Extrahepatic Replication Sites of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Extrahepatic Replication of HEV
2.1. Insights of Extrahepatic Replication
2.2. Pathogenesis of Extrahepatic Replication
3. List of Body Systems Affected by HEV in Humans
3.1. Nervous and Musculoskeletal System
3.2. Cardiovascular System
3.3. Digestive System
3.4. Other Body Systems
4. List of the Animal Models Studied with Involved Body Systems and Extrahepatic Replication Sites for HEV
5. Notable Abilities of HEV
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lhomme, S.; Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Clinical Manifestations, Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hepatitis E Virus Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Kenney, S.P. Hepatitis E Virus Immunopathogenesis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rein, D.B.; Stevens, G.A.; Theaker, J.; Wittenborn, J.S.; Wiersma, S.T. The global burden of hepatitis E virus genotypes 1 and 2 in 2005. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2012, 55, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Yang, X.L. Chirohepevirus from Bats: Insights into Hepatitis E Virus Diversity and Evolution. Viruses 2022, 14, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdy, M.A.; Drexler, J.F.; Meng, X.J.; Norder, H.; Okamoto, H.; Van der Poel, W.H.M.; Reuter, G.; de Souza, W.M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Smith, D.B. ICTV Virus Taxonomy Profile: Hepeviridae 2022. J. Gen. Virol. 2022, 103, 1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand-Abravanel, F.; Kamar, N.; Sandres-Saune, K.; Garrouste, C.; Dubois, M.; Mansuy, J.M.; Muscari, F.; Sallusto, F.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J. Characteristics of autochthonous hepatitis E virus infection in solid-organ transplant recipients in France. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johne, R.; Plenge-Bönig, A.; Hess, M.; Ulrich, R.G.; Reetz, J.; Schielke, A. Detection of a novel hepatitis E-like virus in faeces of wild rats using a nested broad-spectrum RT-PCR. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 750–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Situ, J.; Cai, J.-P.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Wu, S.; Zhang, A.J.-X.; Wen, L.; Chew, N.F.-S.; Chan, W.-M.; Poon, R.W.-S. Multimodal investigation of rat hepatitis E virus antigenicity: Implications for infection, diagnostics, and vaccine efficacy. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Juarez, A.; Frias, M.; Lopez-Lopez, P.; de Los Angeles Risalde, M.; Brieva, T.; Machuca, I.; Camacho, A.; Martinez-Peinado, A.; Gomez-Villamandos, J.C.; Rivero, A. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection in anti-HEV immunoglobulin G-carrying patients after successful hepatitis C virus treatment: Reactivation or reinfection? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, 964–966. [Google Scholar]
- Andonov, A.; Robbins, M.; Borlang, J.; Cao, J.; Hatchette, T.; Stueck, A.; Deschambault, Y.; Murnaghan, K.; Varga, J.; Johnston, L. Rat hepatitis E virus linked to severe acute hepatitis in an immunocompetent patient. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 220, 951–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.; Wu, S.; Cai, J.; Zhang, A.J.-X.; Leung, K.-H.; Chung, T.W.; Chan, J.F.; Chan, W.-M.; Teng, J.L. Rat hepatitis E virus as cause of persistent hepatitis after liver transplant. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.P.; Meng, X.J. Hepatitis E Virus Genome Structure and Replication Strategy. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a031724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, V.; Taneja, S.; Kalia, M.; Jameel, S. Molecular biology and pathogenesis of hepatitis E virus. J. Biosci. 2008, 33, 451–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, V.P.; Anang, S.; Subramani, C.; Madhvi, A.; Bakshi, K.; Srivastava, A.; Shalimar; Nayak, B.; Ranjith Kumar, C.T.; Surjit, M. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Synthesis of a Novel Viral Factor Mediates Efficient Replication of Genotype-1 Hepatitis E Virus. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, K.K.; Boley, P.A.; Fritts, Z.; Kenney, S.P. Ectopic Expression of Genotype 1 Hepatitis E Virus ORF4 Increases Genotype 3 HEV Viral Replication in Cell Culture. Viruses 2021, 13, 10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koonin, E.V.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Purdy, M.A.; Rozanov, M.N.; Reyes, G.R.; Bradley, D.W. Computer-assisted assignment of functional domains in the nonstructural polyprotein of hepatitis E virus: Delineation of an additional group of positive-strand RNA plant and animal viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 8259–8263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, S.P.; Meng, X.J. Hepatitis E Virus: Animal Models and Zoonosis. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2019, 7, 427–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H. Culture systems for hepatitis E virus. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvatits, T.; Ozga, A.K.; Westhölter, D.; Hartl, J.; Manthey, C.F.; Lütgehetmann, M.; Rauch, G.; Kriston, L.; Lohse, A.W.; Bendall, R.; et al. Hepatitis E seroprevalence in the Americas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2018, 38, 1951–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xiang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Yao, Y.; Bortolanza, M.; Cao, H.; Li, L. Extrahepatic manifestations related to hepatitis E virus infection and their triggering mechanisms. J. Infect. 2021, 83, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Othman, E.R.; Khashbah, M.Y.; Ismael, A.; Ghaliony, M.A.; Seddik, M.I.; Sayed, I.M. Evidence of the extrahepatic replication of Hepatitis E virus in human endometrial stromal cells. Pathogens 2020, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knegendorf, L.; Drave, S.A.; Dao Thi, V.L.; Debing, Y.; Brown, R.J.P.; Vondran, F.W.R.; Resner, K.; Friesland, M.; Khera, T.; Engelmann, M.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication and interferon responses in human placental cells. Hepatol. Commun. 2018, 2, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouilly, J.; Chen, Q.; Siewiera, J.; Cartron, G.; Levy, C.; Dubois, M.; Al-Daccak, R.; Izopet, J.; Jabrane-Ferrat, N.; El Costa, H. Genotype specific pathogenicity of hepatitis E virus at the human maternal-fetal interface. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratho, R.K.; Thakur, V.; Arya, S.; Singh, M.P.; Suri, V.; Das, A. Placenta as a site of HEV replication and inflammatory cytokines modulating the immunopathogenesis of HEV in pregnant women. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 3457–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muldoon, L.L.; Alvarez, J.I.; Begley, D.J.; Boado, R.J.; Del Zoppo, G.J.; Doolittle, N.D.; Engelhardt, B.; Hallenbeck, J.M.; Lonser, R.R.; Ohlfest, J.R.; et al. Immunologic privilege in the central nervous system and the blood-brain barrier. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. Off. J. Int. Soc. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Li, W.; Heffron, C.L.; Wang, B.; Mahsoub, H.M.; Sooryanarain, H.; Hassebroek, A.M.; Clark-Deener, S.; LeRoith, T.; Meng, X.-J. Hepatitis E virus infects brain microvascular endothelial cells, crosses the blood–brain barrier, and invades the central nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201862119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Long, F.; Yu, W.; Situ, J.; Fu, L.; He, Z.; Dong, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, F. High prevalence of hepatitis E virus in semen of infertile male and causes testis damage. Gut 2018, 67, 1199–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.-S.; Han, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Park, B.-J.; Kim, D.-H.; Lee, J.-B.; Park, S.-Y.; Song, C.-S.; Lee, S.-W.; Choi, C.; et al. Adverse fetal outcomes in pregnant rabbits experimentally infected with rabbit hepatitis E virus. Virology 2017, 512, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Mickael, H.K.; Xu, L.; Xia, Y.; Cong, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qian, Z.; Li, T.; Wei, D.; et al. Uterine Injury Caused by Genotype 4 Hepatitis E Virus Infection Based on a BALB/c Mice Model. Viruses 2021, 13, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallabhajosyula, S.; Prabhu, M.; Stanley, W.; Vallabhajosyula, S. 510: Multiorgan Dysfunction from Hepatitis E infection. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 46, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Seo, D.J.; Yeo, D.; Wang, Z.; Min, A.; Zhao, Z.; Song, M.; Choi, I.S.; Myoung, J.; Choi, C. Experimental infection of hepatitis E virus induces pancreatic necroptosis in miniature pigs. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mokhtar, M.A.; Seddik, M.I.; Osman, A.O.B.; Mahmoud, A.A.; Mandour, S.A.; Radwan, E.; Ali, M.; Ismael, A.E.; Twisy, H.O.; Karam-Allah Ramadan, H.; et al. No evidence of HEV genotype 1 infections harming the male reproductive system. Virology 2021, 554, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, K.; Nishimura, T.; Seki, M.; Kinoshita, M.; Mishima, N.; Irimajiri, S.; Yamato, M. Genotype 1 hepatitis E virus infection with acute acalculous cholecystitis as an extrahepatic symptom: A case report. Trop. Med. Health 2016, 44, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z. Causation by HEV of extrahepatic manifestations remains unproven. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2016, 36, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Huang, F.; Xu, L.; Lin, Z.; de Vrij, F.M.S.; Ayo-Martin, A.C.; van der Kroeg, M.; Zhao, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus Infects Neurons and Brains. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drave, S.A.; Debing, Y.; Walter, S.; Todt, D.; Engelmann, M.; Friesland, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Neyts, J.; Behrendt, P.; Steinmann, E. Extra-hepatic replication and infection of hepatitis E virus in neuronal-derived cells. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abravanel, F.; Pique, J.; Couturier, E.; Nicot, F.; Dimeglio, C.; Lhomme, S.; Chiabrando, J.; Saune, K.; Péron, J.M.; Kamar, N.; et al. Acute hepatitis E in French patients and neurological manifestations. J. Infect. 2018, 77, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripellino, P.; Pasi, E.; Melli, G.; Staedler, C.; Fraga, M.; Moradpour, D.; Sahli, R.; Aubert, V.; Martinetti, G.; Bihl, F.; et al. Neurologic complications of acute hepatitis E virus infection. Neurol. R Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 7, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrin, H.B.; Cintas, P.; Abravanel, F.; Gerolami, R.; d’Alteroche, L.; Raynal, J.-N.; Alric, L.; Dupuis, E.; Prudhomme, L.; Vaucher, E. Neurologic disorders in immunocompetent patients with autochthonous acute hepatitis E. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marion, O.; Lhomme, S.; Nayrac, M.; Dubois, M.; Pucelle, M.; Requena, M.; Migueres, M.; Abravanel, F.; Peron, J.M.; Carrere, N.; et al. Hepatitis E virus replication in human intestinal cells. Gut 2020, 69, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayed, I.M.; Seddik, M.I.; Gaber, M.A.; Saber, S.H.; Mandour, S.A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A. Replication of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) in Primary Human-Derived Monocytes and Macrophages In Vitro. Vaccines 2020, 8, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billman, G.E. Homeostasis: The Underappreciated and Far Too Often Ignored Central Organizing Principle of Physiology. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Kumar, G.; Dayal, V.M.; Ranjan, A.; Suchismita, A. Neurological manifestations of hepatitis E virus infection: An overview. World J. Gastroenterol. 2021, 27, 2090–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, J.D.; Lacomis, D.; Lam, E.M. Neuralgic Amyotrophy Associated With Hepatitis E Virus Infection: First Case in the United States. J. Clin. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2016, 18, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garofoli, R.; Zauderer, J.; Seror, P.; Roren, A.; Guerini, H.; Rannou, F.; Drapé, J.L.; Nguyen, C.; Lefèvre-Colau, M.M. Neuralgic amyotrophy and hepatitis E infection: 6 prospective case reports. RMD Open 2020, 6, e001401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, H.R.; van Eijk, J.J.J.; Cintas, P.; Madden, R.G.; Jones, C.; Webb, G.W.; Norton, B.; Pique, J.; Lutgens, S.; Devooght-Johnson, N.; et al. Hepatitis E virus infection and acute non-traumatic neurological injury: A prospective multicentre study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dartevel, A.; Colombe, B.; Bosseray, A.; Larrat, S.; Sarrot-Reynauld, F.; Belbezier, A.; Lagrange, E.; Bouillet, L. Hepatitis E and neuralgic amyotrophy: Five cases and review of literature. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2015, 69, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroux, A.; Brion, J.P.; Hyerle, L.; Belbezier, A.; Vaillant, M.; Mosnier, E.; Larrat, S.; Morand, P.; Pavese, P. Association between hepatitis E and neurological disorders: Two case studies and literature review. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2014, 60, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, F.; Illahi, M. Neuralgic amyotrophy associated with hepatitis E virus. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, M.; Berger, B.; Schemmerer, M.; Endres, D.; Wenzel, J.J.; Stich, O.; Panning, M. Pathological Cerebrospinal Fluid Findings in Patients With Neuralgic Amyotrophy and Acute Hepatitis E Virus Infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 217, 1897–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.; Van Eijk, J.; Ripellino, P.; Madden, R.; Herrod, J.; Lissmann, R.; Webb, G.; Abdelrahim, M.; Ashraf, H.; Almasri, O. Clinical phenotype and outcome of hepatitis E virus associated neuralgic amyotrophy; an international retrospective comparative cohort study. J. Hepatol. 2017, 1, S59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Azofra, M.; Romero-Portales, M.; Tortajada-Laureiro, L.; García-Samaniego, J.; Mora-Sanz, P. Hepatitis E virus in neurological disorders: A case of Parsonage-Turner syndrome. Rev. Esp. Enfermadades Dig. REED 2018, 110, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanvion, Q.; Perez, T.; Cassim, F.; Outteryck, O.; Lanteri, A.; Hatron, P.-Y.; Lambert, M.; Morell-Dubois, S. Neuralgic amyotrophy triggered by hepatitis E virus: A particular phenotype. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.; Wicki, B.; Tsouni, P.; Cunningham, S.; Doerig, C.; Zanetti, G.; Aubert, V.; Sahli, R.; Moradpour, D.; Kuntzer, T. Hepatitis E virus infection as a direct cause of neuralgic amyotrophy. Muscle Nerve 2016, 54, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, B.; Boeynaems, S.; Schrooten, M.; Saegeman, V.; Claeys, K.G.; Van Damme, P. Anterior interosseous mononeuropathy associated with HEV infection. Neurol. R Neuroimmunol. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 5, e429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velay, A.; Kack-Kack, W.; Abravanel, F.; Lhomme, S.; Leyendecker, P.; Kremer, L.; Chamouard, P.; Izopet, J.; Fafi-Kremer, S.; Barth, H. Parsonage-Turner syndrome due to autochthonous acute genotype 3f hepatitis E virus infection in a nonimmunocompromised 55-year-old patient. J. Neurovirol. 2017, 23, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolson, K.L.; Forbes, A.; Vine, L.; Beynon, L.; McElhinney, L.; Panayi, V.; Hunter, J.G.; Madden, R.G.; Glasgow, T.; Kotecha, A.; et al. Extra-hepatic manifestations of autochthonous hepatitis E infection. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 1282–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saffar, A.; Al-Fatly, B. Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy in Association with Hepatitis E. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, M.C.; Bajpai, V.; Anand, L.; Gupta, E. Guillain-Barré syndrome in a patient of acute Hepatitis E virus infection associated with genotype 1: Case report and literature review. Intractable Rare Dis. Res. 2019, 8, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukae, J.; Tsugawa, J.; Ouma, S.; Umezu, T.; Kusunoki, S.; Tsuboi, Y. Guillain-Barré and Miller Fisher syndromes in patients with anti-hepatitis E virus antibody: A hospital-based survey in Japan. Neurol. Sci Off. J. Ital. Neurol. Soc. Ital. Soc. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2016, 37, 1849–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.H.; Tian, Y.; Luo, H.Y.; Chen, Z.; Peng, F. Guillain-Barré syndrome following acute co-super-infection of hepatitis E virus and cytomegalovirus in a chronic hepatitis B virus carrier. J. Med. Virol. 2017, 89, 368–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, O.J.; Davidson, A.; Li, K.; Leach, J.P.; Heath, C. Brainstem encephalitis and acute polyneuropathy associated with hepatitis E infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2017, 2017, 220799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, O.; Claeys, K.G.; Poesen, K.; Saegeman, V.; Van Damme, P. Diagnostic Challenges and Clinical Characteristics of Hepatitis E Virus-Associated Guillain-Barré Syndrome. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Berg, B.; van der Eijk, A.A.; Pas, S.D.; Hunter, J.G.; Madden, R.G.; Tio-Gillen, A.P.; Dalton, H.R.; Jacobs, B.C. Guillain-Barré syndrome associated with preceding hepatitis E virus infection. Neurology 2014, 82, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Yang, C.; Tang, H.; Guo, N.; et al. Hepatitis E virus infection in acute non-traumatic neuropathy: A large prospective case-control study in China. EBioMedicine 2018, 36, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belbezier, A.; Deroux, A.; Sarrot-Reynauld, F.; Larrat, S.; Bouillet, L. Myasthenia gravis associated with acute hepatitis E infection in immunocompetent woman. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 908–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belliere, J.; Abravanel, F.; Nogier, M.B.; Martinez, S.; Cintas, P.; Lhomme, S.; Lavayssière, L.; Cointault, O.; Faguer, S.; Izopet, J.; et al. Transfusion-acquired hepatitis E infection misdiagnosed as severe critical illness polyneuromyopathy in a heart transplant patient. Transpl. Infect. Dis. Off. J. Transplant. Soc. 2017, 19, 12784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Despierres, L.A.; Kaphan, E.; Attarian, S.; Cohen-Bacrie, S.; Pelletier, J.; Pouget, J.; Motte, A.; Charrel, R.; Gerolami, R.; Colson, P. Neurologic disorders and hepatitis E, France, 2010. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murkey, J.A.; Chew, K.W.; Carlson, M.; Shannon, C.L.; Sirohi, D.; Sample, H.A.; Wilson, M.R.; Vespa, P.; Humphries, R.M.; Miller, S.; et al. Hepatitis E Virus-Associated Meningoencephalitis in a Lung Transplant Recipient Diagnosed by Clinical Metagenomic Sequencing. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, A.K.; Nijhawan, S.; Nepalia, S.; Suchismita, A. Association of Bell’s Palsy with Hepatitis E Virus Infection: A Rare Entity. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2012, 2, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazaki, Y.; Sugawara, K.; Honda, M.; Ohnishi, H.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Okamoto, H. Characteristics of 20 Patients with Autochthonous Acute Hepatitis E in Hokkaido, Japan: First Report of Bilateral Facial Palsy Following the Infection with Genotype 4 Hepatitis E Virus. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2015, 236, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vries, M.A.; Samijn, J.P.; de Man, R.; Boots, J.M. Hepatitis E-associated encephalopathy in a renal transplant recipient. BMJ Case Rep. 2014, 2014, 204244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasha, S.A.; Pasha, S.A.; Suhasini, T.; Rao, D.A. Hepatitis E Virus-Associated Acute Encephalitic Parkinsonism. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2018, 66, 92–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar, P.; Morgan, C.; Ijaz, S. Transverse myelitis caused by hepatitis E: Previously undescribed in adults. BMJ Case Rep. 2015, 2015, 209031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, S.; Li, K.; Gunson, R.N. Hepatitis E virus infection presenting with paraesthesia. Scott. Med. J. 2015, 60, e27–e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengel, A.M.; Stenzel, W.; Meisel, A.; Büning, C. Hepatitis E-induced severe myositis. Muscle Nerve 2016, 53, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, M.; Rangegowda, D.; Vashishtha, C.; Bhatia, V.; Khumuckham, J.S.; Kumar, B. Acute viral hepatitis e is associated with the development of myocarditis. Case Rep. Hepatol. 2015, 2015, 458056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, T.; Showkat, B.; Adam, M.; Borum, M. Acute myopericarditis due to Hepatitis E virus infection: The first reported case in the western hemisphere. J. Gastrointest. Dig. Syst. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, J.; Sen, M. Parvovirus B19-induced thrombocytopenia and anemia in a child with fatal fulminant hepatic failure coinfected with hepatitis A and E viruses. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2009, 55, 335–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Karki, P.; Malik, S.; Mallick, B.; Sharma, V.; Rana, S.S. Massive Hemolysis Causing Renal Failure in Acute Hepatitis E Infection. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 345–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Del Bello, A.; Esposito, L.; Lhomme, S.; Puissant-Lubrano, B.; Alric, L.; Faguer, S.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Hepatitis E virus-associated cryoglobulinemia in solid-organ-transplant recipients. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2018, 38, 2178–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aiqin, Z.; Dongming, X.; Kejun, T.; Yun, Z. Long Qt Syndrome and Torsades De Points in a patient with acute hepatitis E virus infection: An unusual case. Heart 2012, 98, E222–E223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Deniel, C.; Coton, T.; Brardjanian, S.; Guisset, M.; Nicand, E.; Simon, F. Acute pancreatitis: A rare complication of acute hepatitis E. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2011, 51, 202–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raj, M.; Kumar, K.; Ghoshal, U.C.; Saraswat, V.A.; Aggarwal, R.; Mohindra, S. Acute Hepatitis E-Associated Acute Pancreatitis: A Single Center Experience and Literature Review. Pancreas 2015, 44, 1320–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S.; Jha, R.; Lakhtakia, S.; Narayan, G. Acute pancreatitis following kidney transplantation—Role of viral infections. Clin. Transplant. 2003, 17, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Basu, P.P. Acute Non-Fulminant Viral Hepatitis E Presenting with Acute Pancreatitis-An Unusual Presentation. Malays. J. Med. Sci. MJMS 2017, 24, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, S.K.; Ghosh, A.; Awasthi, G. Severe acute pancreatitis with pseudocyst bleeding due to hepatitis E virus infection. Clin. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 2, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumoulin, F.L.; Liese, H. Acute hepatitis E virus infection and autoimmune thyroiditis: Yet another trigger? BMJ Case Rep. 2012, 2012, 5441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallet, V.; Bruneau, J.; Zuber, J.; Alanio, C.; Leclerc-Mercier, S.; Roque-Afonso, A.M.; Kraft, A.R.M.; Couronné, L.; Roulot, D.; Wedemeyer, H.; et al. Hepatitis E virus-induced primary cutaneous CD30(+) T cell lymphoproliferative disorder. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 1334–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bello, A.; Guilbeau-Frugier, C.; Josse, A.G.; Rostaing, L.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Successful treatment of hepatitis E virus-associated cryoglobulinemic membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis with ribavirin. Transpl. Infect. Dis. Off. J. Transplant. Soc. 2015, 17, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinault, D.; Ribes, D.; Delas, A.; Milongo, D.; Abravanel, F.; Puissant-Lubrano, B.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Hepatitis E Virus-Induced Cryoglobulinemic Glomerulonephritis in a Nonimmunocompromised Person. Am. J. Kidney Dis. Off. J. Natl. Kidney Found. 2016, 67, 660–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.; Kumar, H.K.; Manjunath, V.; Umesh, L. Pleural effusion: A rare complication of co-infection of hepatitis A and hepatitis E. Ann. Trop. Med. Public Health 2012, 5, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillebrandt, K.H.; Arsenic, R.; Hofmann, J.; Eurich, D.; Gül, S.; Strücker, B.; Sauer, I.M.; Pratschke, J.; Stockmann, M.; Raschzok, N. Acute Graft Dysfunction 17 Years After Liver Transplant: A Challenging Clinical and Histologic Manifestation of Hepatitis E. Exp. Clin. Transplant. Off. J. Middle East Soc. Organ Transplant. 2018, 16, 348–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneillie, L.; Banda, D.H.; Meuleman, P. Animal Models for Hepatitis E virus. Viruses 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Sun, Q.; She, R.; Wang, D.; Duan, X.; Yin, J.; Ding, Y. Experimental infection of Mongolian gerbils by a genotype 4 strain of swine hepatitis E virus. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 1591–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; He, Z.J.; Tao, W.; Fu, T.; Wang, Y.K.; Chen, Y. Experimental infection of Z:ZCLA Mongolian gerbils with human hepatitis E virus. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 862–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.D.; Zhang, F.; Chen, C.; Peng, L.; Luo, W.T.; Chen, R.; Xu, P.; Huang, Y.W. Revisiting the Mongolian Gerbil Model for Hepatitis E Virus by Reverse Genetics. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0219321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soomro, M.H.; Shi, R.; She, R.; Yang, Y.; Wang, T.; Wu, Q.; Li, H.; Hao, W. Molecular and structural changes related to hepatitis E virus antigen and its expression in testis inducing apoptosis in Mongolian gerbil model. J. Viral Hepat. 2017, 24, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; He, Z.; Huang, F. Vertical transmission of hepatitis E virus in pregnant rhesus macaques. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longer, C.F.; Denny, S.L.; Caudill, J.D.; Miele, T.A.; Asher, L.V.S.; Myint, K.S.A.; Huang, C.-C.; Engler, W.F.; LeDuc, J.W.; Binn, L.N.; et al. Experimental Hepatitis E: Pathogenesis in Cynomolgus Macaques (Macaca fascicularis). J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 602–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottino, F.O.; Gardinali, N.R.; Salvador, S.B.S.; Figueiredo, A.S.; Cysne, L.B.; Francisco, J.S.; de Oliveira, J.M.; Machado, M.P.; Pinto, M.A. Cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) experimentally and naturally infected with hepatitis E virus: The bone marrow as a possible new viral target. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardinali, N.R.; Guimarães, J.R.; Melgaço, J.G.; Kevorkian, Y.B.; Bottino, F.O.; Vieira, Y.R.; da Silva, A.C.; Pinto, D.P.; da Fonseca, L.B.; Vilhena, L.S.; et al. Cynomolgus monkeys are successfully and persistently infected with hepatitis E virus genotype 3 (HEV-3) after long-term immunosuppressive therapy. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balayan, M.S.; Usmanov, R.K.; Zamyatina, N.A.; Djumalieva, D.I.; Karas, F.R. Experimental hepatitis E infection in domestic pigs. J. Med. Virol. 1990, 32, 58–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J.; Halbur, P.G.; Haynes, J.S.; Tsareva, T.S.; Bruna, J.D.; Royer, R.L.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Experimental infection of pigs with the newly identified swine hepatitis E virus (swine HEV), but not with human strains of HEV. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-J.; Halbur, P.G.; Shapiro, M.S.; Govindarajan, S.; Bruna, J.D.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Purcell, R.H.; Emerson, S.U. Genetic and Experimental Evidence for Cross-Species Infection by Swine Hepatitis E Virus. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 9714–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Cao, Q.M.; Subramaniam, S.; Yugo, D.M.; Heffron, C.L.; Rogers, A.J.; Kenney, S.P.; Tian, D.; Matzinger, S.R.; Overend, C.; et al. Pig model mimicking chronic hepatitis E virus infection in immunocompromised patients to assess immune correlates during chronicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 6914–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Y.; DanBaZhaXi; Xu, S.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, E.M. Identification and pathogenicity of hepatitis E Virus from laboratory Bama miniature pigs. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, Y.; Sun, Y.; Nan, Y.; Li, H.; Du, T.; Hiscox, J.A.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, E.-M. Experimental infection of rabbit with swine-derived hepatitis E virus genotype 4. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 229, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Lei, Y.; Liu, L.; Liu, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. SPF rabbits infected with rabbit hepatitis E virus isolate experimentally showing the chronicity of hepatitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, H.; Liu, P.; Zou, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhuang, H. Experimental infection of pregnant rabbits with hepatitis E virus demonstrating high mortality and vertical transmission. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Zhang, F.; Shu, J.; Li, S.; Liang, Z.; Du, M.; Liu, X.; Liu, T.; Li, M.; Yin, X.; et al. Immunocompromised rabbit model of chronic HEV reveals liver fibrosis and distinct efficacy of different vaccination strategies. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2022, 76, 788–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zhang, W.; Gong, G.; Yuan, C.; Yan, Y.; Yang, S.; Cui, L.; Zhu, J.; Yang, Z.; Hua, X. Experimental infection of Balb/c nude mice with Hepatitis E virus. BMC Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Hao, X.; Li, Y.; Long, F.; He, Q.; Huang, F.; Yu, W. Successful Establishment of Hepatitis E Virus Infection in Pregnant BALB/c Mice. Viruses 2019, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneerat, Y.; Clayson, E.T.; Myint, K.S.; Young, G.D.; Innis, B.L. Experimental infection of the laboratory rat with the hepatitis E virus. J. Med. Virol. 1996, 48, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, S.; Wu, S.; Situ, J.; Shun, E.H.-K.; Li, Z.; Zhang, A.J.-X.; Hui, K.; Fong, C.H.-Y.; Poon, V.K.-M.; Chew, N.F.-S.; et al. A small animal model of chronic hepatitis E infection using immunocompromised rats. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heaton, N.S.; Randall, G. Multifaceted roles for lipids in viral infection. Trends Microbiol. 2011, 19, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figlerowicz, M.; Alejska, M.; Kurzyńska-Kokorniak, A.; Figlerowicz, M. Genetic variability: The key problem in the prevention and therapy of RNA-based virus infections. Med. Res. Rev. 2003, 23, 488–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauring, A.S.; Andino, R. Quasispecies theory and the behavior of RNA viruses. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Meng, X.J. Molecular biology and replication of hepatitis E virus. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2012, 1, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropp, S.; Tam, A.; Beames, B.; Purdy, M.; Frey, T. Expression of the hepatitis E virus ORF1. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 1321–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, D.; Thomas, S.; Chakraborty, M.; Jameel, S. Expression and processing of the Hepatitis E virus ORF1 nonstructural polyprotein. Virol. J. 2006, 3, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppiah, S.; Zhou, Y.; Frey, T.K. Lack of processing of the expressed ORF1 gene product of hepatitis E virus. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvez, M.K. Molecular characterization of hepatitis E virus ORF1 gene supports a papain-like cysteine protease (PCP)-domain activity. Virus Res. 2013, 178, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perttilä, J.; Spuul, P.; Ahola, T. Early secretory pathway localization and lack of processing for hepatitis E virus replication protein pORF1. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paliwal, D.; Panda, S.K.; Kapur, N.; Varma, S.P.K.; Durgapal, H. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) protease: A chymotrypsin-like enzyme that processes both non-structural (pORF1) and capsid (pORF2) protein. J. Gen. Virol. 2014, 95, 1689–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, V.E.; Shanks, M.; Lomonossoff, G. Polyprotein processing as a strategy for gene expression in RNA viruses. In Seminars in Virology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 15–23. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.B.; Vanek, J.; Ramalingam, S.; Johannessen, I.; Templeton, K.; Simmonds, P. Evolution of the hepatitis E virus hypervariable region. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, D.; Gisa, A.; Radonic, A.; Nitsche, A.; Behrendt, P.; Suneetha, P.V.; Pischke, S.; Bremer, B.; Brown, R.J.; Manns, M.P. In vivo evidence for ribavirin-induced mutagenesis of the hepatitis E virus genome. Gut 2016, 65, 1733–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debing, Y.; Gisa, A.; Dallmeier, K.; Pischke, S.; Bremer, B.; Manns, M.; Wedemeyer, H.; Suneetha, P.V.; Neyts, J. A mutation in the hepatitis E virus RNA polymerase promotes its replication and associates with ribavirin treatment failure in organ transplant recipients. Gastroenterology 2014, 147, 1008–1011.e1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debing, Y.; Ramière, C.; Dallmeier, K.; Piorkowski, G.; Trabaud, M.-A.; Lebossé, F.; Scholtès, C.; Roche, M.; Legras-Lachuer, C.; de Lamballerie, X. Hepatitis E virus mutations associated with ribavirin treatment failure result in altered viral fitness and ribavirin sensitivity. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todt, D.; Walter, S.; Brown, R.J.; Steinmann, E. Mutagenic effects of ribavirin on hepatitis E virus—Viral extinction versus selection of fitness-enhancing mutations. Viruses 2016, 8, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhomme, S.; Nicot, F.; Jeanne, N.; Dimeglio, C.; Roulet, A.; Lefebvre, C.; Carcenac, R.; Manno, M.; Dubois, M.; Peron, J.-M. insertions and duplications in the polyproline region of the hepatitis E virus. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Tong, H.; Hoan, N.X.; Wang, B.; Wedemeyer, H.; Bock, C.T.; Velavan, T.P. Hepatitis E Virus Mutations: Functional and Clinical Relevance. EBioMedicine 2016, 11, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.; Chen, S.; He, Q.; Wang, W.; Gong, S.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, D.; Yu, W.; Huang, F. The different replication between nonenveloped and quasi-enveloped hepatitis E virus. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 6267–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, X.; Ambardekar, C.; Lu, Y.; Feng, Z. Distinct Entry Mechanisms for Nonenveloped and Quasi-Enveloped Hepatitis E Viruses. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 4232–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvatits, T.; Wißmann, J.E.; Johne, R.; Groschup, M.H.; Gadicherla, A.K.; Schulze Zur Wiesch, J.; Eiden, M.; Todt, D.; Reimer, R.; Dähnert, L.; et al. Hepatitis E virus persists in the ejaculate of chronically infected men. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anheyer-Behmenburg, H.E.; Szabo, K.; Schotte, U.; Binder, A.; Klein, G.; Johne, R. Hepatitis E Virus in Wild Boars and Spillover Infection in Red and Roe Deer, Germany, 2013–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sabato, L.; Amoroso, M.G.; Ianiro, G.; Esposito, C.; De Grossi, L.; Fusco, G.; Barone, A.; Martini, E.; Ostanello, F.; Di Bartolo, I. Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Livers and Muscle Tissues of Wild Boars in Italy. Food Env. Virol 2020, 12, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, G.; Lauteri, C.; Festino, A.R.; Piccinini, A.; Olivastri, A.; Vergara, A. Hepatitis E Virus Detection in Hunted Wild Boar Liver and Muscle Tissues in Central Italy. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grange, Z.L.; Goldstein, T.; Johnson, C.K.; Anthony, S.; Gilardi, K.; Daszak, P.; Olival, K.J.; O’Rourke, T.; Murray, S.; Olson, S.H.; et al. Ranking the risk of animal-to-human spillover for newly discovered viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2002324118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
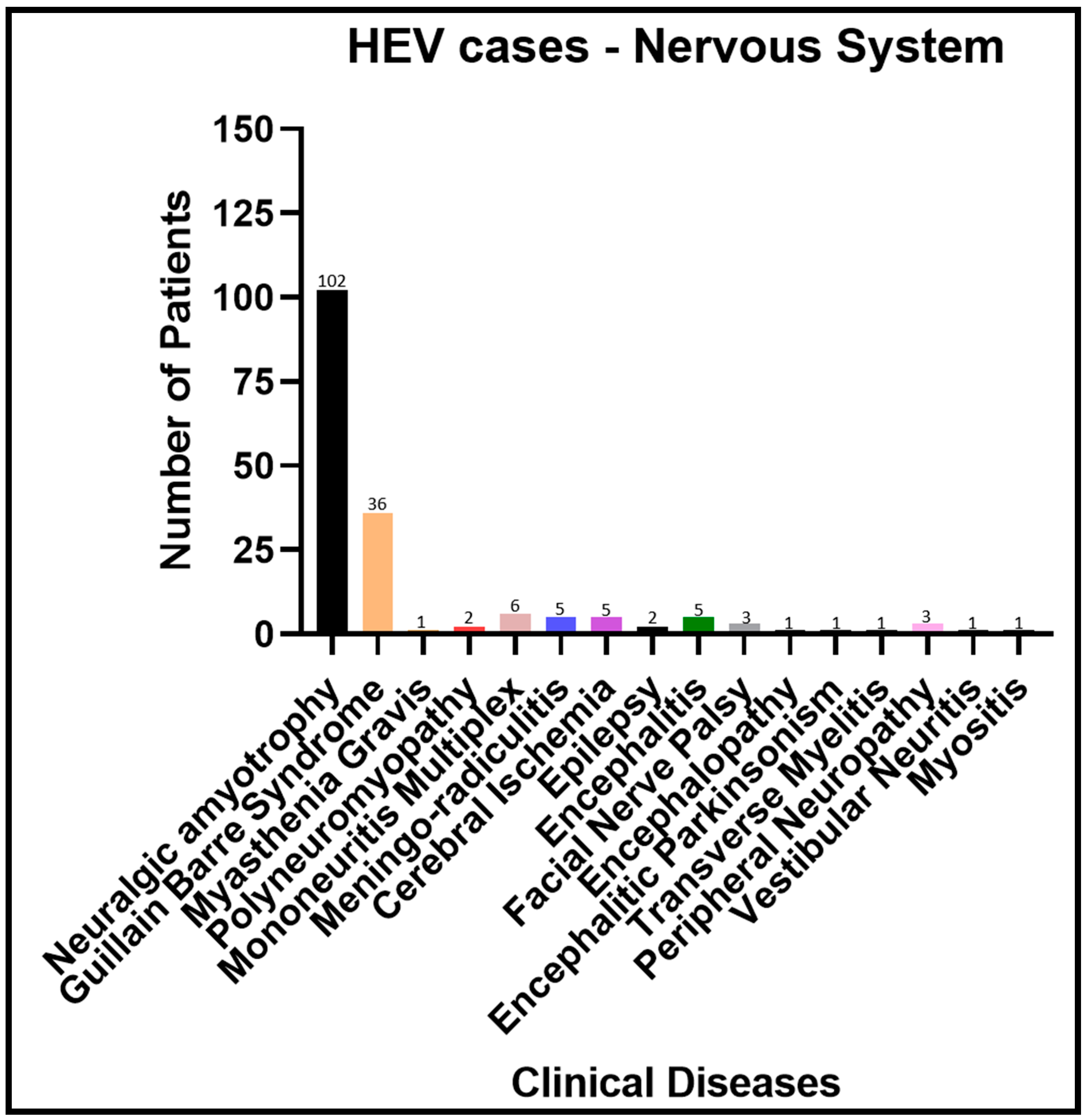
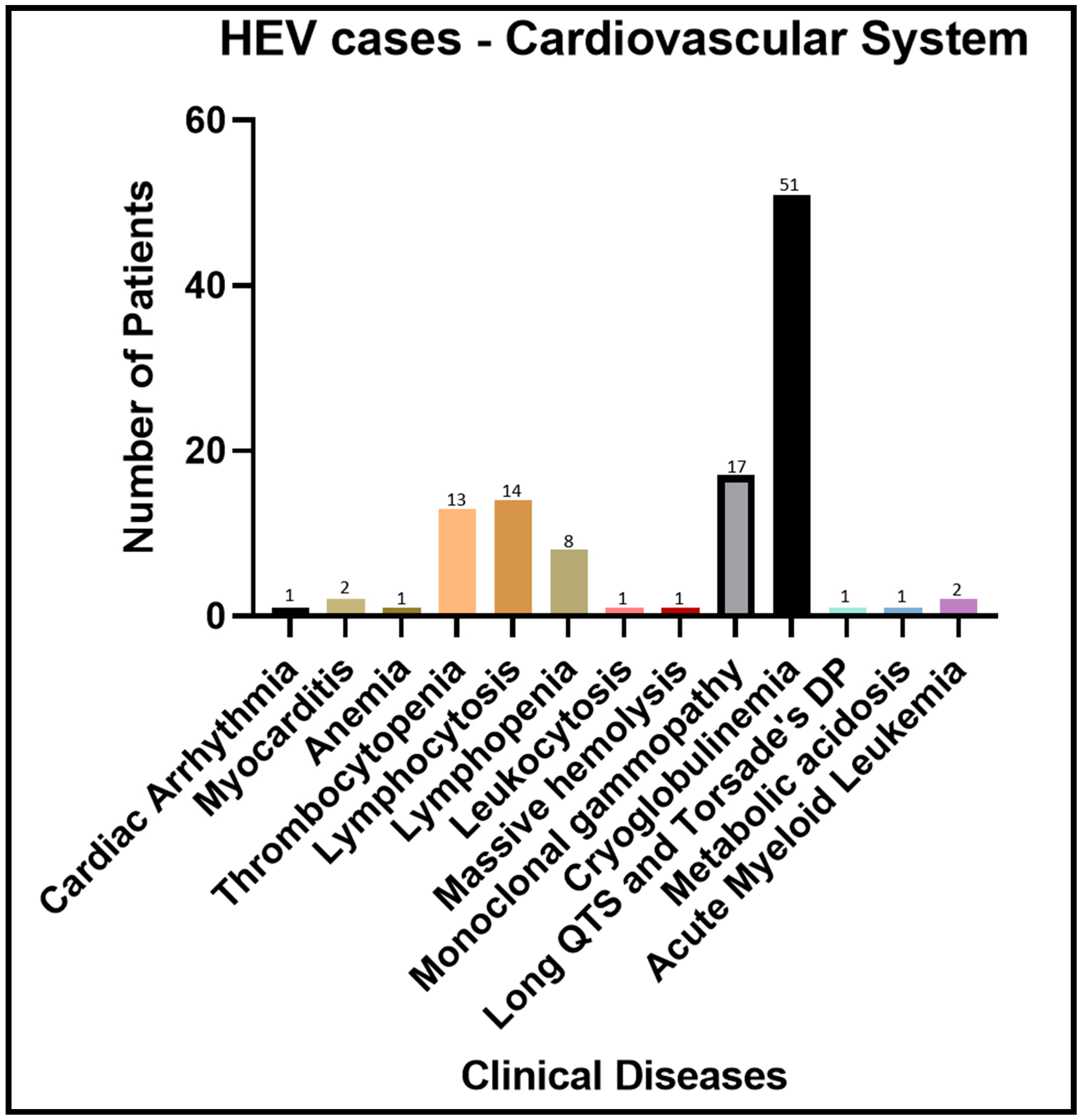
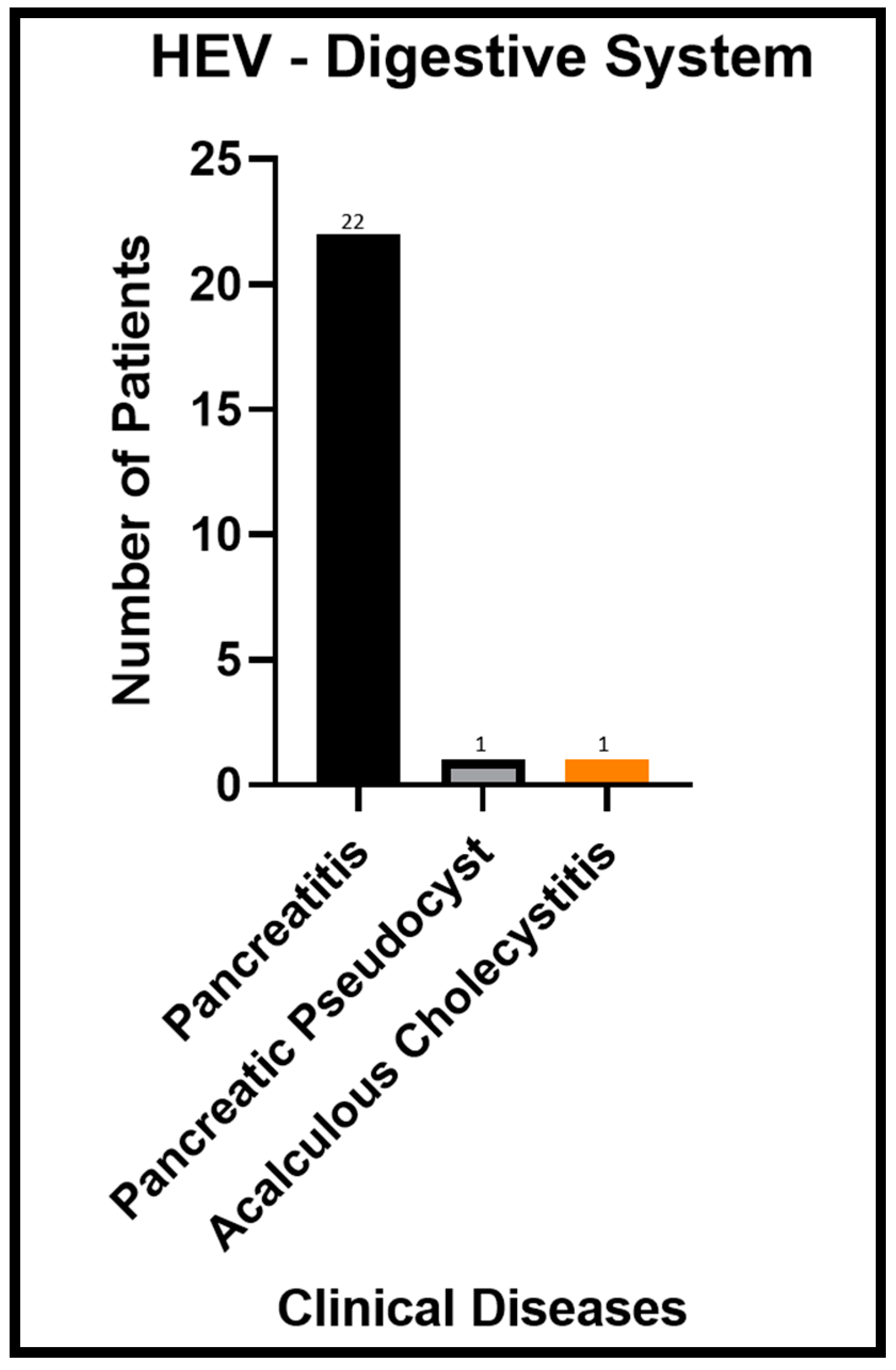
| SN | Clinical Disease | Number of Patients | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Neuralgic amyotrophy | 102 | [44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56] |
| 2 | Guillain–Barre syndrome | 36 | [39,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65] |
| 3 | Myasthenia gravis | 1 | [66] |
| 4 | Polyneuromyopathy | 2 | [57,67] |
| 5 | Mononeuritis multiplex | 6 | [39] |
| 6 | Meningo-radiculitis | 5 | [39,68] |
| 7 | Cerebral ischemia | 5 | [46,65] |
| 8 | Epilepsy | 2 | [46] |
| 9 | Encephalitis | 5 | [46,48,65,69] |
| 10 | Facial Nerve Palsy | 3 | [46,70,71] |
| 11 | Encephalopathy | 1 | [72] |
| 12 | Encephalitic Parkinsonism | 1 | [73] |
| 13 | Transverse myelitis | 1 | [74] |
| 14 | Peripheral neuropathy | 3 | [57,65,75] |
| 15 | Vestibular neuritis | 1 | [57] |
| 16 | Myositis | 1 | [76] |
| SN | Clinical Disease | Number of Patients | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Cardiac arrhythmia | 1 | [57] |
| 2 | Myocarditis | 2 | [77,78] |
| 3 | Anemia | 1 | [79] |
| 4 | Thrombocytopenia | 13 | [57,79] |
| 5 | Lymphocytosis | 14 | [57] |
| 6 | Lymphopenia | 8 | [57] |
| 7 | Leukocytosis | 1 | [30] |
| 8 | Massive hemolysis | 1 | [80] |
| 9 | Monoclonal gammopathy | 17 | [57] |
| 10 | Cryoglobulinemia | 51 | [81] |
| 11 | Long QT syndrome and Torsades de pointes | 1 | [82] |
| 12 | Metabolic acidosis | 1 | [30] |
| 13 | Acute myeloid leukemia | 2 | [57] |
| SN | Clinical Disease | Number of Patients | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pancreatitis | 22 | [30,83,84,85,86] |
| 2 | Pancreatic Pseudocyst | 1 | [87] |
| 3 | Acalculous cholecystitis | 1 | [33] |
| SN | Clinical Disease | Body System | Number of Patients | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Autoimmune Thyroiditis | Endocrine | 1 | [88] |
| 2 | Cutaneous T-Cell lymphoproliferative disorder | Integumentary | 1 | [89] |
| 3 | Acute Kidney Injury | Renal | 2 | [30,80] |
| 4 | Cryoglobulinemic membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis | Renal | 2 | [90,91] |
| 5 | Pleural Effusion | Respiratory | 1 | [92] |
| 6 | Acute Graft Dysfunction | Immune | 1 | [93] |
| 7 | Infertility | Reproductive | 52 | [27] |
| SN | Animal Model | HEV Genotype/Strain | Body System Involved | Extrahepatic Sites | Demonstration of Viral Replication Via | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mongolian Gerbil | Human Gt4 | Digestive, Renal, Lymphatic | Kidneys, Spleen, Small Intestine | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [95] |
| Gt1 (clinical human sample) | Digestive, Renal, Lymphatic | Spleen, Kidney | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [96] | ||
| Human Gt3 | Digestive, Lymphatic | Spleen | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [97] | ||
| Swine HEV Gt4 (CHN-HB-HD-L2) | Digestive, Renal, Lymphatic, Respiratory, Reproductive | Brain, Spinal cord, Spleen, Peripheral blood monocytes, Pancreas, Lung, Lymph node, Kidney, Duodenum, Jejunum, Ileum, Colon, Placenta, Urine | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [98] | ||
| 2 | Pregnant Rhesus Macaques | Gt4 (KM01) | Digestive, Fetal (Digestive, Renal) | Spleen, Kidneys, Intestine | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [99] |
| Cynomolgus Macaques | Human derived HEV | Digestive | Not listed | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [100] | |
| Human Gt3 | Digestive, Nervous, Lymphatics | Bone marrow | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [101] | ||
| Immunocompromised Cynomolgus Monkey | Gt3 | Digestive, Lymphatic | Spleen, Duodenum, Colon, Lymph node, Pancreas | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [102] | |
| 3 | Pig | unknown | Digestive | Not listed | Visualization of virus-like particles | [103] |
| Swine HEV | Digestive, Respiratory | Not listed | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [104] | ||
| US2 | Digestive | Not listed | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [105] | ||
| Immunosuppressed pigs | Human HEV (US2 strain), Gt3 | Digestive, Immune | Not listed | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [106] | |
| 4 | Miniature pigs | Gt3 | Digestive, Endocrine, Respiratory, Renal, Nervous | Pancreas, Kidney, Brain, Peyer’s patches, Lungs (bronchioles) | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [31,107] |
| 5 | Rabbit | Swine derived HEV Gt4 | Digestive, Lymphatic, | Spleen | Negative strand RT-qPCR | [108] |
| Rabbit derived HEV Gt3 | Digestive, lymphatic | Spleen | Negative strand RT-qPCR | [108] | ||
| SPF rabbits | Rabbit HEV | Digestive, Renal, Lymphatic, Respiratory, Nervous | Stomach, Duodenum, Kidney, Bile, Lung, Bladder, Brain | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [109] | |
| Swine Gt4 | Mild digestive | Not listed | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [109] | ||
| Pregnant rabbits | Rabbit HEV (CHN-BJ-R14) | Digestive, Reproductive | Placenta | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [110] | |
| Rabbit gt3 (KOR-Rb-1) | Digestive, Reproductive | Uterus | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [28] | ||
| Immunosuppressed Rabbit | Rabbit derived HEV-3ra | Digestive, Renal, Nervous | Kidney, Duodenum, Jejunum, Cecum, Colon, Urine, Cerebrospinal fluid | Positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [111] | |
| 6 | BALB/c nude mice | Swine HEV Gt4 | Digestive, Lymphatic, Renal | Spleen, Kidney, Jejunum, Ileum, Colon | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [112] |
| Pregnant BALB/c mice | Swine derived Gt4 (KM01) | Digestive, Reproductive, Renal, Placenta and neonatal liver | Spleen, Kidney, Colon, Uterus, Placenta | IHC and negative strand RT-qPCR | [113] | |
| 7 | Rat | Human feces derived (TK-037/92) | Digestive, Lymphatic | Spleen, Mesenteric lymph nodes, Small intestine | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [114] |
| Immunocompromised rats | Human derived rat strain (CCY) | Digestive | Not listed | IHC and positive strand RT-qPCR (not confirmatory) | [115] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yadav, K.K.; Kenney, S.P. Extrahepatic Replication Sites of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 3, 68-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3010007
Yadav KK, Kenney SP. Extrahepatic Replication Sites of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). Zoonotic Diseases. 2023; 3(1):68-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleYadav, Kush Kumar, and Scott P. Kenney. 2023. "Extrahepatic Replication Sites of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV)" Zoonotic Diseases 3, no. 1: 68-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3010007
APA StyleYadav, K. K., & Kenney, S. P. (2023). Extrahepatic Replication Sites of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV). Zoonotic Diseases, 3(1), 68-84. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3010007







