Abstract
Educational learning spaces encompass a spectrum, from traditional classrooms to contemporary online platforms and immersive virtual reality settings, fostering versatile teaching methods like collaboration, project-based, and experiential learning. Our study delves into modern higher education environments, particularly the shift from conventional to innovative spaces. Our focus centers on the benefits and challenges intrinsic to these emerging learning spaces, intending to enlighten educators, policymakers, and researchers. Our exploration commences by revealing the limitations entrenched within traditional learning environments, emphasizing the vital need for inventive solutions to meet evolving educational demands. We further investigate diverse learning scenarios, ranging from hybrid and remote setups to the integration of online platforms and virtual tools. Through this lens we navigate complexities introduced by these novel modalities, including potential reductions in face-to-face interactions and heightened demand for adept instructional and technological support. Lastly, our inquiry underscores the disparities between traditional and contemporary learning spaces, accentuating the potential for innovative settings to elevate higher education quality. Here, we illuminate the anticipated merits of such spaces, notably heightened student engagement, enriched collaboration, and amplified creativity. Concurrently, we explore technology’s pivotal role in shaping learning environments and ultimately influencing pedagogical methodologies. Our future research will explore how Artificial Intelligence can improve higher education.
1. Introduction
Contemporary higher education utilizes diverse learning spaces such as traditional classrooms, online platforms, and virtual reality settings. These spaces enable various teaching and learning approaches, including collaboration, projects, and experiential learning. Physical spaces such as flexible classrooms, technology-rich environments, and outdoor areas, along with virtual spaces including online forums and video conferencing platforms, support different learning styles [1].
The design and utilization of educational learning environments may have a substantial influence on student engagement and motivation [2]. Technology has the potential to enhance the quality of education. It has the benefit of creating a more personalized and flexible learning experience adjusted to each student’s needs. The adoption of learning platforms can enhance communication and create a more interactive experience for students. The above issues have attracted researchers’ attention, and numerous research papers have been published regarding learning spaces in higher education [1].
1.1. Background of Learning Spaces in Higher Education
P. Temple and Fillippakou, in [3], examined learning space design in higher education to accommodate evolving pedagogical practices in a diverse mass education system. They identified the relevant literature and suggested considering designs from other sectors and various countries to inform future criteria for design. Their study aimed to inform policy, practice, and further empirical research on learning space design.
Temple’s work [4] explores the impact of space design on teaching, learning, and research in higher education. His literature review covers various perspectives, including campus design, community development, specialized space requirements, and the influence of technology on space utilization. The review underscores the importance of space considerations in higher education and highlights the need for further research on their relevance with institutional effectiveness.
Furthermore, Ward et al. [5] established a practical framework for knowledge transfer interventions, identifying five components and three types of information transmission processes through case studies. This framework underscores the interconnected nature of these components, promoting repeated and simultaneous occurrences throughout the knowledge transfer process. These components, encompassing problem identification, knowledge/research development and selection, analysis of context, knowledge transfer activities or interventions, and knowledge/research utilization, collectively guide effective knowledge dissemination. This framework’s alignment with the intricacies of learning spaces in higher education reveals a complex synergy where pedagogical, contextual, and outcome-focused elements converge. This correlation underscores the multifaceted essence of educational design and implementation, emphasizing the shared quest for proficient knowledge dissemination and enhanced learning encounters.
Following an alternative approach, Finkelstein et al. [6] proposed a teaching and learning space design approach based on research-informed pedagogical principles. This approach, implemented at McGill University, translates these principles into classroom design features, promoting a cohesive and effective learning environment. The practical and conceptual impacts of implementing these principles have positively influenced the campus.
Byers et al. [7] conducted a systematic review on the impact of learning environments on student learning outcomes in primary and secondary schooling. Their review identified a focus on literacy and numeracy domains in assessments, with limited evaluation of spatial layout impacts on 21st century learning domains. Nevertheless, the study found a positive correlation between learning environments and improved academic achievement. According to the authors, further longitudinal evaluation is needed to understand the broader effects on student outcomes. While Byers et al.’s [7] research may be rooted in primary and secondary education, its findings and implications are inherently relevant to higher education. The positive correlation between learning environments and academic achievement and the call for longitudinal exploration align with the aspirations of enhancing the educational experience across all levels of learning, including higher education.
During and after the COVID-19 crisis, existential questions have arisen throughout higher education. Eringfeld [8] examines the utopian and dystopian imaginaries that have emerged in response to the COVID-19 crisis in higher education. Through a podcast series and research interviews at Cambridge University, the study reveals significant concerns among students and academics regarding the shift to online learning. The loss of embodied and communal educational experiences is a common fear, emphasizing the importance of maintaining face-to-face interactions and a sense of community in higher education.
The pandemic has highlighted the advantages of online education in terms of accessibility and participation. Eringfeld [8] proposes a hybrid approach to post-pandemic education that combines virtual and face-to-face teaching, addressing diverse student needs while maintaining a sense of embodiment and community. It is essential to consider the aspirations and concerns of students and academics in shaping the future of higher education.
1.2. Importance of Investigating Learning Spaces and Technologies
Researchers are studying the design and use of spaces in higher education, focusing on teaching, learning, and research outcomes. Literature highlights various factors for evaluating higher education spaces, including campus design, university community support, specialty space requirements, and the impact of technology on space utilization. Empirical evidence indicates that different learning environments can greatly influence student learning outcomes [1,9,10]. However, further research is required to explore how specific spatial layouts relate to 21st century learning domains, including creativity, critical thinking, communication, collaboration, and problem-solving.
Further research is needed to explore the design and utilization of learning environments that effectively support emerging pedagogies such as project-based and collaborative learning. It is crucial to improve and evaluate existing knowledge transfer frameworks and identify effective ways to assess the impact of different learning environment types on student academic achievement. Learning space design in higher education can be informed by examining designs from other educational sectors [11]. Ultimately, these findings have the potential to shape the future design and use of learning spaces, supporting diverse students in a large-scale higher education system.
This research endeavor is distinctly aimed at providing an exhaustive review of cutting-edge learning spaces prevalent within the educational milieu. This paper navigates the intricate interplay between the opportunities and challenges posed by emerging learning spaces and technological innovations in higher education.
The initial section of the paper meticulously dissects the paradigms governing traditional learning spaces while concurrently unearthing the underlying drivers propelling the surging interest in contemporary learning environments. It undertakes a thorough analysis of the foundational shifts from conventional setups to dynamic modern alternatives.
The subsequent segment undertakes an in-depth exploration of the constraints and limitations enveloping learning spaces, encompassing a spectrum ranging from traditional to hybrid and remote learning spheres. By meticulously navigating these constraints, the paper facilitates a nuanced comprehension of the evolving landscape of education.
The paper concludes with a nuanced discussion, elucidating how the synergy between conventional and innovative learning spaces actively contributes to the advancement of higher education quality. This culminating section accentuates the transformative potential inherent in these spaces, thereby shaping the trajectory of higher education.
This research study aligns seamlessly with the exigencies articulated by prior research. It responds directly to the imperative for an exhaustive exploration of the prospects and challenges introduced by modern learning spaces and technologies. Prior research underscores the transformative potential of innovative pedagogical environments while underscoring the need for a comprehensive comprehension of accompanying complexities.
In response to these identified requisites, our study assumes a distinctive role within the academic landscape. By meticulously dissecting both advantages and obstacles intrinsic to modern learning spaces, we bridge the gap between theoretical discourse and pragmatic application. Our study acknowledges the imperative of not merely envisioning the potential of these spaces, but also critically assessing their constraints to engender a comprehensive and enriching learning journey.
2. Research Methodology
In this study, a narrative review was conducted to investigate cutting-edge learning environments in higher education [12]. The review allowed for a comprehensive mapping of the existing literature on learning space design and its influence on student engagement and learning outcomes. By identifying key concepts and topics, the goal was to gain a broad understanding of the research landscape and highlight the most relevant aspects in the field.
The review centered on six primary topics of paramount significance within higher education. These encompassed the impact of physical learning spaces, the efficacy of diverse learning space designs, the role of technology, classroom layout and seating arrangements, virtual and augmented reality, and online learning platforms. Additionally, the exploration extended to include critical themes such as inclusivity, sustainability, and the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on learning spaces. While six central topics were the focus, the review also encompassed these additional key aspects, collectively providing a comprehensive analysis of the multifaceted landscape of contemporary learning environments.
At the core of this narrative literature review are specific research questions (step 1 of Figure 1), serving as precise guides within our exploration of modern learning spaces in higher education. These research questions provide a focused framework for our analysis and delve into distinct facets of our inquiry. For instance, we study how the design of physical learning spaces impacts collaborative learning outcomes in universities. We also investigate the challenges and benefits of online learning platforms in enhancing inclusivity and accessibility in higher education. Additionally, we explore the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the utilization of learning spaces and technology and its implications for future educational practices. We analyze the role of technology in elevating student engagement and collaboration in hybrid learning environments. Finally, we examine the impact of diverse learning space designs on student creativity and critical thinking within project-based learning contexts in universities. Each of these research questions delineates a specific facet of our inquiry, guiding our systematic examination of contemporary learning environments in higher education.
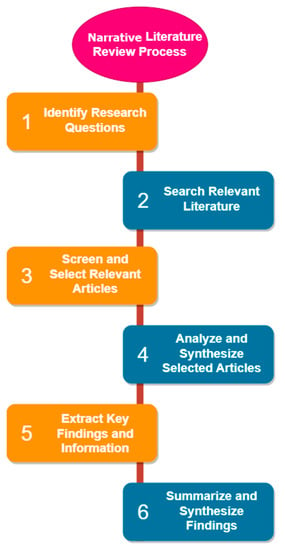
Figure 1.
Narrative Literature Review Process.
To ensure rigor and comprehensiveness, relevant search keywords including Learning Spaces, Higher Education, Interactive Learning, Traditional Learning Spaces, Hybrid Learning, Phycological Learning Factors were defined. Parameters, several databases (including scholarly publications), conference proceedings, and relevant academic websites were searched. To capture the most current developments in the subject, the search was mainly focused on publications published within the last two decades (step 2 of Figure 1). We conducted a comprehensive literature search across multiple databases to identify relevant studies (see Appendix A). The databases searched included PubMed, Google Scholar, PsycINFO, and Scopus.
A final set of research papers was chosen for comprehensive analysis after evaluating the original pool of publications based on their relevance and quality (step 3 of Figure 1). Each work was critically assessed, and pertinent information about the research aim, methods, findings, and implications was retrieved and consolidated.
The analysis and synthesis of findings from the selected research papers revealed several significant discoveries, shedding light on various aspects of learning space design in higher education (step 4 of Figure 1) [13].
In conducting our narrative review, we adhered to specific inclusion and exclusion criteria to ensure the relevance and quality of the studies included in our analysis. First, to maintain the currency of our review and align it with contemporary research, we considered studies published between 2003 and 2022. Second, we prioritized the inclusion of peer-reviewed empirical studies and qualitative research that offered comprehensive insights into the topic under investigation. This selection criterion aimed to provide a solid foundation for our qualitative analysis and synthesis of the literature. Finally, to ensure that the studies we included directly contributed to addressing our key research questions, we carefully assessed their alignment with the primary objectives of our narrative review. By applying these criteria, we aimed to construct a coherent and informative narrative that reflected the most pertinent and insightful contributions of our research topic.
The findings of this narrative literature review provided significant insights into current trends and breakthroughs in higher education learning space design (step 5 of Figure 1). These findings will be used to guide the next sections of this article, in which we will address the potential and problems connected with new forms of learning spaces and technology, as well as how conventional and modern learning spaces might improve the quality of future higher education (step 6 of Figure 1).
3. Growing interest in Modern Learning Spaces in Higher Education
During the medieval period, the concept of a structured learning environment began with the adoption of organized desks in cathedral schools. These desks were arranged in two rows facing each other, resembling the layout used during religious ceremonies. As education evolved, larger and more dedicated spaces were required, leading to the development of spatial patterns in medieval universities [1].
In a time when paper and books were scarce, the primary purpose of lectures was to transmit knowledge directly from the instructor through oral discourse. The term “lecture” emerged from the Latin word “lectus”, which referred to the act of delivering instructional information on a specific subject.
With the advent of the industrial age, the expansion of education from an exclusive domain to a mass phenomenon led to the growth of classrooms. Universities responded to the increasing demand for enrollment by constructing larger and taller buildings. These classrooms were designed with efficiency and production in mind, reflecting the principles of “Scientific Management” that emphasized efficiency in all aspects of [1].
3.1. Need for Creative Alternatives in Education
Classroom design dates to the 1800s, when formal education began to grow and become more accessible to the public. Originally, classrooms were arranged with rows of desks facing a teacher’s desk or blackboard at the front of the room. This design was intended to encourage students’ focus and discipline.
Educational reformers began to advocate for more student-centered learning environments in the early 1900s. This resulted in the introduction of the “open classroom” idea in the 1960s and 1970s, which stressed collaborative learning and flexibility in classroom design. To foster student participation and creativity, open classrooms had adjustable dividers, soft seating, and flexible learning areas.
Weinstein’s [14] analysis of school physical environments emphasizes the critical importance of educational design in providing a suitable learning environment. Classroom and school building design can have a significant impact on student performance and attainment. One critical component is proper illumination, which can influence mood, productivity, and behavior. High-quality acoustics are also essential, as poor acoustics can cause distractions and impede learning. The proper temperature is also important, as severe temperatures can have a negative impact on student performance. Another essential component is air quality, as poor air quality can cause health concerns and diminish student participation. The use of proper colors and furniture design can also help to create a relaxing and cheerful environment, which can improve student mood and learning. Designers can help enhance student progress and achievement by taking these elements into account in educational design.
By the 1980s and 1990s, educational reformers were emphasizing the integration of technology into classroom design. Learning environments were outfitted with projectors, smartboards, and other interactive technologies, as well as computer laboratories and multimedia centers. The “21st century classroom”, which focused on building environments that were flexible to diverse learning styles and accommodated a variety of educational activities, rose to prominence in the early 2000s.
Orr’s research in 1993 [2] underlines the necessity of evaluating not only what is taught in the classroom, but also how the classroom is designed and built. He contends that the physical environment of the classroom can influence learning by influencing how students and teachers interact with one another and with the subject matter being taught. A classroom with fixed seating and desks facing the front of the room, for example, may foster a more hierarchical dynamic between the teacher and students, with the teacher at the center of attention and the students playing a more passive role. A classroom with mobile furniture and areas for small group collaboration, on the other hand, may encourage a more egalitarian approach to learning, with students and teachers cooperating as partners in the learning process. Orr’s concept of the “hidden curriculum” suggests that classroom design can have a significant impact on the values and attitudes that students learn, in addition to the explicit content of the curriculum. By paying attention to the physical environment of the classroom and considering how it may influence the learning experience, educators and designers can create spaces that support and enhance the educational goals of the institution.
3.2. Emerging Learning Spaces and Technologies
Carmean and Haefner [15] examine the role of course management systems (CMS) in establishing successful learning environments. They argue that CMS should be viewed as more than just tools for maintaining and transmitting course content, but as essential components of the learning process. The authors stress the importance of CMS in facilitating communication and collaboration among students, as well as between students and professors. They also emphasize the value of personalization, stating that CMS should be developed to support a variety of learning styles and preferences.
North Carolina State University (NCSU) constructed one of the most notable instances of modern classroom design. SCALE-UP (Student-Centered Active Learning Environment for Undergraduate Programs) was created to establish student-centered, collaborative learning environments that included technology to facilitate active learning [9]. The classrooms are set up with round tables, each with its own computer, and whiteboards around the periphery. Students engage in small groups to complete hands-on activities that encourage critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. The technology facilitates group cooperation by allowing students to share and receive feedback on their work with the class. The SCALE-UP project’s success has led to its acceptance in colleges across the United States and around the world.
Likewise, the TEAL approach (Technology-Enabled Active Learning) is a teaching and learning strategy that integrates technology, active learning methodologies, and collaborative cooperation to improve the educational experience [10]. While TEAL was first established at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) for physics teaching, its ideas and tactics may be applied to a variety of fields in higher education. Some key components of TEAL are Technology Integration, Active Learning, Collaborative Learning and Physical Environment. The benefits of TEAL in higher education are: improved learning outcomes, enhanced student engagement, collaboration and communication skills, adaptability to diverse learners, and preparation for real-world challenges.
The University of Minnesota has built two experimental Active Learning Classrooms (ALC) based on slightly altered versions of the SCALE-UP and TEAL methodologies. Classrooms are intended to promote active, collaborative, and technologically enhanced learning. Round tables with seating for nine students and two teachers are provided in the classes. Tables have whiteboards, power outlets, and network connections. To involve students in active learning, teachers can employ several technological tools such as interactive projectors, document cameras, and wireless microphones. The classrooms are meant to be adaptable and quickly modified to accommodate a variety of activities. According to the survey of Alexander et al. [11], students in ALCs were more engaged in their learning and were more likely to participate in class discussions and activities. Faculty members also reported feeling more connected to their students and were facilitating more engaged learning experiences. However, the report identified some challenges with ALCs, such as technical issues with classroom technology and difficulties managing large groups of students in a more open and collaborative environment. Overall, the study advised the institution to continue investing in ALCs as a means of improving student engagement and learning outcomes, while simultaneously addressing the constraints and limits of this strategy.
Shortly after, McGill University initiated the Teaching and Learning facilities Working Group (TLSWG) project to meet the campus’ demand for new and innovative teaching and learning facilities. In 2009, two active learning classrooms were built as part of this initiative. These classrooms were built with mobile furniture, whiteboards, and projection systems to encourage cooperation, discussion, and group work. The classrooms were also outfitted with technology that enabled simple material exchange and participation in online discussions. With the addition of more active learning classrooms and other creative learning spaces around campus, the TLSWG project has continued to adapt and expand.
In 2010, the University of Iowa launched the Transform, Interact, Learn, and Engage (TILE) initiative, with the goal of creating flexible and technology-rich active learning classrooms. TILE was influenced by the SCALE-UP and TEAL models and was created to give students greater chances for collaborative learning and involvement with course material. The classrooms are outfitted with modular furniture, various screens, and adjustable layouts to accommodate a wide range of teaching and learning activities. The TILE project has received excellent comments from both students and teachers on its influence on student engagement and learning outcomes. Van Horne et al. [16] conducted research at the University of Iowa to evaluate the impact of TILE classrooms. According to the study, students in TILE classrooms exhibited better levels of engagement, interaction, and cooperation than students in conventional classrooms. Students in TILE classrooms also performed better academically, as shown by higher test scores and grades. The authors conclude that TILE classrooms improve teaching and learning in higher education.
As technology advances, video conferencing has become a more common tool in higher education. It allows students and professors to connect in real-time, regardless of location, and has the potential to create more participatory and engaging learning experiences. One of the primary benefits of video conferencing is that it allows for remote learning, which has grown increasingly important in recent years. Students who are unable to attend classes in person can still engage and learn alongside their peers. Furthermore, it can save time and money spent on commuting or traveling, which may inspire more people to seek higher education.
In [17] the author explores the application of videoconferencing technology in education. The article focuses on the “Global Classroom” program, which attempts to improve communication and collaboration among students and instructors from many nations and cultures. The article includes an overview of the technical features of videoconferencing, as well as the pedagogical benefits and problems of employing this technology in the classroom. The author contends that videoconferencing can improve student engagement and learning results by allowing contact and cooperation among students from various backgrounds, and providing access to expert information and resources from across the world.
The use of a Technology Boot Camp to provide professional development for faculty to support active learning environments for students has been discussed by Munger et al. [18]. The Technology Boot Camp was created to meet the demands of academics with varied degrees of technology competence and was implemented at a mid-sized institution in the United States [18]. Hands-on seminars, online tutorials, and individual meetings with instructional designers were all part of the curriculum. A series of seminars and training sessions on leveraging technology to improve teaching and learning were held. Faculty development, according to the authors, is critical for the effective deployment of technology-enhanced active learning settings. According to the authors, the Technology Boot Camp was a success in terms of providing teachers with the skills and knowledge needed to build active learning environments employing technology. They also discovered that the program enhanced teacher cooperation and the usage of technology in the classroom.
Various studies have emphasized the positive impact of hybrid synchronous delivery modes on student learning outcomes and overall experience. One of the most cited benefits is the increased flexibility and sense of freedom, allowing students to participate in real-time discussions and activities regardless of their physical location.
A literature study of mixed synchronous delivery formats in graduate programs was undertaken by Lakhal et al. [19]. They discovered that mixed synchronous learning is growing in popularity, since it combines the benefits of both face-to-face and online learning settings. According to the authors, research on mixed synchronous learning has focused on three areas: technology, pedagogy, and student satisfaction. They concluded that mixed synchronous learning could improve student engagement, learning results, and satisfaction in graduate programs. The authors also presented a case study of how the Université Laval’s Master Teacher Program adopted mixed synchronous learning.
Despite the promising findings regarding increased freedom, social connections, and perceived control in synchronous hybrid learning environments, there is a lack of consistency in the definition and operationalization of synchronous hybrid learning. Raes et al. [20] conducted a systematic literature review on synchronous hybrid learning and identified gaps in current research. They also emphasized the need for more research on the influence of synchronous hybrid learning on student learning outcomes, as well as the instructor’s role in enabling the learning experience. Furthermore, the authors emphasized the necessity for additional study on the usefulness of various technology tools employed in synchronous hybrid learning.
3.3. COVID-19 Era in Higher Education
Eringfeld [8] conducted private research interviews with both students and academics, using podcast conversations as a tool to sonically elicit further reflections on the potential futures of HE in the post-coronial period. The findings from these interviews revealed a tension between utopian hopes and dystopian fears regarding the future of education. Notably, the shift to online learning triggered concerns about the loss of education as an embodied and communal experience. While a fully online university was often portrayed as a dystopian outcome, Eringfeld’s research also highlighted the potential benefits of increased accessibility and participation in HE through certain online educational activities. Ultimately, the study underscored the need for a blended approach to higher education in the post-coronial era, one that adeptly combines virtual and face-to-face teaching to accommodate the diverse needs of students while preserving a sense of embodiment and community in higher education.
3.4. Augmented and Virtual Reality in Higher Education
The COVID-19 epidemic increased interest in hybrid AR/VR (Augmented Reality/Virtual Reality) learning in higher education by underlining the limitations of traditional online learning and emphasizing the need for new and compelling alternatives.
Through smart devices, augmented reality (AR) represents superimposing instructional text and other content onto the real world to give students engaging and interactive learning opportunities. As opposed to this, VR surrounds users in a thorough digital world, giving them a wholly immersive and all-encompassing experience that closely resembles reality. Students may engage with the virtual world as if they were there in a VR environment. Virtual reality in education offers a variety of other advantages in addition to immersive learning opportunities. It could spark students’ imagination and creative juices, encouraging them to pursue novel academic pursuits. Additionally, both AR and VR have shown to be useful tools for aiding students who have trouble understanding difficult academic subjects. For instance, using AR, geometry students may modify forms, spin them to see them from various angles, and even look inside three-dimensional geometric structures. The benefits of virtual reality in education go beyond academics to include the development of cultural competency, which is an essential ability in our globally linked and interconnected world. VR is an effective educational technology that has several advantages for both teachers and students.
Specifically, in [21] the authors present the Cognitive Affective Model of Immersive Learning (CAMIL), with the goal of offering a theoretical framework grounded on research for comprehending learning in immersive settings. Based on earlier empirical work in learning with immersive technology, CAMIL specifies some of the most significant factors that impact an immersive learning experience. Experiential learning is an educational setting in virtual reality. Furthermore, Kwon [22] looked at whether direct interactions with virtual environments and objects, which have grown in popularity recently, could feel more authentic than indirect interactions offered by existing VR systems like gamepads or joysticks. Simulation-Based Training is studied in [23], where the nuclear business has tried to take advantage of the same digital and educational revolution to prepare their staff for risky situations. Researchers conducted a pilot study to assess the VR training scenario created for the target audience and the acceptability of VR technology in general for this type of training.
Another relevant field looks at enhancing understanding by offering students interactive and visual representations through virtual reality (VR) aids, focusing on understanding difficult and abstract ideas. Students may, for instance, study the human body in 3D in biology class, carefully examining the organs and systems. They can envision complex concepts in physics, such as gravitational forces or atomic structures, which makes learning more concrete and natural. Andersson et al. [24] introduced Hamlin, a system for scientific teaching that uses augmented reality (AR) to identify unseen physical forces in the natural world. It gathers and analyzes unprocessed data in 3D space and presents spatial renderings of them. Students may watch the concepts their teacher is discussing in real-time on their cell phones using the Hamlin mobile app. Hamlin offers a variety of methods to see physics data, since it is a visualization tool and not just a sensor box. This article describes the implementation of the prototype for sound visualizations, and how teachers and students may switch between different wave and frequency representations to connect the ideas and enhance student understanding.
In concluding, our analysis shows that numerous factors such as students’ placement in the classroom, classroom color, air quality, temperature, and the availability of technical equipment (e.g., projectors, tablets, laptops) may influence student motivation in learning.
In addition, we highlight the advent of hybrid learning and the presence of augmented and virtual reality in learning spaces, which has grown in prominence throughout the epidemic. Students can engage in classroom activities without physically being present in the classroom. Students who find it difficult to attend classes on campus may benefit from this kind of learning environment. Therefore, the growth of learning spaces and the rise of new learning technologies have altered how students study and connect with their teachers, allowing for greater flexibility and accessibility.
4. Challenges and Limitations in Learning Spaces over the Years
In this section, we will look at the challenges and constraints that learning environments in higher education have encountered over time. The first subsection discusses the issues that traditional educational spaces have faced. It has been observed that student seating is a significant aspect that can contribute to a variety of concerns such as discomfort, a bad mood, and inattention. Furthermore, the second subsection will examine the limits of hybrid and distant learning, such as a lack of personal connection and involvement, difficulties measuring students’ knowledge, and technological concerns that may interrupt the learning process. These constraints were compounded by the COVID-19 epidemic, which forced many universities to quickly move to remote and hybrid learning, highlighting the need for more effective and sustainable online teaching and learning practices.
4.1. Constraints and Challenges of Traditional Learning Spaces
In Figure 2, we illustrate the challenges inherent in traditional learning spaces, as derived from an extensive review of the existing literature. This visual representation succinctly captures the essence of these challenges, categorizing them into eight fundamental domains. These challenges exert their influence not only on students, but also extend their impact to educators and the environment of their interaction. The subsequent section delves into an in-depth analysis of the primary categories delineated within Figure 2.
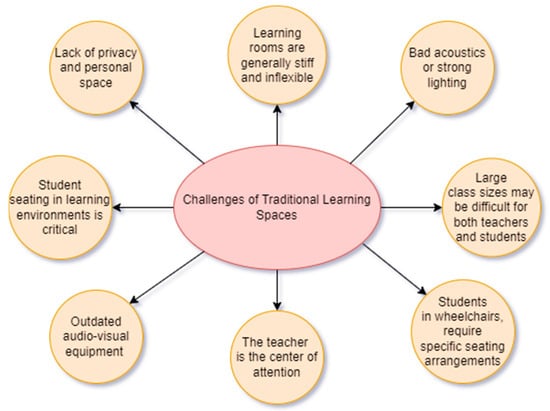
Figure 2.
Challenges of Traditional Learning Spaces.
Students in traditional classes are often expected to listen and take notes while the lecturer teaches. This method of teaching may result in low student engagement and little contact between students and teachers. Students may not be completely interested in the topic and may struggle to apply what they learn in real-life circumstances. Oblinger [25] highlights in his study report that traditional learning rooms are generally stiff and inflexible, with set seating configurations and limited choices for rearrangement. This can limit teachers’ ability to design activities that require diverse seating arrangements or equipment setups. It was also mentioned that traditional learning environments may not be accessible to all students, especially those with impairments or mobility concerns. Students with sensory processing issues may also suffer in surroundings with bad acoustics or strong lighting.
It has become apparent that traditional learning environments may not be intended to support technology as it continues to play an increasingly important role in education. Outdated audio-visual (AV) equipment or insufficient Wi-Fi connectivity may limit or prevent students from engaging in online activities. This may be a significant issue since it limits access to important materials and learning opportunities. Students may be hampered in their capacity to interact with course material and acquire the skills required for success in the contemporary world if they do not have access to digital resources or online activities. Furthermore, technical constraints may have an immediate influence on students’ learning experiences [25]. The inability to fully participate in online activities can lead to a loss of interest and motivation, resulting in a less effective learning experience. Students may be expected to complete coursework or assignments online in some situations, which means that technical constraints could have a direct influence on their grades and general academic performance.
Large class sizes may be difficult for both teachers and students in conventional learning situations. When class numbers are excessively high, classrooms may be unable to accommodate every student. This may lead to a lack of interest and participation among students, because they may be unable to see or hear the instructor well or connect successfully with their peers [25]. Large classrooms can be difficult for teachers to manage, since it can be difficult to monitor and regulate student conduct or offer specialized attention to each student’s needs. It may be difficult in such instances to create a conducive learning atmosphere in which students can grow and succeed.
Another challenge is the lack of privacy and personal space, which can be difficult for certain students. Learners with impairments, for example, or those who require special accommodations may demand private rooms for tasks such as medical procedures or quiet study [25]. These places, however, are frequently lacking in traditional learning environments, making it difficult for these students to fully participate in class or connect with the topic. Furthermore, students who require physical adjustments, such as bigger desks or wheelchair accessibility, may find it difficult to navigate traditional learning rooms that were not constructed with these requirements in consideration. Overall, a lack of privacy and personal space in traditional learning environments can pose substantial challenges for students with special needs, potentially restricting their capacity to succeed in the classroom.
Student seating in learning environments is critical to establishing a healthy learning environment. A badly planned seating arrangement can cause a variety of problems, including pain, lack of engagement, and distraction, all of which can have a detrimental influence on the learning process. For instance, pain caused by poor sitting can induce physical distractions, which can impair a student’s ability to focus on the content being taught. Students may, for example, have back discomfort or a headache, resulting in a lack of attention and potentially a diminished capacity to study. This is especially true for students who must sit in one place for long periods of time. Students may not interact much in classes where students are seated in straight rows facing the teacher, since the attention is mostly on the instructor. Students may be more interested, participate more in conversations, and feel more engaged in the topic being taught if the seating is organized in a way that allows for easy interaction, such as in small groups. If students are seated too far away from the teacher, they may feel awkward asking questions or participating in class discussions [25]. On the other hand, if students are seated too close to the teacher, they may feel intimidated or uncomfortable, leading to a lack of participation. When planning student seating, the needs of students with disabilities or physical limitations should be considered. Students in wheelchairs, for example, may require specific seating arrangements, such as a lower desk or an open area to move around. Failure to accommodate the requirements of all students in chair design can result in exclusion, discomfort, and unfairness.
Park and Choi [1] conducted an analysis of the effect of seating arrangements on students’ learning experiences. They observed that typical classroom seating arrangements were predominantly lecture-style, with rows of desks facing the front of the classroom. This approach frequently resulted in a passive learning environment, with students’ attention focused on the lecturer rather than on each other or the content being taught. Furthermore, students near the rear of the classroom were shown to be less interested and less inclined to participate in class discussions, resulting in a lack of involvement and enthusiasm. In contrast, active learning classrooms frequently use a collaborative learning method, with students seated in groups facing each other to stimulate interaction and conversation. This seating configuration encourages active involvement, group work, and the exchange of ideas. According to research, students in active learning classes are more interested, motivated, and likely to remember the material they have learned. Furthermore, Park and Choi’s research discovered that classroom physical design, such as lighting, air quality, and temperature, influences students’ learning experiences. Poor lighting, unpleasant temperatures, and poor air quality can all contribute to negative moods and a lack of attention, impairing students’ ability to learn and engage successfully.
4.2. Constraints and Challenges of Hybrid Learning Spaces
The visual representation in Figure 3 delineates the challenges inherent in hybrid learning spaces, as drawn from an extensive review of existing literature. This graphical depiction succinctly captures the intricate web of challenges that extend their impact beyond students, affecting educators and the interactive learning environment as well. The subsequent section embarks on an in-depth analysis of the core categories elucidated within Figure 3.
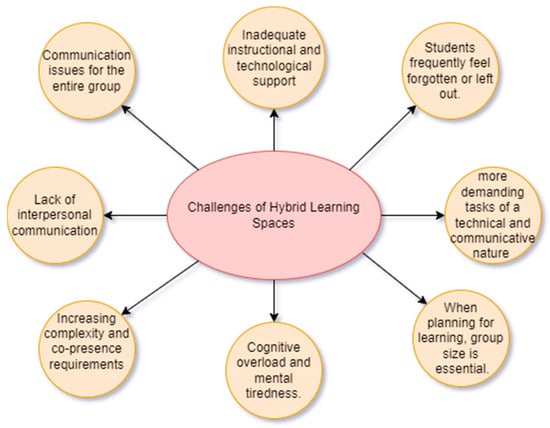
Figure 3.
Challenges of Hybrid Learning Spaces.
Numerous research works on classroom instruction shows the difficulties that may occur in a typical classroom. These difficulties are hard to understand until both students and teachers see them firsthand. Education includes not just the subjects that students must study, but also their perception of and reactions to environmental changes. The classroom design set includes a collection of resources, tools, and learning spaces that are employed to facilitate the teaching and learning process. Additionally, the epistemic design encompasses the specific activities or tasks that learners are expected to undertake. Lastly, the social structure pertains to how learners are grouped and the construction of communities or networks within the learning environment.
Hybrid courses, which blend face-to-face and online learning, are becoming increasingly popular; there is a need for further study on the factors that impact students’ happiness and engagement in such courses. The importance of technology and social design, as well as instructor experience, are particularly crucial to explore. According to [26], students show a preference for courses designed in a hybrid format only if they have prior experience with it and are comfortable with the established design. The success of technology in hybrid classes was closely linked to the teacher’s ability to utilize the technology effectively and encourage discussions. The study discovered that technical challenges were frequently related to the amount of expertise and competence of the instructor, which had a direct influence on student satisfaction and involvement. These findings highlight the necessity of teacher preparation and support for technology use in hybrid classrooms to provide students with a pleasant learning experience.
Learning activities are significantly impacted by their setting as well as the accessible resources and artifacts. However, in the situation of synchronous hybrid learning, when lessons are held both in a regular school environment and in the homes of students, the set design may vary greatly. This makes it difficult for teachers and students to construct learning activities. According to [26], the uniformity of the learning design in synchronous hybrid learning challenges the design of student activities even more. They discovered that technological constraints and limits in the software utilized for synchronous course delivery have no effect on students’ involvement or motivation to participate in open discussions. However, the authors found that when compared to the more robust conversations in traditional classes, the discussions in online virtual synchronous classrooms tended to be less vibrant. They explained this by pointing to the limitations of the prevailing technology. It is interesting that students’ desire to participate in class discussions and debates did not rise, as expected, because of the software’s complexity. These results show that synchronous hybrid learning settings require instructors and students to specifically design compelling learning activities that encourage active participation and insightful debates, despite technological limitations.
Although technological limitations may not have a measurable impact on student satisfaction, a lack of relevant affordance is reported to have a negative impact on communication in situations where the educator, for example, utilizes breakout rooms on a video conference platform and the text messaging system restricts the number of characters that may be communicated. According to [27], studies conducted in the past regarding hybrid learning have highlighted the impact of the absence of audio and visual indicators, which are typically present in traditional face-to-face learning environments, on the quality of education that students receive.
Students frequently feel forgotten or neglected when the teacher pays attention to either the physically present students or the distant students. Sequencing, pace, and repeated aspects operate differently in each modality. Several studies have been conducted on students’ behaviors in synchronous hybrid earning settings, especially from the students’ perspective.
Yang et al. [28] conducted a large quantitative study in which the behaviors of 41,781 Chinese dentistry students were recorded from February to May 2020. The researchers gathered information on a variety of elements of student behavior, such as online learning engagement, attendance, and interaction with learning resources. They looked at how these behaviors altered before and after the COVID-19 epidemic and the move to remote learning. The study’s findings indicated substantial changes in student habits during the epidemic. Student participation in online debates and activities has expanded dramatically, as has their time spent on virtual platforms. Attendance rates improved as well, indicating a greater dedication to virtual learning.
The authors discovered that the availability and accessibility of technology, as well as internet connectivity, had an important effect in students’ involvement and participation. Students who had better access to resources and technology were more likely to actively participate in online learning activities. The study also addressed the problems and constraints that students encountered when transitioning to remote learning. Student complaints included connection issues, a lack of human engagement, and a lack of hands-on practical instruction. These difficulties emphasized the need for novel tactics and support mechanisms to enable effective teaching and learning in a distant environment.
Organizational challenges are frequently tied to the physical environment, such as architecture (e.g., small and inadequate classrooms), or they may be related to logistics and digital connection. One major issue with synchronous hybrid learning is that teachers find it difficult to use all of the digital resources at the same time. They must concentrate on the students while simultaneously considering how to employ technology to assist them to study. This may be quite exhausting for instructors, who may feel as if they are zooming in and out or are becoming bored of all the intellectual work they must complete.
According to [29], students’ voices are not given enough importance in hybrid learning when teachers are overwhelmed by time pressure and the demands of teaching in multiple places at once. Teachers and students perceive hybrid learning spaces differently, and research shows that agreement on norms and rules is crucial for learning outcomes. When only some students attend class via online platforms, others may feel socially disconnected and isolated from classmates and teachers. This can lead to a critical consequence of hybrid learning, where professors may forget about students attending via an online platform if they are not using it themselves.
The failure of teachers to divide their attention evenly between in-person and online students, according to [30], prompted them to argue that it could be better for all students to attend online. However, Zydney et al. [31] provided a possible solution to this problem in comparative research. If the group size is small enough, hybrid instructional approaches can be successful, with experienced instructors facilitating both audiences. The key factor here is experience, which is mentioned in several articles. The debate on the feasibility of hybrid learning spaces often overlooks the potential of including support staff, allocating time for teacher training, and allowing them to practice carefully selected pedagogical approaches collectively in different physical and digital settings, as noted by [32].
The integration of hybrid learning spaces poses a potential obstacle to achieving a satisfactory work–life balance for both students and teachers. Family commitments can impede their active participation in educational activities. One of the most significant challenges is the difficulty in establishing clear boundaries between personal and academic time, as interruptions from family members may disrupt the learning process. Additionally, the hybrid model necessitates a significant adjustment in the way teachers allocate time for course design and planning.
The epistemic design dimension is concerned with the teacher’s planned behaviors and activities for students. However, it is often most challenging to identify the epistemic design dimension in existing literature, which primarily focuses on social and set designs. The methods of organizing knowledge and assessing its quality within a specific field are seldom discussed or evaluated. As a result, we rely on the descriptions of teachers’ and facilitators’ duties as a substitute for identifying the epistemic design aspects of the students’ learning environment. Given the larger number of students, teaching in hybrid settings requires teachers to manage multiple tasks, which can be more demanding than traditional face-to-face or online classes.
In [33], a qualitative experimental study consisting of 54 h of teaching to a group of 28 engineering students, the author discovered that the teachers displayed a tendency to concentrate on a specific group and slow down the teaching pace. Teachers attempted to encourage synchronous participation between the two groups, but this led to the physically present students becoming disengaged and rating the quality of teaching less favorably.
In this experiment, the students’ interaction developed in an unexpected way. The physically present students interacted with each other, while the online students struggled to establish collaborative learning. The experiment failed to establish peer feedback and synchronous discussions were challenging, with instances of awkward silences and students speaking at the same time. The opportunities for making simultaneous comments via chat and raising hands were insufficient, and distance students felt disconnected. Some students admitted to lacking self-discipline.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
There has been an increasing interest in researching novel learning environments in higher education in recent years. The purpose of this article is to dive into the subject and throw light on the numerous efforts and advances in this field. SCALE-UP [9] and TEAL [10] are two of these efforts, both of which tried to build futuristic learning environments that deviated from the typical classroom design.
A significant finding from our comprehensive study is that minor factors may have a major impact on students’ motivation and interest in learning. The color of the classroom, the temperature of the room, technological equipment, and, most significantly, student seating patterns have all been proved to have an impact on the learning experience. These investigations discovered that when students are put in situations that encourage such interactions, they are more motivated to engage with their classmates and develop innovative ideas. This contrasts with typical learning environments, where cooperation and creativity may be constrained.
Notably, the impact of physical learning spaces on student engagement and learning outcomes was consistently highlighted. Classroom design, furniture arrangement, lighting, and acoustics were identified as key factors influencing student enthusiasm and productivity [14].
Additionally, numerous learning space designs have been found to encourage interactive and collaborative learning experiences, such as flexible classrooms, collaborative spaces, and technology-rich environments [2,15]. These designs encourage student-centered methods that foster higher engagement and active participation.
Furthermore, technological integration, such as integrating virtual and augmented reality into conventional learning spaces, has emerged as a potential technique to creating immersive learning environments. These tools increase student engagement, stimulate critical thinking, and allow for experiential learning [26].
In addition, the review emphasized the growing relevance of online learning platforms and hybrid learning models, particularly considering the COVID-19 pandemic. These platforms have enabled distant learning and offered students freedom, but issues such as connectivity, technological assistance, and social contact must be addressed [8,30,31].
Likewise, this study stresses the need for inclusive learning environments that accommodate students’ various needs. Accessibility, ergonomic design, and considering various learning styles emerged as critical aspects in increasing inclusion.
Finally, it was found that sustainability and environmental factors in learning space design are becoming more prominent. Creating environmentally friendly and energy-efficient environments adds not only to sustainability goals, but also to a healthy and conducive learning environment [25].
Our investigation also includes an emphasis on the influence of the COVID-19 epidemic on higher education. As universities quickly shifted to remote learning to maintain educational continuity, numerous online learning platforms and hybrid learning systems were launched. These technological developments have proven to be advantageous, especially for students with mobility issues or who live in rural areas. These students may now participate in lessons as if they were physically there in the classroom.
It is crucial to highlight, however, that this quick change to remote and hybrid learning has not been without its obstacles. One significant disadvantage is the possible lack of interpersonal communication that happens in conventional learning environments. Inadequate instructional and technological assistance may also impede learning for some students. These aspects emphasize the importance of continual upgrades and assistance to provide a smooth and successful learning experience in these altered learning settings.
Finally, the investigation of innovative learning environments in higher education has opened new avenues for improving student motivation, cooperation, and creativity. SCALE-UP and TEAL projects have produced useful insights on the significance of aspects such as student seating arrangements and the overall learning environment. While technical advancements have improved remote and hybrid learning, issues relating to interpersonal communication and assistance must be addressed to guarantee that all students have the most effective educational experience possible. In addition, there has been an increase in interest in studying innovative learning environments in higher education in recent years. This involves using technology such as virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR). VR provides immersive experiences that allow students to explore virtual simulations, whilst AR overlays digital information over the actual environment. These tools could increase student engagement and comprehension. However, incorporating VR and AR into higher education is fraught with difficulties. The cost of the required equipment and training may be prohibitively expensive, and technological challenges can develop in remote or hybrid learning contexts. For successful deployment, dependable technical assistance and continuing training are essential. Despite these limitations, the integration of VR and AR has the potential to improve student motivation and learning results.
Higher education institutions may build dynamic and engaging environments that fulfill the increasing demands of students in the current period by continuing to invest in the creation of learning spaces and leveraging technology breakthroughs.
6. Future Work and Recommendations
Future research endeavors will delve into the transformative potential of Artificial Intelligence (AI) with the goal of enhancing the higher education landscape. Researchers could examine how AI may impact traditional educational models and lead to more personalized and effective learning experiences, given the constantly evolving technological landscape. The forthcoming investigation aims to explore inventive strategies that harness AI-powered tools such as intelligent tutoring systems, adaptive learning platforms, and data analytics. These approaches aim to enhance curriculum design, elevate student engagement, and improve educational outcomes. This exploration is expected to shed light on the intricate interplay between advancements in teaching methodologies and cutting-edge technology, offering new possibilities for educators and institutions to utilize AI in establishing a higher education environment that is not only more comprehensive and accessible, but also more conducive to fostering effective learning.
In light of the imperative to harness the transformative capabilities of AI for the advancement of higher education, several key recommendations emerge. Firstly, institutions should embark on collaborative partnerships with AI experts and educators to develop tailored AI-driven solutions that address specific educational challenges. Secondly, investing in robust data infrastructure and analytics systems will enable institutions to collect and analyze student performance data, facilitating the creation of personalized learning pathways. Additionally, it is crucial to prioritize ethical considerations and transparent communication when implementing AI-powered tools, ensuring students’ privacy and fostering trust in the technology. Furthermore, ongoing professional development programs should be instituted for educators to empower them with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively integrate AI into their teaching practices. Lastly, fostering a culture of experimentation and innovation within educational institutions will facilitate the exploration of new AI applications that cater to evolving learning needs. By adhering to these recommendations, higher education can unlock the full potential of AI to revolutionize teaching, learning, and educational outcomes.
Funding
This research was funded by the Research e-Infrastructure “[e-Aegean R&D Network] R&D Network in Aegean Archipelagos: Supporting Regional Innovation, Entrepreneurship and Excellence” {Code Number MIS 5046494} which is implemented within the framework of the “Regional Excellence” Action of the Operational Program “Competitiveness, Entrepreneurship and Innovation”. The action was co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF) and the Greek State [Partnership Agreement 2014–2020].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A. List of Reviewed Papers
In this section, we present a list of the papers reviewed in our narrative literature review. These papers were included based on our predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria and contributed to the synthesis of findings in the main body of this paper.
- Temple, P.; Fillippakou, O. Learning Spaces for the 21st Century. Higher Education Academy 2007, 1–80.
- Temple, P.H. Learning Spaces in Higher Education: An Under-Researched Topic. London Review of Education 2008.
- Ward, V.; House, A.; Hamer, S. Developing a Framework for Transferring Knowledge Into Action: A Thematic Analysis of the Literature. Journal of Health Services Research & Policy 2009, 14, 156–164.
- Finkelstein, A., Finkelstein; Jennie, Ferris; Cynthia, Weston; Laura, Winer. Research-Informed Principles for (Re)Designing Teaching and Learning Spaces. Journal of Learning Spaces 2018.
- Byers, T.B.; Marian Mahat; Kirra Liu; Anne Knock; Wesley Imms. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Learning Environments on Student Learning Outcomes; University of Melbourne, 2018.
- Eringfeld, S. Higher Education and Its Post-Coronial Future: Utopian Hopes and Dystopian Fears at Cambridge University during COVID-19. Studies in Higher Education 2021, 46, 146–157, doi:10.1080/03075079.2020.1859681.
- Peterson, J.; Pearce, P.F.; Ferguson, L.A.; Langford, C.A. Understanding Scoping Reviews: Definition, Purpose, and Process. Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners 2017, 29, 12–16, doi:10.1002/2327-6924.12380.
- Horsley, T. Tips for Improving the Writing and Reporting Quality of Systematic, Scoping, and Narrative Reviews. J Contin Educ Health Prof 2019, 39, 54–57, doi:10.1097/CEH.0000000000000241.
- Park, E.L.; Choi, B.K. Transformation of Classroom Spaces: Traditional versus Active Learning Classroom in Colleges. Higher Education 2014, 68, 749–771.
- Weinstein, C.S. The Physical Environment of the School: A Review of the Research. Review of Educational Research 1979, 49, 577–610.
- Orr, D.W., Orr Architecture as Pedagogy. Conservation Biology 1993.
- Carmean, C., Carmean; Haefner, J., Haefner. Mind over Matter: Transforming Course Management Systems into Effective Learning Environments. Educause Review 2002.
- Beichner, John., Beichner, Robert & Deardorff, Duane & Allain, Rhett & Bonham, Scott & Dancy, Melissa & Risley; Saul, J., Saul; Abbott, D., Abbott; Abbott, M., Abbott. Student-Centered Activities for Large Enrollment Undergraduate Programs (SCALE-UP). Research-based Reform of University Physics. 2008.
- Belcher, J.W. Improving Student Understanding with TEAL. Faculty Newsletters 2003.
- Alexander, A., Alexander, D., Cohen, B.A., Fitzgerald, S., Honsey, P., Jorn, L., Knowles, J., Oberg, P., Todd, J., Walker, J.D., & Whiteside; Cohen, B.A., Cohen; Fitzgerald, S., Fitzgerald Active Learning Classrooms Pilot Evaluation: Fall 2007 Findings and Recommendations. University of Minnesota. 2008.
- Van Horne, Van Horne S.; Murniati, C., Murniati; Saichaie, K., Saichaie. Assessing Teaching and Learning in Technology-Infused TILE Classrooms at the University of Iowa. EDUCAUSE Learning Initiative’s Seeking Evidence of Impact. 2012.
- Nielsen, F. Global Classroom - Videokonference i Undervisning. Tidsskriftet Læring og Medier (LOM) 2013, 6.
- Munger, M.H., Munger; Campbell, B., Campbell; Banister, S., Banister Technology Boot Camp: Providing Professional Development for Faculty and Supporting Active Learning Environments for Students. Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference 2014.
- Lakhal, S.; Bateman, D.; Bédard, J. Blended Synchronous Delivery Modes in Graduate Programs: A Literature Review and How it is Implemented in the Master Teacher Program. Collected Essays on Learning and Teaching 2017, 10, 47–60.
- Raes, A.; Detienne, L.; Windey, I.; Depaepe, F. A Systematic Literature Review on Synchronous Hybrid Learning: Gaps Identified. Learning Environments Research 2019, 23, 269–290.
- Shamir-Inbal, T.; Blau, I. Facilitating Emergency Remote K-12 Teaching in Computing-Enhanced Virtual Learning Environments During COVID-19 Pandemic—Blessing or Curse? Journal of Educational Computing Research 2021, 59, 1243–1271.
- Makransky, G.; Petersen, G.B. The Cognitive Affective Model of Immersive Learning (CAMIL): A Theoretical Research-Based Model of Learning in Immersive Virtual Reality. Educ Psychol Rev 2021, 33, 937–958, doi:10.1007/s10648-020-09586-2.
- Kwon, C. Verification of the Possibility and Effectiveness of Experiential Learning Using HMD-Based Immersive VR Technologies. Virtual Reality 2019, 23, 101–118, doi:10.1007/s10055-018-0364-1.
- Masiello, I.; Herault, R.; Mansfeld, M.; Skogqvist, M. Simulation-Based VR Training for the Nuclear Sector—A Pilot Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7984, doi:10.3390/su14137984.
- Andersson, R.; Anker, M.; Dunford, A.; Lundqvist, J.; Weiss, A. HAMLIN: An Augmented Reality Solution to Visualize Abstract Concepts for Science Education. Human Nature, SIDeR 2016 2016.
- Oblinger, D., Oblinger. Learning Spaces (Vol. 2); Washington, DC: Educause, 2006; Vol. 2.
- Flynn-Wilson, L.; Reynolds, K.E. Student Responses to Virtual Synchronous, Hybrid, and Face-to-Face Teaching/Learning. International Journal of Technology in Education 2020, 4, 46.
- Weitze, C.L.W.; Ørngreen, R.Ø.; Levinsen, K., Levinsen. The Global Classroom Video Conferencing Model and First Evaluations. I M. Ciussi, & M. Augier (Red.). Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on E-Learning: SKEMA Business School, Sophia Antipolis France 2013.
- Yang, X.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Tan, J. Learner Behaviors in Synchronous Online Prosthodontic Education during the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 2021, 126, 653–657.
- Chemi, T. It Is Impossible: The Teacher’s Creative Response to the COVID-19 Emergency and Digitalized Teaching Strategies. Qualitative Inquiry 2020, 27, 853–860.
- Smith, J.; Schreder, K. Are They Paying Attention, or Are They Shoe-Shopping? Evidence from Online Learning. JIMPHE 2021, 5, 200–209, doi:10.32674/jimphe.v5i1.2643.
- Zydney, J.M.; Warner, Z.; Angelone, L. Learning through Experience: Using Design- Based Research to Redesign Protocols for Blended Synchronous Learning Environments. Computers & Education 2020, 143, 103678.
- Szeto, E. A Comparison of Online/Face-to-Face Students’ and Instructor’s Experiences: Examining Blended Synchronous Learning Effects. Procedia—Social and Behavioral Sciences 2014, 116, 4250–4254, doi:10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.01.926.
- Green, B.N.; Johnson, C.D.; Adams, A. Writing Narrative Literature Reviews for Peer-Reviewed Journals: Secrets of the Trade. Journal of Chiropractic Medicine 2006, 5, 101–117, doi:10.1016/s0899-3467(07)60142-6
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535–b2535, doi:10.1136/bmj.b2535.
References
- Park, E.L.; Choi, B.K. Transformation of Classroom Spaces: Traditional versus Active Learning Classroom in Colleges. High. Educ. 2014, 68, 749–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orr, D.W. Architecture as Pedagogy. Conserv. Biol. 1993, 7, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temple, P.; Fillippakou, O. Learning Spaces for the 21st Century. High. Educ. Acad. 2007, 1–80. [Google Scholar]
- Temple, P.H. Learning Spaces in Higher Education: An under-Researched Topic. Lond. Rev. Educ. 2008, 6, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, V.; House, A.; Hamer, S. Developing a Framework for Transferring Knowledge Into Action: A Thematic Analysis of the Literature. J. Health Serv. Res. Policy 2009, 14, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, A.; Ferris, J.; Weston, C.; Winer, L. Research-Informed Principles for (Re)Designing Teaching and Learning Spaces. J. Learn. Spaces 2016, 5, 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Byers, T.B.; Mahat, M.; Liu, K.; Knock, A.; Imms, W. A Systematic Review of the Effects of Learning Environments on Student Learning Outcomes; University of Melbourne: Parkville, Australia, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Eringfeld, S. Higher Education and Its Post-Coronial Future: Utopian Hopes and Dystopian Fears at Cambridge University during COVID-19. Stud. High. Educ. 2021, 46, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beichner, R.J.; Duane, D.L.; Allain, R.J.; Bonham, S.W.; Dancy, M.H.; Risley, J.S.; Abbott, D.S. The Student-Centered Activities for Large Enrollment Undergraduate Programs (SCALE-UP). Res.-Based Reform Univ. Phys. 2007, 1, 2–39. [Google Scholar]
- Belcher, J.W. Improving Student Understanding with TEAL. Fac. Newsl. 2003, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, A.; Alexander, D.; Cohen, B.A.; Fitzgerald, S.; Honsey, P.; Jorn, L.; Knowles, J.; Oberg, P.; Todd, J.; Walker, J.D.; et al. Active Learning Classrooms Pilot Evaluation: Fall 2007 Findings and Recommendations; University of Minnesota: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Horsley, T. Tips for Improving the Writing and Reporting Quality of Systematic, Scoping, and Narrative Reviews. J. Contin. Educ. Health Prof. 2019, 39, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; for the PRISMA Group. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. BMJ 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, C.S. The Physical Environment of the School: A Review of the Research. Rev. Educ. Res. 1979, 49, 577–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmean, C.; Haefner, J. Mind over Matter: Transforming Course Management Systems into Effective Learning Environments. Educ. Rev. 2002, 37, 27–33. [Google Scholar]
- Van Horne, S.; Murniati, C.; Saichaie, K. Assessing Teaching and Learning in Technology-Infused TILE Classrooms at the University of Iowa. Educ. Learn. Initiat. Seek. Evid. Impact 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, F. Global Classroom-Videokonference i Undervisning. Tidsskriftet Læring Og Medier (LOM) 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munger, M.H.; Campbell, B.; Banister, S. Technology Boot Camp: Providing Professional Development for Faculty and Supporting Active Learning Environments for Students. In Society for Information Technology & Teacher Education International Conference; Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education: Jacksonville, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Lakhal, S.; Bateman, D.; Blended, J. Synchronous Delivery Modes in Graduate Programs: A Literature Review and How It Is Implemented in the Master Teacher Program. Collect. Essays Learn. Teach. 2017, 10, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raes, A.; Detienne, L.; Windey, I.; Depaepe, F. A Systematic Literature Review on Synchronous Hybrid Learning: Gaps Identified. Learn. Environ. Res. 2019, 23, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makransky, G.; Petersen, G.B. The Cognitive Affective Model of Immersive Learning (CAMIL): A Theoretical Research-Based Model of Learning in Immersive Virtual Reality. Educ. Psychol. Rev. 2021, 33, 937–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, C. Verification of the Possibility and Effectiveness of Experiential Learning Using HMD-Based Immersive VR Technologies. Virtual Real. 2019, 23, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masiello, I.; Herault, R.; Mansfeld, M.; Skogqvist, M. Simulation-Based VR Training for the Nuclear Sector—A Pilot Study. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, R.; Anker, M.; Dunford, A.; Lundqvist, J.; Weiss, A. Hamlin: An Augmented Reality Solution to Visualize Abstract Concepts for Science Education. In Proceedings of the SIDeR’16–Student Interaction Design Research Conference, Malmö, Sweden, 1–2 April 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Oblinger, D. Learning Spaces; Educause: Washington, DC, USA, 2006; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn-Wilson, L.; Reynolds, K.E. Student Responses to Virtual Synchronous, Hybrid, and Face-to-Face Teaching/Learning. Int. J. Technol. Educ. 2020, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitze, C.L.W.; Ørngreen, R.Ø.; Levinsen, K. The Global Classroom Video Conferencing Model and First Evaluations. In Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on E-Learning: SKEMA Business School, Sophia Antipolis, France, 30–31 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, D.; Liu, X.; Tan, J. Learner Behaviors in Synchronous Online Prosthodontic Education during the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2021, 126, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemi, T. It Is Impossible: The Teacher’s Creative Response to the COVID-19 Emergency and Digitalized Teaching Strategies. Qual. Inq. 2020, 27, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Schreder, K. Are They Paying Attention, or Are They Shoe-Shopping? Evidence from Online Learning. JIMPHE 2021, 5, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydney, J.M.; McKimmy, P.; Lindberg, R.; Schmidt, M. Here or There Instruction: Lessons Learned in Implementing Innovative Approaches to Blended Synchronous Learning. TechTrends 2018, 63, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zydney, J.M.; Warner, Z.; Angelone, L. Learning through Experience: Using Design Based Research to Redesign Protocols for Blended Synchronous Learning Environments. Comput. Educ. 2020, 143, 103678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szeto, E. A Comparison of Online/Face-to-Face Students’ and Instructor’s Experiences: Examining Blended Synchronous Learning Effects. Procedia-Soc. Behav. Sci. 2014, 116, 4250–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).