Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Analytical Techniques
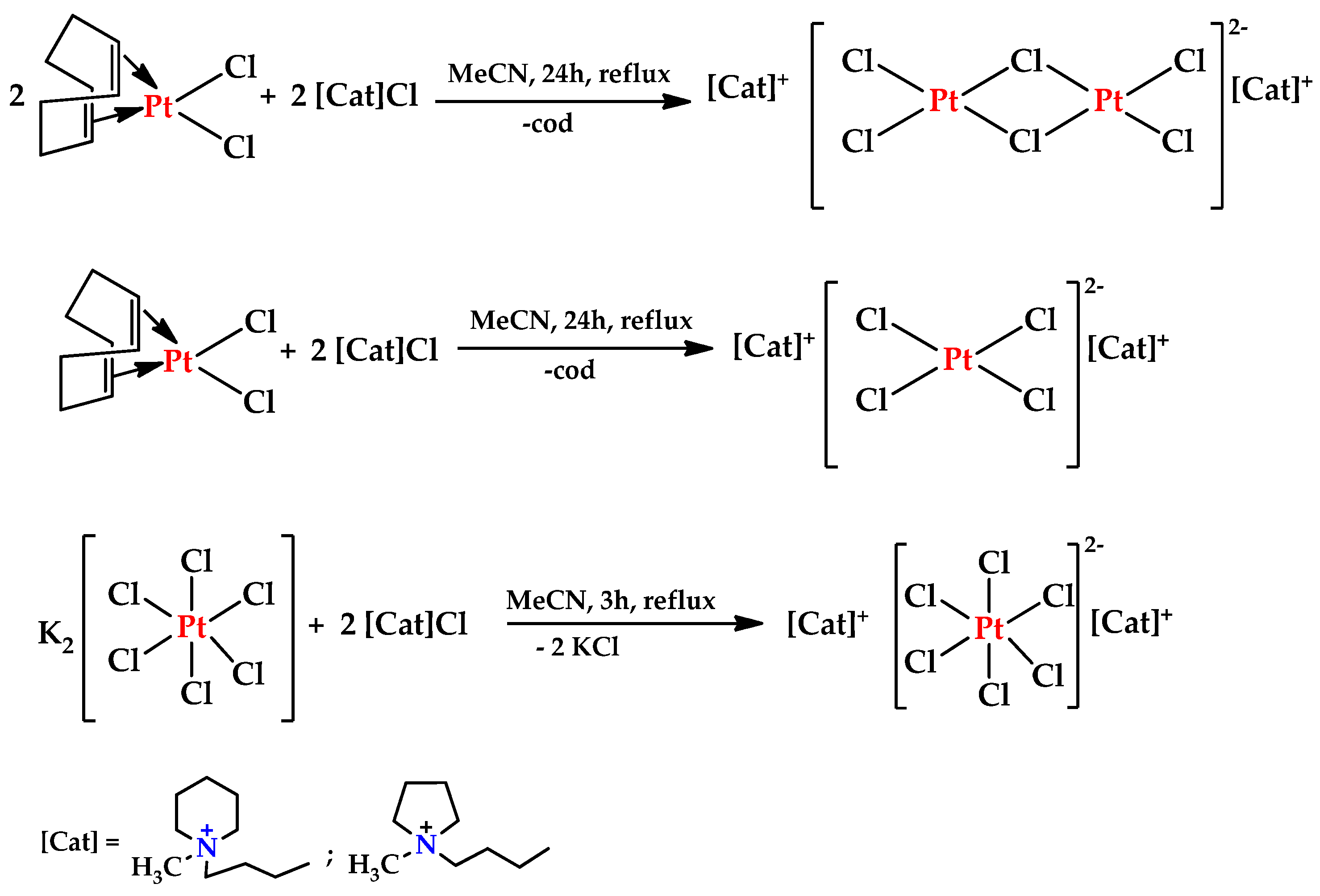
3.3. Synthesis of Transition-Metal-Based Complexes
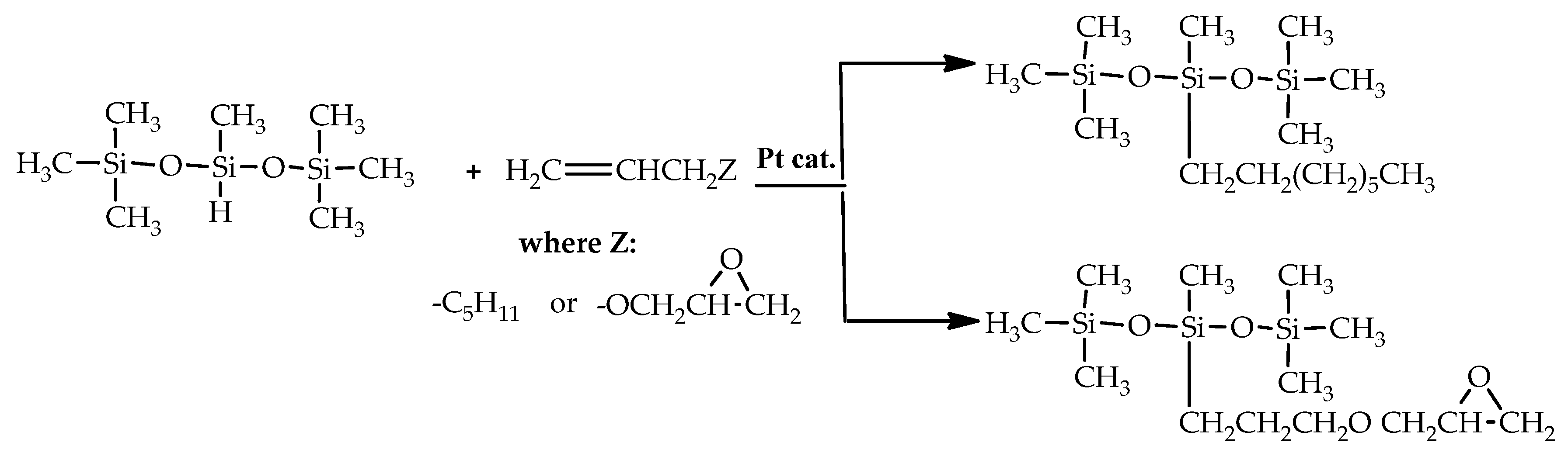
3.4. General Procedure for Catalytic Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anastas, P.T.; Warner, J.C. Green Chemistry: Theory and Practice; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1998; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniec, B.; Maciejewski, H.; Pietraszuk, C.; Pawluć, P. Hydrosilylation: A Comprehensive Review on Recent Advances; Marciniec, B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Trogel, D.; Strohrer, J. Recent advances and actual challenges in late transition metal catalyzed hydrosilylation of olefins from an industrial point of view. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2011, 255, 1440–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciniec, B.; Maciejewski, H.; Pawluć, P. Organosilicon Compounds; Lee, V.Y., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; Chapter 5; pp. 169–218. [Google Scholar]
- Marciniec, B.; Maciejewski, H.; Pietraszuk, C.; Pawluć, P. Applied Homogeneous Catalysis with Organometallic Compounds; Cornils, B., Hermann, W.A., Belier, M., Pawelo, R., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Chapter 8; pp. 569–620. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, Y.; Shimada, S. Hydrosilylation reaction of olefins: Recent advances and perspectives. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 20603–20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, R.D.; Seddon, K.R. (Eds.) Ionic Liquids–Industrial Applications to Green Chemistry; ACS: Washington, DC, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Dyson, P.J.; Geldbach, T.J. Metal Catalysed Reactions in Ionic Liquids; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hardacre, C.; Parvulescu, V. Catalysis in Ionic Liquids. From Catalyst Synthesis to Application; RS Chemistry: London, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Vekariya, R.L. A review of ionic liquids: Applications towards catalytic organic transformations. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 227, 44–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozokwelu, D.; Zhang, S.; Okafor, O.C.; Cheng, W.; Litombe, N. Novel Catalytic and Separation Processes Based on Ionic Liquids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lozano, P. (Ed.) Sustainable Catalysis in Ionic Liquids; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Behr, A.; Toslu, N. Hydrosilylation reactions in single and two phases. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2000, 23, 122–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, N.; Bauer, A.; Auer, T.; Stanjek, V.; Schulz, P.; Taccardi, N.; Wasserscheid, P. Liquid-liquid biphasic, platinum-catalyzed hydrosilylation of allyl chloride with trichlorosilane using an ionic liquid catalyst phase in a continuous loop reactor. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2008, 350, 2599–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taccardi, N.; Fekete, M.; Berger, M.E.; Stanjek, V.; Schulz, P.; Wasserscheid, P. Catalyst recycling in monophasic Pt-catalyzed hydrosilylation reactions using ionic liquids. Appl. Catal. A 2011, 399, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyershausen, B.; Hell, K.; Hesse, U. Industrial application of ionic liquids as process aid. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, T.; Strassner, T. Biphasic platinum catalyzed hydrosilylation of terminal alkenes in TAAILs. J. Organometal. Chem. 2013, 744, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Szubert, K.; Marciniec, B.; Pernak, J. Hydrosilylation of functionalised olefins catalysed by rhodium siloxide complexes in ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielinski, W.; Kukawka, R.; Maciejewski, H.; Smiglak, M. Ionic liquids as solvents for rhodium and platinum catalysts used in hydrosilylation reaction. Molecules 2016, 21, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Szubert, K.; Fiedorow, R.; Giszter, R.; Niemczak, M.; Pernak, J. Diallyldimethylammonium and trimethylvinylammonium ionic liquids—Synthesis and application to catalysis. Appl. Catal. A 2013, 451, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Dabek, I.; Fiedorow, R. The effect of the morpholinium ionic liquid anion on the catalytic activity of Rh (or Pt) complex–ionic liquid systems in hydrosilylation processes. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 26922–26927. [Google Scholar]
- Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Kukawaka, R.; Smiglak, M.; Maciejewski, H. The effect of the catalyst and the type of ionic liquid on the hydrosilylation process under batch and continuous reaction conditions. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 5229–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luska, K.L.; Demmans, K.Z.; Stratton, S.A.; Moores, A. Rhodium complexes stabilized by phosphine-functionalized phosphonium ionic liquids used as higher alkene hydroformylation catalysts: Influence of the phosphonium headgroup on catalytic activity. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 13533–13540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Xu, X.-F.; Zhao, K. Amino acid- and imidazolium-tagged chiral pyrrolidinodiphosphine ligands and their applications in catalytic asymmetric hydrogenations in ionic liquid systems. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 2012, 23, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yao, W.M.; Zhao, X.L.; Vo-Thanh, G.; Liu, Y. An ionic phosphine-ligated rhodium (III) complex as the efficient and recyclable catalyst for biphasic hydroformylation of 1-octene. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2013, 378, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O.; Szpecht, A.; Zając, A.; Smiglak, M.; Maciejewski, H. Platinum and rhodium complexes ligated by imidazolium-substituted phosphine as efficient and recyclable catalysts for hydrosilylation. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 29396–29404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlewicz, O.; Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Maciejwski, H. Highly efficient and reusable alkyne hydrosilylation catalysts based on rhodium complexes ligated by imidazolium- substituted phosphine. Catalysts 2020, 10, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvulescu, V.I.; Hardacre, C.h. Catalysis in ionic liquids. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2615–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Chan, Y.S.; Jang, H.B.; Song, C.E.; Lee, S.-G. Toward understanding the origin of positive effects of ionic liquids on catalysis: Formation of more reactive catalysts and stabilization of reactive intermediates and transition states in ionic liquids. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hui, S.; Shengjie, C.h.; Honqxing, Y.H.; Ye, L. Applications of transition metallates in catalysis. Prog. Chem. 2012, 24, 2287–2298. [Google Scholar]
- Estager, J.; Holbrey, J.D.; Swadzba-Kwasny, M. Halometallate ionic liquids–revisited. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappe, C.; Ghilardi, T.; Pomelli, C.S. Structural features and properties of metal complexes in ionic liquids: Application in alkylation reactions. Top. Organomet. Chem. 2015, 51, 79–94. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.C.; Hogg, J.M.; Swadzba-Kwasny, M. Lewis Acidic Ionic Liquids. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 5, 78–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, J.S. A short history of ionic liquids—From molten salts to neoteric solvents. Green Chem. 2002, 4, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Kozhevnikov, I.V.; Siddiqui, M.R.H.; Femoni, C.; Steiner, A.; Winterton, N. N,N‘-dialkylimidazolium chloroplatinate(II), chloroplatinate(IV), and chloroiridate(IV) salts and an N-heterocyclic carbene complex of platinum(II): Synthesis in ionic liquids and crystal structures. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 795–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Sasaki, T.; Jimbo-Kobayashi, A.; Fujiwara, E.; Kobayashi, A.; Tada, M.; Iwasawa, Y. Syntheses, structures, and properties of a series of metal ion-containing dialkylimidazolium ionic liquids. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2007, 12, 2365–2374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O.; Walczak, A.; Stefankiewicz, A.R.; Maciejewski, H. Highly efficient hydrosilylation catalysts based on chloroplatinate ionic liquids. J. Catal. 2019, 374, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maciejewski, H.; Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O. New Anionic Platinum Complexes, Method for Obtaining Them and Application, Preferably for Hydrosilylation Processes. Polish Patent PL 233547, 11 March 2019. [Google Scholar]

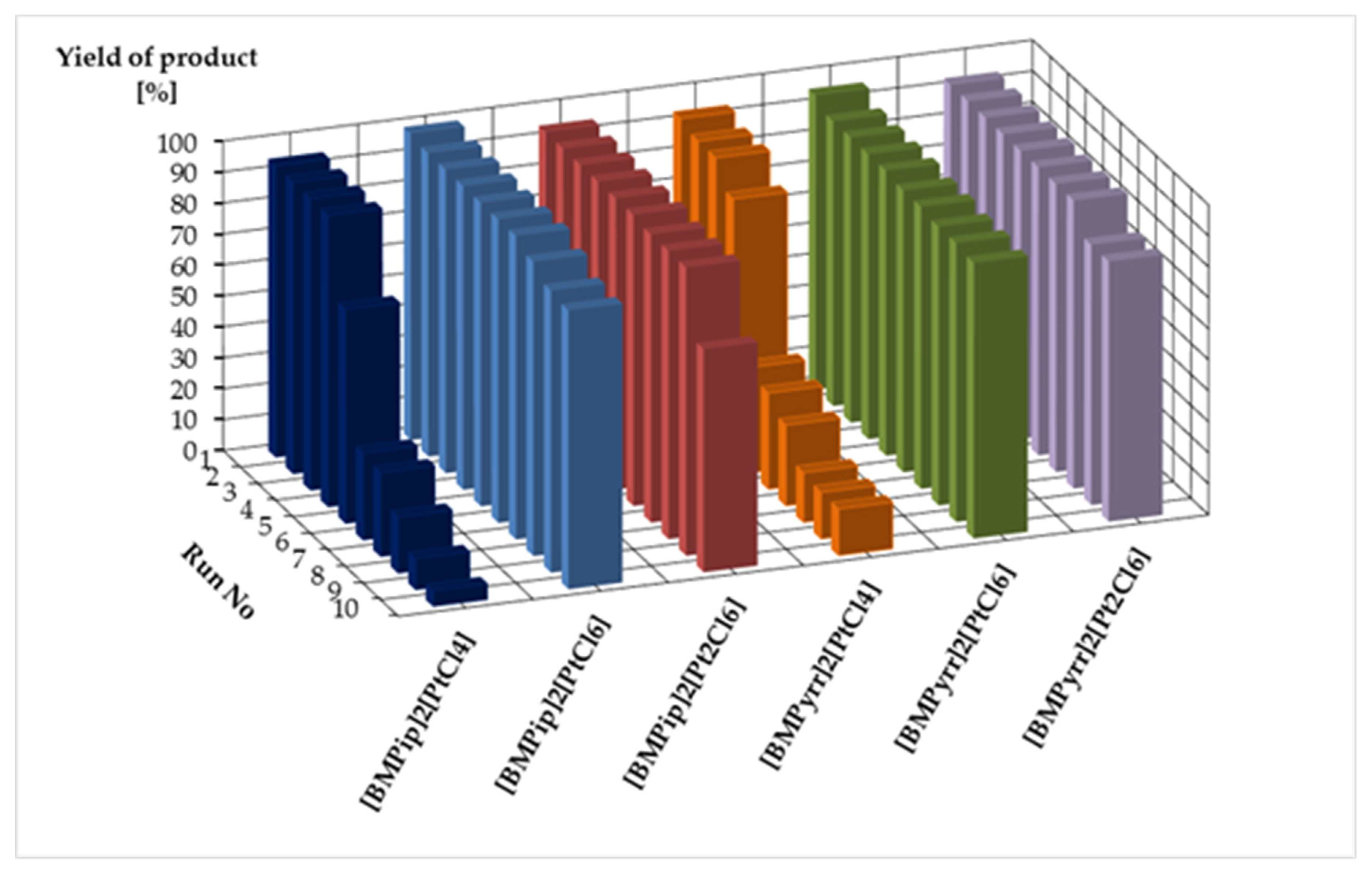
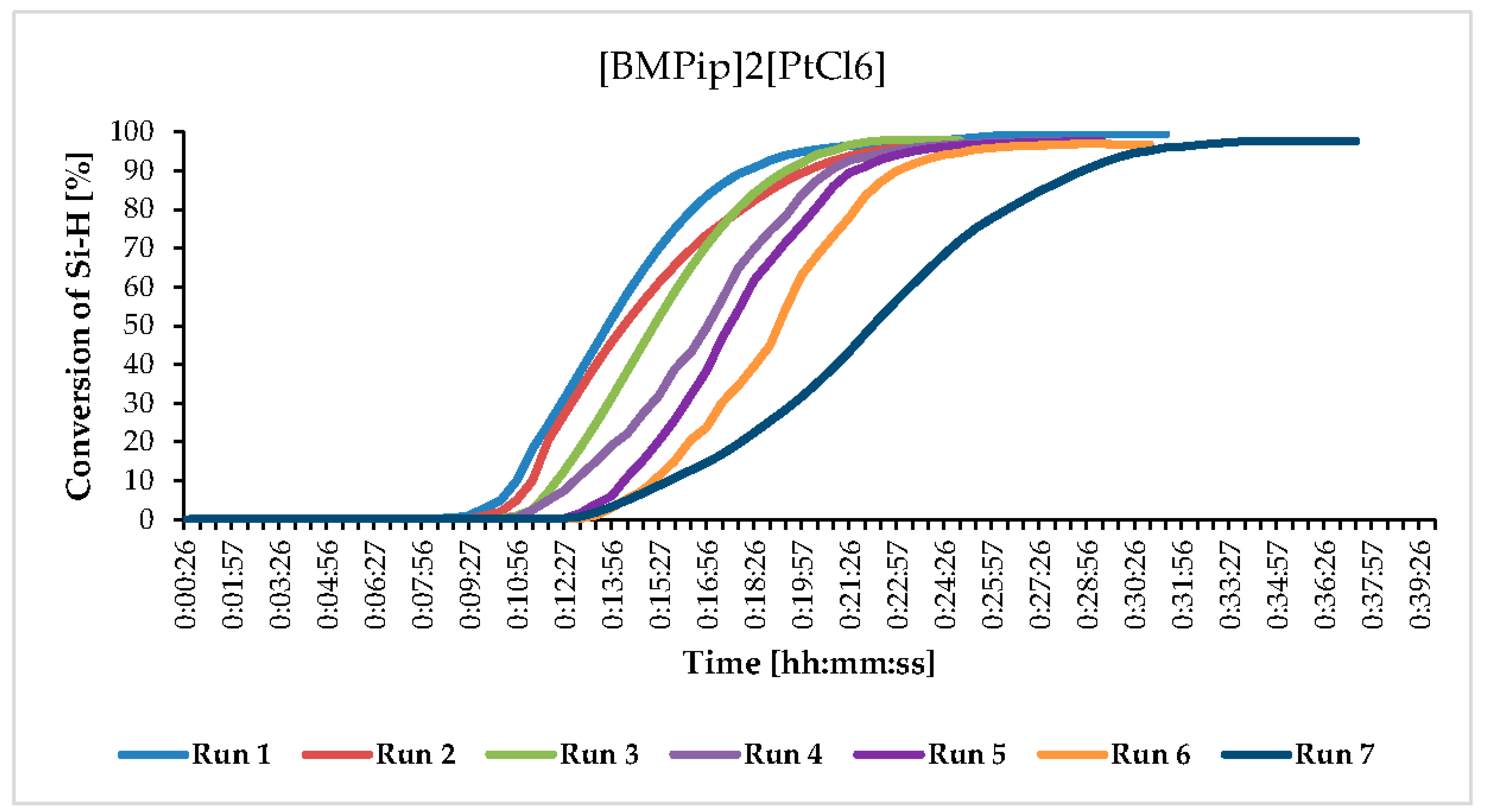
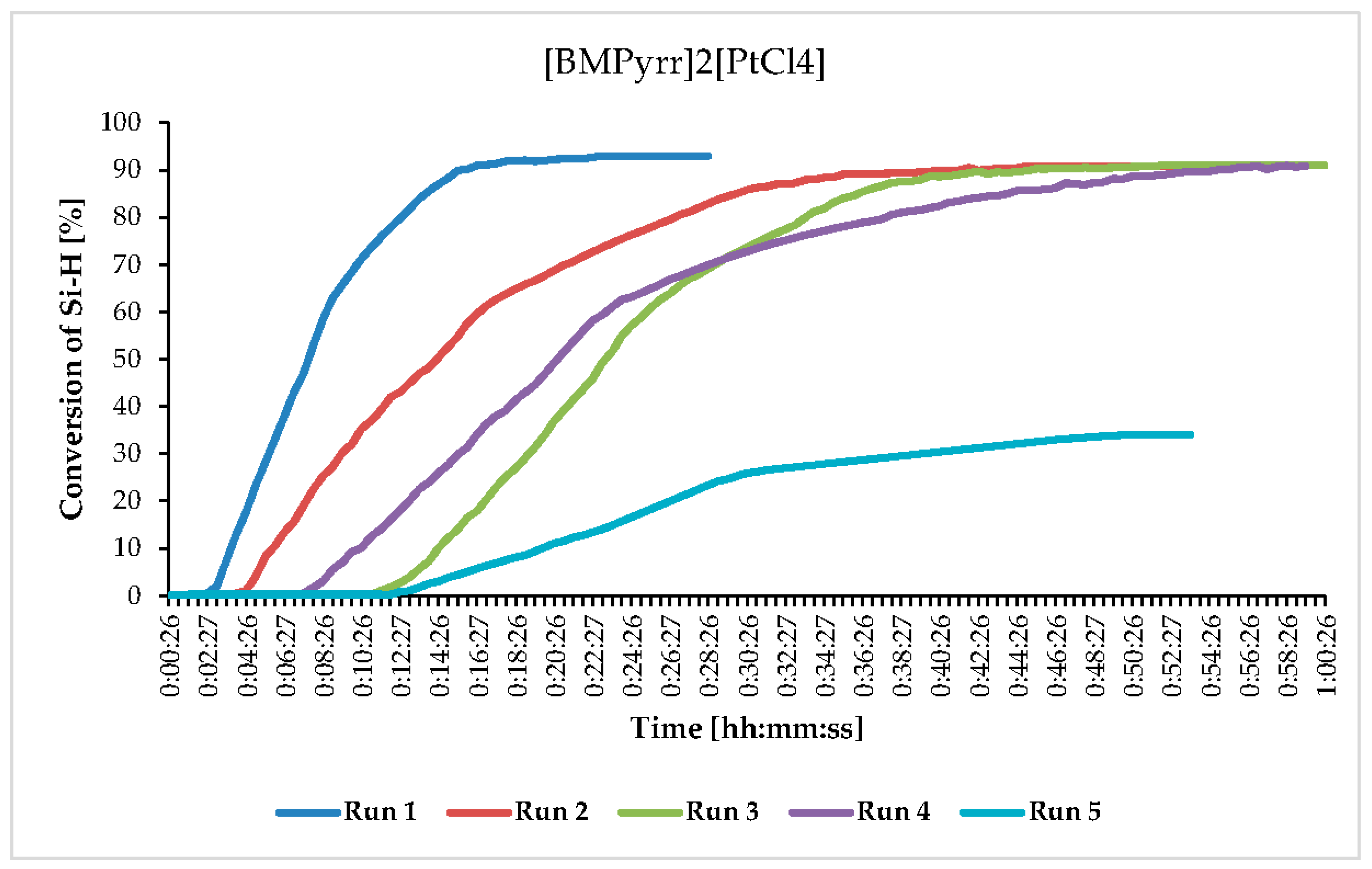

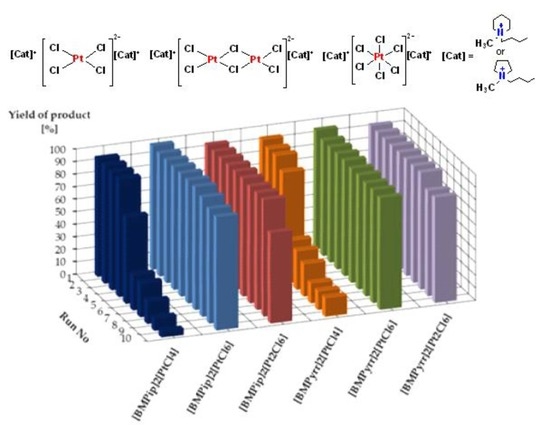
| Catalyst | Melting Point [°C] |
|---|---|
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl4] | 151 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl4] | 134 |
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl6] | 178 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl6] | 169 |
| [BMPip]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 189 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 165 |
| Catalyst | Decomposition Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl4] | 219.84 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl4] | 212.95 |
| [BMPip]2 [PtCl6] | 225.88 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [PtCl6] | 233.07 |
| [BMPip]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 220.69 |
| [BMPyrr]2 [Pt2Cl6] | 237.40 |
| Catalyst | Product Yield in the Reaction with | |
|---|---|---|
| 1-octene 1 [%] | Allyl Glycidyl Ether 2 [%] | |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl4] | 94 | 96 |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl6] | 99 | 94 |
| [BMPip]2[Pt2Cl6] | 94 | 99 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl4] | 93 | 85 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl6] | 95 | 89 |
| [BMPyrr]2[Pt2Cl6] | 93 | 98 |
| Catalyst | Yield of Product in Subsequent Cycle [%] | Total TON |
|---|---|---|
| [BMPip]2[PtCl4] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 69, 28, 27, 18, 10, 5) | 53,300 |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl6] | 99 (98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 95, 91, 90) | 96,300 |
| [BMPip]2[Pt2Cl6] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 93, 93, 93, 72) | 91,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl4] | 93 (91, 91, 83, 34, 31, 26, 16, 15, 15) | 49,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl6] | 95 (92, 92, 92, 92, 91, 91, 90, 90, 89) | 91,400 |
| [BMPyrr]2[Pt2Cl6] | 93 (93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 84, 84) | 91,200 |
| Catalyst | Yield of Product in Subsequent Cycle [%] | Total TON |
|---|---|---|
| [BMPip]2[PtCl4] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 69, 28, 27, 18, 10, 5) | 53,300 |
| [BMPip]2[PtCl6] | 99 (98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 98, 95, 91, 90) | 96,300 |
| [BMPip]2[Pt2Cl6] | 94 (94, 94, 94, 94, 94, 93, 93, 93, 72) | 91,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl4] | 93 (91, 91, 83, 34, 31, 26, 16, 15, 15) | 49,500 |
| [BMPyrr]2[PtCl6] | 95 (92, 92, 92, 92, 91, 91, 90, 90, 89) | 91,400 |
| [BMPyrr]2[Pt2Cl6] | 93 (93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 93, 84, 84) | 91,200 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jankowska-Wajda, M.; Bartlewicz, O.; Pietras, P.; Maciejewski, H. Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation. Catalysts 2020, 10, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919
Jankowska-Wajda M, Bartlewicz O, Pietras P, Maciejewski H. Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation. Catalysts. 2020; 10(8):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919
Chicago/Turabian StyleJankowska-Wajda, Magdalena, Olga Bartlewicz, Przemysław Pietras, and Hieronim Maciejewski. 2020. "Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation" Catalysts 10, no. 8: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919
APA StyleJankowska-Wajda, M., Bartlewicz, O., Pietras, P., & Maciejewski, H. (2020). Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids as Precursors in the Synthesis of New Platinum Catalysts for Hydrosilylation. Catalysts, 10(8), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10080919