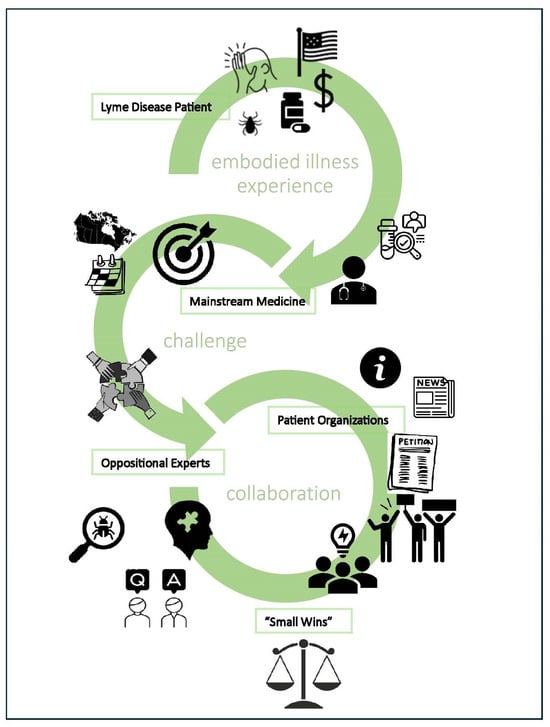
“Small Wins” for those with Lyme Disease in Canada: Patients in an Embodied Health Movement
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Approach
2.1. Embodied Health Movements Framework
2.2. A Small Wins Approach
3. Results
3.1. Polly Murray—The First Lyme Disease Patient Advocate
3.2. Patients Challenged by LD Diagnosis and Treatment Protocols
3.3. Chronic Lyme Disease
3.3.1. Chronic Lyme Disease versus Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome
3.3.2. The Burden of Untreated Chronic Lyme Disease
3.4. Small Wins for Patient Organizations—Reassurances Then Status Quo
4. Discussion and Conclusions
4.1. Ongoing Challenges: Discrediting Patient Organizations
4.2. Ongoing Challenges: The Funding Dilemma
4.3. “Small Wins” and Patients in an Embodied Health Movement
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vrbova, L.; Middleton, D. Descriptive Epidemiology of Lyme Disease in Ontario: 1999–2004. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2006, 32, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. How Many People Get Lyme Disease? Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/lyme/stats/humancases.html (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Levesque, M.; Klohn, M. A Multiple Streams Approach to Understanding the Issues and Challenges of Lyme Disease Management in Canada’s Maritime Provinces. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, V.; Hawkins, R. Under-detection of Lyme Disease in Canada. Healthcare 2018, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health Canada. Lyme Disease: Surveillance. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/lyme-disease/surveillance-lyme-disease.html (accessed on 13 January 2024).
- Semproni, M.; Rusk, R.; Wuerz, T. Fatal Lyme Carditis Presenting as Fluctuating High-grade Atrioventricular Block. CMAJ 2020, 192, E574–E577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, A.; Herman, R.; Rebman, A.; Moon, K.; Aucott, J.; Heaney, C.; Schwartz, B. Obstacles to Diagnosis and Treatment of Lyme Disease in the USA: A Qualitative Study. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e021367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feder, H.M.; Johnson, B.J.; O’Connell, S.; Shapiro, E.D.; Steere, A.; Wormser, G. A Critical Appraisal of “Chronic Lyme Disease”. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 1422–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, E.; Wormser, G. Lyme Disease in 2018 What is New (and What is Not). JAMA 2018, 320, 635–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wormser, G.; Dattwyler, R.; Shapiro, E.; Halperin, J.; Steere, A.; Klempner, M.; Krause, P.; Bakken, J.; Strle, F.; Stanek, G.; et al. The Clinical Assessment, Treatment, and Prevention of Lyme Disease, Human Granulocytic Anaplasmosis, and Babesiosis: Clinical Practice Guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 43, 1089–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.; Loughlin, M. Models in the Balance: Evidence-based Medicine Versus Evidence-informed Individualized Care. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2011, 17, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.; Zavestoski, S.; McCormick, S.; Mayer, B.; Morello-Frosch, R.; Gasior Altman, R. Embodied Health Movements: New Approaches to Social Movements in Health. Sociol. Health Illn. 2004, 26, 50–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jason, L. Small Wins Matter in Advocacy Movements: Giving Voice to Patients. Am. J. Community Psychol. 2012, 49, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripoche, M.; Irace-Cima, A.; Adam-Poupart, A.; Baron, G.; Bouchard, C.; Carignan, A.; Milord, F.; Ouhoummane, N.; Pilon, P.A.; Thivierge, K.; et al. Current and future burden from Lyme disease in Québec as a result of climate change. Can. Commun. Dis. Rep. 2023, 49, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulc, K. Canadians Are Travelling to Mexico for Lyme Disease Treatments. That Worries Health Experts. 9 October 2023. Available online: https://www.cbc.ca/news/health/lyme-disease-mexico-treatment-1.6982720 (accessed on 12 December 2023).
- Green, K. Calgary Family Shares Dire Tale to Raise Awareness of Lyme Disease. 24 April 2023. Available online: https://calgary.ctvnews.ca/calgary-family-shares-dire-tale-to-raise-awareness-of-lyme-disease-1.6369795 (accessed on 6 July 2023).
- Hinds, K.; Sutcliffe, K. Heterodox and Orthodox Discourses in the Case of Lyme Disease: A Synthesis of Arguments. Qual. Health Res. 2019, 29, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, T. ‘Mostly Accurate with Occasional Piles of Bullshit’: Patient ‘Boundary-work’ in an Online Scientific Controversy. Health Sociol. Rev. 2019, 28, 261–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumit, J. Illnesses You Have to Fight to Get: Facts as Forces in Uncertain, Emergent Illnesses. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 577–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebman, A.; Aucott, J.; Weinstein, E.; Bechtold, K.; Smith, K.; Leonard, L. Living in Limbo: Contested Narratives of Patients with Chronic Symptoms Following Lyme Disease. Qual. Health Res. 2017, 27, 534–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleton, S. ‘I Just Want Permission to be Ill’: Towards a Sociology of Medically Unexplained Symptoms. Soc. Sci. Med. 2006, 62, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, D. ‘Keep Complaining til Someone Listens’: Exchanges of Tacit Healthcare Knowledge in Online Illness Communities. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 166, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, C.R.; Lloyd, V.; Gould, O. Motivations and Experiences of Canadians Seeking Treatment for Lyme Disease Outside of the Conventional Canadian Health-care System. J. Patient Exp. 2018, 5, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stricker, R.; Johnson, L. Chronic Lyme Disease and the “Axis of Evil”. Future Microbiol. 2008, 3, 621–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrie, H. (Ed.) Ending Denial: The Lyme Disease Epidemic: A Canadian Public Health Disaster; Kos Publishing: Caledon, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Donta, S.T. Issues in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lyme Disease. Open Neurol. J. 2012, 6, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fumano, D. Chronology of Lyme Disease in B.C. and the Complex Chronic Disease Program. The Province. 23 April 2015. Available online: https://www.pressreader.com/canada/the-province/20150423/281599534041366 (accessed on 15 July 2023).
- Kingston, A. How the New Impatient Patient is Disrupting Medicine. MacLean’s. 21 October 2017. Available online: https://www.macleans.ca/society/health/how-the-new-impatient-patient-is-disrupting-medicine/ (accessed on 12 June 2023).
- Murray, P. The Widening Circle: A Lyme Disease Pioneer Tells Her Story; St. Martin’s Press: New York, NY, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, E.D., Jr. Lyme Disease-Success for Academia and the Community. N. Eng. J. Med. 1983, 308, 773–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Vitulano, L.; Lee, R.; Weiss, T.; Colson, E. Experiences of Patients Identifying with Chronic Lyme Disease in the Healthcare System: A Qualitative Study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2014, 15, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dankyi, J. Stress, Despair, and Quality of Life: The Lived Experience of Families with Children below 26 Years of Age Diagnosed with Lyme Disease. Ph.D. Dissertation, Capella University, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Guidance for Primary Care and Emergency Medicine Providers in the Management of Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia. IDEG. Available online: https://novascotia.ca/dhw/CDPC/documents/statement_for_managing_LD.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Henry, B.; Crabtree, A.; Roth, D.; Blackman, D.; Morshed, M. Lyme Disease: Knowledge, Beliefs, and Practices of Physicians in a Low-endemic Area. Can. Fam. Physician 2012, 58, e289–e295. Available online: https://www.cfp.ca/content/cfp/58/5/e289.full.pdf (accessed on 26 May 2020). [PubMed]
- Smith, R.; Schoen, R.; Rahn, D.; Sikand, V.; Nowakowski, J.; Parenti, D.; Holman, M.; Persing, D.; Steere, A. Clinical Characteristics and Treatment Outcome of Early Lyme Disease in Patients with Microbiologically Confirmed Erythema Migrans. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 136, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stonehouse, A.; Studdiford, J.; Henry, C.A. An Update on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Early Lyme Disease: “Focusing on the Bull’s Eye, You May Miss the Mark”. J. Emerg. Med. 2010, 39, e147–e151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, N.; Bouchard, C.; Badcock, J.; Drebot, M.; Elias, S.; Hatchette, T.; Koffi, J.; Leighton, P.; Lindsay, L.R.; Lubelczyk, C.; et al. What is the Real Number of Lyme Disease Cases in Canada? BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, D.J. Consequences of Treatment Delay in Lyme Disease. J. Eval. Clin. Pract. 2007, 13, 470–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Health Canada. Lyme Disease Test Kits and Limitations. Can. Advers. React. Newsl. 2012, 22, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Teotonio, I. Lyme Disease is Steeped in Controversy. Now Some Doctors Are Too Afraid to Treat Patients. The Hamilton Spectator. 14 December 2018. Available online: https://www.thespec.com/life/health-wellness/2018/12/14/lyme-disease-is-steeped-in-controversy-now-some-doctors-are-too-afraid-to-treat-patients.html (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Johnson, L.; Maloney, E. The Ad Hoc Patient and Physician Coalition Comments of the IDSA Proposed Lyme Guidelines 8 August 2019. 2019. Available online: https://www.lymedisease.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/08/Ad-Hoc-Patient-Physician-Coalition-Comments.pdf (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- ILADS. Peer-Reviewed Evidence of Persistence of Lyme Disease Spirochete Borrelia Burgdorferi and Tick-Borne Diseases. 2017. Available online: https://www.ilads.org/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/CLDList-ILADS.pdf (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Ferguson, J. Cure Unwanted Exploring the Chronic Lyme Disease Controversy and Why Conflicts of Interest in Practice Guidelines May be Guiding us Down the Wrong Path. Am. J. Law Med. 2012, 38, 196–224. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, J. Lyme Disease Guidelines. CMAJ 2016, 188, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine. Clinical Practice Guidelines We Can Trust; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011; Available online: http://books.nap.edu/openbook.php?record_id=13058 (accessed on 16 August 2023).
- Government of Canada. For Health Professionals: Lyme Disease. 2020. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/diseases/lyme-disease/health-professionals-lyme-disease.html#a3 (accessed on 17 September 2023).
- AMMI. AMMI Canada Position Statement on the Diagnosis and Treatment of People with Persistent Symptoms That Have Been Attributed to Lyme Disease. 2020. Available online: https://www.ammi.ca/?ID=137 (accessed on 15 June 2023).
- Glauser, W. Combatting Lyme Disease Myths and the “Chronic Lyme Industry”. CMAJ 2019, 191, E1111–E1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrouillet, C.; Milord, F.; Lambert, L.; Vibien, A.; Ravel, A. Lyme Disease: Knowledge and Practices of Family Practitioners in Southern Quebec. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 26, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, P.J. Is it Possible to Make a Correct Diagnosis of Lyme Disease on Symptoms Alone? Review of Key Issues and Public Health Implications. Am. J. Med. 2019, 132, 1148–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webber, B.; Burganowski, R.; Colton, L.; Escobar, J.; Pathak, S.; Gambino-Shirley, K. Lyme Disease Overdiagnosis in a Large Healthcare System: A Population-based, Retrospective Study. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 1233–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayerman, P. Crowdsourcing Used to Fund Lyme Disease FOI Request. Vancouver Sun. 9 September 2014. Available online: http://www.vancouversun.com/health/crowdsourcing+used+fund+lyme+disease+request/10186216/story.html (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Csallner, G.; Hofmann, H.; Hausteiner-Wiehle, C. Patients with “Organically Unexplained Symptoms” Presenting to a Borreliosis Clinic: Clinical and Psychobehavioral Characteristics and Quality of Life. Psychosomatics 2013, 54, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fallon, B.; Nields, J. Lyme Disease: A Neuropsychiatric Illness. Am. J. Psychiatry 1994, 151, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar]
- Sherr, V.T. Munchausen’s Syndrome by Proxy and Lyme Disease: Medical Misogyny or Diagnostic Mystery? Med. Hypotheses 2005, 65, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettleton, S.; Watt, I.; O’Malley, L.; Duffey, P. Understanding the Narratives of People Who Live with Medically Unexplained Illness. Patient Educ. Couns. 2005, 56, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, K. Electronic Support Groups, Patient-consumers, and Medicalization: The Case of Contested Illness. J. Health Soc. Behav. 2008, 49, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Lyme Petition. 2020. Available online: https://www.lymehope.ca/lyme-petition.html (accessed on 21 June 2023).
- Aucott, J.; Rebman, A.; Crowder, L.; Kortte, K. Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome Symptomatology and the Impact on Life Functioning: Is There Something Here? Qual. Life Res. 2013, 22, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shor, S.; Green, C.; Szantyr, B.; Phillips, S.; Liegner, K.; Burrascano, J., Jr.; Bransfield, R.; Maloney, E.L. Chronic Lyme Disease: An Evidence-Based Definition by the ILADS Working Group. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Lyme Disease in Canada: A Federal Framework. Government of Canada. 2017. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/diseases-conditions/lyme-disease-canada-federal-framework.html (accessed on 13 September 2023).
- Adrion, E.; Aucott, J.; Lemke, K.; Weiner, J. Health Care Costs, Utilization and Patterns of Care Following Lyme Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noorani, T.; Karlsson, M.; Borkman, T. Deep Experiential Knowledge: Reflections from Mutual Aid Groups for Evidence-based Practice. Evid. Policy 2019, 15, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, D.; Hewitt, H. A Qualitative Approach to Understanding Patients’ Diagnosis of Lyme Disease. Public Health Nurs. 2006, 23, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.; Wilcox, S.; Mankoff, J.; Stricker, R. Severity of Chronic Lyme Disease Compared to Other Chronic Conditions: A Quality of Life Survey. PeerJ 2014, 2, e322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Wijngaard, C.; Hofhuis, A.; Wong, A.; Harms, M.; de Wit, G.A.; Lugnér, A.; Suijkerbuijk, A.; Mangen, M.-J.; van Pelt, W. The cost of Lyme Borreliosis. Eur. J. Public Health 2017, 27, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henningsson, A.; Malmvall, B.; Ernerudh, J.; Matussek, A.; Forsberg, P. Neuroborreliosis—An Epidemiological, Clinical and Healthcare Cost Study from an Endemic Area in the South-east of Sweden. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2010, 16, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidsson, M. The Financial Implications of a Well-hidden and Ignored Chronic Lyme Disease Pandemic. Healthcare 2018, 6, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luché-Thayer, J.; Ahern, H.; Bransfield, R.; Burrascano, J.; Fierlafijn, A.; Denham, T.; Kraaijeveld, H.; Kravis, J.; McManus, M.; Meseko, C.; et al. The Situation of Human Rights Defenders of Lyme and Relapsing Fever Borreliosis Patients; CreateSpace Independent Publishing Platform: Scotts Valley, CA, USA, 14 July 2018; Available online: http://www.canlyme.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/07/Defendersreport.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2023).
- CanLyme. About. Available online: https://canlyme.com/about/ (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Canadian Lyme Consortium. Welcome. Available online: http://www.clymec.ca/ (accessed on 4 December 2022).
- Schmidt, B.T. Chronic Lyme Disease in British Columbia. BC: Provincial Health Services Authority. Available online: https://canlyme.com/uploads/Full_Schmidt.pdf (accessed on 24 November 2022).
- Fumano, D. ‘The Health-Care System Has Turned Its Back on Me’: Lyme Disease Sufferers Say Vancouver Clinic Has Been a Failure. The Province. 23 April 2015. Available online: https://www.pressreader.com/canada/the-province/20150423/281479274957078 (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- Hume, M. Crowdfunding Meets Goal to Procure Lyme Disease Program Files. The Globe and Mail. 9 September 2014. Available online: https://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/british-columbia/crowdfunding-for-files-on-treatment-of-lyme-disease-meets-goal/article20487550/ (accessed on 17 August 2023).
- HESA. House of Commons Canada Standing Committee on Health, Meeting No. 30, 2nd Session, 41st Parliament, 29 May 2014. Parliament of Canada. Available online: https://www.ourcommons.ca/DocumentViewer/en/41-2/HESA/meeting-30/evidence (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Green Party of Canada. Senate Unanimously Passes Elizabeth May’s Federal Framework on Lyme Disease Act. 2014. Available online: https://www.greenparty.ca/en/media-release/2014-12-12/senate-unanimously-passes-elizabeth-may%E2%80%99s-federal-framework-lyme-disease (accessed on 14 May 2023).
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Conference to Develop a Federal Framework on Lyme Disease—15–17 May 2016—Conference Summary Report. 2016. Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/diseases-conditions/conference-develop-federal-framework-lyme-disease-may-15-17-2016-conference-summary-report.html (accessed on 17 February 2023).
- HESA. Federal Framework on Lyme Disease. House of Commons Standing Committee on Health, 1st Session, 42nd Parliament, 8 June 2017. Parliament of Canada. Available online: https://www.ourcommons.ca/Committees/en/HESA/StudyActivity?studyActivityId=9527827 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- LymeHope. Meeting with Federal Health Minister Jane Philpott: Delivery of Lyme Letters & Petition. 2017. Available online: https://www.lymehope.ca/advocacy-updates/meeting-with-federal-health-minister-jane-philpott-delivery-of-lyme-letters-petition (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Kingston, A. The Rise of the Impatient Patient. Maclean’s. 1 December 2017. Available online: https://archive.macleans.ca/article/2017/12/1/the-rise-of-the-impatient-patient (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Walter, K. Battle with Lyme Disease an Education for St. Catharines Grade 3 Teacher. The Standard. 13 November 2019. Available online: https://www.stcatharinesstandard.ca/news-story/9701837-battle-with-lyme-disease-an-education-for-st-catharines-grade-3-teacher/ (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Bransfield, R.C. Suicide and Lyme and Associated Diseases. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, 13, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Journault, A.-A.; Richard, L.; Aenishaenslin, C. Lyme Disease Prevention: A Content Analysis of Canadian Patient Group and Government Websites. Zoonoses Public Health 2020, 67, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, S. The Politics of Health Mobilization in the United States: The Promise and Pitfalls of “Disease Constituencies”. Soc. Sci. Med. 2016, 165, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lantos, P.; Shapiro, E.; Auwaerter, P.; Baker, P.; Halperin, J.; McSweegan, E.; Wormser, G. Unorthodox Alternative Therapies Marketed to Treat Lyme Disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1776–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rideout, D. Queen’s Receives $4M for New Lyme Disease Research Network. Queen’s Gazette. 15 October 2018. Available online: https://www.queensu.ca/gazette/stories/queen-s-receives-4m-new-lyme-disease-research-network (accessed on 7 November 2022).
- CanLyme. Latest Research Shows Canada’s Decision to Fund Only One Large National Lyme Research Conglomerate Goes against Creation of New Ideas. 2019. Available online: https://canlyme.com/2019/02/16/latest-research-shows-canadas-decision-to-fund-only-one-large-national-lyme-research-conglomerate-goes-against-creation-of-new-ideas/ (accessed on 19 January 2023).
- AMMI. AMMI Position Statement on the Federal Framework on Lyme Disease. 3 April 2017. Available online: https://ammi.ca/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/PositionStatement-PHACFederalFrameworkonLyme-En.pdf (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Bucchi, M.; Neresini, F. Science and Public Participation. In The Handbook of Science and Technology Studies; Hackett, E.J., Amsterdamska, O., Lynch, M., Wajcman, J., Eds.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2008; pp. 499–539. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, K. Realizing the Vision of Patient-relevant Clinical Research. CMAJ 2016, 188, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd, V.; Wills, M.; Sperling, J.; Wilson, J.; Kravis, J.; Faber, S. An Update from the Canadian Lyme Consortium—5 March 2018. Available online: http://www.canlyme.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/CLC_moving%20forward.pdf (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Kingston, A. The Truth about Lyme Disease-Lyme Disease Can Masquerade as MS, ALS, Even Dementia, and Its Numbers Are Growing. So Why is Canada Lagging Behind in Treating It? MacLean’s. 24 March 2014. Available online: https://www.macleans.ca/society/health/the-truth-about-lyme-disease/ (accessed on 5 January 2023).
- Ubelacker, S. University of Guelph Setting up Lab to Research Lyme Disease with $1.4M Donation; The Canadian Press: Toronto, ON, Canada, 14 June 2017; Available online: https://www.ctvnews.ca/health/university-of-guelph-setting-up-lab-to-research-lyme-disease-with-1-4m-donation-1.3458844 (accessed on 5 June 2020).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cox, M.; Levesque, M. “Small Wins” for those with Lyme Disease in Canada: Patients in an Embodied Health Movement. Zoonotic Dis. 2024, 4, 22-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010004
Cox M, Levesque M. “Small Wins” for those with Lyme Disease in Canada: Patients in an Embodied Health Movement. Zoonotic Diseases. 2024; 4(1):22-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010004
Chicago/Turabian StyleCox, Marilyn, and Mario Levesque. 2024. "“Small Wins” for those with Lyme Disease in Canada: Patients in an Embodied Health Movement" Zoonotic Diseases 4, no. 1: 22-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010004
APA StyleCox, M., & Levesque, M. (2024). “Small Wins” for those with Lyme Disease in Canada: Patients in an Embodied Health Movement. Zoonotic Diseases, 4(1), 22-36. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis4010004