The Association of Cardiovascular Disease with the T3111C Polymorphism in the CLOCK Gene †
Abstract
1. Introduction
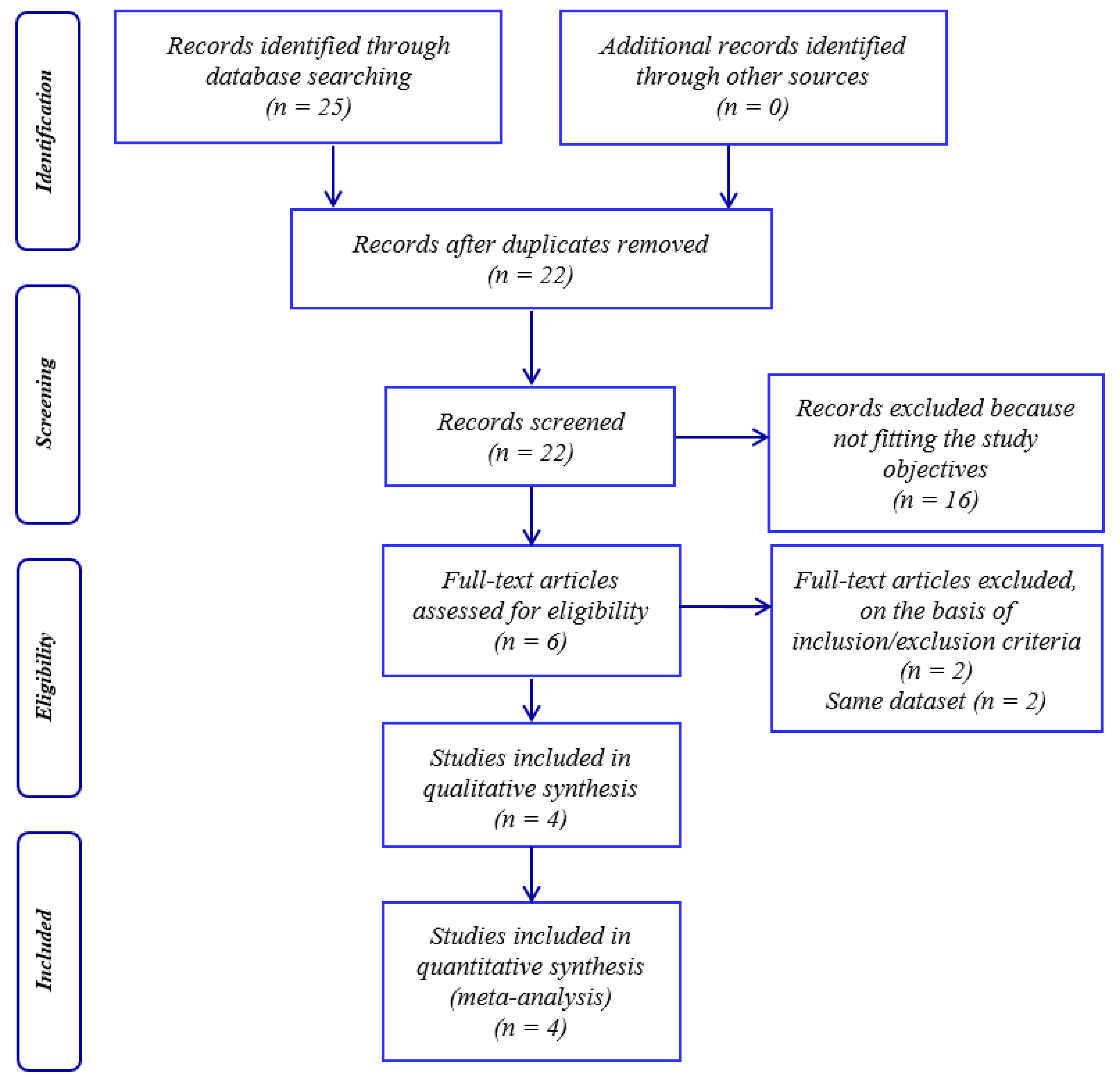
2. Methods
2.1. Study Selection
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Škrlec, I.; Milić, J.; Heffer, M.; Peterlin, B.; Wagner, J. Genetic variations in circadian rhythm genes and susceptibility for myocardial infarction. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2018, 41, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thosar, S.S.; Butler, M.P.; Shea, S.A. Role of the circadian system in cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 2157–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrlec, I. Circadian rhythm and myocardial infarction. Med. Flum. 2019, 55, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Crnko, S.; Du Pré, B.C.; Sluijter, J.P.G.G.; Van Laake, L.W. Circadian rhythms and the molecular clock in cardiovascular biology and disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrlec, I.; Milić, J.; Heffer, M.; Wagner, J.; Peterlin, B. Circadian clock genes and circadian phenotypes in patients with myocardial infarction. Adv. Med. Sci. 2019, 64, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, E.M.; Carter, A.M.; Grant, P.J. Association between polymorphisms in the Clock gene, obesity and the metabolic syndrome in man. Int. J. Obes. 2008, 32, 658–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrlec, I.; Milić, J.; Cilenšek, I.; Petrovič, D.; Wagner, J.; Peterlin, B. Circadian clock genes and myocardial infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Gene 2019, 701, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorokhova, S.G.; Generozov, E.V.; Yu, A.O.; Muraseeva, E.V.; Naumov, V.A.; Babikova, E.A.; Zaharczevskaya, N.B.; Prigorovskaya, T.S. Different association of CRY1 and CLOCK circadian genes with coronary atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Exp. Cardiol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corella, D.; Asensio, E.M.; Coltell, O.; Sorlí, J.V.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Castañer, O.; Arós, F.; Lapetra, J.; et al. CLOCK gene variation is associated with incidence of type-2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in type-2 diabetic subjects: Dietary modulation in the PREDIMED randomized trial. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Gemma, C.; Gianotti, T.F.; Burgueño, A.; Castaño, G.; Pirola, C.J. Genetic variants of Clock transcription factor are associated with individual susceptibility to obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Škrlec, I.; Milić, J.; Steiner, R. The Impact of the Circadian Genes CLOCK and ARNTL on Myocardial Infarction. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, P.; Tortorella, A.; Docimo, L.; Maldonato, M.N.; Canestrelli, B.; De Luca, L.; Maj, M. Investigation of 3111T/C polymorphism of the CLOCK gene in obese individuals with or without binge eating disorder: Association with higher body mass index. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 435, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galbete, C.; Contreras, R.; Martínez, J.A.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Guillén-Grima, F.; Marti, A. Physical activity and sex modulate obesity risk linked to 3111T/C gene variant of the clock gene in an elderly population: The sun project. Chronobiol. Int. 2012, 29, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolomeichuk, S.N.; Kurbatova, I.V.; Topchieva, L.V.; Korneva, V.A.; Poltorak, A.N.; Chambers, T.C.; Nemova, N.N. Association between CLOCK genetic variants and individual susceptibility to essential hypertension and coronary artery disease in Russian population. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2014, 20, 1798–1813. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, H. Association of insulin resistance with polymorphic variants of Clock and Bmal1 genes: A case–control study. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2020, 42, 371–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, R.; Álvarez-Pasquin, M.J.; Díaz, C.; Del Barrio, J.L.; Estrada, J.M.; Gil, Á. Are healthcare workers intentions to vaccinate related to their knowledge, beliefs and attitudes? A systematic review. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolomeichuk, S.N.; Makeeva, I.V.V.; Topchieva, L.V.V.; Korneva, V.A.A.; Nemova, N.N.N.; Kolomeĭchuk, S.N.; Makeeva, I.V.V.; Topchieva, L.V.V.; Korneva, V.A.A.; Nemova, N.N.N. Association of T3111C polymorphism in 3’-untranslated region of the Clock gene with the risk of essential arterial hypertension and coronary artery disease in the Russian population (Residents of Karelia). Russ. J. Genet. 2011, 47, 1256–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| First Author | Monteleone et al. | Galbete et al. | Kolomeichuk et al. | Kolomeichuk et al. | Li et al. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2008 [12] | 2012 [13] | 2014a [14] | 2014b [14] | 2020 [15] |
| Country | Italy | Spain | Russia | Russia | China |
| Ethnicity | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian | Caucasian | Asian |
| Disorder | Obesity | Obesity | Hypertension | Coronary artery disease | Hypertension/insulin resistance |
| Population type | General | General | Hospital | Hospital | Hospital |
| Study type | Case-control | Cross-sectional | Cross-sectional | Cross-sectional | Cross-sectional |
| Case | 192 | 532 | 434 | 299 | 103 |
| Control | 92 | 371 | 435 | 434 | 231 |
| Male (%) | 14.79% | 72.76% | 48.33% | 49.11% | 57.78% |
| Age (year ± SD) cases | 38.4 ± 10.9 | 69 ± 5 | 51.9 ± 6.9 | 52.3 ± 7.1 | 54 ± 13.81 |
| Age (year ± SD) control | 26.1 ± 4.6 | 69 ± 5 | 50.8 ± 8.1 | 50.8 ± 8.1 | 53.1 ± 11.27 |
| Genotyping method | RFLP-PCR | RT-PCR | RFLP-PCR | RFLP-PCR | PCR sequencing |
| NOS score * | 8 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| First Author | Cases | Controls | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genotype Frequencies, N (%) | Allele Frequencies, N (%) | Genotype Frequencies, N (%) | Allele Frequencies, N (%) | |||||||
| TT | TC | CC | T | C | TT | TC | CC | T | C | |
| Monteleone et al. | 103 (53.6) | 68 (35.4) | 21 (10.9) | 272 (70.8) | 112 (29.1) | 46 (50) | 39 (42.4) | 7 (7.6) | 131 (71.2) | 53 (28.8) |
| Galbete et al. | 278 (52.2) | 217 (40.8) | 37 (7) | 789 (72.7) | 297 (27.3) | 181 (48.8) | 151 (41.5) | 36 (9.7) | 516 (69.5) | 226 (30.5) |
| Kolomeichuk et al. a | 143 (33) | 213 (49) | 78 (18) | 252 (58.1) | 182 (41.9) | 209 (48) | 187 (43) | 39 (9) | 300 (69) | 135 (31) |
| Kolomeichuk et al. b | 81 (27) | 161 (54) | 57 (19) | 162 (53.8) | 137 (46.2) | 209 (48) | 187 (43) | 39 (9) | 300 (69) | 135 (31) |
| Li et al. | 51 (49.5) | 44 (42.7) | 8 (7.8) | 146 (70.9) | 60 (29.1) | 186 (80.5) | 40 (17.3) | 5 (2.2) | 412 (89.2) | 50 (10.8) |
| Comparison | Test of Association | Test of Heterogeneity | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p | I2 | p | ||
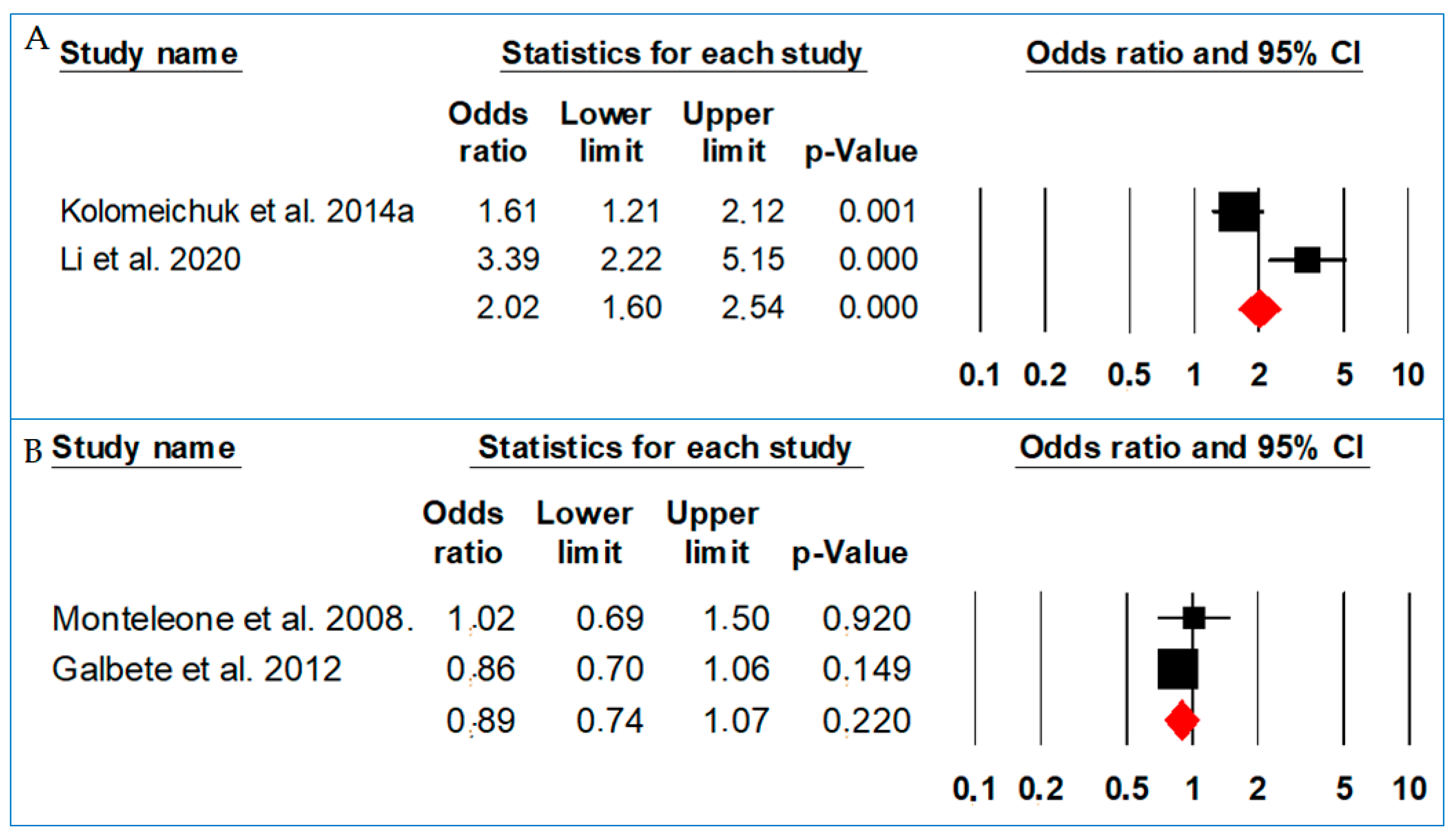
| Allelic model | T vs. C | 0.73 (0.62–0.84) | <0.001 | 97.93 | <0.001 |
| Dominant model | TT + CT vs. CC | 0.59 (0.46–0.71) | <0.001 | 79.59 | 0.001 |
| Recessive model | TT vs. CT + CC | 0.63 (0.54–0.73) | <0.001 | 91.64 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Škrlec, I.; Talapko, J.; Džijan, S.; Lepeduš, H. The Association of Cardiovascular Disease with the T3111C Polymorphism in the CLOCK Gene. Med. Sci. Forum 2021, 6, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECMD2021-10314
Škrlec I, Talapko J, Džijan S, Lepeduš H. The Association of Cardiovascular Disease with the T3111C Polymorphism in the CLOCK Gene. Medical Sciences Forum. 2021; 6(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECMD2021-10314
Chicago/Turabian StyleŠkrlec, Ivana, Jasminka Talapko, Snježana Džijan, and Hrvoje Lepeduš. 2021. "The Association of Cardiovascular Disease with the T3111C Polymorphism in the CLOCK Gene" Medical Sciences Forum 6, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECMD2021-10314
APA StyleŠkrlec, I., Talapko, J., Džijan, S., & Lepeduš, H. (2021). The Association of Cardiovascular Disease with the T3111C Polymorphism in the CLOCK Gene. Medical Sciences Forum, 6(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECMD2021-10314







