From Antibodies to Crystals: Understanding the Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Related Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
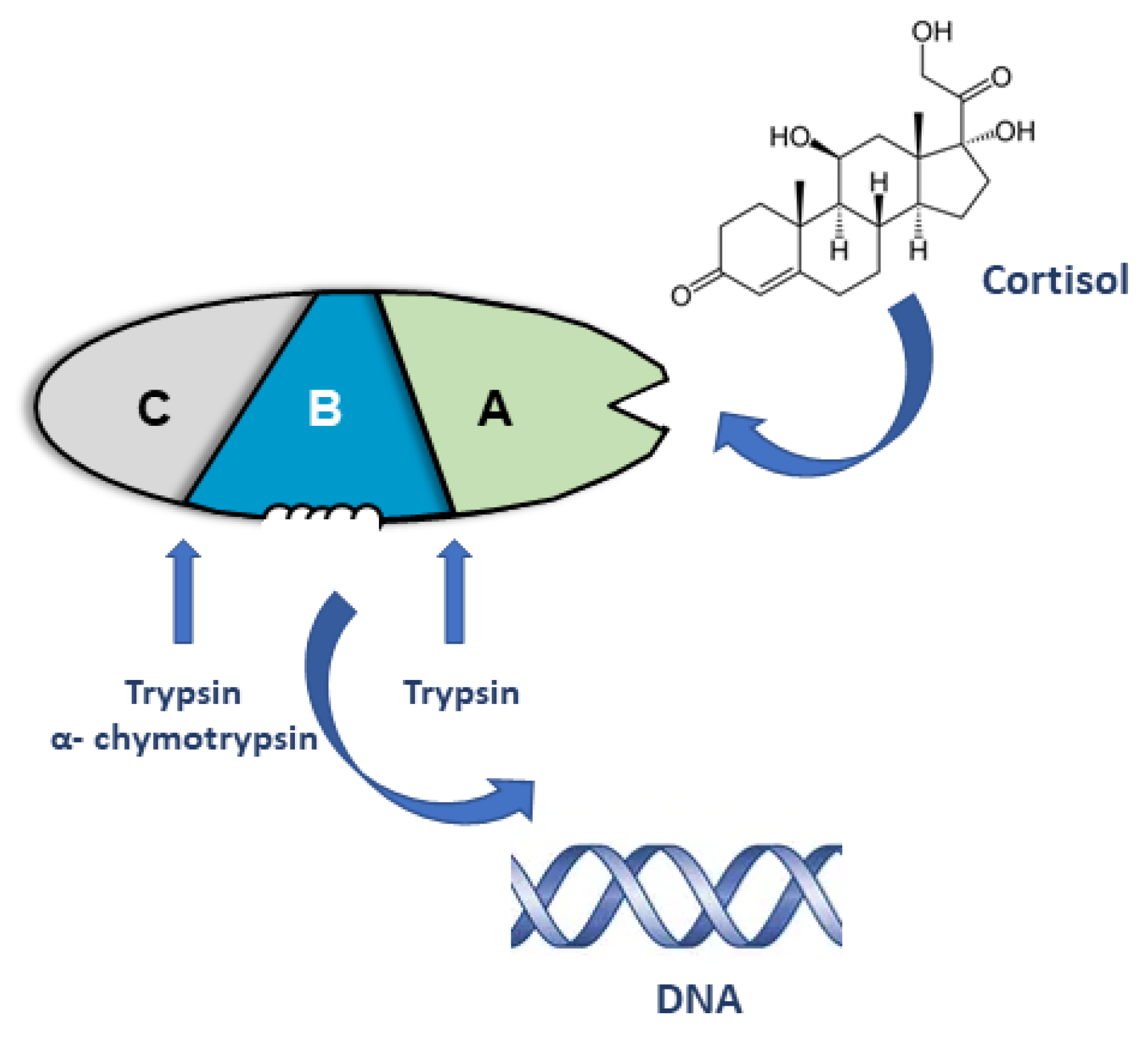
2. Early Models of Steroid Receptor Structure and Function
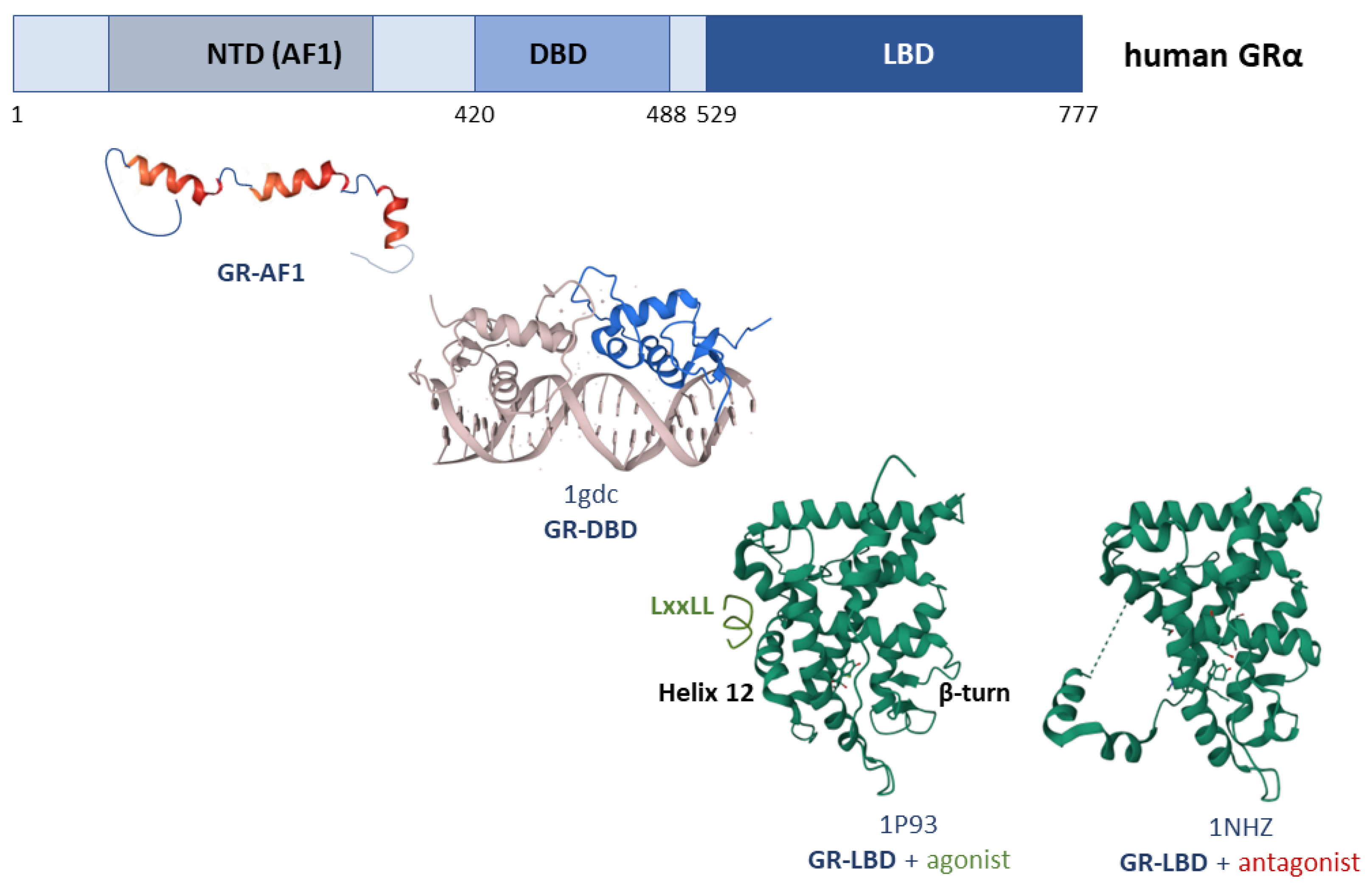
3. Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor
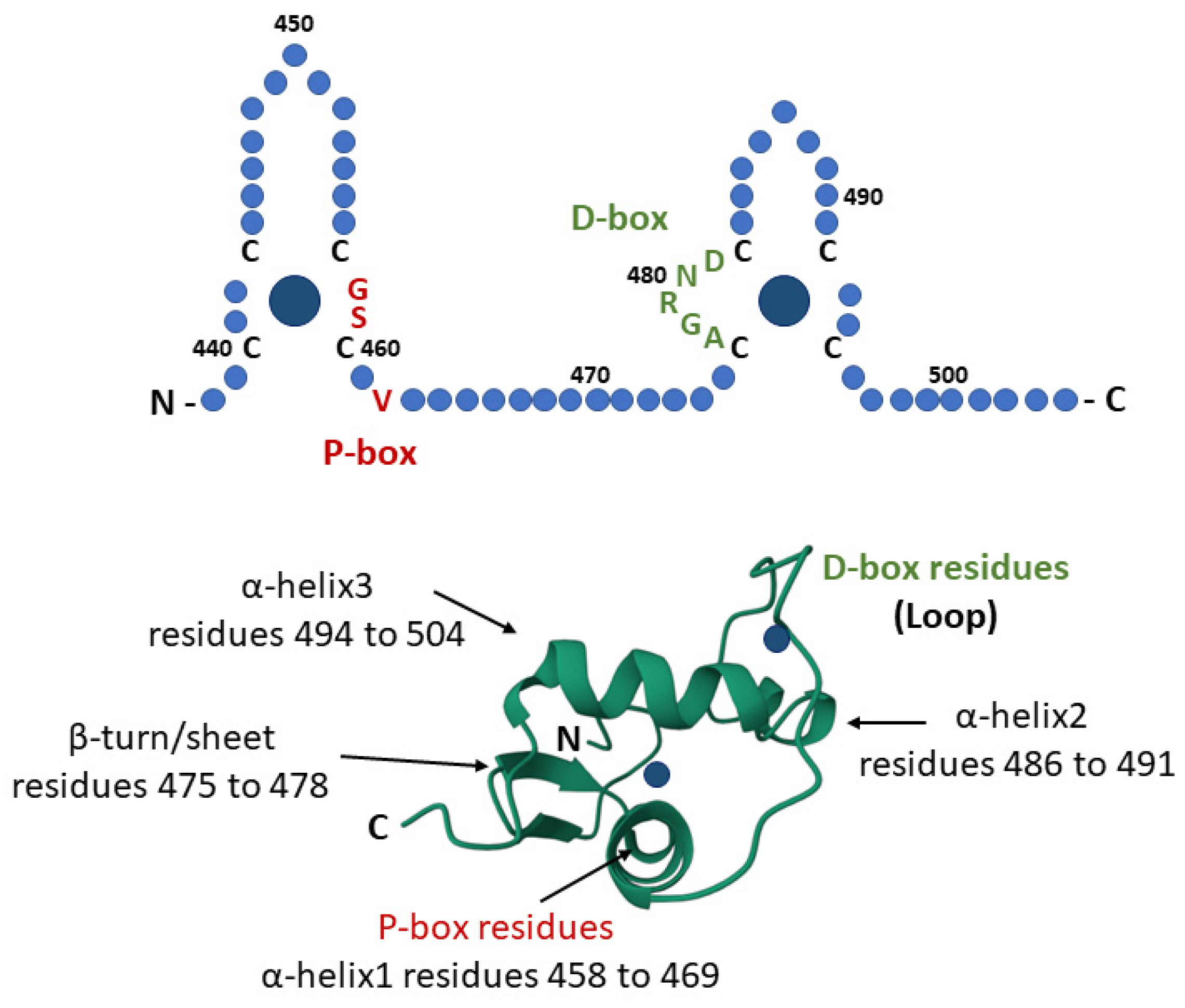
3.1. GR-DBD
3.2. GR-NTD
3.3. GR-LBD
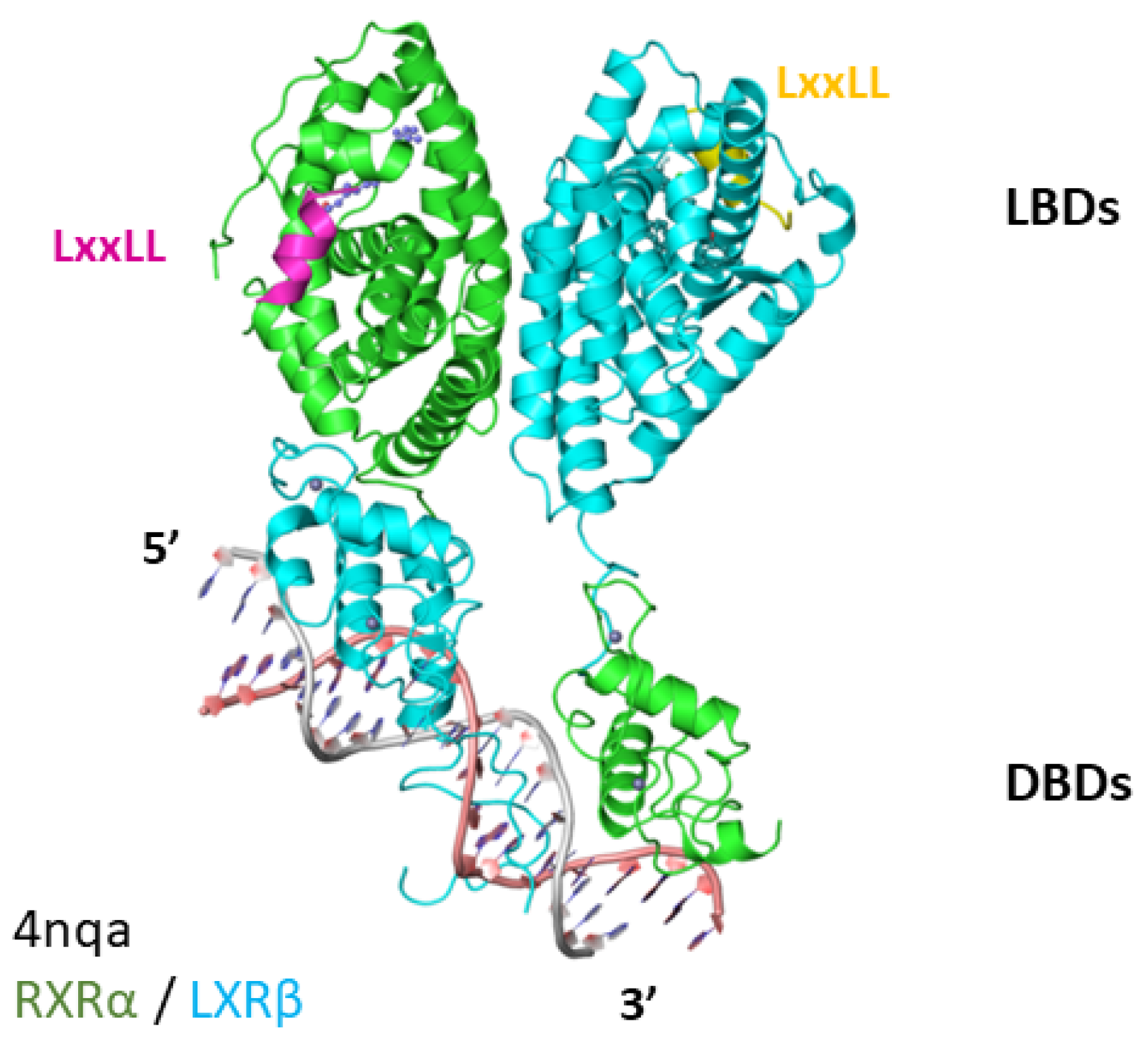
4. LXR-RXR Complex Bound to DNA
5. Future Studies
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, R.M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science 1988, 240, 889–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Chandra, V.; Rastinejad, F. Structural Overview of the Nuclear Receptor Superfamily: Insights into Physiology and Therapeutics. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2010, 72, 247–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weikum, E.R.; Liu, X.; Ortlund, E.A. The nuclear receptor superfamily: A structural perspective. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1876–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmermans, S.; Souffriau, J.; Libert, C. A General Introduction to Glucocorticoid Biology. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, M.V.; Devic, M.; Green, S.; Gronemeyer, H.; Chambon, P. Cloning of the human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 8293–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Weinberger, C.; Ong, E.S.; Cerelli, G.; Oro, A.; Lebo, R.; Thompson, E.B.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Evans, R.M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature 1985, 318, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberger, C.; Hollenberg, S.M.; Ong, E.S.; Harmon, J.M.; Brower, S.T.; Cidlowski, J.; Thompson, E.B.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Evans, R.M. Identification of Human Glucocorticoid Receptor Complementary DNA Clones by Epitope Selection. Science 1985, 228, 740–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesfeld, R.; Rusconi, S.; Godowski, P.J.; Maler, B.A.; Okret, S.; Wikström, A.C.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Genetic complementation of a glucocorticoid receptor deficiency by expression of cloned receptor cDNA. Cell 1986, 46, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrange, O.; Gustafsson, J.A. Separation of the hormone- and DNA-binding sites of the hepatic glucocorticoid receptor by means of proteolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Okret, S.; Wrange, O.; Gustafsson, J.A. Immunochemical analysis of the glucocorticoid receptor: Identification of a third domain separate from the steroid-binding and DNA-binding domains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 4260–4264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrange, O.; Okret, S.; Radojćić, M.; Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Characterization of the purified activated glucocorticoid receptor from rat liver cytosol. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 4534–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payvar, F.; Defranco, D.; Firestone, G.L.; Edgar, B.; Wrange, O.; Okret, S.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Sequence-specific binding of glucocorticoid receptor to MTV DNA at sites within and upstream of the transcribed region. Cell 1983, 35 Pt 1, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Gampe, R.T., Jr.; Kole, A.J.; Hnat, A.T.; Stanley, T.B.; An, G.; Stewart, E.L.; Kalman, R.I.; Minges, J.T.; Wilson, E.M. Structural basis for androgen receptor interdomain and coactivator interactions suggests a transition in nuclear receptor activation function dominance. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giguère, V.; Hollenberg, S.M.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; Evans, R.M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell 1986, 46, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Giguère, V.; Segui, P.; Evans, R.M. Colocalization of DNA-binding and transcriptional activation functions in the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell 1987, 49, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miesfeld, R.; Godowski, P.J.; Maler, B.A.; Yamamoto, K.R. Glucocorticoid Receptor Mutants That Define a Small Region Sufficient for Enhancer Activation. Science 1987, 236, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.; Chambon, P. Oestradiol induction of a glucocorticoid-responsive gene by a chimaeric receptor. Nature 1987, 325, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusconi, S.; Yamamoto, K.R. Functional dissection of the hormone and DNA binding activities of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, S.; Kumar, V.; Theulaz, I.; Wahli, W.; Chambon, P. The N-terminal DNA-binding ‘zinc finger’ of the oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors determines target gene specificity. EMBO J. 1988, 7, 3037–3044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, M.; Hinck, L.; Ringold, G.M. Two amino acids within the knuckle of the first zinc finger specify DNA response element activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell 1989, 57, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härd, T.; Kellenbach, E.; Boelens, R.; Maler, B.A.; Dahlman, K.; Freedman, L.P.; Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Yamamoto, K.R.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Kaptein, R. Solution Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor DNA-Binding Domain. Science 1990, 249, 157–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, H.; Paulsen, K.; Kovács, H.; Berglund, H.; Wright, A.P.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Härd, T. Refined solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 13463–13471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freedman, L.P.; Luisi, B.F.; Korszun, Z.R.; Basavappa, R.; Sigler, P.B.; Yamamoto, K.R. The function and structure of the metal coordination sites within the glucocorticoid receptor DNA binding domain. Nature 1988, 334, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zilliacus, J.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Zinc coordination scheme for the C-terminal zinc binding site of nuclear hormone receptors. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1992, 42, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umesono, K.; Evans, R.M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell 1989, 57, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.Y.; Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Weigel, N.L.; Dahlman, K.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Tsai, M.-J.; O’Malley, B.W. Molecular interactions of steroid hormone receptor with its enhancer element: Evidence for receptor dimer formation. Cell 1988, 55, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, P.; Wrange, O. Protein-protein contacts in the glucocorticoid receptor homodimer influence its DNA binding properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 3535–3542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman-Wright, K.; Wright, A.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlstedt-Duke, J. Interaction of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain with DNA as a dimer is mediated by a short segment of five amino acids. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; McEwan, I.J. Allosteric Modulators of Steroid Hormone Receptors: Structural Dynamics and Gene Regulation. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 271–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Evans, R.M. Multiple and cooperative trans-activation domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell 1988, 55, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.P.H.; McEwan, I.J.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Gustafsson, J.A. High Level Expression of the Major Transactivation Domain of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor in Yeast Cells Inhibits Endogenous Gene Expression and Cell Growth. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 1366–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwan, I.J.; Wright, A.P.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Carlstedt-Duke, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Direct interaction of the tau 1 transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor with the basal transcriptional machinery. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1993, 13, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, J.; McEwan, I.J.; Wright, A.P.H.; Gustafsson, J.A. Involvement of the Transcription Factor IID Protein Complex in Gene Activation by the N-Terminal Transactivation Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor In Vitro. Mol. Endocrinol. 1997, 11, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Volk, D.E.; Li, J.; Lee, J.C.; Gorenstein, D.G.; Thompson, E.B. TATA box binding protein induces structure in the recombinant glucocorticoid receptor AF1 domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 16425–16430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman-Wright, K.; Almlöf, T.; McEwan, I.J.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Wright, A.P. Delineation of a small region within the major transactivation domain of the human glucocorticoid receptor that mediates transactivation of gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1619–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almlöf, T.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Wright, A.P.H. Role of Hydrophobic Amino Acid Clusters in the Transactivation Activity of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1997, 17, 934–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilser, V.J.; Thompson, E.B. Intrinsic disorder as a mechanism to optimize allosteric coupling in proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 8311–8315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.L.; Webb, M.S.; Copik, A.J.; Wang, Y.; Johnson, B.H.; Kumar, R.; Thompson, E.B. p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Is a Key Mediator in Glucocorticoid-Induced Apoptosis of Lymphoid Cells: Correlation between p38 MAPK Activation and Site-Specific Phosphorylation of the Human Glucocorticoid Receptor at Serine 211. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 19, 1569–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Dang, T.; Blind, R.D.; Wang, Z.; Cavasotto, C.N.; Hittelman, A.B.; Rogatsky, I.; Logan, S.K.; Garabedian, M.J. Glucocorticoid Receptor Phosphorylation Differentially Affects Target Gene Expression. Mol. Endocrinol. 2008, 22, 1754–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garza, A.M.S.; Khan, S.H.; Kumar, R. Site-Specific Phosphorylation Induces Functionally Active Conformation in the Intrinsically Disordered N-Terminal Activation Function (AF1) Domain of the Glucocorticoid Receptor. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.H.; McLaughlin, W.A.; Kumar, R. Site-specific phosphorylation regulates the structure and function of an intrinsically disordered domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, C.W.; Suh, J.H.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Webb, P. Phosphorylation of glucocorticoid receptor tau1c transactivation domain enhances binding to CREB binding protein (CBP) TAZ2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 457, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, F.; Liu, X.; Ortlund, E.A. Glucocorticoid receptor condensates link DNA-dependent receptor dimerization and transcriptional transactivation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2024685118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stortz, M.; Pecci, A.; Presman, D.M.; Valeria Levi, V. Unraveling the molecular interactions involved in phase separation of glucocorticoid receptor. BMC Biol. 2020, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asangani, I.; Blair, I.A.; Van Duyne, G.; Hilser, V.J.; Moiseenkova-Bell, V.; Plymate, S.; Sprenger, C.; Wand, A.J.; Penning, T.M. Using biochemistry and biophysics to extinguish androgen receptor signaling in prostate cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, J.J.; Otero, J.H.; Scott, D.C.; Szulc, E.; Martin, E.W.; Sabri, N.; Granata, D.; Marzahn, M.R.; Lindorff-Larsen, K.; Salvatella, X.; et al. Cancer Mutations of the Tumor Suppressor SPOP Disrupt the Formation of Active, Phase-Separated Compartments. Mol. Cell 2018, 72, 19–36.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Meszaros, A.; Lazar, T.; Tompa, P. DNA-binding domain as the minimal region driving RNA-dependent liquid–liquid phase separation of androgen receptor. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEwan, I.J. Breaking apart condensates. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 1292–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; He, H.; Kong, W.; Li, Z.; Gao, Z.; Xie, D.; Sun, L.; Fan, X.; Jiang, X.; Zheng, Q.; et al. Targeting androgen receptor phase separation to overcome antiandrogen resistance. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2022, 18, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlman-Wright, K.; Baumann, H.; McEwan, I.J.; Almlöf, T.; Wright, A.P.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Härd, T. Structural characterization of a minimal functional transactivation domain from the human glucocorticoid receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1699–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskakov, I.V.; Kumar, R.; Srinivasan, G.; Ji, Y.S.; Bolen, D.W.; Thompson, E.B. Trimethylamine N-oxide-induced cooperative folding of an intrinsically unfolded transcription-activating fragment of human glucocorticoid receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 10693–10696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, R.; Lee, J.C.; Bolen, D.W.; Thompson, E.B. The conformation of the glucocorticoid receptor af1/tau1 domain induced by osmolyte binds co-regulatory proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 18146–18152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, J.; Kelly, S.M.; Watt, K.; Price, N.C.; McEwan, I.J. Conformational Analysis of the Androgen Receptor Amino-terminal Domain Involved in Transactivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20079–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mol, E.; Szulc, E.; Di Sanza, C.; Martínez-Cristóbal, P.; Bertoncini, C.W.; Fenwick, R.B.; Frigolé-Vivas, M.; Masín, M.; Hunter, I.; Buzón, V.; et al. Regulation of Androgen Receptor Activity by Transient Interactions of Its Transactivation Domain with General Transcription Regulators. Structure 2018, 26, 145–152.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wärnmark, A.; Wikström, A.; Wright, A.P.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Härd, T. The N-terminal regions of estrogen receptor alpha and beta are unstructured in vitro and show different TBP binding properties. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45939–45944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, K.; Kelly, S.M.; Watt, K.; Price, N.C.; McEwan, I.J. Conformation of the mineralocorticoid receptor N-terminal domain: Evidence for induced and stable structure. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Moure, C.M.; Khan, S.H.; Callaway, C.; Grimm, S.L.; Goswami, D.; Griffin, P.R.; Edwards, D.P. Regulation of the Structurally Dynamic N-terminal Domain of Progesterone Receptor by Protein-induced Folding. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 30285–30299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bledsoe, R.K.; Montana, V.G.; Stanley, T.B.; Delves, C.J.; Apolito, C.J.; McKee, D.D.; Consler, T.G.; Parks, D.J.; Stewart, E.L.; Willson, T.M.; et al. Crystal Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor Ligand Binding Domain Reveals a Novel Mode of Receptor Dimerization and Coactivator Recognition. Cell 2002, 110, 93–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, B.; Jakob, C.; Färnegårdh, M.; Yang, J.; Ahola, H.; Alarcon, M.; Calles, K.; Engström, O.; Harlan, J.; Muchmore, S.; et al. The three-dimensional structures of antagonistic and agonistic forms of the glucocorticoid receptor ligand-binding domain: RU-486 induces a transconformation that leads to active antagonism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 22748–22754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yi, W.; Suino-Powell, K.; Zhou, X.E.; Tolbert, W.D.; Tang, X.; Yang, J.; Yang, H.; Shi, J.; Hou, L.; et al. Structures and mechanism for the design of highly potent glucocorticoids. Cell Res. 2014, 24, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, A.M.; Pike, A.C.W.; Dauter, Z.; Hubbard, R.E.; Bonn, T.; Engström, O.; Öhman, L.; Greene, G.L.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlquist, M. Molecular basis of agonism and antagonism in the oestrogen receptor. Nature 1997, 389, 753–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, D.W.; Suen, C.S.; Brass, A.; Soden, J.; White, A. Structure/function of the human glucocorticoid receptor: Tyrosine 735 is important for transactivation. Mol. Endocrinol. 1999, 13, 1855–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaría, E.; A Letelier, N.; Valledor, A.F. Integrating the roles of liver X receptors in inflammation and infection: Mechanisms and outcomes. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2020, 53, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buñay, J.; Fouache, A.; Trousson, A.; de Joussineau, C.; Bouchareb, E.; Zhu, Z.; Kocer, A.; Morel, L.; Baron, S.; Lobaccaro, J.A. Screening for liver X receptor modulators: Where are we and for what use? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 3277–3293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Wu, W.; Warner, M.; Gustafsson, J.A. Liver X Receptor Regulation of Glial Cell Functions in the CNS. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apfel, R.; Benbrook, D.; Lernhardt, E.; Ortiz, M.A.; Salbert, G.; Pfahl, M. A Novel Orphan Receptor Specific for a Subset of Thyroid Hormone-Responsive Elements and Its Interaction with the Retinoid/Thyroid Hormone Receptor Subfamily. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 7025–7035. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, X.; Toresson, G.; Benod, C.; Suh, J.H.; Philips, K.J.; Webb, P.; Gustafsson, J.A. Structure of the retinoid X receptor α-liver X receptor β (RXRα-LXRβ) heterodimer on DNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlov, I.; Rochel, N.; Moras, D.; Klaholz, B.P. Structure of the full human RXR/VDR nuclear receptor heterodimer complex with its DR3 target DNA. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.; Dias, S.M.G.; Santos, M.A.M.; Alves, A.C.; Zanchin, N.; Craievich, A.; Apriletti, J.W.; Baxter, J.D.; Webb, P.; Neves, F.A.R.; et al. Low Resolution Structures of the Retinoid X Receptor DNA-binding and Ligand-binding Domains Revealed by Synchrotron X-ray Solution Scattering. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16030–16038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochel, N.; Ciesielski, F.; Godet, J.; Moman, E.; Rössle, M.; Peluso-Iltis, C.; Moulin, M.; Haertlein, M.; Callow, P.; Mély, Y.; et al. Common architecture of nuclear receptor heterodimers on DNA direct repeat elements with different spacings. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chalmers, M.J.; Stayrook, K.R.; Burris, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Busby, S.A.; Pascal, B.D.; Garcia-Ordonez, R.D.; Bruning, J.B.; Istrate, M.A.; et al. DNA binding alterscoactivator interaction surfaces of the intact VDR-RXR complex. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2011, 18, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, V.; Huang, P.; Hamuro, Y.; Raghuram, S.; Wang, Y.; Burris, T.P.; Rastinejad, F. Structure of the intact PPAR-gamma-RXR- nuclear receptor complex on DNA. Nature 2008, 456, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Färnegårdh, M.; Bonn, T.; Sun, S.; Ljunggren, J.; Ahola, H.; Wilhelmsson, A.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Carlquist, M. The three-dimensional structure of the liver X receptor beta reveals a flexible ligand-binding pocket that can accommodate fundamentally different ligands. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 38821–38828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, P.; Wang, Z.; Feng, Q.; Pintilie, G.D.; Foulds, C.E.; Lanz, R.B.; Ludtke, S.J.; Schmid, M.F.; Chiu, W.; O’Malley, B.W. Structure of a biologically active estrogen receptor-coactivator complex on DNA. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Yi, P.; Hamilton, R.A.; Shen, H.; Chen, M.; Foulds, C.E.; Mancini, M.A.; Ludtke, S.J.; Wang, Z.; O’malley, B.W. Structural Insights of Transcriptionally Active, Full-Length Androgen Receptor Coactivator Complexes. Mol. Cell 2020, 79, 812–823.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadmiel, M.; Cidlowski, J.A. Glucocorticoid receptor signaling in health and disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 34, 518–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
McEwan, I.J. From Antibodies to Crystals: Understanding the Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Related Proteins. Receptors 2023, 2, 166-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2030011
McEwan IJ. From Antibodies to Crystals: Understanding the Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Related Proteins. Receptors. 2023; 2(3):166-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2030011
Chicago/Turabian StyleMcEwan, Iain J. 2023. "From Antibodies to Crystals: Understanding the Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Related Proteins" Receptors 2, no. 3: 166-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2030011
APA StyleMcEwan, I. J. (2023). From Antibodies to Crystals: Understanding the Structure of the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Related Proteins. Receptors, 2(3), 166-175. https://doi.org/10.3390/receptors2030011





