Proteomics Approaches for the Discovery of Potential Enzymatic Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rontogianni, S.; Synadaki, E.; Li, B.; Liefaard, M.C.; Lips, E.H.; Wesseling, J.; Wu, W.; Altelaar, M. Proteomic profiling of extracellular vesicles allows for human breast cancer subtyping. Commun. Biol. 2019, 2, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marar, C.; Starich, B.; Wirtz, D. Extracellular vesicles in immunomodulation and tumor progression. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, K.R.; Hall, J.K.; Schedin, T.; Borakove, M.; Xian, J.J.; Dzieciatkowska, M.; Lyons, T.R.; Schedin, P.; Hansen, K.C.; Borges, V.F. Extracellular vesicles from young women’s breast cancer patients drive increased invasion of non-malignant cells via the Focal Adhesion Kinase pathway: A proteomic approach. Breast Cancer Res. 2020, 22, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Guan, X.; Fan, Z.; Ching, L.M.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Cao, W.M.; Liu, D.X. Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Detection of Breast Cancer. Cancers 2020, 12, 2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minic, Z.; Hüttmann, N.; Poolsup, S.; Li, Y.; Susevski, V.; Zaripov, E.; Berezovski, M.V. Phosphoproteomic Analysis of Breast Cancer-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Reveals Disease-Specific Phosphorylated Enzymes. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risha, Y.; Minic, Z.; Ghobadloo, S.M.; Berezovski, M.V. The proteomic analysis of breast cell line exosomes reveals disease patterns and potential biomarkers. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraoka, S.; Hirano, M.; Isoyama, J.; Nagayama, S.; Tomonaga, T.; Adachi, J. Comprehensive proteomic profiling of plasma and serum phosphatidylserine-positive extracellular vesicles reveals tissue-specific proteins. iScience 2022, 25, 104012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kverneland, A.H.; Østergaard, O.; Emdal, K.B.; Svane, I.M.; Olsen, J.V. Differential ultracentrifugation enables deep plasma proteomics through enrichment of extracellular vesicles. Proteomics 2022, 23, e2200039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.-L.; Chan, D.W. Enzymes and related proteins as cancer biomarkers: A proteomic approach. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 381, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dower, C.M.; Bhat, N.; Gebru, M.T.; Chen, L.; Wills, C.A.; Miller, B.A.; Wang, H.G. Targeted Inhibition of ULK1 Promotes Apoptosis and Suppresses Tumor Growth and Metastasis in Neuroblastoma. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 2365–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, D.Y.; Eom, J.I.; Jang, J.E.; Jeung, H.K.; Chung, H.; Kim, J.S.; Cheong, J.W.; Min, Y.H. ULK1 inhibition as a targeted therapeutic strategy for FLT3-ITD-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Hu, P.; Yang, Z.; Xue, C.; Gong, J.; Sun, S.; Shi, L.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, C.; et al. SBI0206965, a novel inhibitor of Ulk1, suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell growth by modulating both autophagy and apoptosis pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 3449–3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.A.; Pitarresi, J.R.; Sharma, N.; Palettas, M.; Cuitiño, M.C.; Sizemore, S.T.; Yu, L.; Sanderlin, A.; Rosol, T.J.; Mehta, K.D.; et al. Protein Kinase C Beta in the Tumor Microenvironment Promotes Mammary Tumorigenesis. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogués, L.; Reglero, C.; Rivas, V.; Salcedo, A.; Lafarga, V.; Neves, M.; Ramos, P.; Mendiola, M.; Berjón, A.; Stamatakis, K.; et al. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 2 (GRK2) Promotes Breast Tumorigenesis Through a HDAC6-Pin1 Axis. eBioMedicine 2016, 13, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grisouard, J.; Medunjanin, S.; Hermani, A.; Shukla, A.; Mayer, D. Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 Protects Estrogen Receptor α from Proteasomal Degradation and Is Required for Full Transcriptional Activity of the Receptor. Mol. Endocrinol. 2007, 21, 2427–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Biological role of estrogen and estrogen receptors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2002, 37, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couse, J.F.; Korach, K.S. Estrogen receptor null mice: What have we learned and where will they lead us? Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 358–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Zheng, Y.; Lu, W.; Chen, B. Identification of ubiquitination-related gene classification and a novel ubiquitination-related gene signature for patients with triple-negative breast cancer. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 932027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soond, S.M.; Smith, P.G.; Wahl, L.; Swingler, T.E.; Clark, I.M.; Hemmings, A.M.; Chantry, A. Novel WWP2 ubiquitin ligase isoforms as potential prognostic markers and molecular targets in cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Mol. Basis Dis. 2013, 1832, 2127–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobler, J.E.; Jacobson, K.B. Multiple Forms of Alpha-Galactosidase of the Mouse and Their Use as a Cell Marker in Tumorigenesis2. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1978, 61, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezawa, Y.; Daigo, Y.; Takano, A.; Miyagi, Y.; Yokose, T.; Yamashita, T.; Morimoto, C.; Hino, O.; Orimo, A. CD26 expression is attenuated by TGF-β and SDF-1 autocrine signaling on stromal myofibroblasts in human breast cancers. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 3936–3948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Mu, C.; Li, Z.; Xu, L. Imazamethabenz inhibits human breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via combination with Pin1. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3210–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Fu, S.; Wang, X.; Chen, D. Acetyl-CoA Synthetase 2 as a Therapeutic Target in Tumor Metabolism. Cancers 2022, 14, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Han, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. CTP synthase 2 predicts inferior survival and mediates DNA damage response via interacting with BRCA1 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, Z.; Peshkova, M.; Gonen, Z.B.; Coretchi, I.; Eken, A.; Yay, A.H.; Dogan, M.E.; Gokce, N.; Akalin, H.; Kosheleva, N.; et al. EVs vs. EVs: MSCs and Tregs as a source of invisible possibilities. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 101, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagishi, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Matsuda, S. Defective DNA repair systems and the development of breast and prostate cancer (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 42, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
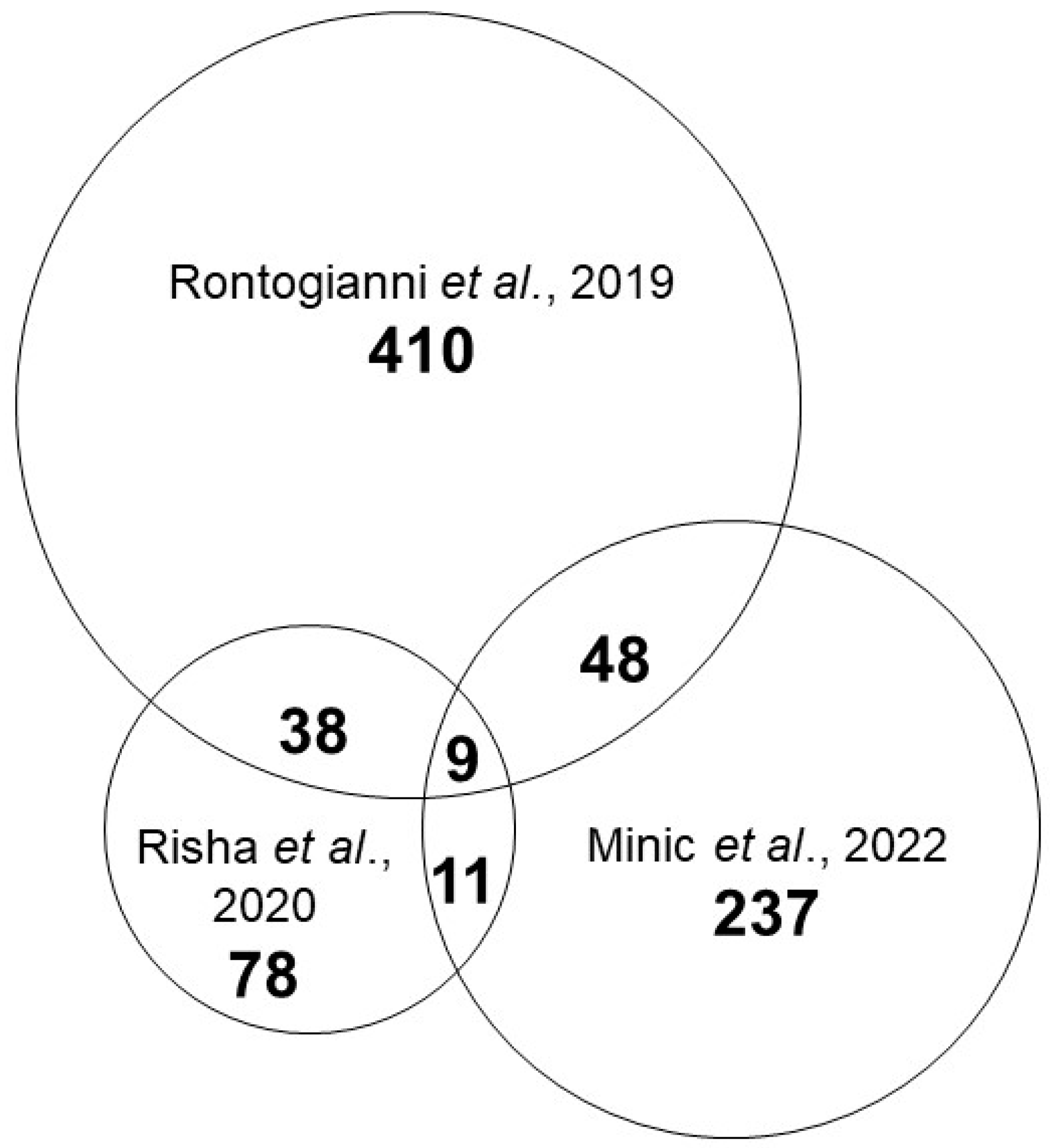
| Publication | Sample Types | Breast Cancer Subtypes | Control |
|---|---|---|---|
| Risha et al. [6] | BC cell lines | MDA-MB-231 | MCF-10A |
| Minic et al. [5] | BC cell lines | MDA-MB-231, MCF-7 | MCF-10A |
| Rontogianni et al. [1] | BC cell lines | MCF-7, Hs578T, BT549, MDA-MB-231, LM2, HCC1954, HCC1419, JIMT1, SKBR3 | MCF-10A |
| Muraoka et al. [7] | Plasma and serum | Healthy human subjects | |
| UniProt ID | Enzyme | Gene | Name | Ref. [6] | Ref. [5] | Ref. [1] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q14669 | 6.3.2.19 | TRIP12 | Thyroid hormone receptor interactor 12 | T | T | T |
| Q6PHR2 | 2.7.11.1 | ULK3 | Unc-51-like kinase 3 | T | T | |
| P05771 | 2.7.11.13 | PRKCB | Protein kinase C beta | T | T | |
| P25098 | 2.7.11.15 | GRK2 | G-protein-coupled receptor kinase 2 | T | T | |
| P49840 | 2.7.11.26 | GSK3A | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha | T | T | |
| P06280 | 3.2.1.22 | GLA | Galactosidase alpha | T | T | |
| P27487 | 3.4.14.5 | DPP4 | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 | T | T | |
| Q13526 | 5.2.1.8 | PIN1 | Peptidylprolyl cis/trans isomerase, NIMA-interacting 1 | T | T | |
| Q9NR19 | 6.2.1.1 | ACSS2 | Acyl-CoA synthetase short-chain family member 2 | T | T | |
| O00308 | 6.3.2.19 | WWP2 | WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 2 | T | T | |
| Q9NRF8 | 6.3.4.2 | CTPS2 | CTP synthase 2 | T | T |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Hüttmann, N.; Minic, Z.; Berezovski, M.V. Proteomics Approaches for the Discovery of Potential Enzymatic Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 21, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14099
Li Y, Hüttmann N, Minic Z, Berezovski MV. Proteomics Approaches for the Discovery of Potential Enzymatic Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Medical Sciences Forum. 2023; 21(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14099
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingxi, Nico Hüttmann, Zoran Minic, and Maxim V. Berezovski. 2023. "Proteomics Approaches for the Discovery of Potential Enzymatic Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer" Medical Sciences Forum 21, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14099
APA StyleLi, Y., Hüttmann, N., Minic, Z., & Berezovski, M. V. (2023). Proteomics Approaches for the Discovery of Potential Enzymatic Biomarkers for Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Medical Sciences Forum, 21(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/ECB2023-14099








