The Relationship between Controlling Nutritional (CONUT) Score and Clinical Markers among Adults with Hepatitis C Virus Related Liver Cirrhosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Inclusion Criteria
2.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.3. CONUT Score
2.4. Our Objectives and Ethical Approval
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Relationship between the CONUT Score and Other Clinical Variables (Spearman’s Rank Correlation Coefficient rs)
3.3. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Factors associated with CONUT Score ≥ 2 (Mild, Moderate or Severe Malnutrition)
3.4. Univariate and Multivariate Analyses of Factors Associated with CONUT Score ≥ 5 (Moderate or Severe Malnutrition)
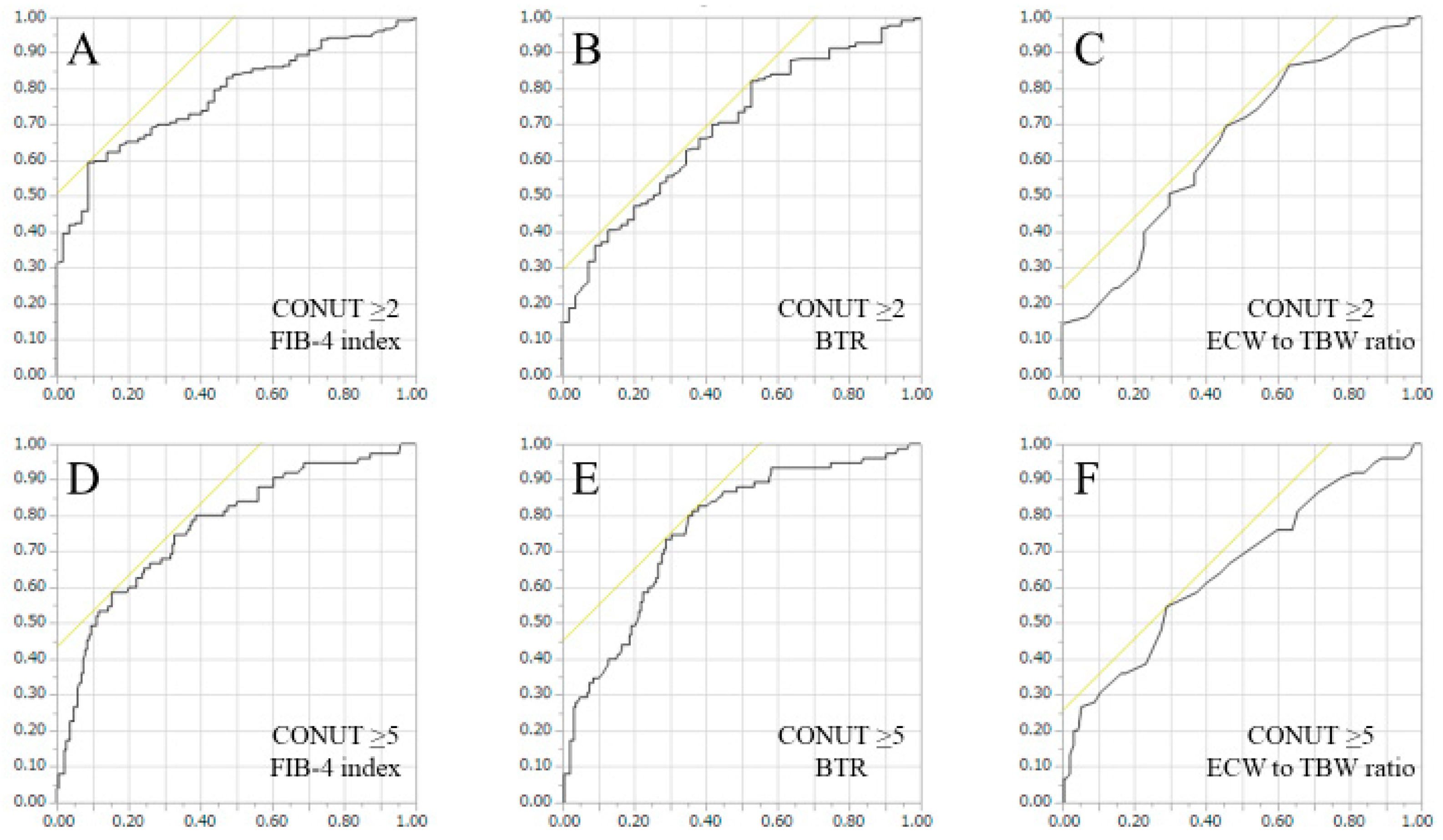
3.5. ROC Analyses for Predicting CONUT Score ≥ 2 or CONUT Score ≥ 5 in FIB-4 Index, BTR and ECW to TBW Ratio
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Charlton, M.R. Branched-chain amino acid enriched supplements as therapy for liver disease. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 295S–298S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Izumi, N.; Charlton, M.R.; Sata, M. Branched-chain amino acids as pharmacological nutrients in chronic liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 54, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, P.; Ismond, K.P.; Riess, K.; Duarte-Rojo, A.; Al-Judaibi, B.; Dunn, M.A.; Holman, J.; Howes, N.; Haykowsky, M.J.F.; Josbeno, D.A.; McNeely, M. Exercise in cirrhosis: Translating evidence and experience to practice. J. Hepatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, H.; Saito, H.; Ueno, Y.; Uto, H.; Obara, K.; Sakaida, I.; Shibuya, A.; Seike, M.; Nagoshi, S.; Segawa, M.; et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for liver cirrhosis 2015. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 629–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Ishii, A.; Iwata, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishii, N.; Yuri, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Elevated serum myostatin level is associated with worse survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2017, 8, 915–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polaris Observatory HCVC. Global prevalence and genotype distribution of hepatitis C virus infection in 2015: A modelling study. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanaway, J.D.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C.; Vos, T.; Abubakar, I.; Abu-Raddad, L.J.; Assadi, R.; Bhala, N.; Cowie, B.; et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: Findings from the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet 2016, 388, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberino, F.; Gatta, A.; Amodio, P.; Merkel, C.; Di Pascoli, L.; Boffo, G.; Caregaro, L. Nutrition and survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrition 2001, 17, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Yoh, K.; Iwata, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Takata, R.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Serum hyaluronic acid predicts protein-energy malnutrition in chronic hepatitis C. Medicine 2016, 95, e3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Osaki, Y. Liver cirrhosis: Evaluation, nutritional status, and prognosis. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 872152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Yoh, K.; Enomoto, H.; Iwata, Y.; Kishino, K.; Shimono, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Takata, R.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Factors associated with protein-energy malnutrition in chronic liver disease: Analysis using indirect calorimetry. Medicine 2016, 95, e2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Enomoto, H.; Ishii, A.; Iwata, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Ishii, N.; Yuri, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Nakano, C.; Nishimura, T.; et al. Comparison of prognostic impact between the child-pugh score and skeletal muscle mass for patients with liver cirrhosis. Nutrients 2017, 9, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Shiraki, M.; Hiramatsu, A.; Moriya, K.; Hino, K.; Nishiguchi, S. Japan society of hepatology guidelines for sarcopenia in liver disease: Recommendation from the working group for creation of sarcopenia assessment criteria. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvares-da-Silva, M.R.; Reverbel da Silveira, T. Comparison between handgrip strength, subjective global assessment, and prognostic nutritional index in assessing malnutrition and predicting clinical outcome in cirrhotic outpatients. Nutrition 2005, 21, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabe, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Harata, M.; Nitta, Y.; Murao, M.; Nakano, T.; Shimazaki, H.; Kobayashi, K.; Komura, N.; Ito, H.; et al. Assessment of nutritional status of patients with hepatitis C virus-related liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2008, 38, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, E.; Kawaguchi, T.; Itou, M.; Oriishi, T.; Ibi, R.; Torii, M.; Yoshida, K.; Adachi, Y.; Otsuka, M.; Uchida, Y.; et al. Subjective global assessment is not sufficient to screen patients with defective hepatic metabolism. Nutrition 2011, 27, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X. Controlling nutritional status score, a promising prognostic marker in patients with gastrointestinal cancers after surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 55, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harimoto, N.; Yoshizumi, T.; Inokuchi, S.; Itoh, S.; Adachi, E.; Ikeda, Y.; Uchiyama, H.; Utsunomiya, T.; Kajiyama, K.; Kimura, K.; et al. Prognostic significance of preoperative controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score in patients undergoing hepatic resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: A multi-institutional study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Yamada, S.; Suenaga, M.; Takami, H.; Niwa, Y.; Hayashi, M.; Iwata, N.; Kanda, M.; Tanaka, C.; Nakayama, G.; et al. Impact of the controlling nutritional status score on the prognosis after curative resection of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2018, 47, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, D.; Lin, E.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Z. Preoperative controlling nutritional status (CONUT) score as a predictor of long-term outcome after curative resection followed by adjuvant chemotherapy in stage II-III gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, I.; Seo, Y.; Hamada-Harimura, Y.; Sato, K.; Sai, S.; Yamamoto, M.; Ishizu, T.; Sugano, A.; Obara, K.; Wu, L.; et al. Utility of nutritional screening in predicting short-term prognosis of heart failure patients. Int. Heart J. 2018, 59, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihisa, A.; Kanno, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Yokokawa, T.; Abe, S.; Miyata, M.; Sato, T.; Suzuki, S.; Oikawa, M.; Kobayashi, A.; et al. Impact of nutritional indices on mortality in patients with heart failure. Open Heart 2018, 5, e000730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignacio de Ulibarri, J.; Gonzalez-Madrono, A.; de Villar, N.G.; Gonzalez, P.; Gonzalez, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodriguez, F.; Fernandez, G. CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- González-Madroño, A.; Mancha, A.; Rodríguez, F.J.; Culebras, J.; de Ulibarri, J.I. Confirming the validity of the CONUT system for early detection and monitoring of clinical undernutrition: Comparison with two logistic regression models developed using SGA as the gold standard. Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liang, R.F.; Li, J.H.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.H.T. The prognostic role of controlling nutritional status scores in patients with solid tumors. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 474, 155–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, K.; Ueno, Y.; Kawagishi, N.; Kondo, Y.; Inoue, J.; Kakazu, E.; Ninomiya, M.; Wakui, Y.; Saito, N.; Satomi, S.; et al. The nutritional index ‘CONUT’ is useful for predicting long-term prognosis of patients with end-stage liver diseases. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2011, 224, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirakabe, A.; Hata, N.; Kobayashi, N.; Okazaki, H.; Matsushita, M.; Shibata, Y.; Nishigoori, S.; Uchiyama, S.; Asai, K.; Shimizu, W. The prognostic impact of malnutrition in patients with severely decompensated acute heart failure, as assessed using the Prognostic Nutritional Index (PNI) and Controlling Nutritional Status (CONUT) score. Heart Vessels 2018, 33, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, R.N.; Koehler, K.M.; Gallagher, D.; Romero, L.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Ross, R.R.; Garry, P.J.; Lindeman, R.D. Epidemiology of sarcopenia among the elderly in New Mexico. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malczyk, E.; Dzięgielewska-Gęsiak, S.; Fatyga, E.; Ziółko, E.; Kokot, T.; Muc-Wierzgon, M. Body composition in healthy older persons: Role of the ratio of extracellular/total body water. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2016, 30, 767–772. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, H.; Nishijima, N.; Enomoto, H.; Sakamoto, A.; Nasu, A.; Komekado, H.; Nishimura, T.; Kita, R.; Kimura, T.; Iijima, H.; et al. Comparison of FIB-4 index and aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index on carcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis B treated with entecavir. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallet-Pichard, A.; Mallet, V.; Nalpas, B.; Verkarre, V.; Nalpas, A.; Dhalluin-Venier, V.; Fontaine, H.; Pol, S. FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology 2007, 46, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Tsuji, K.; Hiraoka, A.; Tanaka, J. Impact of FIB-4 index on hepatocellular carcinoma incidence during nucleos(t)ide analogue therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B: An analysis using time-dependent receiver operating characteristic. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 32, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Toyoda, H.; Kiriyama, S.; Tanikawa, M.; Hisanaga, Y.; Kanamori, A.; Kitabatake, S.; Yama, T.; Tanaka, J. Long-term prognosis of patients with chronic hepatitis C who did not receive interferon-based therapy: Causes of death and analysis based on the FIB-4 index. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 380–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, A.; Kakazu, E.; Morosawa, T.; Inoue, J.; Kogure, T.; Ninomiya, M.; Iwata, T.; Umetsu, T.; Nakamura, T.; Takai, S.; et al. The profiling of plasma free amino acids and the relationship between serum albumin and plasma-branched chain amino acids in chronic liver disease: A single-center retrospective study. J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 53, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinclair, M.; Gow, P.J.; Grossmann, M.; Angus, P.W. Review article: Sarcopenia in cirrhosis—Aetiology, implications and potential therapeutic interventions. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panorchan, K.; Nongnuch, A.; El-Kateb, S.; Goodlad, C.; Davenport, A. Changes in muscle and fat mass with haemodialysis detected by multi-frequency bioelectrical impedance analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 69, 1109–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Normal | Mild | Moderate | Severe |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serum albumin (g/dL) | ≥3.5 | 3.0–3.49 | 2.5–2.99 | <2.5 |
| Corresponding score | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 |
| Total lymphocyte count (/mm3) | ≥1600 | 1200–1599 | 800–1199 | <800 |
| Corresponding score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dL) | ≥180 | 140–179 | 100–139 | <100 |
| Corresponding score | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Classification (sum of each score) | 0 or 1 | Normal nutrition status | ||
| 2, 3 or 4 | Mild malnutrition status | |||
| 5, 6, 7 or 8 | Moderate malnutrition status | |||
| More than 8 | Severe malnutrition status | |||
| Variables | All Cases (n = 264) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.0 (25.5–94.0) |
| Gender, Male/Female | 141/123 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 22.9 (13.1–34.4) |
| ECW to TBW Ratio | 0.390 (0.369–0.433) |
| SMI (cm2/m2), Male | 7.24 (4.66–10.21) |
| SMI (cm2/m2), Female | 5.94 (3.90–7.68) |
| Upper-SMI (cm2/m2), Male | 1.87 (0.80–2.82) |
| Upper-SMI (cm2/m2), Female | 1.41 (0.83–2.03) |
| Lower-SMI (cm2/m2), Male | 5.33 (3.86–8.19) |
| Lower-SMI (cm2/m2), Female | 4.52 (2.93–5.88) |
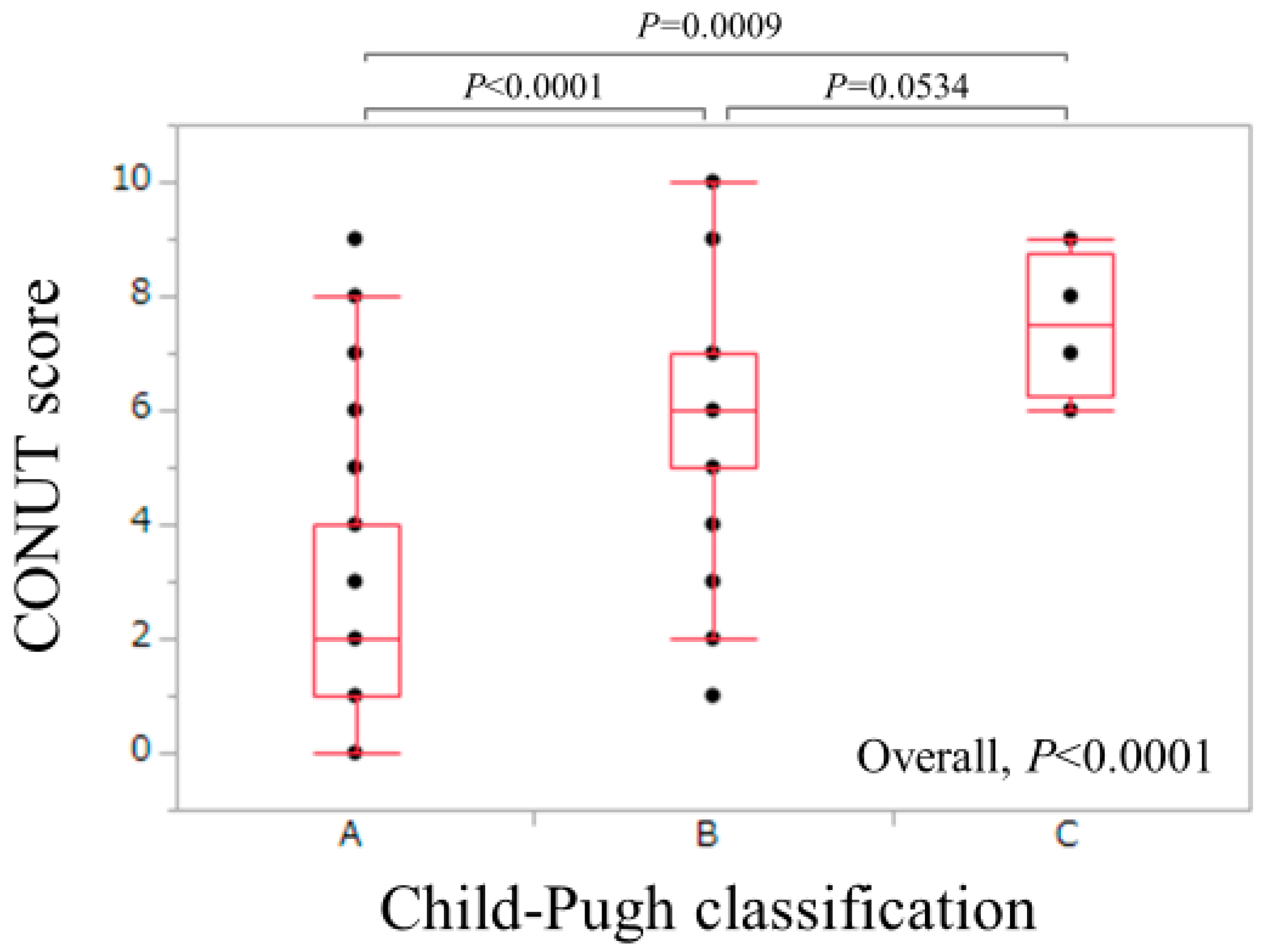
| Child-Pugh A/B/C | 198/62/4 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.2–5.1) |
| Serum Albumin (g/dL) | 3.7 (2.3–5.0) |
| Prothrombin Time (%) | 78.6 (39.2–123.4) |
| Platelet Count (×104/mm3) | 9.9 (3.0–32.0) |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | 79.9 (6.2–164.5) |
| White Blood Cell (/mm3) | 4040 (1150–9450) |
| Lymphocyte Count (/mm3) | 1249 (119–3646) |
| Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 149 (73–292) |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 82.5 (25–318) |
| CONUT Score | 3 (0–10) |
| AST (IU/L) | 43 (14–182) |
| ALT (IU/L) | 34 (9–167) |
| BTR | 4.05 (1.65–8.37) |
| BCAA (μmol/L) | 423.3 (230.4–860.3) |
| Tyrosine (μmol/L) | 107.3 (12.2–656.4) |
| FIB-4 Index | 5.38 (0.89–20.04) |
| Hyaluronic Acid (ng/mL) | 229 (11–3730) |
| Fasting Blood Glucose (mg/dL) | 101 (72–403) |
| All Cases (n = 264) | ||
|---|---|---|
| rs | p Value | |
| Age | 0.1071 | 0.0823 |
| Body Mass Index | −0.0002 | 0.9969 |
| ECW to TBW Ratio | 0.3470 | <0.0001 |
| SMI, Male | 0.0035 | 0.9667 |
| SMI, Female | 0.0964 | 0.2888 |
| Upper-SMI, Male | −0.0982 | 0.2467 |
| Upper-SMI, Female | −0.0179 | 0.8439 |
| Lower-SMI, Male | −0.0462 | 0.5868 |
| Lower-SMI, Female | −0.0120 | 0.8955 |
| Total Bilirubin | 0.2828 | <0.0001 |
| Prothrombin Time | −0.4565 | <0.0001 |
| Platelet Count | −0.5039 | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride | −0.2919 | <0.0001 |
| AST | 0.1541 | 0.0122 |
| ALT | −0.0066 | 0.9151 |
| eGFR | −0.0512 | 0.4075 |
| BTR | −0.4213 | <0.0001 |
| BCAA | −0.2530 | <0.0001 |
| Tyrosine | 0.2888 | <0.0001 |
| FIB-4 Index | 0.5465 | <0.0001 |
| Hyaluronic Acid | 0.3890 | <0.0001 |
| Fasting Blood Glucose | −0.0591 | 0.3386 |
| Variables | CONUT Score ≥ 2 (n = 207) | CONUT Score < 2 (n = 57) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.0 (25.5–94.0) | 66.5 (40.0–81.9) | 0.1779 |
| Gender, Male/Female | 113/94 | 28/29 | 0.5490 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 22.5 (13.1–34.4) | 23.8 (18.2–30.3) | 0.0920 |
| ECW to TBW ratio | 0.392 (0.372–0.433) | 0.387 (0.369–0.400) | 0.0007 |
| SMI (cm2/m2) | 6.61 (3.90–10.21) | 6.57 (4.17–9.15) | 0.6994 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.0 (0.2–5.1) | 0.8 (0.4–2.2) | <0.0001 |
| Prothrombin Time (%) | 76.1 (39.2–123.4) | 84.4 (60.5–118.7) | 0.0003 |
| Platelet Count (×104/mm3) | 8.9 (3.0–30.0) | 13.4 (4.7–32.0) | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 77 (25–281) | 98 (39–318) | 0.0006 |
| AST (IU/L) | 45 (14–168) | 35 (15–182) | 0.0296 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 35 (9–150) | 31 (9–167) | 0.5416 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 79.7 (6.2–164.5) | 81.0 (46.9–140.8) | 0.8502 |
| BTR | 3.95 (1.65–8.37) | 4.84 (2.56–8.31) | <0.0001 |
| FIB-4 Index | 6.39 (0.89–20.04) | 3.45 (0.95–8.16) | <0.0001 |
| Hyaluronic Acid (ng/mL) | 253 (25–3730) | 141 (11–1210) | <0.0001 |
| Fasting Blood Sugar (mg/ dL) | 101 (72–403) | 103 (85–195) | 0.6724 |
| Variables | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value | |
| FIB-4 index | 0.0011 | 3.274 × 10−5–0.0353 | <0.0001 |
| BTR | 9.3126 | 0.9337–92.8789 | 0.0497 |
| ECW to TBW ratio | 0.0511 | 0.0033–0.7848 | 0.0243 |
| Variables | CONUT Score ≥ 5 (n = 75) | CONUT Score < 5 (n = 189) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.0 (29.4–84.6) | 67.3 (25.5–94.0) | 0.8123 |
| Gender, Male/Female | 37/38 | 104/85 | 0.4151 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 23.1 (17.3–34.4) | 22.7 (13.1–31.8) | 0.0988 |
| ECW to TBW Ratio | 0.394 (0.375–0.431) | 0.389 (0.369–0.433) | 0.0001 |
| Skeletal Muscle Index | 6.69 (4.47–9.71) | 6.58 (3.90–10.21) | 0.5398 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.1 (0.4–5.1) | 0.9 (0.2–2.8) | <0.0001 |
| Prothrombin Time (%) | 66.9 (39.2–104.1) | 82.2 (51.5–123.4) | <0.0001 |
| Platelet Count (×104/mm3) | 7.2 (3.0–27.8) | 10.9 (3.2–32.0) | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride (mg/dL) | 69 (25–239) | 90 (25–318) | 0.0066 |
| AST (IU/L) | 50 (14–139) | 40 (15–182) | 0.2065 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 35 (10–131) | 34 (9–167) | 0.7660 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 79.4 (23.3–146.2) | 80.2 (6.2–164.5) | 0.6830 |
| BTR | 3.29 (1.76–7.70) | 4.44 (1.65–8.37) | <0.0001 |
| FIB-4 index | 8.40 (1.83–20.04) | 4.51 (0.89–18.54) | <0.0001 |
| Hyaluronic Acid (ng/mL) | 375 (55.8–3730) | 190 (11–1420) | <0.0001 |
| Fasting Blood Sugar (mg/dL) | 101 (72–233) | 101 (76–403) | 0.8739 |
| Variables | Multivariate Analysis | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p Value | |
| FIB-4 Index | 0.0437 | 0.0052–0.3180 | 0.0018 |
| BTR | 51.082 | 2.5561–1220.436 | 0.0095 |
| ECW to TBW Ratio | 0.0662 | 0.0058–0.7278 | 0.0266 |
| CONUT ≥ 2 | AUC | Cutoff Point | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FIB-4 Index | 0.781 | 5.60 | 59.4 | 91.3 |
| BTR | 0.694 | 5.27 | 82.1 | 47.3 |
| ECW to TBW Ratio | 0.647 | 0.388 | 69.6 | 54.4 |
| CONUT ≥ 5 | AUC | Cutoff point | Sensitivity (%) | Specificity (%) |
| FIB-4 Index | 0.768 | 7.89 | 58.7 | 84.7 |
| BTR | 0.762 | 4.03 | 81.3 | 63.6 |
| ECW to TBW Ratio | 0.653 | 0.394 | 54.7 | 70.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nishikawa, H.; Yoh, K.; Enomoto, H.; Ishii, N.; Iwata, Y.; Takata, R.; Nishimura, T.; Aizawa, N.; Sakai, Y.; Ikeda, N.; et al. The Relationship between Controlling Nutritional (CONUT) Score and Clinical Markers among Adults with Hepatitis C Virus Related Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091185
Nishikawa H, Yoh K, Enomoto H, Ishii N, Iwata Y, Takata R, Nishimura T, Aizawa N, Sakai Y, Ikeda N, et al. The Relationship between Controlling Nutritional (CONUT) Score and Clinical Markers among Adults with Hepatitis C Virus Related Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients. 2018; 10(9):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091185
Chicago/Turabian StyleNishikawa, Hiroki, Kazunori Yoh, Hirayuki Enomoto, Noriko Ishii, Yoshinori Iwata, Ryo Takata, Takashi Nishimura, Nobuhiro Aizawa, Yoshiyuki Sakai, Naoto Ikeda, and et al. 2018. "The Relationship between Controlling Nutritional (CONUT) Score and Clinical Markers among Adults with Hepatitis C Virus Related Liver Cirrhosis" Nutrients 10, no. 9: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091185
APA StyleNishikawa, H., Yoh, K., Enomoto, H., Ishii, N., Iwata, Y., Takata, R., Nishimura, T., Aizawa, N., Sakai, Y., Ikeda, N., Hasegawa, K., Takashima, T., Iijima, H., & Nishiguchi, S. (2018). The Relationship between Controlling Nutritional (CONUT) Score and Clinical Markers among Adults with Hepatitis C Virus Related Liver Cirrhosis. Nutrients, 10(9), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10091185




