Application of Digestate from a Methane Fermentation Process for Supplying Water and Nutrients in Sweet Potato Cultivation in Sandy Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
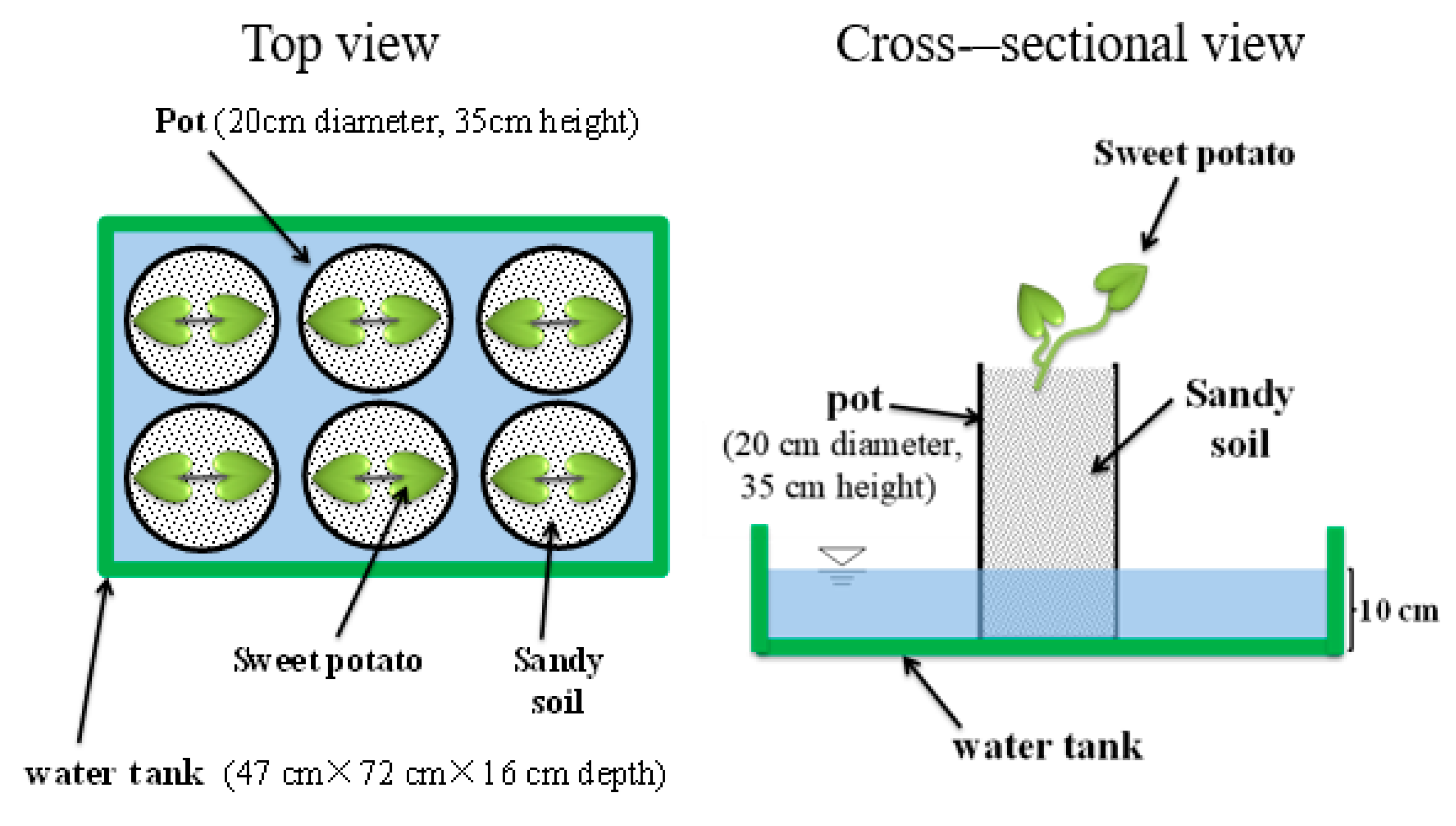
2.1. Preparation of Plant Materials
2.2. Raw Material of the Methane Fermentation Digestate
2.3. Determination of Suitable Digestate Concentration
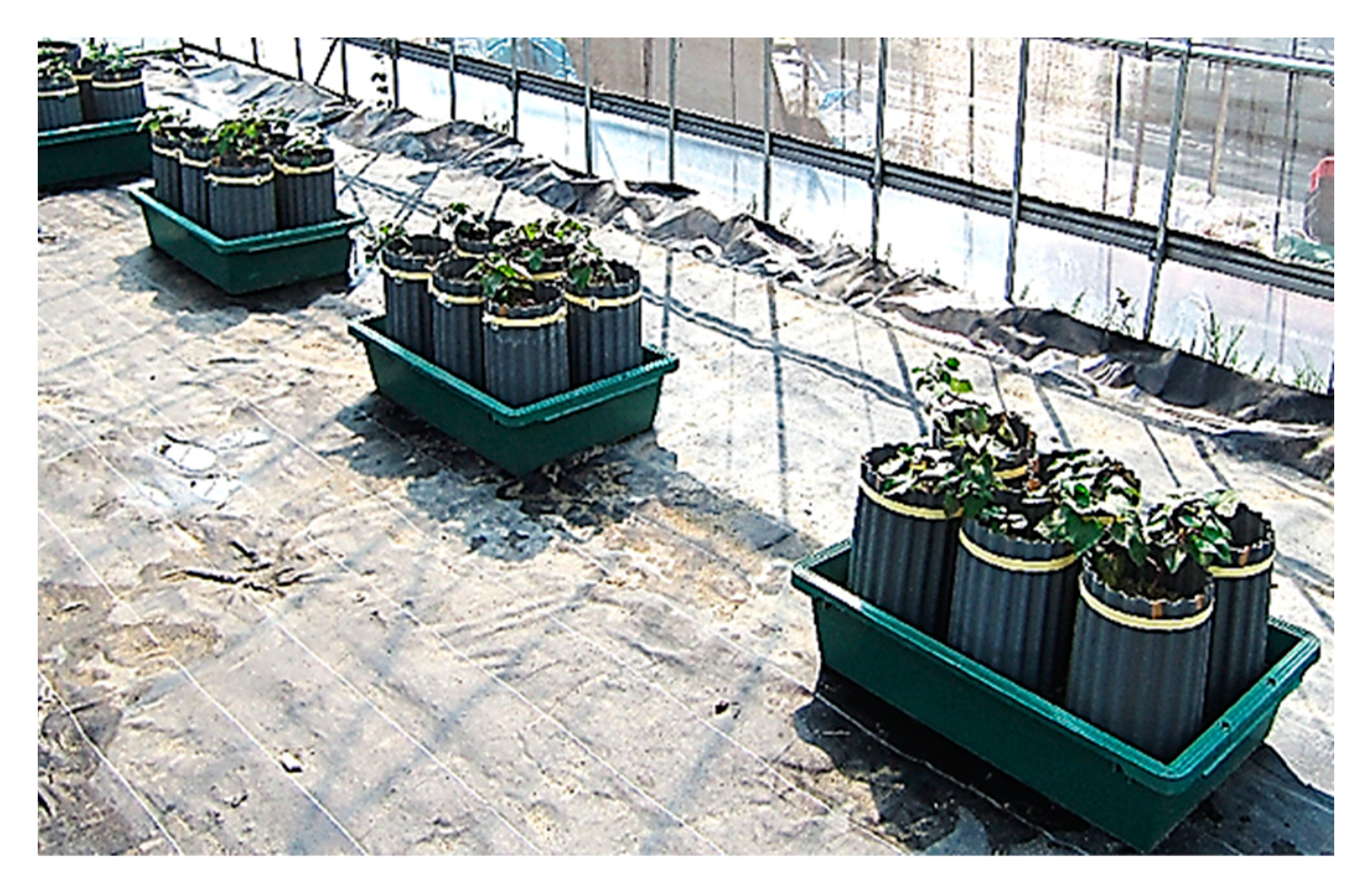
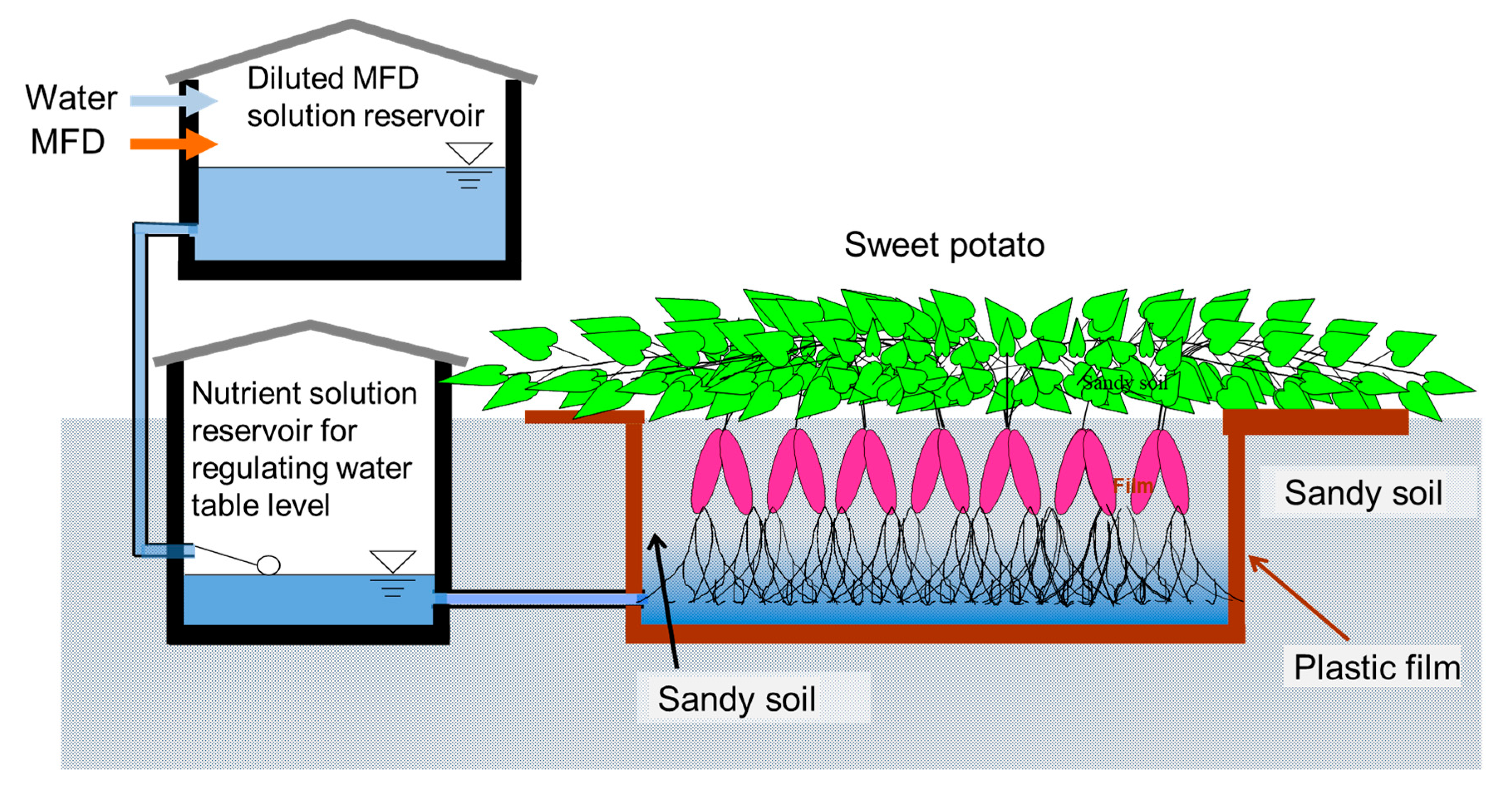
2.4. Assessment of the Feasibility of Sweet Potato Cultivation with Digestate from Methane Fermentation
3. Results
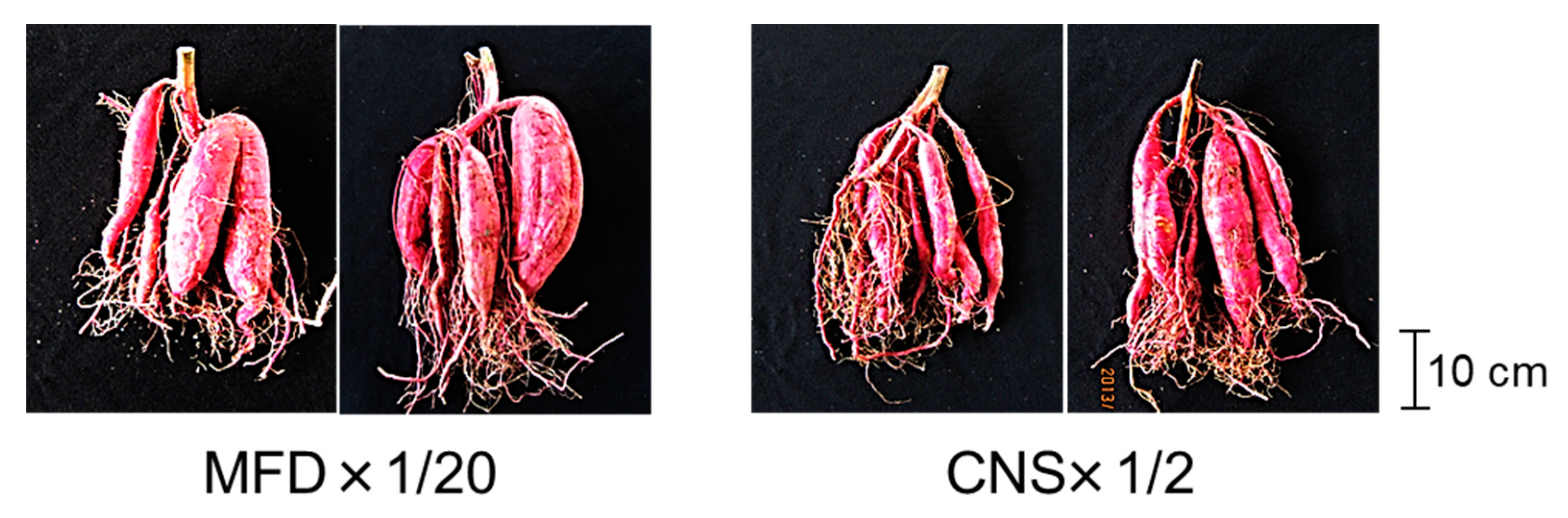
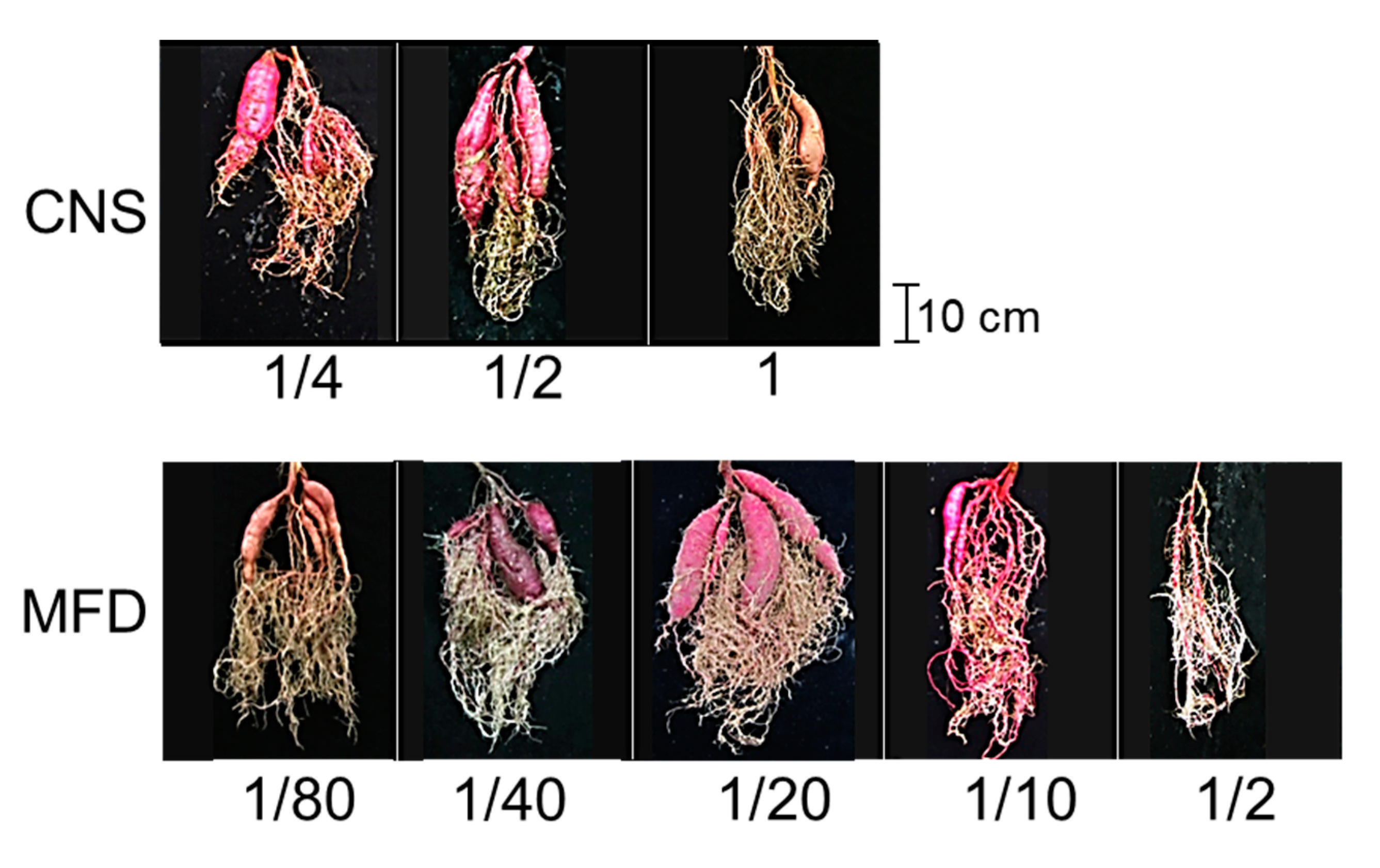
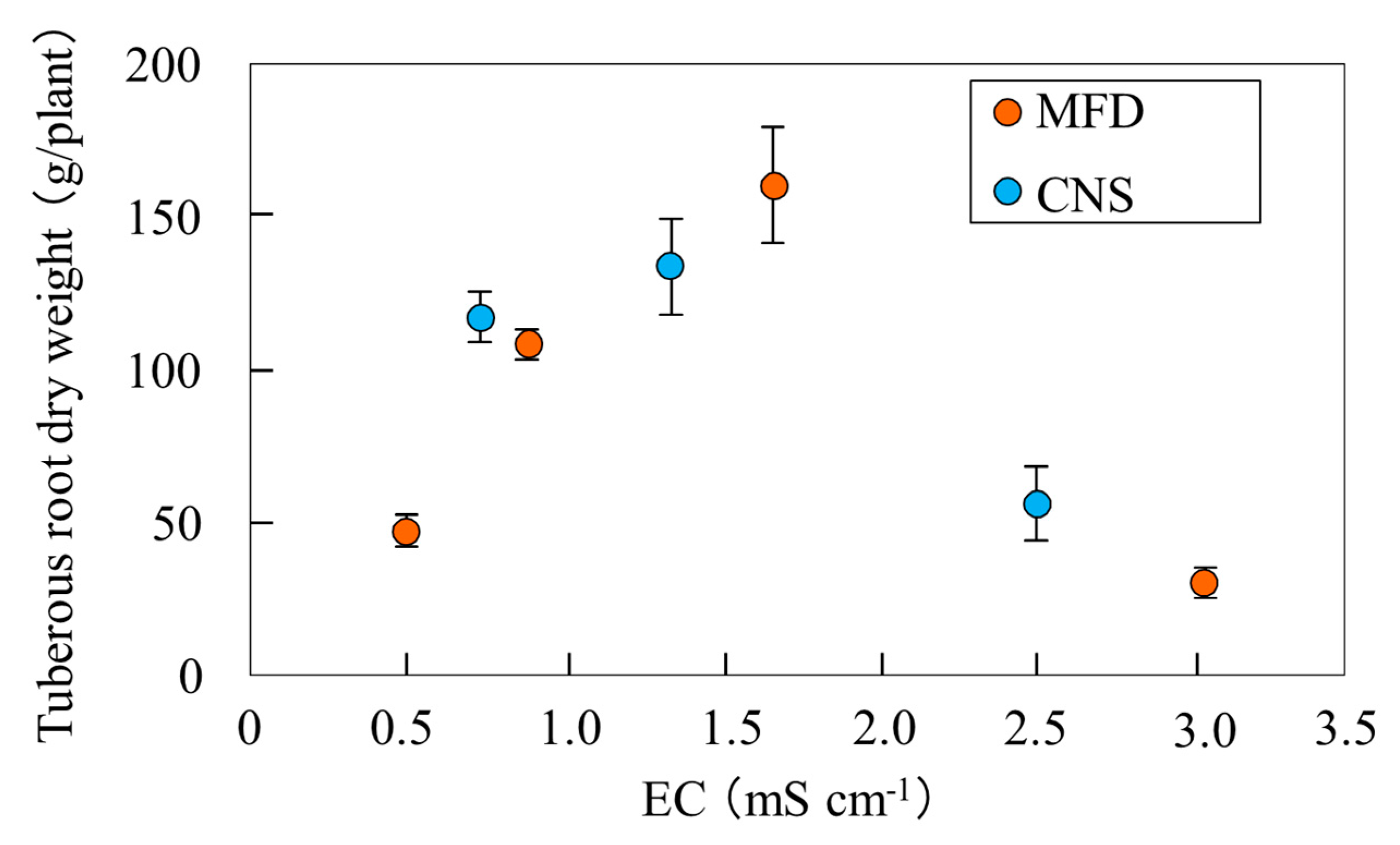
3.1. Determination of a Suitable Digestate Concentration
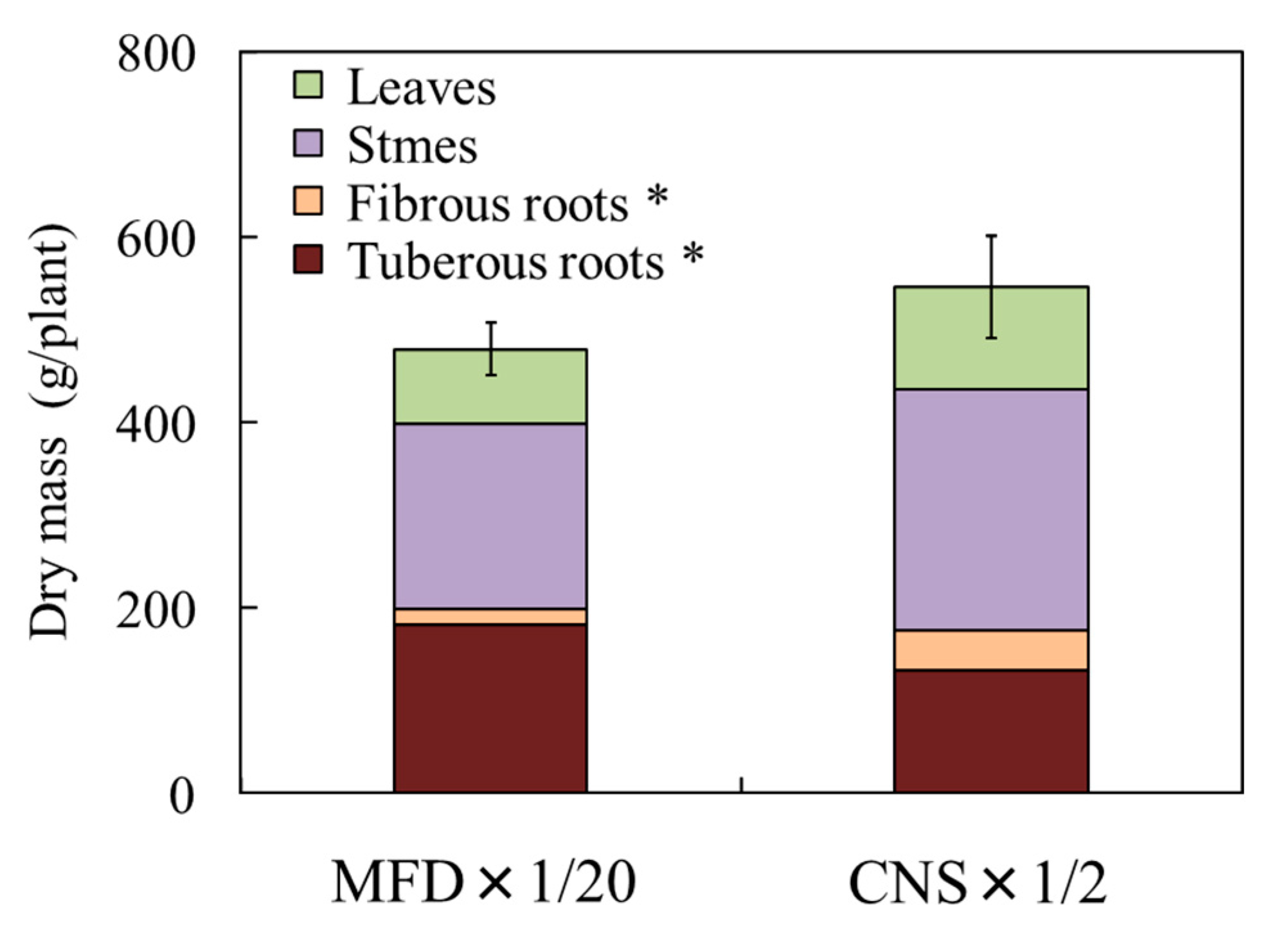
3.2. Assessment of the Feasibility of Sweet Potato Cultivation with Digestate from Methane Fermentation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, J.; Othman, M.; Burn, S. A review of policy drivers and barriers for the use of anaerobic digestion in Europe, the United States and Australia. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, P.; Hephzibah, D.; Sivasankari, R.; Saifuddin, N.; Shamsuddin, A.H. A review on industrial scale anaerobic digestion systems deployment in Malaysia: Opportunities and challenges. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 56, 929–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrere, H.; Antonopoulou, G.; Affes, R.; Passos, F.; Battimelli, A.; Lyberatos, G.; Ferrer, I. Review of feedstock pretreatment strategies for improved anaerobic digestion: From lab–scale research to full–scale application. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 199, 386–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camacho, C.I.; Estévez, S.; Conde, J.J.; Feijoo, G.; Moreira, M.T. Dark fermentation as an environmentally sustainable WIN–WIN solution for bioenergy production. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiland, P. Biogas production: Current state and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 849–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, C.; Feng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ren, G. Review on research achievements of biogas from anaerobic digestion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijazi, O.; Munro, S.; Zerhusen, B.; Effenberger, M. Review of life cycle assessment for biogas production in Europe. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 54, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, J.; Dong, R.; Ahring, B.K.; Zhang, W. Properties of plant nutrient: Comparison of two nutrient recovery techniques using liquid fraction of digestate from anaerobic digester treating pig manure. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 544, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monlau, F.; Sambusiti, C.; Ficara, E.; Aboulkas, A.; Barakat, A.; Carrère, H. New opportunities for agricultural digestate valorization: Current situation and perspectives. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2600–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endo, R.; Yamashita, K.; Shibuya, T.; Kitaya, Y. Use of methane fermentation digestate for hydroponic culture: Analysis of potential inhibitors in digestate to cucumber seedling. Eco-Engineering 2016, 28, 67–72. [Google Scholar]
- Chojnacka, K.; Moustakas, K. Anaerobic digestate management for carbon neutrality and fertilizer use: A review of current practices and future opportunities. Biomass Bioenergy 2024, 180, 106991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havukainen, J.; Saud, A.; Astrup, T.F.; Peltola, P.; Horttanainen, M. Environmental performance of dewatered sewage sludge digestate utilization based on life cycle assessment. Waste Manag. 2022, 137, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillo, F.; Piccoli, I.; Furlanetto, I.; Ragazzi, F.; Obber, S.; Bonato, T.; Meneghetti, F.; Morari, F. Agro–environmental sustainability of anaerobic digestate fractions in intensive cropping systems: Insights regarding the nitrogen use efficiency and crop performance. Agronomy 2021, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makádi, M.; Tomócsik, A.; Orosz, V. Digestate: A new nutrient source–review. Biogas 2012, 14, 295–312. [Google Scholar]
- Niemiec, M.; Sikora, J.; Szeląg–Sikora, A.; Gródek–Szostak, Z.; Komorowska, M. Assessment of the possibilities for the use of selected waste in terms of biogas yield and further use of its digestate in agriculture. Materials 2022, 15, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carraro, G.; Tonderski, K.; Enrich–Prast, A. Solid–liquid separation of digestate from biogas plants: A systematic review of the techniques’ performance. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 356, 120585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzee, T.J.; Edalati, A.; El–Mashad, H.; Wang, D.; Scow, K.; Zhang, R. Digestate biofertilizers support similar or higher tomato yields and quality than mineral fertilizer in a subsurface drip fertigation system. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 3, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panuccio, M.R.; Mallamaci, C.; Attinà, E.; Muscolo, A. Using digestate as fertilizer for a sustainable tomato cultivation. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antón–Herrero, R.; García–Delgado, C.; Alonso–Izquierdo, M.; Cuevas, J.; Carreras, N.; Mayans, B.; Camacho–Arévalo, R.; Eymar, E. New uses of treated urban waste digestates on stimulation of hydroponically grown tomato (Solanum lycopersicon L.). Waste Biomass Valorization 2021, 12, 1877–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, H.A. Diversifying Description: Sweet Potato Science and International Agricultural Research after the Green Revolution. Agric. Hist. 2023, 97, 414–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolfe, J.A. Sweet Potato: An Untapped Food Resource; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1992; p. 643. [Google Scholar]
- Bovell–Benjamin, A.C. Sweet potato: A review of its past, present, and future role in human nutrition. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2007, 52, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sawicka, B.; Michałek, W.; Pszczółkowski, P.; Danilcenko, H. Variation in productivity of Ipomoea batatas at various rates of nitrogen fertilization. Zemdirb.–Agric. 2018, 105, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botheju, D.; Svalheim, Ø.; Bakke, R. Digestate nitrification for nutrient recovery. Open Waste Manag. J. 2010, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, K.; Müller, T. Effects of anaerobic digestion on digestate nutrient availability and crop growth: A review. Eng. Life Sci. 2012, 12, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tampio, E.; Ervasti, S.; Paavola, T.; Heaven, S.; Banks, C.; Rintala, J. Anaerobic digestion of autoclaved and untreated food waste. Waste Manag. 2014, 34, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britto, D.T.; Kronzucker, H.J. NH4+ toxicity in higher plants: A critical review. J. Plant. Physiol. 2002, 159, 567–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachiya, T.; Watanabe, C.K.; Fujimoto, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Takahara, K.; Kawai–Yamada, M.; Uchimiya, H.; Uesono, Y.; Terashima, I.; Noguchi, K. Nitrate addition alleviates ammonium toxicity without lessening ammonium accumulation, organic acid depletion and inorganic cation depletion in Arabidopsis thaliana shoots. Plant. Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 577–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.-H. Sustainable nitrogen elimination biotechnologies: A review. Process. Biochem. 2006, 41, 1709–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Meng, J.; Li, J.; Wang, C.; Deng, K.; Sun, K.; Buelna, G. The effect and biological mechanism of COD/TN ratio on nitrogen removal in a novel upflow microaerobic sludge reactor treating manure–free piggery wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siqinbatu Kitaya, Y.; Hirai, H.; Endo, R.; Shibuya, T. Effects of water contents and CO2 concentrations in soil on growth of sweet potato. Field Crops Res. 2013, 152, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, A.F.M.S.; Kitaya, Y.; Hirai, H.; Yanase, M.; Mori, G.; Kiyota, M. Sweetpotato [Ipomoea batatas] cultivation with rice husk charcoal as a soil aerating material under wet lowland field conditions. Environ. Control. Biol. 1998, 36, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyeni, M.O.; Stulpinaite, U.; Baksinskaite, A.; Suproniene, S.; Tilvikiene, V. The effectiveness of digestate use for fertilization in an agricultural cropping system. Plants 2021, 10, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, K.; Endo, R.; Shibuya, T.; Kitaya, Y. Application of biogas digestate as a nutrient solution for the hydroponic culture of Chrysanthemum morifolium ramat with rockwool substrate. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 11, 2645–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.E.; Steiman, M.W.; Angelo, S.K.S. Biogas digestate as a renewable fertilizer: Effects of digestate application on crop growth and nutrient composition. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2021, 36, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakas, M.C.; Kurunc, A.; Dincer, C. Effects of water deficit on growth and performance of drip irrigated sweet potato varieties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2961–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Solution Medium | EC (mS cm−1) | pH | NO3−–N (mg L−1) | NH4+–N (mg L−1) | K+ (mg L−1) | Na+ (mg L−1) | PO43− (mg L−1) | SO42− (mg L−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | 2.52 | 6.7 | 230 | 34 | 368 | 238 | 134 | 224 |
| MFD | 31.0 | 8.1 | – | 2787 | 3311 | 447 | 638 | 332 |
| Dry Mass (g/plant) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leaves (a) | Stems (b) | Shoot (a + b) | Fibrous Roots (c) | Tuberous Roots (d) | Roots (c + d) | Total (a + b + c + d) | Shoot/Roots | SPAD | |
| MDF×1/80 | 8.4 | 22.9 | 31.3 | 10.4 | 74.6 | 85.0 | 116.3 | 0.37 | 38 |
| MDF×1/40 | 19.2 | 40.9 | 60.1 | 13.4 | 108.2 | 121.6 | 181.7 | 0.49 | 40 |
| MDF×1/20 | 27.7 | 50.5 | 78.2 | 18.0 | 167.1 | 185.1 | 263.3 | 0.42 | 50 |
| MDF×1/10 | 30.5 | 41.6 | 72.1 | 6.4 | 30.0 | 36.4 | 108.5 | 1.98 | 32 |
| MDF×1/2 | 2.6 | 3.7 | 6.3 | 7.1 | – | 7.1 | 13.4 | 0.89 | 23 |
| CNS×1/4 | 23.8 | 67.4 | 91.2 | 16.9 | 116.7 | 133.6 | 224.8 | 0.68 | 43 |
| CNS×1/2 | 23.7 | 85.8 | 109.5 | 13.1 | 133.7 | 146.8 | 256.3 | 0.75 | 45 |
| CNS×1 | 11.4 | 70.3 | 81.7 | 13.8 | 55.7 | 69.5 | 151.2 | 1.16 | 41 |
| LSD* | 13.6 | 35.8 | 45.2 | 14.1 | 55.2 | 65.3 | 107.7 | 0.14 | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitaya, Y.; Siqinbatu; Endo, R.; Shibuya, T. Application of Digestate from a Methane Fermentation Process for Supplying Water and Nutrients in Sweet Potato Cultivation in Sandy Soil. Methane 2024, 3, 410-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/methane3030023
Kitaya Y, Siqinbatu, Endo R, Shibuya T. Application of Digestate from a Methane Fermentation Process for Supplying Water and Nutrients in Sweet Potato Cultivation in Sandy Soil. Methane. 2024; 3(3):410-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/methane3030023
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitaya, Yoshiaki, Siqinbatu, Ryosuke Endo, and Toshio Shibuya. 2024. "Application of Digestate from a Methane Fermentation Process for Supplying Water and Nutrients in Sweet Potato Cultivation in Sandy Soil" Methane 3, no. 3: 410-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/methane3030023
APA StyleKitaya, Y., Siqinbatu, Endo, R., & Shibuya, T. (2024). Application of Digestate from a Methane Fermentation Process for Supplying Water and Nutrients in Sweet Potato Cultivation in Sandy Soil. Methane, 3(3), 410-420. https://doi.org/10.3390/methane3030023






