The CBL–CIPK Pathway in Plant Response to Stress Signals
Abstract
:1. Introduction
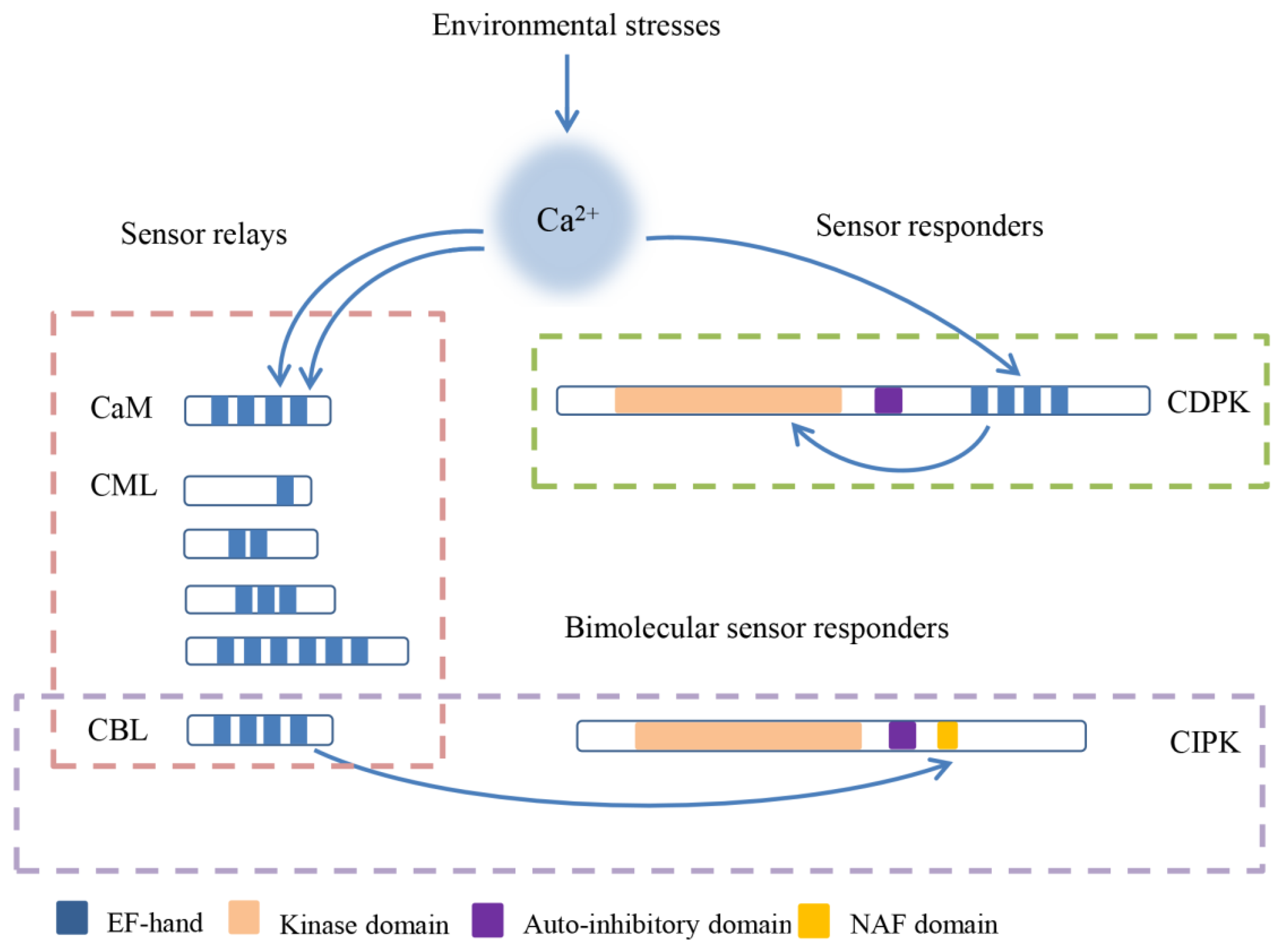
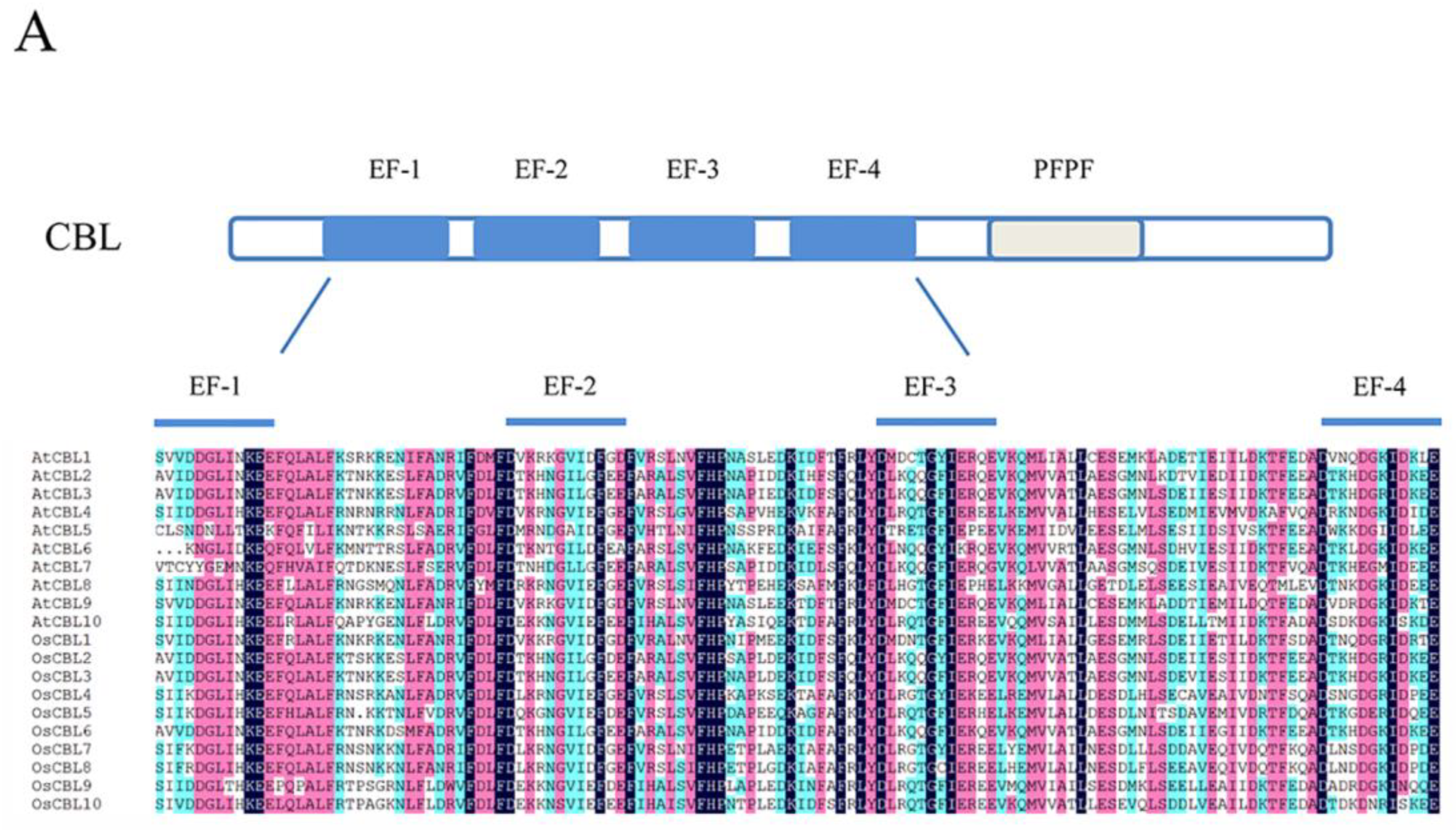
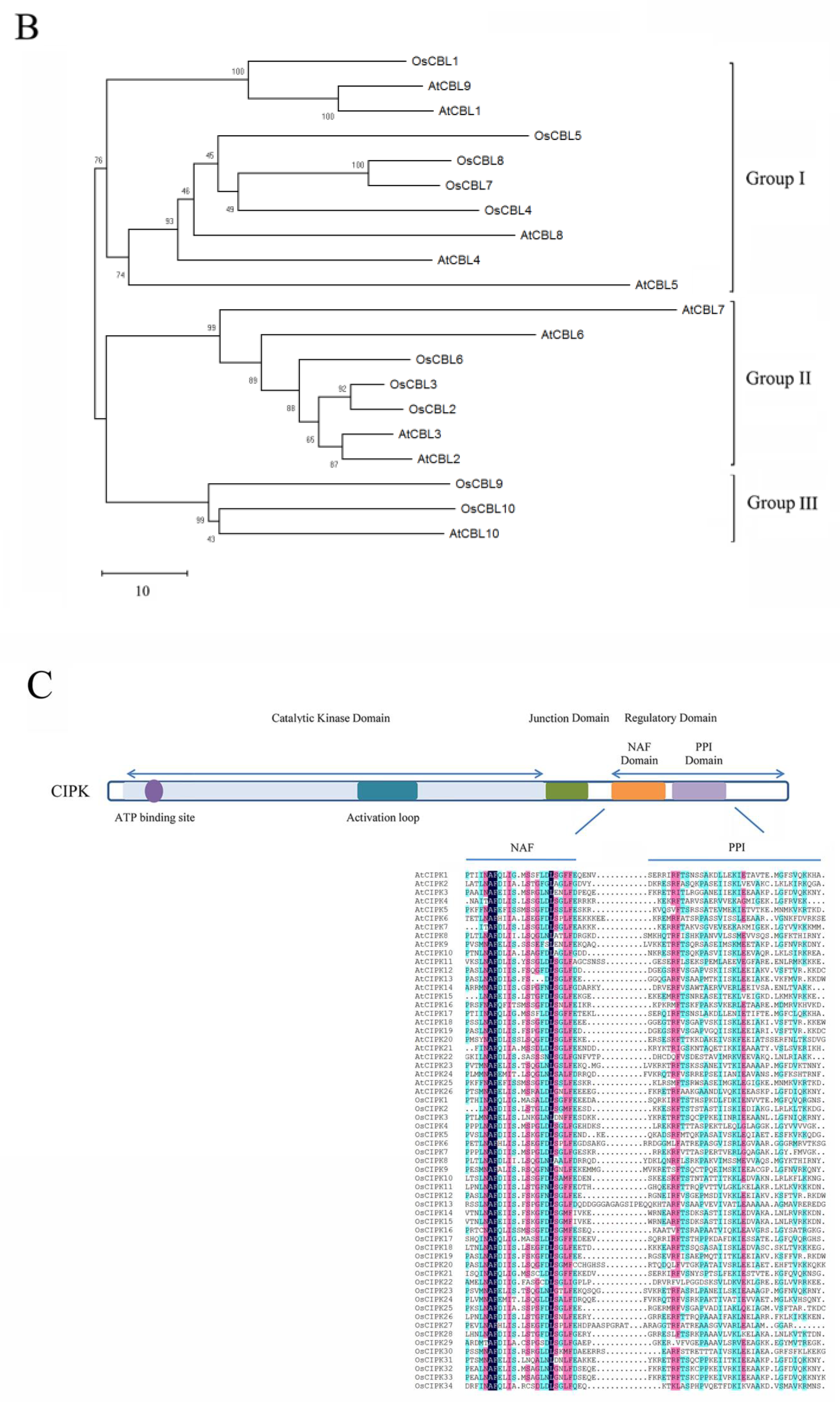
2. Structure and Classification of CBLs and CIPKs
| Species | No. of CBLs | No.of CIPKs | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana | 10 | 26 | [38,39] |
| Canola (Brassica napus) | 7 | 23 | [29] |
| Cassava (Manihot esculenta) | 8 | 26 | [43,44] |
| Fern (Selaginella moellendorffii) | 4 | 5 | [13] |
| Grape (Vitis vinifera) | 8 | 20 | [37] |
| Moss (Physcomitrella patens) | 4 | 7 | [13] |
| Populus (Populus trichocarpa) | 10 | 27 | [38,42] |
| Pepper (Capsicum annuum) | 9 | 26 | [34] |
| Rice (Oryza sativa) | 10 | 34 | [29,39,40,64] |
| Tea (Camellia sinensis) | 9 | 18 | [36] |
| Wheat (Triticum aestivum) | 24 | 79 | [35,41] |
3. Mechanisms of the CBL–CIPK Module
4. Subcellular Localization of CBLs, CIPKs, and Their Complexes
5. Functions of the CBL–CIPK Pathway
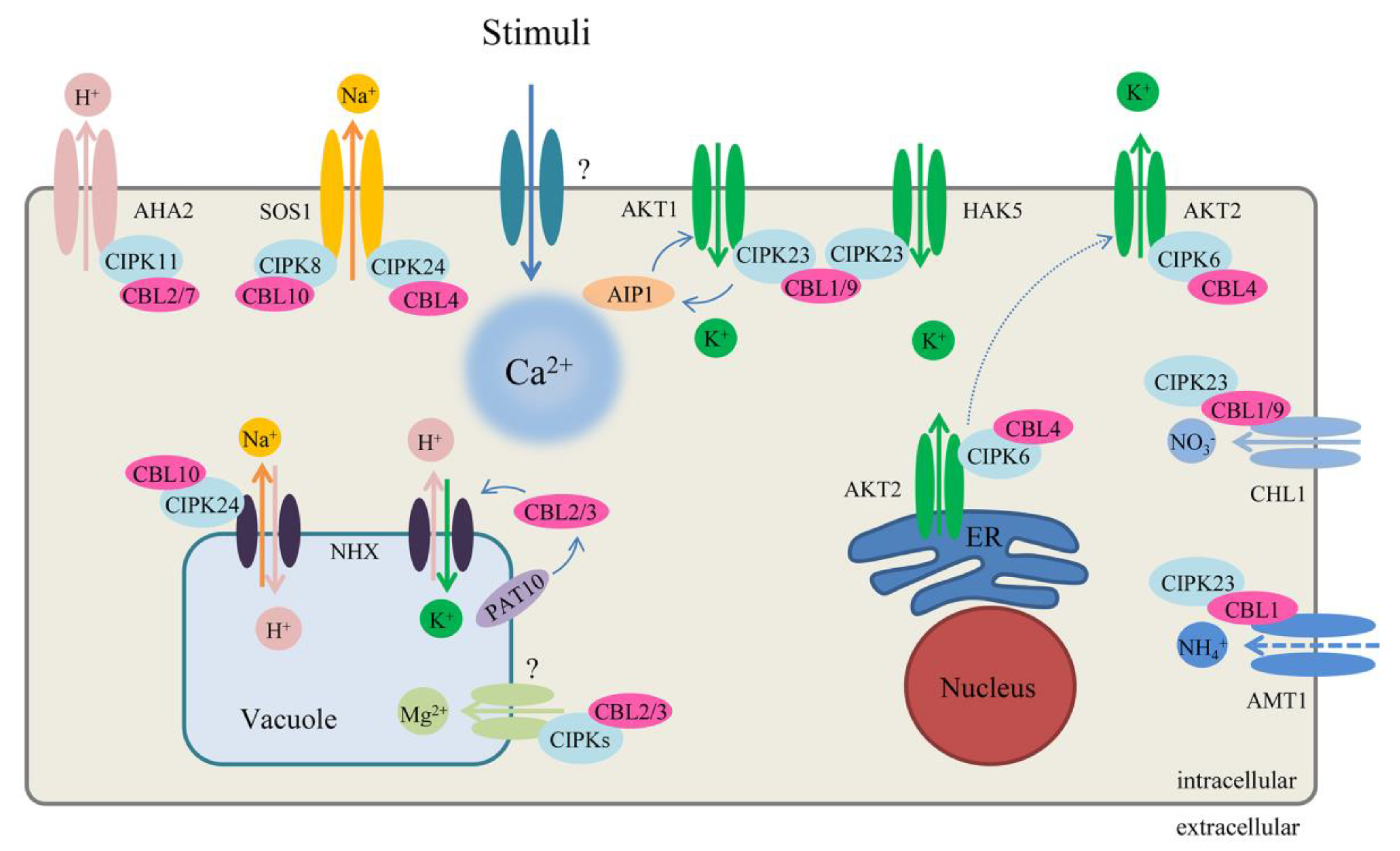
5.1. CBL–CIPK Pathways in Responses to Abiotic Stress
5.1.1. Environmental Stress
5.1.2. Nutrient Deficiency in Plants
5.1.3. Plant Hormone ABA
5.2. The CBL–CIPK Network in Biotic Stress
5.3. The Role of CBL–CIPK Network in Plant Development
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| ABR | Abscisic acid repressor |
| ABRE | Abscisic acid responsiveness element |
| ABI | Abscisic acid insensitive |
| AHA2 | Arabidopsis H+ ATPase 2 |
| AKT | Arabidopsis K+ transporter |
| AIP1 | AKT1-interacting PP2C 1 |
| AMT1 | Ammonium transporter 1 |
| AREB | ABA-responsive element binding factor |
| CAMs | Calmodulins |
| CBLs | Calcineurin-B-like proteins |
| CBP | calcium-binding peptide |
| CDPKs | Calcium-dependent protein kinase |
| CMLs | CaM-like proteins |
| CIPKs | CBL-interacting protein kinases |
| DAMP | Damage-associated molecular pattern |
| EF-hand | Elongation factor-hand |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ETH | Ethylene |
| ETI | Effector-triggered immunity |
| HAK5 | High-Affinity K+ transporter 5 |
| KC1 | K+ rectifying Channel 1 |
| LKS1 | Low-K+-sensitive 1 |
| MAMPs | Microbe-associated molecular patterns |
| PAT | Protein S-acyl Transferase |
| PCD | programmed cell death |
| PP2Cs | Type 2C protein phosphatases |
| PPI | Protein phosphatase interaction |
| PTI | Pattern-triggered immunity |
| RBOH | Respiratory burst oxidase homologs; |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| SARE | Salicylic acid responsiveness element |
| SLAC | Slow vacuolar anion channel |
| SnRK3 | SNF1-related serine/threonine kinases group 3 |
| SOS | Salt overly sensitive |
| SUT | Sucrose transporter |
| TST2 | Tonoplast-localized sugar transporter 2 |
References
- Batistic, O.; Kudla, J. Integration and channeling of calcium signalling through the CBL calcium sensor/CIPK protein kinase network. Planta 2004, 219, 915–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Kanwar, P.; Pandey, A. Global Comparative Analysis of CBL–CIPK Gene Families in Plants; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- McAinsh, M.R.; Pittman, J.K. Shaping the calcium signature. New Phytol. 2009, 181, 895–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, A.N.; Kudla, J.; Sanders, D. The Language of Calcium Signaling. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2010, 61, 593–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Luoni, L.; Marrano, C.A.; Hashimoto, K.; Köster, P.; Giacometti, S.; De Michelis, M.I.; Kudla, J.; Bonza, M.C. Ca2+-dependent phosphoregulation of the plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase ACA8 modulates stimulus-induced calcium signatures. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 3215–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bose, J.; Pottosin, I.I.; Shabala, S.S.; Palmgren, M.G.; Shabala, S. Calcium efflux systems in stress signaling and adaptation in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corso, M.; Doccula, F.G.; De Melo, R.J.F.; Costa, A.; Verbruggen, N. Endoplasmic reticulum-localized CCX2 is required for osmotolerance by regulating ER and cytosolic Ca2+ dynamics in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3966–3971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinhorst, L.; Kudla, J. Signaling in cells and organisms—Calcium holds the line. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 22, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedrich, R.; Mueller, T.D.; Becker, D.; Marten, I. Structure and Function of TPC1 Vacuole SV Channel Gains Shape. Mol. Plant 2018, 11, 764–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeFalco, T.A.; Moeder, W.; Yoshioka, K. Opening the Gates: Insights into Cyclic Nucleotide-Gated Channel-Mediated Signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2016, 21, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Navazio, L.; Szabo, I. The contribution of organelles to plant intracellular calcium signalling. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4175–4193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navazio, L.; Formentin, E.; Cendron, L.; Szabò, I. Chloroplast Calcium Signaling in the Spotlight. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weinl, S.; Kudla, J. The CBL-CIPK Ca2+-decoding signaling network: Function and perspectives. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhorst, L.; Kudla, J. Calcium and Reactive Oxygen Species Rule the Waves of Signaling. Plant Physiol. 2013, 163, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanders, D.; Pelloux, J.; Brownlee, C.; Harper, J.F. Calcium at the Crossroads of Signaling Calcium Signals: A Central Paradigm in. Plant Cell 2002, S401–S417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, K.; Kudla, J. Calcium decoding mechanisms in plants. Biochimie 2011, 93, 2054–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, J.F.; Harmon, A. Plants, symbiosis and parasites: A calcium signalling connection. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 555–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistič, O.; Kudla, J. Analysis of calcium signaling pathways in plants. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Gen. Subj. 2012, 1820, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batistič, O.; Kudla, J. Plant calcineurin B-like proteins and their interacting protein kinases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Res. 2009, 1793, 985–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luan, S.; Kudla, J.; Rodriguez-concepcion, M.; Yalovsky, S.; Gruissem, W. Calmodulins and Calcineurin B–like Proteins: Calcium Sensors for Specific Signal Response Coupling in Plants. Plant Cell 2002, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCormack, E.; Braam, J. Calmodulins and related potential calcium sensors of Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2003, 159, 585–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perochon, A.; Aldon, D.; Galaud, J.P.; Ranty, B. Calmodulin and calmodulin-like proteins in plant calcium signaling. Biochimie 2011, 93, 2048–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudla, J.; Xu, Q.; Harter, K.; Gruissem, W.; Luan, S. Genes for calcineurin B-like proteins in Arabidopsis are differentially regulated by stress signals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 4718–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luan, S.; Lan, W.; Chul Lee, S. Potassium nutrition, sodium toxicity, and calcium signaling: Connections through the CBL-CIPK network. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2009, 12, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Mahiwal, S.; Nambiar, D.M.; Pandey, G.K. CBL-CIPK module-mediated phosphoregulation: Facts and hypothesis. Biochem. J. 2020, 477, 853–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Kim, K.N.; Ritz, O.; Albrecht, V.; Gupta, R.; Harter, K.; Luan, S.; Kudla, J. Novel protein kinases associated with calcineurin B-like calcium sensors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 2393–2405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S. The CBL-CIPK network in plant calcium signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2009, 14, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoday-Kennedy, E.L.; Jacobs, A.K.; Roy, S.J. The role of the CBL-CIPK calcium signalling network in regulating ion transport in response to abiotic stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Liu, W.-Z.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Deng, M.; Liang, W.; Deyholos, M.K.; Jiang, Y.-Q. Identification and characterization of CBL and CIPK gene families in canola (Brassica napus L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.-J.; Zhao, F.-G.; Garcia, V.J.; Kleist, T.J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.-X.; Luan, S. Tonoplast CBL–CIPK calcium signaling network regulates magnesium homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3134–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, S.-J.; Feng, Q.-N.; Li, C.; Li, E.; Liu, Q.; Kang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S. A tonoplast-associated calcium-signaling module dampens ABA signaling during stomatal movement. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 1666–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, K.-N.; Pandey, G.K.; Gupta, R.; Grant, J.J.; Luan, S. CBL1, a calcium sensor that differentially regulates salt, drought, and cold responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 1833–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.-N.; Cheong, Y.H.; Grant, J.J.; Pandey, G.K.; Luan, S. CIPK3, a calcium sensor—Associated protein kinase that regulates abscisic acid and cold signal transduction in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ma, X.; Gai, W.; Qiao, Y.; Ali, M.; Wei, A.; Luo, D.; Li, Q. Identification of CBL and CIPK gene families and functional characterization of CaCIPK1 under Phytophthora capsici in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Duan, Y.; Liu, C.; Xue, Q.; Guo, J.; Qi, T.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. The calcium sensor TaCBL4 and its interacting protein TaCIPK5 are required for wheat resistance to stripe rust fungus. J. Exp. Bot. 2018, 69, 4443–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Li, H.; Teng, R.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhuang, J. Genome-Wide Identification and Expression Analysis of Calcineurin B-Like Protein and Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinase Family Genes in Tea Plant. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 824–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Liu, J.; Dong, C.; Cheng, Z.-M.M. The CBL and CIPK Gene Family in Grapevine (Vitis vinifera): Genome-Wide Analysis and Expression Profiles in Response to Various Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Xia, X.; Yin, W.; Zhang, H. Comparative genomic analysis of CIPK gene family in Arabidopsis and Populus. Plant Growth Regul. 2007, 52, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolukisaoglu, Ü.; Weinl, S.; Blazevic, D.; Batistic, O.; Kudla, J.J. Calcium Sensors and Their Interacting Protein Kinases: Genomics of the Arabidopsis and Rice CBL-CIPK Signaling Networks. Plant Physiol. 2004, 134, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiong, L. Characterization of Stress-Responsive CIPK Genes in Rice for Stress Tolerance Improvement. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 1416–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, T.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Wei, S.; He, G.; Yang, G. Identification and comprehensive analyses of the CBL and CIPK gene families in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, W.; Xia, X. Calcineurin B-Like family in Populus: Comparative genome analysis and expression pattern under cold, drought and salt stress treatment. Plant Growth Regul. 2008, 56, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, C.; Wan, S.; Xia, Y.; Ren, N.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X. Expression Patterns and Identified Protein-Protein Interactions Suggest That Cassava CBL-CIPK Signal Networks Function in Responses to Abiotic Stresses. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Xia, Z.; Yan, Y.; Ding, Z.; Tie, W.; Wang, L.; Zou, M.; Wei, Y.; Lu, C.; Hou, X.; et al. Genome-wide gene phylogeny of CIPK family in cassava and expression analysis of partial drought-induced genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lewit-Bentley, A.; Réty, S. EF-hand calcium-binding proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gifford, J.L.; Walsh, M.P.; Vogel, H.J. Structures and metal-ion-binding properties of the Ca2+-binding helix–loop–helix EF-hand motifs. Biochem. J. 2007, 405, 199–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Ito, T. Structure and Function of CDPK: A Sensor Responder of Calcium. In Coding and Decoding of Calcium Signals in Plants; Luan, S., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011; pp. 129–146. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Barrena, M.J.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Albert, A. Structural biology of a major signaling network that regulates plant abiotic stress: The CBL-CIPK mediated pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5734–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hashimoto, K.; Eckert, C.; Anschütz, U.; Scholz, M.; Held, K.; Waadt, R.; Reyer, A.; Hippler, M.; Becker, D.; Kudla, J. Phosphorylation of calcineurin B-like (CBL) calcium sensor proteins by their CBL-interacting protein kinases (CIPKs) is required for full activity of CBL-CIPK complexes toward their target proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 7956–7968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Mohanta, N.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Parida, P.; Bae, H. Genome-wide identification of Calcineurin B-Like (CBL) gene family of plants reveals novel conserved motifs and evolutionary aspects in calcium signaling events. BMC Plant Biol. 2015, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleist, T.J.; Spencley, A.L.; Luan, S. Comparative phylogenomics of the CBL-CIPK calcium-decoding network in the moss Physcomitrella, Arabidopsis, and other green lineages. Front. Plant Sci. 2014, 5, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Batistic, O.; Sorek, N.; Schultke, S.; Yalovsky, S.; Kudla, J. Dual Fatty Acyl Modification Determines the Localization and Plasma Membrane Targeting of CBL/CIPK Ca2+ Signaling Complexes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Online 2008, 20, 1346–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.G.; Waadt, R.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Dominguez-Solis, J.R.; Schültke, S.; Lee, S.C.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor CBL10 mediates salt tolerance by regulating ion homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2007, 52, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batistič, O.; Waadt, R.; Steinhorst, L.; Held, K.; Kudla, J. CBL-mediated targeting of CIPKs facilitates the decoding of calcium signals emanating from distinct cellular stores. Plant J. 2010, 61, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrabak, E.M.; Chan, C.W.M.; Gribskov, M.; Harper, J.F.; Choi, J.H.; Halford, N.; Luan, S.; Nimmo, H.G.; Sussman, M.R.; Thomas, M.; et al. The Arabidopsis CDPK-SnRK Superfamily of Protein Kinases. Plant Physiol. 2003, 132, 666–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.N.; Cheong, Y.H.; Gupta, R.; Luan, S. Interaction specificity of Arabidopsis calcineurin B-like calcium sensors and their target kinases. Plant Physiol. 2000, 124, 1844–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, G.K. The CBL-CIPK signaling module in plants: A mechanistic perspective. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 155, 89–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.N.; Noble, M.E.M.; Owen, D.J. Active and inactive protein kinases: Structural basis for regulation. Cell 1996, 85, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, D.; Guo, Y.; Jagendorf, A.T.; Zhu, J.-K. Biochemical characterization of the Arabidopsis protein kinase SOS2 that functions in salt tolerance. Plant Physiol. 2002, 130, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Ishitani, M.; Zhu, J.K. Molecular characterization of functional domains in the protein kinase SOS2 that is required for plant salt tolerance. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1383–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fujii, H.; Zhu, J.K. An autophosphorylation site of the protein kinase SOS2 is important for salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2009, 2, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaves-Sanjuan, A.; Sanchez-Barrena, M.J.; Gonzalez-Rubio, J.M.; Moreno, M.; Ragel, P.; Jimenez, M.; Pardo, J.M.; Martinez-Ripoll, M.; Quintero, F.J.; Albert, A. Structural basis of the regulatory mechanism of the plant CIPK family of protein kinases controlling ion homeostasis and abiotic stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4532–E4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohta, M.; Guo, Y.; Halfter, U.; Zhu, J. A novel domain in the protein kinase SOS2 mediates interaction with the protein phosphatase 2C ABI2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 11771–11776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Piao, H.L.; Xuan, Y.H.; Park, S.H.; Je, B., II; Park, S.J.; Park, S.H.; Kim, C.M.; Huang, J.; Wang, G.K.; Kim, M.J.; et al. OsCIPK31, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is involved in germination and seedling growth under abiotic stress conditions in rice plants. Mol. Cells 2010, 30, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.Y.; Xia, X.; Yin, W. Evolutionary analysis of CBL-interacting protein kinase gene family in plants. Plant Growth Regul. 2013, 71, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.W.; Penny, D. Patterns of intron loss and gain in plants: Intron loss-dominated evolution and genome-wide comparison of O.sativa and A.thaliana. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Filichkin, S.; Priest, H.D.; Megraw, M.; Mockler, T.C. Alternative splicing in plants: Directing traffic at the crossroads of adaptation and environmental stress. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2015, 24, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Kanwar, P.; Samtani, H.; Kaur, K.; Jha, S.K. Alternative Splicing of CIPK3 Results in Distinct Target Selection to Propagate ABA Signaling in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.J.; Wang, C.; Li, K.; Luan, S. The CBL–CIPK Calcium Signaling Network: Unified Paradigm from 20 Years of Discoveries. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barrena, M.J.; Fujii, H.; Angulo, I.; Martínez-Ripoll, M.; Zhu, J.K.; Albert, A. The Structure of the C-Terminal Domain of the Protein Kinase AtSOS2 Bound to the Calcium Sensor AtSOS3. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akaboshi, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Ishida, H.; Saijo, S.; Koizumi, N.; Sato, M.; Shimizu, T. The Crystal Structure of Plant-Specific Calcium-Binding Protein AtCBL2 in Complex with the Regulatory Domain of AtCIPK14. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 377, 246–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Schroeder, J. Two-electrode Voltage-clamp Recordings in Xenopus laevis Oocytes: Reconstitution of Abscisic Acid Activation of SLAC1 Anion Channel via PYL9 ABA Receptor. Bio-Protocol 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, H.; Yang, Y.; Quan, R.; Mendoza, I.; Wu, Y.; Du, W.; Zhao, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. Phosphorylation of SOS3-like calcium binding protein8 by SOS2 protein kinase stabilizes their protein complex and regulates salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1607–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, X.L.; Qi, G.N.; Feng, H.Q.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, S.S.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.H. Calcineurin B-like protein CBL10 directly interacts with AKT1 and modulates K+homeostasis in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2013, 74, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, S.H.; Cho, J.H.; Oh, S.I.; Choi, M.N.; Ma, J.Y.; Shin, J.S.; Kim, K.N. Calcineurin B-like 3 calcium sensor associates with and inhibits 5′-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase 2 in Arabidopsis. Plant Sci. 2015, 238, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Kaur, K.; Sanyal, S.K.; Jha, S.K.; Fernandes, J.L.; Sharma, P.; Tokas, I.; Pandey, A.; Luan, S.; et al. A Protein phosphatase 2C, AP2C1 interacts with and negatively regulates the function of CIPK9 under potassium deficient conditions in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yasuda, S.; Aoyama, S.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sato, T.; Yamaguchi, J. Arabidopsis CBL-Interacting Protein Kinases Regulate Carbon/Nitrogen-Nutrient Response by Phosphorylating Ubiquitin Ligase ATL31. Mol. Plant 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mogami, J.; Fujita, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Tsukiori, Y.; Nakagami, H.; Nomura, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; Nishida, S.; Yanagisawa, S.; Ishida, T.; et al. Two distinct families of protein kinases are required for plant growth under high external Mg2+ concentrations in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1039–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Q.J.; Sun, M.H.; Lu, J.; Liu, Y.J.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. An apple CIPK protein kinase targets a novel residue of AREB transcription factor for ABA-dependent phosphorylation. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 2207–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.J.; Sun, M.H.; Kang, H.; Lu, J.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. A CIPK protein kinase targets sucrose transporter MdSUT2.2 at Ser254for phosphorylation to enhance salt tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2018, 42, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Saito, S.; Hamamoto, S.; Moriya, K.; Matsuura, A.; Sato, Y.; Muto, J.; Noguchi, H.; Yamauchi, S.; Tozawa, Y.; Ueda, M.; et al. N -myristoylation and S -acylation are common modifications of Ca 2+ -regulated Arabidopsis kinases and are required for activation of the SLAC1 anion channel. New Phytol. 2018, 218, 1504–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quan, R.; Lin, H.; Mendoza, I.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, W.; Yang, Y.; Shang, M.; Chen, S.; Pardo, J.M.; Guo, Y. SCABP8/CBL10, a putative calcium sensor, interacts with the protein kinase SOS2 to protect Arabidopsis shoots from salt stress. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1415–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gu, Z.; Ma, B.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Su, X.; Zhang, H. Expression analysis of the calcineurin B-like gene family in rice (Oryza sativa L.) under environmental stresses. Gene 2008, 415, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.Y.; Du, Y.T.; Fu, J.D.; Yu, T.F.; Wang, C.T.; Chen, M.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.S. Wheat CBL-interacting protein kinase 23 positively regulates drought stress and ABA responses. BMC Plant Biol. 2018, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hwang, Y.S.; Bethke, P.C.; Yong, H.C.; Chang, H.S.; Zhu, T.; Jones, R.L. A gibberellin-regulated calcineurin B in rice localizes to the tonoplast and is implicated in vacuole function. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1347–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, R.J.; Yang, Y.; Yang, L.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.T.; Yu, M.M.; Gao, X.S.; Zhang, H.X. Poplar calcineurin B-like proteins PtCBL10A and PtCBL10B regulate shoot salt tolerance through interaction with PtSOS2 in the vacuolar membrane. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 573–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.; Zhou, S.; Hu, W.; Feng, J.; Zhang, F.; Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Luo, Q.; He, Y.; Yang, G.; et al. Ectopic expression of wheat TaCIPK14, encoding a calcineurin B-like protein-interacting protein kinase, confers salinity and cold tolerance in tobacco. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 149, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Batistic, O.; Pandey, G.K.; Cheong, Y.H.; Schültke, S.; Albrecht, V.; Ehlert, B.; Schulz, B.; Harter, K.; et al. Alternative complex formation of the Ca2+-regulated protein kinase CIPK1 controls abscisic acid-dependent and independent stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2006, 48, 857–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Li, H.D.; Chen, L.Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.L.; He, L.; Wu, W.H. A Protein Kinase, Interacting with Two Calcineurin B-like Proteins, Regulates K+ Transporter AKT1 in Arabidopsis. Cell 2006, 125, 1347–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, Q.-S.; Guo, Y.; Dietrich, M.A.; Schumaker, K.S.; Zhu, J.-K. Regulation of SOS1, a plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchanger in Arabidopsis thaliana, by SOS2 and SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 8436–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yin, X.; Xia, Y.; Xie, Q.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Hao, G.; Song, J.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X. The protein kinase complex CBL10–CIPK8–SOS1 functions in Arabidopsis to regulate salt tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, G.K.; Kanwar, P.; Singh, A.; Steinhorst, L.; Pandey, A.; Yadav, A.K.; Tokas, I.; Sanyal, S.K.; Kim, B.-G.; Lee, S.-C.; et al. Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinase CIPK21 Regulates Osmotic and Salt Stress Responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 780–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Ding, S.; Zhang, H.; Du, H.; An, L. CIPK7 is involved in cold response by interacting with CBL1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Sci. 2011, 181, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuglsang, A.T.; Guo, Y.; Cuin, T.A.; Qiu, Q.; Song, C.; Kristiansen, K.A.; Bych, K.; Schulz, A.; Shabala, S.; Schumaker, K.S.; et al. Arabidopsis protein kinase PKS5 inhibits the plasma membrane H+-ATPase by preventing interaction with 14-3-3 protein. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 1617–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; He, L.; Li, H.D.; Xu, J.; Wu, W.H. Potassium channel α-subunit AtKC1 negatively regulates AKT1-mediated K+ uptake in Arabidopsis roots under low-K+ stress. Cell Res. 2010, 20, 826–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ho, C.H.; Lin, S.H.; Hu, H.C.; Tsay, Y.F. CHL1 Functions as a Nitrate Sensor in Plants. Cell 2009, 138, 1184–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Straub, T.; Ludewig, U.; Neuhäuser, B. The Kinase CIPK23 Inhibits Ammonium Transport in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Kim, B.-G.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Luan, S. A Ca2+ signaling pathway regulates a K+ channel for low-K response in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12625–12630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ragel, P.; Ródenas, R.; García-Martín, E.; Andrés, Z.; Villalta, I.; Nieves-Cordones, M.; Rivero, R.M.; Martínez, V.; Pardo, J.M.; Quintero, F.J.; et al. CIPK23 regulates HAK5-mediated high-affinity K+ uptake in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Held, K.; Pascaud, F.; Eckert, C.; Gajdanowicz, P.; Hashimoto, K.; Corratgé-Faillie, C.; Offenborn, J.N.; Lacombe, B.; Dreyer, I.; Thibaud, J.B.; et al. Calcium-dependent modulation and plasma membrane targeting of the AKT2 potassium channel by the CBL4/CIPK6 calcium sensor/protein kinase complex. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 1116–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maierhofer, T.; Diekmann, M.; Offenborn, J.N.; Lind, C.; Bauer, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Luan, S.; Kudla, J.; Geiger, D.; et al. Site- and kinase-specific phosphorylation-mediated activation of SLAC1, a guard cell anion channel stimulated by abscisic acid. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.K.; Kanwar, P.; Yadav, A.K.; Sharma, C.; Kumar, A.; Pandey, G.K. Arabidopsis CBL interacting protein kinase 3 interacts with ABR1, an APETALA2 domain transcription factor, to regulate ABA responses. Plant Sci. 2017, 254, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Xiong, L.; Song, C.P.; Gong, D.; Halfter, U.; Zhu, J.K. A calcium sensor and its interacting protein kinase are global regulators of abscisic acid signaling in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, W.; Qin, Y.; Yuan, F.; Zhao, F.; Wang, M.; Hu, J.; et al. PKS5/CIPK11, a SnRK3-type protein kinase, is important for ABA responses in Arabidopsis through phosphorylation of ABI5. Plant Physiol. 2015, 168, 659–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, J.P.; Köster, P.; Drerup, M.M.; Scholz, M.; Li, S.; Edel, K.H.; Hashimoto, K.; Kuchitsu, K.; Hippler, M.; Kudla, J. Fine-tuning of RBOHF activity is achieved by differential phosphorylation and Ca2+ binding. New Phytol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Guo, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J.; Liu, C.; Qi, T.; Duan, Y.; Kang, Z.; Guo, J. TaCIPK10 interacts with and phosphorylates TaNH2 to activate wheat defense responses to stripe rust. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 956–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurusu, T.; Hamada, J.; Nokajima, H.; Kitagawa, Y.; Kiyoduka, M.; Takahashi, A.; Hanamata, S.; Ohno, R.; Hayashi, T.; Okada, K.; et al. Regulation of Microbe-Associated Molecular Pattern-Induced Hypersensitive Cell Death, Phytoalexin Production, and Defense Gene Expression by Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinases, OsCIPK14/15, in Rice Cultured Cells. Plant Physiol. 2010, 153, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Long, Y.; Qi, G.-N.; Li, J.; Xu, Z.-J.; Wu, W.-H.; Wang, Y. The Os-AKT1 Channel Is Critical for K+ Uptake in Rice Roots and Is Modulated by the Rice CBL1-CIPK23 Complex. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 3387–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Deng, J.; Yang, X.; Sun, W.; Miao, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, X. The calcium sensor CBL2 and its interacting kinase CIPK6 are involved in plant sugar homeostasis via interacting with tonoplast sugar transporter TST2. Plant Physiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Torre, F.; Gutiérrez-Beltrán, E.; Pareja-Jaime, Y.; Chakravarthy, S.; Martin, G.B.; del Pozo, O. The tomato calcium sensor Cbl10 and its interacting protein kinase cipk6 define a signaling pathway in plant immunity. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 2748–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; He, X.; Hu, W.; Liu, G.; Wang, P.; He, C.; Shi, H.; Calmodulin, C. Functional analysis of MeCIPK23 and MeCBL1/9 in cassava defense response against Xanthomonas axonopodis pv.manihotis. Plant Cell Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.G.; Ma, Q.J.; Sun, C.H.; Sun, M.H.; You, C.X.; Hao, Y.J. Overexpression of MdSOS2L1, a CIPK protein kinase, increases the antioxidant metabolites to enhance salt tolerance in apple and tomato. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 156, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.K. Abiotic Stress Signaling and Responses in Plants. Cell 2016, 167, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Wei, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, R. Functions and mechanisms of the CBL-CIPK signaling system in plant response to abiotic stress. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2009, 19, 667–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, J. A calcium sensor homolog required for plant salt tolerance. Science 1998, 280, 1943–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halfter, U. The Arabidopsis SOS2 protein kinase physically interacts with and is activated by the calcium-binding protein SOS3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3735–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishitani, M. SOS3 Function in Plant Salt Tolerance Requires N-Myristoylation and Calcium Binding. Plant Cell Online 2000, 12, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quintero, F.J.; Ohta, M.; Shi, H.; Zhu, J.K.; Pardo, J.M. Reconstitution in yeast of the Arabidopsis SOS signaling pathway for Na+ homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9061–9066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintero, F.J.; Martinez-atienza, J.; Villalta, I.; Jiang, X.; Kim, W.; Ali, Z. Activation of the plasma membrane Na/H antiporter an auto-inhibitory C-terminal domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2611–2616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, H.; Lee, B.H.; Wu, S.J.; Zhu, J.K. Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, A.; Seki, M.; Umezawa, T.; Ishida, J.; Satou, M.; Akiyama, K.; Zhu, J.K.; Shinozaki, K. Analysis of gene expression profiles in Arabidopsis salt overly sensitive mutants sos2-1 and sos3-1. Plant Cell Environ. 2005, 28, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, N.H.; Pittman, J.K.; Zhu, J.K.; Hirschi, K.D. The Protein Kinase SOS2 Activates the Arabidopsis H+/Ca 2+ Antiporter CAX1 to Integrate Calcium Transport and Salt Tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 2922–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Tang, R.-J.; Xu, H.-X.; Lan, W.-Z.; Zhao, F.; Luan, S. Calcineurin B-Like Proteins CBL4 and CBL10 Mediate Two Independent Salt Tolerance Pathways in Arabidopsis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, H.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; Becker, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Kudla, J.; Schumaker, K.S.; Guo, Y. Inhibition of the Arabidopsis Salt Overly Sensitive Pathway by 14-3-3 proteins. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1166–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mähs, A.; Steinhorst, L.; Han, J.-P.; Shen, L.-K.; Wang, Y.; Kudla, J. The Calcineurin B-Like Ca2+ Sensors CBL1 and CBL9 Function in Pollen Germination and Pollen Tube Growth in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ligaba-Osena, A.; Fei, Z.; Liu, J.; Xu, Y.; Shaff, J.; Lee, S.-C.; Luan, S.; Kudla, J.; Kochian, L.; Piñeros, M. Loss-of-function mutation of the calcium sensor CBL1 increases aluminum sensitivity in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.Y.; Xu, Z.S.; Chen, Y.; He, G.Y.; Yang, G.X.; Chen, M.; Li, L.C.; Ma, Y.Z. A Novel Role for Arabidopsis CBL1 in Affecting Plant Responses to Glucose and Gibberellin during Germination and Seedling Development. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheong, Y.H.; Sung, S.J.; Kim, B.G.; Pandey, G.K.; Cho, J.S.; Kim, K.N.; Luan, S. Constitutive overexpression of the calcium sensor CBL5 confers osmotic or drought stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Mol. Cells 2010, 29, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, P.L.; Lee, S.Y.; Allen, N.S.; Winter-Sederoff, H.; Robertson, D. An ER-targeted calcium-binding peptide confers salt and drought tolerance mediated by CIPK6 in Arabidopsis. Planta 2012, 235, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Kong, Z.; Omo-Ikerodah, E.; Xu, W.; Li, Q.; Xue, Y. Calcineurin B-like interacting protein kinase OsCIPK23 functions in pollination and drought stress responses in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Genet. Genom. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, F.; Yuan, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, Q.; Liu, F.; Wang, W. ZmCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates maize response to drought stress. Plant Cell Tissue Organ. Cult. 2016, 124, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Wu, G.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Wei, J. HbCIPK2, a novel CBL-interacting protein kinase from halophyte Hordeum brevisubulatum, confers salt and osmotic stress tolerance. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1582–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, T.; Shimazaki, K.I. Blue light activates the plasma membrane H+-ATPase by phosphorylation of the C-terminus in stomatal guard cells. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5548–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adamczyk-Szabela, D.; Markiewicz, J.; Wolf, W.M. Heavy Metal Uptake by Herbs. IV. Influence of Soil pH on the Content of Heavy Metals in Valeriana officinalis L. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2015, 226, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.; Dong, Q.; Li, Q.; Ni, X.; Kudla, J.; Song, C.P.; Guo, Y. The Ca2+ sensor SCaBP3/CBL7 Modulates Plasma Membrane H+-ATPase Activity and Promotes Alkali Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2019, 31, 1367–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M. Metals, Toxicity and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gransee, A.; Führs, H. Magnesium mobility in soils as a challenge for soil and plant analysis, magnesium fertilization and root uptake under adverse growth conditions. Plant Soil. 2013, 368, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, W.; Shen, J.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, X.; Shou, J.; Wang, W.; Jiang, L. Overexpression of the Tibetan Plateau annual wild barley (Hordeum spontaneum) HsCIPKs enhances rice tolerance to heavy metal toxicities and other abiotic stresses. Rice 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tokas, I.; Pandey, A.; Pandey, G.K. Role of Calcium-Mediated CBL–CIPK Network in Plant Mineral Nutrition and Abiotic Stress. Mol. Stress Physiol. Plants 2013, 241–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coruzz, G.; Bush, D.R. Nitrogen and carbon nutrient and metabolite signaling in plants. Plant Physiol. 2001, 125, 61–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forde, B.G. Nitrate transporters in plants: Structure, function and regulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2000, 1465, 219–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Liu, D.; Crawford, N.M. The Arabidopsis CHL1 protein plays a major role in high-affinity nitrate uptake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15134–15139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, H.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tsay, Y.F. AtCIPK8, a CBL-interacting protein kinase, regulates the low-affinity phase of the primary nitrate response. Plant J. 2009, 57, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanquar, V.; Loqué, D.; Hörmann, F.; Yuan, L.; Bohner, A.; Engelsberger, W.R.; Lalonde, S.; Schulze, W.X.; von Wirén, N.; Frommer, W.B. Feedback inhibition of ammonium uptake by a phospho-dependent allosteric mechanism in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3610–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marschner, P. Marschner’s Mineral Nutrition of Higher Plants, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- White, P.J.; Karley, A.J. Potassium. In Cell Biology of Metals and Nutrients; Hell, R., Mendel, R.-R., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 199–224. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Xu, G.; Alli, A.; Yu, L. Plant HAK/KUP/KT K+ transporters: Function and regulation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 74, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, E.; Rains, D.W.; Elzam, O.E. Resolution of dual mechanisms of potassium absorption by barley roots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1963, 49, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.P.; Chen, L.M.; Liu, W.X.; Shen, L.K.; Wang, F.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, W.H.; Wang, Y. AtKC1 and CIPK23 synergistically modulate AKT1-mediated low-potassium stress responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 2264–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yang, A.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.H. CIPK23 is involved in iron acquisition of Arabidopsis by affecting ferric chelate reductase activity. Plant Sci. 2016, 246, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Léran, S.; Edel, K.H.; Pervent, M.; Hashimoto, K.; Corratge-Faillie, C.; Offenborn, J.N.; Tillard, P.; Gojon, A.; Kudla, J.; Lacombe, B. Nitrate sensing and uptake in Arabidopsis are enhanced by ABI2, a phosphatase inactivated by the stress hormone abscisic acid. Sci. Signal 2015, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.Z.; Lee, S.C.; Che, Y.F.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Luan, S. Mechanistic analysis of AKT1 regulation by the CBL-CIPK-PP2CA interactions. Mol. Plant 2011, 4, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Lan, W.-Z.; Kim, B.-G.; Li, L.; Cheong, Y.H.; Pandey, G.K.; Lu, G.; Buchanan, B.B.; Luan, S. A protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation network regulates a plant potassium channel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15959–15964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lacombe, B.; Pilot, G.; Michard, E.; Gaymard, F.; Sentenac, H.; Thibaud, J.B. A shaker-like K+ channel with weak rectification is expressed in both source and sink phloem tissues of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K.; Shinozaki, K. Transcriptional Regulatory Networks in Cellular Responses and Tolerance to Dehydration and Cold Stresses. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2006, 57, 781–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshida, T.; Mogami, J.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. ABA-dependent and ABA-independent signaling in response to osmotic stress in plants. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2014, 21, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, G.K.; Yong, H.C.; Kim, K.N.; Grant, J.J.; Li, L.; Hung, W.; D’Angelo, C.; Weinl, S.; Kudla, J.; Luan, S. The calcium sensor calcineurin B-like 9 modulates abscisic acid sensitivity and biosynthesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2004, 16, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pandey, G.K.; Grant, J.J.; Cheong, Y.H.; Kim, B.G.; Li, L.G.; Luan, S. Calcineurin-B-like protein CBL9 interacts with target kinase CIPK3 in the regulation of ABA response in seed germination. Mol. Plant 2008, 1, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batistič, O.; Rehers, M.; Akerman, A.; Schlücking, K.; Steinhorst, L.; Yalovsky, S.; Kudla, J. S-acylation-dependent association of the calcium sensor CBL2 with the vacuolar membrane is essential for proper abscisic acid responses. Cell Res. 2012, 22, 1155–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.-Z.; Li, S.; Feng, Q.-N.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Zhao, X.; Zeng, Y.-l.; Wang, H.; Jiang, L.; Zhang, Y. PROTEIN S-ACYL TRANSFERASE10 Is Critical for Development and Salt Tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2013, 25, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geiger, D.; Scherzer, S.; Mumm, P.; Marten, I.; Ache, P.; Matschi, S.; Liese, A.; Wellmann, C.; Al-Rasheid, K.A.S.; Grill, E.; et al. Guard cell anion channel SLAC1 is regulated by CDPK protein kinases with distinct Ca 2+ affinities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 8023–8028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Li, T.; John, S.J.; Chen, M.; Chang, J.; Yang, G.; He, G. A CBL-interacting protein kinase TaCIPK27 confers drought tolerance and exogenous ABA sensitivity in transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 123, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgin, D.D.; Zavala, J.A.; Zhu, J.; Clough, S.J.; Ort, D.R.; Delucia, E.H. Biotic stress globally downregulates photosynthesis genes. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 33, 1597–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bai, B.B. Biological Invasions: Economic and Environmental Costs of Alien Plant, Animal, and Microbe Species. Environ. Entomol. 2014, 37, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, J.D.G.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boller, T.; Felix, G. A Renaissance of Elicitors: Perception of Microbe-Associated Molecular Patterns and Danger Signals by Pattern-Recognition Receptors Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2009, 60, 379–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, K.; Hirt, H. REACTIVE OXYGEN SPECIES: Metabolism, Oxidative Stress, and Signal Transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2004, 55, 373–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oxidases, N.; Sagi, M.; Fluhr, R. Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by Plant. Structure 2006, 141, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, D.; Dunand, C.; Puppo, A.; Pauly, N. A burst of plant NADPH oxidases. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardar, A.; Nandi, A.K.; Chattopadhyay, D. CBL-interacting protein kinase 6 negatively regulates immune response to Pseudomonas syringae in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 3573–3584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drerup, M.M.; Schlücking, K.; Hashimoto, K.; Manishankar, P.; Steinhorst, L.; Kuchitsu, K.; Kudla, J. The calcineurin B-like calcium sensors CBL1 and CBL9 together with their interacting protein kinase CIPK26 regulate the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase RBOHF. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 559–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, S.; Kawarazaki, T.; Nibori, H.; Michikawa, M.; Imai, A.; Kaya, H.; Kuchitsu, K. The CBL-interacting protein kinase CIPK26 is a novel interactor of Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase AtRbohF that negatively modulates its ROS-producing activity in a heterologous expression system. J. Biochem. 2013, 153, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, T. A Flower Specific Calcineurin B-Like Molecule (CBL)-Interacting Protein Kinase (CIPK) Homolog in Tomato Cultivar Micro-Tom (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Am. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Johnson, M.A.A. Plant Reproduction: Teaching a New Language of Love. Curr. Biol. 2012, 22, R528–R529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, L.; Lan, W.; Chen, B.; Fang, W.; Luan, S. A calcium sensor-regulated protein kinase, CALCINEURIN B-LIKE PROTEIN-INTERACTING PROTEIN KINASE19, is required for pollen tube growth and polarity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 167, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monihan, S.M.; Magness, C.A.; Yadegari, R.; Smith, S.E.; Schumaker, K.S. Arabidopsis CALCINEURIN B-LIKE10 Functions Independently of the SOS Pathway during Reproductive Development in Saline Conditions. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.Y.; Ali, Z.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Perez-Hormaeche, J.; Quintero, F.J.; Shin, G.; Kim, M.R.; Qiang, Z.; et al. Release of SOS2 kinase from sequestration with GIGANTEA determines salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1312–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Comas, L.H.; Becker, S.R.; Cruz, V.M.V.; Byrne, P.F.; Dierig, D.A. Root traits contributing to plant productivity under drought. Front. Plant Sci. 2013, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tripathi, V.; Parasuraman, B.; Laxmi, A.; Chattopadhyay, D. CIPK6, a CBL-interacting protein kinase is required for development and salt tolerance in plants. Plant J. 2009, 58, 778–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. SOS3 mediates lateral root development under low salt stress through regulation of auxin redistribution and maxima in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 1122–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, M.K.; Vishwakarma, N.K.; Tripathi, V.; Chattopadhyay, D. CBL-interacting protein kinase 25 contributes to root meristem development. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 133–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeekens, S. Sugar-induced signal transduction in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 2000, 51, 49–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gibson, S.I. Control of plant development and gene expression by sugar signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol 2005, 8, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekkers, B.J.W.; Schuurmans, J.A.M.J.; Smeekens, S.C.M. Glucose delays seed germination in Arabidopsis thaliana. Planta 2004, 218, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

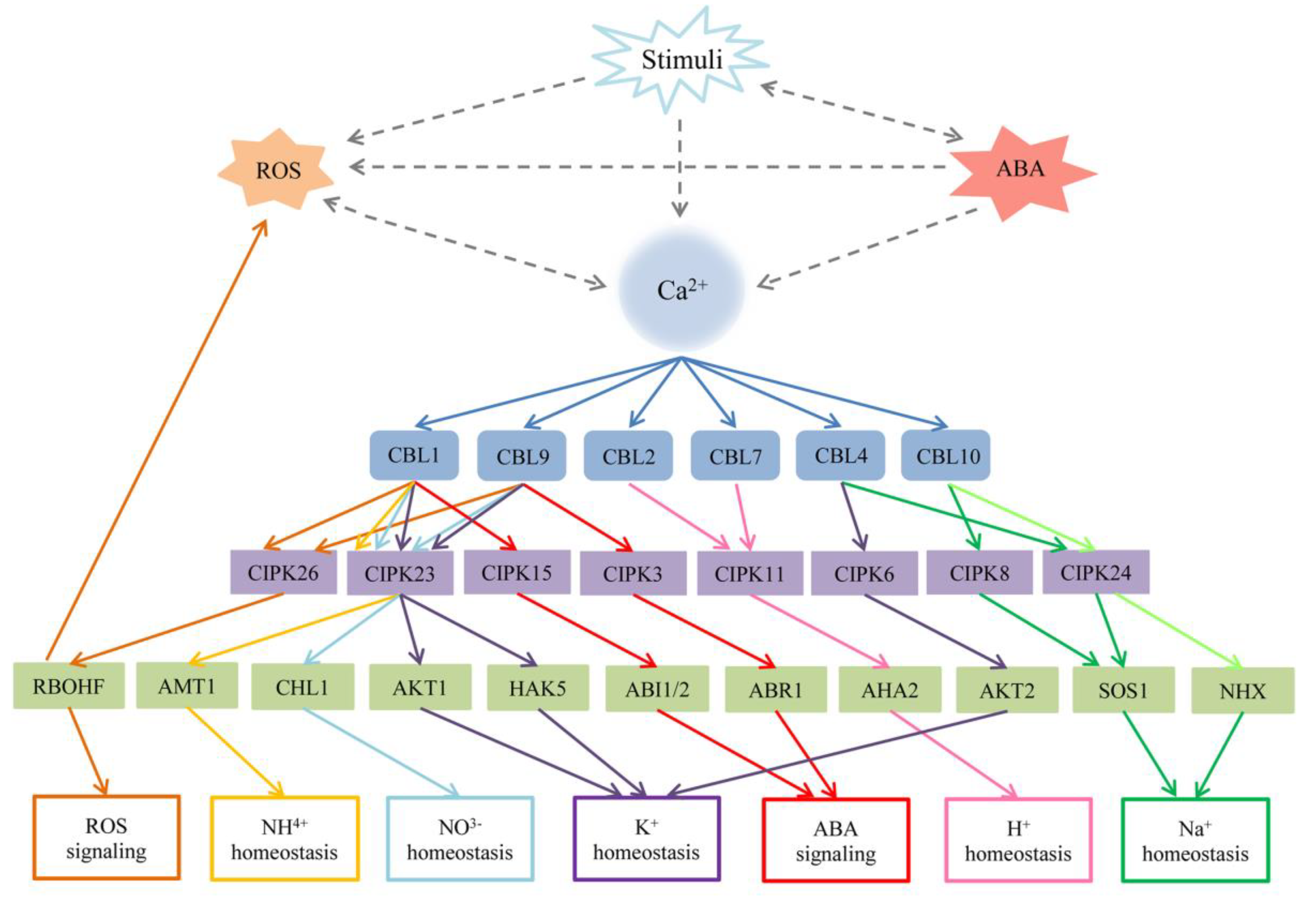
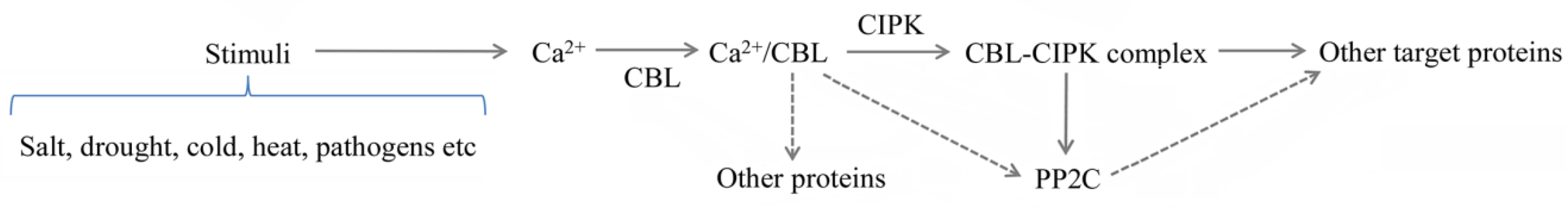
| Species | CBL | CIPK | Target Protein | Localization of Complex | Stimulus or Pathway Affected | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arabidopsis thaliana | AtCBL4/SOS3 | AtCIPK24/ SOS2 | SOS1 | Plasma membrane | Salt stress | [90] |
| AtCBL10 | - | Tonoplast/Plasma membrane | Salt stress | [38,73] | ||
| AtCBL10 | AtCIPK8 | SOS1 | Plasma membrane | Salt stress | [91] | |
| AtCBL2/-3 | AtCIPK21 | - | Tonoplast | Salt and osmotic stress | [92] | |
| AtCBL1 | AtCIPK7 | - | - | Cold | [93] | |
| AtCBL7 | AtCIPK11 | AHA2 | Plasma membrane | H+ homeostasis | [94] | |
| AtCBL2/-3 | AtCIPK3/-9/ -23/-26 | SRK2D/E/I | Tonoplast | Mg2+ homeostasis | [30,78] | |
| - | AtCIPK8 | CHL1 | - | NO3− homeostasis | [95] | |
| AtCBL1/-9 | AtCIPK23 | CHL1 | Plasma membrane | NO3− homeostasis | [96] | |
| AtCBL1 | AtCIPK23 | AMT1 | Plasma membrane | NH4+ homeostasis | [97] | |
| AtCBL1/-9 | AtCIPK23 | AKT1 | Plasma membrane | K+ homeostasis | [89,98] | |
| AtCBL1/-9 | AtCIPK23 | HAK5 | Plasma membrane | K+ homeostasis | [99] | |
| AtCBL10 | - | AKT1 | Plasma membrane | K+ homeostasis | [74] | |
| AtCBL4 | AtCIPK6 | AKT2 | Plasma membrane | K+ homeostasis | [100] | |
| AtCBL1/-9 | AtCIPK23 | SLAC1/ SLAH3 | - | ABA signaling | [101] | |
| AtCBL5 | AtCIPK11 | SLAC1 | Plasma membrane | ABA signaling | [81] | |
| AtCBL2/-3 | AtCIPK9/-17 | - | Tonoplast | ABA signaling | [31] | |
| AtCBL9 | AtCIPK3 | ABR1 | - | ABA signaling | [102] | |
| AtCBL1 | AtCIPK15 | ABI1/ABI2 | - | ABA signaling | [103] | |
| - | AtCIPK15 | ABI5 | - | ABA signaling | [104] | |
| AtCBL1/-9 | AtCIPK26 | RBOHF | Plasma membrane | ROS signaling | [105] | |
| Triticum aestivum | TaCBL4 | TaCIPK5 | - | - | Pst | [35] |
| - | TaCIPK10 | TaNH2 | - | Pst | [106] | |
| Oryza sativa | OsCBL4 | OsCIPK14/-15 | - | - | TvX/EIX | [107] |
| OsCBL1 | OsCIPK23 | OsAKT1 | Plasma membrane | K+ homeostasis | [108] | |
| Gossypium hirsutum | GhCBL2 | GhCIPK6 | GhTST2 | Tonoplast | Sugar homeostasis | [109] |
| Solanum lycopersicum | SlCBL10 | SlCIPK6 | RBOHB | Plasma membrane | ROS signaling | [110] |
| Manihot esculenta | MeCBL1/-9 | MeCIPK23 | - | Plasma membrane | Xam | [111] |
| Malus domestica | - | MdCIPK13 | MdSUT2.2 | - | Salt stress | [80] |
| MdCBL1/-4/-10 | MdSOS2L1 | - | - | Salt stress | [112] | |
| - | MdCIPK22 | MdAREB2 | - | ABA signaling | [79] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Li, Q.-H.; Yu, Y.-N.; Qiao, Y.-M.; Haq, S.u.; Gong, Z.-H. The CBL–CIPK Pathway in Plant Response to Stress Signals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165668
Ma X, Li Q-H, Yu Y-N, Qiao Y-M, Haq Su, Gong Z-H. The CBL–CIPK Pathway in Plant Response to Stress Signals. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2020; 21(16):5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165668
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiao, Quan-Hui Li, Ya-Nan Yu, Yi-Ming Qiao, Saeed ul Haq, and Zhen-Hui Gong. 2020. "The CBL–CIPK Pathway in Plant Response to Stress Signals" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21, no. 16: 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165668
APA StyleMa, X., Li, Q.-H., Yu, Y.-N., Qiao, Y.-M., Haq, S. u., & Gong, Z.-H. (2020). The CBL–CIPK Pathway in Plant Response to Stress Signals. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 21(16), 5668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165668





