Common Anatomical Variations of Neurovascular Canals and Foramina Relevant to Oral Surgeons: A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Retromolar Canal and Foramen
3.1.1. Retromolar Canal
Classification of RMC
- Type A1: RMC with a vertical course that branches off from the MC and courses postero-superiorly to open into the retromolar fossa.
- Type A2: RMC with a vertical course that forms an additional horizontal anterior branch before opening posterosuperiorly into the retromolar fossa
- Type B1: RMC with a posteriorly curved course
- Type B2: RMC with posteriorly curved course forming an additional anterior horizontal branch before opening into the retromolar fossa
- Type C: RMC with a horizontal or transverse course with a posterior opening behind the temporal crest and an anterior opening in front of the temporal crest in the retromolar fossa.
- Subtype 1, which runs directly over the surface of the bone;
- Subtype 2, which reaches the retromolar region with a single curve, giving the impression of a “V”;
- Subtype 3, with three segments and two main curves before ending in the retromolar region, resembling a “U”.
- Type A: superior type;
- Type B: radicular retromolar type;
- Type C: dental type;
- Type D: plexus type;
- Type E: forward type. Further subclassified in: E1, where RMC branches off the MC and runs forward without fusing to the MC; E2, where RMC branches off the MC, runs forward for some distance and then fuses with the MC.
Prevalence of RMC
Content of the RMC
Morphometric Measurement of RMC
3.1.2. Retromolar Foramen
Prevalence of RMF
Morphometric Measurement of RMF
Clinical Significance
Local Anesthetic Failure
Haemorrhage
Neurosensory Disturbance
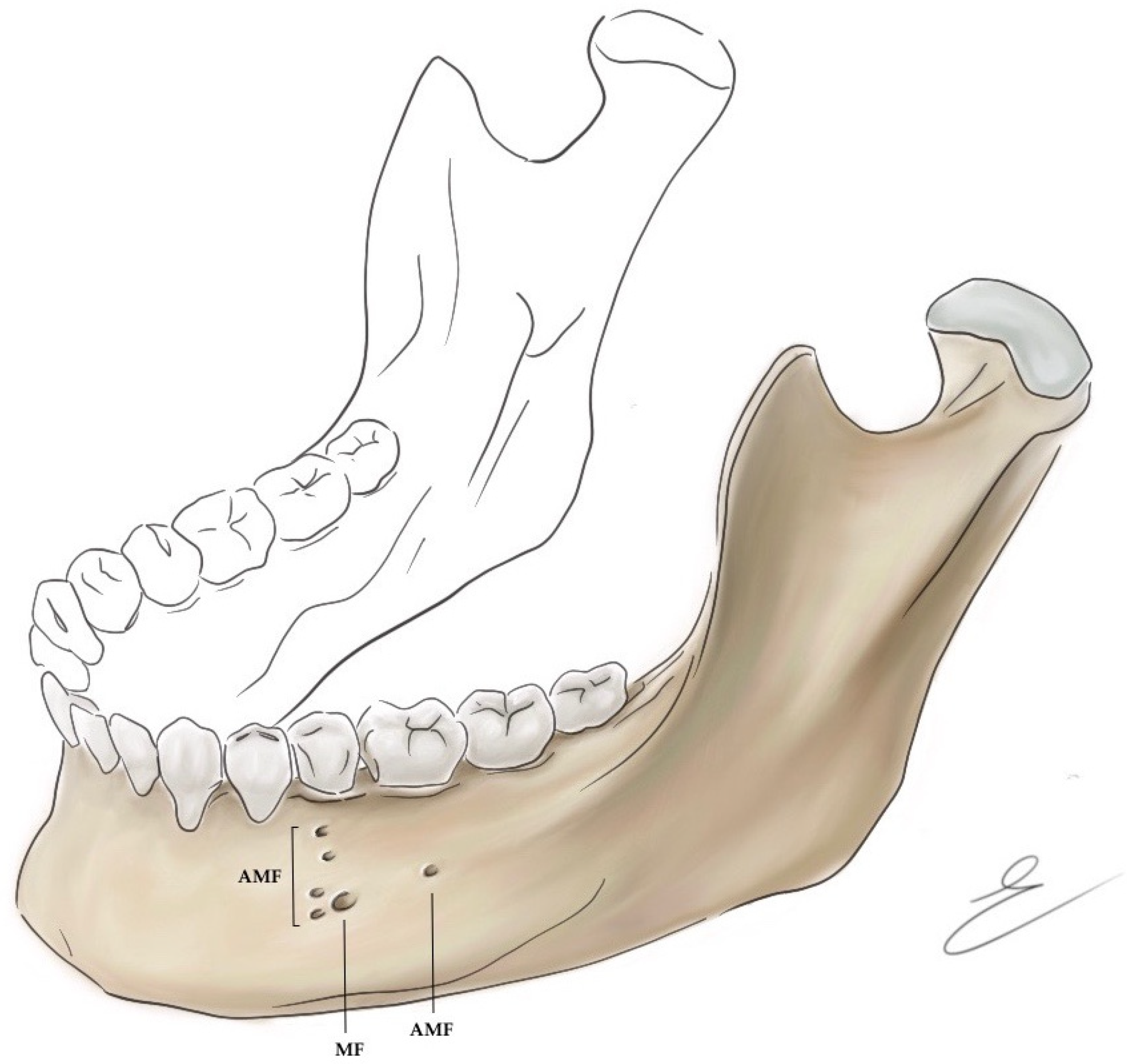
3.2. Accessory Mental Foramina
3.2.1. Prevalence and Morphometric Measurement of AMF
3.2.2. Clinical Significance
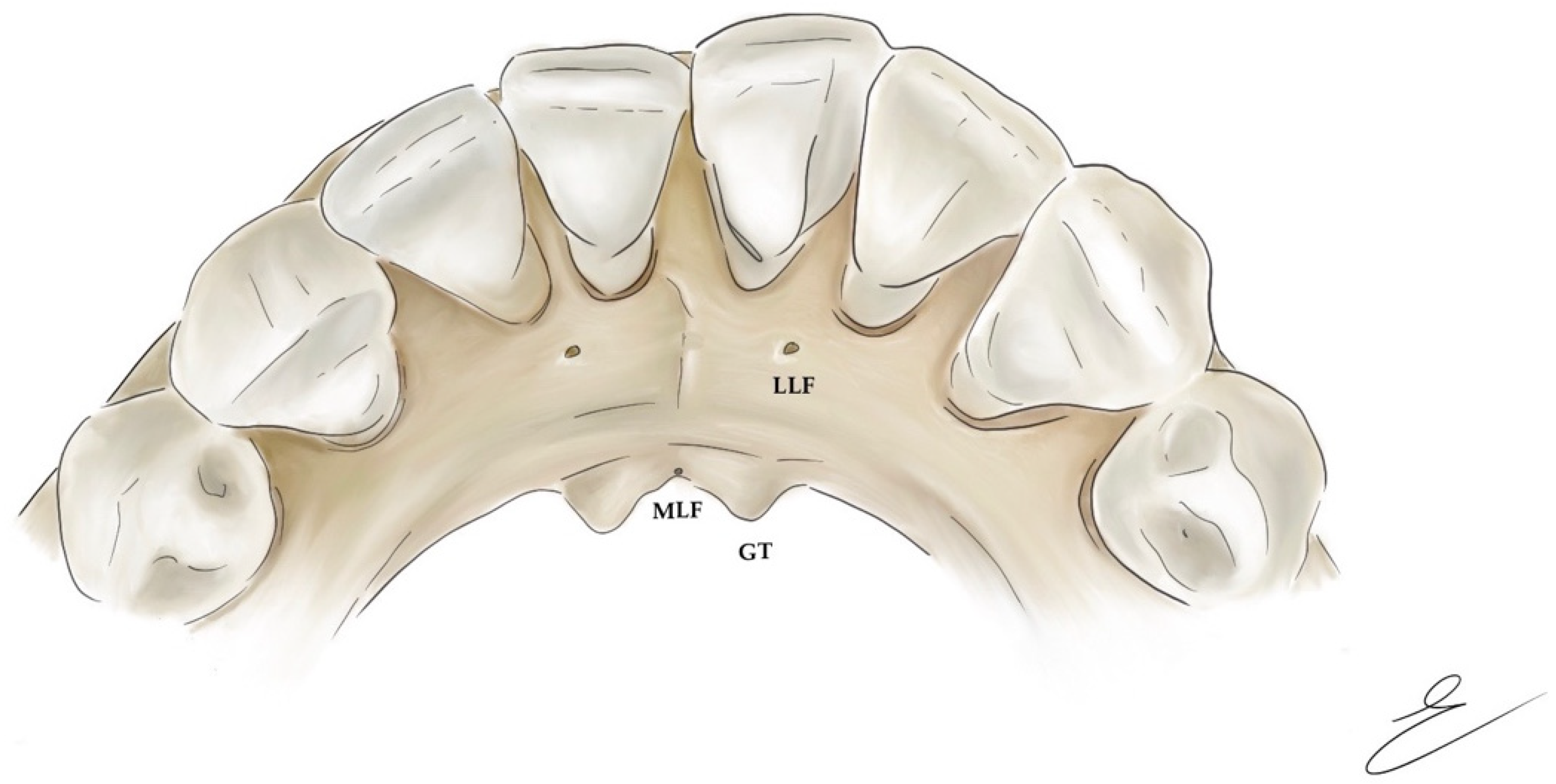
3.3. Mandibular Lingual Foramina
3.3.1. Classification of Lingual Foramina
- Median or midline lingual foramina (MLF), located on the midline of the lingual aspect of the mandible, close to the genial tubercles;
- Paramedian lingual foramina, located up to the posterior margin of the canine;
- Posterior lingual foramina, located distal to the canine [61].
Midline Lingual Foramina
Lateral Lingual Foramina
3.3.2. Morphometric Measurement of Lingual Foramina
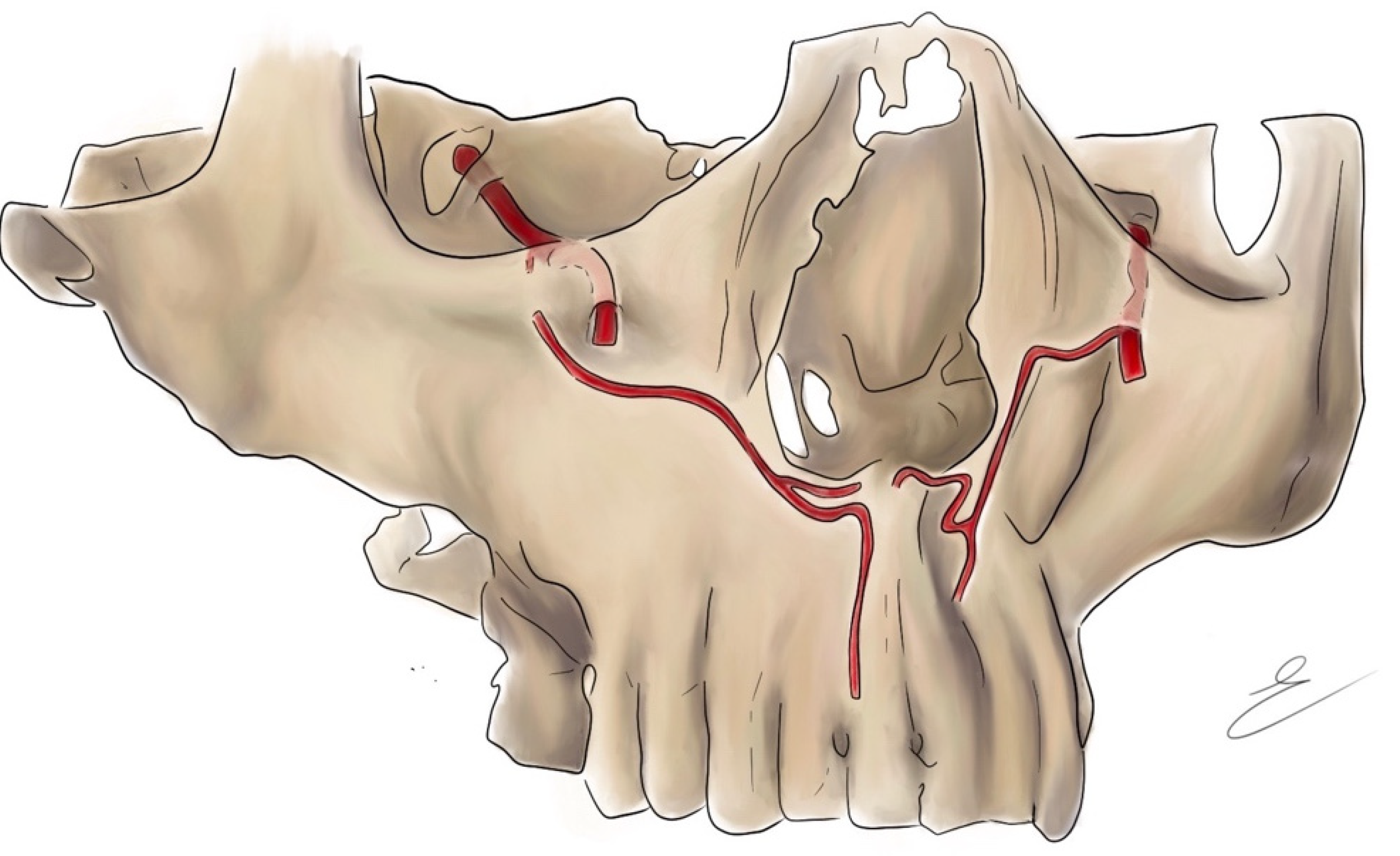
3.3.3. Canals of Lingual Foramina
3.3.4. Content of Lingual Foramina and Canals
3.3.5. Clinical Significance
Dental Implantation
Haemorrhage
3.4. Canalis Sinuosus
3.4.1. Prevalence of CS
3.4.2. Morphometric Measurement of CS
3.4.3. Clinical Significance
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Żytkowski, A.; Tubbs, R.S.; Iwanaga, J.; Clarke, E.; Polguj, M.; Wysiadecki, G. Anatomical normality and variability: Historical perspective and methodological considerations. Transl. Res. Anat. 2021, 23, 100105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieser, J.; Kieser, D.; Hauman, T. The course and distribution of the inferior alveolar nerve in the edentulous mandible. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2005, 16, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, S.C.; Pharoah, M.J. Oral Radiology-E-Book: Principles and Interpretation; Elsevier Health Sciences: St. Louis, MI, USA, 2014; ISBN 0-323-09634-4. [Google Scholar]
- Motamedi, M.H.K.; Gharedaghi, J.; Mehralizadeh, S.; Navi, F.; Badkoobeh, A.; Valaei, N.; Azizi, T. Anthropomorphic assessment of the retromolar foramen and retromolar nerve: Anomaly or variation of normal anatomy? Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossenberg, N.S. Retromolar foramen of the human mandible. Am. J. Phys. Anthropol. 1987, 73, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Arx, T.; Hänni, A.; Sendi, P.; Buser, D.; Bornstein, M.M. Radiographic study of the mandibular retromolar canal: An anatomic structure with clinical importance. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.; Matsuda, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Araki, K.; Okano, T. Retromolar canals as observed on cone-beam computed tomography: Their incidence, course, and characteristics. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2013, 115, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-Q.; Zhao, Y.-N.; Liu, D.-G.; Meng, Y.; Ma, X.-C. Bifid variations of the mandibular canal: Cone beam computed tomography evaluation of 1000 Northern Chinese patients. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2018, 126, e271–e278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luangchana, P.; Pornprasertsuk-Damrongsri, S.; Kitisubkanchana, J.; Wongchuensoontorn, C. The retromolar canal and its variations: Classification using cone beam computed tomography. Quintessence Int. 2018, 49, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Lizio, G.; Pelliccioni, G.A.; Ghigi, G.; Fanelli, A.; Marchetti, C. Radiographic assessment of the mandibular retromolar canal using cone-beam computed tomography. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2013, 71, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.-K.; Jung, W.; Bae, J.-H.; Kwak, H.-H. Anatomical and radiographic study of the mandibular retromolar canal. J. Dent. Sci. 2016, 11, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Capote, T.S.d.O.; de Almeida Gonçalves, M.; Campos, J.Á.D.B. Retromolar canal associated with age, side, sex, bifid mandibular canal, and accessory mental foramen in panoramic radiographs of Brazilians. Anat. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 434083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sisman, Y.; Ercan-Sekerci, A.; Payveren-Arıkan, M.; Sahman, H. Diagnostic accuracy of cone-beam CT compared with panoramic images in predicting retromolar canal during extraction of impacted mandibular third molars. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2015, 20, e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palma, L.F.; Buck, A.F.; Kfouri, F.d.Á.; Blachman, I.T.; Lombardi, L.A.; Cavalli, M.A. Evaluation of retromolar canals on cone beam computerized tomography scans and digital panoramic radiographs. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 21, 307–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fuentes, R.; Arias, A.; Farfán, C.; Astete, N.; Garay, I.; Navarro, P.; Dias, F.J. Morphological variations of the mandibular canal in digital panoramic radiographs: A retrospective study in a Chilean population. Folia Morphol. 2019, 78, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuta, S.; Iwanaga, J.; Nakamura, K.; Hino, K.; Nakamura, M.; Kusukawa, J. The retromolar canals and foramina: Radiographic observation and application to oral surgery. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2018, 40, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwanaga, J.; Watanabe, K.; Saga, T.; Tubbs, R.S.; Tanaka, K.; Kikuta, S.; Tabira, Y.; Fisahn, C.; Kamura, Y.; Kusukawa, J. A novel method for observation of the mandibular foramen: Application to a better understanding of dental anatomy. Anat. Rec. 2017, 300, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yafei, C.; Jun, P.; Yuanyuan, L.; Shuqun, Q.; Jian, P. Cone beam computed tomography evaluation of bifid mandibular canals in the adult population in Sichuan Province. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi Huaxi Kouqiang Yixue Zazhi West China J. Stomatol. 2017, 35, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, J.-H.; Lee, K.-S.; Oh, M.-G.; Choi, H.-Y.; Lee, S.-R.; Oh, S.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kim, G.-T.; Choi, Y.-S.; Hwang, E.-H. The incidence and configuration of the bifid mandibular canal in Koreans by using cone-beam computed tomography. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2014, 44, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alves, N.; Deana, N.F. Anatomical and radiographical study of the retromolar canal and retromolar foramen in macerated mandibles. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 4292. [Google Scholar]
- Jeyaseelan, N.; Sharma, J.K. Morphological study of unnamed foramina in north Indian human mandibles and its possible role in neurovascular transmission. Int. J. Oral Surg. 1984, 13, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potu, B.K.; Kumar, V.; Salem, A.-H.; Abu-Hijleh, M. Occurrence of the retromolar foramen in dry mandibles of South-eastern part of India: A morphological study with review of the literature. Anat. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 296717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawai, T.; Asaumi, R.; Sato, I.; Kumazawa, Y.; Yosue, T. Observation of the retromolar foramen and canal of the mandible: A CBCT and macroscopic study. Oral Radiol. 2012, 28, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, A.C.; Freire, A.R.; Prado, G.B.; Prado, F.B.; Botacin, P.R.; Ferreira Caria, P.H. Incidence of retromolar foramen in human mandibles: Ethnic and clinical aspects. Int. J. Morphol. 2012, 30, 1074–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ngeow, W.C.; Chai, W.L. The clinical significance of the retromolar canal and foramen in dentistry. Clin. Anat. 2021, 34, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muinelo-Lorenzo, J.; Suárez-Quintanilla, J.A.; Fernández-Alonso, A.; Marsillas-Rascado, S.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.M. Descriptive study of the bifid mandibular canals and retromolar foramina: Cone beam CT vs. panoramic radiography. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2014, 43, 20140090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lofgren, A.B. Foramina retromolaria mandibulae. Odont Tidskr 1957, 65, 552–570. [Google Scholar]
- Bilodi, A.K.S.; Singh, S.; Ebenezer, D.A.; Suman, P.; Kumar, K. A study on retromolar foramen and other accessory foramina in human mandibles of Tamil Nadu region. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2013, 3, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Shantharam, V.; Manjunath, K.Y.; Aruna, N.; Shastri, D. Retromolar foramen in South Indian mandibles. Anat. Karnataka 2013, 7, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, L.F.; Dutra, K.; Porporatti, A.L.; Mezzomo, L.A.; De Luca Canto, G.; Flores-Mir, C.; Corrêa, M. Anatomical variations of mandibular canal detected by panoramic radiography and CT: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2016, 45, 20150310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tiwari, S.; Ramakrishna, R.; Sangeeta, M. A study on the incidence of retromolar foramen in South Indian adult dried human mandibles and its clinical relevance. Int. J. Res. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 1383–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bilecenoglu, B.; Tuncer, N. Clinical and anatomical study of retromolar foramen and canal. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 64, 1493–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arakeri, G.; Sagoo, M.G.; Brennan, P.A. Neurovascular plexus theory for “escape pain phenomenon” in lower third molar surgery. Plast Aesthet Res. 2015, 2, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suazo Galdames, I.C.; Cantín López, M.G.; Zavando Matamala, D.A. Inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia via the retromolar triangle, an alternative for patients with blood dyscrasias. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2008, 13, E43–E47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azaz, B.; Lustmann, J. Anatomical configurations in dry mandibles. Br. J. Oral Surg. 1973, 11, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S. Aberrant buccal nerve encountered at third molar surgery. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. 1981, 52, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenstein, G.; Tarnow, D. The mental foramen and nerve: Clinical and anatomical factors related to dental implant placement: A literature review. J. Periodontol. 2006, 77, 1933–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, H.; Kodama, J.; Yanagisako, M.; Ohmori, T. Anatomical study of the accessory mental foramen and the distribution of its nerve. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 1992, 69, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naitoh, M.; Hiraiwa, Y.; Aimiya, H.; Gotoh, K.; Ariji, E. Accessory mental foramen assessment using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2009, 107, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, J.; Saga, T.; Tabira, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kitashima, S.; Watanabe, K.; Kusukawa, J.; Yamaki, K.-I. The clinical anatomy of accessory mental nerves and foramina. Clin. Anat. 2015, 28, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, J.; Saga, T.; Tabira, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Yamaki, K. A novel method for visualization of the inferior alveolar nerve for clinical and educational purposes. J. Oral Biosci. 2016, 58, 66–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwanaga, J.; Watanabe, K.; Saga, T.; Kikuta, S.; Tabira, Y.; Kitashima, S.; Fisahn, C.; Alonso, F.; Tubbs, R.S.; Kusukawa, J. Undetected small accessory mental foramina using cone-beam computed tomography. Cureus 2017, 9, e1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aytugar, E.; Özeren, C.; Lacin, N.; Veli, I.; Çene, E. Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of accessory mental foramen in a Turkish population. Anat. Sci. Int. 2019, 94, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawlinson, J.E.; Bass, L.; Campoy, L.; Lesser, C.; Prytherch, B. Evaluation of the equine mental foramen block: Cadaveric and in vivo injectate diffusion. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2018, 45, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Torres, M.; Padial-Molina, M.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; García-Delgado, R.; Catena, A.; Galindo-Moreno, P. Inferior alveolar nerve trajectory, mental foramen location and incidence of mental nerve anterior loop. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2017, 22, e630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainy, M.A.A.M. Mental Foramen and Accessory Mental Foramen Variations: A Systematic Review; Boston University: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Muinelo-Lorenzo, J.; Suárez-Quintanilla, J.-A.; Fernández-Alonso, A.; Varela-Mallou, J.; Suárez-Cunqueiro, M.-M. Anatomical characteristics and visibility of mental foramen and accessory mental foramen: Panoramic radiography vs. cone beam CT. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2015, 20, e707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, A.; Di Carlo, F.; Quaranta, A.; Piattelli, A. Injury of the inferior alveolar nerve after overfilling of the root canal with endodontic cement: A case report. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endodontol. 2007, 104, e56–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wismeijer, D.; Van Waas, M.A.J.; Vermeeren, J.I.J.F.; Kalk, W. Patients’ perception of sensory disturbances of the mental nerve before and after implant surgery: A prospective study of 110 patients. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 35, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Elahi, F.; Manolitsis, N.; Ranganath, Y.S.; Reddy, C.G. Mental nerve neuropathy following dental extraction. Pain Physician 2014, 17, E375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, N.; Zhang, W.; Jadhav, A.; Ioannou, A.; Eswaran, S.; Weltman, R. Cone-beam computed tomography analysis of the prevalence, length, and passage of the anterior loop of the mandibular canal. J. Oral Implantol. 2019, 45, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, M.; Koong, C.; Kruger, E.; Tennant, M. Prevalence of accessory mental foramina: A study of 4000 CBCT scans. Clin. Anat. 2019, 32, 1048–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, R.; Farfán, C.; Astete, N.; Garay, I.; Dias, F.; Arias, A. Bilateral bifid mandibular canal: A case report using cone beam computed tomography. Folia Morphol. 2018, 77, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagaya, A.; Matsuda, Y.; Nakajima, K.; Seki, K.; Okano, T. Assessment of the blood supply to the lingual surface of the mandible for reduction of bleeding during implant surgery. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 351–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, C.R.S.; da Silva Ramos, L.M.P.; Poleti, M.L.; Capelozza, A.L.A.; Rubira-Bullen, I.R.F. Anatomical study of the posterior mandible: Lateral lingual foramina in cone beam computed tomography. Implant Dent. 2016, 25, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katakami, K.; Mishima, A.; Kuribayashi, A.; Shimoda, S.; Hamada, Y.; Kobayashi, K. Anatomical characteristics of the mandibular lingual foramina observed on limited cone-beam CT images. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 386–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bari, R.; Coronelli, R.; Cicconetti, A. Intraosseous vascularization of anterior mandible: A radiographic analysis. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2014, 25, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolstunov, L. Implant zones of the jaws: Implant location and related success rate. J. Oral Implantol. 2007, 33, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosano, G.; Taschieri, S.; Gaudy, J.F.; Testori, T.; Del Fabbro, M. Anatomic assessment of the anterior mandible and relative hemorrhage risk in implant dentistry: A cadaveric study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Jacobs, R.; Lambrichts, I.; Vandewalle, G. Lingual foramina on the mandibular midline revisited: A macroanatomical study. Clin. Anat. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Clin. Anat. Br. Assoc. Clin. Anat. 2007, 20, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Arx, T.; Lozanoff, S. Lingual foramina and canals. In Clinical Oral Anatomy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 463–487. [Google Scholar]
- Von Arx, T.; Matter, D.; Buser, D.; Bornstein, M.M. Evaluation of location and dimensions of lingual foramina using limited cone-beam computed tomography. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 2777–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Kawai, T.; Okutsu, K.; Yosue, T.; Takamori, H.; Sunohara, M.; Sato, I. The appearance of foramen in the internal aspect of the mental region of mandible from Japanese cadavers and dry skulls under macroscopic observation and three-dimensional CT images. Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn. 2005, 82, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tepper, G.; Hofschneider, U.B.; Gahleitner, A.; Ulm, C. Computed tomographic diagnosis and localization of bone canals in the mandibular interforaminal region for prevention of bleeding complications during implant surgery. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2001, 16, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Babiuc, I.; Tarlungeanu, I.; Pauna, M. Cone beam computed tomography observations of the lingual foramina and their bony canals in the median region of the mandible. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2011, 52, 827–829. [Google Scholar]
- Sheikhi, M.; Mosavat, F.; Ahmadi, A. Assessing the anatomical variations of lingual foramen and its bony canals with CBCT taken from 102 patients in Isfahan. Dent. Res. J. 2012, 9, S45. [Google Scholar]
- Oettlé, A.C.; Fourie, J.; Human-Baron, R.; van Zyl, A.W. The midline mandibular lingual canal: Importance in implant surgery. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2015, 17, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakajima, K.; Tagaya, A.; Otonari-Yamamoto, M.; Seki, K.; Araki, K.; Sano, T.; Okano, T.; Nakamura, M. Composition of the blood supply in the sublingual and submandibular spaces and its relationship to the lateral lingual foramen of the mandible. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2014, 117, e32–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sato, I.; Yosue, T.; Takamori, H.; Sunohara, M. Anastomosis between the inferior alveolar artery branches and submental artery in human mandible. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2006, 28, 308–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Truong, M.K.; Adeeb, N.; Tubbs, R.S.; Iwanaga, J. Clinical anatomy and surgical significance of the lingual foramina and their canals. Clin. Anat. 2017, 30, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaravilli, M.S.; Mariniello, M.; Sammartino, G. Mandibular lingual vascular canals (MLVC): Evaluation on dental CTs of a case series. Eur. J. Radiol. 2010, 76, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, M.Y.; Kim, C.-H. Distribution of the lingual foramina in mandibular cortical bone in Koreans. J. Korean Assoc. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 39, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Oliveira-Santos, C.; Rubira-Bullen, I.R.; Monteiro, S.A.; León, J.E.; Jacobs, R. Neurovascular anatomical variations in the anterior palate observed on CBCT images. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 1044–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanzeler, A.M.V.; Marinho, C.G.; Junior, S.M.A.; Manzi, F.R.; Tuji, F.M. Anatomical study of the canalis sinuosus in 100 cone beam computed tomography examinations. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 19, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurler, G.; Delilbasi, C.; Ogut, E.E.; Aydin, K.; Sakul, U. Evaluation of the morphology of the canalis sinuosus using cone-beam computed tomography in patients with maxillary impacted canines. Imaging Sci. Dent. 2017, 47, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Arx, T.; Lozanoff, S. Anterior superior alveolar nerve (ASAN). Swiss Dent. J. 2015, 125, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Machado, V.d.C.; Chrcanovic, B.R.; Felippe, M.B.; Júnior, L.M.; De Carvalho, P.S.P. Assessment of accessory canals of the canalis sinuosus: A study of 1000 cone beam computed tomography examinations. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 45, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghandourah, A.O.; Rashad, A.; Heiland, M.; Hamzi, B.M.; Friedrich, R.E. Cone-beam tomographic analysis of canalis sinuosus accessory intraosseous canals in the maxilla. GMS Ger. Med. Sci. 2017, 15, Doc20. [Google Scholar]
- Orhan, K.; Gorurgoz, C.; Akyol, M.; Ozarslanturk, S.; Avsever, H. An anatomical variant: Evaluation of accessory canals of the canalis sinuosus using cone beam computed tomography. Folia Morphol. 2018, 77, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Arx, T.; Lozanoff, S.; Sendi, P.; Bornstein, M.M. Assessment of bone channels other than the nasopalatine canal in the anterior maxilla using limited cone beam computed tomography. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2013, 35, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manhães Júnior, L.R.C.; Villaça-Carvalho, M.F.L.; Moraes, M.E.L.; Lopes, S.L.P.d.C.; Silva, M.B.F.; Junqueira, J.L.C. Location and classification of Canalis sinuosus for cone beam computed tomography: Avoiding misdiagnosis. Braz. Oral Res. 2016, 30, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCrea, S.J. Aberrations causing neurovascular damage in the anterior maxilla during dental implant placement. Case Rep. Dent. 2017, 2017, 5969643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, M.G.G.; de Faro Valverde, L.; Vidal, M.T.A.; Crusoé-Rebello, I.M. Branch of the canalis sinuosus: A rare anatomical variation—A case report. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2015, 37, 879–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olenczak, J.B.; Hui-Chou, H.G.; Aguila III, D.J.; Shaeffer, C.A.; Dellon, A.L.; Manson, P.N. Posttraumatic midface pain: Clinical significance of the anterior superior alveolar nerve and canalis sinuosus. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 75, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arruda, J.A.; Silva, P.; Silva, L.; Álvares, P.; Silva, L.; Zavanelli, R.; Rodrigues, C.; Gerbi, M.; Sobral, A.P.; Silveira, M. Dental implant in the canalis sinuosus: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep. Dent. 2017, 2017, 4810123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, R.; Quirynen, M.; Bornstein, M.M. Neurovascular disturbances after implant surgery. Periodontol. 2000 2014, 66, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenzuela-Fuenzalida, J.J.; Cariseo, C.; Gold, M.; Díaz, D.; Orellana, M.; Iwanaga, J. Anatomical variations of the mandibular canal and their clinical implications in dental practice: A literature review. Surg. Radiol. Anat. 2021, 43, 1259–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanibunda, K.; Matthews, J.N.S. The relationship between accessory foramina and tumour spread on the medial mandibular surface. J. Anat. 2000, 196, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sferlazza, L.; Zaccheo, F.; Campogrande, M.E.; Petroni, G.; Cicconetti, A. Common Anatomical Variations of Neurovascular Canals and Foramina Relevant to Oral Surgeons: A Review. Anatomia 2022, 1, 91-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia1010010
Sferlazza L, Zaccheo F, Campogrande ME, Petroni G, Cicconetti A. Common Anatomical Variations of Neurovascular Canals and Foramina Relevant to Oral Surgeons: A Review. Anatomia. 2022; 1(1):91-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia1010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleSferlazza, Laura, Fabrizio Zaccheo, Maria Elisabetta Campogrande, Giulia Petroni, and Andrea Cicconetti. 2022. "Common Anatomical Variations of Neurovascular Canals and Foramina Relevant to Oral Surgeons: A Review" Anatomia 1, no. 1: 91-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia1010010
APA StyleSferlazza, L., Zaccheo, F., Campogrande, M. E., Petroni, G., & Cicconetti, A. (2022). Common Anatomical Variations of Neurovascular Canals and Foramina Relevant to Oral Surgeons: A Review. Anatomia, 1(1), 91-106. https://doi.org/10.3390/anatomia1010010




