The Evolving Landscape of Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis: From Foundational Mechanisms to Organ-Specific Modifiers
Abstract
1. Introduction
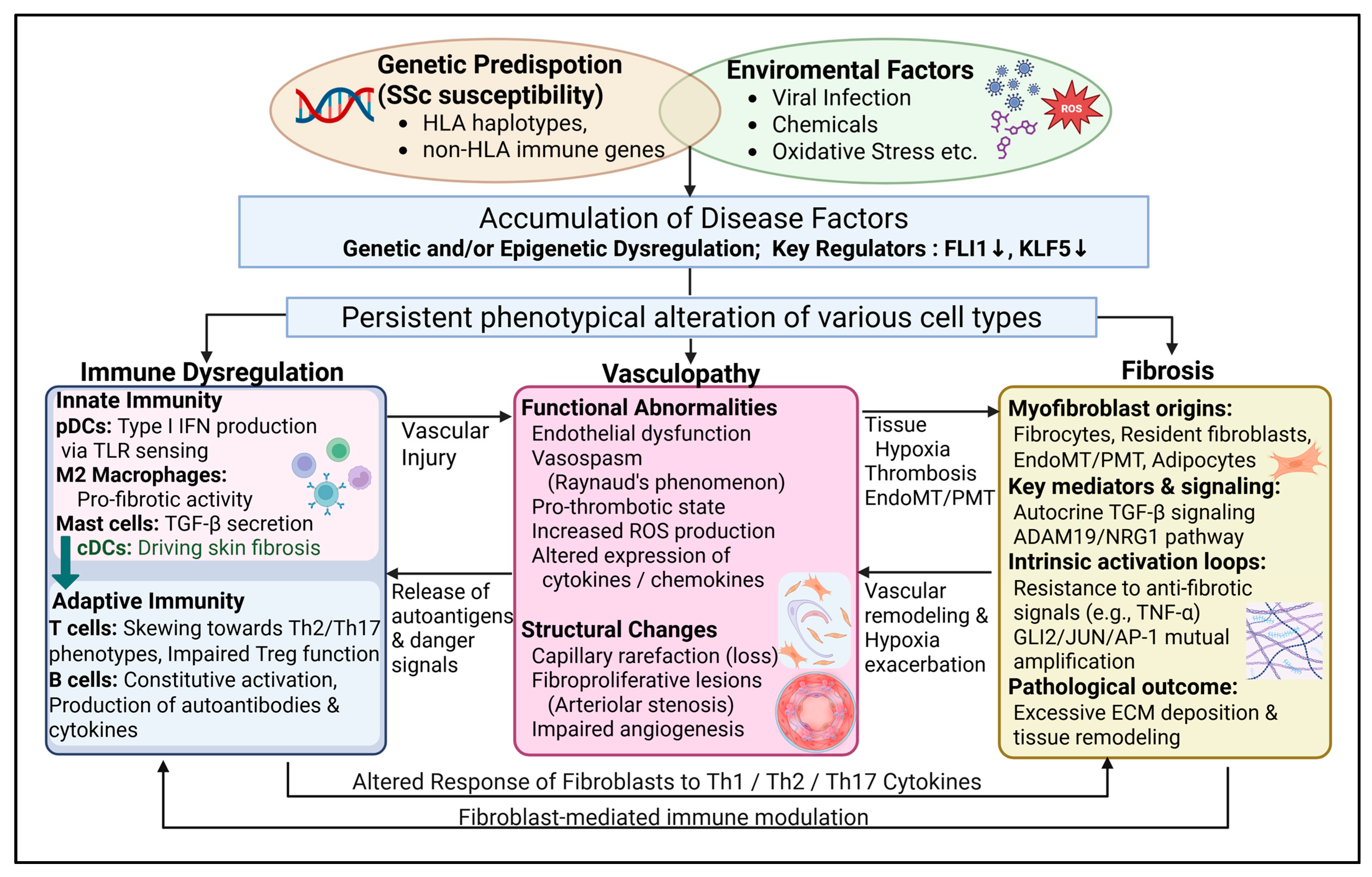
2. Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis: Foundational Trans-Organ Pathophysiology
2.1. “Genetics” in SSc
2.2. “Epigenetics” in SSc
2.3. Genetic Polymorphisms of FLI1 and SSc Susceptibility
2.4. Inflammation and Immunological Dysfunction in SSc
2.5. Vascular Injury in SSc
2.6. Fibrosis in SSc
3. Verification of Pathogenesis Hypotheses: Insights from Recent Analytical Innovations
3.1. Scleroderma-Associated Fibroblast (ScAF) Identification via scRNA-Seq Analysis
3.2. Spatial Transcriptomics Analysis
3.3. Integrated Analysis: scRNA-Seq and snATAC-Seq, Focusing on Vascular Endothelial Cells
3.4. Vascular Niche Analysis by Spatial Proteomics Using Imaging Mass Cytometry
3.5. Novel Pathogenesis Mechanism of SSc Skin Fibrosis Suggested by Epigenetic Analysis Using ATAC-Seq
3.6. Novel Therapeutic Targets Identified by Gene Expression Meta-Analysis of Lung Tissue
4. Organ-Specific Pathophysiology Modifiers: Refining the Landscape of SSc Organ Involvement
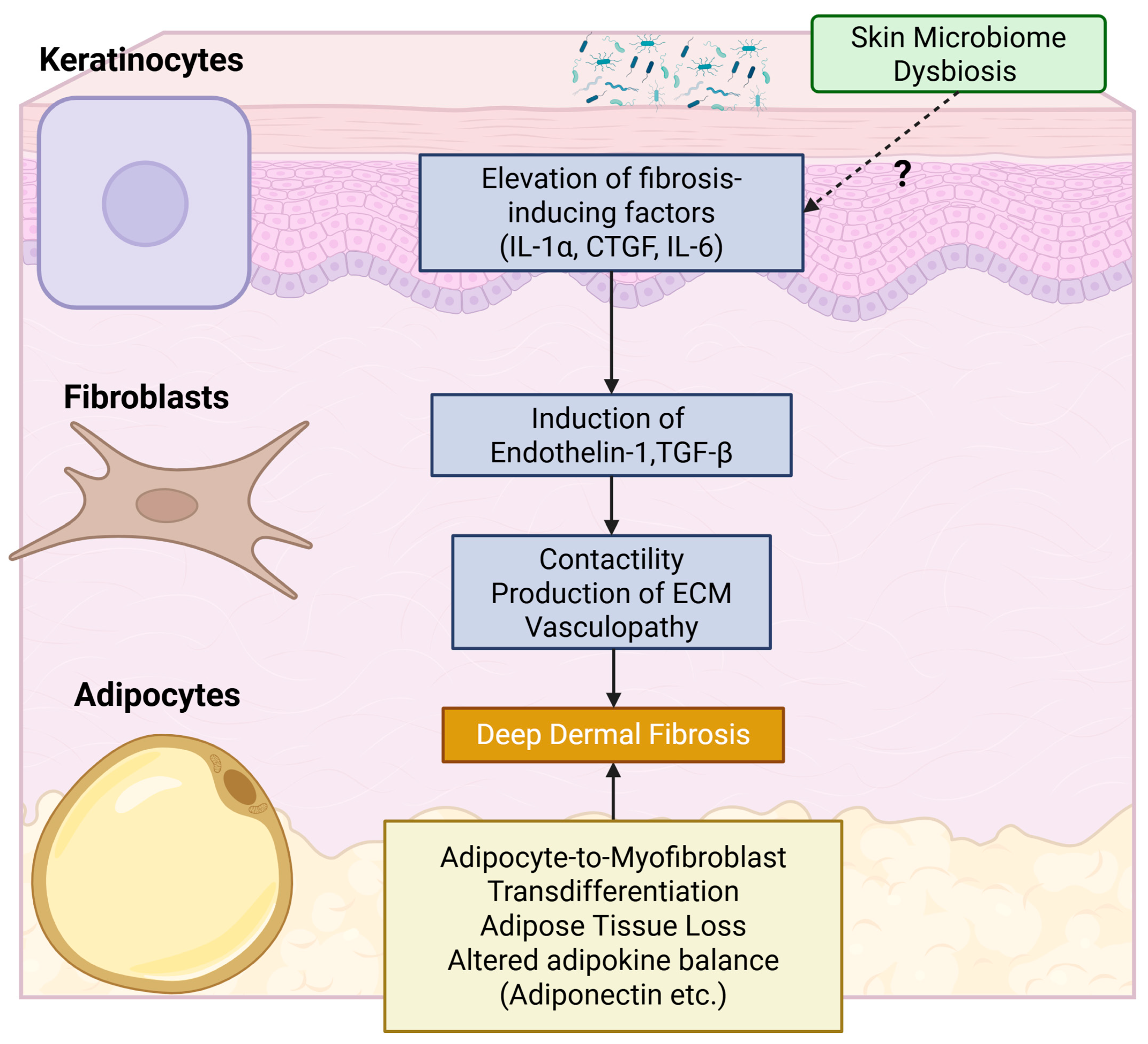
4.1. Cutaneous Pathology
4.1.1. Keratinocytes
4.1.2. Adipocytes
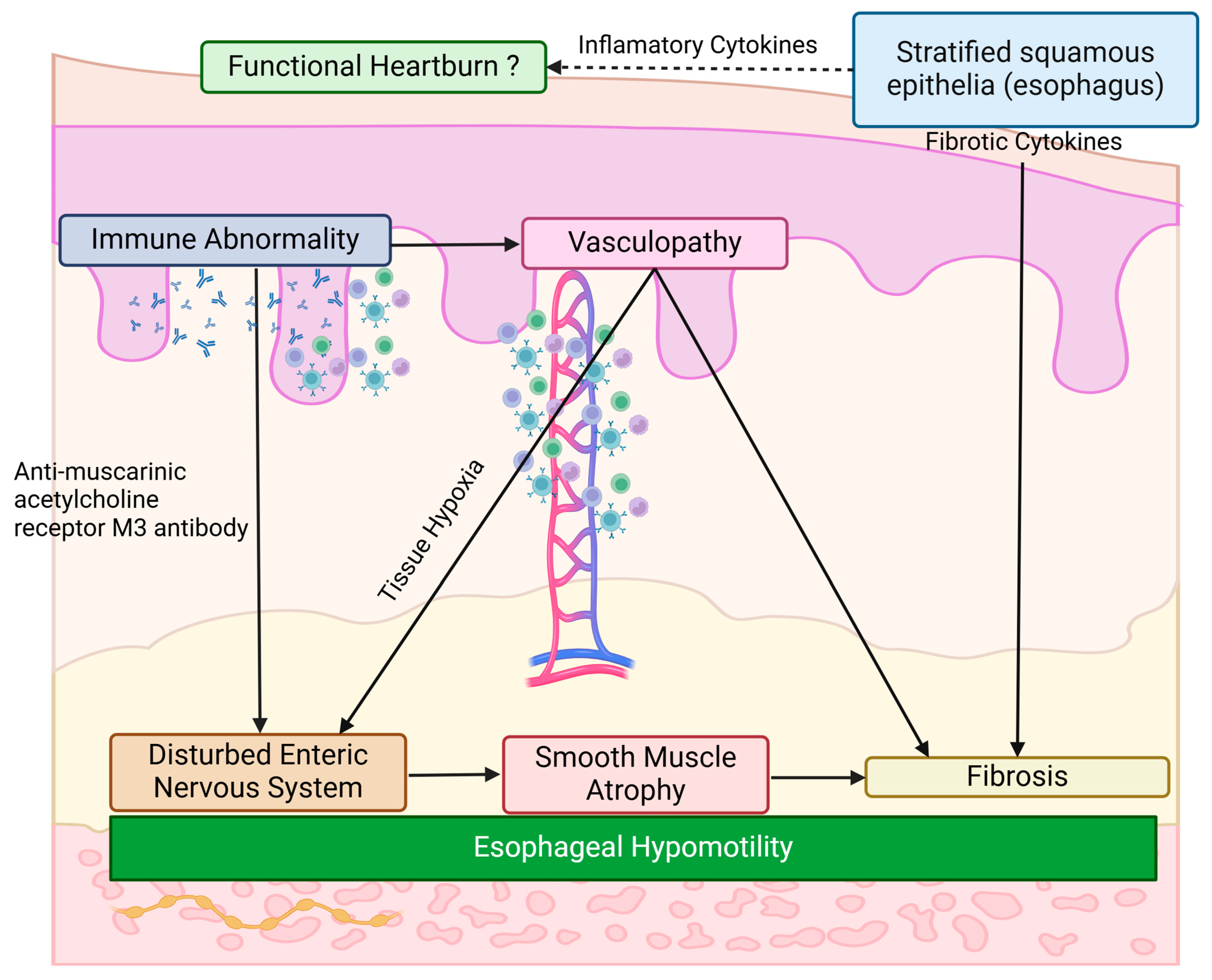
4.2. Gastrointestinal Pathology
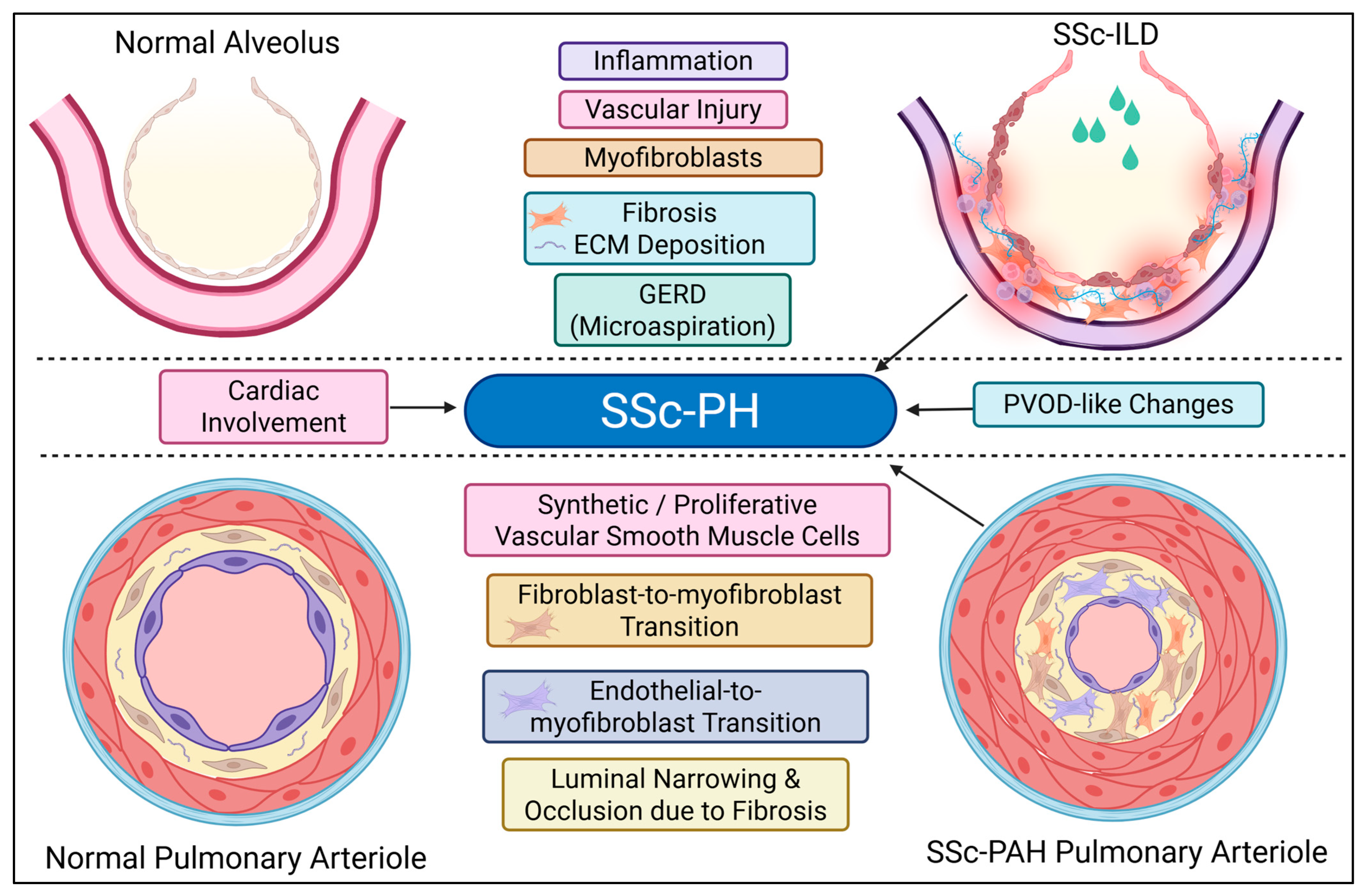
4.3. Pulmonary Pathology
- * Stage 1 (Initial): Characterized by microvessel overdevelopment with structural abnormalities, and alveolar septal thickening with numerous α-SMA-positive myofibroblasts. The overdeveloped microvessels contain blood cells within their lumina, indicating maintained functional circulation.
- * Stage 2 (Progressive ECM Deposition): Marked by substantial and progressive ECM deposition, irregular and indistinct alveolar septal borders, further structural disorganization of microvessels, and obliteration of larger blood vessels. Disarray or partial loss of the alveolar epithelium is also evident.
- * Stage 3 (Extensive Fibrosis): Progression of fibrosis extensively damages vital lung structures, including alveoli and vasculature.
- * Stage 4 (Final): The lung transforms into a contracted fibrous organ devoid of alveoli and vasculature.
4.4. Cardiovascular Pathology
4.5. Scleroderma Renal Crisis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic Sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnett, F.C.; Cho, M.; Chatterjee, S.; Aguilar, M.B.; Reveille, J.D.; Mayes, M.D. Familial Occurrence Frequencies and Relative Risks for Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma) in Three United States Cohorts. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 1359–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Wright, T.M. Analysis of Systemic Sclerosis in Twins Reveals Low Concordance for Disease and High Concordance for the Presence of Antinuclear Antibodies. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 1956–1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, K.; Kawasaki, A.; Matsushita, T.; Furukawa, H.; Kondo, Y.; Okiyama, N.; Nagaoka, S.; Shimada, K.; Sugii, S.; Katayama, M.; et al. Association of Functional (GA)n Microsatellite Polymorphism in the FLI1 Gene with Susceptibility to Human Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2020, 59, 3553–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.K. The Genetics of Systemic Sclerosis. Discov. Med. 2010, 10, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dieudé, P.; Guedj, M.; Wipff, J.; Avouac, J.; Fajardy, I.; Diot, E.; Granel, B.; Sibilia, J.; Cabane, J.; Mouthon, L.; et al. Association between the IRF5 Rs2004640 Functional Polymorphism and Systemic Sclerosis: A New Perspective for Pulmonary Fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, I.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Kawasaki, A.; Hasegawa, M.; Ohashi, J.; Hikami, K.; Kawamoto, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S.; et al. Association of a Functional Polymorphism in the IRF5 Region with Systemic Sclerosis in a Japanese Population. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 1845–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Gorlova, O.; Rueda, B.; Martin, J.-E.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; Palomino-Morales, R.; Coenen, M.J.; Vonk, M.C.; Voskuyl, A.E.; Schuerwegh, A.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Systemic Sclerosis Identifies CD247 as a New Susceptibility Locus. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Chen, B.; Ma, B.; Nie, S. Association between IRF5 Polymorphisms and Autoimmune Diseases: A Meta-Analysis. Genet. Mol. Res. 2014, 13, 4473–4485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, R.; Mayes, M.D.; Tan, F.K.; Gorlova, O.Y.; Hummers, L.K.; Shah, A.A.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Martin, J.; Bossini-Castillo, L.; et al. IRF5 Polymorphism Predicts Prognosis in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfaremo, D.; Svegliati Baroni, S.; Manfredi, L.; Moroncini, G.; Gabrielli, A. Putative Functional Pathogenic Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis. Eur. J. Rheumatol. 2020, 7, S181–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senécal, J.-L.; Hoa, S.; Yang, R.; Koenig, M. Pathogenic Roles of Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: Current Understandings in Pathogenesis. J. Scleroderma Relat. Disord. 2020, 5, 103–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y. The Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis: An Understanding Based on a Common Pathologic Cascade across Multiple Organs and Additional Organ-Specific Pathologies. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Fan, P.-S.; Kahaleh, B. Association between Enhanced Type I Collagen Expression and Epigenetic Repression of the FLI1 Gene in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 2271–2279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubo, M.; Czuwara-Ladykowska, J.; Moussa, O.; Markiewicz, M.; Smith, E.; Silver, R.M.; Jablonska, S.; Blaszczyk, M.; Watson, D.K.; Trojanowska, M. Persistent Down-Regulation of Fli1, a Suppressor of Collagen Transcription, in Fibrotic Scleroderma Skin. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Asano, Y.; Nishimura, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Fujiu, K.; Manabe, I.; Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Akamata, K.; et al. Simultaneous Downregulation of KLF5 and Fli1 Is a Key Feature Underlying Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Noda, S.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Trojanowska, M.; Sato, S. Fibrosis, Vascular Activation, and Immune Abnormalities Resembling Systemic Sclerosis in Bleomycin-Treated Fli-1-Haploinsufficient Mice: SSc Phenotype Induction by Bleomycin in Fli-1+/−Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, N.; Manabe, I.; Uchino, Y.; Eguchi, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Nishimura, S.; Shindo, T.; Sano, M.; Otsu, K.; Snider, P.; et al. Cardiac Fibroblasts Are Essential for the Adaptive Response of the Murine Heart to Pressure Overload. J Clin Investig. 2010, 120, 254–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiu, K.; Manabe, I.; Nagai, R. Renal Collecting Duct Epithelial Cells Regulate Inflammation in Tubulointerstitial Damage in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3425–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, M.L.; Finlay, D.R.; Murray, J.I.; Troyanskaya, O.G.; Chi, J.-T.; Pergamenschikov, A.; McCalmont, T.H.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D.; Connolly, M.K. Systemic and Cell Type-Specific Gene Expression Patterns in Scleroderma Skin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12319–12324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Tang, R.; Ding, K. Epigenetic Modifications in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 3155–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemekasten, G.; Distler, J.H.W. A Broad Look into the Future of Systemic Sclerosis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2022, 14, 1759720X221109404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angiolilli, C.; Marut, W.; van der Kroef, M.; Chouri, E.; Reedquist, K.A.; Radstake, T.R.D.J. New Insights into the Genetics and Epigenetics of Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altorok, N.; Kahaleh, B. Epigenetics and Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Lu, Q. The Critical Importance of Epigenetics in Autoimmune-Related Skin Diseases. Front. Med. 2023, 17, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchetet, M.E.; Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. Current Concepts on the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 262–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Maskan Bermudez, N.; Sa, B.; Maderal, A.D.; Jimenez, J.J. Epigenetic Mechanisms Driving the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, Systemic Sclerosis and Dermatomyositis. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi-Kuwata, N.; Jinnin, M.; Makino, T.; Fukushima, S.; Inoue, Y.; Muchemwa, F.C.; Yonemura, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Takeya, M.; Mitsuya, H.; et al. Characterization of Monocyte/Macrophage Subsets in the Skin and Peripheral Blood Derived from Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yukawa, S.; Yamaoka, K.; Sawamukai, N.; Shimajiri, S.; Kubo, S.; Miyagawa, I.; Sonomoto, K.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, Y. Dermal Mast Cell Density in Fingers Reflects Severity of Skin Sclerosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2013, 23, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, K.G.; Dawson, N.A.J.; Huang, Q.; Dunne, J.V.; Levings, M.K.; Broady, R. Regulatory T Cells Produce Profibrotic Cytokines in the Skin of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 135, 946–955.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosello, S.; Angelucci, C.; Lama, G.; Alivernini, S.; Proietti, G.; Tolusso, B.; Sica, G.; Gremese, E.; Ferraccioli, G. Characterization of Inflammatory Cell Infiltrate of Scleroderma Skin: B Cells and Skin Score Progression. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafyatis, R.; O’Hara, C.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A.; Matteson, E. B Cell Infiltration in Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3167–3168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Takehara, K.; Sato, S. Longitudinal Analysis of Serum Cytokine Concentrations in Systemic Sclerosis: Association of Interleukin 12 Elevation with Spontaneous Regression of Skin Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Xing, X.; Wan, L.; Li, M. Increased Frequency of Th17 Cells in Systemic Sclerosis Is Related to Disease Activity and Collagen Overproduction. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Matsushita, T.; Hamaguchi, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K.; Komura, K.; Sato, S. Clinical Association of Serum Interleukin-17 Levels in Systemic Sclerosis: Is Systemic Sclerosis a Th17 Disease? J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 50, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hou, W.; Xu, K.; Han, D.; Jiang, C.; Mou, K.; Li, Y.; Meng, L.; Lu, S. The Elevated Expression of Th17-Related Cytokines and Receptors Is Associated with Skin Lesion Severity in Early Systemic Sclerosis. Hum. Immunol. 2015, 76, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frantz, C.; Auffray, C.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y. Regulatory T Cells in Systemic Sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K. Serum Levels of Interleukin-6 and Interleukin-10 Correlate with Total Skin Thickness Score in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2001, 27, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, T.; Jinnin, M.; Yamane, K.; Honda, N.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, T.; Masuguchi, S.; Fukushima, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Hasegawa, M.; et al. Impaired IL-17 Signaling Pathway Contributes to the Increased Collagen Expression in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3573–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankamp, L.; Preuß, B.; Pecher, A.-C.; Beucke, N.; Henes, J.; Klein, R. Functionally Active Antibodies to the Angiotensin II Type 1-Receptor Measured by a Luminometric Bioassay Do Not Correlate with Clinical Manifestations in Systemic Sclerosis: A Comparison with Antibodies to Vascular Receptors and Topoisomerase I Detected by ELISA. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 786039. [Google Scholar]
- van Oostveen, W.M.; Hoekstra, E.M.; Levarht, E.W.N.; Kotliar, I.B.; Sakmar, T.P.; Toes, R.E.M.; de Vries-Bouwstra, J.K.; Heitman, L.H.; Fehres, C.M. Absence of Functional Autoantibodies Targeting Angiotensin II Receptor Type 1 and Endothelin-1 Type A Receptor in Circulation and Purified IgG from Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, S.; Hasegawa, M.; Fujimoto, M.; Tedder, T.F.; Takehara, K. Quantitative Genetic Variation in CD19 Expression Correlates with Autoimmunity. J. Immunol. 2000, 165, 6635–6643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, S.; Fujimoto, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Takehara, K. Altered Blood B Lymphocyte Homeostasis in Systemic Sclerosis: Expanded Naive B Cells and Diminished but Activated Memory B Cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1918–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizaki, A. B Lymphocytes in Systemic Sclerosis: Abnormalities and Therapeutic Targets. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, S.; Distler, J.H.W.; Maurer, B.; Huscher, D.; van Laar, J.M.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; EUSTAR Rituximab study group. Effects and Safety of Rituximab in Systemic Sclerosis: An Analysis from the European Scleroderma Trial and Research (EUSTAR) Group. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1188–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daoussis, D.; Melissaropoulos, K.; Sakellaropoulos, G.; Antonopoulos, I.; Markatseli, T.E.; Simopoulou, T.; Georgiou, P.; Andonopoulos, A.P.; Drosos, A.A.; Sakkas, L.; et al. A Multicenter, Open-Label, Comparative Study of B-Cell Depletion Therapy with Rituximab for Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2017, 46, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosello, S.L.; De Luca, G.; Rucco, M.; Berardi, G.; Falcione, M.; Danza, F.M.; Pirronti, T.; Ferraccioli, G. Long-Term Efficacy of B Cell Depletion Therapy on Lung and Skin Involvement in Diffuse Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 44, 428–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebata, S.; Yoshizaki, A.; Fukasawa, T.; Miura, S.; Takahashi, T.; Sumida, H.; Asano, Y.; Sato, S. Rituximab Therapy Is More Effective than Cyclophosphamide Therapy for Japanese Patients with Anti-Topoisomerase I-Positive Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoussis, D.; Antonopoulos, I.; Liossis, S.-N.C.; Yiannopoulos, G.; Andonopoulos, A.P. Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Calcinosis: A Case Report of Rituximab-Induced Regression of CREST-Related Calcinosis and Review of the Literature. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 41, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khor, C.-G.; Chen, X.L.-F.; Lin, T.-S.; Lu, C.-H.; Hsieh, S.-C. Rituximab for Refractory Digital Infarcts and Ulcers in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 33, 1019–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslyanskiy, A.; Lapin, S.; Kolesova, E.; Peñín, I.; Cheshuina, M.D.; Feist, E.; Konradi, A. Effects of Rituximab Therapy on Elastic Properties of Vascular Wall in Patients with Progressive Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, S-228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.; Müller, F.; Distler, J.H.W.; Györfi, A.-H.; Völkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Kretschmann, S.; Reimann, H.; Harrer, T.; Bayerl, N.; et al. Treatment of a Patient with Severe Systemic Sclerosis (SSc) Using CD19-Targeted CAR T Cells. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1117–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, F.; Taubmann, J.; Bucci, L.; Wilhelm, A.; Bergmann, C.; Völkl, S.; Aigner, M.; Rothe, T.; Minopoulou, I.; Tur, C.; et al. CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Autoimmune Disease—A Case Series with Follow-Up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 687–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Wu, X.; Tan, B.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, L.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, A.; Wan, X.; Liu, S.; et al. Allogeneic CD19-Targeted CAR-T Therapy in Patients with Severe Myositis and Systemic Sclerosis. Cell 2024, 187, 4890–4904.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkt, W.; Freitag, M.; Claus, M.; Kolb, P.; Falcone, V.; Röhrich, M.; Rodon, L.; Deicher, F.; Andreeva, I.; Tretter, T.; et al. Third-Generation CD19.CAR-T Cell-Containing Combination Therapy in Scl70+ Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hügle, T.; Hogan, V.; White, K.E.; van Laar, J.M. Mast Cells Are a Source of Transforming Growth Factor β in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 795–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Denton, C.P.; Jahreis, A.; van Laar, J.M.; Frech, T.M.; Anderson, M.E.; Baron, M.; Chung, L.; Fierlbeck, G.; Lakshminarayanan, S.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Subcutaneous Tocilizumab in Adults with Systemic Sclerosis (FaSScinate): A Phase 2, Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 2630–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamata, K.; Asano, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Nakamura, K.; Noda, S.; Aozasa, N.; Toyama, T.; Takahashi, T.; et al. Increased Expression of Chemerin in Endothelial Cells Due to Fli1 Deficiency May Contribute to the Development of Digital Ulcers in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Fleming, J.; Pritchard, D.K.; Amon, L.M.; Xue, J.; Arnett, H.A.; Chen, G.; Breen, P.; Buckner, J.H.; Molitor, J.A.; et al. Combined Analysis of Monocyte and Lymphocyte Messenger RNA Expression with Serum Protein Profiles in Patients with Scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1465–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Asano, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Yamashita, T.; Saigusa, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Tamaki, Z.; et al. A Potential Contribution of Antimicrobial Peptide LL-37 to Tissue Fibrosis and Vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2016, 175, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Peck, A.; Santer, D.; Patole, P.; Schwartz, S.M.; Molitor, J.A.; Arnett, F.C.; Elkon, K.B. Induction of Interferon-Alpha by Scleroderma Sera Containing Autoantibodies to Topoisomerase I: Association of Higher Interferon-Alpha Activity with Lung Fibrosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 2163–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, C.M.; Silman, A.J.; Herrick, A.I.; Denton, C.P.; Wilson, H.; Newman, J.; Pompon, L.; Shi-Wen, X. Interferon-Alpha Does Not Improve Outcome at One Year in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Scleroderma: Results of a Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hügle, T.; Gratzl, S.; Daikeler, T.; Frey, D.; Tyndall, A.; Walker, U.A. Sclerosing Skin Disorders in Association with Multiple Sclerosis. Coincidence, Underlying Autoimmune Pathology or Interferon Induced? Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelidou, S.-H.; Tsifetaki, N.; Giannopoulos, S.; Deretzi, G.; Voulgari, P.; Kyritsis, A. Multiple Sclerosis Associated with Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatol. Int. 2007, 27, 771–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, A.; Sensi, F.; Barrella, M.; Francia, A. Systemic Sclerosis and Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahara, H.; Kojima, A.; Hirokawa, T.; Oyama, T.; Naganuma, A.; Maruta, S.; Okada, K.; Ban, S.; Yoshida, K.; Takagi, H.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis after Interferon Alphacon-1 Therapy for Hepatitis C. Intern. Med. 2007, 46, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteban, I.; Vilardell, M.R.; Solans, J.A. Bosch. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22, 625–628. [Google Scholar]
- Beretta, L.; Caronni, M.; Vanoli, M.; Scorza, R. Systemic Sclerosis after Interferon-Alfa Therapy for Myeloproliferative Disorders. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 385–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pammer, J.; Reinisch, C.; Birner, P.; Pogoda, K.; Sturzl, M.; Tschachler, E. Interferon-Alpha Prevents Apoptosis of Endothelial Cells after Short-Term Exposure but Induces Replicative Senescence after Continuous Stimulation. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ah Kioon, M.D.; Tripodo, C.; Fernandez, D.; Kirou, K.A.; Spiera, R.F.; Crow, M.K.; Gordon, J.K.; Barrat, F.J. Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells Promote Systemic Sclerosis with a Key Role for TLR8. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaam8458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, B.H.; Silva, I.S.; Mendes, A.; Leite-Pinheiro, F.; Paton, A.W.; Paton, J.C.; Duarte, I.F.; Pierre, P.; Almeida, C.R. Promoting ER Stress in a Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Line Drives Fibroblast Activation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2025, 23, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.J.; Krieg, T.; Distler, J.; Distler, O. Overview of Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48 (Suppl. S3), iii3–iii7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y. Future Treatments in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 54–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Sato, S. Vasculopathy in Scleroderma. Semin. Immunopathol. 2015, 37, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, R.J.; Freemont, A.J.; Jones, C.J.; Hoyland, J.; Fielding, P. Sequential Dermal Microvascular and Perivascular Changes in the Development of Scleroderma. J. Pathol. 1992, 166, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgonc, R.; Gruschwitz, M.S.; Dietrich, H.; Recheis, H.; Gershwin, M.E.; Wick, G. Endothelial Cell Apoptosis Is a Primary Pathogenetic Event Underlying Skin Lesions in Avian and Human Scleroderma. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 98, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Gordon, S.M.; Waldman, M.; Edison, J.D.; Little, D.J.; Stitt, R.S.; Bailey, W.T.; Hughes, J.B.; Olson, S.W. Autoantibodies Are Present before the Clinical Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihn, H. Scleroderma, Fibroblasts, Signaling, and Excessive Extracellular Matrix. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2005, 7, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Fioretto, B.S.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Manetti, M. New Insights into Profibrotic Myofibroblast Formation in Systemic Sclerosis: When the Vascular Wall Becomes the Enemy. Life 2021, 11, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Asano, Y.; Amiya, E.; Hatano, M.; Tamaki, Z.; Takata, M.; Ozeki, A.; Watanabe, A.; Kawarasaki, S.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. Clinical Correlation of Brachial Artery Flow-Mediated Dilation in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2014, 24, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerinic, M.M.; Valentini, G.; Sorano, G.G.; D’Angelo, S.; Cuomo, G.; Fenu, L.; Generini, S.; Cinotti, S.; Morfini, M.; Pignone, A.; et al. Blood Coagulation, Fibrinolysis, and Markers of Endothelial Dysfunction in Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 32, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihn, H. Autocrine TGF-Beta Signaling in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Sclerosis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 49, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Kelley, K.; Melichian, D.S.; Tamaki, Z.; Fang, F.; Su, Y.; Feng, G.; Pope, R.M.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Mutlu, G.M.; et al. Toll-like Receptor 4 Signaling Augments Transforming Growth Factor-β Responses: A Novel Mechanism for Maintaining and Amplifying Fibrosis in Scleroderma. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 192–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahaleh, M. Raynaud’s Phenomenon and Vascular Disease in Scleroderma. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 1994, 6, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourkina, E.; Bonner, M.; Oates, J.; Hofbauer, A.; Richard, M.; Znoyko, S.; Visconti, R.P.; Zhang, J.; Hatfield, C.M.; Silver, R.M.; et al. Altered Monocyte and Fibrocyte Phenotype and Function in Scleroderma Interstitial Lung Disease: Reversal by Caveolin-1 Scaffolding Domain Peptide. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2011, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitorowicz-Buniak, J.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.; Stratton, R. Partially Evoked Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Is Associated with Increased TGFβ Signaling within Lesional Scleroderma Skin. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0134092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, F.A.; Piera-Velazquez, S.; Farber, J.L.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Jiménez, S.A. Endothelial Cells Expressing Endothelial and Mesenchymal Cell Gene Products in Lung Tissue from Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manetti, M.; Romano, E.; Rosa, I.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; De Paulis, A.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Contributes to Endothelial Dysfunction and Dermal Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangoni, R.G.; Korman, B.D.; Wei, J.; Wood, T.A.; Graham, L.V.; Whitfield, M.L.; Scherer, P.E.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Varga, J. Myofibroblasts in Murine Cutaneous Fibrosis Originate from Adiponectin-Positive Intradermal Progenitors: Adipocyte-Myofibroblast Transition in Skin Fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1062–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruschwitz, M.; Müller, P.U.; Sepp, N.; Hofer, E.; Fontana, A.; Wick, G. Transcription and Expression of Transforming Growth Factor Type Beta in the Skin of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis: A Mediator of Fibrosis? J. Investig. Dermatol. 1990, 94, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querfeld, C.; Eckes, B.; Huerkamp, C.; Krieg, T.; Sollberg, S. Expression of TGF-Beta 1, -Beta 2 and -Beta 3 in Localized and Systemic Scleroderma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1999, 21, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulozik, M.; Hogg, A.; Lankat-Buttgereit, B.; Krieg, T. Co-Localization of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 2 with Alpha 1(I) Procollagen MRNA in Tissue Sections of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Kubo, M.; Tamaki, K. Impaired Smad7-Smurf-Mediated Negative Regulation of TGF-Beta Signaling in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Jinnin, M.; Mimura, Y.; Tamaki, K. Increased Expression of Integrin Alpha(v)Beta3 Contributes to the Establishment of Autocrine TGF-Beta Signaling in Scleroderma Fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 7708–7718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Kubo, M.; Tamaki, K. Increased Expression Levels of Integrin Alphavbeta5 on Scleroderma Fibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 1275–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Jinnin, M.; Mimura, Y.; Tamaki, K. Involvement of Alphavbeta5 Integrin-Mediated Activation of Latent Transforming Growth Factor Beta1 in Autocrine Transforming Growth Factor Beta Signaling in Systemic Sclerosis Fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2897–2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Jinnin, M.; Tamaki, K. Increased Expression of Integrin Alphavbeta5 Induces the Myofibroblastic Differentiation of Dermal Fibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimura, Y.; Ihn, H.; Jinnin, M.; Asano, Y.; Yamane, K.; Tamaki, K. Constitutive Thrombospondin-1 Overexpression Contributes to Autocrine Transforming Growth Factor-Beta Signaling in Cultured Scleroderma Fibroblasts. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Bao, D.; Liu, S.; Huang, J.; Guo, M.; Dai, B.; Ding, L.; Xie, S.; Meng, M.; Lv, C.; et al. ADAM Metallopeptidase Domain 19 Promotes Skin Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis via Neuregulin-1. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizzolini, C.; Rezzonico, R.; Ribbens, C.; Burger, D.; Wollheim, F.A.; Dayer, J.M. Inhibition of Type I Collagen Production by Dermal Fibroblasts upon Contact with Activated T Cells: Different Sensitivity to Inhibition between Systemic Sclerosis and Control Fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 2039–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizzolini, C.; Parel, Y.; De Luca, C.; Tyndall, A.; Akesson, A.; Scheja, A.; Dayer, J.-M. Systemic Sclerosis Th2 Cells Inhibit Collagen Production by Dermal Fibroblasts via Membrane-Associated Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha: Th2 Cells Inhibit Collagen Synthesis by Dermal Fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2003, 48, 2593–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichimura, Y.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Toyama, T.; Tada, Y.; Sugaya, M.; Sato, S.; et al. Progranulin Overproduction Due to Fli-1 Deficiency Contributes to the Resistance of Dermal Fibroblasts to Tumor Necrosis Factor in Systemic Sclerosis: THE ROLE OF PROGRANULIN IN SSc. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 3245–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergmann, C.; Chenguiti Fakhouri, S.; Trinh-Minh, T.; Filla, T.; Rius Rigau, A.; Ekici, A.B.; Merlevede, B.; Hallenberger, L.; Zhu, H.; Dees, C.; et al. Mutual Amplification of GLI2/Hedgehog and Transcription Factor JUN/AP-1 Signaling in Fibroblasts in Systemic Sclerosis: Potential Implications for Combined Therapies. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025, 77, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saigusa, R.; Asano, Y.; Taniguchi, T.; Hirabayashi, M.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, S.; Yamashita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; et al. Fli1-Haploinsufficient Dermal Fibroblasts Promote Skin-Localized Transdifferentiation of Th2-like Regulatory T Cells. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigusa, R.; Asano, Y.; Nakamura, K.; Hirabayashi, M.; Miura, S.; Yamashita, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis Dermal Fibroblasts Suppress Th1 Cytokine Production via Galectin-9 Overproduction Due to Fli1 Deficiency. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 1850–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, C.; Wang, S.-Y.; Sheban, F.; Zada, M.; Li, B.; Kharouf, F.; Peleg, H.; Aamar, S.; Yalin, A.; Kirschenbaum, D.; et al. LGR5 Expressing Skin Fibroblasts Define a Major Cellular Hub Perturbed in Scleroderma. Cell 2022, 185, 1373–1388.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Tsou, P.-S.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Plazyo, O.; Xing, X.; Kirma, J.; Wasikowski, R.; Hile, G.A.; Harms, P.W.; Jiang, Y.; et al. Systems-Based Identification of the Hippo Pathway for Promoting Fibrotic Mesenchymal Differentiation in Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Tabib, T.; Khanna, D.; Assassi, S.; Domsic, R.; Lafyatis, R. Single-Cell Transcriptomes and Chromatin Accessibility of Endothelial Cells Unravel Transcription Factors Associated with Dysregulated Angiogenesis in Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 83, 1335–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rius Rigau, A.; Li, Y.-N.; Matei, A.-E.; Györfi, A.-H.; Bruch, P.-M.; Koziel, S.; Devakumar, V.; Gabrielli, A.; Kreuter, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Characterization of Vascular Niche in Systemic Sclerosis by Spatial Proteomics. Circ. Res. 2024, 134, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zaba, L.C.; Satpathy, A.T.; Longmire, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, K.; Granja, J.; Guo, C.; Lin, J.; Li, R.; et al. Chromatin Accessibility Landscapes of Skin Cells in Systemic Sclerosis Nominate Dendritic Cells in Disease Pathogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Asano, Y.; Saigusa, R.; Yamashita, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Sato, S.; et al. Regulation of Skin Fibrosis by RALDH1-Producing Dermal Dendritic Cells via Retinoic Acid-Mediated Regulatory T Cell Induction: A Role in Scleroderma. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 97, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Saigusa, R.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hirabayashi, M.; Miyagawa, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Trojanowska, M.; Sato, S.; et al. Fli1 Deficiency Suppresses RALDH1 Activity of Dermal Dendritic Cells and Related Induction of Regulatory T Cells: A Possible Role in Scleroderma. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.M.; Lee, S.; Neely, J.; Hinchcliff, M.; Wolters, P.J.; Sirota, M. Gene Expression Meta-Analysis Reveals Aging and Cellular Senescence Signatures in Scleroderma-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1326922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, D.E.; Rai, R.; Khan, S.S.; Eren, M.; Ghosh, A.K. Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Is a Marker and a Mediator of Senescence. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 1446–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, T.; Jiang, C.; Liu, G.; Miyata, T.; Antony, V.; Thannickal, V.J.; Liu, R.-M. PAI-1 Regulation of TGF-Β1-Induced Alveolar Type II Cell Senescence, SASP Secretion, and SASP-Mediated Activation of Alveolar Macrophages. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eren, M.; Boe, A.E.; Murphy, S.B.; Place, A.T.; Nagpal, V.; Morales-Nebreda, L.; Urich, D.; Quaggin, S.E.; Budinger, G.R.S.; Mutlu, G.M.; et al. PAI-1-Regulated Extracellular Proteolysis Governs Senescence and Survival in Klotho Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7090–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.S.; Shah, S.J.; Klyachko, E.; Baldridge, A.S.; Eren, M.; Place, A.T.; Aviv, A.; Puterman, E.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; Heiman, M.; et al. A Null Mutation in SERPINE1 Protects against Biological Aging in Humans. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, eaao1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, Y. The Role of Fibrinolytic Regulators in Vascular Dysfunction of Systemic Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, Y. The UPA/UPAR System Orchestrates the Inflammatory Response, Vascular Homeostasis, and Immune System in Fibrosis Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancheeswaran, R.; Azam, A.; Black, C.; Dashwood, M.R. Localization of Endothelin-1 and Its Binding Sites in Scleroderma Skin. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicka, L.; Varga, J.; Christiano, A.M.; Iozzo, R.V.; Jimenez, S.A.; Uitto, J. Elevated Expression of Type VII Collagen in the Skin of Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Regulation by Transforming Growth Factor-Beta. J. Clin. Investig. 1994, 93, 1709–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distler, O.; Pap, T.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Meyringer, R.; Guiducci, S.; Landthaler, M.; Schölmerich, J.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, R.E.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; et al. Overexpression of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1 in Systemic Sclerosis: Role of Platelet-Derived Growth Factor and Effects on Monocyte Chemotaxis and Collagen Synthesis. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 2665–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.A.; Jeziorska, M.; Freemont, A.J.; Herrick, A.L. The Differential Expression of VEGF, VEGFR-2, and GLUT-1 Proteins in Disease Subtypes of Systemic Sclerosis. Hum. Pathol. 2006, 37, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distler, J.H.W.; Jüngel, A.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Michel, B.A.; Gay, R.E.; Sprott, H.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Chilla, M.; Reich, K.; Kalden, J.R.; et al. Expression of Interleukin-21 Receptor in Epidermis from Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Altered Expression Pattern of Keratinocytes in SSc. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 856–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aden, N.; Nuttall, A.; Shiwen, X.; de Winter, P.; Leask, A.; Black, C.M.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.J.; Stratton, R.J. Epithelial Cells Promote Fibroblast Activation via IL-1alpha in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2010, 130, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitorowicz-Buniak, J.; Shiwen, X.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.; Stratton, R. Abnormally Differentiating Keratinocytes in the Epidermis of Systemic Sclerosis Patients Show Enhanced Secretion of CCN2 and S100A9. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCoy, S.S.; Reed, T.J.; Berthier, C.C.; Tsou, P.-S.; Liu, J.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Khanna, D.; Kahlenberg, J.M. Scleroderma Keratinocytes Promote Fibroblast Activation Independent of Transforming Growth Factor Beta. Rheumatology 2017, 56, 1970–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Asano, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamura, K.; Saigusa, R.; Miura, S.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Hirabayashi, M.; Taniguchi, T.; et al. A Potential Contribution of Psoriasin to Vascular and Epithelial Abnormalities and Inflammation in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2018, 32, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigusa, R.; Yamashita, T.; Miura, S.; Hirabayashi, M.; Nakamura, K.; Miyagawa, T.; Fukui, Y.; Yoshizaki, A.; Sato, S.; Asano, Y. A Potential Contribution of Decreased Galectin-7 Expression in Stratified Epithelia to the Development of Cutaneous and Oesophageal Manifestations in Systemic Sclerosis. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, T.; Asano, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamura, K.; Saigusa, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Akamata, K.; et al. Epithelial Fli1 Deficiency Drives Systemic Autoimmunity and Fibrosis: Possible Roles in Scleroderma. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 1129–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Stawski, L.; Hant, F.; Highland, K.; Silver, R.; Szalai, G.; Watson, D.K.; Trojanowska, M. Endothelial Fli1 Deficiency Impairs Vascular Homeostasis: A Role in Scleroderma Vasculopathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1983–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, Y.; Markiewicz, M.; Kubo, M.; Szalai, G.; Watson, D.K.; Trojanowska, M. Transcription Factor Fli1 Regulates Collagen Fibrillogenesis in Mouse Skin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujor, A.M.; El Adili, F.; Parvez, A.; Marden, G.; Trojanowska, M. Fli1 Downregulation in Scleroderma Myeloid Cells Has Profibrotic and Proinflammatory Effects. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, T.; Miyagawa, T.; Toyama, S.; Yamashita, T.; Nakamura, K.; Saigusa, R.; Ichimura, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Toyama, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; et al. CXCL13 Produced by Macrophages Due to Fli1 Deficiency May Contribute to the Development of Tissue Fibrosis, Vasculopathy and Immune Activation in Systemic Sclerosis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.S.; Venanzi, E.S.; Klein, L.; Chen, Z.; Berzins, S.P.; Turley, S.J.; von Boehmer, H.; Bronson, R.; Dierich, A.; Benoist, C.; et al. Projection of an Immunological Self Shadow within the Thymus by the Aire Protein. Science 2002, 298, 1395–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathis, D.; Benoist, C. Aire. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 287–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saigusa, R.; Asano, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Nakamura, K.; Miura, S.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Sumida, H.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis Complicated with Localized Scleroderma-like Lesions Induced by Köbner Phenomenon. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The Human Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terui, H.; Yamasaki, K.; Wada-Irimada, M.; Onodera-Amagai, M.; Hatchome, N.; Mizuashi, M.; Yamashita, R.; Kawabe, T.; Ishii, N.; Abe, T.; et al. Staphylococcus Aureus Skin Colonization Promotes SLE-like Autoimmune Inflammation via Neutrophil Activation and the IL-23/IL-17 Axis. Sci. Immunol. 2022, 7, eabm9811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grice, E.A.; Segre, J.A. The Skin Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.E.; Franks, J.M.; Cai, G.; Mehta, B.K.; Wood, T.A.; Archambault, K.; Pioli, P.A.; Simms, R.W.; Orzechowski, N.; Arron, S.; et al. Microbiome Dysbiosis Is Associated with Disease Duration and Increased Inflammatory Gene Expression in Systemic Sclerosis Skin. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wei, J.; Varga, J. Understanding Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis: Shifting Paradigms, Emerging Opportunities. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 8, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.; Watt, F.M. Fibroblast Heterogeneity: Implications for Human Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shao, M.; Hepler, C.; Zi, Z.; Zhao, S.; An, Y.A.; Zhu, Y.; Ghaben, A.L.; Wang, M.-Y.; Li, N.; et al. Dermal Adipose Tissue Has High Plasticity and Undergoes Reversible Dedifferentiation in Mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 5327–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.; Marangoni, R.G. Systemic Sclerosis in 2016: Dermal White Adipose Tissue Implicated in SSc Pathogenesis: Systemic Sclerosis in 2016. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T. Importance of Adipocytokines in Obesity-Related Diseases. Horm. Res. 2003, 60 (Suppl. S3), 56–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masui, Y.; Asano, Y.; Shibata, S.; Noda, S.; Aozasa, N.; Akamata, K.; Yamada, D.; Tamaki, Z.; Tada, Y.; Sugaya, M.; et al. Serum Adiponectin Levels Inversely Correlate with the Activity of Progressive Skin Sclerosis in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis: Significance of Serum Adiponectin Levels in SSc. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2012, 26, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, Y.; Asano, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Shibata, S.; Akamata, K.; Aozasa, N.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; et al. Clinical Significance of Monitoring Serum Adiponectin Levels during Intravenous Pulse Cyclophosphamide Therapy in Interstitial Lung Disease Associated with Systemic Sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2013, 23, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, Y.; Asano, Y.; Shibata, S.; Noda, S.; Akamata, K.; Aozasa, N.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; et al. A Possible Contribution of Visfatin to the Resolution of Skin Sclerosis in Patients with Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis via a Direct Anti-Fibrotic Effect on Dermal Fibroblasts and Th1 Polarization of the Immune Response. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1239–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aozasa, N.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Noda, S.; Masui, Y.; Yamada, D.; Tamaki, Z.; Tada, Y.; Sugaya, M.; Kadono, T.; et al. Serum Apelin Levels: Clinical Association with Vascular Involvements in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Significance of Serum Apelin Levels in SSc. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, Y.; Asano, Y.; Akamata, K.; Aozasa, N.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Sumida, H.; et al. Serum Resistin Levels: A Possible Correlation with Pulmonary Vascular Involvement in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyama, T.; Asano, Y.; Takahashi, T.; Aozasa, N.; Akamata, K.; Noda, S.; Taniguchi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Sumida, H.; Tamaki, Z.; et al. Clinical Significance of Serum Retinol Binding Protein-4 Levels in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Significance of Serum RBP4 Levels in SSc. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, T.; Asano, Y.; Noda, S.; Aozasa, N.; Akamata, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Sumida, H.; Kuwano, Y.; et al. A Possible Contribution of Lipocalin-2 to the Development of Dermal Fibrosis, Pulmonary Vascular Involvement and Renal Dysfunction in Systemic Sclerosis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 173, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Asano, Y.; Saigusa, R.; Yamashita, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Tamaki, Z.; Tada, Y.; et al. Serum Omentin Levels: A Possible Contribution to Vascular Involvement in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, S.; Asano, Y.; Saigusa, R.; Yamashita, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Takahashi, T.; Ichimura, Y.; Toyama, T.; Tamaki, Z.; Tada, Y.; et al. Serum Vaspin Levels: A Possible Correlation with Digital Ulcers in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2015, 42, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakota, K.; Wei, J.; Carns, M.; Hinchcliff, M.; Lee, J.; Whitfield, M.L.; Sodin-Semrl, S.; Varga, J. Levels of Adiponectin, a Marker for PPAR-Gamma Activity, Correlate with Skin Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis: Potential Utility as Biomarker? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomčík, M.; Arima, K.; Hulejová, H.; Kuklová, M.; Filková, M.; Braun, M.; Beláček, J.; Novák, M.; Bečvář, R.; Vencovský, J.; et al. Adiponectin Relation to Skin Changes and Dyslipidemia in Systemic Sclerosis. Cytokine 2012, 58, 165–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, H.; Jinnin, M.; Muchemwa, F.C.; Makino, T.; Kajihara, I.; Makino, K.; Honda, N.; Sakai, K.; Fukushima, S.; Ihn, H. Adiponectin Expression Is Decreased in the Involved Skin and Sera of Diffuse Cutaneous Scleroderma Patients: Letter to the Editor. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 20, 764–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marangoni, R.G.; Masui, Y.; Fang, F.; Korman, B.; Lord, G.; Lee, J.; Lakota, K.; Wei, J.; Scherer, P.E.; Otvos, L.; et al. Adiponectin Is an Endogenous Anti-Fibrotic Mediator and Therapeutic Target. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Lakota, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Yoshizaki, A.; Sato, S.; Hong, W.; Zhou, X.; Sodin-Semrl, S.; Fang, F.; Asano, Y.; et al. An Orally-Active Adiponectin Receptor Agonist Mitigates Cutaneous Fibrosis, Inflammation and Microvascular Pathology in a Murine Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjogren, R. Gastrointestinal Features of Scleroderma. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 1996, 8, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poirier, T.; Rankin, G. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Progressive Systemic Scleroderma Based on a Review of 364 Cases. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1972, 58, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, M.A.; Rose, S.; Reynolds, J.C. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Scleroderma. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 1996, 22, 797–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, A. Current Management of the Gastrointestinal Complications of Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lock, G.; Holstege, A.; Lang, B.; Schölmerich, J. Gastrointestinal Manifestations of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1997, 92, 763–771. [Google Scholar]
- Malandrini, A.; Selvi, E.; Villanova, M.; Berti, G.; Sabadini, L.; Salvadori, C.; Gambelli, S.; De Stefano, R.; Vernillo, R.; Marcolongo, R.; et al. Autonomic Nervous System and Smooth Muscle Cell Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: Ultrastructural Study of 3 Cases. J. Rheumatol. 2000, 27, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Lepri, G.; Guiducci, S.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Giani, I.; Bruni, C.; Blagojevic, J.; Carnesecchi, G.; Radicati, A.; Pucciani, F.; Marco, M.-C. Evidence for Oesophageal and Anorectal Involvement in Very Early Systemic Sclerosis (VEDOSS): Report from a Single VEDOSS/EUSTAR Centre. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 124–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, S.; Thumshirn, M.; Wiste, J.; Camilleri, M. Clinical and Upper Gastrointestinal Motility Features in Systemic Sclerosis and Related Disorders. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, S.; Hot, A.; Fabien, N.; Cordier, J.-F.; Miossec, P.; Ninet, J.; Mion, F.; Réseau Sclérodermie des Hospices Civils de Lyon. Esophageal Dysmotility Associated with Systemic Sclerosis: A High-Resolution Manometry Study: Systemic Sclerosis and Esophageal HRM. Dis. Esophagus 2011, 24, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, N.M.; Boonstra, M.; Fretheim, H.; Brunborg, C.; Midtvedt, Ø.; Garen, T.; Molberg, Ø.; Huizinga, T.W.J.; de Vries-Bouwstra, J.K.; Hoffman-Vold, A.-M. Gastrointestinal Symptom Severity and Progression in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4024–4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaker, E.Y.; Kuldau, J.G.; Verne, G.N.; Ross, S.O.; Sallustio, J.E. Myenteric Neuronal Antibodies in Scleroderma: Passive Transfer Evokes Alterations in Intestinal Myoelectric Activity in a Rat Model. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1999, 133, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsumoto, I.; Nishimagi, E.; Satoh, T.; Kuwana, M.; Sumida, T.; Hara, M. Muscarinic-3 Acetylcholine Receptor Autoantibody in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Contribution to Severe Gastrointestinal Tract Dysmotility. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Mehendiratta, V.; Del Galdo, F.; Jimenez, S.A.; Cohen, S.; DiMarino, A.J.; Rattan, S. Immunoglobulins from Scleroderma Patients Inhibit the Muscarinic Receptor Activation in Internal Anal Sphincter Smooth Muscle Cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2009, 297, G1206–G1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafaja, S.; Valera, I.; Divekar, A.A.; Saggar, R.; Abtin, F.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; Singh, R.R. PDCs in Lung and Skin Fibrosis in a Bleomycin-Induced Model and Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. JCI Insight 2018, 3, e98380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas, R.O.; Aprile, L.R.O. Esophageal Striated Muscle Contractions in Patients with Gastroesophageal Reflux Symptoms. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2002, 47, 2586–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miwa, H.; Kondo, T.; Oshima, T. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease-Related and Functional Heartburn: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2016, 32, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessein, P.H.; Joffe, B.I.; Metz, R.M.; Millar, D.L.; Lawson, M.; Stanwix, A.E. Autonomic Dysfunction in Systemic Sclerosis: Sympathetic Overactivity and Instability. Am. J. Med. 1992, 93, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Wu, C.; Zeng, X.; Wang, Q. The Role of Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis of Rheumatic Diseases. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, F.; Shoenfeld, Y. The Microbiome in Autoimmune Diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 195, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosser, E.C.; Mauri, C. A Clinical Update on the Significance of the Gut Microbiota in Systemic Autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellocchi, C.; Volkmann, E.R. Update on the Gastrointestinal Microbiome in Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2018, 20, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R. Intestinal Microbiome in Scleroderma: Recent Progress. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2017, 29, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fretheim, H.; Chung, B.K.; Didriksen, H.; Bækkevold, E.S.; Midtvedt, Ø.; Brunborg, C.; Holm, K.; Valeur, J.; Tennøe, A.H.; Garen, T.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Systemic Sclerosis: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Randomized Pilot Trial. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A. Changes in Causes of Death in Systemic Sclerosis, 1972-2002. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 940–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and Predicting Mortality from Systemic Sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic Definitions and Updated Clinical Classification of Pulmonary Hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, A.C.; Cordeiro, A.; Loureiro, M.J.; Ferreira, F. Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease: A Probably Underdiagnosed Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.J.; Naranjo, M.; Ayoub, N.; Housten, T.; Hsu, S.; Balasubramanian, A.; Simpson, C.E.; Damico, R.L.; Mathai, S.C.; Kolb, T.M.; et al. Improved Survival for Patients with Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: The Johns Hopkins Registry. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillén-Del-Castillo, A.; Meseguer, M.L.; Fonollosa-Plá, V.; Giménez, B.S.; Colunga-Argüelles, D.; Revilla-López, E.; Rubio-Rivas, M.; Ropero, M.J.C.; Argibay, A.; Barberà, J.; et al. Impact of Interstitial Lung Disease on the Survival of Systemic Sclerosis with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamanian, R.T.; Badesch, D.; Chung, L.; Domsic, R.T.; Medsger, T.; Pinckney, A.; Keyes-Elstein, L.; D’Aveta, C.; Spychala, M.; White, R.J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of B-Cell Depletion with Rituximab for the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 204, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liem, S.I.E.; Boonstra, M.; le Cessie, S.; Riccardi, A.; Airo, P.; Distler, O.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Caimmi, C.; Siegert, E.; Allanore, Y.; et al. Sex-Specific Risk of Anti-Topoisomerase Antibodies on Mortality and Disease Severity in Systemic Sclerosis: 10-Year Analysis of the Leiden CCISS and EUSTAR Cohorts. Lancet Rheumatol. 2022, 4, e699–e709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Rivas, M.; Homs, N.A.; Cuartero, D.; Corbella, X. The Prevalence and Incidence Rate of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, Z.; Proudman, S.; Morrisroe, K.; Stevens, W.; Hansen, D.; Nikpour, M. Screening for the Early Detection of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Long-Term Outcomes. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 495–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraban, A.M.; Enache, R.; Predescu, L.; Platon, P.; Constantinescu, T.; Mihai, C.; Coman, I.M.; Ginghina, C.; Jurcuţ, R. Pulmonary Veno-Occlusive Disease: A Rare Cause of Pulmonary Hypertension in Systemic Sclerosis. Case Presentation and Review of the Literature. Rom. J. Intern. Med. 2015, 53, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, R.; Hudson, M.; Lo, E.; Baron, M.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Clinical Decision Rule to Predict the Presence of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2012, 64, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, B. Interstitial Lung Disease in Scleroderma. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2003, 29, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihtyanova, S.I.; Schreiber, B.E.; Ong, V.H.; Rosenberg, D.; Moinzadeh, P.; Coghlan, J.G.; Wells, A.U.; Denton, C.P. Prediction of Pulmonary Complications and Long-Term Survival in Systemic Sclerosis: Pulmonary Complications and Survival in SSc. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.; Domsic, R.T.; Lucas, M.; Fertig, N.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. A Clinical and Serologic Comparison of African American and Caucasian Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2986–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, V.K.; Wirz, E.G.; Allanore, Y.; Rossbach, P.; Riemekasten, G.; Hachulla, E.; Distler, O.; Airò, P.; Carreira, P.E.; Balbir Gurman, A.; et al. Incidences and Risk Factors of Organ Manifestations in the Early Course of Systemic Sclerosis: A Longitudinal EUSTAR Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojić, P.; Damjanov, N. Different Clinical Features in Patients with Limited and Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 25, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, Y.; Ihn, H.; Yamane, K.; Kubo, M.; Tamaki, K. The Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anti-U1 RNA Antibodies in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 120, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, A.; Davidyock, T.; Ferguson, L.T.; Ieong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Simms, R.W. Changes in Forced Vital Capacity over Time in Systemic Sclerosis: Application of Group-Based Trajectory Modelling. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1464–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, V.D.; Conte, C.; Owens, G.R.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Severe Restrictive Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1994, 37, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, C.; Knight, C.; Lunt, M.; Black, C.M.; Silman, A.J. Predictors of End Stage Lung Disease in a Cohort of Patients with Scleroderma. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2003, 62, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouros, D.; Wells, A.U.; Nicholson, A.G.; Colby, T.V.; Polychronopoulos, V.; Pantelidis, P.; Haslam, P.L.; Vassilakis, D.A.; Black, C.M.; du Bois, R.M. Histopathologic Subsets of Fibrosing Alveolitis in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis and Their Relationship to Outcome. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 165, 1581–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.S.; Yoo, B.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, E.K.; Lim, C.M.; Lee, S.D.; Koh, Y.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, W.D.; Colby, T.V.; et al. The Major Histopathologic Pattern of Pulmonary Fibrosis in Scleroderma Is Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffuse Lung Dis. 2002, 19, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, A.; Swigris, J.J.; Groshong, S.D.; Cool, C.D.; Sahin, H.; Lynch, D.A.; Curran-Everett, D.; Gillis, J.Z.; Meehan, R.T.; Brown, K.K. Clinically Significant Interstitial Lung Disease in Limited Scleroderma: Histopathology, Clinical Features, and Survival. Chest 2008, 134, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winstone, T.A.; Assayag, D.; Wilcox, P.G.; Dunne, J.V.; Hague, C.J.; Leipsic, J.; Collard, H.R.; Ryerson, C.J. Predictors of Mortality and Progression in Scleroderma-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Systematic Review. Chest 2014, 146, 422–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beon, M.; Harley, R.A.; Wessels, A.; Silver, R.M.; Ludwicka-Bradley, A. Myofibroblast Induction and Microvascular Alteration in Scleroderma Lung Fibrosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2004, 22, 733–742. [Google Scholar]
- Savarino, E.; Bazzica, M.; Zentilin, P.; Pohl, D.; Parodi, A.; Cittadini, G.; Negrini, S.; Indiveri, F.; Tutuian, R.; Savarino, V.; et al. Gastroesophageal Reflux and Pulmonary Fibrosis in Scleroderma: A Study Using PH-Impedance Monitoring: A Study Using PH-Impedance Monitoring. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 408–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appel, J.Z., 3rd; Lee, S.M.; Hartwig, M.G.; Li, B.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Cantu, E., 3rd; Yoon, Y.; Lin, S.S.; Parker, W.; Davis, R.D. Characterization of the Innate Immune Response to Chronic Aspiration in a Novel Rodent Model. Respir. Res. 2007, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christmann, R.B.; Wells, A.U.; Capelozzi, V.L.; Silver, R.M. Gastroesophageal Reflux Incites Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis: Clinical, Radiologic, Histopathologic, and Treatment Evidence. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 40, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, R.B.C.; Borges, C.T.L.; Capelozzi, V.L.; Parra, E.R.; Jatene, F.B.; Kavakama, J.; Kairalla, R.A.; Bonfá, E. Centrilobular Fibrosis: An Underrecognized Pattern in Systemic Sclerosis. Respiration 2009, 77, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venalis, P.; Kumánovics, G.; Schulze-Koops, H.; Distler, A.; Dees, C.; Zerr, P.; Palumbo-Zerr, K.; Czirják, L.; Mackevic, Z.; Lundberg, I.E.; et al. Cardiomyopathy in Murine Models of Systemic Sclerosis: Histopathologic Features of Cardiomyopathy in SSc. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 508–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Meune, C. Primary Myocardial Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: Evidence for a Microvascular Origin. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2010, 28, S48–S53. [Google Scholar]
- Hachulla, A.-L.; Launay, D.; Gaxotte, V.; de Groote, P.; Lamblin, N.; Devos, P.; Hatron, P.-Y.; Beregi, J.-P.; Hachulla, E. Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Systemic Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Observational Study of 52 Patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1878–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesselstrand, R.; Scheja, A.; Akesson, A. Mortality and Causes of Death in a Swedish Series of Systemic Sclerosis Patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1998, 57, 682–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Vlachoyiannopoulos, P.G.; Haidich, A.-B.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Lucas, M.; Michet, C.J.; Kuwana, M.; Yasuoka, H.; van den Hoogen, F.; Te Boome, L.; et al. Mortality in Systemic Sclerosis: An International Meta-Analysis of Individual Patient Data. Am. J. Med. 2005, 118, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Severe Organ Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis with Diffuse Scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2437–2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahan, A.; Coghlan, G.; McLaughlin, V. Cardiac Complications of Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2009, 48 (Suppl. S3), iii45–iii48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Meune, C.; Kahan, A. Outcome Measures for Heart Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2008, 47 (Suppl. S5), v51–v53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferri, C.; Valentini, G.; Cozzi, F.; Sebastiani, M.; Michelassi, C.; La Montagna, G.; Bullo, A.; Cazzato, M.; Tirri, E.; Storino, F.; et al. Systemic Sclerosis: Demographic, Clinical, and Serologic Features and Survival in 1,012 Italian Patients. Medicine 2002, 81, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purevsuren, M.; Uehara, M.; Ishizuka, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Shimbo, M.; Kakuda, N.; Ishii, S.; Sumida, H.; Miyazaki, M.; Yamashita, T.; et al. Native T1 Mapping in Early Diffuse and Limited Systemic Sclerosis, and Its Association with Diastolic Function. J. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulkley, B.H.; Ridolfi, R.L.; Salyer, W.R.; Hutchins, G.M. Myocardial Lesions of Progressive Systemic Sclerosis. A Cause of Cardiac Dysfunction. Circulation 1976, 53, 483–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belloli, L.; Carlo-Stella, N.; Ciocia, G.; Chiti, A.; Massarotti, M.; Marasini, B. Myocardial Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 1070–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Desai, C.S.; Lee, D.C.; Shah, S.J. Systemic Sclerosis and the Heart: Current Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzelepis, G.E.; Kelekis, N.L.; Plastiras, S.C.; Mitseas, P.; Economopoulos, N.; Kampolis, C.; Gialafos, E.J.; Moyssakis, I.; Moutsopoulos, H.M. Pattern and Distribution of Myocardial Fibrosis in Systemic Sclerosis: A Delayed Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 3827–3836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekakis, J.; Mavrikakis, M.; Emmanuel, M.; Prassopoulos, V.; Papazoglou, S.; Papamichael, C.; Moulopoulou, D.; Kostamis, P.; Stamatelopoulos, S.; Moulopoulos, S. Cold-Induced Coronary Raynaud’s Phenomenon in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 1998, 16, 135–140. [Google Scholar]
- Meune, C.; Allanore, Y.; Devaux, J.-Y.; Dessault, O.; Duboc, D.; Weber, S.; Kahan, A. High Prevalence of Right Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction in Early Systemic Sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2004, 31, 1941–1945. [Google Scholar]
- Kahan, A.; Devaux, J.Y.; Amor, B.; Menkès, C.J.; Weber, S.; Venot, A.; Strauch, G. The Effect of Captopril on Thallium 201 Myocardial Perfusion in Systemic Sclerosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1990, 47, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, D.; Kahan, A.; Maziere, B.; Loc’h, C.; Crouzel, C.; Menkès, C.J.; Amor, B.; Strauch, G.; Guérin, F.; Syrota, A. The Effect of Nifedipine on Myocardial Perfusion and Metabolism in Systemic Sclerosis. A Positron Emission Tomographic Study. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahan, A.; Jy, D.; Amor, B.; Menkes, C.-J.; Weber, S.; Guerin, F.; Venot, A.; Strauch, G. Pharmacodynamic Effect of Nicardipine on Left Ventricular Function in Systemic Sclerosis. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1990, 15, 249–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigante, A.; Leodori, G.; Pellicano, C.; Villa, A.; Rosato, E. Assessment of Kidney Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis: From Scleroderma Renal Crisis to Subclinical Renal Vasculopathy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 364, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewandowski, B.; Domysławska, I.; Klimiuk, P.A.; Sierakowski, S. Kidney Crisis in Systemic Sclerosis. Rocz. Akad. Med. Bialymst. 2005, 50 (Suppl. S1), 294–296. [Google Scholar]
- Denton, C.P.; Lapadula, G.; Mouthon, L.; Müller-Ladner, U. Renal Complications and Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Rheumatology 2009, 48 (Suppl. S3), iii32–iii35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D. Kidney Involvement in Systemic Sclerosis. Presse Med. 2014, 43, e305–e314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, A.; Ong, V.H.; Denton, C.P. Renal Disease and Systemic Sclerosis: An Update on Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 64, 378–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, M.; Wang, R.J.; Yangco, D.T.; Sharp, G.C.; Komatireddy, G.R.; Hoffman, R.W. Analysis of Autoantibodies against RNA Polymerases Using Immunoaffinity-Purifed RNA Polymerase I, II, and III Antigen in an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Clin. Immunol. Immunopathol. 1998, 89, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steen, V.D. Autoantibodies in Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 35, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, M.; Baron, M.; Hudson, M.; Burlingame, R.W.; Fritzler, M.J. Antibodies to RNA Polymerase III in Systemic Sclerosis Detected by ELISA. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 34, 1528–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Haviv, Y.S.; Safadi, R. Normotensive Scleroderma Renal Crisis: Case Report and Review of the Literature. Ren. Fail. 1998, 20, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steen, V.D.; Medsger, T.A., Jr. Case-Control Study of Corticosteroids and Other Drugs That Either Precipitate or Protect from the Development of Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, T.; Soumura, M.; Danno, K.; Kaji, K.; Kondo, M.; Hirata, K.; Nakazawa, J.; Uzu, T.; Nishio, Y.; Kashiwagi, A. Scleroderma Renal Crisis in a Patient with Anticentromere Antibody-Positive Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2006, 16, 309–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Sanada, M.; Kashiwagi, A. Is Scleroderma Renal Crisis with Anti-Centromere Antibody-Positive Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis Overlooked in Patients with Hypertension and/or Renal Dysfunction? Nephrology 2008, 13, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batal, I.; Domsic, R.T.; Shafer, A.; Medsger, T.A., Jr.; Kiss, L.P.; Randhawa, P.; Bastacky, S. Renal Biopsy Findings Predicting Outcome in Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, M.; Baron, M.; Tatibouet, S.; Furst, D.E.; Khanna, D.; International Scleroderma Renal Crisis Study Investigators. Exposure to ACE Inhibitors Prior to the Onset of Scleroderma Renal Crisis-Results from the International Scleroderma Renal Crisis Survey. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2014, 43, 666–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, N.; Chiesa-Vottero, A.; Chatterjee, S. Scleroderma Renal Crisis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2015, 44, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bütikofer, L.; Varisco, P.A.; Distler, O.; Kowal-Bielecka, O.; Allanore, Y.; Riemekasten, G.; Villiger, P.M.; Adler, S.; EUSTAR collaborators. ACE Inhibitors in SSc Patients Display a Risk Factor for Scleroderma Renal Crisis-a EUSTAR Analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, J.E.; Denton, C.P.; Johnson, S.R.; Fernandez-Codina, A.; Hudson, M.; Nevskaya, T. State-of-the-Art Evidence in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2023, 19, 212–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, C.; Allanore, Y. An Update on Targeted Therapies in Systemic Sclerosis Based on a Systematic Review from the Last 3 Years. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukiri, H.; Volkmann, E.R. Current Advances in the Treatment of Systemic Sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2022, 64, 102211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volkmann, E.R.; Andréasson, K.; Smith, V. Systemic Sclerosis. Lancet 2023, 401, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takahashi, T.; Asano, Y. The Evolving Landscape of Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis: From Foundational Mechanisms to Organ-Specific Modifiers. Sclerosis 2025, 3, 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020020
Takahashi T, Asano Y. The Evolving Landscape of Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis: From Foundational Mechanisms to Organ-Specific Modifiers. Sclerosis. 2025; 3(2):20. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020020
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakahashi, Toshiya, and Yoshihide Asano. 2025. "The Evolving Landscape of Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis: From Foundational Mechanisms to Organ-Specific Modifiers" Sclerosis 3, no. 2: 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020020
APA StyleTakahashi, T., & Asano, Y. (2025). The Evolving Landscape of Systemic Sclerosis Pathogenesis: From Foundational Mechanisms to Organ-Specific Modifiers. Sclerosis, 3(2), 20. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020020






