Abstract
Corynebacterium rouxii is one of the recently described species of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae complex. As this species can potentially infect different hosts and harbor the tox gene, producing diphtheria toxin, we present its first pangenomic analysis in this work. A total of fifteen genomes deposited in online databases were included. After confirming the taxonomic position of the isolates by genomic taxonomy, the genomes were submitted to genomic plasticity, gene synteny, and pangenome prediction analyses. In addition, virulence and antimicrobial resistance genes were investigated. Finally, epidemiological data were obtained through molecular typing, clustering, and phylogenetic analysis. Our data demonstrated genetic diversity within the species with low synteny. However, the gene content is extensively conserved, and the pangenome is composed of 2606 gene families, of which 1916 are in the core genome and 80 are related to unique genes. Prophages, insertion sequences, and genomic islands were found. A type I-E CRISPR-Cas system was also detected. Besides the tox gene, determinants involved in adhesion and iron acquisition and two putative antimicrobial resistance genes were predicted. These findings provide valuable insight about this species’ pathogenicity, evolution, and diversity. In the future, our data can contribute to different areas, including vaccinology and epidemiology.
1. Introduction
Corynebacterium comprises a collection of aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, non-acid-fast, non-spore-forming, and irregular rod-shaped microorganisms with a high GC content. The type species is Corynebacterium diphtheriae, known as the main etiological agent of diphtheria, a contagious infection that can affect the respiratory tract and skin. The main signs and symptoms result from the action of diphtheria toxin (DT), an exotoxin produced by the microorganism when lysogenized by phages carrying the tox gene [1].
Despite advances resulting from universal vaccination programs with the diphtheria toxoid, which drastically reduced the number of cases worldwide, diphtheria is still reported even in immunized individuals [2,3]. In recent years, the number of cases and outbreaks of diphtheria have been reported in several countries, including Brazil, where diphtheria is endemic, as well as Austria, Belgium, France, Norway, Switzerland, and the United Kingdom [2,3,4,5,6].
Besides C. diphtheriae, the closely related species Corynebacterium belfantii, Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis, Corynebacterium rouxii, Corynebacterium silvaticum, and Corynebacterium ulcerans, which form the C. diphtheriae complex, can also harbor the tox gene and produce DT [7,8,9].
C. rouxii was described in 2020 based on the genomic taxonomy of six atypical maltose-negative strains, isolated from humans and one dog, previously identified as C. diphtheriae biovar Belfanti [10]. In this same study, atypical biovar Belfanti strains isolated from cats in the USA [9] were also reclassified as C. rouxii. Considering these recent taxonomic reclassifications, some earlier names should be corrected to C. rouxii. Until this moment, the latest cases of C. rouxii infection have been reported in the USA [11], Germany [12], Spain [13], and Brazil [14].
In the present work, we present the first pangenomic analysis of C. rouxii, contributing to the identification of potential virulence factors and genes related to antimicrobial resistance and a better understanding of the pathogenic potential and evolution of this recently described species of Corynebacterium.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Genome Data Retrieval from Public Database
For comparative analysis of C. rouxii, we used the National Center of Biotechnology Information (NCBI—https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, accessed on 12 January 2024) and the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA—https://www.ebi.ac.uk/ena/browser/home, accessed on 14 January 2024) databases to retrieve the genomic sequences. A total of 15 genomes of C. rouxii were downloaded in nucleotide FASTA format from NCBI and in text-based format FASTQ from ENA. The quality analysis of the sequences was performed using FastQC (https://github.com/s-andrews/FastQC, accessed on 21 January 2024). All genomes downloaded from ENA were assembled using Unicycler v.0.5.0 (https://github.com/rrwick/Unicycler, accessed on 21 January 2024) and contigs with less than 200 bp were trimmed. To evaluate the guanine and cytosine (GC) content, size, and fragmentation of the genomes, we used QUAST (https://github.com/ablab/quast, accessed on 22 January 2024). The completeness and contamination levels were estimated using CheckM2 (https://github.com/chklovski/CheckM2, accessed on 22 January 2024) and the completeness of rRNA genes was estimated using Barnapp (https://github.com/tseemann/barrnap, accessed on 22 January 2024). Information about the sequences is provided in Table 1. All genomes were annotated using Prokka v.1.14.6 (https://github.com/tseemann/prokka, accessed on 22 January 2024) [15].

Table 1.
Information about the fifteen genomic sequences of C. rouxii strains.
2.2. Taxonomy, Typing, and Phylogeny
The taxonomy of the strains was determined using TYGS (https://tygs.dsmz.de/, accessed on 3 February 2024). Sequence type (ST) was determined in silico considering seven housekeeping genes, atpA, dnaE, dnaK, fusA, leuA, odhA, and rpoB, according to the MLST scheme defined in PubMLST [16] and using the FastMLST script (https://github.com/EnzoAndree/FastMLST, accessed on 3 February). Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) values among the C. rouxii strains were calculated using PyANI v.0.2.12 (https://github.com/widdowquinn/pyani, accessed on 6 February 2024). DNA-DNA hybridization (DDH) was determined in silico for the genomes using the Type (Strain) Genome Server (https://tygs.dsmz.de, accessed on 6 February 2024). Genomes were clustered using PopPUNK v.2.6.0 [17], and the network was visualized using Cytoscape v.3.10.1 [18].
The phylogenetic tree based on the MLST scheme was built using OrthoFinder pipeline v.2.5.5 (https://github.com/davidemms/OrthoFinder, accessed on 22 March 2024) with the MAFFT algorithm [19] for protein sequence alignment and FastTree (http://www.microbesonline.org/fasttree/, accessed on 22 March 2024) for tree inference (parameter “-M msa”). The tree was visualized using iTOL v.6 (https://itol.embl.de/, accessed 22 March 2024). For the wgMLSTtree, whole genome sequences were uploaded into PGAdg-builder (http://wgmlstdb.imst.nsysu.edu.tw/, accessed on 24 March 2024), and the core genes with default parameters (90% coverage and 90% identity) were chosen [20].
2.3. Prediction of Mobile Genetic Elements, CRISPR-Cas Systems, and Genomic Islands
PlasmidFinder v.2.1.6 was used for the in silico detection of plasmids [21], and IntegronFinder v.2.0 was used for identifying and analyzing integrons across the genomes [22]. The prophage sequences were identified and annotated with Phage Search Tool Enhanced Release (PHASTER) [23]. Average Nucleotide Identity (ANI) values were calculated among the predicted intact prophages and their closest phages using PyANI v.0.2.12. Prophage regions with ANI identity values > 95.0% were aligned using tblastx [24], and compared and visualized using the Easyfig application [25]. Moreover, the Insertion Sequences (IS) were identified using ISEScan [26]. CRISPRCasFinder v.1.1.2 was used to analyze the presence of Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPRs) and Cas proteins [27]. In our analyses, we included only CRISPR arrays with evidence levels equal to 3 or 4 [27], and the type of CRISPR-Cas cassette was determined following the previously described nomenclature and classification [28]. Spacer sequences were analyzed for their identity in the CRISPRTarget database [29]. Spacer hits were selected from the CRISPRTarget with a cut-off Identity Cover (IC) score above 0.80 [30].
The prediction of putative genomic islands was performed using GIPSy v.1.1.2 [31], with Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13,032 (GenBank accession number GCA_000011325.1) as a reference for non-pathogenic closely related organism [32]. Circular genome map comparisons were built using BRIG (Blast Ring Image Generator) software v.0.95 [33], including reference positions for antimicrobial resistance genes, virulence factors, and genomic islands. Functional annotation was performed with EggNOG-mapper v.2.1.11 [34] to explore the genes in the islands.
2.4. Gene Synteny
The software Mauve v.20150226 and the progressive Mauve algorithm were used to construct multiple genome alignments, which provided information about evolutionary events such as rearrangement and inversion [35].
2.5. Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
VFanalyzer was implemented to screen potential virulence factors in all C. rouxii strains using the VFDB (Virulence Factor Database) database [36]. Additionally, we used PanViTa v.1.1.3 [37] to search for antimicrobial resistance genes and virulence genes using the CARD (Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database) and VFDB databases, respectively, for more accurate results. The phylogeny of the tox gene from C. rouxii and other species from the C. diphtheriae complex was inferred from the maximum likelihood method based on the Tamura 3-parameter model using Mega v6 and bootstrap values with 1000 replicates [38].
2.6. Pangenome Development and Functional Annotation
Pangenomic analysis was performed with the Bacterial Pan Genome Analysis pipeline (BPGA) v.1.3, using the following options to configure the analysis: 50% identity cut-off and USEARCH as a default-clustering tool [39]. According to Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG), the coding sequences (CDS) of the core genome, accessory, and unique gene subsets were aligned and classified based on the functional categories [40]. EggNOG-mapper v.2.1.11 was used to perform the functional annotation according to orthologous genes [34]. DIAMOND v2.0.14.152 (https://github.com/bbuchfink/diamond/releases, accessed on 10 March 2024) was chosen for the initial sequence-mapping step by eggNOG-mapper. The most suitable matching of sequence mapping was classified according to its taxonomy. Finally, it was categorized and annotated according to gene ontology (GO) [41], KEGG pathways [42], and COG functional categories [43], which have several categories.
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomy, Typing, and Phylogeny
All strains were classified as C. rouxii by TYGS (Supplementary Table S1). Six different STs were identified: 74 (USA, cat), 181 (France, human), 537 (France, human; Spain, human), 538 (France, dog), 899 (Brazil, cat), and 918 (Brazil, dog) (Supplementary Table S2). The ANI values among strains ranged from 0.98 to 1.0 (Supplementary Figure S1). The strains formed five clusters. Four of them had the same host and country: Cluster 1 (USA, cat), Cluster 2 (France, human), Cluster 4 (Brazil, dog), and Cluster 5 (France, dog). Cluster 3 had isolates from cats in Brazil, humans in France, and humans in Spain (Supplementary Figure S2).
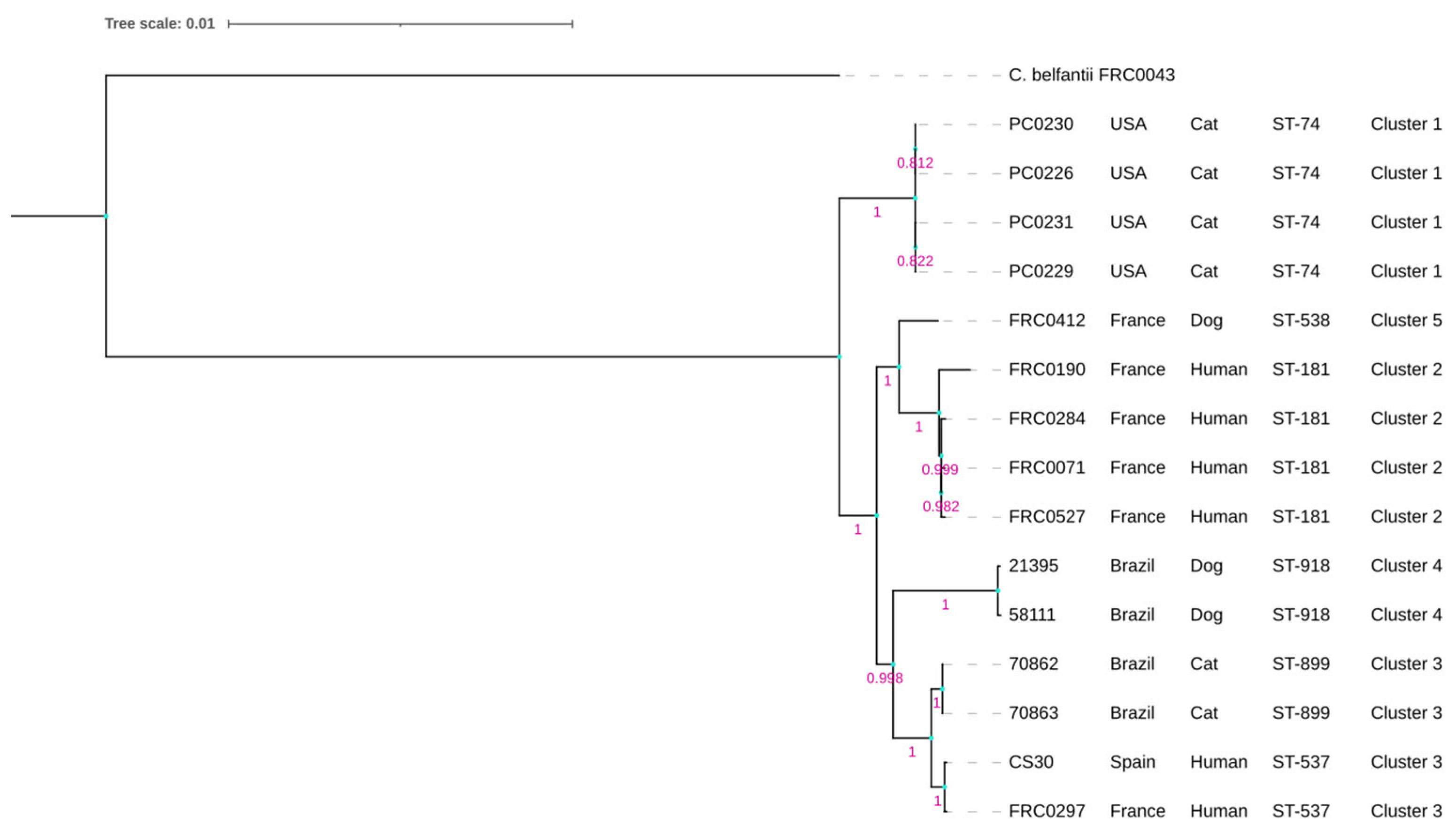
The phylogenetic tree based on the MLST scheme showed two main clades. The first clade contained only the American strains (PC0226, PC0229, PC0230, and PC0231), while the other clade contained the Brazilian, French, and Spanish strains, composed of two main subclades. In the first one, only the French strains were clustered, as FRC0190T, FRC0284, FRC0071, and FRC0527 had more phylogenetic proximity than FRC0412. In the other subclade, we could observe that the Brazilian strains clustered and separated from the French and Spanish strains. However, 70862 and 70863 demonstrated more phylogenetic proximity with the latter than 21395 and 58111 (Figure 1). No phylogenetic difference was observed when constructing the wgMLSTtree (Supplementary Figure S3).
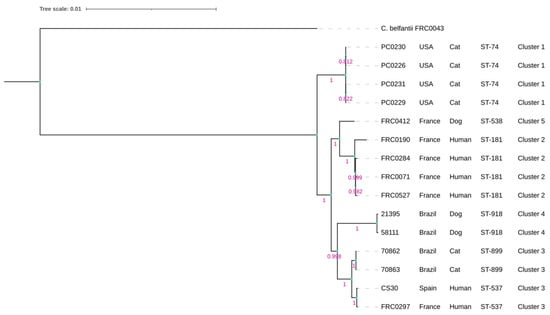
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree based on MLST scheme showing the relationship between all genomes of C. rouxii strains. The tree was built using OrthoFinder pipeline v.2.5.5 and distance was inferred based on neighbor joining (p-distance). Bootstrap values with 1000 replicates. The scale bar indicates 0.01% divergence. C. belfantii FRC0043T was used as an outgroup.
3.2. Prediction of Mobile Genetic Elements, CRISPR-Cas Systems, and Genomic Islands
The analysis performed with PlasmidFinder v.2.1.6 did not detect plasmids in the genomes of any strain, and IntegronFinder v.2.0 did not identify any integrons in the genomes.
Using PHASTER, we predicted 57 prophage regions, which were classified into intact (n = 3), incomplete (n = 46), and questionable (n = 8). Detailed information is presented in Supplementary Table S3. A total of 25 different phages were found. The most common phage was Corynebacterium Poushou, present in 12 strains, followed by Gordonia GMA5 and Rhodococcus Sleepyhead, present in seven and five strains, respectively. Intact prophages were found in the genomes of the 58111, PC0226, and PC0231 strains. After the analysis of ANI values considering all matching regions between intact prophage regions of C. rouxii and the most common phages, we realized that the ANI value between PC0226 and PC0231 was 1.0, and the ANI value between PC0226 and Escherichia phage lato was 0.99, as well as between PC0231 and Escherichia phage lato. On the other hand, 58,111 prophages did not present identity with any of the closest phages detected by PHASTER (Supplementary Figure S4).
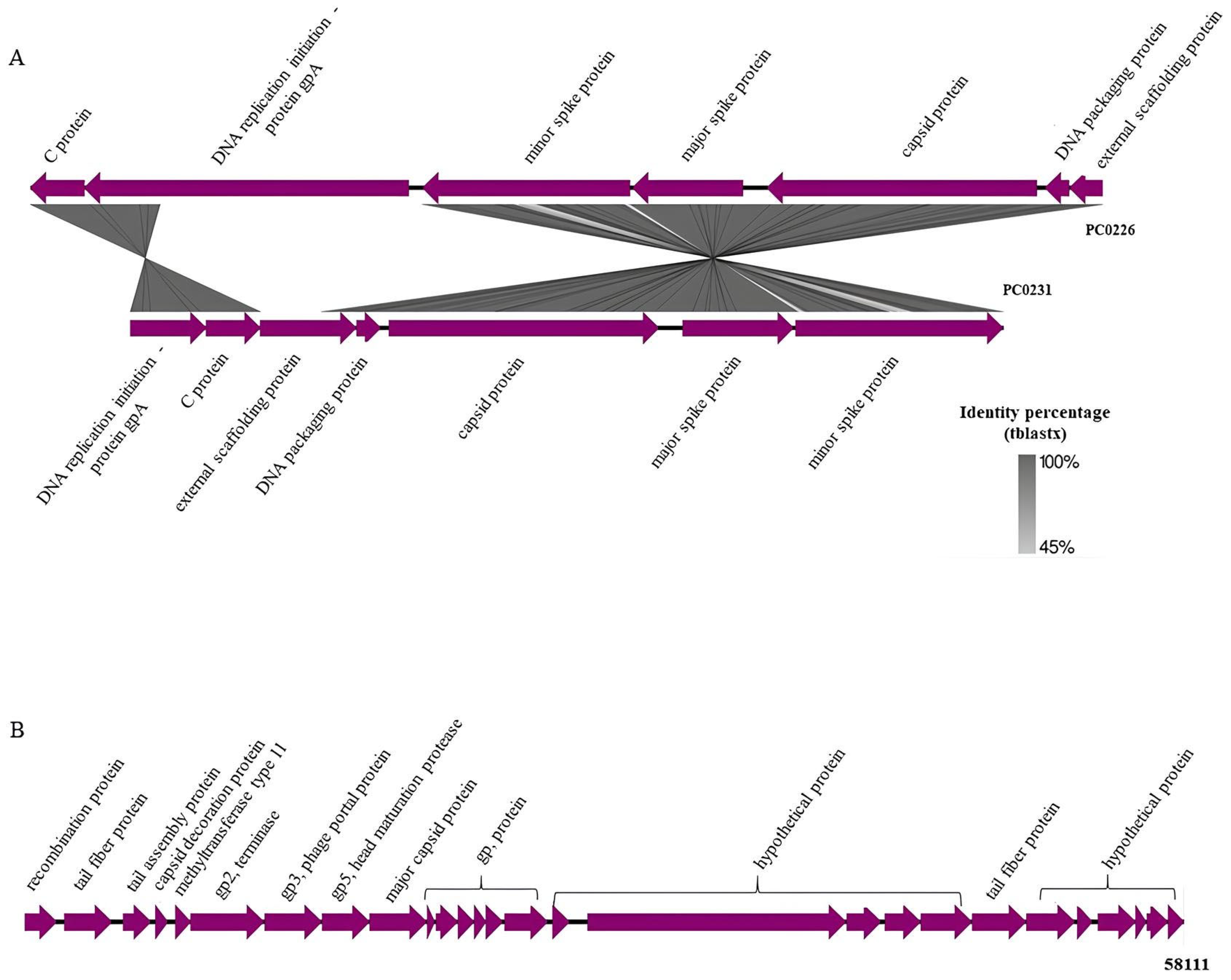
The image generated using the Easyfig application shows the identity between the intact prophages from the PC0226 and PC0231 strains and the similar products of the genes present in these regions, such as C protein, gpA protein, minor and major spike proteins, capsid, DNA packaging, and external scaffolding proteins (Figure 2A). The gpA protein of the PC0231 prophage was found to be translocated and 1179 bases were deleted when compared with the same protein in the PC0226 prophage. On the other hand, the intact prophage from the 58111 strain, more significant than the others, presented the following products in its region: recombination, tail fiber, tail assembly, capsid decoration, phage portal major proteins, besides terminals, head maturation protease, methyltransferase, and some hypothetical proteins (Figure 2B).
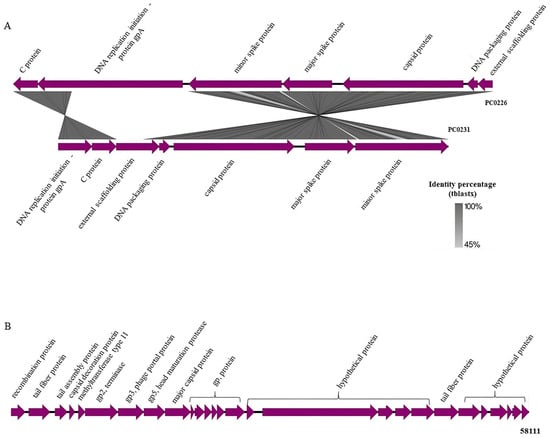
Figure 2.
Intact prophage regions. (A) Comparison between C. rouxii PC0226 and PC0231 strains using Easyfig, and the main products present in each region. The BLAST identity scale is shown on the right with matches ranging from 45% to 100% identity. (B) Products of genes present in C. rouxii 58,111 strain using Easyfig.
The prediction of insertion sequences carried out in ISEScan revealed the following numbers of elements in the genome of each strain: FRC0190T (IS = 33); FRC0071 and FRC0412 (IS = 32); 21395 and 58111 (IS = 30); FRC0284 (IS = 29); 70862 and 70863 (IS = 28); FRC0527 (IS = 27); PC0226 (IS = 26); PC0230, PC0231, and CS30 (IS = 25); and FRC0297 and PC0229 (IS = 24). The IS were grouped into seven families (IS110, IS21, IS256, IS3, IS30, IS5, and ISL3). Information about the number of IS families in each strain is in Supplementary Table S4.
The CRISPRCasFinder server identified the type I-E CRISPR-Cas system, lacking the cas3 gene in all strains. A total of 13 regions related to CRISPR were detected with an evidence level equal to 4 (Supplementary Table S5). FRC0284 and CS30 were the unique strains that did not present a CRISPR system with high precision for spacer repetition and similarity. Analysis of the spacer diversity among all of the CRISPR arrays found 292 spacer sequences, in which the FRC0412 strain carried the largest number of them (70 spacers). The other strains presented the following numbers of sequences: FRC0190T (33 spacers); 21395, 58111, and FRC0071 (29 spacers); FRC0527 (22 spacers); FRC0297 (17 spacers); 70862 and 70863 (16 spacers); PC0226, PC00229, and PC0230 (8 spacers); and PC0231 (7 spacers). All spacers with values above 80% identity from the CRISPRTarget server are presented in Supplementary Table S5.
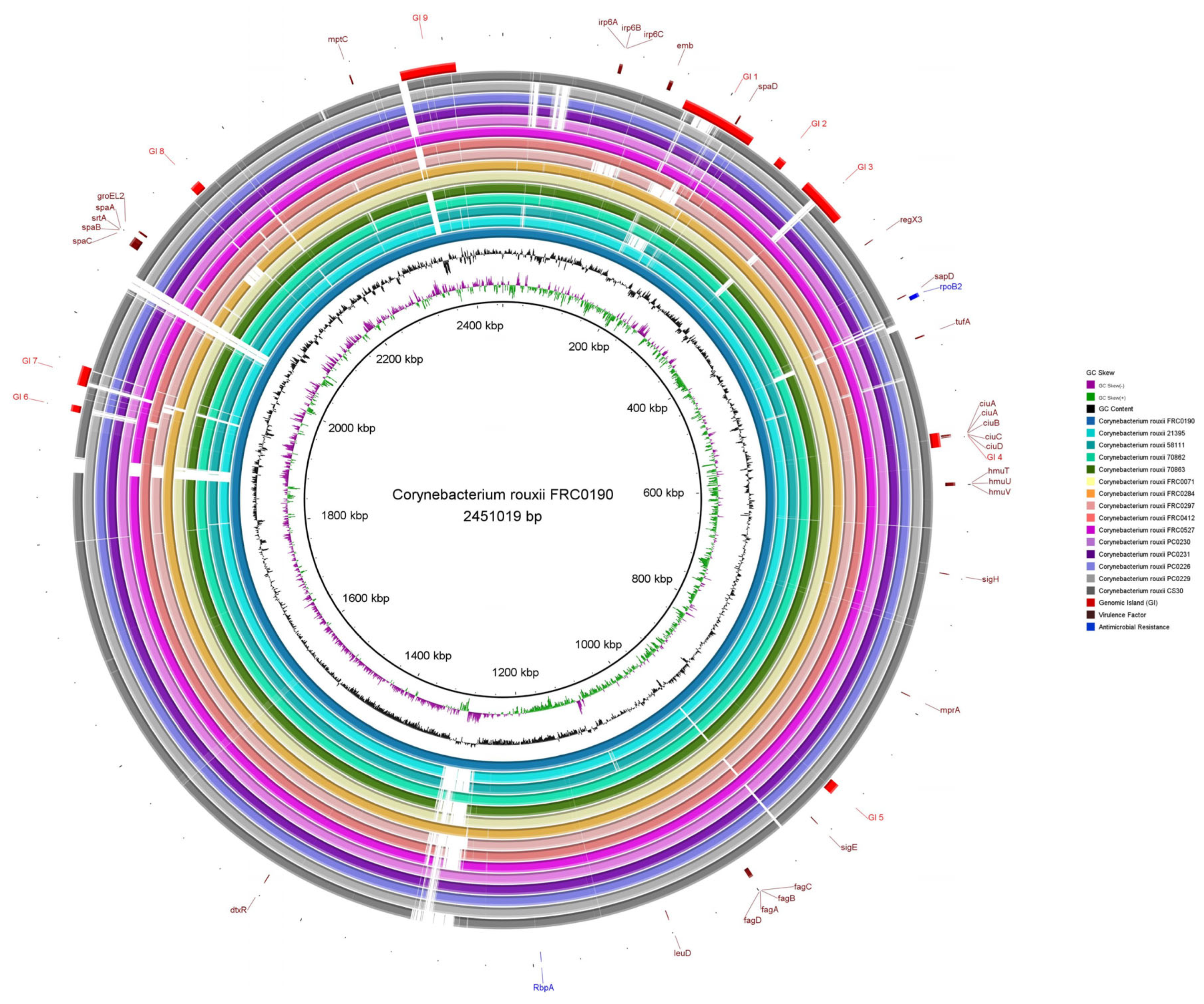
Figure 3 shows the similarity between FRC0190T and the other C. rouxii genomes, providing comparative genomic plasticity results. The GC content was 53.81%. Considering only strong predictions, it was possible to check the presence of nine genomic islands (GI 1–GI 9). We found several genes involved in biological processes: transport (ABC and serine transporter), adherence (spaD-type pili), uptake and translocation of the essential macronutrient phosphorus (phosphate transporter), iron uptake, and the siderophore biosynthesis system (ciuABCD).
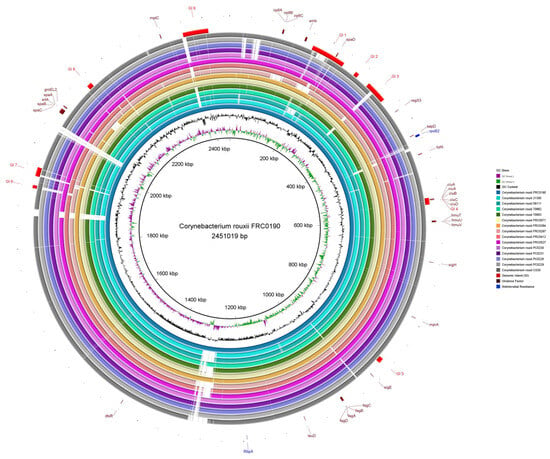
Figure 3.
Circular comparative map of all complete genomes of C. rouxii using BRIG. As a reference genome, we used C. rouxii FRC0190T [10], which is represented in this map in the central position with the first three rings showing its size, GC content, and GC skew. Each outer ring represents the complete genome of one specific strain of C. rouxii. The genomic islands are represented by arcs in red color, the virulence factors by the maroon default, and antimicrobial resistance genes by the blue default.
3.3. Gene Synteny
After multiple alignments between FRC0190T and the other C. rouxii genomes, it was possible to visualize that, although the gene content was conserved inside the blocks, the strains presented rearrangements over large parts of the genome, including inversions and translocations. Some deletion blocks, mainly at the ends of the genomes, were also visible. These results are presented in Supplementary Figure S5.
3.4. Virulence Factors and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
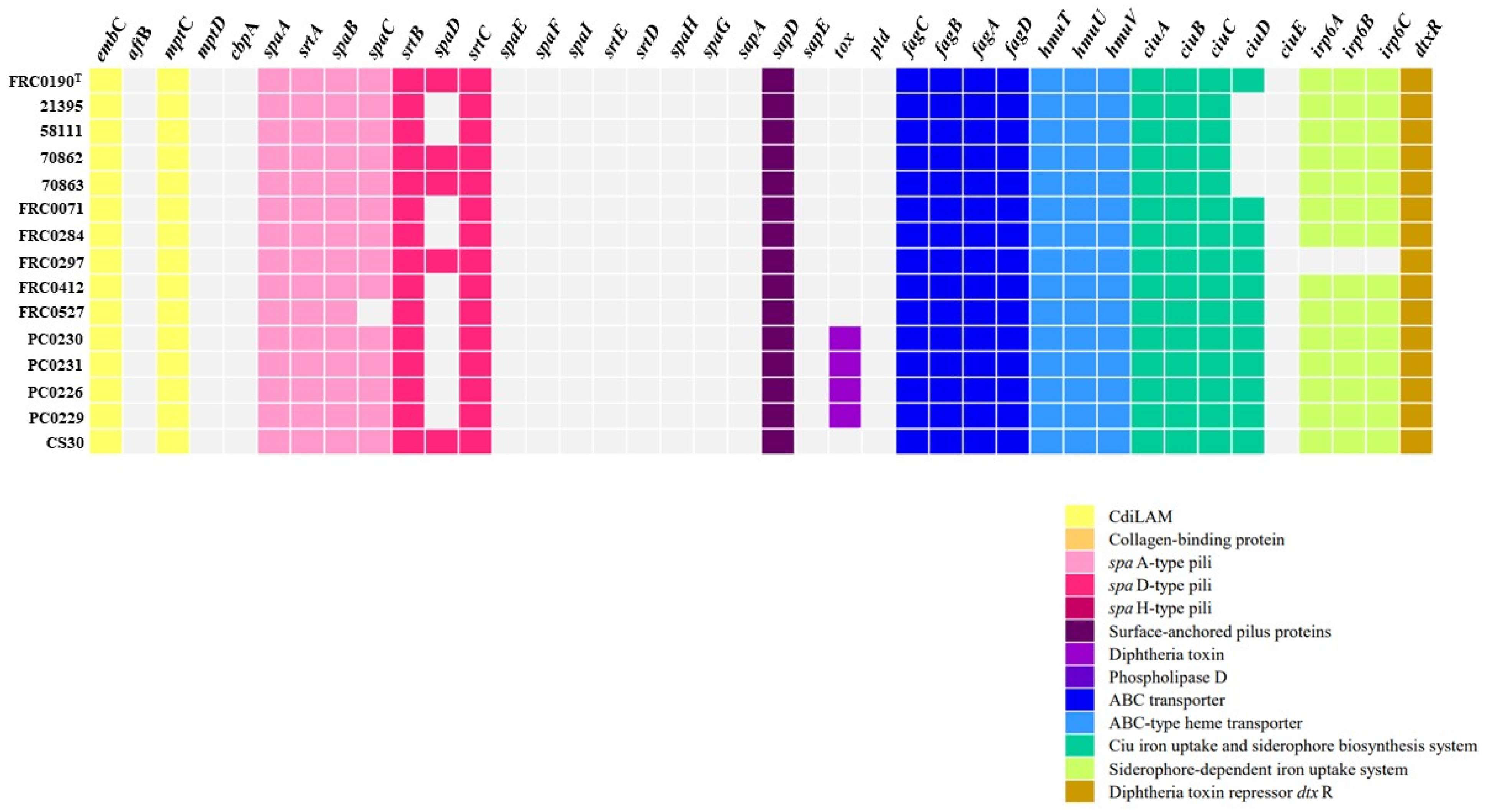
As observed in Figure 4, compared to VFDB reference C. rouxii FRC0190T, the tox gene was identified in four strains (PC0226, PC0229, PC0230, and PC0231), and the sequences of this gene differed from that found in C. diphtheriae, C. pseudotuberculosis, C. silvaticum, and C. ulcerans (Figure 5). Additionally, as shown in Figure 4, in all strains, except the FRC0527 strain, a complete pilus cluster (spaABC) was detected, and in the FRC0190T, 70862, 70863, FRC0297, and CS30 strains, an incomplete spaDEF (only spaD) was detected. In all strains, genes involved in the ABC transporter, ABC-type heme transporter, and Ciu iron uptake systems were detected. All strains, except 21395, 58111, 70862, and 70863, also presented the ciuD gene. FRC0297 was the unique strain in which no gene involved in a siderophore-dependent iron uptake system was detected. Some genes, such as dtxR, embC, and mptC, were also predicted in all strains, including rpoB2 and rbpA.
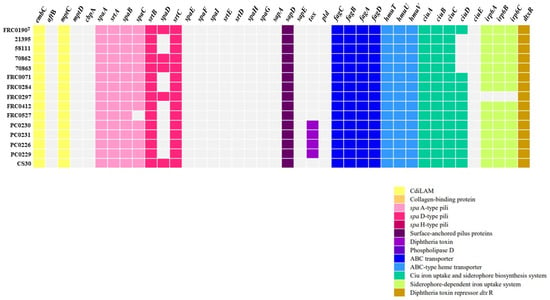
Figure 4.
Distribution of virulence factors in each C. rouxii genomic sequence. For better understanding, virulence factors are grouped into functional classes, represented by a specific color according to the legend.
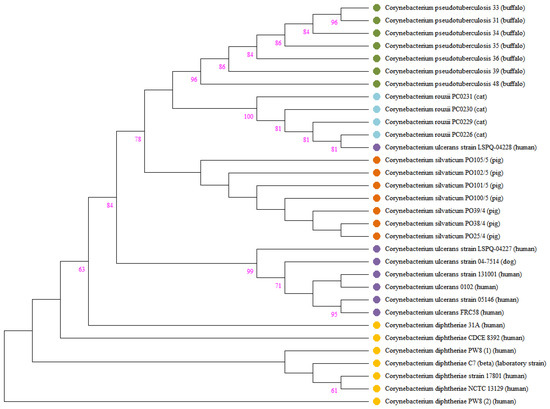
Figure 5.
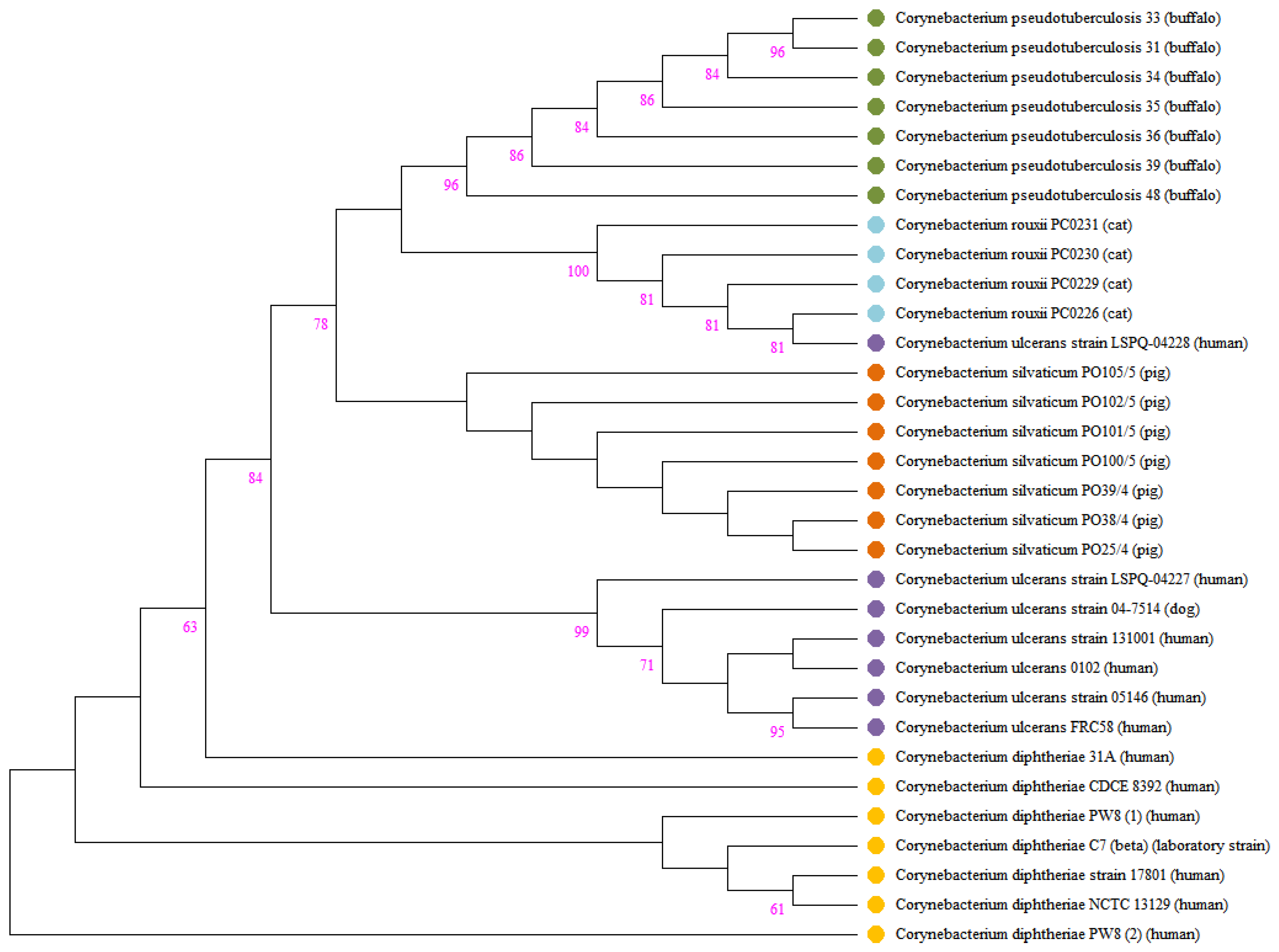
Phylogeny of tox gene from C. rouxii, C. diphteriae, C. pseudotuberculosis, C. silvaticum, and C. ulcerans. The tree was inferred using the maximum likelihood method based on the Tamura 3-parameter model using Mega v6. Bootstrap values with 1000 replicates.
3.5. Pangenome Development and Functional Annotation
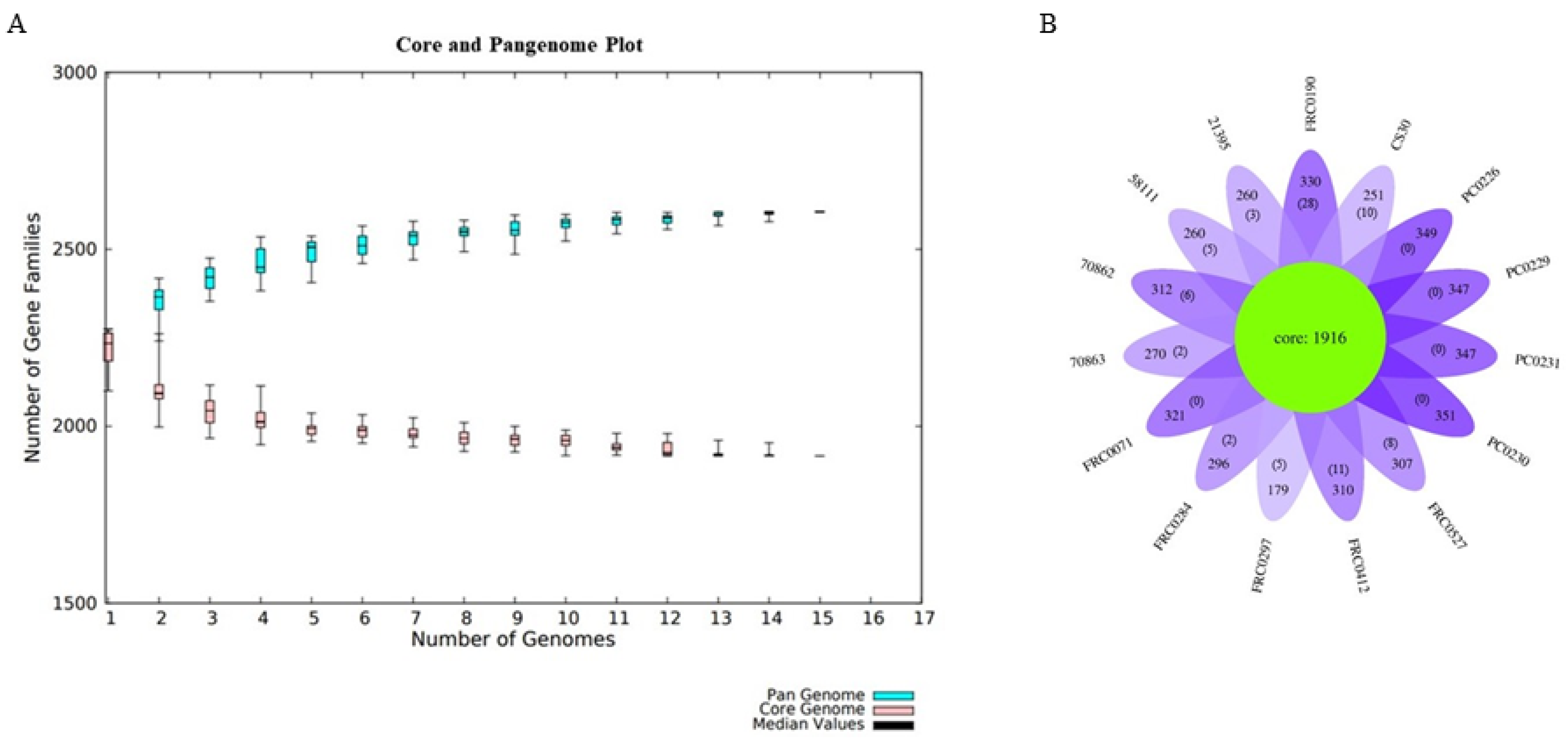
For the pangenome analysis of C. rouxii, we predicted 2606 gene families (Figure 6A), including 1916 in the core genome (73.5%), 610 related to accessory genes (23.4%), and 80 related to unique genes (3.1%). The distribution of accessory and unique genes in each strain is shown in Figure 6B. The α value was less than 1, approximately 0.95 (α = 1 − 0.05).
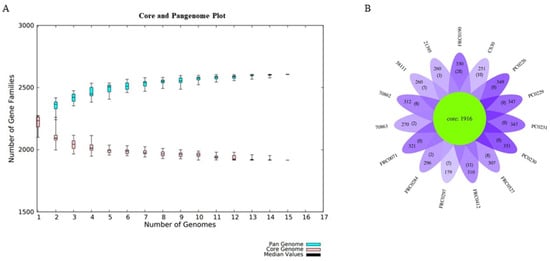
Figure 6.
Pangenome development. (A) Pangenome growth curve with Heap’s law using the BPGA pipeline. The plot shows the number of gene families in the pangenome (blue) and in the core genome (pink). (B) Flower plot diagram of the C. rouxii pangenome generated by R script, showing the core gene families (green). The number of accessory genes for each strain are indicated on each petal and the number of unique genes is in the parentheses.
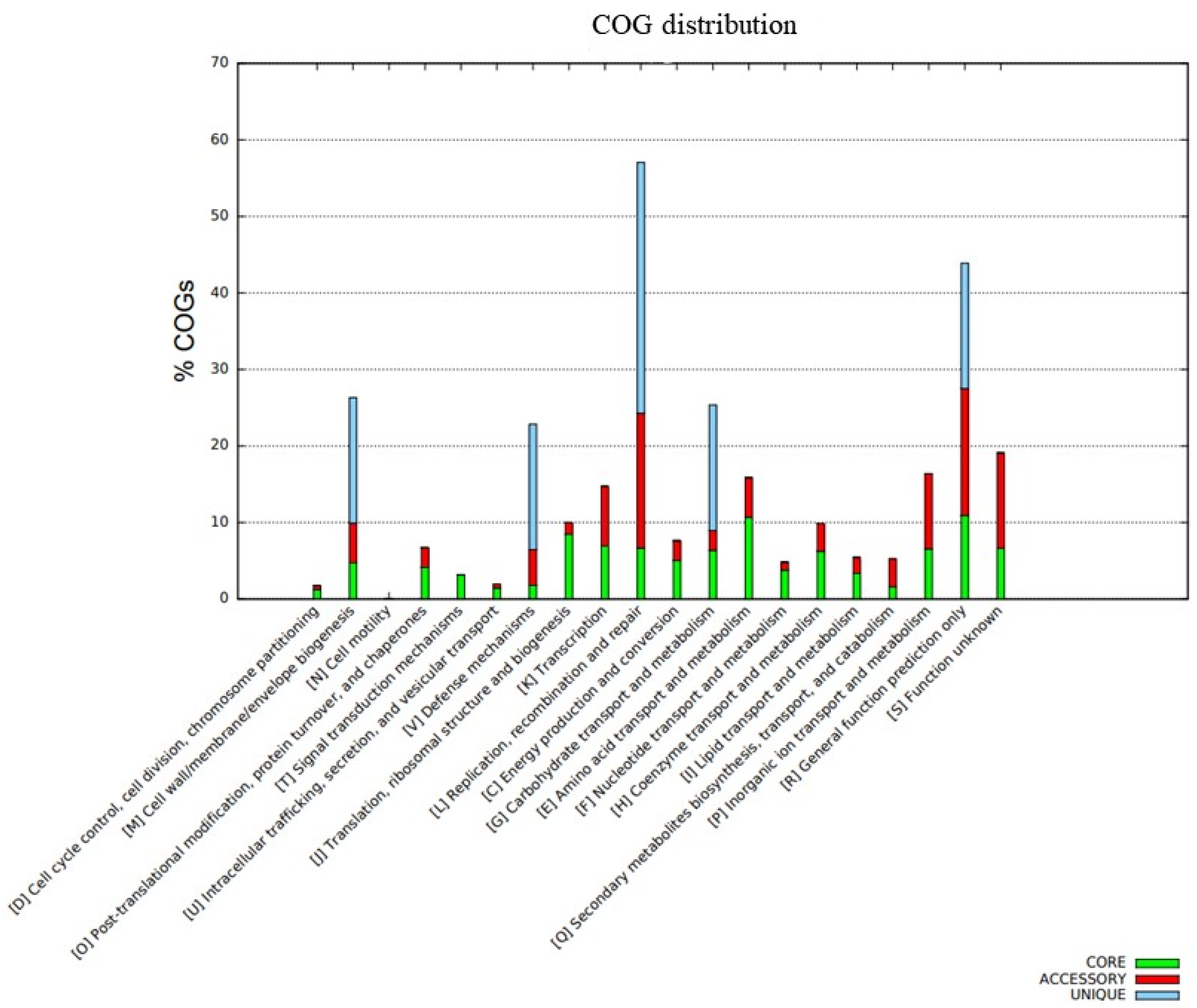
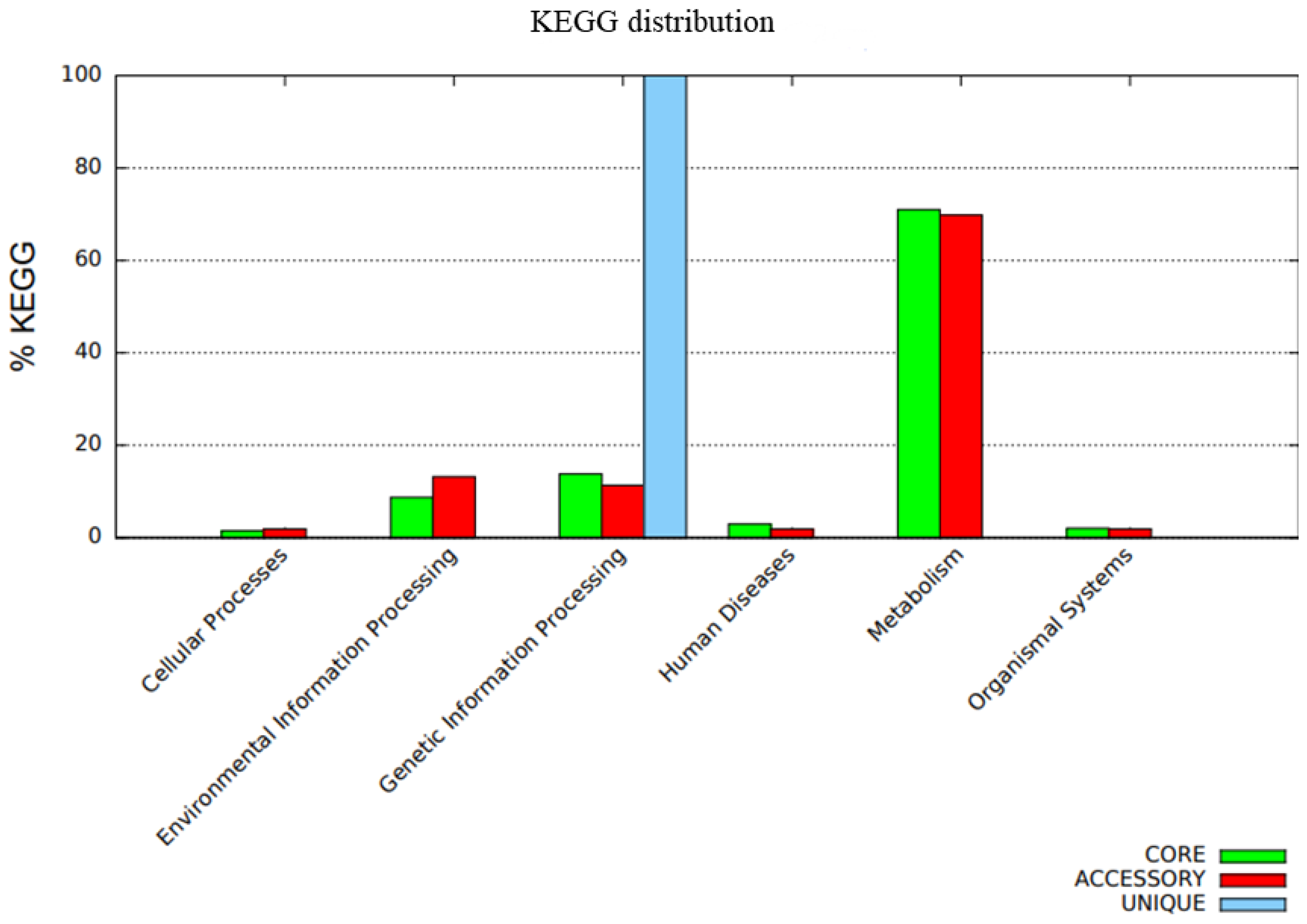
The distribution of COG functional classifications in the pangenome of the C. rouxii strains showed the prevalence of several categories according to the organization of genes into core, accessory, and unique groups (Figure 7). The main COG subcategories in the core genome were amino acid transport and metabolism (10.7%); translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis (8.5%); transcription (7.0%); replication, recombination, and repair (6.7%); and inorganic ion transport and metabolism (6.5%). Accessory genes were mainly related to replication, recombination, and repair (17.6%); inorganic ion transport and metabolism (9.9%); transcription (7.8%); amino acid transport and metabolism (5.2%); and cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis (5.2%). On the other hand, unique genes were mainly involved in replication, recombination, and repair (34.0%); defense mechanisms (16.5%); carbohydrate transport and metabolism (16.5%); and cell wall/membrane/envelope biogenesis (16.5%). A total of 204 genes presented function unknown, comprising 128 genes (6.7%) in the core genome and 76 genes (12.4%) in accessory genes (Figure 7). The functional annotation of KEGG is shown in Figure 8.
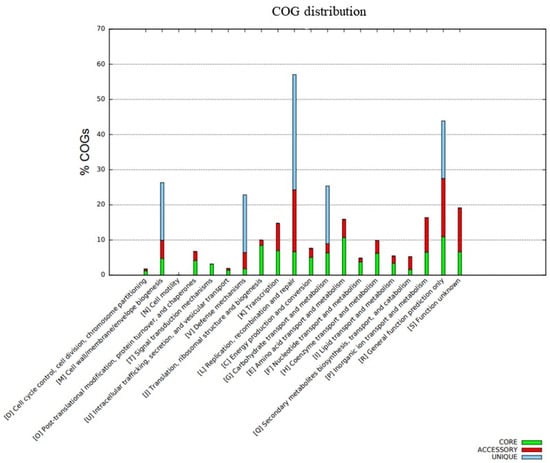
Figure 7.
Function annotation using the BPGA pipeline in which the bar graph represents the COG classifications of the pangenome. The core genome is represented by the green color, the accessory genome is represented by the red color, and unique genes are represented by the blue color.
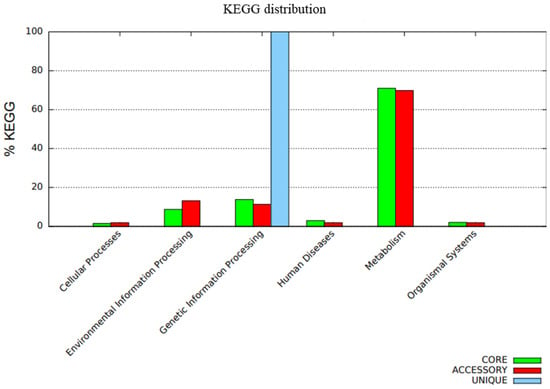
Figure 8.
Functional annotation using the BPGA pipeline in which the bar graph represents the KEGG classifications of the pangenome. The core genome is represented by the green color, the accessory genome is represented by the red color, and unique genes are represented by the blue color.
4. Discussion
In recent years, taxonomic analysis based on the genome of C. diphtheriae strains led to the description of the novel species C. belfantii and C. rouxii [8,10]. Until now, C. rouxii has been found to cause different infections in humans, dogs, and cats [9,10,11,12,13,14]. Although the potential to infect other host species and to produce DT is a matter of concern, few studies in the literature have focused on the virulence factors, mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance, and metabolic pathways of this species. In this sense, we performed the first pangenomic analysis of this species, providing valuable insight into its pathogenicity, evolution, and diversity.
Additionally, to ensure the quality of data, the 15 strains for which their genomes were deposited in the NCBI and ENA databases were first confirmed based on dDDH and ANI values, which were consistent with values above the proposed cut-off points for species limit, corroborating identification of the strains as C. rouxii. Considering the need to obtain epidemiological data on this emerging pathogen, we also submitted the genomes to molecular typing, clustering, and phylogenetic analysis.
MLST has been widely used in different countries for genotyping circulating C. diphtheriae and C. ulcerans strains and in investigations of diphtheria outbreaks [44,45,46]. With the description of novel species of the C. diphtheriae complex, the MLST scheme has also been applied to typing the isolates of these species. In our analyses, six STs could be attributed to the C. rouxii strains. More than one ST was attributed to isolates from each host species (human, cat, and dog), showing a certain genetic diversity. No ST was found simultaneously in animal and human isolates. Moreover, ST-537 was found in two European countries, France and Spain, which alerts for a possible circulation of this ST in these countries.
Classical MLST is typically based on sequences from only seven housekeeping genes; hence, this approach does not fully exploit core and accessory genomic variation. It cannot further discriminate genetically related isolates within STs [17,47]. Thus, we also performed a population analysis and clustering with PopPUNK software. In addition, we constructed a phylogenetic tree based on wgMLST to investigate the genetic diversity between our isolates and compare MLST and PopPUNK results. All of the analyses showed the genetic diversity of C. rouxii. Although MLST and PopPUNK provided similar results, the phylogenetic analysis revealed the little greater discriminatory power and typeability of MLST. Further studies, including more isolates, should be performed to confirm this divergence. As expected, wgMLST was the optimal method for molecular subtyping C. rouxii isolates. Considering that whole genome sequencing is not accessible in many countries, MLST appears to be a satisfactory alternative tool for epidemiological studies involving this species.
It is known that bacterial adaptive evolution relies on the diversity of gene repertories of the species, which can be affected through a variety of processes, including horizontal gene transfer (HGT). In addition to gene acquisition, HGT can result in events of rearrangement and deletions, leading to remarkable changes in the genome over relatively short periods. HGT is one of the main processes responsible for acquiring virulence factors and antibiotic resistance, and it may change the pathogenic profile of bacterial species [48,49,50]. Thus, the 15 genomes used in this study were analyzed regarding the occurrence of gene duplication, rearrangements, and deletions and the presence of mobile elements, including insertion sequences and genomic islands. Verifying several rearrangement events, including inversions, translocations, and deletions, was possible.
It is known that plasmids can be responsible for conferring a selective advantage to bacteria, such as antimicrobial resistance or virulence genes [51]. This can drastically change the prevalence of bacterial clones that are more virulent or multidrug-resistant, facilitating their rapid evolution and adaptation abilities [52]. Although plasmids were not detected in any C. rouxii strain in the present work, they were previously reported in C. diphtheriae strains, including a 14.4 kb plasmid, pNG2, which, despite not having any important function in toxicity, can encode erythromycin resistance [53,54]. More recently, a multi-resistance plasmid (pLRPD) carrying genes related to penicillin (pbp2m, blaB), sulfamethoxazole (sul1), trimethoprim (dfrA16), erythromycin (erm), and tetracycline resistance (tetA family tet(Z)-like) was also predicted in C. diphtheriae [55].
Moreover, our analyses did not identify any integron in the C. rouxii genomes. Integrons are genetic elements that capture and incorporate gene cassettes by site-specific recombination, converting them into functional genes. They are composed of genes for integrase (int) and an adjacent recombination site (attI). Gene cassettes are not necessarily part of an integron but can be incorporated [56]. The same result was obtained in a previous study evaluating the antimicrobial resistance in C. pseudotuberculosis, and no integron was identified [57]. Differently, a recent study detected in C. diphtheriae an integron flanked by two insertion sequences (IS6100 and IS1628), comprising genes involved in the resistance to trimethoprim (dfrA16), sulfamethoxazole (sul1), chloramphenicol (cmlA), and aminoglycosides (aad1) [58]. A class 1 integron mobilized by IS6100 and carrying some of these genes (dfrA16, sul1) had already been identified in the genome of a C. diphtheriae strain [59]. Interestingly, in the pLRPD of C. diphtheriae, some of the antimicrobial resistance genes (dfrA16, sul1) were found in a truncated class 1 integron [55].
The genome of C. diphtheriae complex strains has been characterized by presenting several prophages that are an essential source of genomic plasticity in these species [60]. We identified many incomplete prophage sequences, probably due to the draft or reads sequence status of the genome data retrieved from a public database. On the other hand, we predicted two intact prophages in the 58111, PC0226, and PC0231 strains. The GC content of these prophage sequences was less than the average GC content of 53.0% of C. rouxii genomes, except for the 58111 strain.
The Corynebacterium phage phi673 (GenBank accession number NC042354), predicted in the 58111 strain, belongs to the Siphoviridae family, and was first found as a lytic phage in C. glutamicum ATCC 13,032 [61]. The prophage Entero lato (Escherichia phage phiX174; GenBank accession number J02482.1), found in the PC0226 and PC0231 strains, belongs to the Microviridae family and has a long history of use in several molecular applications [62]. It is commonly found infecting Escherichia coli but was also previously reported in ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates. Since our analyses did not show the presence of prophage-encoding resistance and virulence genes, it seems that they are not acting as vectors for disseminating these genes within our strains.
Insertion sequences (IS) are simple and small mobile genetic elements found in most bacterial genomes. A particular bacterial genome can present different types of IS in a wide range of copy numbers. They can move within the genome and be horizontally transferred as part of other mobile elements, such as phages and plasmids, and they can affect the genome structure and gene expression [63,64,65]. Presently, seven IS families were found in C. rouxii genomes (IS110, IS21, IS256, IS3, IS30, IS5 and ISL3). Among those, IS3, one of the largest IS families widely distributed in nature [66], had the highest number of copies in the C. rouxii strains. All IS families in our strains were reported previously in Corynebacterium striatum isolates [63,66]. In this species, IS110, IS30, IS21, and especially IS3 and IS256 families were associated with antimicrobial resistance [63,66]. The association of IS families with antimicrobial resistance was also verified for other Corynebacterium species, including C. diphtheriae (IS3) and Corynebacterium jeikeium (IS3 and IS256) [66].
Genomic islands are part of the flexible bacterial gene pool that harbors genes derived from mobile elements. They often carry gene clusters with specific functions that can provide a selective advantage to the microorganism. For instance, some genomic islands encode iron-uptake systems, while others carry genes encoding antimicrobial resistance or virulence factors [49]. We investigated the presence and composition of genomic islands in the C. rouxii strains. In the nine genomic islands predicted, several genes were found, including those encoding phage integrases and transposases, in addition to genes involved in acquiring and transporting nutrients and adherence. However, no gene related to antimicrobial resistance was found. These results suggest that genomic islands in C. rouxii, to date, can contribute to establishing and disseminating this bacterial species in the environment or a host. Still, they are not related to antimicrobial resistance.
CRISPR-Cas is an essential adaptive immune system that helps bacteria and archaea cells not to be infected by phages, viruses, and other foreign genetic elements [67]. This system comprises a CRISPR cluster containing an array of short, direct repeats interspersed with spacer sequences and CRISPR-associated genes (cas) [68]. In this study, we found the type I-E CRISPR-Cas system in all strains. CRISPR-Cas systems, especially type I-E, have been reported in Corynebacterium species, including those belonging to the C. diphtheriae complex. In C. diphtheriae strains, besides type I-E CRISPR-Cas, types II and III have already been detected and reported [69]. Using the CRISPRTarget server, the spacer sequences of the strains matched most frequently with corynebacterial (C. diphtheriae and C. ulcerans), Rhodococcus phages, and Corynebacterium phage BFK20, present in the pathogenicity island of C. pseudotuberculosis isolated from buffalo [70]. Some spacers also matched with other phages found in Staphylococcus phage phi7401PVL and Pseudomonas mendocina S5.2.
The production of DT after lysogenization by corynebacteriophages that harbor the tox gene has already been verified in the species C. diphtheriae, C. ulcerans, and C. pseudotuberculosis [71]. For the other species forming the C. diphtheriae complex, there is a consideration that they are potentially toxigenic. To date, no study has demonstrated the presence of the tox gene in C. rouxii genomes. In our study, we detected the presence of this important gene in four strains (PC0226, PC0229, PC0230, and PC0231), all isolated from animal hosts. The sequence of the tox gene was similar in all isolates and differed from that found in C. diphtheriae, C. pseudotuberculosis, C. silvaticum, and C. ulcerans. In agreement with a previous study, the tox genes isolated from C. diphtheriae strains had more phylogenetic proximity with those isolated from C. ulcerans [70]. In contrast, in our research, the tox genes isolated from C. rouxii had more phylogenetic proximity with C. pseudotuberculosis and C. silvaticum. Notification of potentially toxigenic corynebacteria in animals is not mandatory in most countries; thus, epidemiological data are scarce [72]. However, the presence of the tox gene in these species, which are already isolated from humans and animals, may advise about the risk of dissemination of diphtheria.
In the present study, we detected several virulence factors for which their importance has already been demonstrated in previous studies with C. diphtheriae and other species. The embC and mptC genes were identified in all genomes and are related to CdiLAM, which is responsible for forming the characteristic cell envelope in C. diphtheriae strains [73]. The gene cluster spaABC was detected in all strains, encoding the pili SpaA, which is relevant in the adherence to pharyngeal epithelial cells [74]. The surface-anchored pilus protein spaD, involved in adherence, was found in only the FRC0190T, 70862, 70863, FRC0297, and CS30 strains.
Several systems have been related to iron acquisition in C. diphtheriae and related species, including the fagABC operon, which is associated with the fagD gene [75], the irp6 operon (irp6ABC) [76], and the ciu gene cluster, formed by the genes ciuA, ciuB, ciuC, ciuD, and ciuE [77]. Our data revealed the presence of the fagABC operon in all C. rouxii strains. The irp6 operon was not detected in the FRC0297 genome, ciuD in the Brazilian strains 21395, 58111, 70862, and 70863, as well as ciuE, which was absent in all strains. The absence of these genes may reduce siderophore production and iron uptake.
The iron acquisition from hemin by C. diphtheriae requires the ABC-type hemin transporter, HmuTUV, and three hemin-binding proteins (HtaA, HtaB, and HtaC) [78,79]. Unlike previously observations for C. diphtheriae [80], in the present study, only the hmuTUV cluster was detected entirely in all genomes, suggesting a decreased ability to use hemin as the sole iron source. We detected the dtxR gene in all strains, which encodes DtxR, a protein involved in the regulation of DT expression and the synthesis and production of siderophore, besides regulating some other promoters [81]. In addition, DtxR and iron regulate a complex network of genes involved in iron metabolism, including the operon irp6 and the ciu gene cluster [82].
As presented in Figure 3, the genes rbpA and rpoB2, previously associated with rifampin resistance [55,83,84,85,86], were predicted in all genomes. However, additional studies are needed to demonstrate how this resistance occurs in Corynebacterium species.
Across the 15 genomes, we identified a pangenome composed of 2606 gene families, of which 1916 were in the core genome, 610 were in the accessory genome, and 80 were related to unique genes. When α < 1.0, the pangenome is considered open, which means its size will continuously increase when adding new genomes. In contrast, when α > 1, the pangenome is considered closed, meaning that no substantial number of extra genes can be added to the pangenome [87,88]. Our analysis found an alpha value less than 1 (0.95), indicating an open pangenome near to being closed as genes are added. Moreover, there was considerable variation in the number of unique genes, where some strains had more genes, being more variable than others. For example, FRC0190T had 28 unique genes, while PC0226, PC0229, PC0230, and PC0231 did not have any exclusive genes. It is important to emphasize that the number of genomes in this study was not large, and the composition of the pangenome can change as more genomes are sequenced. Since the first description of the C. rouxii strain in 2020, a relatively small number of genomes of this species has been sequenced thus far compared to other related ones belonging to the C. diphtheriae complex. So, when comparing the C. rouxii and C. silvaticum pangenomes, we noticed that they had similar alpha values, in which some studies have shown values between 0.95 and 0.97 for the latter species [84,89]. Moreover, core genome and singleton analyses agreed with this clonal-like behavior in other complex species. They can also be inferred from pangenome data, in which C. pseudotuberculosis, C. ulcerans, and C. diphtheriae had alpha values of 0.89, 0.81, and 0.69, with pangenomes composed of 54%, 40%, and 34% core genes families, respectively [89,90,91].
The distribution of COG showed a high percentage of genes related to replication, recombination, repair, transcription, and amino acid transport and metabolism in the core and accessory genomes of the C. rouxii pangenome. This finding was similar to the results reported for the C. silvaticum and C. ulcerans core genomes [91]. However, regarding the accessory genome in C. ulcerans, most genes were involved in translation, ribosomal structure, and biogenesis; lipid and inorganic ion transport and metabolism; and post-translational modification, protein turnover, and chaperones. Most of the differences were found when the C. rouxii and C. diphtheriae core genomes were compared, mainly because the latter was composed of genes related to the cell wall, membrane, and envelope biogenesis; carbohydrate transport and metabolism; and nucleotide transport and metabolism [92]. Regarding the accessory genome in C. diphtheriae, genes were mainly involved in transporting and metabolizing carbohydrates, lipids, and inorganic ions [93].
These findings are relevant for future studies focusing on the search for resistance and virulence genes. They contribute to different areas, including vaccinology and epidemiology. However, they should be corroborated through in vitro and in vivo experimentation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/bacteria3020007/s1, Table S1: DDH in silico results obtained by the Type Strain Genome Server for C. rouxii strains compared to the closest related type strain; Table S2: Information about the Multilocus Sequence Typing for C. rouxii strains; Table S3: Information about the prophage regions found in the C. rouxii genomes; Table S4: Number of predicted IS families in each C. rouxii strain; Table S5: Hits found to spacer sequences in the CRISPRTarget databases; Figure S1: Heatmap representing the ANI percentage nucleotide identity of all matching regions between C. rouxii genomes using PyANI v.0.2.12.; Figure S2: Clusters of C. rouxii strain genomes generated using PopPUNK v.2.6.0; Figure S3: The wgMLST tree based on genomes from C. rouxii strains using PGAdb-builder; Figure S4: Heatmap representing the ANI percentage nucleotide identity of all matching regions between intact prophage regions of C. rouxii and the most common phages using PyANI v.0.2.12; Figure S5: Gene synteny analysis using the software Mauve.
Author Contributions
Study design, analysis and interpretation of data, and article writing: F.D.P. Study design and acquisition of data: M.R.B.A. Assembling of genomes and annotation: E.G.S. Analysis and interpretation of data: J.N.R. and M.V.C.V. Critical appraisal and article review: S.d.C.S. and L.S.d.S. Conception and design of the study, acquisition of data, analysis, and interpretation of data: V.A.d.C.A. All authors reviewed the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro (E-26/202.088/2020) and by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (88887.830701/2023-00).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Genome sequences are available in the NCBI and ENA database according to BioSample numbers shown in Table 1.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sharma, N.C.; Efstratiou, A.; Mokrousov, I.; Mutreja, A.; Das, B.; Ramamurthy, T. Diphtheria. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 81, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista Araújo, M.R.; Bernardes Sousa, M.Â.; Seabra, L.F.; Caldeira, L.A.; Faria, C.D.; Bokermann, S.; Sant’Anna, L.O.; Dos Santos, L.S.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L. Cutaneous infection by non-diphtheria-toxin producing and penicillin-resistant Corynebacterium diphtheriae strain in a patient with diabetes mellitus. Access Microbiol. 2021, 3, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.R.B.; Ramos, J.N.; de Oliveira Sant’Anna, L.; Bokermann, S.; Santos, M.B.N.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L.; Azevedo, V.; Prates, F.D.; Rodrigues, D.L.N.; Aburjaile, F.F.; et al. Phenotypic and molecular characterization and complete genome sequence of a Corynebacterium diphtheriae strain isolated from cutaneous infection in an immunized individual. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 54, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.S.; Sant’Anna, L.O.; Ramos, J.N.; Ladeira, E.M.; Stavracakis-Peixoto, R.; Borges, L.L.G.; Santos, C.S.; Napoleão, F.; Camello, T.C.F.; Pereira, G.A. Diphtheria outbreak in Maranhão, Brazil: Microbiological, clinical and epidemiological aspects. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badenschier, F.; Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; Sprenger, A.; Hobmaier, B.; Sievers, C.; Prins, H.; Dorre, A.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Kulper-Schiek, W.; et al. Outbreak of imported diphtheria with Corynebacterium diphtheriae among migrants arriving in Germany, 2022. Eurosurveillance 2022, 27, 2200849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.S.; White, J.M.; Crowcroft, N.S.; De Martin, S.; Mann, G.; Efstratiou, A. Diphtheria in the United Kingdom, 1986–2008: The increasing role of Corynebacterium ulcerans. Epidemiol. Infect. 2010, 138, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangel, A.; Berger, A.; Rau, J.; Eisenberg, T.; Kämpfer, P.; Margos, G.; Contzen, M.; Busse, H.J.; Konrad, R.; Peters, M.; et al. Corynebacterium silvaticum sp. nov., a unique group of NTTB corynebacteria in wild boar and roe deer. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2020, 70, 3614–3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dazas, M.; Badell, E.; Carmi-Leroy, A.; Criscuolo, A.; Brisse, S. Taxonomic status of Corynebacterium diphtheriae biovar Belfanti and proposal of Corynebacterium belfantii sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 3826–3831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, A.J.; Cassiday, P.K.; Bernard, K.A.; Bolt, F.; Steigerwalt, A.G.; Bixler, D.; Pawloski, L.C.; Whitney, A.M.; Iwaki, M.; Baldwin, A.; et al. Novel Corynebacterium diphtheriae in Domestic Cats. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badell, E.; Hennart, M.; Rodrigues, C.; Passet, V.; Dazas, M.; Panunzi, L.; Bouchez, V.; Carmi-Leroy, A.; Toubiana, J.; Brisse, S. Corynebacterium rouxii sp. nov., a novel member of the diphtheriae species complex. Res. Microbiol. 2020, 171, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, R.; Rincon, L.; Weigand, M.R.; Xiaoli, L.; Acosta, A.M.; Kurien, D.; Ju, H.; Lingsweiler, S.; Prot, E.Y. Toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae Infection in Cat, Texas, USA. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2022, 28, 1686–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlez, K.; Eisenberg, T.; Rau, J.; Dubielzig, S.; Kornmayer, M.; Wolf, G.; Berger, A.; Dangel, A.; Hoffmann, C.; Ewers, C.; et al. Corynebacterium rouxii, a recently described member of the C. diphtheriae group isolated from three dogs with ulcerative skin lesions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2021, 114, 1361–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefer, A.; Pampaka, D.; Herrera-León, S.; Peiró, S.; Varona, S.; López-Perea, N.; Masacalles, J.; Herrera-León, L. Molecular and Epidemiological Characterization of Toxigenic and Nontoxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Corynebacterium belfantii, Corynebacterium rouxii, and Corynebacterium ulcerans Isolates Identified in Spain from 2014 to 2019. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.N.; Araújo, M.R.B.; Baio, P.V.P.; Sant’Anna, L.O.; Veras, J.F.C.; Vieira, É.M.D.; Sousa, M.A.B.; Camargo, C.H.; Sacchi, C.T.; Campos, K.R.; et al. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic analysis of the first Corynebacterium rouxii strains isolated in Brazil: A recent member of Corynebacterium diphtheriae complex. BMC Genom. Data 2023, 24, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Araya, E.; Muñoz, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Paredes-Sabja, D. FastMLST: A Multi-core Tool for Multilocus Sequence Typing of Draft Genome Assemblies. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2021, 15, 117793222110592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, J.A.; Harris, S.R.; Tonkin-Hill, G.; Gladstone, R.A.; Lo, S.W.; Weiser, J.N.; Corander, J.; Bentley, S.D.; Croucher, N.J. Fast and flexible bacterial genomic epidemiology with PopPUNK. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 304–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A Software Environment for Integrated Models of Biomolecular Interaction Networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K. MAFFT: A novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3059–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.-Y.; Chiou, C.-S.; Chen, C.-C. PGAdb-builder: A web service tool for creating pan-genome allele database for molecular fine typing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; García-Fernández, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Hasman, H. In Silico Detection and Typing of Plasmids using PlasmidFinder and Plasmid Multilocus Sequence Typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Néron, B.; Littner, E.; Haudiquet, M.; Perrin, A.; Cury, J.; Rocha, E. IntegronFinder 2.0: Identification and Analysis of Integrons across Bacteria, with a Focus on Antibiotic Resistance in Klebsiella. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, D.; Grant, J.R.; Marcu, A.; Sajed, T.; Pon, A.; Liang, Y.; Wishart, D.S. PHASTER: A better, faster version of the PHAST phage search tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W16–W21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: A better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, M.J.; Petty, N.K.; Beatson, S.A. Easyfig: A genome comparison visualizer. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1009–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Tang, H. ISEScan: Automated identification of insertion sequence elements in prokaryotic genomes. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3340–3347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couvin, D.; Bernheim, A.; Toffano-Nioche, C.; Touchon, M.; Michalik, J.; Néron, B.; Rocha, E.P.C.; Vergnaud, G.; Gautheret, D.; Pourcel, C. CRISPRCasFinder, an update of CRISRFinder, includes a portable version, enhanced performance and integrates search for Cas proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W246–W251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, K.S.; Koonin, E.V. Annotation and Classification of CRISPR-Cas Systems. In CRISPR. Methods in Molecular Biology; Lundgre, M., Charpentier, E., Fineran, P., Eds.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, A.; Gagnon, J.N.; Brouns, S.J.J.; Fineran, P.C.; Brown, C.M. CRISPRTarget. RNA Biol. 2013, 10, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangal, V.; Fineran, P.C.; Hoskisson, P.A. Novel configurations of type I and II CRISPR–Cas systems in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Microbiology 2013, 159 Pt 10, 2118–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.C.; Geyik, H.; Ramos, R.T.J.; de Sá, P.H.C.G.; Barbosa, E.G.V.; Baumbach, J.; Figueiredo, H.C.P.; Miyoshi, A.; Tauch, A.; Silva, A.; et al. GIPSy: Genomic island prediction software. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 232, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vertès, A.A.; Inui, M.; Yukawa, H. Postgenomic Approaches to Using Corynebacteria as Biocatalysts. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 66, 521–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.-F.; Petty, N.K.; Ben Zakour, N.L.; Beatson, S.A. BLAST Ring Image Generator (BRIG): Simple prokaryote genome comparisons. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J. eggNOG-mapper v2: Functional Annotation, Orthology Assignments, and Domain Prediction at the Metagenomic Scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darling, A.C.E.; Mau, B.; Blattner, F.R.; Perna, N.T. Mauve: Multiple Alignment of Conserved Genomic Sequence with Rearrangements. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zheng, D.; Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Yang, J. VFDB 2022: A general classification scheme for bacterial virulence factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D912–D917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, D.L.N.; Ariute, J.C.; Rodrigues da Costa, F.M.; Benko-Iseppon, A.M.; Barh, D.; Azevedo, V.; Aburjaile, F. PanViTa: Pan Virulence and resisTance analysis. Front. Bioinform. 2023, 3, 1070406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, N.M.; Gupta, V.K.; Dutta, C. BPGA- an ultra-fast pan-genome analysis pipeline. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Wolf, Y.I.; Makarova, K.S.; Vera Alvarez, R.; Landsman, D.; Koonin, E.V. COG database update: Focus on microbial diversity, model organisms, and widespread pathogens. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D274–D281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Gene Ontology Consortium. Gene Ontology Consortium: Going forward. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D1049–D1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Tanabe, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways, diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D353–D361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galperin, M.Y.; Makarova, K.S.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Expanded microbial genome coverage and improved protein family annotation in the COG database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D261–D269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, V.V.; Ramos, J.N.; dos Santos, L.S.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L. Corynebacterium: Molecular Typing and Pathogenesis of Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Zoonotic Diphtheria Toxin-Producing Corynebacterium Species. In Molecular Typing in Bacterial Infections, Volume I; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2022; pp. 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolt, F.; Cassiday, P.; Tondella, M.L.; DeZoysa, A.; Efstratiou, A.; Sing, A.; Zasada, A.; Bernard, K.; Guiso, N.; Badell, E.; et al. Multilocus Sequence Typing Identifies Evidence for Recombination and Two Distinct Lineages of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4177–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- König, C.; Meinel, D.M.; Margos, G.; Konrad, R.; Sing, A. Multilocus Sequence Typing of Corynebacterium ulcerans Provides Evidence for Zoonotic Transmission and for Increased Prevalence of Certain Sequence Types among Toxigenic Strains. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4318–4324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovanen, S.M.; Kivistö, R.I.; Rossi, M.; Schott, T.; Kärkkäinen, U.-M.; Tuuminen, T.; Uksila, J.; Rautelin, H.; Hanninen, M.L. Multilocus Sequence Typing (MLST) and Whole-Genome MLST of Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Human Infections in Three Districts during a Seasonal Peak in Finland. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4147–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hacker, J.; Carniel, E. Ecological fitness, genomic islands and bacterial pathogenicity. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochman, H.; Lawrence, J.G.; Groisman, E.A. Lateral gene transfer and the nature of bacterial innovation. Nature 2000, 405, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, P.H.; Touchon, M.; Cury, J.; Rocha, E.P.C. The chromosomal organization of horizontal gene transfer in bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couturier, M.; Bex, F.; Bergquist, P.L.; Maas, W.K. Identification and classification of bacterial plasmids. Microbiol. Rev. 1988, 52, 375–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, M.; Sanchez, Z.K.; Kimbara, K. Genomics of microbial plasmids: Classification and identification based on replication and transfer systems and host taxonomy. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serwold-Davis, T.M.; Groman, N.; Rabin, M. Transformation of Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Corynebacterium ulcerans, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Escherichia coli with the C. diphtheriae plasmid pNG2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 4964–4968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauch, A.; Bischoff, N.; Brune, I.; Kalinowski, J. Insights into the genetic organization of the Corynebacterium diphtheriae erythromycin resistance plasmid pNG2 deduced from its complete nucleotide sequence. Plasmid 2003, 49, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennart, M.; Panunzi, L.G.; Rodrigues, C.; Gaday, Q.; Baines, S.L.; Barros-Pinkelnig, M.; Carmi-Leroy, A.; Dazas, M.; Wehenkel, A.M.; Didelot, X.; et al. Population genomics and antimicrobial resistance in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fluit, A.C.; Schmitz, F.J. Class 1 Integrons, Gene Cassettes, Mobility, and Epidemiology. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1999, 18, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallardo, A.A.; Toledo, R.A.; González Pasayo, R.A.; Azevedo, V.; Robles, C.; Paolicchi, F.A.; Belchior, S.G.E. Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis biovar ovis: Evaluación de la sensibilidad antibiótica in vitro. Rev. Argent. De Microbiol. 2019, 51, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, G.; Hennart, M.; Badell, E.; Brisse, S. Multidrug-resistant toxigenic Corynebacterium diphtheriae sublineage 453 with two novel resistance genomic islands. Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, 000923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barraud, O.; Badell, E.; Denis, F.; Guiso, N.; Ploy, M.-C. Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Corynebacterium diphtheriae mitis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekizuka, T.; Yamamoto, A.; Komiya, T.; Kenri, T.; Takeuchi, F.; Shibayama, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kuroda, M.; Iwaki, M. Corynebacterium ulcerans 0102 carries the gene encoding diphtheria toxin on a prophage different from the C. diphtheriae NCTC 13129 prophage. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yomantas, Y.A.V.; Abalakina, E.G.; Lobanova, J.S.; Mamontov, V.A.; Stoynova, N.V.; Mashko, S.V. Complete nucleotide sequences and annotations of φ673 and φ674, two newly characterised lytic phages of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 2565–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michel, A.; Clermont, O.; Denamur, E.; Tenaillon, O. Bacteriophage PhiX174′s Ecological Niche and the Flexibility of Its Escherichia coli Lipopolysaccharide Receptor. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 7310–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyton-Carcaman, B.; Abanto, M. Beyond to the Stable: Role of the Insertion Sequences as Epidemiological Descriptors in Corynebacterium striatum. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 806576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consuegra, J.; Gaffé, J.; Lenski, R.E.; Hindré, T.; Barrick, J.E.; Tenaillon, O.; Schneider, D. Insertion-sequence-mediated mutations both promote and constrain evolvability during a long-term experiment with bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandecraen, J.; Chandler, M.; Aertsen, A.; Van Houdt, R. The impact of insertion sequences on bacterial genome plasticity and adaptability. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 43, 709–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyton, B.; Ramos, J.N.; Baio, P.V.P.; Veras, J.F.C.; Souza, C.; Burkovski, A.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L.; Vieira, V.V.; Marin, M.A. Treat Me Well or Will Resist: Uptake of Mobile Genetic Elements Determine the Resistome of Corynebacterium striatum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, Z. CRISPR-Cas systems: Overview, innovations and applications in human disease research and gene therapy. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2401–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karginov, F.V.; Hannon, G.J. The CRISPR System: Small RNA-Guided Defense in Bacteria and Archaea. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 7–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, K.-W.; Asmah Hani, A.W.; Nurul Aina Murni, C.A.; Pusparani, R.R.; Chong, C.K.; Verasahib, K.; Yusoff, W.N.W.; Noordin, N.M.; Tee, K.K.; Yin, W.F.; et al. Comparative genomic and phylogenetic analysis of a toxigenic clinical isolate of Corynebacterium diphtheriae strain B-D-16-78 from Malaysia. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 54, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, M.V.C.; Figueiredo, H.; Ramos, R.; Guimarães, L.C.; Pereira, F.L.; Dorella, F.A.; Selim, S.A.K.; Salaheldean, M.; Silva, A.; Wattam, A.R.; et al. Comparative genomic analysis between Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis strains isolated from buffalo. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkovski, A. Proteomics of Toxigenic Corynebacteria. Proteomes 2023, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Museux, K.; Arcari, G.; Rodrigo, G.; Hennart, M.; Badell, E.; Toubiana, J.; Brisse, S. Corynebacteria of the diphtheriae Species Complex in Companion Animals: Clinical and Microbiological Characterization of 64 Cases from France. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00006-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, L.O.; Mattos-Guaraldi, A.L.; Andrade, A.F.B. Novel lipoarabinomannan-like lipoglycan (CdiLAM) contributes to the adherence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae to epithelial cells. Arch. Microbiol. 2008, 190, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadway, M.M.; Rogers, E.A.; Chang, C.; Huang, I.-H.; Dwivedi, P.; Yildirim, S.; Schmitt, M.P.; Das, A.; Ton-That, H. Pilus Gene Pool Variation and the Virulence of Corynebacterium diphtheriae Clinical Isolates during Infection of a Nematode. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 3774–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billington, S.J.; Esmay, P.A.; Songer, J.G.; Jost, B.H. Identification and role in virulence of putative iron acquisition genes from Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 208, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Holmes, R.K. Identification of a DtxR-Regulated Operon That Is Essential for Siderophore-Dependent Iron Uptake in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Bacteriol. 2002, 184, 4846–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunkle, C.A.; Schmitt, M.P. Analysis of a DtxR-Regulated Iron Transport and Siderophore Biosynthesis Gene Cluster in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, L.R.; Peng, E.D.; Schmitt, M.P. Corynebacterium diphtheriae Iron-Regulated Surface Protein HbpA Is Involved in the Utilization of the Hemoglobin-Haptoglobin Complex as an Iron Source. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drazek, E.S.; Hammack, C.A.; Schmitt, M.P. Corynebacterium diphtheriae genes required for acquisition of iron from haemin and haemoglobin are homologous to ABC haemin transporters. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 68–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Bansal, S.; Deb, J.K.; Kundu, B. Interplay between DtxR and nitric oxide reductase activities: A functional genomics approach indicating involvement of homologous protein domains in bacterial pathogenesis. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2007, 88, 377–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yellaboina, S.; Ranjan, S.; Chakhaiyar, P.; Hasnain, S.; Ranjan, A. Prediction of DtxR regulon: Identification of binding sites and operons controlled by Diphtheria toxin repressor in Corynebacterium diphtheriae. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, C.E.; Schmitt, M.P. Utilization of Host Iron Sources by Corynebacterium diphtheriae: Multiple Hemoglobin-Binding Proteins Are Essential for the Use of Iron from the Hemoglobin-Haptoglobin Complex. J. Bacteriol. 2015, 197, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapartegui-González, I.; Fernández-Martínez, M.; Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Rocha, D.J.P.; Aguiar, E.R.G.R.; Pacheco, L.G.C.; Ramos-Vivas, J.; Calvo, J.; Martínez-Martínez, L.; Navas, J. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Characterization of Resistance Mechanisms of Corynebacterium urealyticum Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, M.V.C.; Galdino, J.H.; Profeta, R.; Oliveira, M.; Tavares, L.; de Castro Soares, S.; Carneiro, P.; Wattam, A.R.; Azevedo, V. Analysis of Corynebacterium silvaticum genomes from Portugal reveals a single cluster and a clade suggested to produce diphtheria toxin. PeerJ 2023, 11, e14895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Luo, H.; Zhang, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Feng, J.; Qu, P.; Chen, C.; Xu, N. Corynebacterium lipophilum sp. nov., a lipophilic bacterium isolated from clinical breast specimens and emended description of the species Corynebacterium pilbarense. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2023, 116, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, J.; Chiba, K.; Kurita, H.; Satoh, H. Contribution of rpoB2 RNA polymerase beta subunit gene to rifampin resistance in Nocardia species. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1342–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosi, E.; Fani, R.; Fondi, M. Defining Orthologs and Pangenome Size Metrics. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1231, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, S.S.; Guimarães, L.C.; Silva, A.; Soares, S.C.; Baraúna, R.A. First Steps in the Analysis of Prokaryotic Pan-Genomes. Bioinform. Biol. Insights 2020, 14, 117793222093806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viana, M.V.C.; Profeta, R.; da Silva, A.L.; Hurtado, R.; Cerqueira, J.C.; Ribeiro, B.F.S.; Almeida, M.O.; Morais-Rodrigues, F.; Soares, S.C.; Oliveira, M.; et al. Taxonomic classification of strain PO100/5 shows a broader geographic distribution and genetic markers of the recently described Corynebacterium silvaticum. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0244210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, S.C.; Silva, A.; Trost, E.; Blom, J.; Ramos, R.; Carneiro, A.; Ali, A.; Santos, A.R.; Pinto, A.C.; Diniz, C.; et al. The Pan-Genome of the Animal Pathogen Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis Reveals Differences in Genome Plasticity between the Biovar ovis and equi Strains. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trost, E.; Blom, J.; de Castro Soares, S.; Huang, I.-H.; Al-Dilaimi, A.; Schröder, J.; Jaenicke, S.; Dorella, F.A.; Rocha, F.S.; Miyoshi, A.; et al. Pangenomic Study of Corynebacterium diphtheriae That Provides Insights into the Genomic Diversity of Pathogenic Isolates from Cases of Classical Diphtheria, Endocarditis, and Pneumonia. J. Bacteriol. 2012, 194, 3199–3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ott, L.; Möller, J.; Burkovski, A. Interactions between the Re-Emerging Pathogen Corynebacterium diphtheriae and Host Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangal, V.; Burkovski, A.; Hunt, A.C.; Edwards, B.; Blom, J.; Hoskisson, P.A. A lack of genetic basis for biovar differentiation in clinically important Corynebacterium diphtheriae from whole genome sequencing. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2014, 21, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).