Quantification of Trace Polymorphic Impurity in Celecoxib with Powder X-Ray Diffraction Technique
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Sample Preparation Method
2.2. Characterization of CEB Polymorphs
2.3. Preparation of Calibration Curve
2.4. Validation of Analytical Method
2.4.1. Accuracy
2.4.2. LOD and LOQ
2.4.3. Precision
2.5. Estimation of Assay Error
3. Results and Discussion
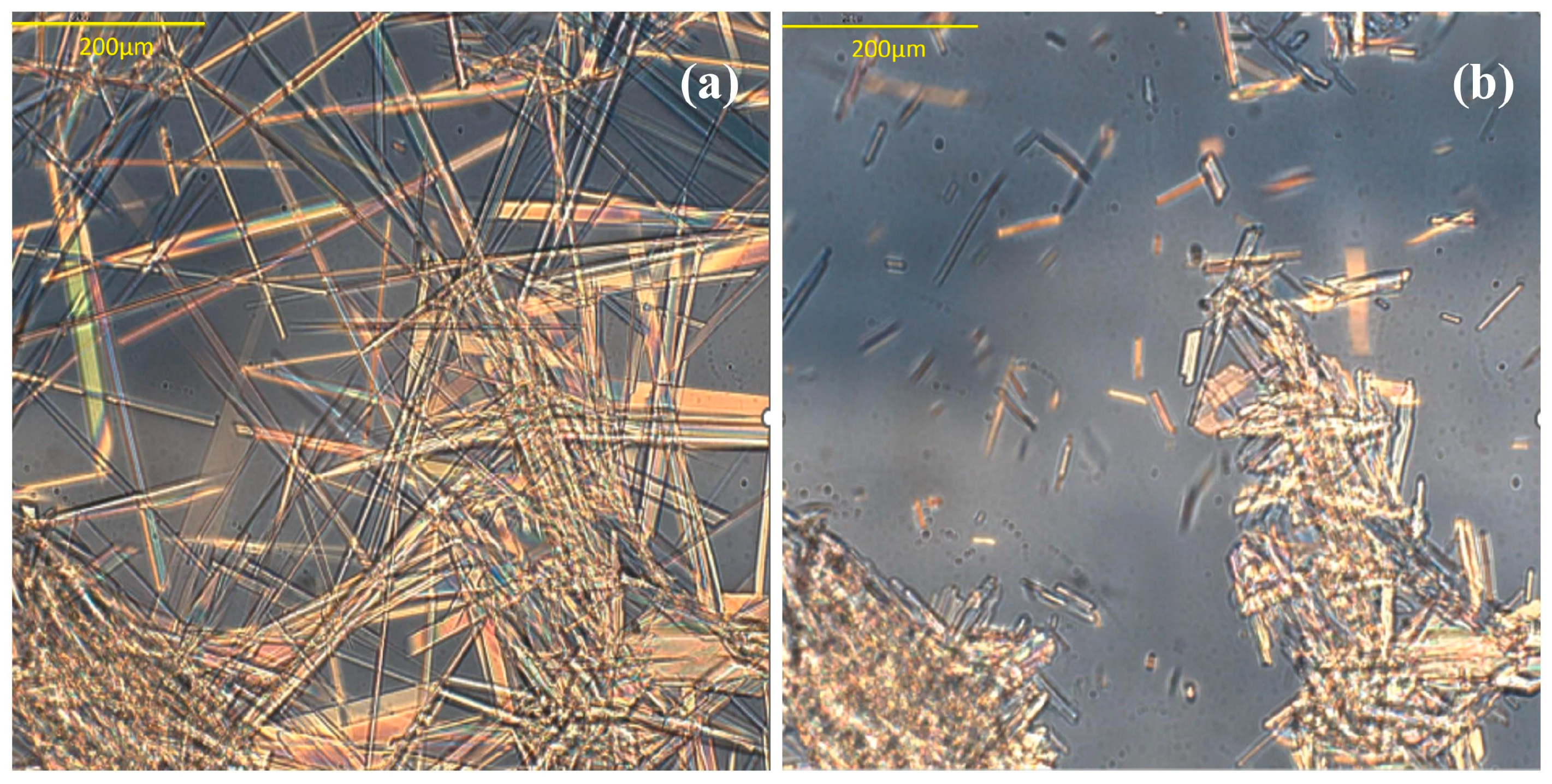
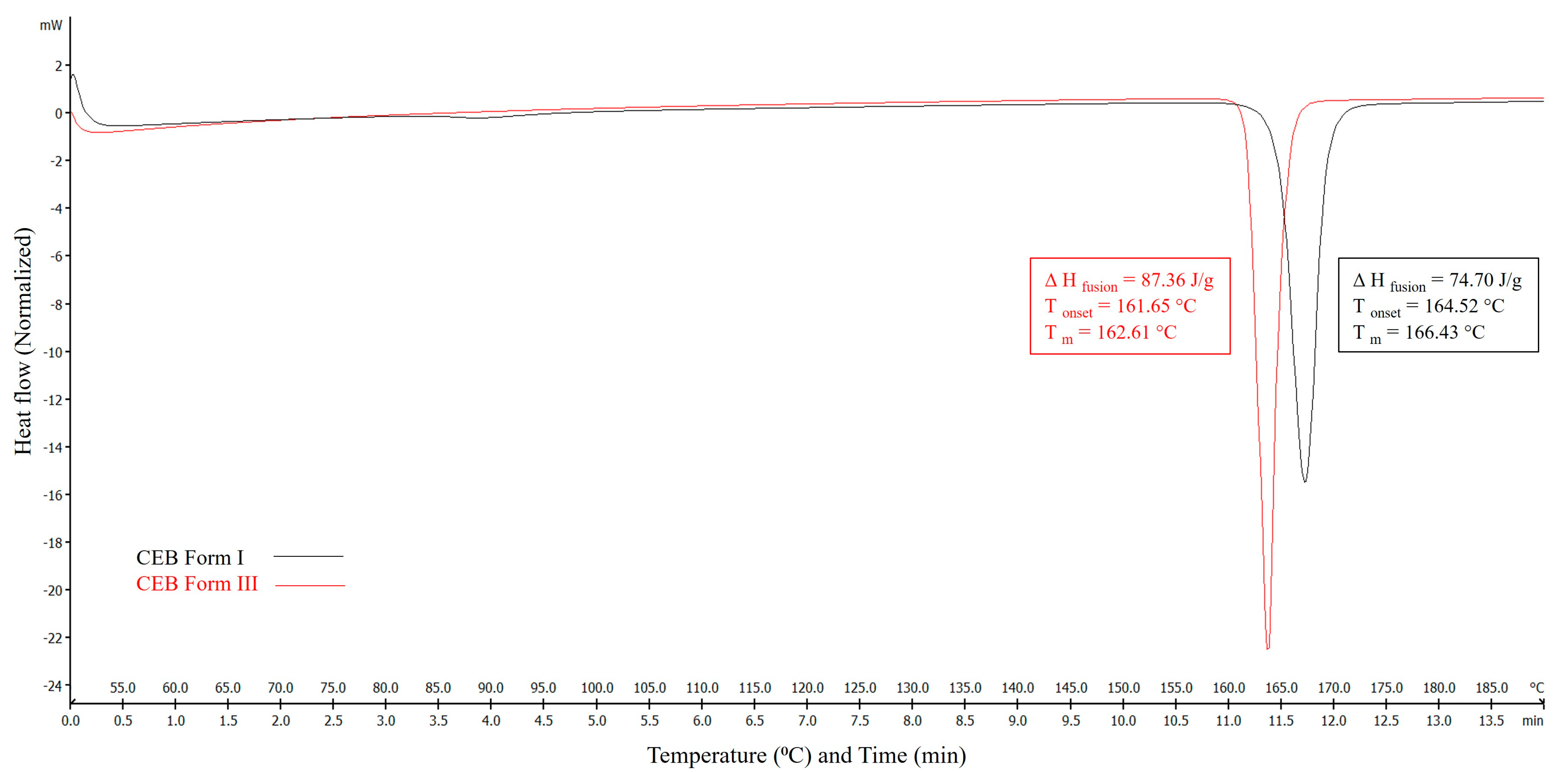
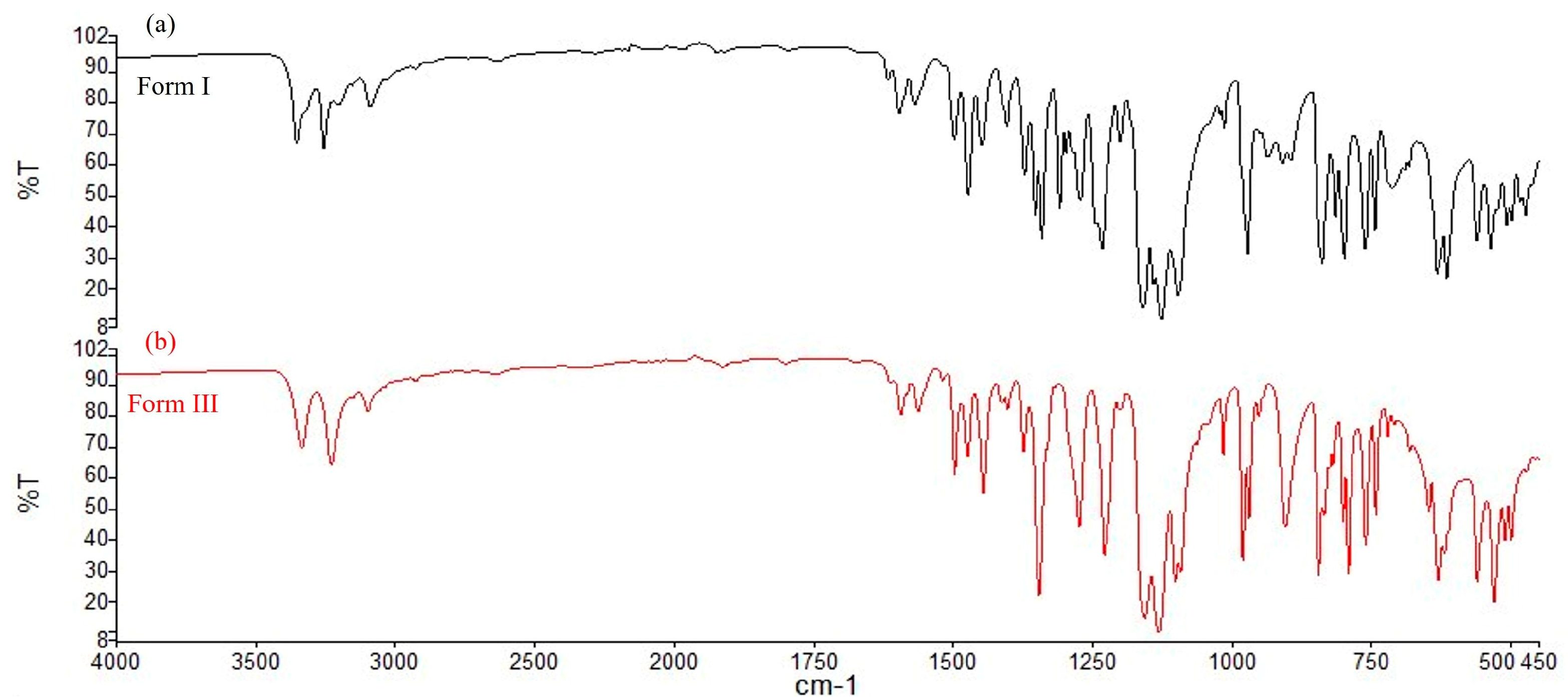
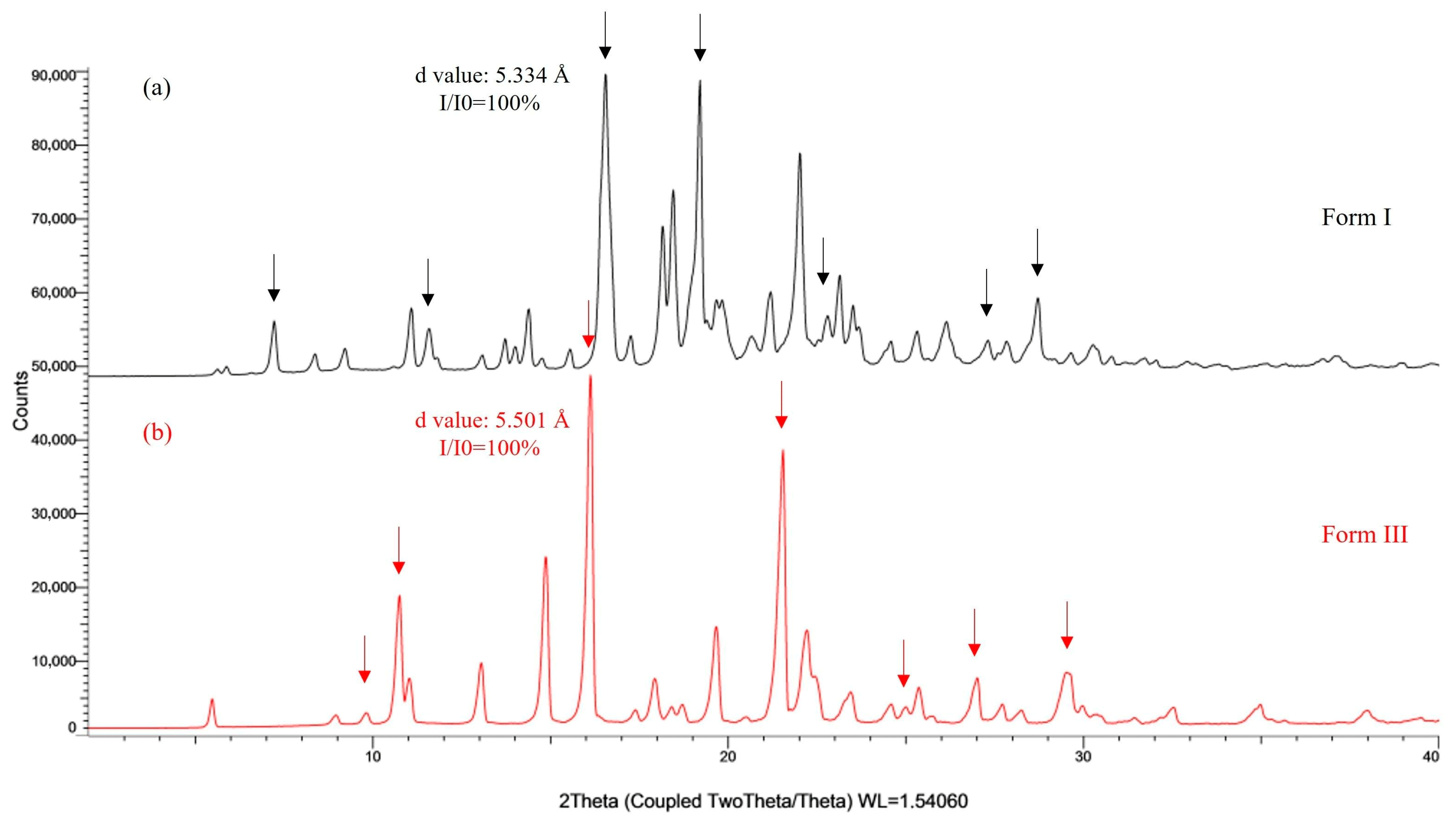
3.1. CEB Polymorphs Characterization
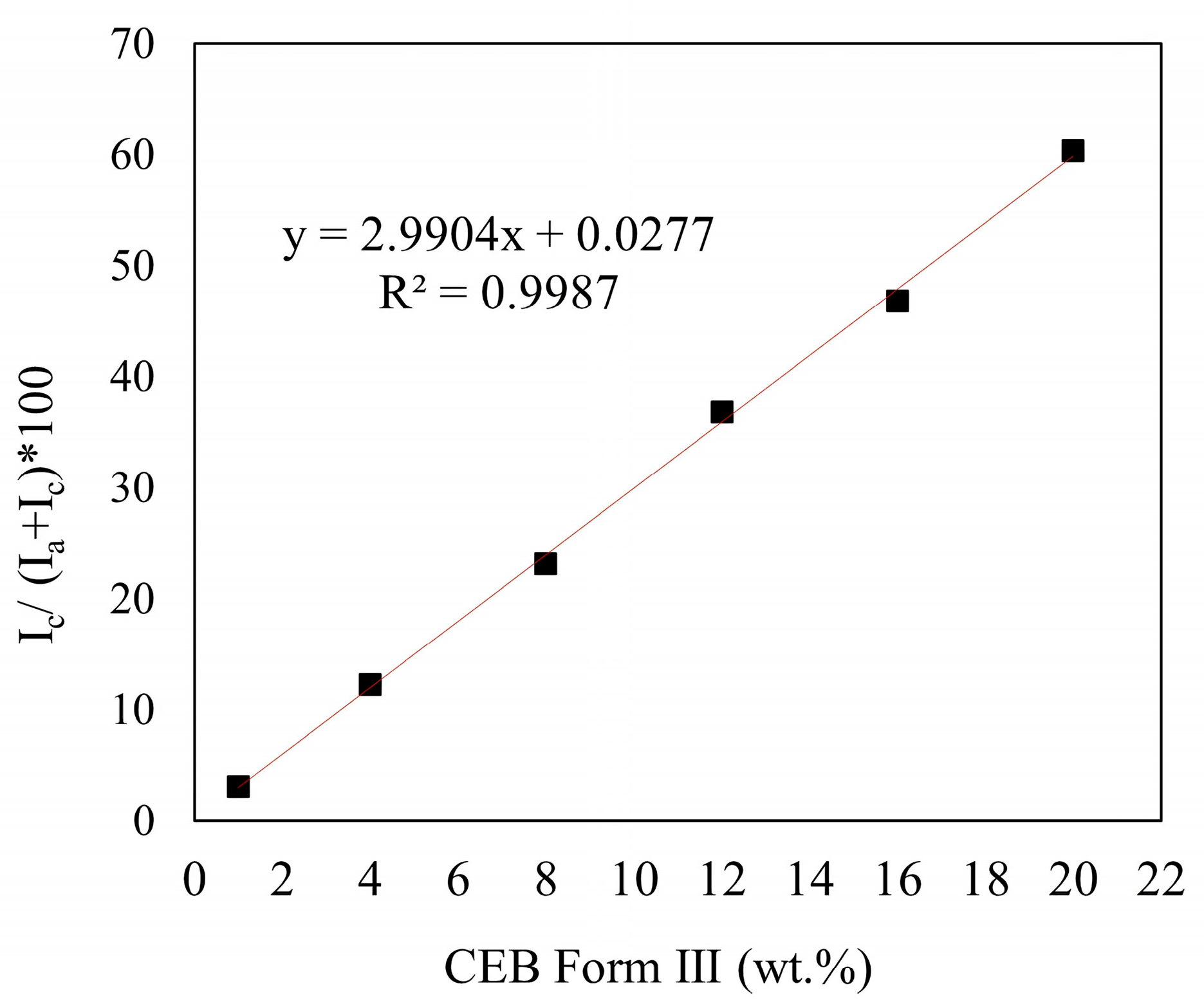
3.2. Calibration Curve Construction
3.3. Analytical Method Validation
3.4. Method Robustness: Assay Error Estimation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alleso, M.; van den Berg, F.; Cornett, C.; Jorgensen, F.S.; Halling-Sorensen, B.; de Diego, H.L.; Hovgaard, L.; Aaltonen, J.; Rantanen, J. Solvent diversity in polymorph screening. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 2145–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vippagunta, S.R.; Brittain, H.G.; Grant, D.J.W. Crystalline solids. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haleblian, J.; McCrone, W. Pharmaceutical applications of polymorphism. J. Pharm. Sci. 1969, 58, 911–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, A.; Ramberger, R. On the Polymorphism of Pharmaceuticals and Other Molecular Crystals. I. Mikrochim. Acta 1979, 72, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, A.; Ramberger, R. On the Polymorphism of Pharmaceuticals and Other Molecular Crystals. II. Mikrochim. Acta 1979, 72, 273–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.D. Polymorphism in molecular crystals. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 2009, 13, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruševski, G.; Zbačnik, M.; Kajdžanoska, M.; Ugarkovic, S.; Trimčeski, V.; Kaitner, B.; Jovanovski, G.; Makreski, P. Pholcodine monohydrate: Crystal structure and polymorphism. J. Cryst. Growth 2013, 375, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Láng, P.; Kiss, V.; Ambrus, R.; Farkas, G.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Aigner, Z.; Várkonyi, E. Polymorph screening of an active material. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 84, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Q6A Specifications: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for New Drug Substances and New Drug Products: Chemical Substances. Fed. Register. 2000, 65, 83041–83063. [Google Scholar]
- Gika, H.; Theodoridou, A.; Michopoulos, F.; Theodoridis, G.; Diza, E.; Settas, L.; Nikolaidis, P.; Smith, C.; Wilson, I. Determination of two COX-2 inhibitors in serum and synovial fluid of patients with inflammatory arthritis by ultra performance liquid chromatography–inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy and quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puljak, L.; Marin, A.; Vrdoljak, D.; Markotic, F.; Utrobicic, A.; Tugwell, P. Celecoxib for osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 5, 1465–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemett, D.; Goa, K.L. Celecoxib: A review of its use in osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis and acute pain. Drugs 2000, 59, 957–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, R.; Sohn, Y. Crystal form of celecoxib: Preparation, characterization and dissolution. J. Korean Chem. Soc. 2018, 62, 352–357. [Google Scholar]
- Ferro, L.; Miyake, P. Polymorphic Crystalline Forms of Celecoxib. US7476744B2, 13 January 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Sun, C. Crystal Growth of Celecoxib from Amorphous State: Polymorphism, Growth Mechanism, and Kinetics. Cryst. Growth Des. 2019, 19, 3592–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, X.; Li, X.; Rong, H.; Yu, L.; Lu, M. A general method for cultivating single crystals from melt microdroplets. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 9950–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Brunskill, A.; Schwartz, E.; Sun, S. Celecoxib–Nicotinamide Cocrystal Revisited: Can Entropy Control Cocrystal Formation. Growth Des. 2017, 17, 2836–2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansa, C.; Mercè, R.; Tesson, N.; Farran, J.; Tomàs, J.; Plata-Salamán, C. Co-crystal of Tramadol Hydrochloride–Celecoxib (ctc): A Novel API–API Co-crystal for the Treatment of Pain. Cryst. Growth Des. 2017, 4, 1884–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Wang, C.; Sun, C. Structural Insights into the Distinct Solid-State Properties and Interconversion of Celecoxib N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone Solvates. Cryst. Growth Des. 2021, 1, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonda, A.; Sun, C. Intermolecular interactions and disorder in six isostructural celecoxib solvates. Acta Cryst. 2020, 76, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remenar, J.; Tawa, M.; Peterson, M.; Almarsson, O.; Hickeya, M.; Foxmanc, B. Celecoxib sodium salt: Engineering crystal forms for performance. CrystEngComm 2011, 13, 1081–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, R.; Rabello, M.; Araujo, I.; Fechine, G.; Canedo, E. Melting and crystallization of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate): Effect of heating/cooling rates on phase transformation. Polímeros 2015, 25, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chow, P.S.; Tan, R.B. Quantification of polymorphic impurity in an enantiotropic polymorph system using differential scanning calorimetry, X-ray powder diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 415, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uvarov, V.; Popov, I. Development and metrological characterization of quantitative X-ray diffraction phase analysis for the mixtures of clopidogrel bisulphate polymorphs. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 46, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, F.L.; Carneiro, R.L. Evaluation of analytical tools and multivariate methods for quantification of co-former crystals in ibuprofen-nicotinamide co-crystals. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 89, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chieng, N.; Rehder, S.; Saville, D.; Rades, T.; Aaltonen, J. Quantitative solid-state analysis of three solid forms of ranitidine hydrochloride in ternary mixtures using Raman spectroscopy and X-ray powder diffraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 49, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vickery, R.D.; Nemeth, G.A.; Maurin, M.B. Solid-state carbon NMR characterization of the polymorphs of roxifiban. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 30, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Jurczak, E.; Zielińska-Pisklak, M.; Harwacki, J.; Pisklak, D.M. Comparison of the analytical methods (solid state NMR, FT-IR, PXRD) in the analysis of the solid drug forms with low concentration of an active ingredient-17-β-estradiol case. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, J.; Font, O.; Moreno, N.; Elvira, J.J.; Alvarez, S.; Querol, X. Quantitative Rietveld analysis of the crystalline and amorphous phases in coal. Fuel 2013, 105, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hestnes, K.H.; Sørensen, B.E. Evaluation of quantitative X-ray diffraction for possible use in the quality control of granitic pegmatite in mineral production. Miner. Eng. 2012, 39, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.; Klug, H.P. Basic aspects of X-ray absorption in quantitative diffraction analysis of powder mixtures. Anal. Chem. 1948, 20, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeleszczuk, Ł.; Pisklak, D.M.; Zielińska-Pisklak, M.; Jurczak, E. A new polymorph of 17-β-estradiol and the application of different analytical techniques (ssNMR, PXRD, DSC, and FTIR) for its study. J. Mol. Struct. 2019, 1183, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Stowell, J.G.; Morris, K.R.; Byrn, S.R. Quantitative study of solid-state acid-base reactions between polymorphs of flufenamic acid and magnesium oxide using X-ray powder diffraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 51, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, M.; Chawla, G.; Bansal, A.K. Quantification of olanzapine polymorphs using powder X-ray diffraction technique. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugay, D.E. Characterization of the solid-state spectroscopic techniques. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 48, 43–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clas, S.-D.; Faizer, R.; O’Connor, R.E.; Vadas, E.B. Quantification of crystallinity in blends of lyophilized and crystalline MK-0591 using x-ray powder diffraction. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 1995, 121, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, R.S.; Vail, K.C. Polymorphism of 1,2-dihydro-6-neopentyl-2-oxonicotinic acid: Characterization, interconversion, and quantitation. Pharm. Res. 1987, 4, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padrela, L.; de Azevedo, E.G.; Velaga, S.P. Powder X-ray diffraction method for the quantification of cocrystals in the crystallization mixture. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 2011, 38, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maddileti, D.; Jayabun, S.K.; Nangia, A. Soluble Cocrystals of the Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitor Febuxostat. Cryst. Growth Des. 2013, 13, 3188–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, T. 2-[3-Cyano-4-(2-methylpropoxy)phenyl]-4-methylthiazole-5-carboxylic acid pyridine solvate. Acta Cryst. 2009, 65, o2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.Y.; Qian, J.J.; Gu, J.M.; Tang, G.P.; Hu, X.R. Febuxostat methanol solvate. Acta Cryst. 2011, 67, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takehira, R.; Momose, Y.; Yamamura, S. Quantitative analysis of crystalline pharmaceuticals in tablets by patternfitting procedure using X-ray diffraction pattern. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 398, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.N.C.; Williams, A.C.; Grimsey, I.M.; Booth, S.W. Quantitative analysis of mannitol polymorphs. X-ray powder diffractometry-Exploring preferred orientation effects. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2002, 28, 1149–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, V.J.; Schroeder, P.A.; Styron, R.W. Accurate quantification of quartz and other phases by powder X-ray diffractometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1997, 337, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and methodology Q2(r1), ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline, 4th ed.; International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005; pp. 6–13. Available online: https://database.ich.org/sites/default/files/Q2%28R1%29%20Guideline.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2024).


| Samples | Composition |
|---|---|
| 2% | 2 wt.% Form III + 98 wt.% Form I |
| 4% | 4 wt.% Form III + 96 wt.% Form I |
| 8% | 8 wt.% Form III + 92 wt.% Form I |
| 12% | 12 wt.% Form III + 88 wt.% Form I |
| 16% | 16 wt.% Form III + 84 wt.% Form I |
| 20% | 20 wt.% Form III + 80 wt.% Form I |
| Actual Concentration (%) | Predicted Concentration (%) | Average Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.00 | 3.03 | 101.10 |
| 6.00 | 6.04 | 100.66 |
| 10.00 | 9.85 | 98.5 |
| 14.00 | 13.97 | 99.8 |
| Concentration (%) | Mean Area Ratio ± SD (%) | % RSD |
|---|---|---|
| 8 | 23.09 ± 0.3 | 2.14 |
| 12 | 36.60 ± 0.7 | 1.70 |
| 16 | 48.14 ± 1.1 | 2.59 |
| Parameter | Mean Area Ratio ± SD (%) | % RSD |
|---|---|---|
| Instrument repeatability | 3.05 ± 0.1 | 2.82 |
| Intra-day repeatability | 3.26 ± 0.2 | 2.35 |
| Inter-day repeatability | 3.40 ± 0.2 | 5.01 |
| Sample repeatability | 3.46 ± 0.2 | 3.71 |
| Validation Parameters | Validation Data |
|---|---|
| Average recovery (Method Acuuracy) (%) | 98.0–101.5% |
| Precision (% RSD) | 1.0–3.0% |
| LOD (%) | 0.344 |
| LOQ (%) | 1.043 |
| Instrument repeatability (% RSD) | 2.82 |
| Intra-day repeatability (% RSD) | 2.35 |
| Inter-day repeatability (% RSD) | 5.01 |
| Sample packing (% RSD) | 3.71 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dhadphale, A.G.; Donde, K.J. Quantification of Trace Polymorphic Impurity in Celecoxib with Powder X-Ray Diffraction Technique. J. Pharm. BioTech Ind. 2025, 2, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2020004
Dhadphale AG, Donde KJ. Quantification of Trace Polymorphic Impurity in Celecoxib with Powder X-Ray Diffraction Technique. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry. 2025; 2(2):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2020004
Chicago/Turabian StyleDhadphale, Amita G., and Kamini J. Donde. 2025. "Quantification of Trace Polymorphic Impurity in Celecoxib with Powder X-Ray Diffraction Technique" Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry 2, no. 2: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2020004
APA StyleDhadphale, A. G., & Donde, K. J. (2025). Quantification of Trace Polymorphic Impurity in Celecoxib with Powder X-Ray Diffraction Technique. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry, 2(2), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi2020004






