The Prevalence of Leptospira Serovars in African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys spp.) from the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania
Simple Summary
Abstract
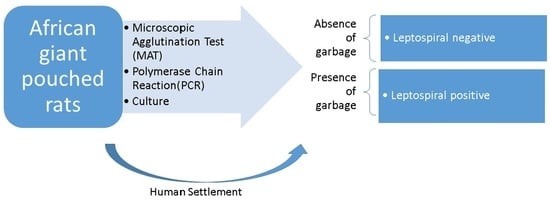
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
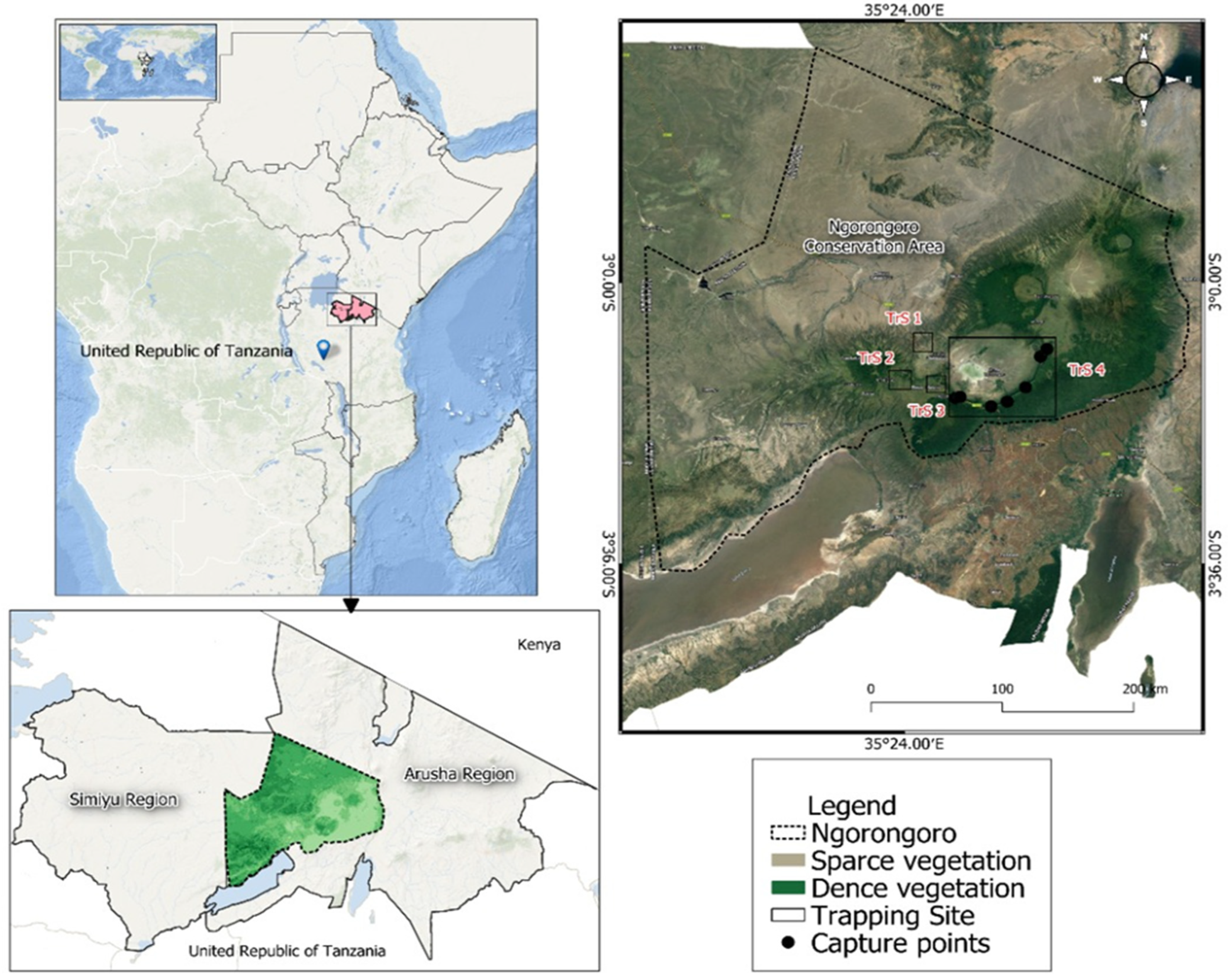
2.1. Study Sites
2.2. Rodent Trapping and Sampling
2.3. Detection of Leptospiral Antibodies by Microscopic Agglutination Test
2.4. Molecular Characterization of Leptospira Serovars
2.4.1. DNA Extraction
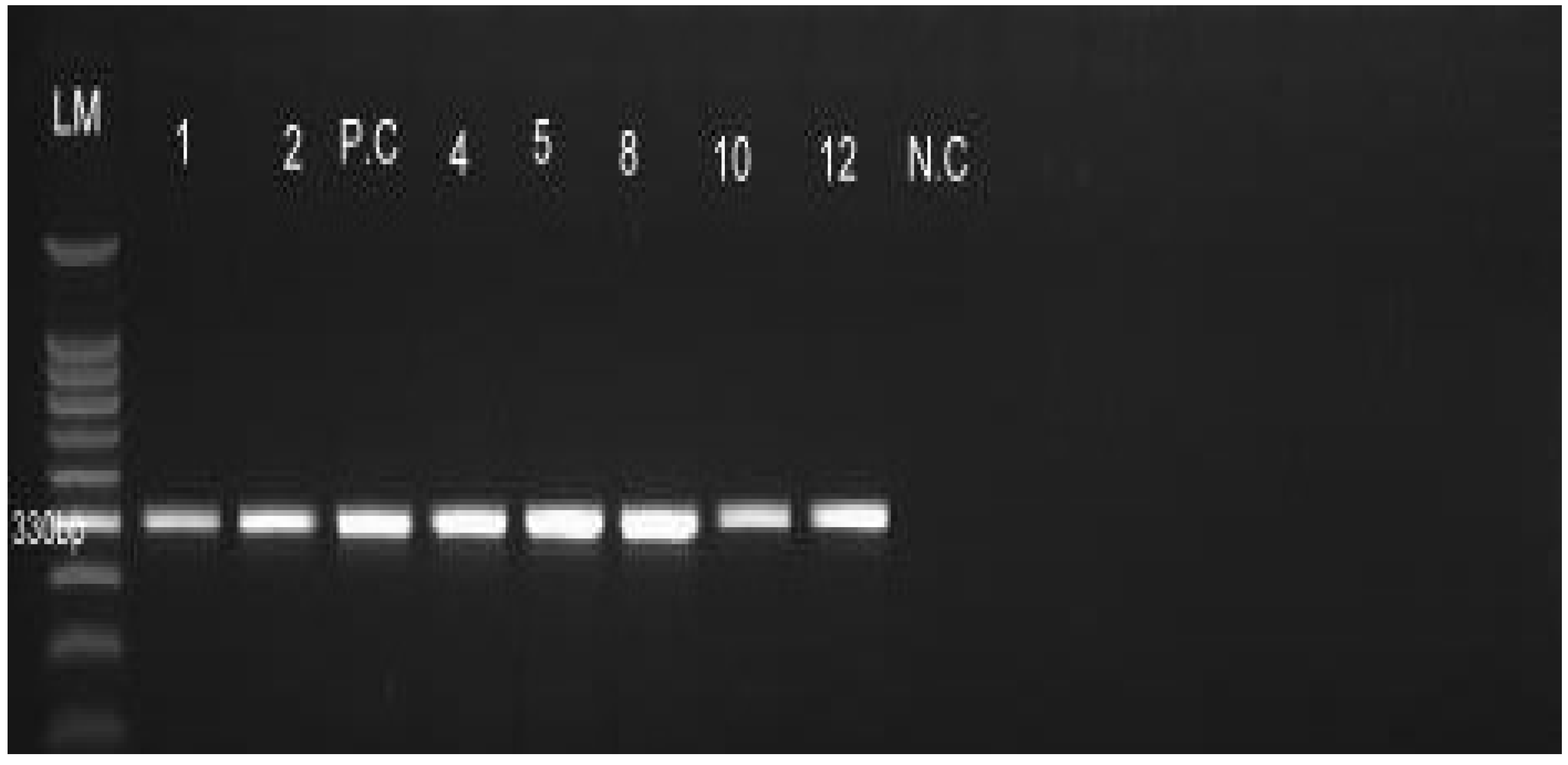
2.4.2. PCR Amplification, Gel Electrophoresis and Visualization
2.5. Culture
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Abundance of Cricetomys spp. in Selected Sites Ngorongoro Conservation Area
3.2. Detection of Leptospira Serovar
3.3. Distribution of Leptospira Serovars in Cricetomys spp.
3.4. Influence of Season on Seroprevalence of Leptospira spp. in Cricetomys Rats in the NCA
4. Discussion
Implications and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, F.; Hagan, J.E.; Calcagno, J.; Kane, M.; Torgerson, P.; Martinez-Silveira, M.S.; Stein, C.; Abela-Rider, B.; Ko, A.I. Global Morbidity and Mortality of Leptospirosis: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machangu, R.S.; Mgode, G.F.; Assenga, J.; Mhamphi, G.; Weetjens, B.; Cox, C.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Serological and Molecular Characterization of Leptospira Serovar Kenya from Captive African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys gambianus) from Morogoro Tanzania. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2004, 41, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mgode, G.F.; Mhamphi, G.; Katakweba, A.; Paemelaere, E.; Willekens, N.; Leirs, H.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Pcr Detection of Leptospira DNA in Rodents and Insecti-Vores from Tanzania. Belg. J. Zool. 2005, 135, 17–19. [Google Scholar]
- Mgode, G.F.; Mbugi, H.A.; Mhamphi, G.G.; Ndanga, D.; Nkwama, E.L. Seroprevalence of Leptospira Infection in Bats Roosting in Human Settlements in Morogoro Municipality in Tanzania. Tanzan. J. Health Res. 2014, 16, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, K.V.; Coburn, J. Leptospira as an Emerging Pathogen: A Review of Its Biology, Pathogenesis and Host Immune Responses. Future Microbiol. 2010, 5, 1413–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamond, C.; LeCount, K.; Browne, A.S.; Anderson, T.; Stuber, T.; Hicks, J.; Camp, P.; Fernandes, L.G.V.; Van Der Linden, H.; Goris, M.G.A.; et al. Concurrent Colonization of Rodent Kidneys with Multiple Species and Serogroups of Pathogenic Leptospira. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 89, e01204-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pui, C.F.; Bilung, L.M.; Apun, K.; Su’ut, L. Diversity of Leptospira Spp. in Rats and Environment from Urban Areas of Sarawak, Malaysia. J. Trop. Med. 2017, 2017, 3760674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krijger, I.M.; Ahmed, A.A.A.; Goris, M.G.A.; Groot Koerkamp, P.W.G.; Meerburg, B.G. Prevalence of Leptospira Infection in Rodents from Bangladesh. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedoya-Pérez, M.A.; Westman, M.E.; Loomes, M.; Chung, N.Y.N.; Knobel, B.; Ward, M.P. Pathogenic Leptospira Species Are Present in Urban Rats in Sydney, Australia. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortes-Gabriel, E.; Carreira, T.; Vieira, M.L. First Isolates of Leptospira Spp., from Rodents Captured in Angola. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 955–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Halliday, J.E.B.; Knobel, D.L.; Allan, K.J.; de C Bronsvoort, B.M.; Handel, I.; Agwanda, B.; Cutler, S.J.; Olack, B.; Ahmed, A.; Hartskeerl, R.A.; et al. Urban Leptospirosis in Africa: A Cross-Sectional Survey of Leptospira Infection in Rodents in the Kibera Urban Settlement, Nairobi, Kenya. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2013, 89, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machang’u, R.; Mgode, G.F.; Asenga, J.; Mhamphi, G.; Hartskeerl, R.; Goris, M.; Verhagen, R. Characterisation of Leptospira Isolates from Captive Giant African Pouched Rats, Cricetomys gambianus. Rats Mice People Rodent Biol. Manag. 2003, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assenga, J.A.; Matemba, L.E.; Muller, S.K.; Mhamphi, G.G.; Kazwala, R.R. Predominant Leptospiral Serogroups Circulating among Humans, Livestock and Wildlife in Katavi-Rukwa Ecosystem. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mgode, G.F.; Machang’u, R.S.; Mhamphi, G.G.; Katakweba, A.; Mulungu, L.S.; Durnez, L.; Belmain, S.R. Leptospira Serovars for Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in Humans and Animals in Africa: Common Leptospira Isolates and Reservoir Hosts. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwachui, M.A.; Crump, L.; Hartskeerl, R.; Zinsstag, J.; Hattendorf, J. Environmental and Behavioural Determinants of Leptospirosis Transmission: A Systematic Review. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscornet, L.; Révillion, C.; Jégo, S.; Lagadec, E.; Gomard, Y.; Le Minter, G.; Rocamora, G.; Guernier-Cambert, V.; Mélade, J.; Dellagi, K.; et al. Predicting the Presence of Leptospires in Rodents from Environmental Indicators Opens Up Opportunities for Environmental Monitoring of Human Leptospirosis. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgode, G.F.; Mhamphi, G.G.; Massawe, A.W.; Machang’u, R.S. Leptospira Seropositivity in Humans, Livestock and Wild Animals in a Semi-Arid Area of Tanzania. Pathogens 2021, 10, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, B.; Adler, B. Leptospira and Leptospirosis; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Budihal, S.; Perwez, K. Leptospirosis Diagnosis: Competancy of Various Laboratory Tests. J. Clin. Diagn Res. 2014, 8, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, I.B.; Souza, G.O.D.; Castro, J.F.D.P.; Cavalini, M.B.; De Souza Filho, A.F.; Heinemann, M.B. Usefulness of the Ranking Technique in the Microscopic Agglutination Test (MAT) to Predict the Most Likely Infecting Serogroup of Leptospira. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 654034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eugene, E.J.; Handunnetti, S.M.; Wickramasinghe, S.A.; Kalugalage, T.L.; Rodrigo, C.; Wickremesinghe, H.; Dikmadugoda, N.; Somaratne, P.; De Silva, H.J.; Rajapakse, S. Evaluation of Two Immunodiagnostic Tests for Early Rapid Diagnosis of Leptospirosis in Sri Lanka: A Preliminary Study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2015, 15, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, B.; Thille, K.; Rametta, N.; Sharma, R. Detection of Leptospira Spp. Using Polymerase Chain Reaction Technique from Kidney of Rattus Norvegicus from Grenada, West Indies. Int. J. One Health 2019, 5, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engeman, R.; Woolard, J.W.; Perry, N.D.; Witmer, G.; Hardin, S.; Brashears, L.; Smith, H.; Muiznieks, B.; Constantin, B. Rapid Assessment for a New Invasive Species Threat: The Case of the Gambian Giant Pouched Rat in Florida. Wildl. Res. 2006, 33, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durnez, L.; Eddyani, M.; Mgode, G.F.; Katakweba, A.; Katholi, C.R.; Machang’u, R.R.; Kazwala, R.R.; Portaels, F.; Leirs, H. First Detection of Mycobacteria in African Rodents and Insectivores, Using Stratified Pool Screening. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vincent, A.T.; Schiettekatte, O.; Goarant, C.; Neela, V.K.; Bernet, E.; Thibeaux, R.; Ismail, N.; Mohd Khalid, M.K.N.; Amran, F.; Masuzawa, T.; et al. Revisiting the Taxonomy and Evolution of Pathogenicity of the Genus Leptospira through the Prism of Genomics. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benacer, D.; Woh, P.Y.; Zain, S.N.M.; Amran, F.; Thong, K.L. Pathogenic and Saprophytic Leptospira Species in Water and Soils from Selected Urban Sites in Peninsular Malaysia. Microbes Environ. 2013, 28, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricardo, T.; Previtali, M.A.; Signorini, M. Meta-Analysis of Risk Factors for Canine Leptospirosis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 181, 105037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, K.J.; Halliday, J.E.; Moseley, M.; Carter, R.W.; Ahmed, A.; Goris, M.G.; Maze, M.J. Assessment of Animal Hosts of Pathogenic Leptospira in Northern Tanzania. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swai, E.S.; Schoonman, L. A Survey of Zoonotic Diseases in Trade Cattle Slaughtered at Tanga City Abattoir: A Cause of Public Health Concern. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricardo, T.; Jacob, P.; Chiani, Y.; Schmeling, M.F.; Cornejo, P.; Ojeda, A.A.; Teta, P.V.; Vanasco, N.B.; Previtali, M.A. Seroprevalence of Leptospiral Antibodies in Rodents from Riverside Communities of Santa Fe, Argentina. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, L.A. Ngorongoro Conservation Area: Spring of Life. Master’s Thesis, University of Pennsylavia, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 9 January 2007. [Google Scholar]
- MNRT (Ministry of Natural Resources and Tourism). The Wildlife Policy of Tanzania; Dar es Salaam. 1998. Available online: https://www.maliasili.go.tz/assets/pdfs/THE_WILDLIFE_POLICY_OF_TANZANIA_2007_(RE).pdf (accessed on 8 May 2023).
- Masao, C.A.; Revocatus, M.; Hussein, S. Will Ngorongoro Conservation Area Remain a World Heritage Site amidst Increasing Human Footprint? Int. J. Biodivers. Conserv. 2015, 7, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawuo, Z.A.; Mbasa, B.; Mnyawi, S. Persistence of Land Conflicts between Maasai Community and Ngorongoro Conservation Area Authority (NCAA) in Ngorongoro Conservation Area (NCA). Int. J. Innov. Sci. Res. 2014, 5, 154–161. [Google Scholar]
- Żaba, J.; Gaidzik, K. The Ngorongoro Crater as the Biggest Geotouristic Attraction of the Gregory Rift (Northern Tanzania, Africa)—Geotouristic Valorization, Touristic Development and Hazard. Geotourism/Geoturystyka 2011, 24–25, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Udechukwu, C.C.; Kudi, C.A.; Abdu, P.A.; Abiayi, E.A.; Orakpoghenor, O. Prevalence of Leptospira Interrogans in Wild Rats (Rattus norvegicus and Cricetomys gambianus) in Zaria, Nigeria. Heliyon 2021, 7, e05950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.M.; Soka, G.E.; Mulungu, L.S.; Makonda, F.B.S. Spatial-Temporal Variations in Dietary Consumption of Two Dominant Rodent Species (Rhabdomys dilectus and Lophuromys acquilus) on Mount Kilimanjaro, Tanzania. Diversity 2022, 14, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadok, G.B. Aspects of the Behaviour of African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys Sp. Nov) Which Impacts Seed Dispersal of Large-Seeded Tree Species in a West African Montane Forest Landscape. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kalemba, L.N.; Morgan, C.N.; Nakazawa, Y.J.; Mauldin, M.R.; Malekani, J.M.; Doty, J.B. Activity Patterns and Burrowing Ecology of the Giant Pouched Rat (Cricetomys emini) in Tshuapa Province, D.R. Congo. Mammalia 2022, 86, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, M.G.A.; Hartskeerl, R.A. Leptospirosis Serodiagnosis by the Microscopic Agglutination Test. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2014, 32, Unit 12E.5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motto, S.K.; Shirima, G.M.; De Clare Bronsvoort, B.M.; Cook, E.A.J. Epidemiology of Leptospirosis in Tanzania: A Review of the Current Status, Serogroup Diversity and Reservoirs. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guedes, I.B.; de Souza, G.O.; de Paula Castro, J.F.; Cavalini, M.B.; de Souza Filho, A.F.; Maia, A.L.P.; Dos Reis, E.A.; Cortez, A.; Heinemann, M.B. Leptospira Interrogans Serogroup Pomona Strains Isolated from River Buffaloes. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgia, R.; Riquelme, N.; Baranton, G.; Cinco, M. Oligonucleotides Specific for Pathogenic and Saprophytic Leptospira Occurring in Water. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2006, 148, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoddard, R.A.; Gee, J.E.; Wilkins, P.P.; McCaustland, K.; Hoffmaster, A.R. Detection of Pathogenic Leptospira Spp. through TaqMan Polymerase Chain Reaction Targeting the LipL32 Gene. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 64, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faine, S. Guidelines for the Control of Leptospirosis; WHO Offset Publication; Obtainable from WHO Publication Centre USA; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland; Albany, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Freitas, J.C.D.; Silva, F.G.D.; Oliveira, R.C.D.; Delbem, Á.C.B.; Müller, E.E.; Alves, L.A.; Teles, P.S. Isolation of Leptospira Spp from Dogs, Bovine and Swine Naturally Infected. Ciênc. Rural 2004, 34, 853–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Elphick, C.S. A Protocol for Data Exploration to Avoid Common Statistical Problems. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2010, 1, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallant, J. SPSS Survival Manual: A Step by Step Guide to Data Analysis Using IBM SPSS; McGraw-Hill Education: Berkshire, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Niboye, E.P. Vegetation Cover Changes in Ngorongoro Conservation Area from 1975 to 2000: The Importance of Remote Sensing Images. Open Geogr. J. 2010, 3, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanby, J.; Bygott, D. Ngorongoro Conservation Area: Guide Book; Regal Press Ltd.: Nairobi, Kenya, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Riediger, I.N.; Stoddard, R.A.; Ribeiro, G.S.; Nakatani, S.M.; Moreira, S.D.R.; Skraba, I.; Biondo, A.W.; Reis, M.G.; Hoffmaster, A.R.; Vinetz, J.M.; et al. Rapid, Actionable Diagnosis of Urban Epidemic Leptospirosis Using a Pathogenic Leptospira lipL32-Based Real-Time PCR Assay. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.R.; Sulzer, C.R.; Pursell, A.R. Improved Microtechnique for the Leptospiral Microscopic Agglutination Test. Appl. Microbiol. 1973, 25, 976–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierque, E.; Thibeaux, R.; Girault, D.; Soupé-Gilbert, M.-E.; Goarant, C. A Systematic Review of Leptospira in Water and Soil Environments. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0227055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.P.; Ellis, W.A.; Macdonald, D.W. Prevalence of Leptospira Spp. in Wild Brown Rats (Rattus Norvegicus) on UK Farms. Epidemiol. Infect. 1995, 114, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Mendis, N.; Trigui, H.; Oliver, J.D.; Faucher, S.P. The Importance of the Viable but Non-Culturable State in Human Bacterial Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hathaway, S.C.; Blackmore, D.K.; Marshall, R.B. Leptospirosis in Free-Living Species in New Zealand. J. Wildl. Dis. 1981, 17, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgode, G.F.; Machang’u, R.S.; Goris, M.G.; Engelbert, M.; Sondij, S.; Hartskeerl, R.A. New Leptospira Serovar Sokoine of Serogroup Icterohaemorrhagiae from Cattle in Tanzania. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 593–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krystosik, A.; Njoroge, G.; Odhiambo, L.; Forsyth, J.E.; Mutuku, F.; LaBeaud, A.D. Solid Wastes Provide Breeding Sites, Burrows, and Food for Biological Disease Vectors, and Urban Zoonotic Reservoirs: A Call to Action for Solutions-Based Research. Front. Public Health 2020, 7, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharti, A.R.; Nally, J.E.; Ricaldi, J.N.; Matthias, M.A.; Diaz, M.M.; Lovett, M.A.; Levett, P.N.; Gilman, R.H.; Willig, M.R.; Gotuzzo, E.; et al. Peru-United States Leptospirosis Consortium. Leptospirosis: A Zoonotic Disease of Global Importance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 757–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, F.C.; Quinn, P.J.; Ellis, W.A.; O’Farrell, K. Association between Cessation of Leptospiruria in Cattle and Urinary Antibody Levels. Res. Vet. Sci. 1993, 55, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Site | Abundance | Male | Female |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kongoni | 14 | 8 | 6 |
| Ngorongoro Wildlife lodge | 6 | 3 | 3 |
| Pongo | 11 | 7 | 4 |
| Viewpoint | 5 | 0 | 5 |
| Lerai | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| Lemala | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| Forest | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 50 | 28 | 22 |
| Titer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Leptospira serovar | 1:20 | 1:40 | 1:160 |
| Sokoine | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Lora | 0 | 1 | 1 |
| Hebdomadis | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Canicola | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Pomona | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SITE | Total Captured | Positive | % Positive | Presence/Absence of Dump Site | Presence/Absence of Water Body |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCA Wildlife lodge | 6 | 3 | 6% | Present | Absent |
| Viewpoint | 5 | 1 | 2% | Present | Absent |
| Pongo | 11 | 3 | 6% | Present | Absent |
| Kongoni | 14 | 3 | 6% | Present | Absent |
| Lerai | 7 | 2 | 4% | Present | Present |
| Lemala | 6 | 0 | 0% | Absent | Present |
| Forest | 1 | 0 | 0% | Absent | Present |
| TOTAL | 50 | 12 | 24% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kahangwa, P.N.; Kitegile, A.S.; Machang’u, R.S.; Mhamphi, G.G.; Katakweba, A.S. The Prevalence of Leptospira Serovars in African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys spp.) from the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania. Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 4, 37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010005
Kahangwa PN, Kitegile AS, Machang’u RS, Mhamphi GG, Katakweba AS. The Prevalence of Leptospira Serovars in African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys spp.) from the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania. Zoonotic Diseases. 2024; 4(1):37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleKahangwa, Prisca N., Amani S. Kitegile, Robert S. Machang’u, Ginethon G. Mhamphi, and Abdul S. Katakweba. 2024. "The Prevalence of Leptospira Serovars in African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys spp.) from the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania" Zoonotic Diseases 4, no. 1: 37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010005
APA StyleKahangwa, P. N., Kitegile, A. S., Machang’u, R. S., Mhamphi, G. G., & Katakweba, A. S. (2024). The Prevalence of Leptospira Serovars in African Giant Pouched Rats (Cricetomys spp.) from the Ngorongoro Conservation Area, Tanzania. Zoonotic Diseases, 4(1), 37-48. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010005