Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to High-Risk Clones Obtained from Fresh Pork Meat in La Plata City, Argentina †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Retail Markets Sampling
2.2. Sample Processing
2.3. Whole Genome Sequencing and Bioinformatics
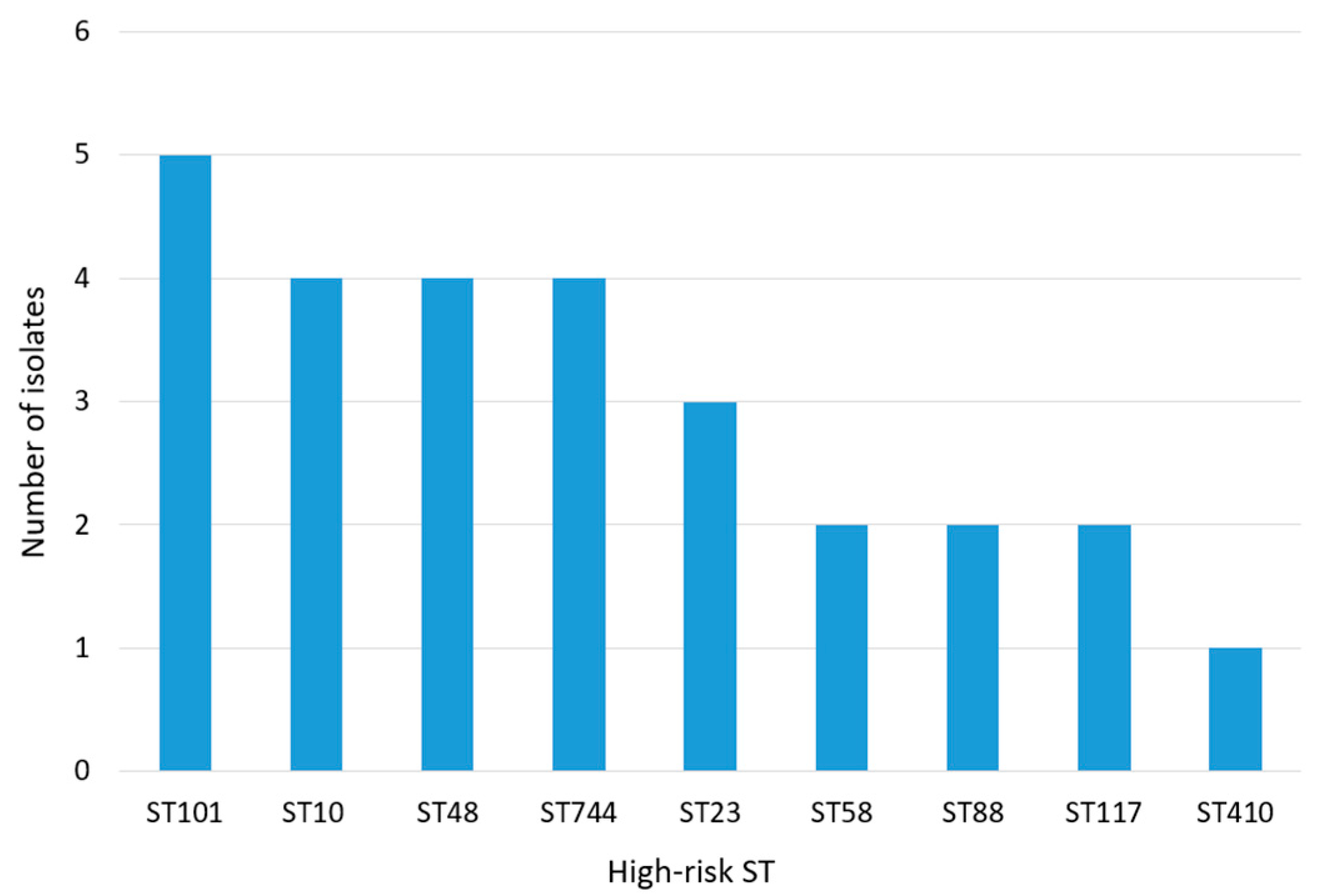
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antimicrobial Resistance Collaborators. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: A systematic analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, A.; Silva, V.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Igrejas, G.; Valentão, P.; Falco, V.; Poeta, P. Antimicrobial Resistance and Clonal Lineages of Escherichia coli from Food-Producing Animals. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncini, J.G.M.; Koga, V.L.; Fuga, B.; Tano, Z.N.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Lincopan, N.; Vespero, E.C. Molecular analysis of Escherichia coli and correlations between phylogroups and sequence types from different sources. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awosile, B.; Eisnor, J.; Saab, M.E.; Heider, L.; McClure, J.T. Occurrence of extended-spectrum β-lactamase and AmpC-producing Escherichia coli in retail meat products from the Maritime Provinces, Canada. Can. J. Microbiol. 2021, 67, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. WHO Medically Important Antimicrobial List. 2023. Available online: https://cdn.who.int/media/docs/default-source/antimicrobial-resistance/amr-gcp-irc/who_mialist_draft_forexternaldiscussion.pdf?sfvrsn=af6f2ebf_1 (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List. 2024. Available online: https://iris.who.int/bitstream/handle/10665/376776/9789240093461-eng.pdf?sequence=1 (accessed on 23 September 2024).
- Kocsis, B.; Gulyás, D.; Szabó, D. Emergence and Dissemination of Extraintestinal Pathogenic High-Risk International Clones of Escherichia coli. Life 2022, 12, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kara, A.; Massaro, C.; Giammanco, G.M.; Alduina, R.; Boussoualim, N. Phylogenetic Diversity, Antibiotic Resistance, and Virulence of Escherichia coli Strains from Urinary Tract Infections in Algeria. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baquero, F.; Tedim, A.P.; Coque, T.M. Antibiotic resistance shaping multi-level population biology of bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounsey, O.; Marchetti, L.; Parada, J.; Alarcón, L.V.; Aliverti, F.; Avison, M.B.; Ayala, C.S.; Ballesteros, C.; Best, C.M.; Bettridge, J.; et al. Genomic epidemiology of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli from Argentinian pig and dairy farms reveals animal-specific patterns of co-resistance and resistance mechanisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e01791-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faccone, D.; Moredo, F.A.; Giacoboni, G.I.; Albornoz, E.; Alarcón, L.V.; Nievas, V.F.; Corso, A. Multidrug-resistant Escherichia coli harbouring mcr-1 and blaCTX-M genes isolated from swine in Argentina. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 18, 160–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, M.F.; Vinocur, F.; Rodríguez Ramos, S.; Garassino, B.J.; Nievas, H.D.; Nievas, V.F.; Alarcón, L.V.; Armocida, A.D.; Pérez, E.M.; Griffo, D.; et al. Aislamientos de Escherichia coli de origen porcino resistentes a antimicrobianos de importancia crítica para la salud pública. Analecta Vet. 2022, 42, e067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramundi, I.; Albornoz, E.; Boutureira, M.; Rapoport, M.; Gomez, S.; Corso, A.; Castro, G.; Faccone, D. Characterization of third-generation cephalosporin-resistant Escherichia coli clinical isolates from Ushuaia, Argentina. Rev. Argent. Microbiol. 2023, 55, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz, M.B.; De Belder, D.; de Mendieta, J.M.; Faccone, D.; Poklepovich, T.; Lucero, C.; Rapoport, M.; Campos, J.; Tuduri, E.; Saavedra, M.O.; et al. Carbapenemase-Producing Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli from Argentina: Clonal Diversity and Predominance of Hyperepidemic Clones CC10 and CC131. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 830209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastidas-Caldes, C.; Romero-Alvarez, D.; Valdez-Vélez, V.; Morales, R.D.; Montalvo-Hernández, A.; Gomes-Dias, C.; Calvopiña, M. Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamases Producing Escherichia coli in South America: A Systematic Review with a One Health Perspective. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 5759–5779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soncini, J.G.M.; Cerdeira, L.; Sano, E.; Koga, V.L.; Tizura, A.T.; Tano, Z.N.; Nakazato, G.; Kobayashi, R.K.T.; Aires, C.A.M.; Lincopan, N.; et al. Genomic insights of high-risk clones of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from community infections and commercial meat in southern Brazil. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| ID Isolates | Sequence Type | Resistance Genes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3GC * | Fosfomycin | Ciprofloxacin | ||
| 003-C1 | 101 | blaCTX-M-14 | - | - |
| 004-X1 | 101 | blaCTX-M-14 | - | - |
| 013-X1 | 117 | blaCTX-M-55 | fosL1 | qnrB19 |
| 014-X1 | 117 | blaCTX-M-55 | fosL1 | qnrB19 |
| 050-X1 | 48 | blaCMY-2 | - | qnrS1 |
| 054-X1 | 23 | blaCTX-M-55 | fosA3 | qnrB19 |
| 071-X1 | 23 | blaCTX-M-14 | - | qnrS1 |
| 091-X1 | 23 | blaCTX-M-14 | - | - |
| 103-X1 | 58 | blaCTX-M-55 | - | - |
| 112-X1 | 10 | blaCTX-M-55 | fosA3 | qnrB19 |
| 122-X1 | 744 | blaCTX-M-55/blaCTX-M-8 | fosA3 | - |
| 124-X1 | 88 | blaCTX-M-55 | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nievas, H.D.; Iza, R.E.; Aurnague, C.; Helman, E.; Nievas, V.F.; Mounsey, O.; Galli, L.; Moredo, F.A. Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to High-Risk Clones Obtained from Fresh Pork Meat in La Plata City, Argentina. Med. Sci. Forum 2025, 35, 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025035008
Nievas HD, Iza RE, Aurnague C, Helman E, Nievas VF, Mounsey O, Galli L, Moredo FA. Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to High-Risk Clones Obtained from Fresh Pork Meat in La Plata City, Argentina. Medical Sciences Forum. 2025; 35(1):8. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025035008
Chicago/Turabian StyleNievas, Hernán D., Raúl E. Iza, Camila Aurnague, Elisa Helman, Victorio F. Nievas, Oliver Mounsey, Lucia Galli, and Fabiana A. Moredo. 2025. "Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to High-Risk Clones Obtained from Fresh Pork Meat in La Plata City, Argentina" Medical Sciences Forum 35, no. 1: 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025035008
APA StyleNievas, H. D., Iza, R. E., Aurnague, C., Helman, E., Nievas, V. F., Mounsey, O., Galli, L., & Moredo, F. A. (2025). Third-Generation Cephalosporin-Resistant Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to High-Risk Clones Obtained from Fresh Pork Meat in La Plata City, Argentina. Medical Sciences Forum, 35(1), 8. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2025035008







