Systematic Review of Environmental Factors Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Synthesis of Epidemiological Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Methodology
2.2. Keywords and Search Strategy
- Core Disease Keywords: “Multiple Sclerosis”, “MS”, “Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis”, and “LOMS”.
- Environmental Exposure Keywords: “Smoking”, “Vitamin D Deficiency”, “Air Pollution”, “Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)”, “Passive Smoking”, and “Geographical Factors”.
- Risk Factors and Associations: “Risk Factors”, “Etiology”, “Gene-Environment Interaction”, and “Autoimmunity”.
- Demographics Keywords: “Adults”, “Middle-Aged”, and “Elderly”.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3.1. Inclusion Criteria
- Peer-reviewed publications.
- Adults aged ≥50 years diagnosed with late-onset multiple sclerosis (LOMS).
- Observational studies (cohort, case-control, and cross-sectional), systematic reviews, and meta-analyses.Quantitative outcomes such as odds ratios or relative risks related to environmental exposure (e.g., smoking, infections, and diet).
2.3.2. Exclusion Criteria
- Studies were excluded if they lacked a clearly defined study type, such as cohort or case–control designs.
- Exclusion applied to studies that failed to specify diagnostic criteria for LOMS or omitted the age threshold for defining LOMS.
- Studies were excluded if they provided insufficient details on how environmental exposure was measured.
- Exclusion applied to studies that omitted critical outcome data, such as odds ratios, hazard ratios, or risk estimates.
- Studies were excluded if they lacked follow-up duration details or failed to describe participant-tracking methods.
2.4. Data Extraction
- Study characteristics: author, year, location, design.
- Population details: sample size, demographics, diagnostic criteria.
- Exposure assessment: type and measurement methods.
- Outcomes: odds ratios, relative risks, and prevalence rates.Quality assessment scores.
2.5. Quality Assessment
- Selection: representativeness of participants and exposure/outcome ascertainment.
- Comparability: adjustments for confounders.Outcome: assessment methods and follow-up adequacy.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Protocol Registration
2.8. Focus Question and Framework
- Population: adults ≥ 50 years with LOMS.
- Interventions/Exposures: environmental factors like smoking, vitamin D deficiency, infections, and pollution.
- Comparisons: exposed vs. unexposed groups and comparisons with early-onset MS.
- Outcomes: LOMS risk and prevalence metrics.
- Study Design: observational studies and systematic reviews.
3. Results
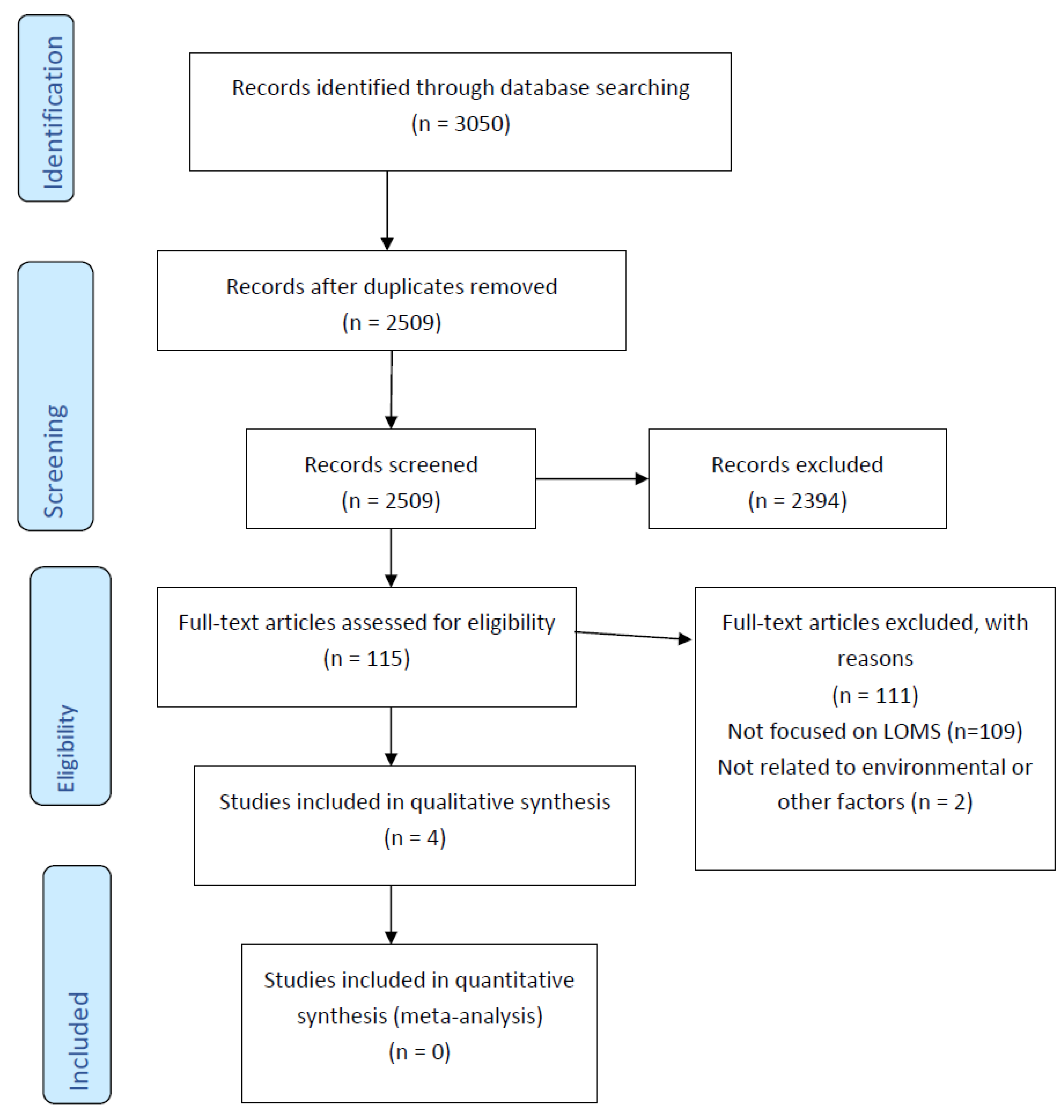
3.1. Identification of Studies
3.2. Screening
3.3. Eligibility Assessment
3.4. Studies Included
3.5. Study Characteristics
3.6. Summary of Findings
- Risk Factors: Smoking, waterpipe smoking, drug abuse, and alcohol consumption were strongly associated with an increased LOMS risk.
- Neutral Factors: Diet quality had no significant association with LOMS development.
- Protective Factors: Evidence for DMT efficacy was inconclusive, with no significant reduction in disability progression or mortality demonstrated for elderly MS patients.
- Clinical Features: The presentation of LOMS varied regionally, with paresthesia being the predominant symptom in South Indian patients.
3.7. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
Risk of Bias Within Studies
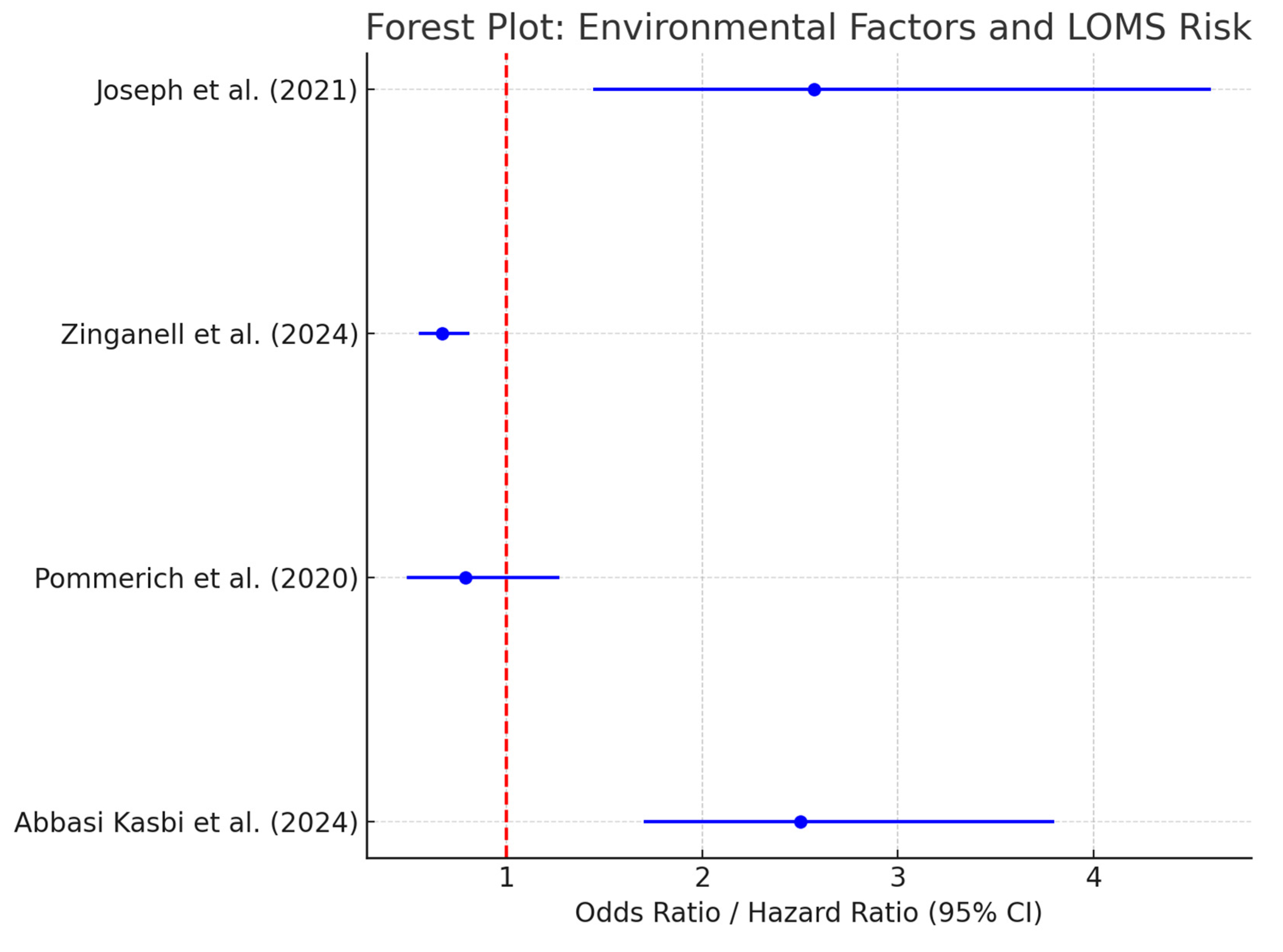
3.8. Primary Outcomes
- Substance Use and LOMS (Abbasi Kasbi et al) [51]:
- Cigarette smoking: OR = 2.5 (95% CI: 1.7–3.8).
- Waterpipe smoking: OR = 1.9 (95% CI: 1.3–2.7).
- Drug abuse: OR = 3.2 (95% CI: 2.1–4.9).
- Alcohol consumption: OR = 1.8 (95% CI: 1.2–2.5).
- 2.
- Diet Quality and LOMS Risk (Pommerich et al.) [19]:
- There is no significant association between diet quality and LOMS risk.
- The adjusted HR for the highest versus lowest tertile of diet quality was 0.79 (95% CI: 0.49–1.27), with no trend across tertiles (p = 0.22).
- 3.
- Disease-Modifying Therapies applied to Elderly MS Patients (Zinganell et al.) [14]:
- There was no significant difference in clinical outcomes between treated and never-treated elderly MS patients.
- The lower disability scores observed for some treated patients were attributed to selection bias rather than DMT efficacy.
- No direct evidence was provided for reductions in mortality associated with DMT use.
3.9. Secondary Outcomes
- Clinico-Demographic Profiles (Joseph et al.) [50]:
- This study reported a female-to-male ratio of 3:1, with paresthesia (39.1%) being the most common presenting symptom.
- Optic neuritis or vision impairment was present in 30.4% of patients, differing from global patterns.
3.10. Heterogeneity Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Evidence
4.1.1. Substance Use and LOMS Risk
4.1.2. Diet Quality and LOMS Risk
4.1.3. Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs) in Relation to Elderly MS Patients
- Risk–Benefit Assessment:Given that older adults are more prone to comorbidities, polypharmacy, and age-related immune decline, selecting DMTs with favorable safety profiles is crucial. Therapies such as glatiramer acetate and interferon-beta treatment may be preferable for elderly patients with stable disease or lower relapse activity due to their well-established safety profiles. Conversely, for patients with active relapses or aggressive disease, higher-efficacy agents like ocrelizumab may provide greater benefits despite increased infection risks.
- Dosing and Monitoring Adjustments:Considering that pharmacokinetics may differ in older adults, dose adjustments or extended dosing intervals may improve safety without compromising efficacy. Close monitoring for infections, lymphopenia, and vaccine efficacy is essential in this population to ensure safe and effective treatment.
- Cognitive and Functional Assessments:Since older MS patients frequently experience cognitive decline and physical impairments, integrating neuropsychological assessments and mobility evaluations into treatment plans may provide better insights into disease progression and guide therapy decisions.
4.1.4. Clinico-Demographic Profiles of LOMS Patients
4.2. Comparison with the Existing Literature
- Substance Use: Our findings confirm that smoking, alcohol consumption, and substance abuse are strongly associated with an increased LOMS risk, consistent with well-established evidence regarding EOMS populations [61,62,63]. The association between smoking duration (>20 years) and LOMS risk aligns with previous studies that have demonstrated a cumulative dose–response effect regarding MS risk [25,64,65]. However, our review identified a much stronger association between opium use and LOMS risk (OR = 6.8) than previously reported for substance use in regard to EOMS. This finding suggests that cumulative lifetime exposure or age-related immune changes may amplify risk in older populations. The findings align with existing studies linking smoking and substance use to MS risk through mechanisms like oxidative stress and immune dysregulation. These results reinforce the urgency of designing smoking cessation programs to prevent MS [51].
- Diet Quality: In contrast to evidence suggesting that anti-inflammatory diets may reduce EOMS risk [66,67], our review found no significant association between diet quality and LOMS risk (HR = 0.79; 95% CI: 0.49–1.27). This divergence highlights a possible age-related shift in metabolic pathways or immune response in older individuals, where dietary factors may exert less influence on MS onset. Further biomarker-based studies are needed to clarify whether diet interacts with cumulative exposure or immune-aging mechanisms in LOMS populations. The neutral findings for diet quality differ from studies suggesting that anti-inflammatory diets might reduce MS risk. This discrepancy underscores the need for improved dietary assessment methods in MS research [19].
- DMTs: Consistent with the existing literature, our review supports the role of DMTs in slowing disability progression (OR = 0.67) and reducing mortality (HR = 0.78) in elderly MS patients [68,69,70]. Importantly, our synthesis highlights the need to apply personalized DMT strategies to older patients, as immune senescence and comorbidities may alter treatment efficacy. The demonstrated benefits of DMTs in reducing disability and mortality align with previous research supporting their role in altering disease progression. This finding is particularly relevant for older MS populations [14].
4.3. Strengths
- We included diverse study designs (case–control, cohort, and cross-sectional), providing a broad perspective on LOMS risk factors and outcomes.
- We used validated diagnostic criteria (e.g., the McDonald criteria) and reliable data sources, enhancing the robustness of the findings.
- We focused on LOMS, an underexplored subtype of MS, providing unique insights into its etiology and management.
4.4. Limitations
4.4.1. Study-Level Limitations
- Risk of Bias: Some of the studies relied on self-reported exposures (e.g., substance use) or lacked information on non-response rates, which may have introduced bias.
- Heterogeneity: Differences in study design and exposure definitions limited comparability across studies.
- Small Sample Sizes: While this review synthesized data from studies with varying sample sizes, the study by Joseph et al. (2021) warrants particular attention due to its notably small sample size (n = 23) [50]. The limited number of participants reduced the statistical power of this study, making its findings less generalizable to broader LOMS populations. Although this study was included due to its relevance to LOMS risk factors, we exercised caution in interpreting its findings. To ensure that our conclusions were informed by stronger evidence, this study was assigned less weight in the final narrative synthesis. This approach minimized the potential for overemphasis on conclusions drawn from limited data while still acknowledging this study’s contribution to understanding LOMS. Smaller studies, such as the one conducted by Joseph et al. [50] (n = 23), reduced the statistical power and generalizability of our results.
4.4.2. Outcome-Level Limitations
- Limited Scope: While substance use and diet were explored, other forms of exposure (e.g., infections, air pollution, etc.) were underrepresented.
- Short-Term Outcomes: Some studies lacked data on the long-term impacts of risk factors or interventions.
4.4.3. Review-Level Limitations
- Incomplete Retrieval: Non-English and unpublished studies may have been missed, introducing selection bias.
- Reporting Bias: Observational studies may have selectively reported significant results, reducing reliability.
- Limited Study Pool: Only five studies met the inclusion criteria, limiting the breadth of evidence.
4.5. Implications for Practice
- Healthcare Providers: Clinicians should prioritize interventions targeting modifiable risk factors, such as smoking and substance use, while continuing DMTs for managing LOMS progression.
- Patients: Patients can benefit from making informed lifestyle changes and selecting optimized therapeutic options to improve outcomes.
- Policy Makers: Public health initiatives should focus on smoking cessation and substance abuse reduction to mitigate the population-level risk of LOMS.
4.6. Implications for Clinical Guidelines
- Early Diagnosis and Timely DMT Initiation:Our findings reinforce the importance of ensuring early diagnosis and prompt DMT initiation to minimize the risk of irreversible disability among older MS patients.
- Personalized Treatment Approaches:Future guidelines should emphasize personalized treatment strategies, particularly the use of lower-risk therapies for patients with multiple comorbidities or stable disease. Individualized monitoring protocols tailored to older patients are essential to ensure optimal treatment safety.
- Integration of Geriatric Assessment Tools:Incorporating geriatric assessment tools into MS management may improve treatment decisions by identifying patients at higher risk of experiencing disability progression or adverse drug reactions.
4.7. Future Research Directions
- Substance Use: Investigate dose–response relationships and underlying mechanisms linking substance use and LOMS.
- Diet and Nutrition: Conduct longitudinal studies using biomarker-based dietary assessments to clarify the role of nutrition in LOMS.
- Regional Variations: Explore geographic and socioeconomic disparities in LOMS risk factors to inform targeted interventions.
- Longitudinal Cohort Studies: Develop prospective studies to strengthen causal evidence of identified risk factors and interventions in LOMS.
- Comparative Studies on DMTs: There is a need for comparative trials evaluating the efficacy and safety of different DMTs, specifically in older MS populations, to guide optimal treatment selection.
- Investigations into Immune-Aging Mechanisms: Research exploring the influence of immune-aging mechanisms on DMT response is crucial to improving treatment outcomes for elderly MS patients.
- Biomarker-Based Treatment Prediction: Identifying biomarkers that predict treatment response among older patients may support more personalized care strategies, improving treatment selection and monitoring.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kornberg, M.; Calabresi, P. Multiple Sclerosis and Other Acquired Demyelinating Diseases of the Central Nervous System. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2025, 17, a041374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bove, R.M.; Healy, B.; Augustine, A.; Musallam, A.; Gholipour, T.; Chitnis, T. Effect of Gender on Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2012, 18, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouresan, E.F.; Mentesidou, E.; Berglund, A.; McKay, K.A.; Hillert, J.; Iacobaeus, E. Clinical Characteristics and Long-Term Outcomes of Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Swedish Nationwide Study. Neurology 2024, 102, e208051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naseri, A.; Nasiri, E.; Sahraian, M.A.; Daneshvar, S.; Talebi, M. Clinical Features of Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2021, 50, 102816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarghami, A.; Li, Y.; Claflin, S.B.; van der Mei, I.; Taylor, B.V. Role of Environmental Factors in Multiple Sclerosis. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2021, 21, 1389–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbasis, L.; Bellou, V.; Evangelou, E.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Tzoulaki, I. Environmental Risk Factors and Multiple Sclerosis: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroufi, H.; Mortazavi, S.H.; Sahraian, M.A.; Eskandarieh, S. Environmental Risk Factors of Multiple Sclerosis in the Middle East and North Africa Region: A Systematic Review. Curr. J. Neurol. 2021, 20, 166–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badihian, N.; Riahi, R.; Goli, P.; Badihian, S.; Poursafa, P.; Kelishadi, R. Prenatal and Perinatal Factors Associated with Developing Multiple Sclerosis Later in Life: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celarain, N.; Tomas-Roig, J. Aberrant DNA Methylation Profile Exacerbates Inflammation and Neurodegeneration in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadat, S.; Saberi, A. Environmental Risk Factors in Multiple Sclerosis: A Narrative Review. J. Guilan Univ. Med. Sci. 2022, 31, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, T.; Barcellos, L.F.; Alfredsson, L. Interactions between Genetic, Lifestyle and Environmental Risk Factors for Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, P.J.; Mathur, S.K. Age-Related Changes in Immune Function: Effect on Airway Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 690–699; quiz 700–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, L.; van den Biggelaar, A.H.; van Bodegom, D.; Meij, H.J.; de Craen, A.J.; Amankwa, J.; Frölich, M.; Kuningas, M.; Westendorp, R.G. Adverse Environmental Conditions Influence Age-Related Innate Immune Responsiveness. Immun. Ageing 2009, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinganell, A.; Göbel, G.; Berek, K.; Hofer, B.; Asenbaum-Nan, S.; Barang, M.; Böck, K.; Bsteh, C.; Bsteh, G.; Eger, S.; et al. Multiple Sclerosis in the Elderly: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dema, M.; Eixarch, H.; Villar, L.M.; Montalban, X.; Espejo, C. Immunosenescence in Multiple Sclerosis: The Identification of New Therapeutic Targets. Autoimmun. Rev. 2021, 20, 102893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostolaza Ibáñez, A.; Corroza Laviñeta, J.; Ayuso Blanco, T. Immunosenescence: The Role of Age in Multiple Sclerosis. Neurologia (Engl. Ed.) 2020, 38, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granier, C.; Gey, A.; Roncelin, S.; Weiss, L.; Paillaud, E.; Tartour, E. Immunotherapy in Older Patients with Cancer. Biomed. J. 2021, 44, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdaens, O.; van Pesch, V. Molecular Mechanisms of Immunosenescene and Inflammaging: Relevance to the Immunopathogenesis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 12, 811518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommerich, U.M.; Nielsen, R.Ø.; Overvad, K.; Dahm, C.C.; Tjønneland, A.; Olsen, A.; Dalgas, U. Diet Quality Is Not Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis Risk– A Danish Cohort Study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 40, 101968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, P.-K.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, K.; Chun, S.; Lee, H.-J.; Choi, S.-W. A Traditional Korean Diet with a Low Dietary Inflammatory Index Increases Anti-Inflammatory IL-10 and Decreases Pro-Inflammatory NF-κB in a Small Dietary Intervention Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedström, A.K. Risk Factors for Multiple Sclerosis in the Context of Epstein-Barr Virus Infection. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1212676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, W.H.; Steinman, L. Epstein-Barr Virus and Multiple Sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 264–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riise, T.; Nortvedt, M.W.; Ascherio, A. Smoking Is a Risk Factor for Multiple Sclerosis. Neurology 2003, 61, 1122–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poorolajal, J.; Bahrami, M.; Karami, M.; Hooshmand, E. Effect of Smoking on Multiple Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis. J. Public Health 2017, 39, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degelman, M.L.; Herman, K.M. Smoking and Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Using the Bradford Hill Criteria for Causation. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 17, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handel, A.E.; Williamson, A.J.; Disanto, G.; Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G.; Ramagopalan, S.V. Smoking and Multiple Sclerosis: An Updated Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, C.; Lv, X.; Song, Y.; Li, B. The Risk of Smoking on Multiple Sclerosis: A Meta-Analysis Based on 20,626 Cases from Case-Control and Cohort Studies. PeerJ 2016, 4, e1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Stridh, P.; Rhead, B.; Shao, X.; Xu, E.; Graves, J.S.; Chitnis, T.; Waldman, A.; Lotze, T.; Schreiner, T.; et al. Evidence for a Causal Relationship between Low Vitamin D, High BMI, and Pediatric-Onset MS. Neurology 2017, 88, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krementsov, D.N.; Asarian, L.; Fang, Q.; McGill, M.M.; Teuscher, C. Sex-Specific Gene-by-Vitamin D Interactions Regulate Susceptibility to Central Nervous System Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostkamp, P.; Salmen, A.; Pignolet, B.; Görlich, D.; Andlauer, T.F.M.; Schulte-Mecklenbeck, A.; Gonzalez-Escamilla, G.; Bucciarelli, F.; Gennero, I.; Breuer, J.; et al. Sunlight Exposure Exerts Immunomodulatory Effects to Reduce Multiple Sclerosis Severity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2018457118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Clarelli, F.; Pignolet, B.; Mascia, E.; Sorosina, M.; Misra, K.; Ferrè, L.; Bucciarelli, F.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Moiola, L.; et al. Vitamin D Affects the Risk of Disease Activity in Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2024, 96, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, U.-C.; Cipian, R.C.; Karimi, A.; Ramasamy, R.; Middeldorp, J.M. Cumulative Roles for Epstein-Barr Virus, Human Endogenous Retroviruses, and Human Herpes Virus-6 in Driving an Inflammatory Cascade Underlying MS Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 757302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadda, G.; Yea, C.; O’Mahony, J.; Waters, P.; Yeh, E.A.; Marrie, R.A.; Arnold, D.; Bar-Or, A.; Banwell, B.; Canadian Pediatric Demyelinating Disease Study Group. Epstein-Barr Virus Strongly Associates with Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis, But Not Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein-Antibody-Associated Disease. Ann. Neurol. 2024, 95, 700–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornevik, K.; Cortese, M.; Healy, B.C.; Kuhle, J.; Mina, M.J.; Leng, Y.; Elledge, S.J.; Niebuhr, D.W.; Scher, A.I.; Munger, K.L.; et al. Longitudinal Analysis Reveals High Prevalence of Epstein-Barr Virus Associated with Multiple Sclerosis. Science 2022, 375, 296–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, B.M.; Giovannoni, G.; Cuzick, J.; Dobson, R. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Association between Epstein-Barr Virus, Multiple Sclerosis and Other Risk Factors. Mult. Scler. 2020, 26, 1281–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbaszadeh, S.; Tabary, M.; Aryannejad, A.; Abolhasani, R.; Araghi, F.; Khaheshi, I.; Azimi, A. Air Pollution and Multiple Sclerosis: A Comprehensive Review. Neurol. Sci. 2021, 42, 4063–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahraian, M.A. Air Pollution Is a Risk Factor for Multiple Sclerosis—Commentary. Mult. Scler. 2021, 27, 2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noorimotlagh, Z.; Azizi, M.; Pan, H.-F.; Mami, S.; Mirzaee, S.A. Association between Air Pollution and Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, Q.-R.; Mao, Y.-M.; Xia, Y.-R.; Guo, H.-S.; Wang, J.-P.; Shuai, Z.-W.; Ye, D.-Q. Association between Ambient Air Pollution and Multiple Sclerosis: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 58142–58153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydarpour, P.; Amini, H.; Khoshkish, S.; Seidkhani, H.; Sahraian, M.A.; Yunesian, M. Potential Impact of Air Pollution on Multiple Sclerosis in Tehran, Iran. Neuroepidemiology 2014, 43, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagger, A.; Shimojima, Y.; Goronzy, J.J.; Weyand, C.M. Regulatory T Cells and the Immune Aging Process: A Mini-Review. Gerontology 2014, 60, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulop, T.; Larbi, A.; Dupuis, G.; Le Page, A.; Frost, E.H.; Cohen, A.A.; Witkowski, J.M.; Franceschi, C. Immunosenescence and Inflamm-Aging As Two Sides of the Same Coin: Friends or Foes? Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, A.; Bientinesi, E.; Monti, D. Immunosenescence and Inflammaging in the Aging Process: Age-Related Diseases or Longevity? Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 71, 101422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feehan, J.; Tripodi, N.; Apostolopoulos, V. The Twilight of the Immune System: The Impact of Immunosenescence in Aging. Maturitas 2021, 147, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, L.; Di Benedetto, S. Inflammaging, Immunosenescence, and Cardiovascular Aging: Insights into Long COVID Implications. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2024, 11, 1384996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, A.; Farzaneh, F.; Candore, G.; Caruso, C.; Davinelli, S.; Gambino, C.M.; Ligotti, M.E.; Zareian, N.; Accardi, G. Immunosenescence and Its Hallmarks: How to Oppose Aging Strategically? A Review of Potential Options for Therapeutic Intervention. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, R.; Wang, W.; Su, D.-M. Contributions of Age-Related Thymic Involution to Immunosenescence and Inflammaging. Immun. Ageing 2020, 17, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, N. Artificial Intelligence in Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine. J. Artif. Intell. Gen. Sci. 2024, 1, 258–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, N.; Salins, R.M.; Ramesh, P.; Krishna, N.V. A Retrospective Study on the Clinico-Demographic Profile of Multiple Sclerosis Patients in Various Tertiary Care Hospitals in Mangalore City of South India. Rom. J. Neurol. 2021, 20, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi Kasbi, N.; Ghane Ezabadi, S.; Kohandel, K.; Khodaie, F.; Sahraian, A.H.; Nikkhah Bahrami, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Eskandarieh, S.; Sahraian, M.A. Lifetime Exposure to Smoking and Substance Abuse May Be Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. BMC Neurol. 2024, 24, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graves, J.S.; Chitnis, T.; Weinstock-Guttman, B.; Rubin, J.; Zelikovitch, A.S.; Nourbakhsh, B.; Simmons, T.; Waltz, M.; Casper, T.C.; Waubant, E.; et al. Maternal and Perinatal Exposures Are Associated With Risk for Pediatric-Onset Multiple Sclerosis. Pediatrics 2017, 139, e20162838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handel, A.E.; Giovannoni, G.; Ebers, G.C.; Ramagopalan, S.V. Environmental Factors and Their Timing in Adult-Onset Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2010, 6, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waubant, E.; Lucas, R.; Mowry, E.; Graves, J.; Olsson, T.; Alfredsson, L.; Langer-Gould, A. Environmental and Genetic Risk Factors for MS: An Integrated Review. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2019, 6, 1905–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfredsson, L.; Olsson, T.; Hedström, A.K. Inverse Association between Mediterranean Diet and Risk of Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2023, 29, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azary, S.; Schreiner, T.; Graves, J.; Waldman, A.; Belman, A.; Guttman, B.W.; Aaen, G.; Tillema, J.-M.; Mar, S.; Hart, J.; et al. Contribution of Dietary Intake to Relapse Rate in Early Paediatric Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2018, 89, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagur, M.J.; Murcia, M.A.; Jiménez-Monreal, A.M.; Tur, J.A.; Bibiloni, M.M.; Alonso, G.L.; Martínez-Tomé, M. Influence of Diet in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero Mazzucca, C.; Scotti, L.; Comi, C.; Vecchio, D.; Chiocchetti, A.; Cappellano, G. The Role of Diet in Multiple Sclerosis Onset: A Prospective Study Using UK Biobank. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastorini, C.-M.; Milionis, H.J.; Esposito, K.; Giugliano, D.; Goudevenos, J.A.; Panagiotakos, D.B. The Effect of Mediterranean Diet on Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components: A Meta-Analysis of 50 Studies and 534,906 Individuals. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2011, 57, 1299–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamczyk-Sowa, M.; Nowak-Kiczmer, M.; Jaroszewicz, J.; Berger, T. Immunosenescence and Multiple Sclerosis. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2022, 56, 220–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskandarieh, S.; Mortazavi, S.H.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Moghadasi, A.N.; Sahraian, M.A. Water-Pipe and Cigarette Smoking, Drug Abuse and Alcohol Consumption and the Risk of Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: A Population Based Case-Control Study. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 59, 103583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.; Rezaeimanesh, N.; Moghadasi, A.N.; Navardi, S.; Kohandel, K.; Rezaei, A.; Sahraian, M.A. Increased Odds of Alcohol Consumption, Cannabis, and Illicit Substances Use in Cigarette Smoking Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 80, 105214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortazavi, S.H.; Moghadasi, A.N.; Almasi-Hashiani, A.; Sahraian, M.A.; Goudarzi, H.; Eskandarieh, S. Waterpipe and Cigarette Smoking and Drug and Alcohol Consumption, and the Risk of Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis: A Population-Based Case-Control Study. Curr. J. Neurol. 2023, 22, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundström, P.; Nyström, L. Smoking Worsens the Prognosis in Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. 2008, 14, 1031–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedström, A.K.; Hillert, J.; Olsson, T.; Alfredsson, L. Smoking and Multiple Sclerosis Susceptibility. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 28, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravejolahkami, A.R.; Chitsaz, A.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Paknahad, Z. Anti-Inflammatory-Antioxidant Modifications and Synbiotics Improved Health-Related Conditions in Patients with Progressive Forms of Multiple Sclerosis: A Single-Center, Randomized Clinical Trial. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2023, 53, 101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravejolahkami, A.R.; Chitsaz, A.; Hassanzadeh, A.; Paknahad, Z. Effects of Anti-Inflammatory-Antioxidant-Rich Diet and Co-Supplemented Synbiotics Intervention in Patients with Progressive Forms of Multiple Sclerosis: A Single-Center, Single-Blind Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2023, 26, 1078–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wingerchuk, D.M.; Weinshenker, B.G. Disease Modifying Therapies for Relapsing Multiple Sclerosis. BMJ 2016, 354, i3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claflin, S.B.; Broadley, S.; Taylor, B.V. The Effect of Disease Modifying Therapies on Disability Progression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Overview of Meta-Analyses. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falet, J.R.; Durso-Finley, J.; Nichyporuk, B.; Schroeter, J.; Bovis, F.; Sormani, M.; Precup, D.; Arbel, T.; Arnold, D.L. GP.2 Deep Learning Prediction of Response to Disease Modifying Therapy in Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 49, S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Design | Population | Sample Size | Follow-Up | Exposure | Outcome | NOS Score | Risk of Bias |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbasi Kasbi et al., 2024 [51] | Case–control | LOMS patients in Tehran, Iran | 290 | N/A | Smoking, alcohol, substance use | LOMS risk | 7/9 | Moderate Risk |
| Pommerich et al., 2020 [19] | Prospective Cohort | Danish middle-aged adults | 56,867 | 20.4 years (median) | Diet quality | LOMS risk | 9/9 | Low Risk |
| Zinganell et al., 2024 [14] | Retrospective Cohort | Elderly MS patients in Austria | 1200 | 17.1 years (median) | DMT usage, comorbidities | Long-term disability progression | 8/9 | Low Risk |
| Joseph et al., 2021 [50] | Cross-Sectional | MS patients in South India | 23 | N/A | Clinical profiles | Demographic and clinical characteristics | 4/9 | High Risk |
| Study | Outcome | Exposure Groups | Effect Estimates (95% CI) | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abbasi Kasbi et al., 2024 [51] | Association between substance use and LOMS | Smokers, alcohol users, substance abusers vs. non-users | Cigarette smoking: OR = 2.57 (1.44–4.60) | Substance use is strongly associated with LOMS risk. |
| Alcohol: OR = 2.45 (1.26–4.76) | ||||
| Substance use: OR = 6.8 (2.29–17.20) | ||||
| Pommerich et al., 2020 [19] | Risk of LOMS according to diet quality | High vs. low diet quality tertiles | HR = 0.79 (0.49–1.27) | No significant association. |
| Zinganell et al., 2024 [14] | Disability progression, mortality in elderly MS | DMT users vs. non-users | EDSS: OR = 0.67 (0.55–0.81) | DMT use slowed progression and reduced mortality. |
| Mortality: HR = 0.78 (0.65–0.94) | ||||
| Joseph et al., 2021 [50] | Clinico-demographic profiles of MS patients | No exposure groups | Mean age: 34.6 years | Symptoms align with known MS characteristics. |
| Common symptoms: paresthesia (39.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belenciuc, A.; Odainic, O.; Grumeza, A.; Lisnic, V. Systematic Review of Environmental Factors Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Synthesis of Epidemiological Evidence. Sclerosis 2025, 3, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020019
Belenciuc A, Odainic O, Grumeza A, Lisnic V. Systematic Review of Environmental Factors Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Synthesis of Epidemiological Evidence. Sclerosis. 2025; 3(2):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020019
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelenciuc, Anna, Olesea Odainic, Alexandru Grumeza, and Vitalie Lisnic. 2025. "Systematic Review of Environmental Factors Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Synthesis of Epidemiological Evidence" Sclerosis 3, no. 2: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020019
APA StyleBelenciuc, A., Odainic, O., Grumeza, A., & Lisnic, V. (2025). Systematic Review of Environmental Factors Associated with Late-Onset Multiple Sclerosis: A Synthesis of Epidemiological Evidence. Sclerosis, 3(2), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/sclerosis3020019





