Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Bacteriophages Specific for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. PCR Analysis for Detection of Virulence Genes mapA and ceuE in Campylobacter Strains
2.3. Susceptibility to Antibiotics
2.4. Isolation of Bacteriophages Specific for C. jejuni and C. Coli
2.5. Bacteriophage Purification and Propagation
2.6. Morphological Characteristics (Electron Microscopy)
2.7. Phages Adsorption Experiment and One-Step Growth Curve
2.8. Determination of Phage Host Range
2.9. Effect of Temperature and pH on the Stability of Phages
2.10. Bacterial Cell Lysis Assay
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Prevalence of Campylobacter Species (C. jejuni and C. coli) in Collected Samples
3.2. PCR Analysis for Detection of Virulence Genes mapA and ceuE
3.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility of C. jejuni and C. coli Isolates
3.4. Phage Isolation and Characterization
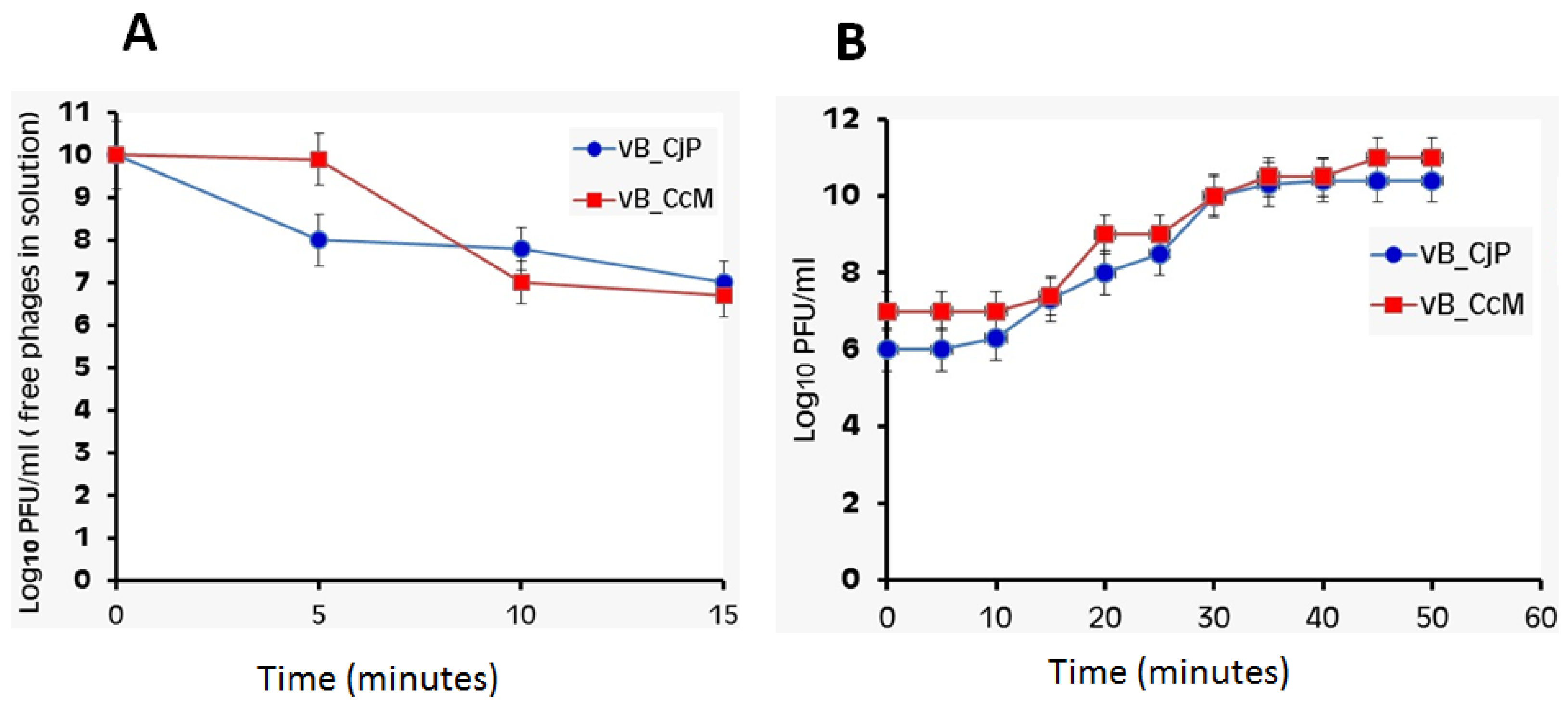
3.5. Phage Adsorption Rate and One-Step Growth Curve of Campylobacter Phages
3.6. Host Range of Isolated Phages
3.7. Effect of Temperature and pH on Bacteriophage Stability
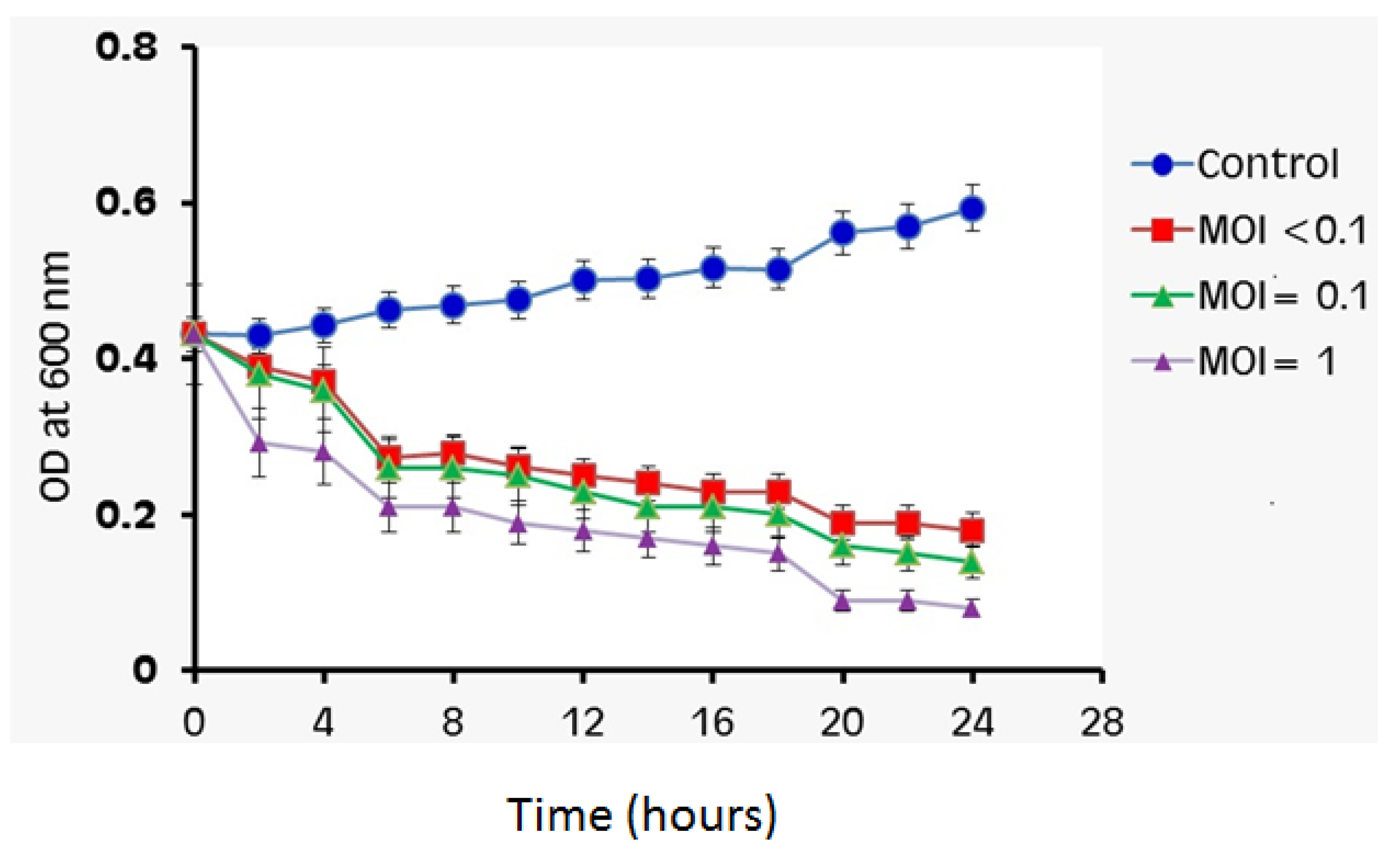
3.8. Bacterial Cell Lysis Assay
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hlashwayo, D.F.; Sigaúque, B.; Bila, C.G. Epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance of Campylobacter spp. in animals in Sub-Saharan Africa: A systematic review. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orhan, S.; Yaeger, M.; Zuowei, W.U.; Zhang, Q. Campylobacter-associated diseases in animals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2017, 5, 21–42. [Google Scholar]
- Sheppard, S.K.; Dallas, J.F.; Strachan, N.J.; MacRae, M.; McCarthy, N.D.; Wilson, D.J.; Gormley, F.J.; Falush, D.; Ogden, I.D.; Maiden, M.C.; et al. Campylobacter genotyping to determine the source of human infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Goossens, H.; Vlaes, L.; De Boeck, M.; Levy, J.; De Mol, P.; Butzler, J.P.; Kersters, K.; Pot, B.; Vandamme, P. Is “Campylobacter upsaliensis” an unrecognised cause of human diarrhoea? Lancet 1990, 335, 584–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenbarger, D.W.; Hoge, C.W.; Srijan, A.; Pitarangsi, C.; Vithayasai, N.; Bodhidatta, L.; Hickey, K.W.; Cam, P.D. Comparative antibiotic resistance of diarrheal pathogens from Vietnam and Thailand, 1996–1999. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2002, 8, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engberg, J.; Neimann, J.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Fussing, V. Quinolone-resistant Campylobacter infections: Risk factors and clinical consequences. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, K.; Lastovica, A.J.; le Roux, E.; Hossain, M.A.; Islam, M.N.; Sen, S.K.; Sur, G.C.; Nair, G.B.; Sack, D.A. Clinical characteristics and serotype distribution of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from diarrhoeic patients in Dhaka, Bangladesh, and Cape Town, South Africa. Bangladesh J. Microbiol. 2006, 23, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hall-Stoodley, L.; Costerton, J.W.; Stoodley, P. Bacterial biofilms: From the natural environment to infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachoo, N.; Frank, J.F.; Stern, N.J. Survival of Campylobacter jejuni in biofilms isolated from chicken houses. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, G.P.; Guthrie-Irons, C.; Karlyshev, A.V.; Wren, B.W. Biofilm formation in Campylobacter jejuni. Microbiology 2006, 152, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Zou, B.; Haruna, M.; Kusukawa, M.; Murakami, M.; Asai, T.; Tsujiyama, Y.; Yamada, Y. Campylobacter cross-contamination of chicken products at an abattoir. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuta, M.; Nasu, T.; Umeki, K.; Minh, D.H.; Honjoh, K.I.; Miyamoto, T. Characterization and application of lytic bacteriophages against Campylobacter jejuni isolated from poultry in Japan. Biocontrol Sci. 2017, 22, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Askoura, M.; Saed, N.; Enan, G.; Askora, A. Characterization of Polyvalent Bacteriophages Targeting Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumonia with Enhanced Anti-Biofilm Activity. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2021, 57, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, B.; Wang, W.; Arshad, M.I.; Khurshid, M.; Muzammil, S.; Rasool, M.H.; Nisar, M.A.; Alvi, R.F.; Aslam, M.A.; Qamar, M.U.; et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clokie, M.R.; Millard, A.D.; Letarov, A.V.; Heaphy, S. Phages in nature. Bacteriophage 2011, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bolocan, A.S.; Upadrasta, A.; de Almeida Bettio, P.H.; Clooney, A.G.; Draper, L.A.; Ross, R.P.; Hill, C. Evaluation of phage therapy in the context of Enterococcus faecalis and its associated diseases. Viruses 2019, 11, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cassini, A.; Högberg, L.D.; Plachouras, D.; Quattrocchi, A.; Hoxha, A.; Simonsen, G.S.; Colomb-Cotinat, M.; Kretzschmar, M.E.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Cecchini, M.; et al. Attributable deaths and disability-adjusted life-years caused by infections with antibiotic-resistant bacteria in the EU and the European Economic Area in 2015: A population-level modelling analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sitohy, M.; Al-Mohammadi, A.R.; Osman, A.; Abdel-Shafi, S.; El-Gazzar, N.; Hamdi, S.; Ismail, S.H.; Enan, G. Silver-Protein Nanocomposites as Antimicrobial Agents. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mohammadi, A.R.; Ibrahim, R.A.; Moustafa, A.H.; Ismaiel, A.A.; Zeid, A.A.; Enan, G. Chemical Constitution and Antimicrobial Activity of Kefir Fermented Beverage. Molecules 2021, 26, 2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, A.; Abdel-Shafi, S.; Al-Mohammadi, A.R.; Kamal, N.; Enan, G.; Sitohy, M. Catfish Glycoprotein, a Highly Powerful Safe Preservative of Minced Beef Stored at 4 °C for 15 Days. Foods 2020, 9, 1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Shafi, S.; Al-Mohammadi, A.R.; Negm, S.; Enan, G. Antibacterial activity of Lactobacillus delbreukii subspecies bulgaricus isolated from Zabady. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Moye, Z.D.; Woolston, J.; Sulakvelidze, A. Bacteriophage applications for food production and processing. Viruses 2018, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- El-Shibiny, A.; Scott, A.; Timms, A.; Metawea, Y.; Connerton, P.; Connerton, I. Application of a group II Campylobacter bacteriophage to reduce strains of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli colonizing broiler chickens. J. Food Prot. 2009, 72, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammerl, J.A.; Jäckel, C.; Alter, T.; Janzcyk, P.; Stingl, K.; Knüver, M.T.; Hertwig, S. Reduction of Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chicken by successive application of group II and group III phages. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e114785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, R.; Adley, C.C. An evaluation of five preservation techniques and conventional freezing temperatures of −20 °C and −85 °C for long-term preservation of Campylobacter jejuni. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2004, 38, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, I.; Grant, K.A.; Richardson, P.T.; Park, S.F.; Collins, M.D. Specific identification of the enteropathogens Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter Coli using a PCR test based on the ceuE gene encoding a putative virulence determinant. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stucki, U.R.S.; Joachim, F.; Nicolet, J.; Burnens, A.P. Identification of Campylobacter jejuni on the basis of a species gene that encodesa membrane protein. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1995, 33, 855–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wayne, P.A. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing: 20th informational supplement. CLSI Doc. M100-S20 2010, 100–121. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, H. Methods of study of bacterial viruses. In Bacteriophages; Adams, H., Ed.; Interscience Publishers: London, UK, 1959; pp. 447–448. [Google Scholar]
- El-Telbany, M.; El-Didamony, G.; Askora, A.; Ariny, E.; Abdallah, D.; Connerton, I.F.; El-Shibiny, A. Bacteriophages to Control Multi-Drug Resistant Enterococcus faecalis Infection of Dental Root Canals. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanachaikunsopon, P.; Phumkhachorn, P. Bacteriophage PPST1 isolated from hospital wastewater, a potential therapeutic agent against drug resistant Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi. Salmonella: Distribution, Adaptation. Control Meas. Mol. Technol. 2012, 18, 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Pajunen, M.; Kiljunen, S.; Skurnik, M. Bacteriophage φYeO3-12, specific for Yersinia enterocolitica serotype O: 3, is related to coliphages T3 and T7. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5114–5120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.G.; Jun, J.W.; Giri, S.S.; Yun, S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, S.W.; Kang, J.W.; Han, S.J.; Jeong, D.; Park, S.C. Isolation and characterisation of pVa-21, a giant bacteriophage with anti-biofilm potential against Vibrio alginolyticus. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Igwaran, A.; Okoh, A.I. Human campylobacteriosis: A public health concern of global importance. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janež, N.; Loc-Carrillo, C. Use of phages to control Campylobacter spp. J. Microbiol. Methods 2013, 95, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrillo, C.L.; Atterbury, R.; El-Shibiny, A.; Connerton, P.; Dillon, E.; Scott, A.; Connerton, I. Bacteriophage Therapy to Reduce Campylobacter jejuni Colonization of Broiler Chickens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 6554–6563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steffan, S.M.; Shakeri, G.; Hammerl, J.A.; Kehrenberg, C.; Peh, E.; Rohde, M.; Jackel, C.; Plotz, M.; Kittler, S. Isolation and Characterization of Group III Campylobacter jejuni-Specific Bacteriophages from Germany and Their Suitability for Use in Food Production. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 761223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowaczek, A.; Urban-Chmiel, R.; Dec, M.; Puchalski, A.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Marek, A.; Pyzik, E. Campylobacter spp. and bacteriophages from broiler chickens: Characterization of antibiotic susceptibility profiles and lytic bacteriophages. Microbiol. Open 2019, 8, e784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, I.; Mahmood, M.S.; Akhtar, M.; Khan, A. Prevalence of Campylobacter species in meat, milk and other food commodities in Pakistan. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafir, Y.; China, B.; Dierick, K.; De Zutter, L.; Daube, G.A. Seven-year survey of Campylobacter contamination in meat at different production stages in Belgium. Int. J. Food Microbial. 2007, 116, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, T.; O’Brien, S.; Madsen, M. Campylobacters as zoonotic pathogens: A food production perspective. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 117, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniak, A.; Wieliczko, A. Tetracycline, erythromycin, and gentamicin resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli isolated from poultry in Poland. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2011, 55, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- von Wintersdorff, C.J.; Penders, J.; van Niekerk, J.M.; Mills, N.D.; Majumder, S.; van Alphen, L.B.; Savelkou, L.P.H.; Wolffs, P.F. Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance in Microbial Ecosystems through Horizontal Gene Transfer. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, J.J.; Hyman, P. Phage choice, isolation, and preparation for phage therapy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2010, 11, 2–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.M.; Gannon, B.W.; Halfhide, D.E.; Santos, S.B.; Hayes, C.M.; Roe, J.M.; Azeredo, J. The in vivo efficacy of two administration routes of a phage cocktail to reduce numbers of Campylobacter coli and Campylobacter jejuni in chickens. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sørensen, M.C.; Gencay, Y.E.; Birk, T.; Baldvinsson, S.B.; Jäckel, C.; Hammerl, J.A.; Vegge, C.S.; Neve, H.; Brøndsted, L. Primary isolation strain determines both phage type and receptors recognised by Campylobacter jejuni bacteriophages. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yehl, K.; Lemire, S.; Yang, A.C.; Ando, H.; Mimee, M.; Torres, M.T.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Lu, T.K. Engineering Phage Host-Range and Suppressing Bacterial Resistance through PhageTail Fiber Mutagenesis. Cell 2019, 179, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cufaoglu, G.; Ayaz, N.D. Listeria monocytogenes risk associated with chicken at slaughter and biocontrol with three new bacteriophages. J. Food Saf. 2019, 39, e12621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly-Chatain, M.H. The factors affecting effectiveness of treatment in phages therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| Sample Sources | No. of Samples | Total No. | Campylobacter spp. Strains | C. jejuni | C. coli | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total No. | % | Total No. | % | Total No. | % | ||||
| Chicken | Feces | 50 | 400 | 15 | 30 | 7 | 47 | 8 | 53 |
| Cecal part | 100 | 41 | 41 | 21 | 51 | 20 | 49 | ||
| Cloacal swabs | 50 | 19 | 38 | 11 | 58 | 8 | 42 | ||
| Fresh gizzard | 50 | 11 | 22 | 6 | 55 | 5 | 45 | ||
| Fresh liver | 50 | 8 | 16 | 4 | 50 | 4 | 50 | ||
| Frozen gizzard | 50 | 6 | 12 | 4 | 67 | 2 | 33 | ||
| Frozen liver | 50 | 4 | 8 | 2 | 50 | 2 | 50 | ||
| Duck | Feces | 30 | 151 | 6 | 20 | 4 | 67 | 2 | 33 |
| Cecal part | 25 | 6 | 24 | 2 | 33 | 4 | 67 | ||
| Cloacal swabs | 24 | 7 | 29 | 4 | 57 | 3 | 43 | ||
| fresh gizzard | 18 | 5 | 28 | 2 | 40 | 3 | 60 | ||
| Fresh liver | 17 | 3 | 18 | 2 | 67 | 1 | 33 | ||
| Frozen gizzard | 17 | 2 | 12 | 1 | 50 | 1 | 50 | ||
| Frozen liver | 20 | 2 | 10 | 1 | 50 | 1 | 50 | ||
| Humans | Child diarrhea | 50 | 100 | 5 | 10 | 2 | 40 | 3 | 60 |
| Adult diarrhea | 50 | 9 | 18 | 5 | 56 | 4 | 44 | ||
| Total | 661 | 149 | 22.5 | 78 | 11.8 | 71 | 10.7 | ||
| Antimicrobial Class | Antibiotic | Disk Code | Disc Conc. (μg) | C. jejuni (n = 78) | C. coli (n = 71) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Resistance | Resistance% | Total Resistance | Resistance% | ||||
| Aminopenicillins (β–Lactam) | Ampicillin | AM | 10 | 71 | 91 | 58 | 82 |
| Cephalosporin | Cephalothin | KF | 30 | 78 | 100 | 71 | 100 |
| Cephradine | CE | 30 | 78 | 100 | 71 | 100 | |
| Quinolones | Nalidixic Acid | NA | 30 | 78 | 100 | 71 | 100 |
| Fluoroquinolone | Levofloxacin | LEV | 5 | 26 | 33 | 15 | 21 |
| Fluoroquinolones | Ciprofloxacin | CIP | 5 | 35 | 45 | 18 | 25 |
| Norfloxacin | NOR | 10 | 33 | 42 | 24 | 34 | |
| Pefloxacin | PEF | 5 | 46 | 59 | 35 | 49 | |
| Aminoglycosides | Streptomycin | S | 10 | 47 | 60 | 28 | 39 |
| Gentamicin | CN | 10 | 43 | 55 | 29 | 41 | |
| Tobramycin | TOB | 10 | 38 | 49 | 24 | 34 | |
| Neomycin | N | 30 | 41 | 53 | 31 | 44 | |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline | TE | 30 | 60 | 77 | 40 | 56 |
| Macrolides | Erythromycin | E | 15 | 78 | 100 | 63 | 89 |
| Nitrofurantoin | Nitrofurantoin | F | 300 | 26 | 33 | 18 | 25 |
| Bacterials Strains | vB-CjP | vB-CcM |
|---|---|---|
| Cj 1 | + | − |
| Cj 2 | + | − |
| Cj 3 | − | − |
| Cj 4 | + | − |
| Cj 5 | + | − |
| CJ 6 | + | − |
| Cj 7 | + | − |
| Cj 8 | + | − |
| Cj 9 | − | − |
| Cj 10 | − | − |
| Cc 11 | − | − |
| Cc 12 | − | + |
| Cc 13 | − | − |
| Cc 14 | − | − |
| Cc 15 | − | − |
| Cc 16 | − | − |
| Cc 17 | − | − |
| Cc 18 | − | + |
| Cc 19 | − | + |
| Cc 20 | − | + |
| L. monocytogenes 1 | − | − |
| P. aeruginosa 2 | − | − |
| E. coli 3 | − | − |
| Staph. aureus 4 | − | − |
| B. cereus 5 | − | − |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Mohammadi, A.-R.; El-Didamony, G.; Abd El Moneem, M.S.; Elshorbagy, I.M.; Askora, A.; Enan, G. Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Bacteriophages Specific for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Zoonotic Dis. 2022, 2, 59-72. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis2020007
Al-Mohammadi A-R, El-Didamony G, Abd El Moneem MS, Elshorbagy IM, Askora A, Enan G. Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Bacteriophages Specific for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Zoonotic Diseases. 2022; 2(2):59-72. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis2020007
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mohammadi, Abdul-Raouf, Gamal El-Didamony, Mohamed S. Abd El Moneem, Ibrahim M. Elshorbagy, Ahmed Askora, and Gamal Enan. 2022. "Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Bacteriophages Specific for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli" Zoonotic Diseases 2, no. 2: 59-72. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis2020007
APA StyleAl-Mohammadi, A.-R., El-Didamony, G., Abd El Moneem, M. S., Elshorbagy, I. M., Askora, A., & Enan, G. (2022). Isolation and Characterization of Lytic Bacteriophages Specific for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli. Zoonotic Diseases, 2(2), 59-72. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis2020007







