The Formulation, Preparation, and Evaluation of Celecoxib Nanosuspensions: Nanosizing via High-Pressure Homogenization and Conversion of the Nanosuspensions into Dry Powders by Spray Drying and Freeze Drying
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Solubility Study
2.2.2. Preparation of CEL Nanosuspensions
Nanoprecipitation
High-Pressure Homogenization
2.2.3. Preparation of Dry Powdered CEL Nanoparticles
Spray Drying
Freeze Drying (Lyophilization)
2.2.4. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
2.2.5. Attenuated Total Reflectance Fourier Transform Infrared (ATR-FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.2.6. Powder X-Ray Diffraction (PXRD)
2.2.7. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.2.8. Dissolution Test
Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Solubility Study
| Solvent | Note | Solubility (mg/mL) * | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solvent screening | Water | 0.002 ± 0.001 | |
| Propylene glycol | Low volatility | 36.49 ± 5.934 | |
| IPA | High toxicity | 49.16 ± 6.102 | |
| Ethanol | 92.34 ± 3.889 | ||
| Methanol | High toxicity | 181.45 ± 12.510 | |
| Acetone | High toxicity | 607.05 ± 8.894 | |
| CAN | High toxicity | ||
| Ethyl acetate | 355.91 ± 20.184 | ||
| Polymer screening | PVP K 30 10% w/w | CEL: PVP K 30 w/w ratio = 1:1 | 0.033 ± 0.002 |
| CEL: PVP K 30 w/w ratio = 1:2 | 0.024 ± 0.001 | ||
| CEL: PVP K 30 w/w ratio = 1:3 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | ||
| PVP K 12 10% w/w | CEL: PVP K 12 w/w ratio = 1:1 | 0.031 ± 0.002 | |
| CEL: PVP K 12 w/w ratio = 1:2 | 0.022 ± 0.002 | ||
| CEL: PVP K 12 w/w ratio = 1:3 | 0.014 ± 0.001 | ||
| PVA 10% w/w | CEL: PVA w/w ratio = 1:1 | 0.001 ± 0.001 | |
| CEL: PVA w/w ratio = 1:2 | 0.017 ± 0.001 | ||
| CEL: PVA w/w ratio = 1:3 | 0.036 ± 0.002 | ||
| HPMC 10% w/w | CEL: HPMC w/w ratio = 1:1 | 0.008± 0.002 | |
| CEL: HPMC w/w ratio = 1:2 | 0.003 ± 0.001 | ||
| CEL: HPMC w/w ratio = 1:3 | 0.002 ± 0.001 | ||
| β-cyclodextrin 10% w/w | CEL: β-cyclodextrin w/w ratio = 1:1 | 0.051± 0.002 | |
| CEL: β-cyclodextrin w/w ratio = 1:2 | 0.067 ± 0.003 | ||
| CEL: β-cyclodextrin w/w ratio = 1:3 | 0.104 ± 0.002 |
3.2. CEL Nanosuspensions
3.3. Characterization of Dry CEL Nanoparticles
3.3.1. DSC Study
3.3.2. ATR FTIR Study
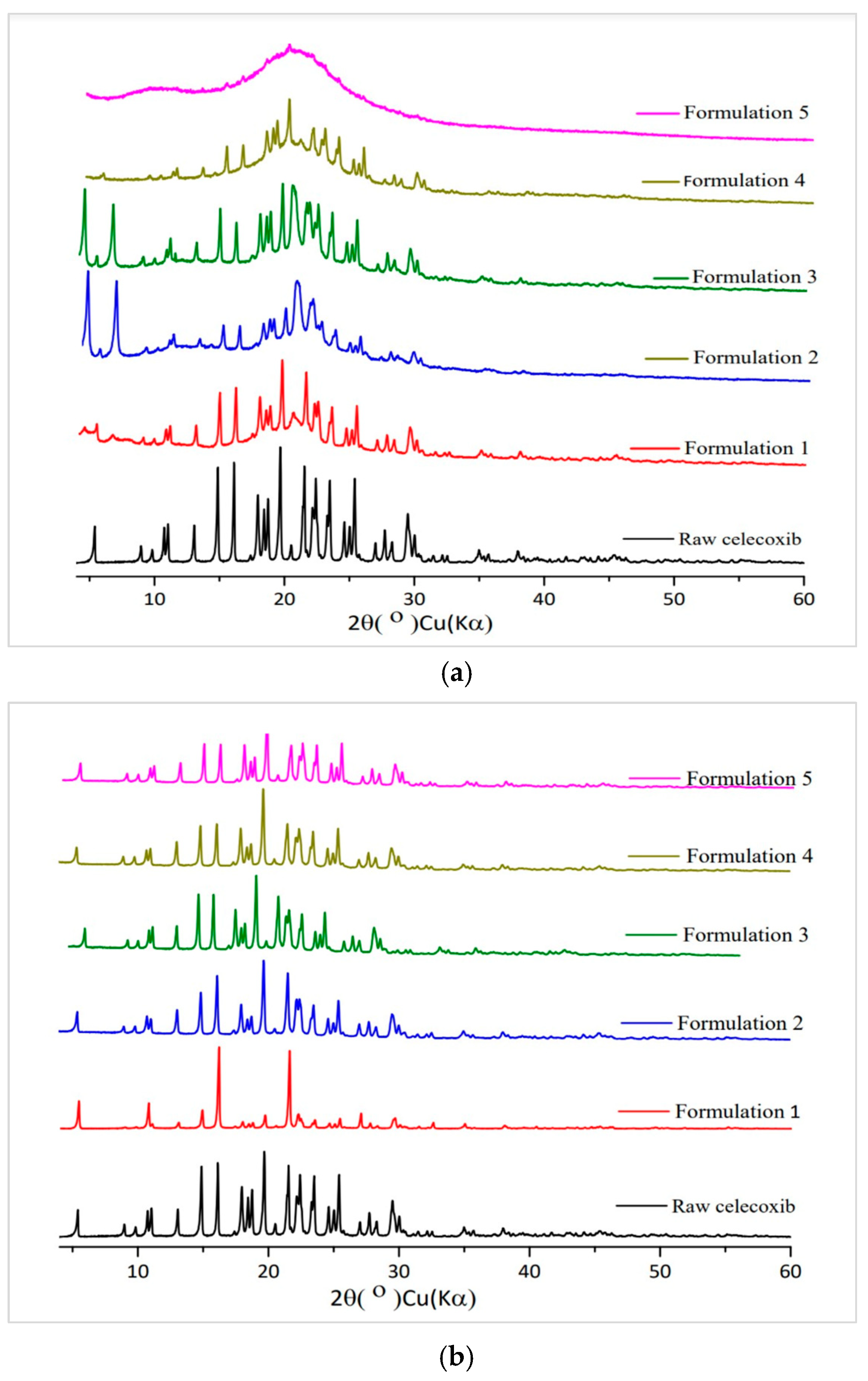
3.3.3. PXRD Study
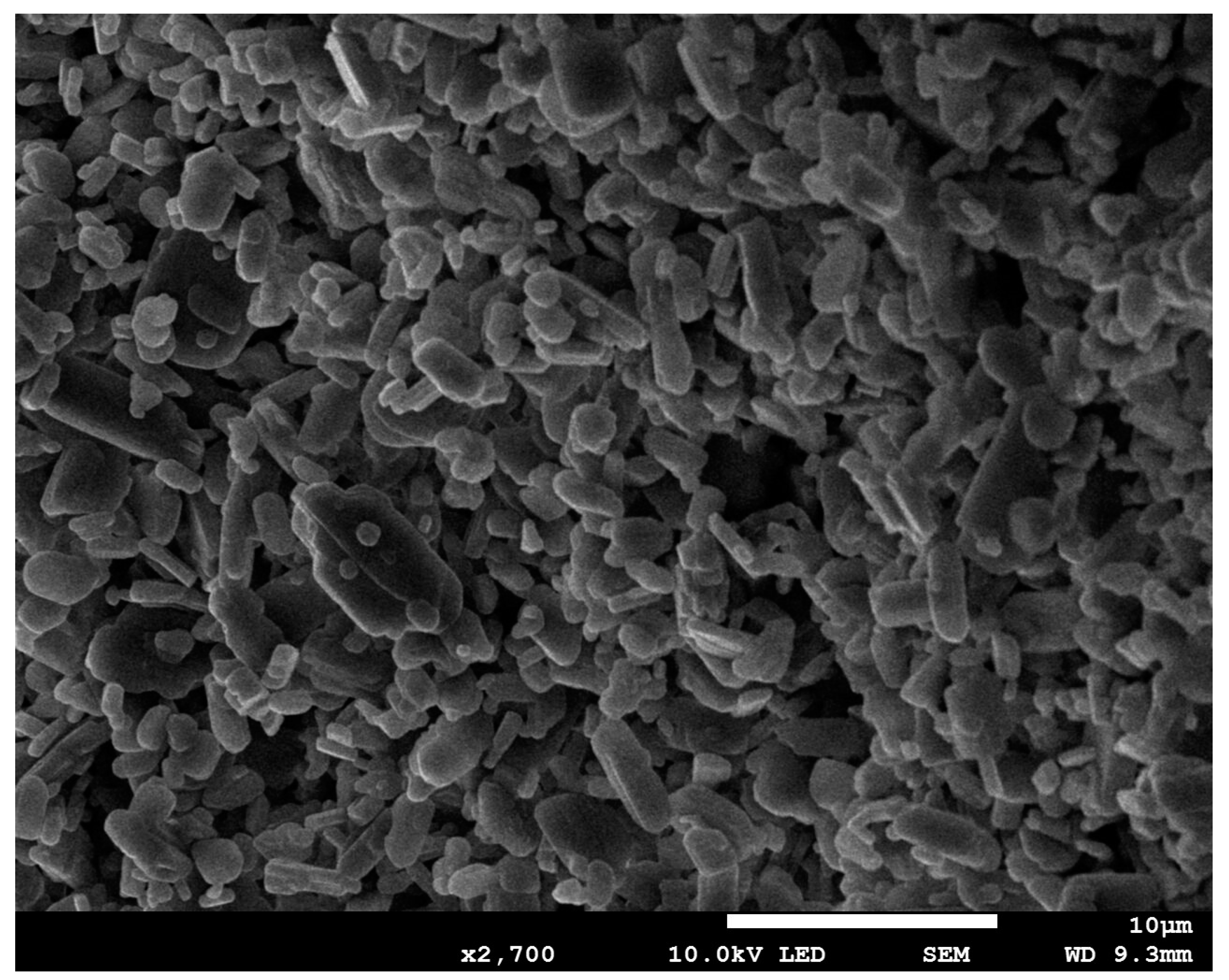
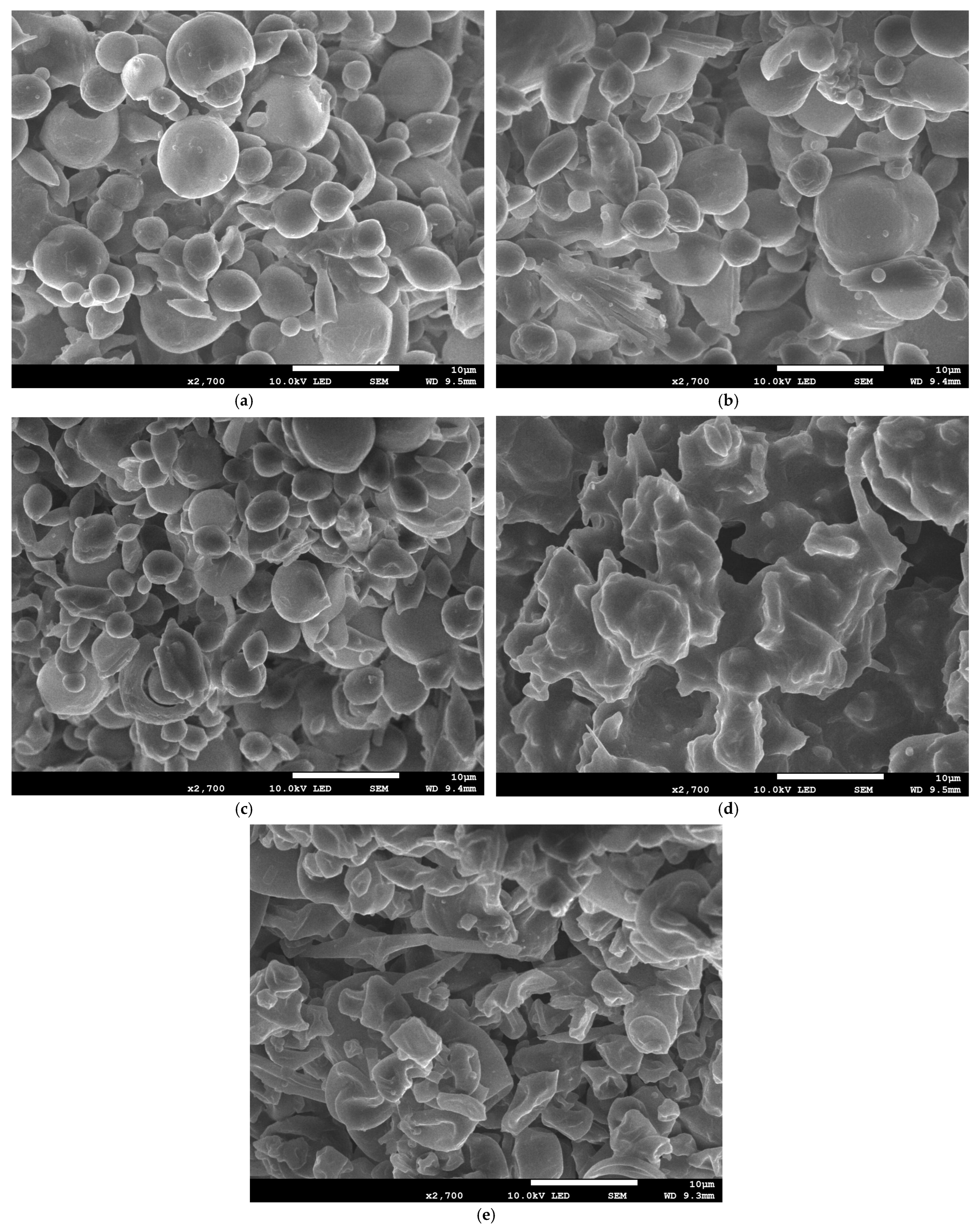
3.3.4. SEM Analysis
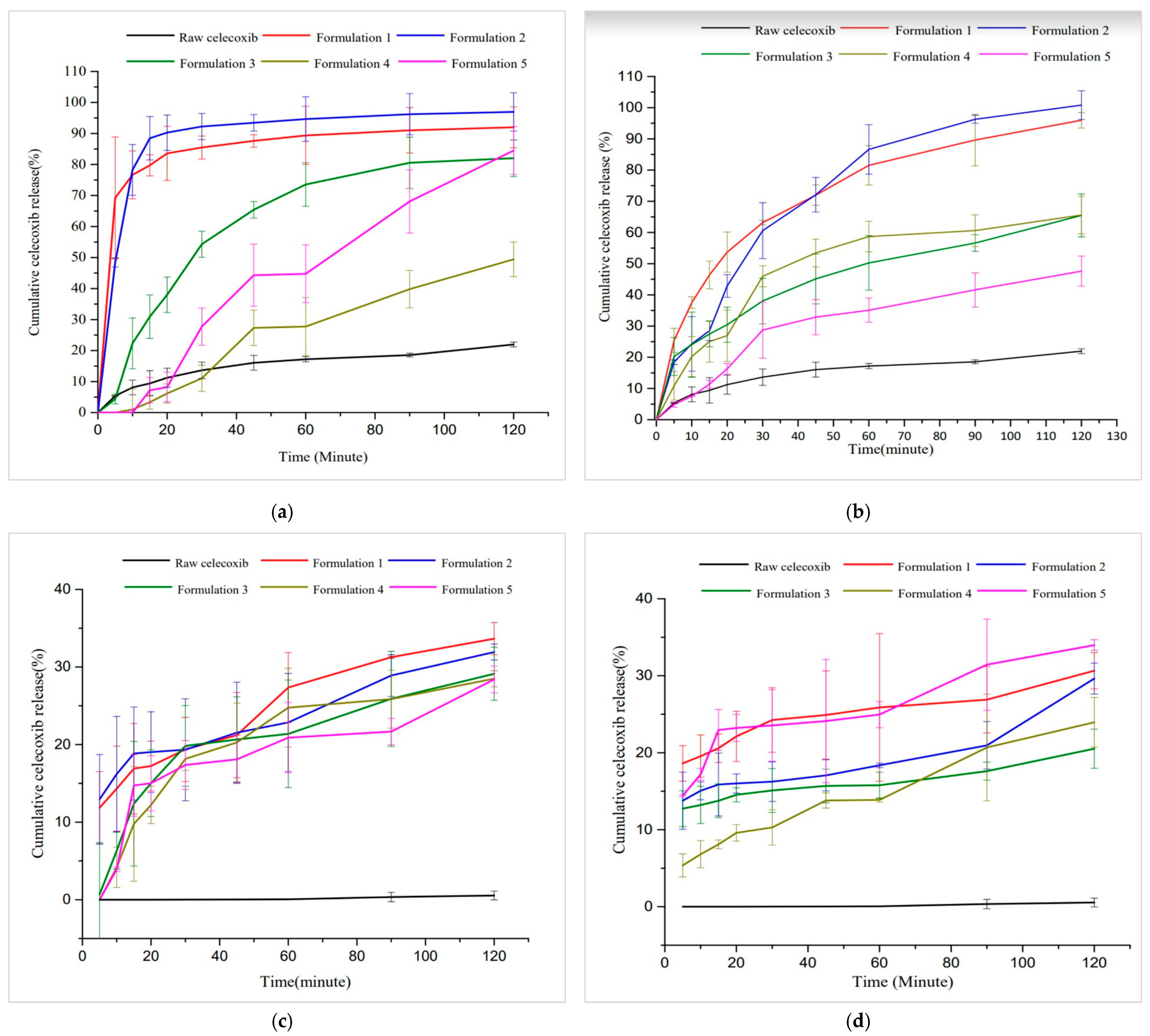
3.3.5. Dissolution Study
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinh, L.; Choi, J.; Machamasi, R.; Lee, J.-J.; Kim, M.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation and characterization of intramuscularly long-acting celecoxib nanosuspensions for postoperative pain management. J. Pharm. Investig. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Thorn, C.F.; Bertagnolli, M.M.; Grosser, T.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Celecoxib pathways: Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2012, 22, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bąk, U.; Krupa, A. Challenges and Opportunities for Celecoxib Repurposing. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 2329–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, S.-M.; Lee, B.J.; Abuzar, S.M.; Lee, S.; Joo, Y.; Hong, S.-H.; Kang, H.; Kwon, K.-A.; Velaga, S.; Hwang, S.-J. Preparation, characterization, and evaluation of celecoxib eutectic mixtures with adipic acid/saccharin for improvement of wettability and dissolution rate. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 554, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.-H.; Dinh, L.; Abuzar, S.M.; Lee, E.S.; Hwang, S.-J. Synthesis of Celecoxib-Eutectic Mixture Particles via Supercritical CO2 Process and Celecoxib Immediate Release Tablet Formulation by Quality by Design Approach. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, A.; Yet, B.; Nemutlu, E.; Akdağ Çaylı, Y.; Eroğlu, H.; Öner, L. Celecoxib Nanoformulations with Enhanced Solubility, Dissolution Rate, and Oral Bioavailability: Experimental Approaches over In Vitro/In Vivo Evaluation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizaj, S.M.; Vazifehasl, Z.; Salatin, S.; Adibkia, K.; Javadzadeh, Y. Nanosizing of drugs: Effect on dissolution rate. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 10, 95–108. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Lee, J.J.; Lee, S.; Dinh, L.; Oh, H.; Abuzar, S.M.; Ahn, J.H.; Hwang, S.J. Preparation of Apixaban Solid Dispersion for the Enhancement of Apixaban Solubility and Permeability. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaji, J.; Lodha, S. Response Surface Methodology for the Optimization of Celecoxib Self-microemulsifying Drug delivery System. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 70, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Dinh, L.; Park, J.; Khraisat, R.; Park, J.W.; Jeong, J.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, M.S.; Ahn, J.H.; et al. Preparation and characterization of lysozyme loaded liposomal dry powder inhalation using non-ionic surfactants. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 646, 123426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.; Cha, K.H.; Cho, W.; Park, J.; Park, H.J.; Sun, B.K.; Hyun, S.M.; Hwang, S.J. Cyclosporine Amicellar delivery system for dry eyes. Int. J. Nanomed. 2016, 11, 2921–2933. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Yuhong, J.; Xin, P.; Han, J.L.; Du, Y.; Yu, X.; Zhu, R.; Zhang, M.; Chen, W.; et al. Advances in Nanotechnology for Enhancing the Solubility and Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 1469–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.Y.; Wang, W. Application of Antisolvent Precipitation Method for Formulating Excipient-Free Nanoparticles of Psychotropic Drugs. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaubal, M.V.; Popescu, C. Conversion of nanosuspensions into dry powders by spray drying: A case study. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2302–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudie, D.M.; Amidon, G.L.; Amidon, G.E. Physiological parameters for oral delivery and in vitro testing. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 1388–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luner, P.E.; Vander Kamp, D. Wetting behavior of bile salt-lipid dispersions and dissolution media patterned after intestinal fluids. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 348–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.; Cho, J.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, E.K.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.; Lee, J. Enhancement of Aqueous Solubility and Dissolution of Celecoxib through Phosphatidylcholine-Based Dispersion Systems Solidified with Adsorbent Carriers. Pharmaceutics 2018, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, H.; Gong, Y. Effects of ethyl acetate extract of Salsola collina on brain-gut peptides and interstitial cells of gastric Cajal in rats with diabetic gastroparesis. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 1218–1224. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, R.J.; Dayal, P.; Singh, M. Effect of cyclodextrins on the complexation and nasal permeation of melatonin. Drug Deliv. 2008, 15, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurakula, M.; Rao, G.S.N.K. Pharmaceutical assessment of polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP): As excipient from conventional to controlled delivery systems with a spotlight on COVID-19 inhibition. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 60, 102046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Stocker, M.W.; Zarrella, S.; Korter, T.M.; Singh, A.; Healy, A.M. In Situ Cocrystallization via Spray Drying with Polymer as a Strategy to Prevent Cocrystal Dissociation. Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 4770–4785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñón-Balderrama, C.I.; Leyva-Porras, C.; Terán-Figueroa, Y.; Espinosa-Solís, V.; Álvarez-Salas, C.; Saavedra-Leos, M.Z. Encapsulation of Active Ingredients in Food Industry by Spray-Drying and Nano Spray-Drying Technologies. Processes 2020, 8, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, G.G.; Figueiredo, S.; Fernandes, A.I.; Pinto, J.F. Polymer Selection for Hot-Melt Extrusion Coupled to Fused Deposition Modelling in Pharmaceutics. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| CEL Suspensions | Particle Size (µm) * | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Antisolvent | |||||||
| Stabilizer | Surfactant | |||||||
| CEL (mg) | PVP K 30 (mg) | PVP K 12 (mg) | PVA (mg) | HPMC (mg) | β-Cyclodextrin (mg) | SLS (mg) | Tween 80 (mg) | |
| 20 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 55.93 ± 2.98 |
| 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 19.96 ± 14.46 |
| 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | 20.28 ± 2.08 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 22.51 ± 3.21 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | 25.56 ± 4.44 |
| 20 | 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | 5.64 ± 3.00 |
| 20 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 20 | 8.51 ± 1.50 |
| 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 20 | - | 12.05 ± 1.16 |
| 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | 10.92 ± 3.49 |
| 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | 20 | - | 37.46 ± 4.46 |
| 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 20 | 19.43 ± 6.05 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 20 | - | 20 | - | 6.69 ± 4.31 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | 20 | 9.24 ± 1.24 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | 20 | - | 2.05 ± 0.91 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | 20 | 28.15 ± 2.15 |
| 20 | 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | - | 7.15 ± 2.59 |
| 20 | 20 | - | - | - | - | - | 40 | 6.13 ± 0.42 |
| 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | 40 | - | 8.38 ± 1.96 |
| 20 | - | 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | 17.71 ± 1.07 |
| 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | 40 | - | 35.13 ± 15.16 |
| 20 | - | - | 20 | - | - | - | 40 | 3.95 ± 1.68 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 20 | - | 40 | - | 13.05 ± 4.97 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 20 | - | - | 40 | 22.52 ± 2.90 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | 40 | - | 5.23 ± 3.05 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | 40 | 5.72 ± 0.91 |
| 20 | 40 | - | - | - | - | 40 | - | 8.43 ± 4.15 |
| 20 | 40 | - | - | - | - | - | 40 | 6.83 ± 2.73 |
| 20 | - | 40 | - | - | - | 40 | - | 4.21 ± 1.81 |
| 20 | - | 40 | - | - | - | - | 40 | 15.45 ± 6.33 |
| 20 | - | - | 40 | - | - | 40 | - | 7.96 ± 1.24 |
| 20 | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | 40 | 10.79 ± 6.58 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 40 | - | 40 | - | 12.21 ± 5.48 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 40 | - | - | 40 | 4.57 ± 4.00 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | 40 | - | 5.06 ± 4.34 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | - | 40 | 17.63 ± 2.60 |
| 20 | 40 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | 71.73 ± 6.12 |
| 20 | 40 | - | - | - | - | - | 20 | 30.86 ± 4.14 |
| 20 | - | 40 | - | - | - | 20 | - | 14.34 ± 8.52 |
| 20 | - | 40 | - | - | - | - | 20 | 6.97 ± 1.15 |
| 20 | - | - | 40 | - | - | 20 | - | 23.01 ± 2.52 |
| 20 | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | 20 | 13.61 ± 1.18 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 40 | - | 20 | - | 7.55 ± 3.11 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 40 | - | - | 20 | 6.67 ± 2.63 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | 20 | - | 5.68 ± 2.56 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | - | 20 | 30.8 ± 3.35 |
| 20 | 40 | - | - | - | - | - | - | 53.78 ± 4.29 |
| 20 | - | 40 | - | - | - | - | - | 12.75 ± 1.64 |
| 20 | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | - | 14.02 ± 11.75 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 40 | - | - | - | 15.87 ± 1.98 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 40 | - | - | 22.95 ± 11.96 |
| 20 | 80 | - | - | - | - | - | 19.58 ± 7.49 | |
| 20 | - | 80 | - | - | - | - | 17.87 ± 2.28 | |
| 20 | - | - | 80 | - | - | - | 11.62 ± 1.50 | |
| 20 | - | - | - | 80 | - | - | 16.83 ± 1.50 | |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 80 | - | 7.94 ± 4.43 | |
| 20 | 80 | - | - | - | - | 20 | - | 29.56 ± 3.10 |
| 20 | 80 | - | - | - | - | - | 20 | 12.54 ± 8.61 |
| 20 | - | 80 | - | - | - | 20 | - | 5.13 ± 0.91 |
| 20 | - | 80 | - | - | - | - | 20 | 7.23 ± 1.01 |
| 20 | - | - | 80 | - | - | 20 | - | 13.01 ± 0.73 |
| 20 | - | - | 80 | - | - | - | 20 | 5.58 ± 2.19 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 80 | - | 20 | - | 31.76 ± 4.08 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 80 | - | - | 20 | 6.56 ± 1.68 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 80 | 20 | - | 4.5 ± 1.29 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 80 | - | 20 | 35.94 ± 2.91 |
| 20 | 80 | - | - | - | - | 40 | - | 10.89 ± 4.75 |
| 20 | 80 | - | - | - | - | - | 40 | 6.64 ± 0.57 |
| 20 | - | 80 | - | - | - | 40 | - | 4.21 ± 1.81 |
| 20 | - | 80 | - | - | - | - | 40 | 15.45 ± 6.33 |
| 20 | - | - | 80 | - | - | 40 | - | 12.15 ± 3.05 |
| 20 | - | - | 80 | - | - | - | 40 | 18.65 ± 11.12 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 80 | - | 40 | - | 8.72 ± 6.97 |
| 20 | - | - | - | 80 | - | - | 40 | 3.30 ± 1.24 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 80 | 40 | - | 22.87 ± 2.03 |
| 20 | - | - | - | - | 80 | - | 40 | 6.07 ± 1.83 |
| Formulation | w/w Ratio | Particle Size (nm) * | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stabilizer | Surfactant | ||||
| No. | CEL | ||||
| 1 | β-cyclodextrin | SLS | 1:1:1 | 747.3 ± 21.09 | |
| 2 | PVP K 12 | SLS | 1:3:2 | 705.2 ± 28.52 | |
| 3 | PVP K 30 | SLS | 1:1:1 | 889.6 ± 55.64 | |
| 4 | PVA | Tween 80 | 1:2:1 | 863.0 ± 41.79 | |
| 5 | HPMC | Tween 80 | 1:3:2 | 960.9 ± 22.51 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machamasi, R.; Hwang, S.-J.; Dinh, L. The Formulation, Preparation, and Evaluation of Celecoxib Nanosuspensions: Nanosizing via High-Pressure Homogenization and Conversion of the Nanosuspensions into Dry Powders by Spray Drying and Freeze Drying. J. Pharm. BioTech Ind. 2024, 1, 20-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010004
Machamasi R, Hwang S-J, Dinh L. The Formulation, Preparation, and Evaluation of Celecoxib Nanosuspensions: Nanosizing via High-Pressure Homogenization and Conversion of the Nanosuspensions into Dry Powders by Spray Drying and Freeze Drying. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry. 2024; 1(1):20-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachamasi, Rukesh, Sung-Joo Hwang, and Linh Dinh. 2024. "The Formulation, Preparation, and Evaluation of Celecoxib Nanosuspensions: Nanosizing via High-Pressure Homogenization and Conversion of the Nanosuspensions into Dry Powders by Spray Drying and Freeze Drying" Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry 1, no. 1: 20-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010004
APA StyleMachamasi, R., Hwang, S.-J., & Dinh, L. (2024). The Formulation, Preparation, and Evaluation of Celecoxib Nanosuspensions: Nanosizing via High-Pressure Homogenization and Conversion of the Nanosuspensions into Dry Powders by Spray Drying and Freeze Drying. Journal of Pharmaceutical and BioTech Industry, 1(1), 20-37. https://doi.org/10.3390/jpbi1010004








