Abstract
Understanding prostate carcinogenesis is crucial not only for identifying new treatment targets but also for developing effective strategies to manage the asymptomatic form of the disease. There is a lack of consensus about predicting the indolent form of the disease prostate cancer, leading to uncertainties regarding treatment initiation. This review aims to enhance the assessment and management of early prostate cancer by providing a comprehensive picture of the molecular anatomy of the prostate, synthesising current evidence, highlighting knowledge gaps, and identifying future directions. It presents evidence for the efficacy of active surveillance as an alternative treatment strategy and its potential benefits in specific patient groups through androgen receptor disruption. Overall, an improved understanding of prostate carcinogenesis and its molecular underpinnings can pave the way for tailored and precise management approaches for this common cancer. Further development and validation of molecule-based assessment tools are needed. Integrating genomic, proteomic, and phenotypic models, as well as functional approaches, can help predict outcomes. This facilitates selecting candidates for active surveillance and targeting interventions for higher-risk cases, contributing to more precise management strategies.
1. Introduction
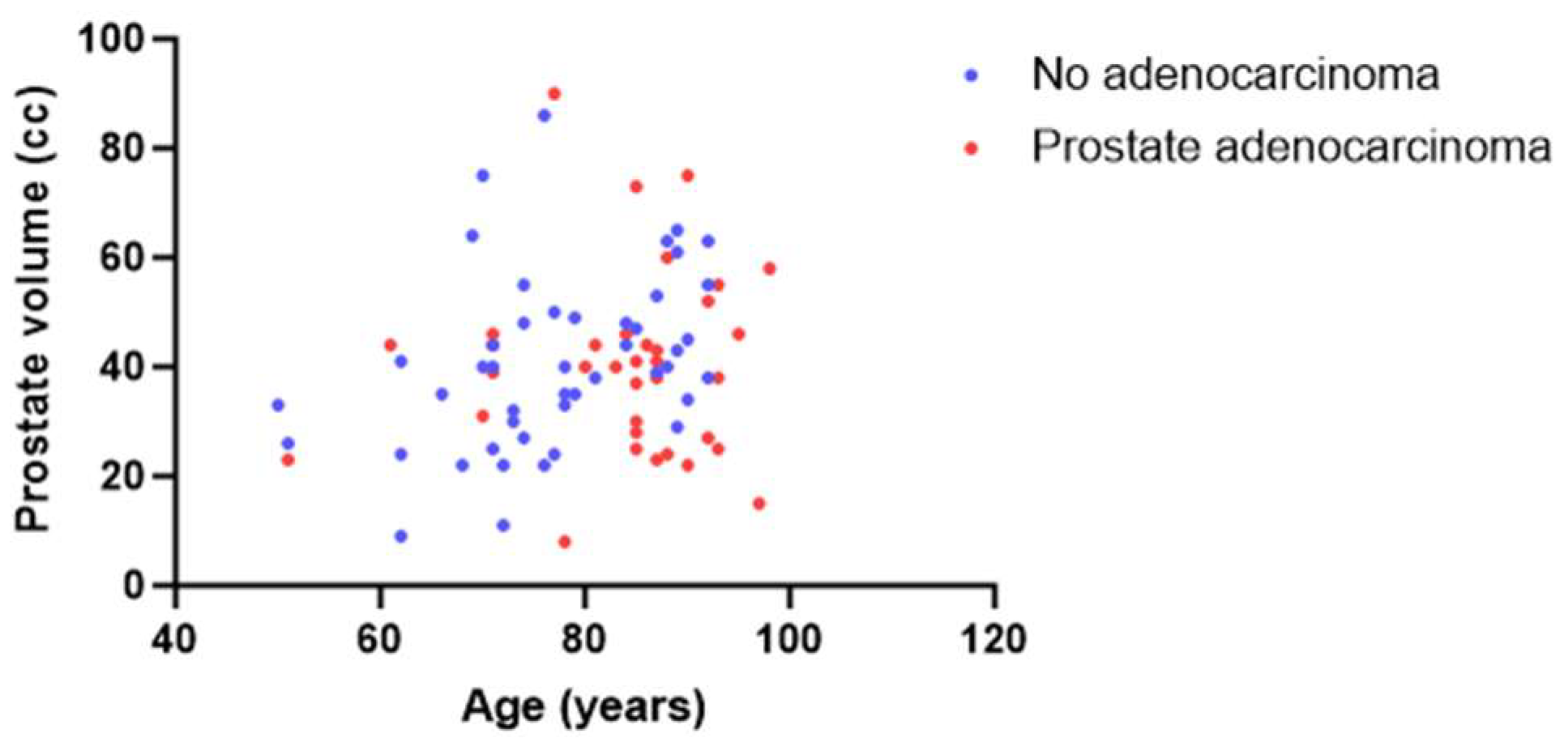
Prostate cancer has exhibited a concerning rise in incidence over the past two decades, particularly in Western countries, resulting in a significant impact on public health with more than 500,000 new cases and 100,000 deaths [1,2,3]. Autopsy investigations have revealed a high rate of age-related neoplastic lesions among men aged 70–79 years old, with 36% of men of European-Caucasian ancestry and 51% of African American men affected [4]. Similarly, we found a prevalence of neoplastic lesions in 35% of autopsied men of French-European Caucasian ancestry over 50 years old [5] (Figure 1).
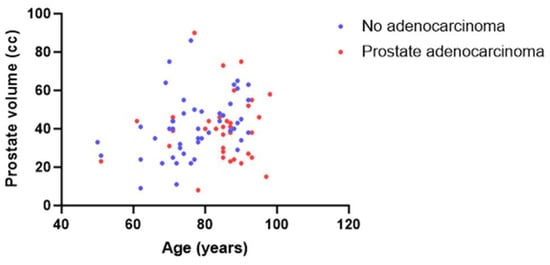
Figure 1.
Series of autopsy cases (men over 50 years old) taken from the CeRePP database [5]. Correlation between age (X) and prostate cc volume (Y) with (blue dot) or without (red dot) prostate adenocarcinoma lesions.
In contrast, emerging evidence from randomised studies indicates that a significant proportion of localised prostate cancer cases may have a low risk of cancer-specific mortality or clinical progression [6,7,8]. Altogether, these observations emphasise the urgent need for new strategies to prevent or manage early stages of prostate cancers. Consequently, the concept of active surveillance has gradually emerged over the years as a viable alternative treatment strategy for these ‘favourable’ tumours, aiming to minimise overtreatment and its potential side effects [9,10,11].
Significant progress has been made in our understanding of prostate carcinogenesis and its natural history, leading to the identification of early and late molecular events and recognition of the heterogeneity of the cellular origins of prostate cancer [12,13,14,15,16,17]. This knowledge has paved the way for the development of molecular predictors that could considerably improve the management of prostate cancers. Clinical observations revealed that intervention in the androgen receptor (AR) pathway during the early stages of the disease conventionally termed as secondary chemoprevention, can effectively reverse low-grade and early-stage prostate cancer [18,19,20,21,22]. Moreover, at advanced stages, a specific subset of prostate cancer characterised by SPOP/SPOPL deficiency has shown remarkable responses to androgen deprivation [23]. These recent advances in our understanding of functional and molecular subtypes of prostate cancer are of considerable clinical relevance in introducing new paradigms for the management of early-stage prostate cancer.
In this review, we aim to provide a comprehensive view of the molecular anatomy of the prostate, encompassing the intricate molecular processes, cellular interactions, and signalling pathways that contribute to the development, function, and disease progression of the prostate. Furthermore, we delve into the concept of active surveillance as an alternative treatment strategy and discuss the potential benefits of early intervention through AR disruption. By synthesising current evidence, identifying gaps in knowledge, and exploring future prospects, this review may contribute to the ongoing efforts to improve the assessment and management of early prostate cancer.
2. Molecular Anatomy of the Prostate
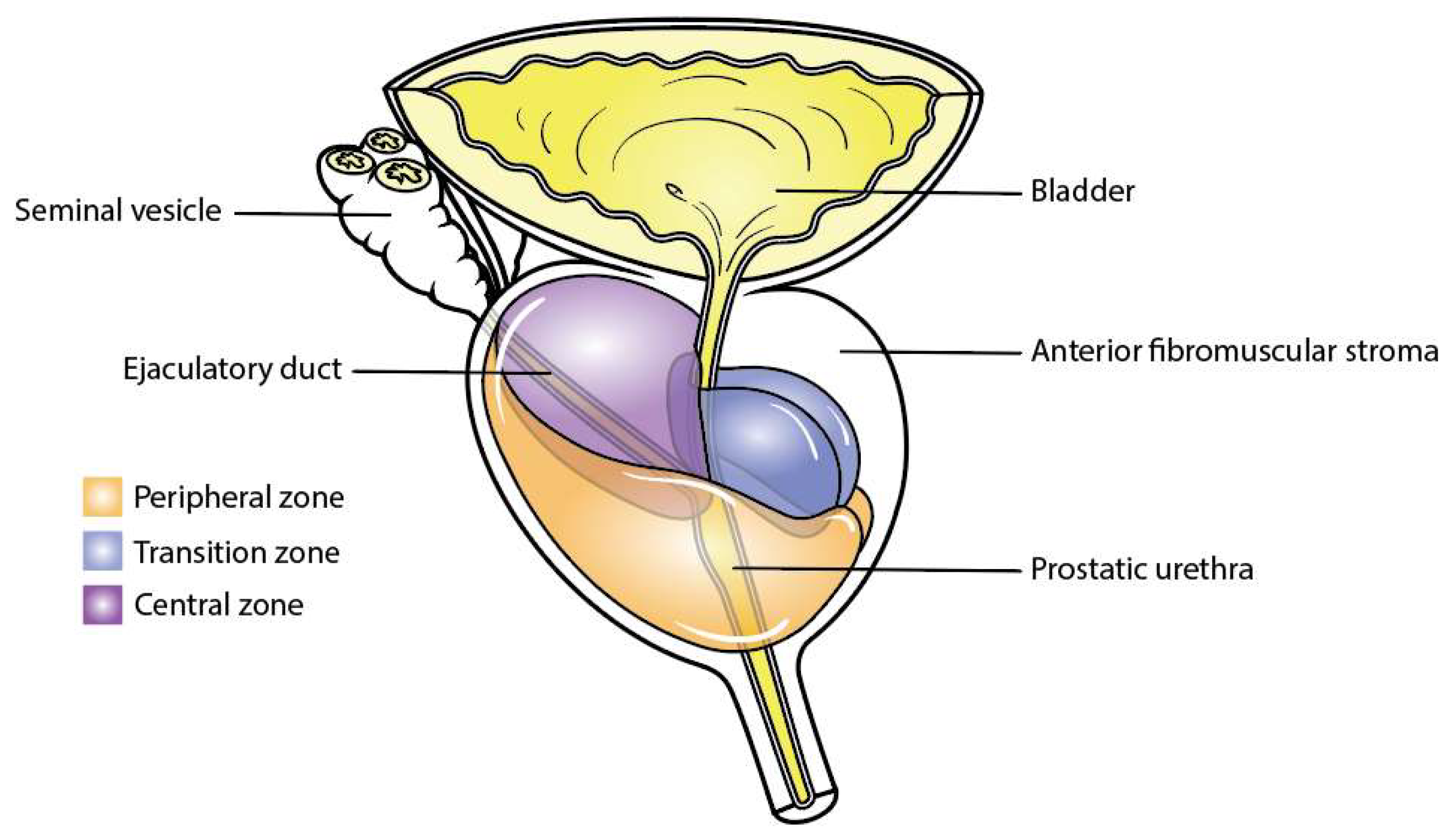
The prostate is divided into different histological zones according to the well-established McNeal segmentation [24,25] (Figure 2), whose foundations were laid by Gil-Vernet [26]. These zones are composed of the anterior fibromuscular stroma, the posterolateral peripheral zone, the periurethral transition zone, and the central zone surrounding the ejaculatory ducts. In pathology, benign prostatic hyperplasia mainly affects the transition zone, whilst prostate cancer is more commonly found in the peripheral zone of the prostate (70%) rather than the transition zone (25%) and the anterior fibromuscular stroma zone (5%) [25]. This discrepancy is mainly due to the varying density of glandular tissue susceptible to transformation in each zone. In normal ageing, the morphological changes occurring in the central zone are increasingly challenging to identify and the mechanisms underlying these changes remain unclear, even in McNeal’s reports [27,28,29].
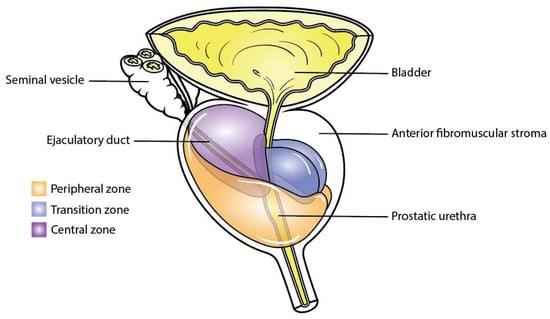
Figure 2.
Zones of the prostate. This figure illustrates the distinct anatomical zones within the prostate gland: the peripheral zone in orange, the central zone in purple, and the transition zone in blue.
2.1. Gene Expression According to Cell Types
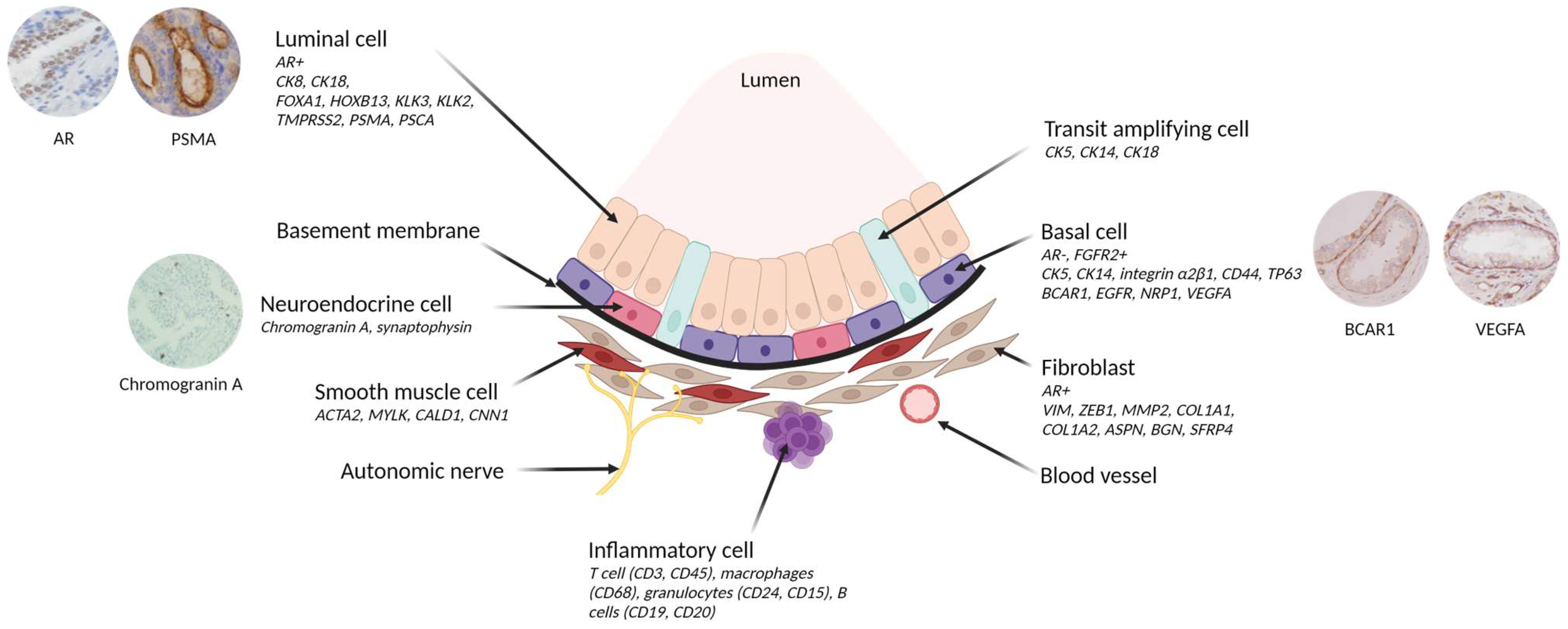
The functional unit of the prostate gland is the acinar which comprises distinct layers of epithelial cells, each characterised by specific gene expression and functions (Figure 3) [30].
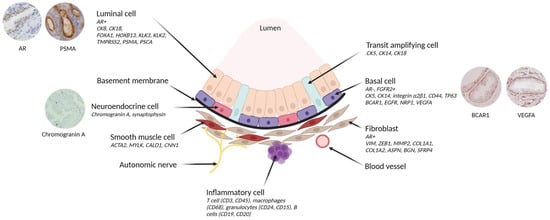
Figure 3.
Cellular architecture of prostate epithelium and expression of its associated gene. The prostate epithelium is composed of luminal cells, responsible for secretion, and a layer of basal cells in direct contact with the basement membrane. The basement membrane acts as a protective barrier between the epithelium and the stromal compartment (including fibroblasts, smooth muscle cells, nerves, blood vessels and inflammatory cells). Transit amplifying cells exhibit features of both basal and luminal cells. In addition, rare neuroendocrine cells are found in the basal layer. Cell type-specific markers are shown in italics. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 7 July 2023) and inspired by Rybak et al., Figure 1 [31].
The basal layer plays a crucial role in ensuring structural support and tissue integrity. It consists of basal cells that express cytokeratin (CK5, CK14), integrin α2β1, CD44, and TP63 genes, while lacking AR expression [30,32,33,34,35]. These basal epithelial cells also express genes associated with castration resistance, such as BCARC1 (p130cas) and EGFR [36,37], and with angiogenesis, such as NRP1 and VEGFA [38]. Of note, rare neuroendocrine cells are found within this layer, exhibiting positive staining for Chromogranin A and other neuropeptides [39]. These cells have a developmental stem cell of origin in common with epithelial cells [40]. The basal stem cells are responsible for the development and renewal of differentiated and functional luminal cells in adult prostatic glands [41,42]. The luminal cells, in direct contact with the basal cells, secrete substances like prostate-specific antigen (KLK3/PSA) and other kallikreins contributing to the secretion of the seminal fluid. These cells express the AR along with a combination of AR pathway drivers such as FOXA1 and HOXB13, as well as AR-targeted genes such as KLK3, KLK2, TMPRSS2, PSMA, and PSCA [43,44].
Additionally, there is a population of transit amplifying cells that may encompass ‘Club’ (KRT4+, SCGB1A1+) and “hillock” (KRT13+) cells described by G.H. Henry et al. [45,46]. In a normal adult prostate, these cells are rare; they are more frequent in foetal prostates and in pre-tumoral conditions [47]. These cells are characterised by the co-expression of basal and luminal cytokeratin, high proliferation, and a lack of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27 (CDKN1B). This gene is involved in cell cycle arrest, wherein increased level of p27 indicates an exit from the cell cycle [48]. In adult prostatic glands, p27 is expressed by all cells in the luminal compartment and by a subpopulation of basal cells. Conversely, p27 downregulation occurs not only in most prostate cancers [49] but also in high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) [50].
Positioned beneath the basal layer and separated by a basement membrane [51], the non-epithelial prostate microenvironment, collectively termed ‘stroma’, is composed of various cell types. The stroma is a complex cellular network that plays a vital role for normal prostate development and related diseases [52,53,54,55].
The predominant cell type within the stroma is fibroblasts, which when beside cancer can be known as cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF). CAFs can be identified by specific markers such as vimentin, ZEB1, MMP2, COL1A1, COL1A2, ASPN, BGN, and SFRP4 [52,56,57]. Smooth muscle cells are also present in the stroma and can be distinguished by the expression of ACTA2, MYLK, CALD1, and CNN1 [15,58]. In prostate cancer, the reactive stroma is characterised by a higher proportion of fibroblasts/myofibroblasts, which is offset by a decrease in differentiated smooth muscle cells [59,60,61].
Apart from fibroblasts and smooth muscle cells, the stroma contains other components, including blood vessels, lined by endothelial cells expressing endothelial receptors (EDNR and CD31) [62,63]. The stroma also houses nerves and a diverse infiltration of inflammatory immune cells, T cell phenotypes (CD3, CD45), macrophage phenotypes (CD68), granulocytes (CD24, CD15), and B cells (CD19, CD20) [64,65].
Altogether, epithelial layers and stroma form a complex and dynamic network, wherein effective bidirectional communication between prostate epithelial cells and the stroma is crucial for prostate development, renewal, and secretory function [66,67]. The secretion of growth factors, such as transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) and fibroblast growth factors (FGF), are key players ensuring these functions and efficient communication [68,69]. Indeed, stroma cells secrete FGF7 and FGF10, primarily affecting epithelial cells and lead to the development of prostate cancer by increasing sensitivity to androgens [70,71,72,73,74]. Conversely, epithelial cells secrete FGF2, which regulates fundamental stromal processes such as angiogenesis and cell proliferation [75]. In addition, TGFβ is an important mediator of bidirectional communication, promoting tumour growth and metastasis by facilitating epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in epithelial cells [76,77]. TGFβ-secreting epithelial cells influence stromal cell behaviour, including proliferation and extracellular matrix production, thereby supporting tumour invasion and metastasis [78,79].
Stromal and epithelial prostate cells collaborate in the metabolism of sexual steroid hormones and fatty acids. Prostate tissue can locally synthesise dihydrotestosterone (DHT), the most potent androgen, from various androgen precursor molecules [80]. As a result, despite androgen deprivation, levels of these hormones in the prostate remain high enough to promote cancer progression [81]. This phenomenon led to the development of new anti-androgen drugs which target the enzymes involved in steroid synthesis or which directly target the AR in prostate cells. Additionally, it is well-established that fatty acid metabolism is a potential target of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a key driver of prostate cancer development [82,83]. Prostate cells undergo a shift in lipid beta-oxidation pathways during carcinogenesis, accompanied by increased expression of AMACR, ACLY, ACACA, and FASN enzymes involved in the lipid metabolism [84].
2.2. Impact of Genetic Susceptibility in Prostate Cancer
Polygenic susceptibility to prostate cancer is influenced by functional polymorphisms of a single nucleotide. These polymorphisms play crucial roles during prostate development and homeostasis, influencing the expression of specific prostate transcripts and carrying implications for prostate cancer risk [85] or fertility. In addition to rare germline mutations, which encompass DNA repair genes associated with prostate cancer susceptibility, these polymorphisms affect key pathways, including those related to the AR (HOXB13, FOXA1) and proliferation (MYC, FGF10) [85]. These genetic variations have been found to correlate with disparities in prostate cancer risk based on ancestral backgrounds. For instance, genes such as KLK3 [86], coding for the prostate-specific antigen (PSA), MSMB [87,88], known as a tumour suppressor, and MLPH [89], thought to facilitate resistance to androgen deprivation, have shown a specific correlation with tissue expression in non-tumour prostate glands.
2.3. Gene Expression According to Prostate Cancer Histopathological Features
Histopathological evaluation of prostate cancer involves the assessment of several key features, including the Gleason score, tumour grade, tumour stage, and the presence of extraprostatic extension [90,91]. Since 1996 [92], the Gleason score has been a widely used grading system that assesses the architectural patterns of cancer cells. The initial scoring system ranged from 2 to 10, where higher scores indicated a more aggressive disease. However, the scoring system has been revised to now range from 6 to 10 and is transposed into the International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system, which ranges from 1 to 5 [93]. Tumour grade refers to the degree of cellular differentiation and is categorised as low grade (Gleason score 6 or ISUP-1), intermediate grade (Gleason score 7 (3 + 4) or ISUP-2 and Gleason score 7 (4 + 3) or ISUP-3), or high grade (Gleason score 8–10 or ISUP-4-5). Tumour stage provides information about the extent of cancer spread beyond the prostate gland and extraprostatic extension indicates the presence of cancer cells outside the prostatic edge.
Prostate cancer primarily consists of adenocarcinoma, but rare variants, comprising less than 5% of cases, have been identified [94,95,96]. These variants include acinar subtypes (such as cribriform, intraductal, mucinous, prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia-like carcinoma, signet ring cell carcinoma, sarcomatoid carcinoma, and pleomorphic giant cell carcinoma) and non-acinar subtypes (such as ductal carcinoma, carcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation as small cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and adenoid cystic carcinoma). Each variant has distinct histological and clinical features, leading to different outcomes. For instance, the mucinous variant tends to have a more favourable prognosis, with an approximately 80% 10-year survival rate, while the neuroendocrine variant has a poorer prognosis, with less than 10% survival at 10 years [39].
Typical acinar adenocarcinoma is characterised by glandular structures with a luminal phenotype, lacking basal cells and basement membrane layers. The diagnosis of typical acinar adenocarcinoma is confirmed in pathological practice by identifying AMARC+/P63- gland pattern using immunohistochemistry [97]. New tissue markers associated with prostate cancer, such as PCA3, DLX1, and HOXB6, as well as hypermethylated genes like GSTP1, APC, RASSF1, and copy number variations, have been identified and used in the development of new diagnostic tests based on molecular changes in prostatic secretions collected in the urine [98,99,100,101]. However, it is important to note that typical prostatic adenocarcinoma exhibits molecular heterogeneity [102,103,104]. In addition, gene expression profiling studies have identified distinct molecular subtypes of prostate cancer, including acinar and non-acinar subtypes [94,105,106]. The acinar subtype, characterised by glandular structures resembling normal prostate tissue, is the most common. In contrast, the non-acinar subtype lacks typical glandular structures and is often associated with more aggressive disease behaviour, higher Gleason scores, and poorer clinical outcomes compared to the acinar subtype [107].
Recent advances in genomic profiling have further subdivided primary prostate cancers into subgroups based on their genetic and epigenetic profiles [108,109,110,111,112]. The main subgroup consists of erythroblast transformation-specific (ETS) fusion-positive tumours (59%), resulting from a fusion between androgen-driven genes (TMPRSS2, SLC45A3) and embryogenic/oncogenic genes (ERG, ETV1/4, FLI1) [113,114]. These fusion-positive tumours, in particular TMPRSS2-ERG fusion-positive tumours (46%), often exhibit PTEN deletion and demonstrate upregulation of HDAC1 which is involved in the regulation of the AR. These tumours also show upregulation of NPY and PLA2G7, which are involved in cell growth, migration and invasion, along with downregulation of AZGP1, known to play a role in lipid metabolism [115,116,117,118]. Although these fusions are predominantly associated with the common acinar adenocarcinoma, they have also been detected in rare variants [119]. Interestingly, in prostate cancer, harbouring androgen dependent fusion genes, such as TMPRSS2-ERG, the AR switches from an antiproliferative to an oncogenic gene [113].
Other genetic alterations have been observed in adenocarcinoma, such as PTEN, AR, and SPOP [120,121]. PTEN plays a crucial role in regulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase kinase (PI3K)- protein kinase B (AKT) signalling pathway, which controls cell growth, survival, and metabolism. PTEN is also known as a tumour suppressor gene in prostate cancer, and its loss or inactivation is associated with patterns of increased tumour aggressiveness in localised prostate cancer [122,123]. AR is a critical driver of prostate cancer, playing a key role in the growth and survival of cancer cells. Alterations in AR signalling, such as AR amplification, mutations, or ligand-independent activation, are frequently observed. Constitutively active variant ARs are also found in prostate cancer [124,125,126]. SPOP is an E3 ubiquitin ligase with mutations accounting for 11% of cases, which affect protein degradation and influence the development of adenocarcinoma [108]. Additional genetic alterations include FOXA1 and IDH1 mutations, found in 3% and 1% of cases, respectively [108].
Similar to acinar adenocarcinoma, rare variants of prostate cancer involve several genes in their development and progression. TP53 mutations are commonly found in small cell carcinoma of the prostate, contributing to its aggressive nature [104,127]. Cribriform patterns can be further classified based on the proportion of cancer cells exhibiting PTEN-loss and PD-L1 overexpression [128]. Genes such as AR, ERG, FOXA1/2, MUC16, RB1, CDH1, BRCA2, and TP53 have also been involved in different variants of prostate cancer [129,130,131]. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying these rare variants are still poorly understood despite extensive research.
2.4. Gene Expression Associated with Prostate Cancer Outcomes
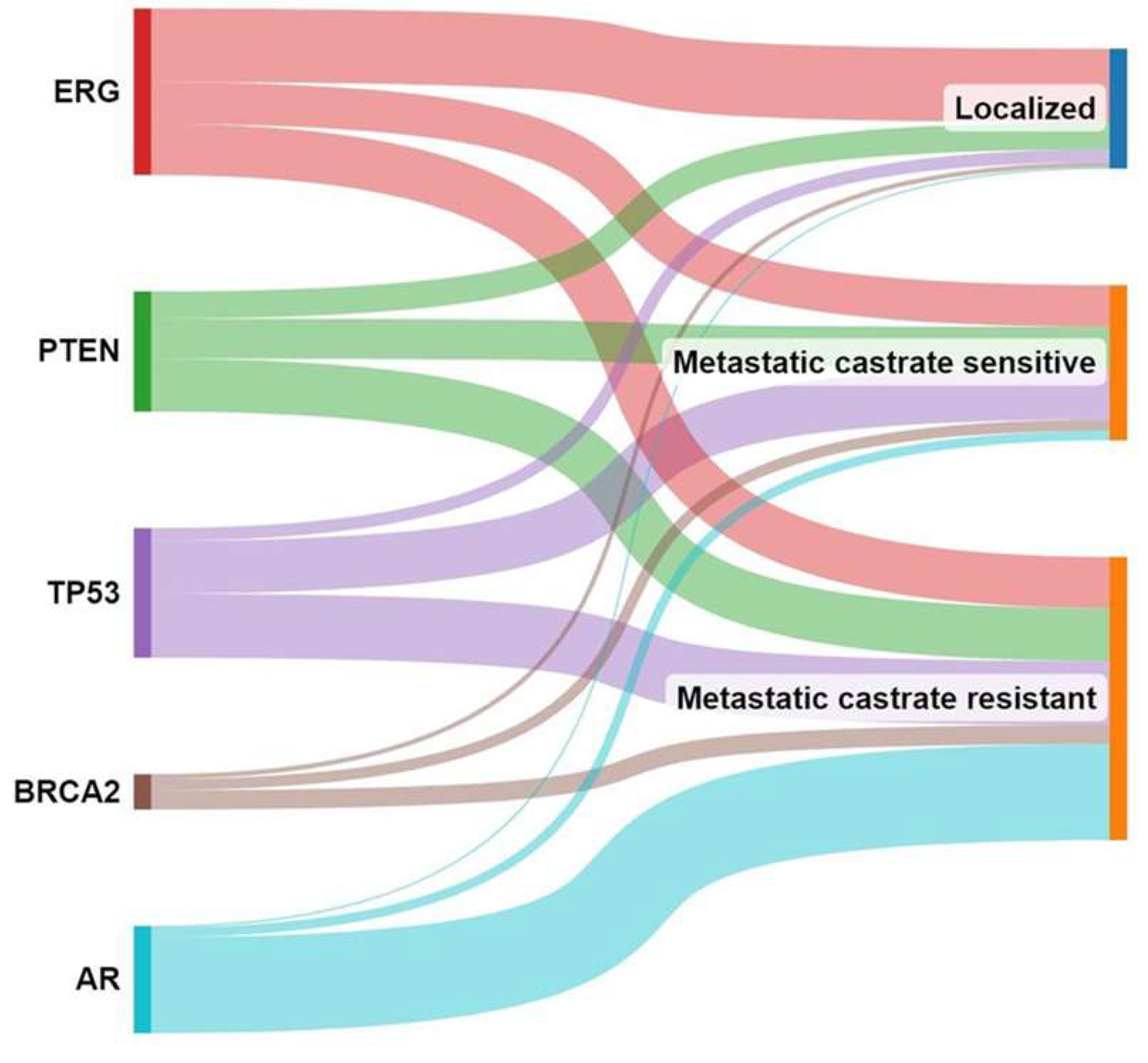
Nowadays, histopathological patterns are well recognised to play a crucial role in determining the management approach for early-stage prostate cancer [132]. However, certain patterns such as large cribriform or intraductal patterns are not recommended for active surveillance due to their association with a higher risk of disease progression [133,134,135]. Rare events like BRCA2 germline mutations, which are known to have a worse prognosis, also exclude patients from active surveillance management [136]. The management approach of prostate cancer is complex, as exemplified by TMPRSS2-ERG, a key player in the initial development of prostate cancer [137], which is not correlated with the progression of the disease to its life-threatening stage. Conversely, molecular events linked to BRCA2, TP53, RB1, and AR become more frequent as prostate cancer progresses from the metastatic stage to the castration-resistant stage, indicating their involvement in the later stages of the disease [138] (Figure 4).
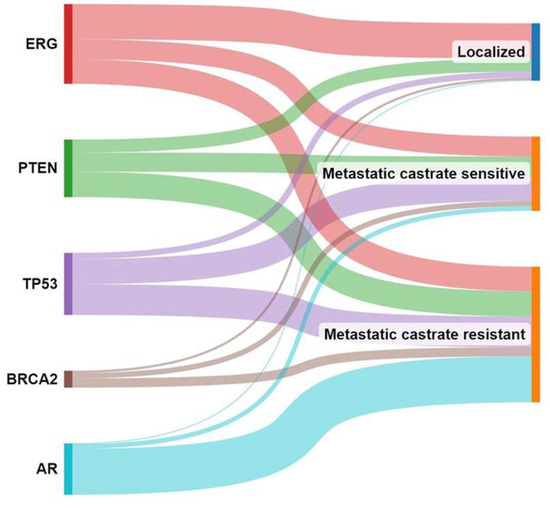
Figure 4.
Molecular events associated with prostate cancer progression. This figure illustrates the changing landscape of molecular events in prostate cancer as it progresses from localised to metastatic to castration-resistant stage.
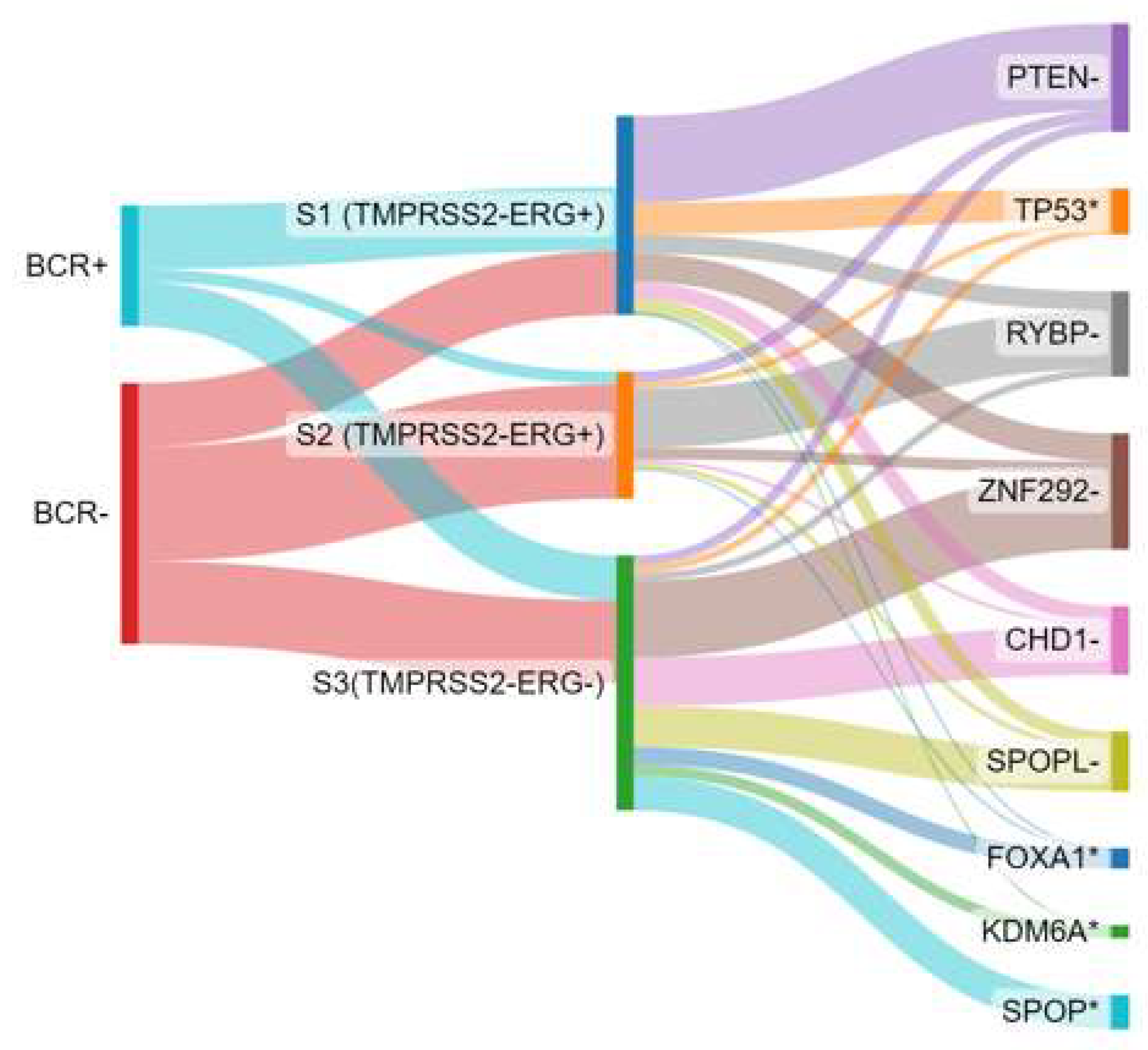
Recently, genomic profiling has emerged as a valuable tool in prostate cancer prognosis and therapeutic decision-making, which may help to decipher the progression of prostate cancer [139,140]. It provides a molecular dimension that complements the traditional histopathological classification. Genomic prognostic signatures based on transcriptomic profiles have been developed to provide clinicians and patients with more confidence in selecting between active surveillance or radical therapies in the early stages of the disease [141]. These genetic signatures encompass biological processes that may play a central role in tumour initiation and progression. For example, the Prolaris® test [142,143] focuses on genes associated with proliferation, providing insights into the tumour’s growth rate. On the other hand, tests like OncotypeDx® [144,145] or Prostadiag® [120] incorporate multifunctional gene patterns, including proliferation, differentiation, androgen responsiveness, epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and the presence of cancer-associated fibroblasts, to provide a more comprehensive assessment of the tumour’s behaviour. In particular, the Prostadiag® signature has been extensively studied [120], wherein three distinct subgroups of tumours based on gene expression patterns have been found (Figure 5). The first subgroup (S1) comprises aggressive tumours (TMPRSS2-ERG+) often characterised by PTEN deletion or TP53 deficiency, indicating a higher risk of disease progression. The second subgroup (S2) consists of tumours (TMPRSS2-ERG+) with a low risk of progression, with a likelihood of less than 10%. The third subgroup (S3) is enriched with SPOP mutations or SPOPL deletions, as well as hypermethylated tumours showing decreased expression of the WNK2 gene and overexpression of EZH2. This subgroup indicates an intermediate risk of aggressiveness (between S1 and S3) for disease progression.
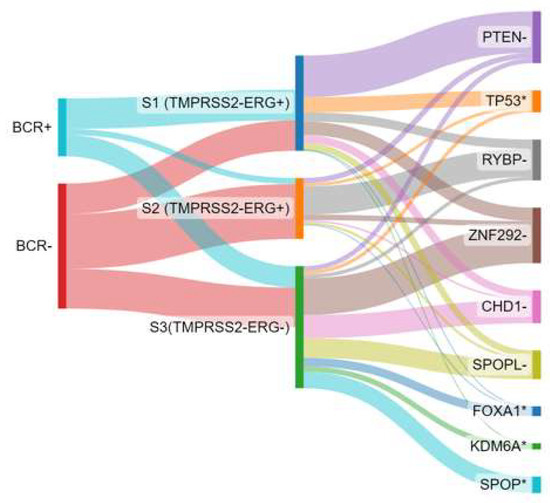
Figure 5.
Biochemical recurrence association (BCR) with Prostadiag® signature subgroups and distribution of driver genes involved by loss of heterozygosity. Based on data from Kamoun et al. [120]. S1: subgroup 1; S2: subgroup 2; S3: subgroup 3; - indicates a deletion and * indicates a mutation.
2.5. Gene Expression According to Key Prostate Cancer Signalling Pathways
One of the key signalling pathways involved in prostate cancer is the AR pathway [146,147,148]. The AR is a transcription factor playing a fundamental role in regulating gene transcription upon binding to androgens. Its activity involves intricate interactions with other transcription factors, nuclear translocation, and binding to response elements, resulting in both genomic and non-genomic activities [149]. In the context of prostate cancer, the dysregulation of the AR signalling pathway leads to increased AR activity and the expression of genes that promote tumour growth [146,147,148]. These modifications arise from various mechanisms, including amplification or mutations in the AR gene, alterations in co-regulatory proteins, and abnormal activation of downstream signalling molecules.
The AR protein is predominantly expressed in the luminal epithelial cells of the prostate [150]. In the luminal layer, the AR pathway maintains differentiation and secretion functions and blocks the cell cycle [151]. Ligand binding induces conformational changes that liberate the AR from heat shock proteins and expose its ligand-binding domain, which contains a nuclear localization signal [152,153]. The ligand-bound AR subsequently forms dimers and undergoes phosphorylation, which are translocated to the nucleus. Within the nucleus, the AR binds to specific elements of the androgen response on DNA and recruits coregulators or coactivators such as FOXA1, GATA2, NKX3-1, and HOXB13 [154,155,156,157,158]. In consequence, the transcription of targeted genes (such as KLK2, KLK3, TMPRSS2, CAMKK2, CDH2, SCL43A1, and FKBP5), playing pivotal roles in various biological functions such as tumour progression, cell cycle regulation, glycosylation, calcium metabolism, and lipid metabolism, is enhanced [157,158,159,160]. AR can also interact with other proteins, such as HES6 and E2F1 [161], during castration resistant conditions, and can also repress gene expression. In fact, by collaborating with EZH2-mediated repressive chromatin remodelling, the AR facilitates the repression of target genes [162].
The WNT/β-catenin pathway also plays an essential role in prostate cancer, influencing cell proliferation, invasion, and stem cell-like properties [163,164]. Although WNT-1 is generally found in low levels in primary prostate epithelial cells, its upregulation has been observed in lymph nodes and bone metastases [165]. Disruption of this pathway can result from genetic mutations or altered expression of key components, including β-catenin or APC. Mutations in APC and CTNNB1 have been identified in up to 22% of castration-resistant prostate cancers [166,167]. Interestingly, stromal cells release WNT proteins that can activate the WNT signalling pathway in tumour cells [163,168,169,170]. An important downstream target of this pathway is FOXA2, whose induction is essential for bone metastasis development in prostate cancer [171].
The PI3K/AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) leads to the increased expression of genes involved in cell proliferation, survival, and metabolism. Furthermore, it contributes to the development of resistance to androgen deprivation therapy [172]. Dysregulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is frequently observed in prostate cancer, with up to 42% of primary tumours and 100% of metastatic samples showing abnormalities in this pathway [138,166,167,173,174].
The RAS/mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade transduces extracellular growth signals through transmembrane receptors to regulate gene expression and cellular functions [175,176]. It is frequently deregulated in cancer, including prostate cancer. The cascade involves activation of RAS and the rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF)/ mitogen-activated protein kinase (MEK)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling pathway, leading to transcription of target genes such as MYC and cFOS.
Feedback loops and interactions between components enable cross-regulation within the cascades. A complex interplay unfolds between the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and other oncogenic signalling cascades, including AR, MAPK, and WNT pathways, which further promotes the growth of prostate cancer and contribute to drug resistance [172,177]. These pathways interact and regulate each other.
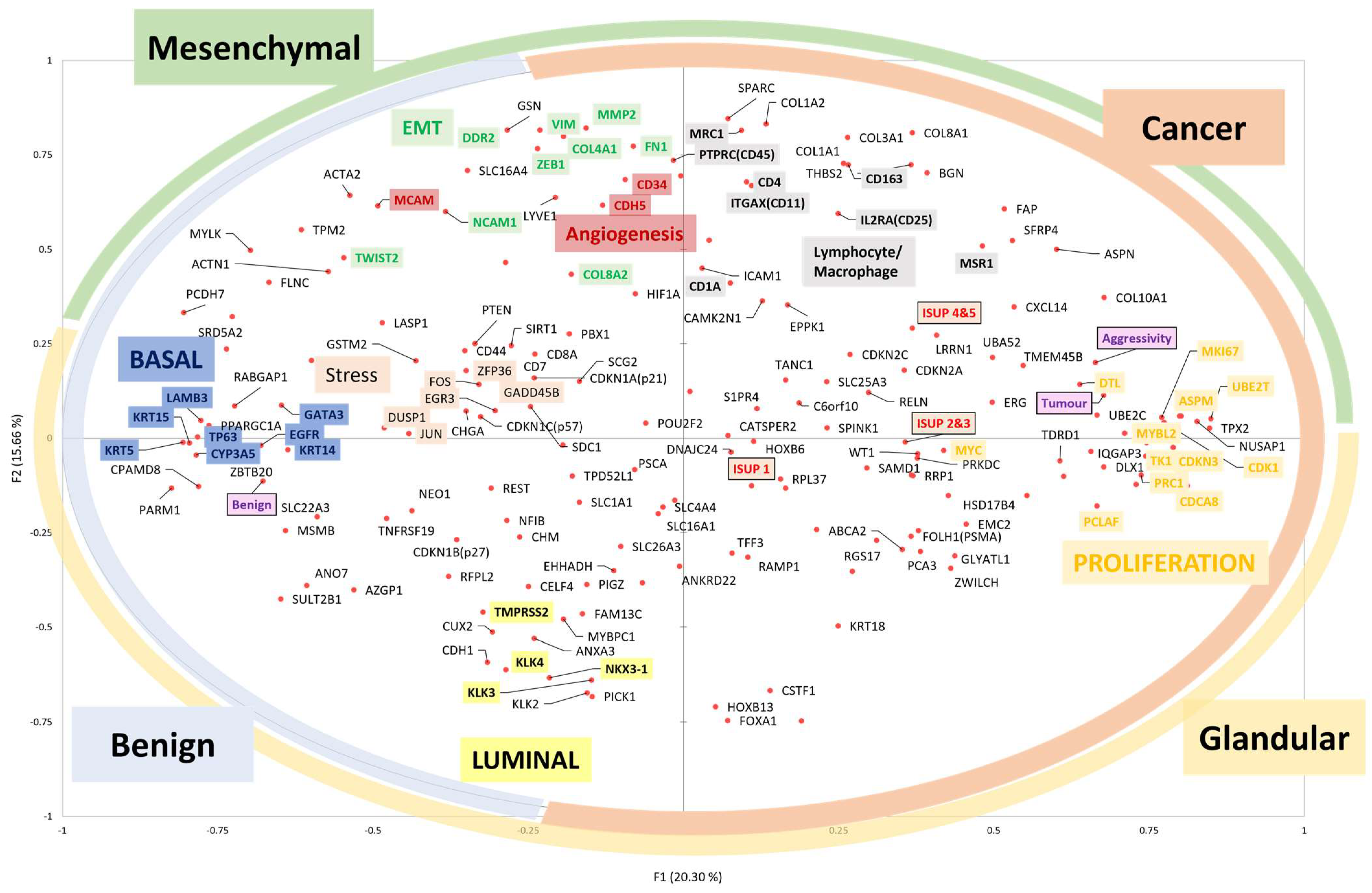
Figure 6 presents a summary of this section, illustrating how the expression of genes in benign and adenocarcinoma prostate tissue relates to the Gleason Grade Group. The analysis is performed using principal component analysis.
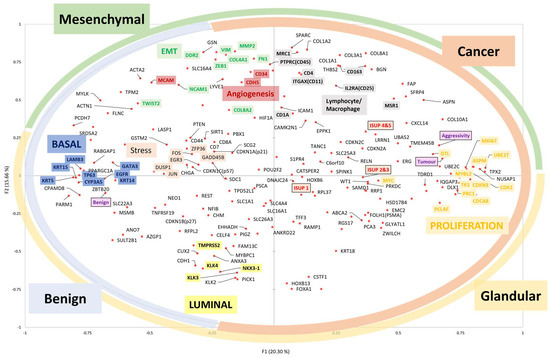
Figure 6.
Principal component analysis reveals gene expression patterns in benign (N = 67) and adenocarcinoma (N = 104) prostate tissues. The more the gene is expressed, the closer it is to the edge. The highly correlated genetic expressions are close. The ‘aggressivity’ variable is defined by the D’Amico clinical aggressiveness score [91]. The coloured circles on the edge indicate the tissue compartments where the genes are expressed. The coloured boxes indicate the functional cells or subtypes where the genes are expressed. ISUP-1: Gleason score 6; ISUP-2 or 3: Gleason score 7; ISUP-4 or 5: Gleason score 8, 9 or 10.
3. Active Surveillance and Early Intervention
This review highlights the importance of considering not only the anatomical and histopathological features, but also functional characteristics. The complex nature of prostate cancer, with its multi-stage development and multiple origins, complicates the initial assessment of aggressiveness in the early stages. Importantly, a biopsy sample alone does not provide a complete representation of the overall aggressiveness of the disease. Furthermore, the small amount of tumour tissue obtained during biopsies, often associated with potentially indolent prostate cancer, can limit the use of relevant biomarkers and signatures of aggressiveness in clinical practice.
Active surveillance is considered an appropriate option for patients diagnosed with low-risk or favourable intermediate-risk prostate cancer [178,179]. This approach is used when the potential benefits of immediate treatment, such as surgery or radiation therapy, may not outweigh the risks and side effects associated with interventions. By opting for active surveillance, patients can avoid unnecessary treatments and their potential complications [6,10,180,181].
The primary goal of active surveillance is to closely monitor the progression of prostate cancer over time, using regular tests such as PSA levels, digital rectal exams, and periodic biopsies. This approach allows clinicians to assess changes in the aggressiveness and growth of the cancer, providing valuable information to determine if and when active treatment should be initiated. However, active surveillance without any treatment potentially allows cells to acquire new molecular changes after mitosis, leading to a sudden increase in disease aggressiveness.
During the initial phase of prostate cancer, clinicians rely on the examination and classification of the disease based on its histopathological features, a particularly useful method for indolent prostate cancer. The definition of indolent prostate cancer encompasses specific criteria defined as (1) a stage termed T1cN0M0 indicating a localised tumour which is not spreading to lymph nodes or distant areas, (2) a low tumour volume estimated to be present in two or fewer biopsy cores with 20% or less tumour involvement in each core, (3) a low Gleason score below 7 without pattern 4 involvement, and (4) a low level of PSA below 10 ng/mL. These criteria form the basis of the active surveillance concept [182].
Despite this well-established stratification, accurately determining the aggressiveness of focal or multifocal prostatic neoplasia during diagnosis and follow-up can be challenging. Indeed, the differences between indolent cancers that may not progress significantly, and cancers that may present a greater risk, remains elusive.
The need for better prognostic factors for patients on active surveillance is crucial, considering the drawbacks associated with this approach [6]. Despite surveillance involving PSA levels, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and repeat biopsies, accurately assessing disease progression remains challenging. Interpreting PSA levels and PSA doubling times becomes particularly difficult in the presence of benign prostate hypertrophy [20,183]. It is therefore key to identify the most reliable indicators likely to improve therapeutic decisions, by enabling a more in-depth understanding and alignment of the tumour phenotype with its genotype [16,17,103].
The role of PSA as a diagnostic and predictive tool for prostate cancer is much debated [184]. This emphasises the crucial necessity for novel molecular markers that can effectively anticipate outcomes and, by extension, provide guidance for therapeutic decisions. Significant progress has been made in prostate cancer biomarker research in recent years. Promising new molecular markers are actively explored to improve the accuracy and specificity of prostate cancer diagnosis and surveillance [185,186]. For instance, studies have investigated the utility of various genetic markers, such as specific gene mutations and alterations in gene expression patterns, as potential indicators of prostate cancer presence and progression. Additionally, investigations into non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs, have unveiled their potential as diagnostic biomarkers due to their involvement in cancer-related processes. Moreover, cutting-edge technologies to detect circulating tumor DNA and RNA in the form of liquid biopsies, could provide a minimally invasive method for monitoring disease status [187].
The integration of multi-omics data, including transcriptomics and proteomics, is contributing to the identification of comprehensive biomarker signatures that could revolutionise the assessment of prostate cancer. As these diverse biomarkers continue to undergo rigorous validation and clinical trials, they hold the promise to significantly impact the criteria and practices underlying current approaches to active surveillance for prostate cancer.
Reversibility of Low-Risk Prostate Cancer and Super-Active Surveillance
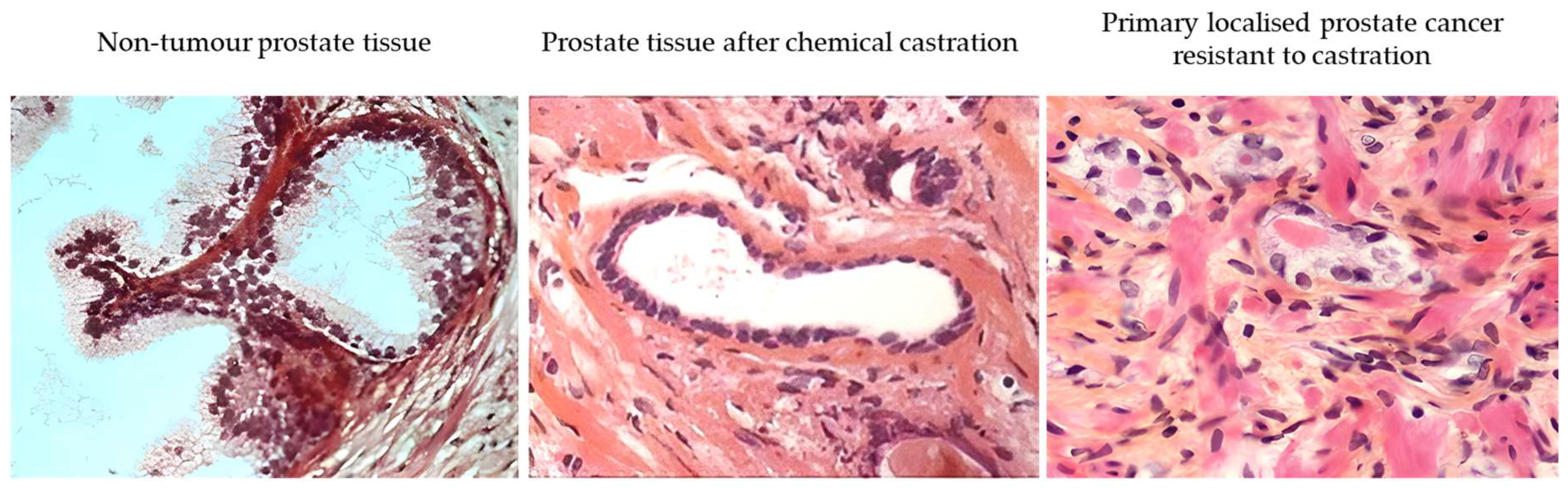
In parallel with active surveillance, the concept of secondary prevention based on reducing AR function has emerged [20]. The aims of secondary prevention are to detect and treat or slow existing prostate cancer lesions at an early stage before they cause significant morbidity. The corollary hypothesis is that early prostate cancer lesions resistant to secondary chemoprevention based on AR reduction are suspected of harbouring molecular events (stem cell-like) leading to metastatic stages and lethality. As an example, a functional classification of prostate cancer based on response to androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) in the early stages has been proposed to identify potentially aggressive disease (persistence of neoplastic lesions after reduction of AR activity) [19,20,22]. On normal prostate acini, chemical castration induces apoptosis of the luminal layer cells (AR+), but basal layer cells (AR−) are constitutively resistant to castration (Figure 7). This approach, applied to the management of prostate cancer, makes it possible to identify early prostate cancer lesions capable of resisting the reduction in AR function like normal basal cells.
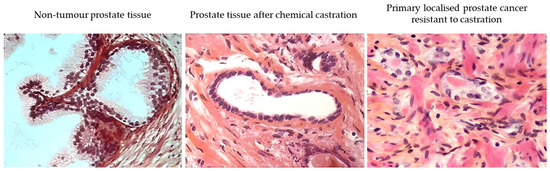
Figure 7.
Comparative analysis (hematoxylin-eosin saffron) of a non-tumour prostate tissue (left) and a prostate tissue after androgen deprivation with a luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) analogue (‘chemical castration’; middle), revealing the lasting presence of basal cells and the disappearance of luminal cells after treatment. Primary localised prostate cancer (initially ISUP-2) resistant to castration (right). These images were generated from tissue obtained during the follow-up (prostate biopsy) of patients included in our previous study [21].
In advanced prostate cancer, initial treatment incudes measures primarily for palliative purposes [188]. However, intriguing findings from animal models suggest that androgen deprivation may also have potential in the treatment of precancerous lesions and even small tumours [189,190]. This potential benefit challenges the idea that ADT must be restricted to a palliative measure. Several clinical reports have further highlighted the primary or secondary preventive effects of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (dutasteride or finasteride), enzymes that convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone, in localised prostate cancers with a well-differentiated (Gleason 6) low-volume profile. The Reduction by Dutasteride of Prostate Cancer Events (REDUCE) trial [191] and the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT) [192,193,194] demonstrated the effectiveness of these inhibitors in reducing the incidence of low-grade prostate cancer, which is admittedly of questionable benefit. However, the notion is further supported by studies showing that androgen depletion for three months prior to radical prostatectomy can result in tumour burnout (stage pT0), highlighting the potential of androgen deprivation in preventing cancer progression [195]. In addition, long-term follow-up studies of participants in the PCPT yielded promising results, suggesting that finasteride reduces overall prostate cancer incidence by approximately one-third [196]. Similarly, the Reduction by Dutasteride of Clinical Progression Events in Expectant Management (REDEEM) randomised controlled trial revealed that androgen modulation with dutasteride delayed disease progression in men on active surveillance for low-risk prostate cancer [19].
Another pilot study examined the effects of secondary chemoprevention within three months of androgen depletion using leuprolide acetate as an alternative to active surveillance for low-risk prostate cancer. In this study, early ADT reversed a subset of 45% of low-risk prostate cancer lesions [21]. This suggests that the response to transient ADT could be used as a stratification tool to assess the aggressiveness and persistence of neoplastic lesions. Lesions that persist after three months of androgen deprivation may be considered aggressive and warrant radical therapy, such as surgery or radiotherapy [195].
More recently, Shore et al. reported a reduction of almost 50% in the risk of prostate cancer progression compared with active surveillance using two years of monotherapy with enzalutamide, an AR signalling inhibitor, for low and intermediate risk localised prostate cancers [22].
Altogether, these clinical reports support the hypothesis that a subset of early-stage prostate cancers can be reversed through AR disruption. The identification of exceptional responses to antiandrogen therapies in ETS fusion-negative tumours with SPOP/SPOL mutation/deletion goes further and suggests a specific profile of early-stage prostate cancer patients which may benefit from AR pathway disruption therapy [197].
4. Concluding Remarks
In this review, we explored the molecular anatomy of prostate cancer and its relevance to the concept of active surveillance as a management strategy for early prostate cancer. We discussed the evidence for its effectiveness in carefully selected patients, highlighting the potential benefits of avoiding unnecessary treatment-related side effects and preserving quality of life.
Despite the unequivocal advances made in implementing active surveillance, there are still gaps in our understanding of the biology of prostate cancer and its implications for risk stratification and disease progression. Molecule-based assessment tools need to be further developed and validated, and it needs to be determined whether the origin of cell types can explain indolent or lethal prostate cancer outcomes. By integrating genomic, proteomic, and phenotypic models, as well as functional approaches based on drug response, we can improve our ability to predict individual patient outcomes. This could help identify those who benefit most from active surveillance and enable targeted interventions for those at higher risk of disease progression.
Author Contributions
S.F. and O.C. conceived the concept for this review. S.F., G.C.-T., I.G.M., A.D.L., G.F. and O.C. performed the literature review. S.F. and O.C. drafted the manuscript. S.F., G.C.-T., I.G.M., A.D.L., G.F. and O.C. edited the intellectual content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The present work was supported by Hanson Trust, Cancer Research UK (CRUK), the John Black Charitable Foundation, AMAMACaP (Endowment Fund for Innovation in Prostate Cancer Care), and SCOR Foundation for Science.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data from the French cohort PROGENE, promoted by Centre de Recherche sur les Pathologies Prostatiques et urologiques (CeRePP), has been approved by the institutional ethics committee CCP Ile de France IV (IRB: 00003835).
Informed Consent Statement
All patients have provided written informed consent to participate in the cohort, which includes the collection of bio-resources such as germline DNA, blood, and urinary samples for biomarker analysis.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jonathan Pansieri from the University of Oxford for his advice and insightful comments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- International Agency for Research Cancer. Global Cancer Observatory. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/ (accessed on 22 June 2023).
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Lu, B.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Du, L. Prostate Cancer Incidence and Mortality: Global Status and Temporal Trends in 89 Countries from 2000 to 2019. Front Public Health 2022, 10, 811044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, J.L.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Stampfer, M.J. The High Prevalence of Undiagnosed Prostate Cancer at Autopsy: Implications for Epidemiology and Treatment of Prostate Cancer in the Prostate-Specific Antigen-Era. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 2795–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzouzi, A.-R.; Cochand-Priollet, B.; Mangin, P.; Fournier, G.; Berthon, P.; Latil, A.; Cussenot, O. Impact of Constitutional Genetic Variation in Androgen/Oestrogen-Regulating Genes on Age-Related Changes in Human Prostate. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002, 147, 479–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, F.C.; Donovan, J.L.; Lane, J.A.; Metcalfe, C.; Davis, M.; Turner, E.L.; Martin, R.M.; Young, G.J.; Walsh, E.I.; Bryant, R.J.; et al. Fifteen-Year Outcomes after Monitoring, Surgery, or Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bill-Axelson, A.; Holmberg, L.; Garmo, H.; Taari, K.; Busch, C.; Nordling, S.; Häggman, M.; Andersson, S.-O.; Andrén, O.; Steineck, G.; et al. Radical Prostatectomy or Watchful Waiting in Prostate Cancer—29-Year Follow-Up. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2319–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilt, T.J.; Jones, K.M.; Barry, M.J.; Andriole, G.L.; Culkin, D.; Wheeler, T.; Aronson, W.J.; Brawer, M.K. Follow-up of Prostatectomy versus Observation for Early Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klotz, L. Active Surveillance: An Individualized Approach to Early Prostate Cancer. BJU Int. 2003, 92, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, L.; Vesprini, D.; Sethukavalan, P.; Jethava, V.; Zhang, L.; Jain, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Mamedov, A.; Loblaw, A. Long-Term Follow-Up of a Large Active Surveillance Cohort of Patients with Prostate Cancer. JCO 2015, 33, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lejeune, C.; Bourredjem, A.; Binquet, C.; Cussenot, O.; Boudrant, G.; Papillon, F.; Bruyère, F.; Haillot, O.; Koutlidis, N.; Bassard, S.; et al. Eliciting Men’s Preferences for Decision-Making Relative to Treatments of Localized Prostate Cancer with a Good or Moderate Prognosis. World J. Urol. 2023, 41, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, A.S.; Huang, J.; Guo, C.; Garraway, I.P.; Witte, O.N. Identification of a Cell of Origin for Human Prostate Cancer. Science 2010, 329, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, A.S.; Stoyanova, T.; Witte, O.N. Primitive Origins of Prostate Cancer: In Vivo Evidence for Prostate-Regenerating Cells and Prostate Cancer-Initiating Cells. Mol. Oncol. 2010, 4, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, D.A.; Zong, Y.; Memarzadeh, S.; Xin, L.; Huang, J.; Witte, O.N. Basal Epithelial Stem Cells Are Efficient Targets for Prostate Cancer Initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 2610–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, M.K.; Chikarmane, R.; Wang, R.; Vaghasia, A.; Gupta, A.; Zheng, Q.; Wodu, B.; Pan, X.; Castagna, N.; Liu, J.; et al. Single-Cell Atlas of Epithelial and Stromal Cell Heterogeneity by Lobe and Strain in the Mouse Prostate. Prostate 2023, 83, 286–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.S.; Eeles, R.; Wedge, D.C.; Van Loo, P.; Gundem, G.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Kremeyer, B.; Butler, A.; Lynch, A.G.; Camacho, N.; et al. Analysis of the Genetic Phylogeny of Multifocal Prostate Cancer Identifies Multiple Independent Clonal Expansions in Neoplastic and Morphologically Normal Prostate Tissue. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 367–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, A.; He, M.; Berglund, E.; Marklund, M.; Mirzazadeh, R.; Schultz, N.; Kvastad, L.; Andersson, A.; Bergenstråhle, L.; Bergenstråhle, J.; et al. Spatially Resolved Clonal Copy Number Alterations in Benign and Malignant Tissue. Nature 2022, 608, 360–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, N.D.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Tomlins, S.A. Antiandrogen Treatment vs Active Surveillance for Patients with Prostate Cancer-Reply. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 150–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleshner, N.E.; Lucia, M.S.; Egerdie, B.; Aaron, L.; Eure, G.; Nandy, I.; Black, L.; Rittmaster, R.S. Dutasteride in Localised Prostate Cancer Management: The REDEEM Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1103–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussenot, O.; Comperat, E.; Bitker, M.-O.; Rouprêt, M. From Active Surveillance to the Concept of Secondary Prevention. Eur. Urol. 2011, 59, 568–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussenot, O.; Cornu, J.-N.; Drouin, S.J.; Mozer, P.; Egrot, C.; Vaessen, C.; Haab, F.; Bitker, M.-O.; Rouprêt, M. Secondary Chemoprevention of Localized Prostate Cancer by Short-Term Androgen Deprivation to Select Indolent Tumors Suitable for Active Surveillance: A Prospective Pilot Phase II Study. World J. Urol. 2014, 32, 545–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shore, N.D.; Renzulli, J.; Fleshner, N.E.; Hollowell, C.M.P.; Vourganti, S.; Silberstein, J.; Siddiqui, R.; Hairston, J.; Elsouda, D.; Russell, D.; et al. Enzalutamide Monotherapy vs Active Surveillance in Patients with Low-Risk or Intermediate-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer: The ENACT Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tewari, A.K.; Cheung, A.T.M.; Crowdis, J.; Conway, J.R.; Camp, S.Y.; Wankowicz, S.A.; Livitz, D.G.; Park, J.; Lis, R.T.; Bosma-Moody, A.; et al. Molecular Features of Exceptional Response to Neoadjuvant Anti-Androgen Therapy in High-Risk Localized Prostate Cancer. Cell Rep. 2021, 36, 109665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeal, J.E. Regional Morphology and Pathology of the Prostate. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1968, 49, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNeal, J.E. The Zonal Anatomy of the Prostate. Prostate 1981, 2, 35–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Vernet, J. Prostate Cancer: Anatomical and Surgical Considerations. Br. J. Urol. 1996, 78, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laschkar, S.; Montagne, S.; De Kerviler, E.; Roupret, M.; Lucidarme, O.; Cussenot, O.; Renard Penna, R. Zonal Anatomy of the Prostate Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Morphometrics, and Radiomic Features: Impact of Age-Related Changes. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, G.; Jardin, A.; Gillot, C. Reflections and Suggestions on the Nomenclature of the Prostate. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 1993, 15, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, K.S.; Kressel, H.Y.; Arger, P.H.; Pollack, H.M. Age-Related Changes of the Prostate: Evaluation by MR Imaging. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1989, 152, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivanen, R.; Shen, M.M. Prostate Organogenesis: Tissue Induction, Hormonal Regulation and Cell Type Specification. Development 2017, 144, 1382–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, A.P.; Bristow, R.G.; Kapoor, A. Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: Deciphering the Origins and Pathways Involved in Prostate Tumorigenesis and Aggression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1900–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, D.; Król, W.; Szliszka, E. Prostate Cancer Stem Cells: Research Advances. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 27433–27449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, A.; Gupta, S.; Mistry, B.; Gupta, S. Prostate Stem Cells in the Development of Benign Prostate Hyperplasia and Prostate Cancer: Emerging Role and Concepts. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 107954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cussenot, O.; Berthon, P.; Cochand-Priollet, B.; Maitland, N.J.; Le Duc, A. Immunocytochemical Comparison of Cultured Normal Epithelial Prostatic Cells with Prostatic Tissue Sections. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 214, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murant, S.; Handley, J.; Stower, M.; Reid, N.; Cussenot, O.; Maitland, N. Co-Ordinated Changes in Expression of Cell Adhesion Molecules in Prostate Cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 1997, 33, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabodi, S.; del Pilar Camacho-Leal, M.; Di Stefano, P.; Defilippi, P. Integrin Signalling Adaptors: Not Only Figurants in the Cancer Story. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fromont, G.; Cussenot, O. The Integrin Signalling Adaptor P130CAS Is Also a Key Player in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latil, A.; Bièche, I.; Pesche, S.; Valéri, A.; Fournier, G.; Cussenot, O.; Lidereau, R. VEGF Overexpression in Clinically Localized Prostate Tumors and Neuropilin-1 Overexpression in Metastatic Forms. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 89, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussenot, O.; Villette, J.M.; Cochand-Priollet, B.; Berthon, P. Evaluation and Clinical Value of Neuroendocrine Differentiation in Human Prostatic Tumors. Prostate Suppl. 1998, 8, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, A.D.; Warren, A.Y.; Neal, D.E. Pre-Malignant Disease in the Prostate. In Pre-Invasive Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Management; Fitzgerald, R.C., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 467–491. ISBN 978-1-4419-6694-0. [Google Scholar]
- De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, W.G.; Meeker, A.K.; Coffey, D.S. Stem Cell Features of Benign and Malignant Prostate Epithelial Cells. J. Urol. 1998, 160, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strand, D.W.; Goldstein, A.S. The Many Ways to Make a Luminal Cell and a Prostate Cancer Cell. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, T187–T197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakht, M.K.; Yamada, Y.; Ku, S.-Y.; Venkadakrishnan, V.B.; Korsen, J.A.; Kalidindi, T.M.; Mizuno, K.; Ahn, S.H.; Seo, J.-H.; Garcia, M.M.; et al. Landscape of Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Heterogeneity and Regulation in AR-Positive and AR-Negative Metastatic Prostate Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 699–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, D.B.; Turco, A.E.; Vezina, C.M.; Strand, D.W. Progenitors in Prostate Development and Disease. Dev. Biol. 2021, 473, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henry, G.H.; Malewska, A.; Joseph, D.B.; Malladi, V.S.; Lee, J.; Torrealba, J.; Mauck, R.J.; Gahan, J.C.; Raj, G.V.; Roehrborn, C.G.; et al. A Cellular Anatomy of the Normal Adult Human Prostate and Prostatic Urethra. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 3530–3542.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, D.B.; Henry, G.H.; Malewska, A.; Reese, J.C.; Mauck, R.J.; Gahan, J.C.; Hutchinson, R.C.; Mohler, J.L.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Strand, D.W. 5-Alpha Reductase Inhibitors Induce a Prostate Luminal to Club Cell Transition in Human Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia. J. Pathol. 2022, 256, 427–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letellier, G.; Perez, M.; Yacoub, M.; Levillain, P.; Cussenot, O.; Fromont, G. Epithelial Phenotypes in the Developing Human Prostate. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Kaur, M.; Agarwal, C.; Tecklenburg, M.; Sclafani, R.A.; Agarwal, R. P21 and P27 Induction by Silibinin Is Essential for Its Cell Cycle Arrest Effect in Prostate Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2696–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsihlias, J.; Kapusta, L.R.; DeBoer, G.; Morava-Protzner, I.; Zbieranowski, I.; Bhattacharya, N.; Catzavelos, G.C.; Klotz, L.H.; Slingerland, J.M. Loss of Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor P27Kip1 Is a Novel Prognostic Factor in Localized Human Prostate Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 542–548. [Google Scholar]
- De Marzo, A.; Meeker, A.; Zha, S.; Luo, J.; Nakayama, M.; Platz, E.; Isaacs, W.; Nelson, W. Human Prostate Cancer Precursors and Pathobiology. Urology 2003, 62, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, Y.; Mannion, C.; Jewett, A.; Hsiao, Y.-H.; Liu, A.; Semczuk, A.; Zarogoulidis, P.; Gapeev, A.B.; Cimadamore, A.; Lee, P.; et al. The Most Effective but Largely Ignored Target for Prostate Cancer Early Detection and Intervention. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 3463–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyekucheva, S.; Bowden, M.; Bango, C.; Giunchi, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Bondi, A.; Lis, R.; Van Hemelrijck, M.; Andrén, O.; et al. Stromal and Epithelial Transcriptional Map of Initiation Progression and Metastatic Potential of Human Prostate Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krušlin, B.; Ulamec, M.; Tomas, D. Prostate Cancer Stroma: An Important Factor in Cancer Growth and Progression. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 15, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmad, H.F.; Jalloul, M.; Azar, J.; Moubarak, M.M.; Samad, T.A.; Mukherji, D.; Al-Sayegh, M.; Abou-Kheir, W. Tumor Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer: Toward Identification of Novel Molecular Biomarkers for Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Therapy Development. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 652747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liu, R.; Gao, W.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Single-Cell Omics Traces the Heterogeneity of Prostate Cancer Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2023, 28, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R. The Biology and Function of Fibroblasts in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J.S.; Clayton, A.; Pearson, H.B. Cancer-Associated Fibroblast Heterogeneity, Activation and Function: Implications for Prostate Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, G.K. Regulation of Differentiation of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Physiol. Rev. 1995, 75, 487–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, G.; Tuxhorn, J.A.; Wheeler, T.M.; Frolov, A.; Scardino, P.T.; Ohori, M.; Wheeler, M.; Spitler, J.; Rowley, D.R. Reactive Stroma as a Predictor of Biochemical-Free Recurrence in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 4792–4801. [Google Scholar]
- Tuxhorn, J.A.; Ayala, G.E.; Smith, M.J.; Smith, V.C.; Dang, T.D.; Rowley, D.R. Reactive Stroma in Human Prostate Cancer: Induction of Myofibroblast Phenotype and Extracellular Matrix Remodeling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 2912–2923. [Google Scholar]
- Pederzoli, F.; Raffo, M.; Pakula, H.; Ravera, F.; Nuzzo, P.V.; Loda, M. “Stromal Cells in Prostate Cancer Pathobiology: Friends or Foes?”. Br. J. Cancer 2023, 128, 930–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncharov, N.V.; Popova, P.I.; Avdonin, P.P.; Kudryavtsev, I.V.; Serebryakova, M.K.; Korf, E.A.; Avdonin, P.V. Markers of Endothelial Cells in Normal and Pathological Conditions. Biochem. (Mosc.) Suppl. Ser. A Membr. Cell Biol. 2020, 14, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidegger, I.; Fotakis, G.; Offermann, A.; Goveia, J.; Daum, S.; Salcher, S.; Noureen, A.; Timmer-Bosscha, H.; Schäfer, G.; Walenkamp, A.; et al. Comprehensive Characterization of the Prostate Tumor Microenvironment Identifies CXCR4/CXCL12 Crosstalk as a Novel Antiangiogenic Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messex, J.K.; Liou, G.-Y. Impact of Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment of Prostate Cancer Metastasis. Life 2023, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Xiong, Q.; Wei, Q.; Yang, L. Cellular Landscape of Tumour Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer. Immunology 2023, 168, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, L.W.K.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Law, A.; Sung, S.-Y.; Gardner, T.A.; Egawa, M.; Matsubara, S.; Zhau, H.E. New Targets for Therapy in Prostate Cancer: Modulation of Stromal–Epithelial Interactions. Urology 2003, 62, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Y.C.; Wang, Y.Z. Growth Factors and Epithelial-Stromal Interactions in Prostate Cancer Development. In International Review of Cytology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2000; Volume 199, pp. 65–116. [Google Scholar]
- Glabman, R.A.; Choyke, P.L.; Sato, N. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts: Tumorigenicity and Targeting for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonollo, F.; Thalmann, G.N.; Kruithof-de Julio, M.; Karkampouna, S. The Role of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Prostate Cancer Tumorigenesis. Cancers 2020, 12, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.; Fukabori, Y.; Nikolaropoulos, S.; Wang, F.; McKeehan, W.L. Heparin-Binding Keratinocyte Growth Factor Is a Candidate Stromal-to-Epithelial-Cell Andromedin. Mol. Endocrinol. 1992, 6, 2123–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, K.; Fukabori, Y.; Itoh, N.; Lu, W.; Kan, M.; McKeehan, W.L.; Yamanaka, H. Androgen-Stimulated Human Prostate Epithelial Growth Mediated by Stromal-Derived Fibroblast Growth Factor-10. Endocr. J. 1999, 46, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Memarzadeh, S.; Xin, L.; Mulholland, D.J.; Mansukhani, A.; Wu, H.; Teitell, M.A.; Witte, O.N. Enhanced Paracrine FGF10 Expression Promotes Formation of Multifocal Prostate Adenocarcinoma and an Increase in Epithelial Androgen Receptor. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 572–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, A.A. Role of Androgens and Fibroblast Growth Factors in Prostatic Development. Reproduction 2001, 121, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, G.R.; Hayward, S.W.; Wang, Y.z.; Ricke, W.A. Role of the Stromal Microenvironment in Carcinogenesis of the Prostate. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ropiquet, F.; Berthon, P.; Villette, J.M.; Le Brun, G.; Maitland, N.J.; Cussenot, O.; Fiet, J. Constitutive Expression of FGF2/BFGF in Non-Tumorigenic Human Prostatic Epithelial Cells Results in the Acquisition of a Partial Neoplastic Phenotype. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 72, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Paskeh, M.D.A.; Saghari, Y.; Zarrabi, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; Entezari, M.; Hashemi, M.; Aref, A.R.; Hushmandi, K.; Kumar, A.P.; et al. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta (TGF-β) in Prostate Cancer: A Dual Function Mediator? Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 435–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, S.; Vasseur, C.; Bruyere, F.; Rozet, F.; Maheo, K.; Fromont, G. Clinical Significance of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Markers in Prostate Cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 61, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guido, C.; Whitaker-Menezes, D.; Capparelli, C.; Balliet, R.; Lin, Z.; Pestell, R.G.; Howell, A.; Aquila, S.; Andò, S.; Martinez-Outschoorn, U.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts by TGF-β Drives Tumor Growth: Connecting TGF-β Signaling with “Warburg-like” Cancer Metabolism and L-Lactate Production. Cell Cycle 2012, 11, 3019–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, B.; Umelo, I.A.; Bellier, J.; Castronovo, V.; Turtoi, A. Stromal Modulators of TGF-β in Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2017, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Balk, S.P. Intratumoral Androgen Biosynthesis in Prostate Cancer Pathogenesis and Response to Therapy. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2011, 18, R175–R182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armandari, I.; Hamid, A.R.; Verhaegh, G.; Schalken, J. Intratumoral Steroidogenesis in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Target for Therapy. Prostate Int. 2014, 2, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, S.; Pinault, M.; Domingo, I.; Guimaraes, C.; Guibon, R.; Besson, P.; Tavernier, E.; Blanchet, P.; Multigner, L.; Bruyère, F.; et al. Fatty Acid Profile in Peri-Prostatic Adipose Tissue and Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness in African-Caribbean and Caucasian Patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 91, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figiel, S.; Bery, F.; Chantôme, A.; Fontaine, D.; Pasqualin, C.; Maupoil, V.; Domingo, I.; Guibon, R.; Bruyère, F.; Potier-Cartereau, M.; et al. A Novel Calcium-Mediated EMT Pathway Controlled by Lipids: An Opportunity for Prostate Cancer Adjuvant Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Daniels, G.; Lee, P.; Monaco, M.E. Lipid Metabolism in Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Urol. 2014, 2, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Compérat, E.; Wasinger, G.; Oszwald, A.; Kain, R.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Cussenot, O. The Genetic Complexity of Prostate Cancer. Genes 2020, 11, 1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornu, J.-N.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Cox, D.G.; Roupret, M.; Koutlidis, N.; Bigot, P.; Valeri, A.; Ondet, V.; Gaffory, C.; Fournier, G.; et al. Impact of Body Mass Index, Age, Prostate Volume, and Genetic Polymorphisms on Prostate-Specific Antigen Levels in a Control Population. Eur. Urol. 2016, 70, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, H.C.; Kote-Jarai, Z.; Ross-Adams, H.; Warren, A.Y.; Burge, J.; George, A.; Bancroft, E.; Jhavar, S.; Leongamornlert, D.; Tymrakiewicz, M.; et al. The Rs10993994 Risk Allele for Prostate Cancer Results in Clinically Relevant Changes in Microseminoprotein-Beta Expression in Tissue and Urine. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, H.; Yeager, M.; Li, H.; Bosquet, J.G.; Hayes, R.B.; Orr, N.; Yu, K.; Hutchinson, A.; Jacobs, K.B.; Kraft, P.; et al. Fine Mapping and Functional Analysis of a Common Variant in MSMB on Chromosome 10q11.2 Associated with Prostate Cancer Susceptibility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7933–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; James, M.; Huang, C.-C.; Wang, L.; Wang, L. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism Rs13426236 Contributes to an Increased Prostate Cancer Risk via Regulating MLPH Splicing Variant 4. Mol. Carcinog. 2020, 59, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eastham, J.A.; Auffenberg, G.B.; Barocas, D.A.; Chou, R.; Crispino, T.; Davis, J.W.; Eggener, S.; Horwitz, E.M.; Kane, C.J.; Kirkby, E.; et al. Clinically Localized Prostate Cancer: AUA/ASTRO Guideline, Part I: Introduction, Risk Assessment, Staging, and Risk-Based Management. J. Urol. 2022, 208, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overview|Prostate Cancer: Diagnosis and Management|Guidance|NICE. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng131 (accessed on 15 December 2021).
- Gleason, D.F. Classification of Prostatic Carcinomas. Cancer Chemother. Rep. 1966, 50, 125–128. [Google Scholar]
- Epstein, J.I.; Egevad, L.; Amin, M.B.; Delahunt, B.; Srigley, J.R.; Humphrey, P.A.; Grading Committee The 2014 International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP). Consensus Conference on Gleason Grading of Prostatic Carcinoma: Definition of Grading Patterns and Proposal for a New Grading System. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 40, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marra, G.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H.; Zattoni, F.; Kesch, C.; Rajwa, P.; Cornford, P.; van der Kwast, T.; van den Bergh, R.C.N.; Briers, E.; Van den Broeck, T.; et al. Impact of Epithelial Histological Types, Subtypes, and Growth Patterns on Oncological Outcomes for Patients with Nonmetastatic Prostate Cancer Treated with Curative Intent: A Systematic Review. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cussenot, O.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Comperat, E.; Benbouzid, S.; Lamb, A. Total Pelvic Exenteration Surgery for Loco-Regionally Advanced Prostate Cancer, Is It Justifiable? BJU Int. 2022, 130, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinha, N.; Omer, A.; Philippou, Y.; Harriss, E.; Davies, L.; Chow, K.; Chetta, P.M.; Erickson, A.; Rajakumar, T.; Mills, I.G.; et al. Ductal Adenocarcinoma of the Prostate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Incidence, Presentation, Prognosis, and Management. BJUI Compass 2021, 2, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathod, S.G.; Jaiswal, D.G.; Bindu, R.S. Diagnostic Utility of Triple Antibody (AMACR, HMWCK and P63) Stain in Prostate Neoplasm. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 2651–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mytsyk, Y.; Nakonechnyi, Y.; Dosenko, V.; Kowal, P.; Pietrus, M.; Gazdikova, K.; Labudova, M.; Caprnda, M.; Prosecky, R.; Dragasek, J.; et al. The Performance and Limitations of PCA3, TMPRSS2:ERG, HOXC6 and DLX1 Urinary Markers Combined in the Improvement of Prostate Cancer Diagnostics. Clin. Biochem. 2023, 116, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouprêt, M.; Hupertan, V.; Yates, D.R.; Catto, J.W.F.; Rehman, I.; Meuth, M.; Ricci, S.; Lacave, R.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; de la Taille, A.; et al. Molecular Detection of Localized Prostate Cancer Using Quantitative Methylation-Specific PCR on Urinary Cells Obtained Following Prostate Massage. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1720–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thuret, R.; Chantrel-Groussard, K.; Azzouzi, A.-R.; Villette, J.-M.; Guimard, S.; Teillac, P.; Berthon, P.; Houlgatte, A.; Latil, A.; Cussenot, O. Clinical Relevance of Genetic Instability in Prostatic Cells Obtained by Prostatic Massage in Early Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 92, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornu, J.-N.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Egrot, C.; Gaffory, C.; Haab, F.; Cussenot, O. Urine TMPRSS2:ERG Fusion Transcript Integrated with PCA3 Score, Genotyping, and Biological Features Are Correlated to the Results of Prostatic Biopsies in Men at Risk of Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2013, 73, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, M.C.; Zwart, W.; Roudier, M.P.; True, L.D.; Nelson, W.G.; Epstein, J.I.; De Marzo, A.M.; Nelson, P.S.; Yegnasubramanian, S. Genomic and Phenotypic Heterogeneity in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, A.; Hayes, A.; Rajakumar, T.; Verrill, C.; Bryant, R.J.; Hamdy, F.C.; Wedge, D.C.; Woodcock, D.J.; Mills, I.G.; Lamb, A.D. A Systematic Review of Prostate Cancer Heterogeneity: Understanding the Clonal Ancestry of Multifocal Disease. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2021, 4, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, P.; Dimitrov, T.; Stower, M.; Cussenot, O.; Maitland, N.J. A Microdissection Approach to Detect Molecular Markers during Progression of Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1995, 72, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronkema, C.; Arora, S.; Sood, A.; Dalela, D.; Keeley, J.; Borchert, A.; Baumgarten, L.; Rogers, C.G.; Peabody, J.O.; Menon, M.; et al. Rare Histological Variants of Prostate Adenocarcinoma: A National Cancer Database Analysis. J. Urol. 2020, 204, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grignon, D.J. Unusual Subtypes of Prostate Cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2004, 17, 316–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraban, E.; Epstein, J. Prostate Cancer: Update on Grading and Reporting. Surg. Pathol. Clin. 2022, 15, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. The Molecular Taxonomy of Primary Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 163, 1011–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rebello, R.J.; Oing, C.; Knudsen, K.E.; Loeb, S.; Johnson, D.C.; Reiter, R.E.; Gillessen, S.; Van der Kwast, T.; Bristow, R.G. Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Testa, U.; Castelli, G.; Pelosi, E. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Prostate Cancer Development: Therapeutic Implications. Medicines 2019, 6, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoenborn, J.R.; Nelson, P.; Fang, M. Genomic Profiling Defines Subtypes of Prostate Cancer with the Potential for Therapeutic Stratification. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4058–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Hua, J.T.; Li, H. Recent Advances in Understanding DNA Methylation of Prostate Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1182727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlins, S.A.; Rhodes, D.R.; Perner, S.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Mehra, R.; Sun, X.-W.; Varambally, S.; Cao, X.; Tchinda, J.; Kuefer, R.; et al. Recurrent Fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS Transcription Factor Genes in Prostate Cancer. Science 2005, 310, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, M.A.; Maher, C.A.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. Common Gene Rearrangements in Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 3659–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. John, J.; Powell, K.; Conley-LaComb, M.K.; Chinni, S.R. TMPRSS2-ERG Fusion Gene Expression in Prostate Tumor Cells and Its Clinical and Biological Significance in Prostate Cancer Progression. J. Cancer Sci. Ther. 2012, 4, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iljin, K.; Wolf, M.; Edgren, H.; Gupta, S.; Kilpinen, S.; Skotheim, R.I.; Peltola, M.; Smit, F.; Verhaegh, G.; Schalken, J.; et al. TMPRSS2 Fusions with Oncogenic ETS Factors in Prostate Cancer Involve Unbalanced Genomic Rearrangements and Are Associated with HDAC1 and Epigenetic Reprogramming. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 10242–10246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burdelski, C.; Kleinhans, S.; Kluth, M.; Hube-Magg, C.; Minner, S.; Koop, C.; Graefen, M.; Heinzer, H.; Tsourlakis, M.C.; Wilczak, W.; et al. Reduced AZGP1 Expression Is an Independent Predictor of Early PSA Recurrence and Associated with ERG-Fusion Positive and PTEN Deleted Prostate Cancers. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1199–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massoner, P.; Kugler, K.G.; Unterberger, K.; Kuner, R.; Mueller, L.A.J.; Fälth, M.; Schäfer, G.; Seifarth, C.; Ecker, S.; Verdorfer, I.; et al. Characterization of Transcriptional Changes in ERG Rearrangement-Positive Prostate Cancer Identifies the Regulation of Metabolic Sensors Such as Neuropeptide Y. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamar, M.; Tudor Vladislav, I.; Smith, S.C.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Favazza, L.A.; Alani, A.M.; Ittmann, M.M.; Riddle, N.D.; Whiteley, L.J.; et al. Gene Fusion Characterisation of Rare Aggressive Prostate Cancer Variants—Adenosquamous Carcinoma, Pleomorphic Giant-Cell Carcinoma, and Sarcomatoid Carcinoma: An Analysis of 19 Cases. Histopathology 2020, 77, 890–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamoun, A.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Fromont, G.; Elarouci, N.; Armenoult, L.; Ayadi, M.; Irani, J.; Leroy, X.; Villers, A.; Fournier, G.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Classification of Localized Prostate Adenocarcinoma Reveals a Tumour Subtype Predictive of Non-Aggressive Disease. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léon, P.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Drouin, S.; Audouin, M.; Varinot, J.; Comperat, E.; Cathelineau, X.; Rozet, F.; Vaessens, C.; Stone, S.; et al. Comparison of Cell Cycle Progression Score with Two Immunohistochemical Markers (PTEN and Ki-67) for Predicting Outcome in Prostate Cancer after Radical Prostatectomy. World J. Urol. 2018, 36, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesche, S.; Latil, A.; Muzeau, F.; Cussenot, O.; Fournier, G.; Longy, M.; Eng, C.; Lidereau, R. PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 Involvement in Primary Prostate Cancers. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2879–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, H.M.; Hermida, M.A.; Leslie, N.R. Prostate Cancer, PI3K, PTEN and Prognosis. Clin. Sci. 2017, 131, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceder, Y.; Bjartell, A.; Culig, Z.; Rubin, M.A.; Tomlins, S.; Visakorpi, T. The Molecular Evolution of Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. Focus 2016, 2, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, C.C.T.; Plymate, S.R. The Link between Androgen Receptor Splice Variants and Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Horm. Cancer 2014, 5, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, K.; Nonomura, N. Role of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer: A Review. World J. Mens. Health 2019, 37, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, Y.; Shuin, T.; Uemura, H.; Fujinami, K.; Miyamoto, H.; Torigoe, S.; Dobashi, Y.; Kitamura, H.; Iwasaki, Y.; Danenberg, K. Tumor Suppressor Gene P53 Mutations in Human Prostate Cancer. Prostate 1995, 27, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kir, G.; Cecikoglu, G.E.; Olgun, Z.C.; Kazan, H.O.; Yildirim, A. PTEN Loss and PD-L1 Expression of Different Histological Patterns of Prostate Cancer. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2022, 229, 153738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkens, L.; Sailer, V.; Lessel, D.; Janzen, E.; Greimeier, S.; Kirfel, J.; Perner, S.; Pantel, K.; Werner, S.; von Amsberg, G. Aggressive Variants of Prostate Cancer: Underlying Mechanisms of Neuroendocrine Transdifferentiation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, W.; Wen, Z.; Ji, X.; Zhou, R.; Tuo, X.; Chen, Y.; Gong, X.; Liu, G.; et al. A Rare Multiple Primary Sarcomatoid Carcinoma (SCA) of Small Intestine Harboring Driver Gene Mutations: A Case Report and a Literature Review. Transl. Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1150–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterberg, A.B.; Gordetsky, J.B.; Hurley, P.J. Cribriform Prostate Cancer: Clinical Pathologic and Molecular Considerations. Urology 2021, 155, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraban, E.; Erak, E.; Fatima, A.; Akbari, A.; Zhao, J.; Fletcher, S.A.; Bhanji, Y.; de la Calle, C.M.; Mamawala, M.; Landis, P.; et al. Identifying Men Who Can Remain on Active Surveillance Despite Biopsy Reclassification to Grade Group 2 Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2023, 210, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweldam, C.F.; Wildhagen, M.F.; Steyerberg, E.W.; Bangma, C.H.; van der Kwast, T.H.; van Leenders, G.J.L.H. Cribriform Growth Is Highly Predictive for Postoperative Metastasis and Disease-Specific Death in Gleason Score 7 Prostate Cancer. Mod. Pathol. 2015, 28, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downes, M.R.; Xu, B.; van der Kwast, T.H. Gleason Grade Patterns in Nodal Metastasis and Corresponding Prostatectomy Specimens: Impact on Patient Outcome. Histopathology 2019, 75, 715–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenland, N.Y.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Wong, A.C.; Chan, E.; Carroll, P.R.; Simko, J.P.; Stohr, B.A. Molecular Risk Classifier Score and Biochemical Recurrence Risk Are Associated with Cribriform Pattern Type in Gleason 3+4=7 Prostate Cancer. Investig. Clin. Urol. 2022, 63, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halstuch, D.; Ber, Y.; Margel, D. Screening, Active Surveillance, and Treatment of Localized Prostate Cancer Among Carriers of Germline BRCA Mutations. Eur. Urol. Focus 2020, 6, 212–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Y.; Xin, L.; Goldstein, A.S.; Lawson, D.A.; Teitell, M.A.; Witte, O.N. ETS Family Transcription Factors Collaborate with Alternative Signaling Pathways to Induce Carcinoma from Adult Murine Prostate Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 12465–12470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abida, W.; Cyrta, J.; Heller, G.; Prandi, D.; Armenia, J.; Coleman, I.; Cieslik, M.; Benelli, M.; Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; et al. Genomic Correlates of Clinical Outcome in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 11428–11436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucchiara, V.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Dall’Era, M.; Lin, D.W.; Montorsi, F.; Schalken, J.A.; Evans, C.P. Genomic Markers in Prostate Cancer Decision Making. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretschmer, A.; Tilki, D. Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer—Current Clinical Utility and Future Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 120, 180–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard-Penna, R.; Cancel-Tassin, G.; Comperat, E.; Roupret, M.; Mozer, P.; Cussenot, O. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Molecular Pathology at the Crossroad of the Management of Early Prostate Cancer. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 929–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuzick, J.; Berney, D.M.; Fisher, G.; Mesher, D.; Møller, H.; Reid, J.E.; Perry, M.; Park, J.; Younus, A.; Gutin, A.; et al. Prognostic Value of a Cell Cycle Progression Signature for Prostate Cancer Death in a Conservatively Managed Needle Biopsy Cohort. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1095–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhl, V.; Clegg, W.; Meek, S.; Lenz, L.; Flake, D.D.; Ronan, T.; Kornilov, M.; Horsch, D.; Scheer, M.; Farber, D.; et al. Development and Validation of a Cell Cycle Progression Signature for Decentralized Testing of Men with Prostate Cancer. Biomark. Med. 2022, 16, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.A.; Cooperberg, M.R.; Magi-Galluzzi, C.; Simko, J.P.; Falzarano, S.M.; Maddala, T.; Chan, J.M.; Li, J.; Cowan, J.E.; Tsiatis, A.C.; et al. A 17-Gene Assay to Predict Prostate Cancer Aggressiveness in the Context of Gleason Grade Heterogeneity, Tumor Multifocality, and Biopsy Undersampling. Eur. Urol. 2014, 66, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.; Rosner, I.L.; Brand, T.C.; Zhang, N.; Tsiatis, A.C.; Moncur, J.; Ali, A.; Chen, Y.; Knezevic, D.; Maddala, T.; et al. A Biopsy-Based 17-Gene Genomic Prostate Score Predicts Recurrence After Radical Prostatectomy and Adverse Surgical Pathology in a Racially Diverse Population of Men with Clinically Low- and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2015, 68, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C. Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 276–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aurilio, G.; Cimadamore, A.; Mazzucchelli, R.; Lopez-Beltran, A.; Verri, E.; Scarpelli, M.; Massari, F.; Cheng, L.; Santoni, M.; Montironi, R. Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathway in Prostate Cancer: From Genetics to Clinical Applications. Cells 2020, 9, 2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.-L.; Kyprianou, N. Role of Androgens and the Androgen Receptor in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, A.D.; Massie, C.E.; Neal, D.E. The Transcriptional Programme of the Androgen Receptor (AR) in Prostate Cancer. BJU Int. 2014, 113, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonkhoff, H.; Remberger, K. Widespread Distribution of Nuclear Androgen Receptors in the Basal Cell Layer of the Normal and Hyperplastic Human Prostate. Vichows Arch. A Pathol. Anat. 1993, 422, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthon, P.; Waller, A.S.; Villette, J.M.; Loridon, L.; Cussenot, O.; Maitland, N.J. Androgens Are Not a Direct Requirement for the Proliferation of Human Prostatic Epithelium in Vitro. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 73, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.K.; Tyagi, R.K.; Song, C.S.; Lavrovsky, Y.; Ahn, S.C.; Oh, T.S.; Chatterjee, B. Androgen Receptor: Structural Domains and Functional Dynamics after Ligand-Receptor Interaction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2001, 949, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Abboud, K. Targeting the Androgen Receptor Signaling Pathway in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2022, 79, 1224–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Yu, J. Androgen Receptor Genomic Regulation. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2013, 2, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.D.; Chang, C.-Y.; Wittmann, B.M.; Kunder, R.S.; Cui, H.; Fan, D.; Joseph, J.D.; McDonnell, D.P. The Homeodomain Protein HOXB13 Regulates the Cellular Response to Androgens. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.Y.; Chang, C.W.; Chng, K.R.; Wansa, K.D.S.A.; Sung, W.-K.; Cheung, E. Integration of Regulatory Networks by NKX3-1 Promotes Androgen-Dependent Prostate Cancer Survival. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 32, 399–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Stable, C.M.; Pozas, A.; Roos, B.A. A Role for GATA Transcription Factors in the Androgen Regulation of the Prostate-Specific Antigen Gene Enhancer. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2000, 167, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Liu, X.S.; Carroll, J.S.; Jänne, O.A.; Keeton, E.K.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Pienta, K.J.; Brown, M. A Hierarchical Network of Transcription Factors Governs Androgen Receptor-Dependent Prostate Cancer Growth. Mol. Cell 2007, 27, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massie, C.E.; Lynch, A.; Ramos-Montoya, A.; Boren, J.; Stark, R.; Fazli, L.; Warren, A.; Scott, H.; Madhu, B.; Sharma, N.; et al. The Androgen Receptor Fuels Prostate Cancer by Regulating Central Metabolism and Biosynthesis. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2719–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takayama, K.; Inoue, S. Transcriptional Network of Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer Progression. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 756–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Montoya, A.; Lamb, A.D.; Russell, R.; Carroll, T.; Jurmeister, S.; Galeano-Dalmau, N.; Massie, C.E.; Boren, J.; Bon, H.; Theodorou, V.; et al. HES6 Drives a Critical AR Transcriptional Programme to Induce Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer through Activation of an E2F1-Mediated Cell Cycle Network. EMBO Mol. Med. 2014, 6, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Runkle, C.; Jin, H.-J.; Yu, J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Kuzel, T.; Lee, C.; Yu, J. CCN3/NOV Gene Expression in Human Prostate Cancer Is Directly Suppressed by the Androgen Receptor. Oncogene 2014, 33, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Garzón, V.; Kypta, R. WNT Signalling in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2017, 14, 683–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Q.; Xu, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signal Transduction Pathway in Prostate Cancer and Associated Drug Resistance. Discov. Oncol. 2021, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Shukeir, N.; Potti, A.; Sircar, K.; Aprikian, A.; Goltzman, D.; Rabbani, S.A. Up-Regulation of Wnt-1 and Beta-Catenin Production in Patients with Advanced Metastatic Prostate Carcinoma: Potential Pathogenetic and Prognostic Implications. Cancer 2004, 101, 1345–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasso, C.S.; Wu, Y.-M.; Robinson, D.R.; Cao, X.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Khan, A.P.; Quist, M.J.; Jing, X.; Lonigro, R.J.; Brenner, J.C.; et al. The Mutational Landscape of Lethal Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer. Nature 2012, 487, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, D.; Van Allen, E.M.; Wu, Y.-M.; Schultz, N.; Lonigro, R.J.; Mosquera, J.-M.; Montgomery, B.; Taplin, M.-E.; Pritchard, C.C.; Attard, G.; et al. Integrative Clinical Genomics of Advanced Prostate Cancer. Cell 2015, 161, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Placencio, V.; Iturregui, J.M.; Uwamariya, C.; Sharif-Afshar, A.-R.; Koyama, T.; Hayward, S.W.; Bhowmick, N.A. Prostate Tumor Progression Is Mediated by a Paracrine TGF-Beta/Wnt3a Signaling Axis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 7118–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, Y.; Huang, J.; Sankarasharma, D.; Morikawa, T.; Fukayama, M.; Epstein, J.I.; Chada, K.K.; Witte, O.N. Stromal Epigenetic Dysregulation Is Sufficient to Initiate Mouse Prostate Cancer via Paracrine Wnt Signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E3395–E3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dakhova, O.; Ozen, M.; Creighton, C.J.; Li, R.; Ayala, G.; Rowley, D.; Ittmann, M. Global Gene Expression Analysis of Reactive Stroma in Prostate Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Wang, Y.; DeGraff, D.J.; Wills, M.L.; Matusik, R.J. Wnt/β-Catenin Activation Promotes Prostate Tumor Progression in a Mouse Model. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1868–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorning, B.Y.; Dass, M.S.; Smalley, M.J.; Pearson, H.B. The PI3K-AKT-MTOR Pathway and Prostate Cancer: At the Crossroads of AR, MAPK, and WNT Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, B.S.; Schultz, N.; Hieronymus, H.; Gopalan, A.; Xiao, Y.; Carver, B.S.; Arora, V.K.; Kaushik, P.; Cerami, E.; Reva, B.; et al. Integrative Genomic Profiling of Human Prostate Cancer. Cancer Cell 2010, 18, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armenia, J.; Wankowicz, S.A.M.; Liu, D.; Gao, J.; Kundra, R.; Reznik, E.; Chatila, W.K.; Chakravarty, D.; Han, G.C.; Coleman, I.; et al. The Long Tail of Oncogenic Drivers in Prostate Cancer. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Xu, W.; Xiao, Y.-T.; Huang, H.; Gu, D.; Ren, S. Targeting Signaling Pathways in Prostate Cancer: Mechanisms and Clinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Berriguete, G.; Fraile, B.; Martínez-Onsurbe, P.; Olmedilla, G.; Paniagua, R.; Royuela, M. MAP Kinases and Prostate Cancer. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 169170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crumbaker, M.; Khoja, L.; Joshua, A.M. AR Signaling and the PI3K Pathway in Prostate Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastian, P.J.; Carter, B.H.; Bjartell, A.; Seitz, M.; Stanislaus, P.; Montorsi, F.; Stief, C.G.; Schröder, F. Insignificant Prostate Cancer and Active Surveillance: From Definition to Clinical Implications. Eur. Urol. 2009, 55, 1321–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Poel, H.; Klotz, L.; Andriole, G.; Azzouzi, A.-R.; Bjartell, A.; Cussenot, O.; Hamdy, F.; Graefen, M.; Palma, P.; Rivera, A.R.; et al. Role of Active Surveillance and Focal Therapy in Low- and Intermediate-Risk Prostate Cancers. World J. Urol. 2015, 33, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bul, M.; Zhu, X.; Valdagni, R.; Pickles, T.; Kakehi, Y.; Rannikko, A.; Bjartell, A.; van der Schoot, D.K.; Cornel, E.B.; Conti, G.N.; et al. Active Surveillance for Low-Risk Prostate Cancer Worldwide: The PRIAS Study. Eur. Urol. 2013, 63, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.D.; Lopez, J.F.; Leiblich, A.; Leslie, T.A.; Lamb, A.D. Re: Fifteen-Year Outcomes after Monitoring, Surgery, or Radiotherapy for Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2023, 84, 245–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mottet, N.; Bellmunt, J.; Bolla, M.; Briers, E.; Cumberbatch, M.G.; De Santis, M.; Fossati, N.; Gross, T.; Henry, A.M.; Joniau, S.; et al. EAU-ESTRO-SIOG Guidelines on Prostate Cancer. Part 1: Screening, Diagnosis, and Local Treatment with Curative Intent. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loblaw, A.; Zhang, L.; Lam, A.; Nam, R.; Mamedov, A.; Vesprini, D.; Klotz, L. Comparing Prostate Specific Antigen Triggers for Intervention in Men with Stable Prostate Cancer on Active Surveillance. J. Urol. 2010, 184, 1942–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, M.K.; Leslie, S.W. Prostate Specific Antigen. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Alarcón-Zendejas, A.P.; Scavuzzo, A.; Jiménez-Ríos, M.A.; Álvarez-Gómez, R.M.; Montiel-Manríquez, R.; Castro-Hernández, C.; Jiménez-Dávila, M.A.; Pérez-Montiel, D.; González-Barrios, R.; Jiménez-Trejo, F.; et al. The Promising Role of New Molecular Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer: From Coding and Non-Coding Genes to Artificial Intelligence Approaches. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2022, 25, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsen, N.A.; Hamdy, F.C.; Bryant, R.J. Novel Biomarkers for the Detection of Prostate Cancer. J. Clin. Urol. 2016, 9, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alahdal, M.; Perera, R.A.; Moschovas, M.C.; Patel, V.; Perera, R.J. Current Advances of Liquid Biopsies in Prostate Cancer: Molecular Biomarkers. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2023, 30, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huggins, C.; Hodges, C.V. Studies on Prostatic Cancer. I. The Effect of Castration, of Estrogen and Androgen Injection on Serum Phosphatases in Metastatic Carcinoma of the Prostate. CA Cancer J. Clin. 1972, 22, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamoto, M.; Hokaiwado, N.; Cho, Y.M.; Takahashi, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Imaida, K.; Shirai, T. Prostate Carcinomas Developing in Transgenic Rats with SV40 T Antigen Expression under Probasin Promoter Control Are Strictly Androgen Dependent. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4693–4700. [Google Scholar]
- Said, M.M.; Hokaiwado, N.; Tang, M.; Ogawa, K.; Suzuki, S.; Ghanem, H.M.; Esmat, A.Y.; Asamoto, M.; Refaie, F.M.; Shirai, T. Inhibition of Prostate Carcinogenesis in Probasin/SV40 T Antigen Transgenic Rats by Leuprorelin, a Luteinizing Hormone-Releasing Hormone Agonist. Cancer Sci. 2006, 97, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andriole, G.L.; Bostwick, D.G.; Brawley, O.W.; Gomella, L.G.; Marberger, M.; Montorsi, F.; Pettaway, C.A.; Tammela, T.L.; Teloken, C.; Tindall, D.J.; et al. Effect of Dutasteride on the Risk of Prostate Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1192–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feigl, P.; Blumenstein, B.; Thompson, I.; Crowley, J.; Wolf, M.; Kramer, B.S.; Coltman, C.A.; Brawley, O.W.; Ford, L.G. Design of the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT). Control. Clin. Trials 1995, 16, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, P.J.; Tangen, C.M.; Crowley, J.J.; Carlin, S.M.; Ryan, A.; Coltman, C.A.; Ford, L.G.; Thompson, I.M. Implementation of the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial (PCPT). Control. Clin. Trials 2004, 25, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, I.M.; Goodman, P.J.; Tangen, C.M.; Parnes, H.L.; Minasian, L.M.; Godley, P.A.; Lucia, M.S.; Ford, L.G. Long-Term Survival of Participants in the Prostate Cancer Prevention Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 603–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köllermann, J.; Hopfenmüller, W.; Caprano, J.; Budde, A.; Weidenfeld, H.; Weidenfeld, M.; Helpap, B. Prognosis of Stage PT0 after Prolonged Neoadjuvant Endocrine Therapy of Prostate Cancer: A Matched-Pair Analysis. Eur. Urol. 2004, 45, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilt, T.J.; MacDonald, R.; Hagerty, K.; Schellhammer, P.; Kramer, B.S. Five-Alpha-Reductase Inhibitors for Prostate Cancer Prevention. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2008, 2, CD007091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakazawa, M.; Fang, M.; H Marshall, C.; Lotan, T.L.; Isaacsson Velho, P.; Antonarakis, E.S. Clinical and Genomic Features of SPOP-Mutant Prostate Cancer. Prostate 2022, 82, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).