle in european adolescents: The HELENA (Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence) study. Adv. Nutr. 2014, 5, 615s–623s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, L.A.; De Henauw, S.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Kersting, M.; Molnar, D.; Gottrand, F.; Barrios, L.; Sjostrom, M.; Manios, Y.; Gilbert, C.C.; et al. Design and implementation of the Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Beghin, L.; Castera, M.; Manios, Y.; Gilbert, C.C.; Kersting, M.; De Henauw, S.; Kafatos, A.; Gottrand, F.; Molnar, D.; Sjostrom, M.; et al. Quality assurance of ethical issues and regulatory aspects relating to good clinical practices in the HELENA Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, S12–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagy, E.; Vicente-Rodriguez, G.; Manios, Y.; Beghin, L.; Iliescu, C.; Censi, L.; Dietrich, S.; Ortega, F.B.; De Vriendt, T.; Plada, M.; et al. Harmonization process and reliability assessment of anthropometric measurements in a multicenter study in adolescents. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, S58–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cole, T.J.; Bellizzi, M.C.; Flegal, K.M.; Dietz, W.H. Establishing a standard definition for child overweight and obesity worldwide: International survey. BMJ 2000, 320, 1240–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stavnsbo, M.; Resaland, G.K.; Anderssen, S.A.; Steene-Johannessen, J.; Domazet, S.L.; Skrede, T.; Sardinha, L.B.; Kriemler, S.; Ekelund, U.; Andersen, L.B.; et al. Reference values for cardiometabolic risk scores in children and adolescents: Suggesting a common standard. Atherosclerosis 2018, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diethelm, K.; Huybrechts, I.; Moreno, L.; De Henauw, S.; Manios, Y.; Beghin, L.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Le Donne, C.; Cuenca-Garcia, M.; Castillo, M.J.; et al. Nutrient intake of European adolescents: Results of the HELENA (Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence) Study. Public Health Nutr. 2014, 17, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vereecken, C.A.; Covents, M.; Matthys, C.; Maes, L. Young adolescents’ nutrition assessment on computer (YANA-C). Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 59, 658–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vereecken, C.; On behalf of the HELENA Study Group; Covents, M.; Sichert-Hellert, W.; Alvira, J.M.F.; Le Donne, C.; De Henauw, S.; De Vriendt, T.; Phillipp, M.K.; Béghin, L.; et al. Development and evaluation of a self-administered computerized 24-h dietary recall method for adolescents in Europe. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andersen, L.F.; Lioret, S.; Brants, H.; Kaic-Rak, A.; De Boer, E.J.; Amiano, P.; Trolle, E. Recommendations for a trans-European dietary assessment method in children between 4 and 14 years. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, S58–S64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a Mediterranean diet and survival in a Greek population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arenaza, L.; Huybrechts, I.; Ortega, F.B.; Ruiz, J.R.; De Henauw, S.; Manios, Y.; Marcos, A.; Julián, C.; Widhalm, K.; Bueno, G.; et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet in metabolically healthy and unhealthy overweight and obese European adolescents: The Helena study. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreno, L.A.; Bel-Serrat, S.; Santaliestra-Pasias, A.; Bueno, G. Dairy products, yogurt consumption, and cardiometabolic risk in children and adolescents. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A. Traditional Mediterranean diet and longevity in the elderly: A review. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 943–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Gross, M.; On Behalf of the HELENA Study Group; Breidenassel, C.; Martínez, S.G.; Ferrari, M.; Beghin, L.; Spinneker, A.; Díaz, L.E.; Maiani, G.; Demailly, A.; et al. Sampling and processing of fresh blood samples within a European multicenter nutritional study: Evaluation of biomarker stability during transport and storage. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seral-Cortes, M.; Sabroso-Lasa, S.; De Miguel-Etayo, P.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Gesteiro, E.; Molina-Hidalgo, C.; De Henauw, S.; Gottrand, F.; Mavrogianni, C.; Manios, Y.; et al. Development of a Genetic Risk Score to predict the risk of overweight and obesity in European adolescents: The Helena study. Under Rev. 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Serra-Majem, L.; Román-Viñas, B.; Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Corella, D.; La Vecchia, C. Benefits of the Mediterranean diet: Epidemiological and molecular aspects. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Orfanos, P.; Norat, T.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, B.; Ocké, M.; Peeters, P.; van der Schouw, Y.; Boeing, H.; Hoffmann, K.; Boffetta, P.; et al. Modified Mediterranean diet and survival: EPIC-elderly prospective cohort study. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2005, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esposito, K.; Maiorino, M.I.; Ceriello, A.; Giugliano, D. Prevention and control of type 2 diabetes by Mediterranean diet: A systematic review. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2010, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corella, D.; Ordovas, J.M. How does the Mediterranean diet promote cardiovascular health? Current progress toward molecular mechanisms: Gene-diet interactions at the genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenomic levels provide novel insights into new mechanisms. BioEssays 2014, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Azorín, C.; Sorlí, J.V.; Asensio, E.M.; Coltell, O.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Covas, M.I.; Arós, F.; Lapetra, J.; Serra-Majem, L.; et al. Associations of the FTO rs9939609 and the MC4R rs17782313 polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes are modulated by diet, being higher when adherence to the Mediterranean diet pattern is low. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Junyent, M.; Parnell, L.D.; Lai, C.-Q.; Arnett, D.K.; Tsai, M.Y.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Straka, R.J.; Province, M.; An, P.; Smith, C.E.; et al. ADAM17_i33708A>G polymorphism interacts with dietary n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids to modulate obesity risk in the Genetics of Lipid Lowering Drugs and Diet Network study. NMCD 2010, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Real, J.M.F.; Corella, D.; Goumidi, L.; Mercader, J.M.; Valdés, S.; Martínez, G.R.; Ortega, F.; Martínez-Larrad, M.T.; Gómez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Salas-Salvado, J.; et al. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha gene variants increase the risk of developing obesity and show gene-diet interactions. Int. J. Obes. 2013, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, C.E.; Arnett, D.K.; Corella, D.; Tsai, M.Y.; Lai, C.-Q.; Parnell, L.D.; Lee, Y.-C.; Ordovas, J.M. Perilipin polymorphism interacts with saturated fat and carbohydrates to modulate insulin resistance. NMCD 2012, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Svetkey, L.P.; Moore, T.J.; Simons-Morton, D.G.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Ard, J.D.; Mortensen, R.M.; Mitchell, S.R.; Conlin, P.R.; et al. Angiotensinogen genotype and blood pressure response in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) study. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordovas, J.M.; Corella, D.; Cupples, L.A.; Demissie, S.; Kelleher, A.; Coltell, O.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Schaefer, E.J.; Tucker, K. Polyunsaturated fatty acids modulate the effects of the APOA1 G-A polymorphism on HDL-cholesterol concentrations in a sex-specific manner: The Framingham Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2002, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Junyent, M.; Parnell, L.D.; Lai, C.-Q.; Lee, Y.-C.; Smith, E.C.; Arnett, N.K.; Tsai, M.Y.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Straka, R.J.; Province, M.; et al. Novel variants at KCTD10, MVK, and MMAB genes interact with dietary carbohydrates to modulate HDL-cholesterol concentrations in the Genetics of Lipid Lowering Drugs and Diet Network Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Rios, A.; Alcalá-Diaz, J.F.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Marin, C.; León-Acuña, A.; Camargo, A.; Rodriguez-Cantalejo, F.; Blanco-Rojo, R.; Quintana-Navarro, G.; et al. Beneficial effect of CETP gene polymorphism in combination with a Mediterranean diet influencing lipid metabolism in metabolic syndrome patients: CORDIOPREV study. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Delgado, F.; Alcala-Diaz, J.F.; Garcia-Rios, A.; Delgado-Lista, J.; Ortiz-Morales, A.; Rangel-Zuñiga, O.; Tinahones, F.J.; Gonzalez-Guardia, L.; Malagon, M.M.; Bellido-Muñoz, E.; et al. Polymorphism at the TNF-alpha gene interacts with Mediterranean diet to influence triglyceride metabolism and inflammation status in metabolic syndrome patients: From the CORDIOPREV clinical trial. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2014, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, E.S.; Corella, D.; Demissie, S.; Cupples, L.A.; Coltell, O.; Schaefer, E.J.; Tucker, K.L.; Ordovas, J.M. Polyunsaturated fatty acids interact with the PPARA-L162V polymorphism to affect plasma triglyceride and apolipoprotein C-III concentrations in the Framingham Heart Study. J. Nutr. 2005, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, A.E.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.I.; Justice, A.E.; Pers, T.H.; Day, F.R.; Powell, C.; Vedantam, S.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Yang, J.; et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrison, A.C.; Bare, L.A.; Chambless, L.E.; Ellis, S.G.; Malloy, M.; Kane, J.P.; Pankow, J.S.; Devlin, J.J.; Willerson, J.T.; Boerwinkle, E. Prediction of coronary heart disease risk using a genetic risk score: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steele, R.M.; Brage, S.; Corder, K.; Wareham, N.J.; Ekelund, U. Physical activity, cardiorespiratory fitness, and the metabolic syndrome in youth. J. Appl. Physiol. 2008, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magnussen, C.G.; Koskinen, J.; Chen, W.; Thomson, R.; Schmidt, M.D.; Srinivasan, S.R.; Kivimäki, M.; Mattsson, N.; Kähönen, M.; Laitinen, T.; et al. Pediatric metabolic syndrome predicts adulthood metabolic syndrome, subclinical atherosclerosis, and type 2 diabetes mellitus but is no better than body mass index alone: The Bogalusa Heart Study and the Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study. Circulation 2010, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.A.; Friedman, L.A.; Wang, P.; Glueck, C.J. Metabolic syndrome in childhood predicts adult metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus 25 to 30 years later. J. Pediatrics 2008, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sofi, F.; Cesari, F.; Abbate, R.; Gensini, G.F.; Casini, A. Adherence to Mediterranean diet and health status: Meta-analysis. BMJ 2008, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Total | Male | Female | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 605 | n =293 | n =312 | ||
| Age (years) | 14.7 (13.8–15.6) | 14.8 (13.8–15.6) | 14.8 (13.7–15.7) | 0.948 |
| Height (cm) | 166.0 (159.5–172.2) | 170.0 (163.9–177.0) | 162.2 (157.0-167.2) | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) | 58.4 (49.9–64.5) | 61.1 (51.1–68.8) | 55.8 (49.2–61.6) | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 21.1 (18.6–22.9) | 21.0 (18.5–22.7) | 21.2 (18.7–23.0) | 0.194 |
| WC (cm) | 72.1 (66.7–75.8) | 65.75 (46.0–79.0) | 71.5 48.7–83) | <0.001 |
| HOMA index | 2.2 (1.3–2.6) | 2.2 (1.3–2.5) | 2.3 (1.4–2.7) | 0.044 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 116 (108–124) | 120 (112–129) | 112 (105–120) | <0.001 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 64.4 (59.0–70.0) | 64.0 (59.0-69.0) | 64.8 (60.0–70.0) | 0.331 |
| MAP | 0.6 (−0.01–1.1) | 1.1 (0.5–1.6) | 0.2 (−0.4–0.7) | <0.001 |
| HDL-c (mmol/L) | 55.7 (49–63) | 53.3 (47-59) | 57.9 (50–65) | <0.001 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 68.7 (47.0–80.0) | 65.7 (46.0–79.0) | 71.5 (48.7–83.0) | 0.056 |
| TC:HDL ratio | 2.3 (2.5–1.1) | 2.3 (2.5–3.2) | 2.9 (2.5–3.3) | 0.839 |
| PA (mins/day) | 54.8 (40.7–71.5) | 65.4 (51.8–82.4) | 47.3 (35.2–59.8) | <0.001 |
| MetS Score * | 0.02 (-1.2–1.0) | 0.3 (−0.7–1.3) | −0.3 (−1.5–0.8) | <0.001 |
| MDS ** | 4 (0–8) | 4 (0–8) | 4 (0–8) | 0.495 |
| Obesity-GRS *** | 23 (21–24) | 23 (21–25) | 22 (21–24) | 0.087 |
| p-Values | Male | Female | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Obesity-GRSxMD | MD | Obesity-GRSxMD | MD | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.003 | 0.008 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| WC (cm) | 0.009 | 0.030 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| HOMA | 0.495 | 0.836 | 0.027 | 0.013 |
| SBP (mmHg) | 0.994 | 0.739 | 0.310 | 0.047 |
| DBP (mmHg) | 0.005 | 0.014 | 0.795 | 0.626 |
| MAP | 0.031 | 0.045 | 0.872 | 0.325 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.421 | 0.413 | 0.587 | 0.689 |
| TC:HDL | 0.465 | 0.530 | 0.184 | 0.118 |
| MetS Score | 0.014 | 0.047 | 0.006 | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Seral-Cortes, M.; Sabroso-Lasa, S.; De Miguel-Etayo, P.; Gonzalez-Gross, M.; Gesteiro, E.; Molina-Hidalgo, C.; De Henauw, S.; Erhardt, É.; Censi, L.; Manios, Y.; et al. Interaction Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and an Obesity Genetic Risk Score on Adiposity and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: The HELENA Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123841
Seral-Cortes M, Sabroso-Lasa S, De Miguel-Etayo P, Gonzalez-Gross M, Gesteiro E, Molina-Hidalgo C, De Henauw S, Erhardt É, Censi L, Manios Y, et al. Interaction Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and an Obesity Genetic Risk Score on Adiposity and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: The HELENA Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(12):3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123841
Chicago/Turabian StyleSeral-Cortes, Miguel, Sergio Sabroso-Lasa, Pilar De Miguel-Etayo, Marcela Gonzalez-Gross, Eva Gesteiro, Cristina Molina-Hidalgo, Stefaan De Henauw, Éva Erhardt, Laura Censi, Yannis Manios, and et al. 2020. "Interaction Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and an Obesity Genetic Risk Score on Adiposity and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: The HELENA Study" Nutrients 12, no. 12: 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123841
APA StyleSeral-Cortes, M., Sabroso-Lasa, S., De Miguel-Etayo, P., Gonzalez-Gross, M., Gesteiro, E., Molina-Hidalgo, C., De Henauw, S., Erhardt, É., Censi, L., Manios, Y., Karaglani, E., Widhalm, K., Kafatos, A., Beghin, L., Meirhaeghe, A., Salazar-Tortosa, D., Ruiz, J. R., Moreno, L. A., Esteban, L. M., & Labayen, I. (2020). Interaction Effect of the Mediterranean Diet and an Obesity Genetic Risk Score on Adiposity and Metabolic Syndrome in Adolescents: The HELENA Study. Nutrients, 12(12), 3841. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123841
















