Abstract
Introduction: Renal lobulation (also known as fetal or embryonic lobulation) is a rare variation during development in which renal lobules have a visible anatomical space between them, and this can be seen in 0.5–4% of adults. Material and methods: this study was conducted on 54 human kidneys from patients who died due to causes unrelated to renal pathology which were fixed in a 10% formaldehyde solution and then carefully dissected. Results: The group with fetal lobulation (n = 16) was associated with a length M = 9.89 (SD = 0.6, p = 0.15). By comparison, the kidneys without lobulation (n = 38) were associated with a numerically longer length M = 10.29 (SD = 0.607, p = 0.098). To test the hypothesis that lobulation is associated with a statistically significant different length a Mann–Whitney test was performed, which indicated that the length of the kidneys is smaller in scase of lobulation U = 198, Z = −2.04, p = 0.04. Cross-tabulation also demonstrated that kidney lobulation may be influenced by the presence of polar arteries with r = 0.41 (p < 0.02). The likelihood ratio was 7.28, df 1, p = 0.003, with an odds ratio of 6.857 (CI 95% = 1.84–25.61). Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that kidneys with lobulation were 6.85 times more likely to have polar arteries than kidneys without lobulation. Conclusions: the data from our research indicate that even though no pathological conditions have been linked with lobulated kidneys, the incidence of vascular variations (specifically polar arteries) is higher when there is persistent fetal lobulation.
1. Introduction
Developmental variations in kidney anatomy occupy a special place in fundamental and applied medical disciplines. In our time, the number of invasive and non-invasive procedures on the organs of the urinary system has significantly increased. This requires the training of specialists, including a detailed study of the anatomy of organs. The structure of the human body should be studied, taking into account age, sex and individual characteristics. Equally important is the anatomy, given the needs of the clinical disciplines where these specialists’ knowledge will be applied. The problem has increased significantly, given the progress in recent years in urology, nephrology, vascular surgery and oncology. The list and complexity of procedures has increased markedly, but the importance of fundamental disciplines for the implementation of complex surgical and diagnostic procedures has remained unchanged [1,2,3].
The development of medicine has led to the introduction, into wide practice, of modern methods for the diagnosis and treatment of kidney diseases. Many of these methods are based on a deep understanding of the normal anatomy and developmental patterns of the kidney. The preoperative assessment of variant anatomy using CT has become one of the fundamental research methods to avoid iatrogenic injuries and assess operative risk. Selective angiography of the kidneys and denervation of the renal arteries are becoming more widely used procedures for the treatment of acute and chronic conditions. Given the frequency of the occurrence of anomalies and variants in the development of the genitourinary system, the relevance of these procedures is higher than ever [2,4].
Renal lobulation (also known as fetal or embryonic lobulation) is a rare variation of development in which the renal lobules have a visible anatomical space between them. Renal lobulation appears at 18 weeks of embryogenesis and remains evident until the age of 3–5 years. After 3 to 5 years the cortex losses its lobulated appearance [5,6,7]. In a small percent of patients, the lobules tend to persist and are considered to be a benign variation. Fetal lobulation is considered to be rare in adult patients and can be seen in 0.5–4% of cases depending on the study and method that was used for its assessment [8,9].
There are three main types of kidney surface anatomy: normal (bean shaped), with fetal lobulation, and with a dromedary hump. All three variants are considered to be normal. However, kidneys with fetal lobulation and dromedary humps can sometimes be confused with pathological conditions such as tumors and nephrosclerosis [10,11,12]. Kidney lobulation may lead to unnecessary testing and subsequent clinical complications by masquerading as other lesions [13]. It is also present in some developmental anomalies. For instance, in Bardet–Biedl syndrome fetal lobulation is present in 12–84% of cases [14,15]. Therefore, there is a number of coincidental relationships between developmental variations of the kidney and other conditions.
The current study is an attempt to analyze factors that may lead to the lobulated appearance of the kidneys.
2. Materials and Methods
This study was conducted on 54 human kidneys, from patients who died due to causes unrelated to renal pathology, which were fixed in a 10% formaldehyde solution. After seven days of preservation in a formaldehyde solution the kidneys were dissected manually. The kidneys were considered to have fetal lobulation based on their surface anatomy (the presence of anatomical spaces between the lobules), as seen in Figure 1. Bean-shaped kidneys without surface lobulations were included in the second group (Figure 2). The data acquired during the study were analyzed statistically (Spearman’s correlation, cross-tabulation analysis, Mann–Whitney test and logistic regression). Spearman’s correlational analysis was used to determine the correlation between the presence of fetal lobulation and the length, width and number of major calyces. Cross-tabulation analysis was used to determine the associations between fetal lobulation, sex, kidney position (right or left), presence of any vascular variation (double arteries, early bi- or trifurcation), presence of polar arteries and the position of arteries in the renal sinus (vein–artery–pelvis or artery–vein–pelvis). A Mann–Whitney test was performed to test the hypothesis that lobulation is associated with a statistically significant difference in the length or width of the parenchyma.
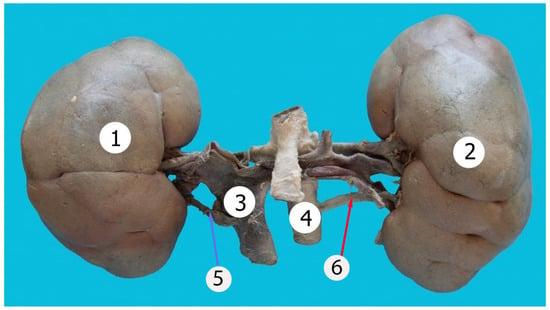
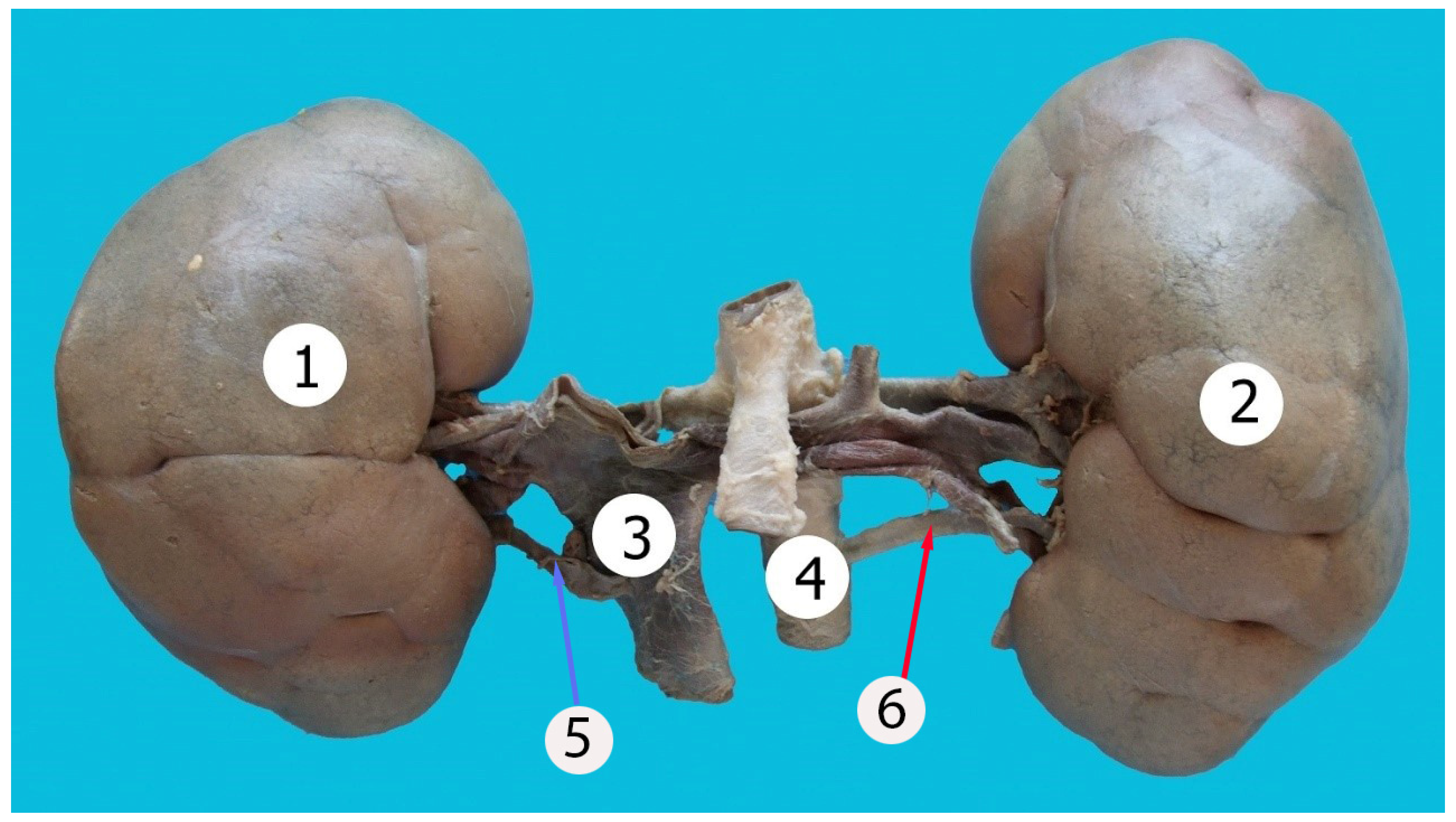
Figure 1.
Kidneys with lobulated appearance. 1—right kidney; 2—left kidney; 3—inferior vena cava; 4—aorta, 5—accessory renal vein, 6—accessory renal artery.
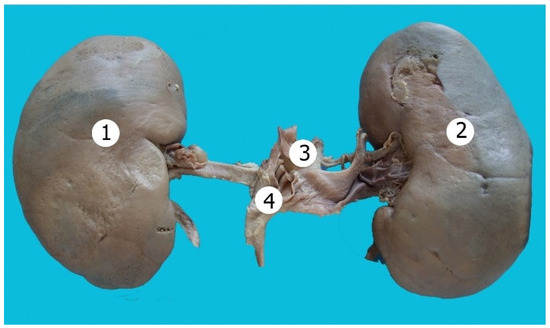
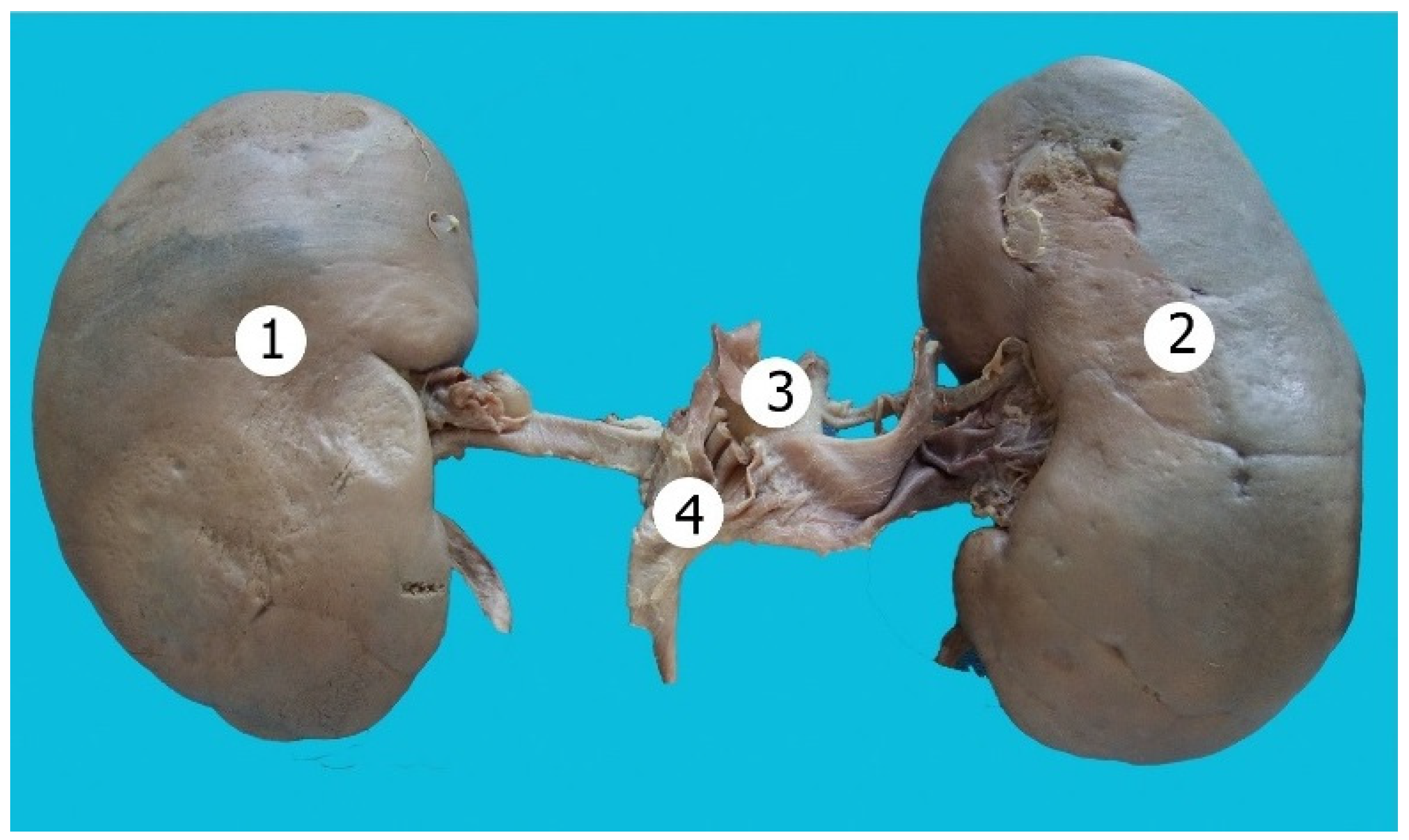
Figure 2.
Bean-shaped kidneys. 1—right kidney; 2—left kidney; 3—inferior vena cava; 4—aorta.
The study was conducted according to the ethical laws of the institution and was approved by the ethics committee (19 August 2018 nr. 80/85).
3. Results
During our study, out of 54 kidneys 29.6% (16 cases) displayed fetal lobulation. The remaining 70.4% (38 cases) had a normal bean-shaped structure, including a dromedary hump that was seen in 20.3% of kidneys (11 cases). Descriptive statistics of the kidneys are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive statistics.
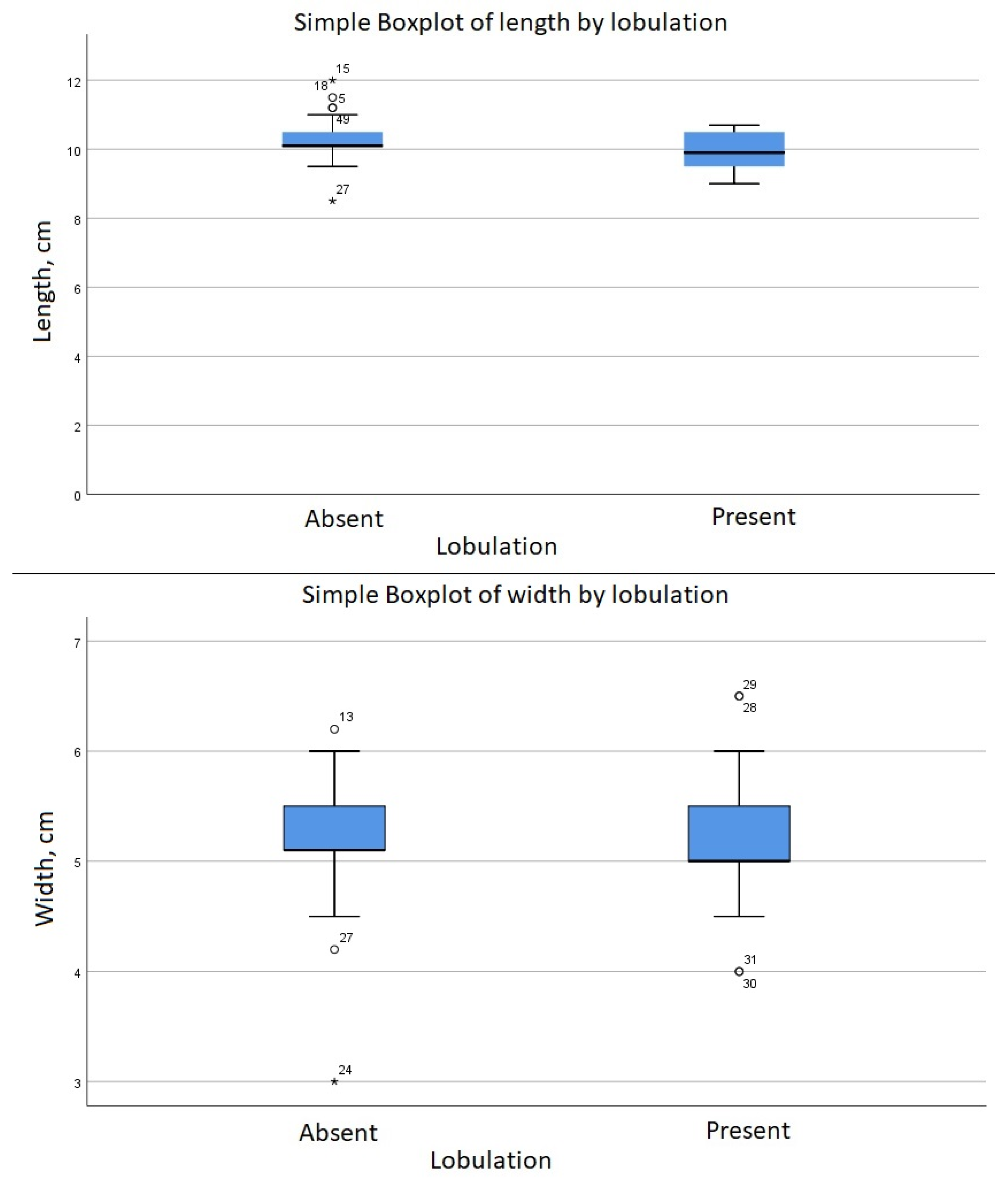
The group with fetal lobulation (n = 16) was associated with a length M = 9.89 (SD = 0.6, p = 0.15). By comparison, the kidneys without lobulation (n = 38) were associated with a numerically longer length M = 10.29 (SD = 0.607, p = 0.098) (Figure 3). To test the hypothesis that lobulation is associated with a statistically significant different length a Mann–Whitney test was performed, which indicated that the length of the kidneys is smaller in case of lobulation; U = 198, Z = −2.04, p = 0.04 (Figure 4).
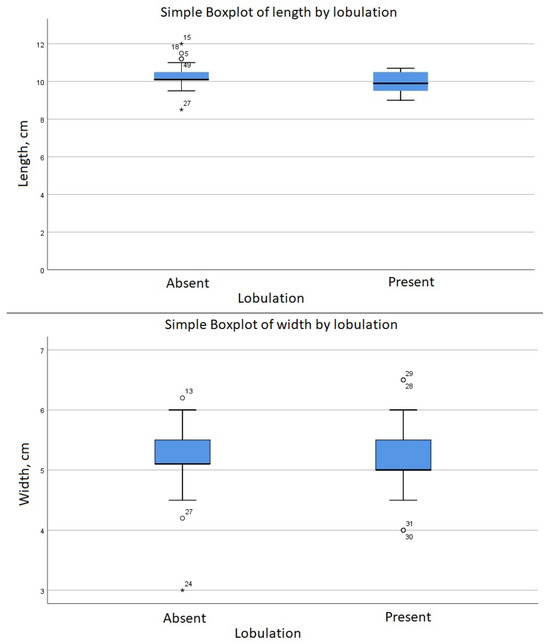
Figure 3.
Comparison of length between groups (asterisk and circles indicates outliers).
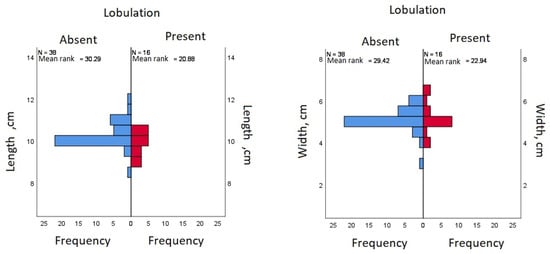
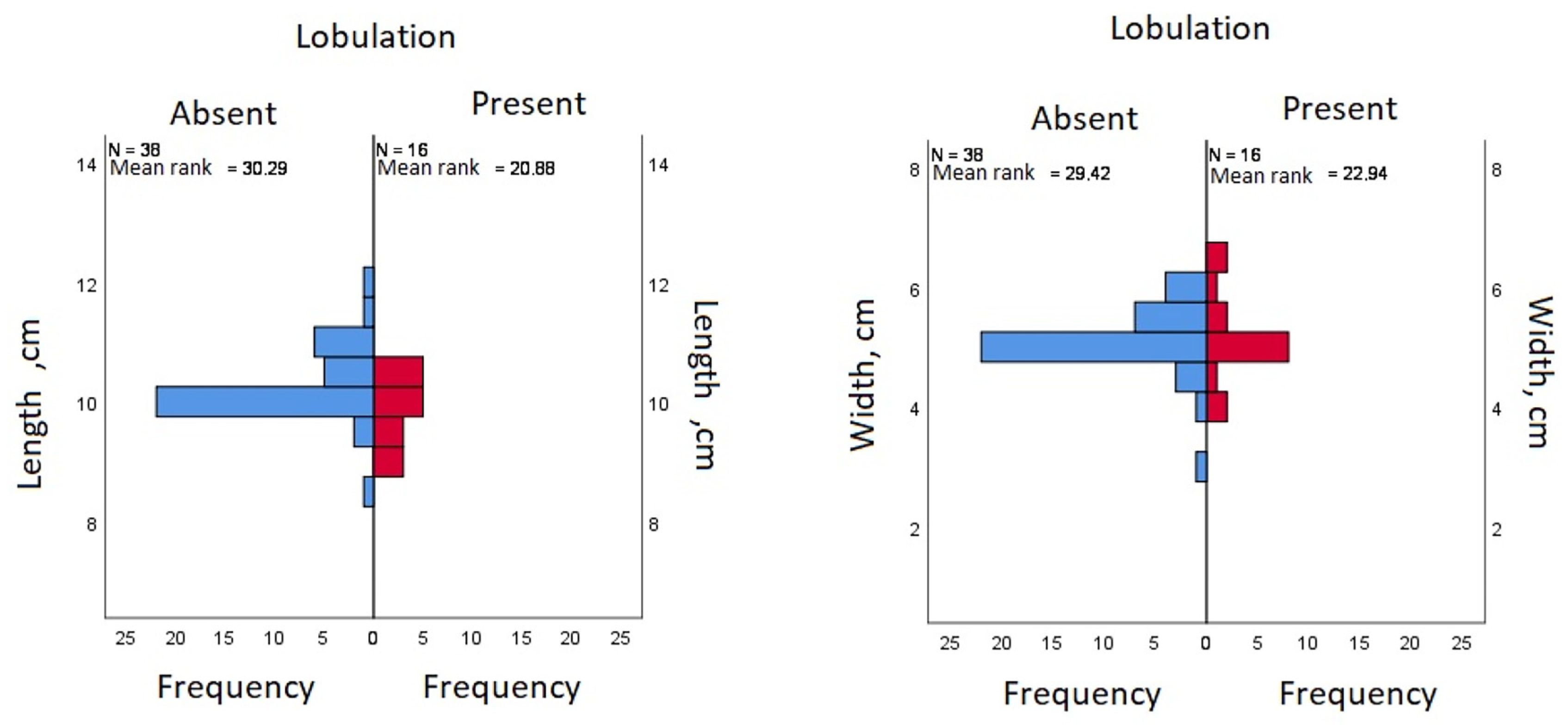
Figure 4.
Comparison of means (blue indicates kidneys with no surface lobulation, red indicates presence of surface lobules).
Spearman’s correlation showed an r = −0.28 (p = 0.04) between the presence of renal lobulation and the length of the kidneys. There was no correlation between renal lobulation and width. This correlation is considered to be medium, thus, the relationship may be not that evident and other factors may be involved. Based on these results, the group with fetal lobulation was associated with a statistically significant shorter length than the group without fetal lobulation (Figure 3).
The association between the kidney lobulation and vascular variation was identified using a Chi-square test (ꭓ2 = 21.11, df = 1, p < 0.001) with no correction for continuity, which reduced the Chi-square test ꭓ2 value to 18.46; the result remaining significant (p < 0.001). Similarly, the Chi-square test of independence found the relationship between the polar arteries’ presence and fetal lobulation (ꭓ2 = 9.19, df = 1, p = 0.002) had an odds ratio of 6.857 (CI 95% = 1.84, 25.61). There was no relationship between fetal lobulation and the number of major calyces or sex.
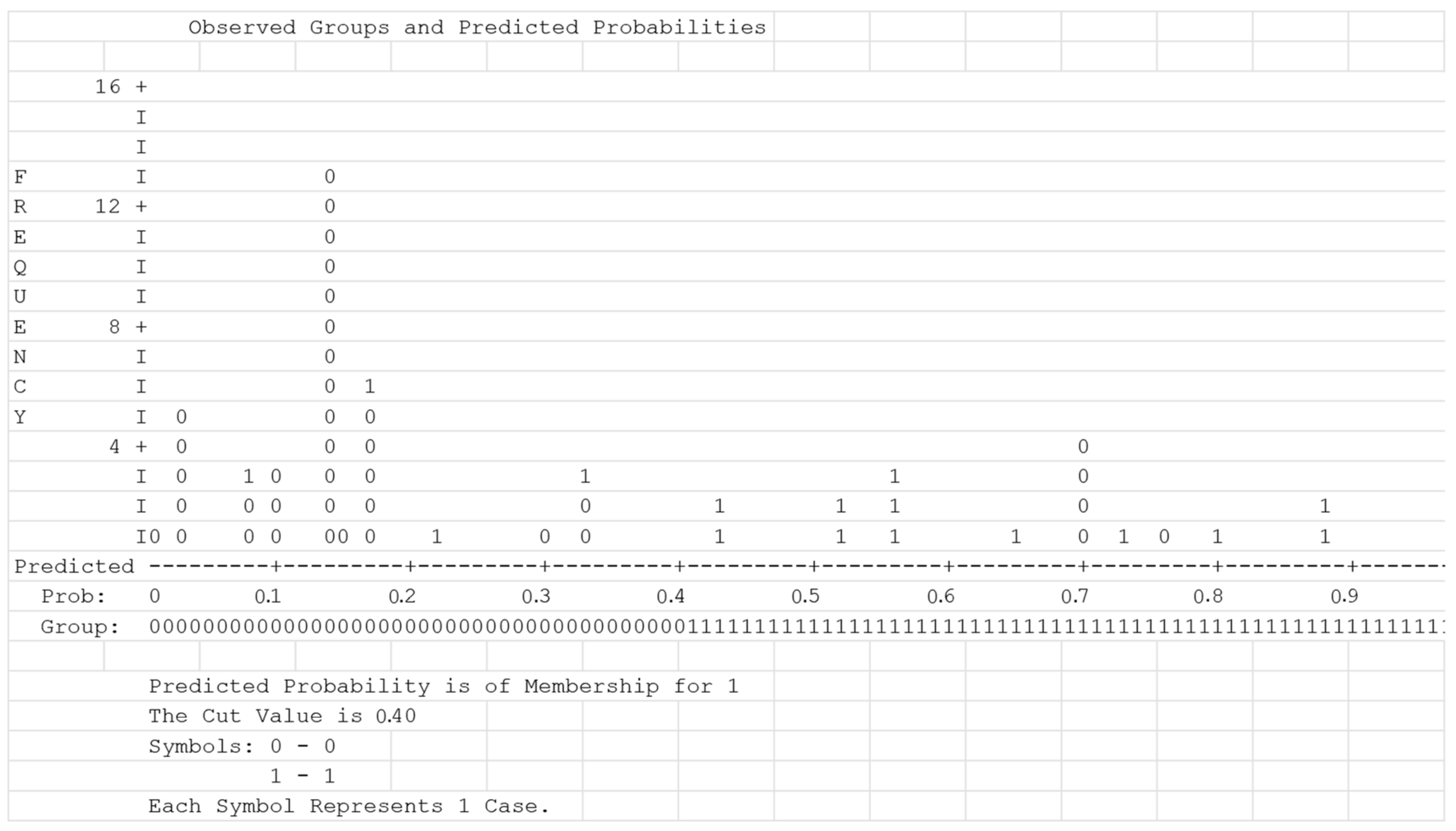
A logistic regression was performed to ascertain the effects of polar arteries on the likelihood that kidneys have cortex lobulation (Step 1) and the effect of both polar arteries and length on the likelihood that kidneys have cortex lobulation (Step 2). In step 1, the logistic regression model was statistically significant, ꭓ2 = 8.73, df = 1, p = 0.003. The model explained 21.2% (Nagelkerke R2) of the variance in kidney lobulation and correctly classified 75.9% of cases. Kidneys with lobulation were 6.85 times more likely to have polar arteries than kidneys without lobulation (OR = 6.85; CI 95% = 1.84, 25.61). Width, sex, number of calyces, kidney side and the presence of vascular variations other than polar arteries did not influence the model and were excluded.
Sensibility and specificity (x% and y%, respectively) were analyzed based on the cut-off value 0.4 that was estimated after the classification plot analysis (Figure 5).
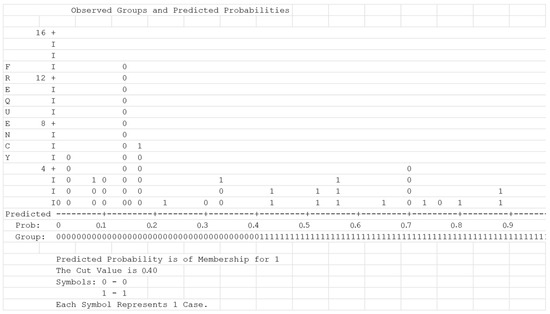
Figure 5.
Classification plot analysis.
In step 2, the logistic regression model was statistically significant, ꭓ2 = 17.63, df = 2, p = <0.001. Determining the coefficient (Nagelkerke R2) of the model explained 39.6% of the variance in kidney lobulation and correctly classified 79.6% of cases. Kidneys with lobulation were 14.01 times more likely to have polar arteries than kidneys without lobulation when length was taken in consideration as a cofactor (OR = 16.87, CI 95% = 2.78, 70.56) (Table 2).

Table 2.
Logistic regression between kidney lobulation, polar arteries and length.
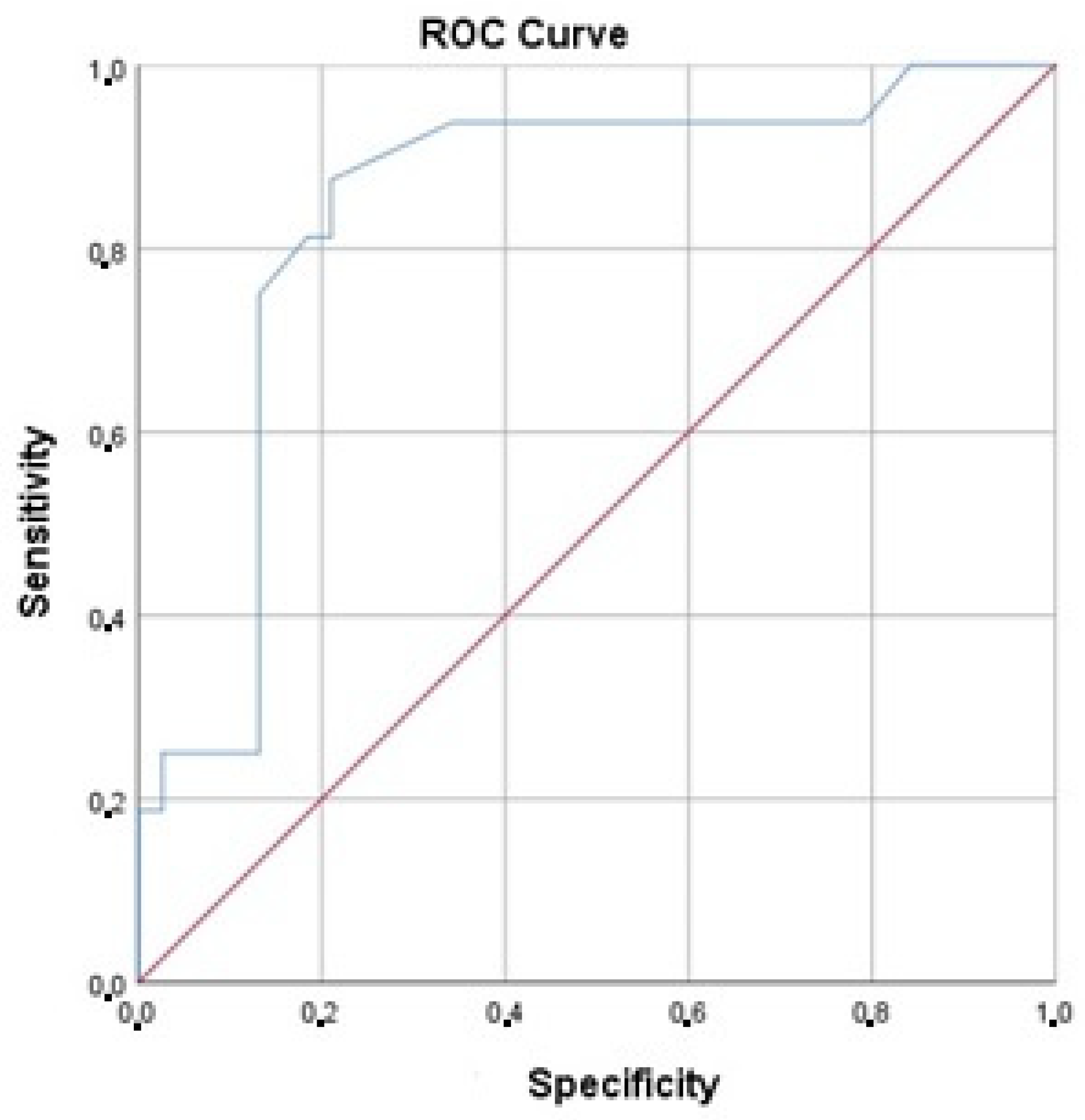
The discrimination analysis showed that the area under the ROC curve was 0.84 (95% CI 0.72, 0.96), which is significantly higher than 0.5 (p < 0.001) (Figure 6).
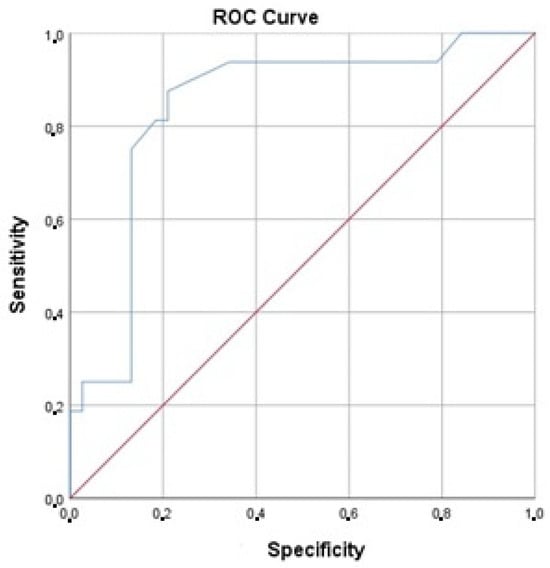
Figure 6.
ROC curve.
The model calibration being estimated as ꭓ2 = 16.5, df = 7, p = 0.21 can be interpreted as a research limitation because of its decreased model fit.
4. Discussion
The kidneys are the largest paired organ of all the organs of the retroperitoneal space, and are located in its upper section in the renal beds on both sides of the spine. Many authors describe the kidney as a paired, bean-shaped organ with a smooth surface in adults, more convex anteriorly, less convex posteriorly, with a convex lateral margin and a concave medial one. The concave, open, medial edge has a recess—the renal gate. Based on this, it is customary to distinguish the anterior and posterior surfaces of the kidney, the outer and inner edges, as well as the upper and lower poles. The renal gates pass into extensive depressions that protrude into the substance of the kidney and are called the renal sinus. In the renal sinus there are elements of the collecting system of the kidneys—the calyces and pelvis, as well as blood, lymphatic vessels, nerves and fatty tissue. Normally, the kidneys are supplied by one artery and drained by one vein [1,3].
Congenital variations of the kidney’s form are persistent fetal lobulation, a hypertrophied column of Bertin, and a dromedary hump. Other anomalies include: fusion anomalies (e.g., horseshoe kidney and pancake kidney); anomalies of the renal position (e.g., renal malrotation, simple renal ectopia, and crossed renal ectopia); renal number (e.g., renal agenesis and supernumerary kidney); and abnormalities in the development of the urinary collecting system (e.g., pyelocaliceal diverticulum, megacalycosis, ureteropelvic junction obstruction, duplex collecting system, megaureter, ectopic ureter and ureterocele) [16]. Of all of the abovementioned variations in developmental structural changes such as fetal lobulation, dromedary humps are relatively understudied. The three main types of kidney shape that are described in the literature are normal (bean-shaped), those with a dromedary hump and lobulated kidneys (fetal). Although the anatomy of the kidney is abundantly studied, the main focus is usually on its vascular supply, while its surface anatomy is often overlooked. There is limited information about the relationship between individual variations during development and later life outcomes.
Lobulated kidneys can be seen in animals, especially in aquatic and marine mammals [17]. Therefore, the lobulated appearance of the kidneys in children likely represents an embryological remnant. Nevertheless, it rarely occurs in adults and is seen more frequently in several pathologic conditions. It is frequently seen in Bardet–Biedl and Zellweger syndromes and may indicate a defect in renal maturation [18]. The lobulated appearance is the result of fetal lobulation that persists into adulthood and is caused by incomplete fusion of the developing renal lobules. It is important in imaging to distinguish between lobulation and scarring, which can occur from reflux and/or chronic infection.
Developmental anomalies of the kidneys in 50–60% of cases are associated with anomalies in other organs and systems. Anomalies of the cardiovascular system occur in 25% of cases, the gastrointestinal tract—18%, the central nervous system—10%, the skeleton—9%, the lungs—6%, the face—7%, the urinary system—4%, the diaphragm—2% and the eyes—1%. In approximately 47% of cases, anomalies are combined and involve several systems [19].
The idea that the kidney shape depends on its vasculature is not new and there have been multiple reports in the past (most of which are single case reports) [20,21,22,23,24].
One study described the bilateral malrotation of the kidney, bilateral lobulated kidneys and the open hilum of the kidney. The renal pelvis was present anterior to the renal vessels instead of in the posterior position. The right kidney was in a lower lumbar position and had three supplementary arteries and two veins [20].
In a study that involved 54 cases of double renal arteries supplying one kidney and originating from the aorta, multiple other variations in development were found, such as double renal veins, double ureter, the persistence of the fetal renal lobulation of the adult kidney and a genital artery originating from the supplementary renal artery [21].
Several reports describe diamond-shaped, discoid-shaped, pyramidal kidneys and in all of the cases there were either additional vessels or a variation in the development of the single vessel [22,23,24].
In another case report, the right kidney was pyramidal in shape and the hilum was directed anteriorly. In this case, the right renal vessels were twisted against each other and could explain the unusual shape of the organ [24].
In an autopsy case of an 87-year-old woman, the left kidney was found to be diamond-shaped and situated lower than usual. The hilum of this kidney was larger and facing anteriorly. Four accessory arteries supplied the organ and it was drained by one ordinary and one supernumerary vein [22]. In another case report, a discoid-shaped ectopic kidney located in front of the right common iliac artery was observed in a 71-year-old Japanese man [23].
Therefore, there are several reports that show that lobulated kidneys and vascular anomalies have obvious links. The exact mechanism of this is still debated but it is probably linked to hemodynamic changes in the kidneys. It is important to mention that these changes are also often seen in some pathological conditions. Further studies may show whether this condition can affect the people’s health or whether it really is benign. Variations or anomalies of shape are usually associated with variations in the arterial supply. However, it is worth mentioning that arterial variations are more common than venous [2,4]. The number of accessory renal veins is also smaller, while in rare instances there can be up to seven renal arteries [4,25,26]. This may partially explain the reason why we did not find any association with venous anomalies. The arterial supply of the internal organs is characterized by a high degree of variation in origin, trajectory, and branching patterns [27]. This is especially true for the kidneys, which have accessory renal arteries in 18.2–23.1% of cases [28,29]. In rare cases the kidney may have up to seven renal arteries, and multiple renal arteries are often seen in other congenital anomalies [21,26,30]. Changes in the vascular supply and drainage may have hemodynamic consequences leading to the persistence of fetal lobulation. Logistic regression analysis demonstrated that that kidneys with surface lobulation were 6.85 times more likely to have polar arteries than kidneys without lobulation. This relationship was more evident when length was taken in consideration as a cofactor (lobulated kidneys were 14.01 times more likely to have polar arteries than kidneys without lobulation).
There are little data on renal lobulation in adults. This is due to the fact that kidney lobulation is seen only in 0.5–4% of adults [8,9]. Favorito and coworkers evaluated fetal lobulation in 108 kidneys obtained from human fetuses and found that renal clefts have great variation, weak correlation and no tendency to decrease during the second gestational trimester [31]. Lorenz and coworkers assessed kidney anatomy and diseases in 1997 potential donors and encountered fetal lobulation in only 0.5% of cases (CI 95%, 0.2–0.9). There was no difference in the incidence of lobulation between males and females [9]. Harrison and coworkers analyzed 166 renal arteriograms and found that 4% of kidneys had kidney lobulation [8]. Our study demonstrated a higher incidence of kidney lobulation (29.6%). Due to the small group size this finding is likely accidental and does not allow us to extrapolate the results to a larger population. Nevertheless, it allowed us to analyze two group of kidneys (with and without lobulation), demonstrating that there is a high prevalence of arterial variations (particularly with accessory arteries and polar arteries).
The major limitation of the current study is the small number of cases. Fetal lobulation is considered rare and it is difficult to collect a large group of specimens. The strength of this study is that this is, to our knowledge, the first study to assess the possible reasons for persistent fetal lobulation in adults.
5. Conclusions
The data from our research indicate that even though no pathological conditions have been linked with lobulated kidneys, the incidence of vascular variations (specifically polar arteries) is higher when there is persistent fetal lobulation. Therefore, this condition could be caused by hemodynamic changes inside the organ. Due to the small number of evaluated cases, further evaluation of this condition may provide additional data. However, this is difficult due to its low incidence in the adult population. Kidneys with fetal lobulation also tend to be smaller. The proposed model requires validation and completion to determine a coefficient value of 0.8.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.C. and O.A.; methodology, S.C. and O.A.; software, O.A.; formal analysis, S.C. and O.A.; investigation, S.C. and O.B.; resources, S.C., O.B. and K.M.; data curation, O.B.; writing—original draft preparation, S.C., O.A., O.B. and K.M.; writing—review and editing, O.B. and O.A.; visualization, S.C.; supervision, O.A. and O.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to the ethical laws of the institution (State University of Medicine and Pharmacy N. Testemitanu) and was approved by the ethics committee (19 August 2018 nr. 80/85).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available and can be presented upon personal request.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to sincerely thank those who donated their bodies to science so that anatomical research could be performed. The results from such research can potentially improve patient care and increase mankind’s overall knowledge. Therefore, these donors and their families deserve our utmost gratitude.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Tubbs, R.S.; Shoja, M.M.; Loukas, M. Bergman’s Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Covantev, S.; Mazuruc, N.; Belic, O. Renal Arteries: A Morphological and Angiographic Assessment. Online J. Health Allied Sci. 2018, 17, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Standring, S. Gray’s Anatomy E-Book: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Covantev, S.; Mazuruc, N.; Belic, O. Renal Veins: Developmental Variations and Clinical Significance. Online J. Health Allied Sci. 2017, 16, 12. [Google Scholar]
- Hodson, J. The lobar structure of the kidney. Br. J. Urol. 1972, 44, 246–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, S.A.; Joshi, R.A.; Herekar, N.G. Histogenesis of Kidney in Human Fetuses. Int. J. Recent Trends Sci. Technol. 2012, 3, 44–48. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Dinesh, A.; Kaul, J.M. Morphological and Morpho-metrical Study of Human Renal Development during Mid-Gestation Period. J. Anat. Soc. India 2006, 55, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, L.H.; Flye, M.W.; Seigler, H.F. Incidence of Anatomical Variants in Renal Vasculature in the Presence of Normal Renal Function. Ann. Surg. 1978, 188, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.C.; Vrtiska, T.J.; Lieske, J.C.; Dillon, J.J.; Stegall, M.D.; Li, X.; Bergstralh, E.B.; Rule, A.D. Prevalence of renal artery and kidney abnormalities by computed tomography among healthy adults. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 431–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaul, A. Unusual Kidney Cancer Presentation, Case Report and Review. Proc. UCLA Healthcare 2013, 17. Available online: https://proceedings.med.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Unusual-Kidney-Cancer-Presentation-Case-Report-and-Review-edited.pdf (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Bhatt, S.; MacLennan, G.; Dogra, V. Renal pseudotumors. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2007, 188, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazim, S.M.; Bangash, M.; Salam, B. Persistent fetal lobulation of kidney mimicking renal tumour. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, bcr-2017-219856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, B.; Nestor, N.; Ruiz, K.; Aldawood, A.; Zdilla, M.; Klinkhachorn, P. Persistent Fetal Kidney Lobulation: Anatomy and Pathology. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 616.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beales, P.L.; Elcioglu, N.; Woolf, A.S.; Parker, D.; Flinter, F.A. New criteria for improved diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome: Results of a population survey. J. Med. Genet. 1999, 36, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, S.J.; Green, J.S.; Fan, Y.; Bhogal, A.K.; Dicks, E.; Fernandez, B.A.; Stefanelli, M.; Murphy, C.; Cramer, B.C.; Dean, J.C.; et al. Clinical and Genetic Epidemiology of Bardet–Biedl Syndrome in Newfoundland: A 22-Year Prospective, Population-Based, Cohort Study. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2005, 132, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houat, A.P.; Guimarães, C.T.S.; Takahashi, M.S.; Rodi, G.P.; Gasparetto, T.P.D.; Blasbalg, R.; Velloni, F.G. Congenital Anomalies of the Upper Urinary Tract: A Comprehensive Review. Radiographics 2021, 41, 462–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.F. Morphological evidence of marine adaptations in human kidneys. Med. Hypotheses 2006, 66, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, M.M. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and the Urinary Tract (CAKUT). Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2014, 33, 293–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barakat, A.; Drougas, J.G.; Barakat, R. Association of congenital abnormalities of the kidney and urinary tract with those of other organ systems in 13,775 autopsies. Child Nephrol. Urol. 1988, 9, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, S.T.; Meshram, M.M.; Kasote, A.P. Bilateral malrotation and lobulation of kidney with altered hilar anatomy: A rare congenital variation. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2011, 33, 941–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordei, P.; Sapte, E.; Iliescu, D. Double renal arteries originating from the aorta. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2004, 26, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morishima, K.; Miyaki, T.; Ito, H. A rare case of a kidney with an widely opened hilus and supernumerary renal vessels. Kaibogaku Zasshi 1996, 71, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsuka, A.; Kikuta, A.; Taguchi, T.; Murakami, T. Ectopic kidney in front of the right common iliac artery and its blood vascular supply—A case report. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 1993, 70, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakesh, V.; Nayak, S.; Potu, B.K.; Vollala, V.R.; Pulakunta, T. Twisted renal vessels producing an abnormal shape of the right kidney. Singap. Med. J. 2008, 49, e252–e253. [Google Scholar]
- Ballesteros, L.E.; Saldarriaga, V.; Ramirez, L.M. Morphologic evaluation of the renal veins: A study with autopsy material from Colombian subjects. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. = Rev. Roum. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 77–81. [Google Scholar]
- Miclăuş, G.D.; Sas, I.; Joseph, S.C.; Matusz, P.; Pleş, H.; Tubbs, R.S.; Loukas, M. Seven renal arteries: A case report using MDCT angiography. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. = Rev. Roum. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55 (Suppl. S3), 1181–1184. [Google Scholar]
- Covanțev, S.; Mazuruc, N.; Belic, O. An unusual case of colon vascularization by the inferior mesenteric artery. J. Vasc. Bras. 2017, 16, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, B. Das Arteriensystem der Japaner II; Maruzen Publishing Co.: Tokyo, Japan, 1928; pp. 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Matusz, P.; Miclaus, G.; Ples, H. Study of the renal additional arteries on 1000 CT angiography continuous series. Clin. Anat. 2011, 24, 408. [Google Scholar]
- Matusz, P.; Miclăuş, G.D.; Banciu, C.D.; Sas, I.; Joseph, S.C.; Pirtea, L.C.; Tubbs, R.S.; Loukas, M. Congenital solitary kidney with multiple renal arteries: Case report using MDCT angiography. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. = Rev. Roum. Morphol. Embryol. 2015, 56 (Suppl. S2), 823–826. [Google Scholar]
- Favorito, L.A.; Lobo, M.L.P.; Fernandes, A.V.; Gallo, C.M.; Sampaio, F.J.B. Kidney surface development in human fetuses: Study applied to radiological diagnosis. Int. Braz. J. Urol. Off. J. Braz. Soc. Urol. 2022, 48, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).