Abstract
Acute localized irradiation accidents may evolve into a musculocutaneous radiation-induced syndrome that leaves a significant underlying muscle defect despite standard treatment. The identification of new therapeutic targets is, therefore, necessary to improve post-irradiation muscle repair. Thus, the validation of an in vivo model of radiation-induced muscle injury has been initiated in C57Bl/6J mice. In the model presented in this study, the high-dose ionizing radiation exposure is focused on gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, does not affect bones, and is a part of hindlimb vascularization. It aims at identifying original metabolic pathways specifically involved in muscle damage and evaluating innovative therapeutic strategies.
1. Introduction
Following a radiotherapy overdose, a radiological accident, or a terrorist act using a hidden source, patients and victims undergo acute local exposure to a high dose of radiation, first affecting physiological barriers such as the skin and the subcutaneous musculature [1]. Depending on the absorbed dose, the type of radiation, and the volume of tissue affected, a cutaneous radiation syndrome (CRS) can occur, evolve, and cause severe, highly inflammatory, and degenerative lesions [1,2].
The current gold standard treatment for CRS consists of a dosimetric reconstruction of the irradiated area to guide the wide excision of the damaged tissues. Then, a reconstructive flap surgery and cell therapy are performed. Despite the fact this treatment limits the progression of CRS and allows partial tissue repair [3,4,5], a muscle defect persists.
Muscle repair is a complex process involving local repair or replacement of damaged fibers through specific stem cells: the satellite cells (SC) [6,7]. Under healthy physiological conditions, these progenitors are activated and proliferate and differentiate into mature myoblasts that fuse, form myotubes, and regenerate functional myofibers. These different stages of differentiation, fusion, and maturation are regulated by a cascade of myogenic factors, including Pax7, Myf5, MyoD1, myogenin, and myosin isoforms [8].
Treatments are being evaluated to improve post-irradiation muscle repair, including cell therapy using BM-MSCs [9] or adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (Ad-MSC) [10]. However, the identification of original therapeutic targets is still necessary to develop effective medical countermeasures. The development of a mouse model of radiation-induced muscle injury is a powerful tool to better describe the pathophysiology of irradiated muscle and identify new targets to develop potential management strategies and ensure optimal care for victims.
The objective of this explorative study is to verify that a unique, acute muscle injury can be induced by ultra-localized high-dose X-ray irradiation in C57Bl/6 mice. In this murine model, in contrast to other described whole-paw irradiation models [11,12], the lesion is localized to the gastrocnemius–soleus muscles and skin of the hindlimb. The bones (tibia/fibula), as well as part of the vascularization of the paw, are not exposed to radiation. This avoids bone loss and necrosis of the limb, especially the foot, observed in some existing rodent models [13,14]. Using this strategy, we aim to identify the induction of a radio-induced muscular injury whose severity can be quantified by analyzing several parameters such as muscle mass, fiber size, and expression of inflammatory and myogenic markers. In this study, GS muscles were irradiated at a dose of 60 Gy and analyzed at day 90 post-irradiation.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics, Animals, and Irradiation
This pilot study was conducted according to French and EU guidelines for animal care. The protocols were approved by the French Armed Forces Health Service Ethics Committee (Project n° IRBA2018-13).
Twelve-week-old female C57Bl/6J mice (n = 5) (Charles River Laboratories, L’Abresle, France) were irradiated with a SARRP X-ray generator (Small Animal Radiation Research Platform, XStrahl, Brownhills, UK). After being anesthetized under 4% isoflurane (induction box), the animals were maintained under 1.5% isoflurane. Then, they were positioned, and the target for irradiation was validated thanks to the SARRP-integrated three-dimensional scanner (CT). The radiation beam, using a 9 mm × 3 mm collimator, on the left GS muscles was visualized using the treatment planning software Muriplan. During irradiation, the muscles were irradiated with a single 60 Gy dose of X-rays (220 kV, 13 mA, with a 0.55 µm Cu filter at a dose rate of about 3.1 Gy/min). A group of control mice (n = 5) were not irradiated but underwent the same anesthesia as the irradiated mice.
2.2. Monitoring of Mice Post-Irradiation Status
After irradiation, the mice were housed 5 per cage in ventilated racks with water and food ad libitum until euthanasia on day 90 post-irradiation. They were weighed two times a week, and a general condition scoring as well as a skin lesion scoring were performed at the same time. General scoring included assessment of weight, appearance, behavior, locomotion, and respiratory rate. The skin scoring was used to assess the presence of erythema, edema, exudative wounds, ulcers, or necrosis, and the extension of the lesions over time (Table 1).

Table 1.
Clinical observations and associated scores for mice hindlimb skin evaluation. The total skin score is calculated by adding each parameter score.
A functional paw extension test was also performed once a week in a similar way to that described by Stone HB in 1984 [15]. Each mouse was anesthetized with 4% isoflurane, maintained at 1.5% under mask, and placed with the base of the hind legs at the origin of a graduated support. The length of each paw was measured by pulling on the limbs with a clamp and stopping the traction as soon as there was resistance. The difference between the non-irradiated paw and the irradiated one was calculated and called contracture.
2.3. Samples Collection and Analysis
At day 90 post-irradiation, the mice were euthanized by cervical dislocation. The GS muscles from the two hindlimbs were harvested and weighed.
A portion of the GS muscles was embedded in paraffin, and 5 µm thick sections were made. The general structure of the muscles was then observed after histological hematoxylin-phloxine-saffron and Sirius red staining. After immunostaining with a fluorescent (Alexa Fluor 488) anti-wheat germ agglutinin antibody (fiber surface; Life Technologies, Courtaboeuf, France), cross-sectional sizes of muscle fibers were detected and measured with Fiji software.
Another portion of the muscle was used to analyze the expression of different pro-inflammatory or fibrosing genes (IL-1beta and TGFbeta1), an anti-inflammatory gene (IL-10), or genes involved in myogenesis (Pax7, Myf5, MyoD1, MyoG and myosin isoforms genes MyH1, MyH2, MyH3, MyH4, MyH6, MyH7b, and MyH8). The extraction was performed after grinding on the Tissuelyser II (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) with Qiazol and 3 mm Tungsten beads, followed by an RNA clean-up with the RNeasy Plus Mini kit (Qiagen). Reverse transcription was performed with the High-Capacity cDNA Reverse Transcription kit (Life Technologies, Courtaboeuf, France). PCR amplifications were performed using specific TaqMan Gene Expression Assays kits, TaqMan Fast Advance Mix, and a QuantStudio 5 thermal cycler (Life Technologies). The relative expression of target genes was determined by the 2−ΔΔCt method, normalized to the geometric mean of three reference genes (HPRT-1, GAPDH, and B2M) and the non-irradiated control group.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed with GraphPad Prism 7 and represented as mean ± SEM. A t-test was used for two samples with a single variable. For more than two samples, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test for one variable or a two-way ANOVA followed by Sidak’s multiple comparison test for two variables was used. A p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant; p-values are indicated in the figure legends.
3. Results and Discussion
In this study, the body weight and general behavior of mice were not impacted, suggesting no major effect of localized high-dose irradiation on the animal’s general condition.
3.1. Radiation-Induced Skin Lesions and Leg Contracture
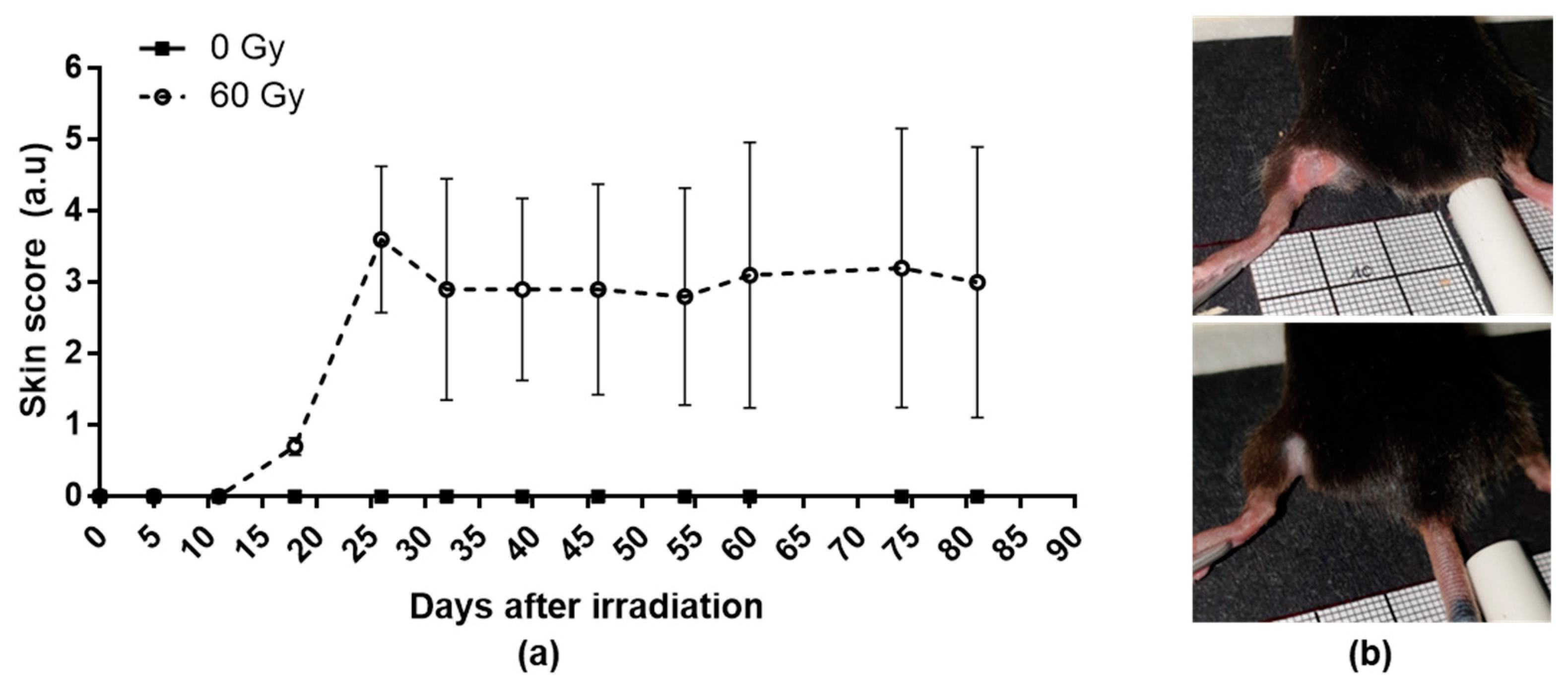
The skin scores increased after irradiation to reach a peak between 25 and 30 days post-irradiation (Figure 1a). However, the cutaneous reactions are heterogeneous between the mice; three of them present depilation or slight erythema (Figure 1b, bottom), whereas two mice present an extensive and ulcerative lesion (Figure 1b, top).
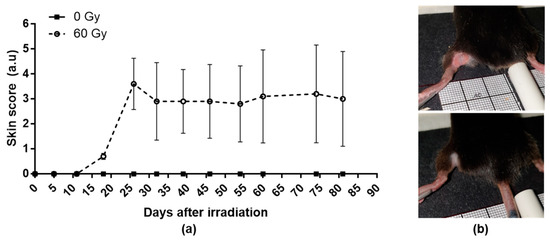
Figure 1.
Weekly evolution of cutaneous scoring in control and irradiated group (a) and examples of slight (b bottom) or severe erythematous and ulcerative lesions (b top). Data are expressed as mean ± SEM at each time.
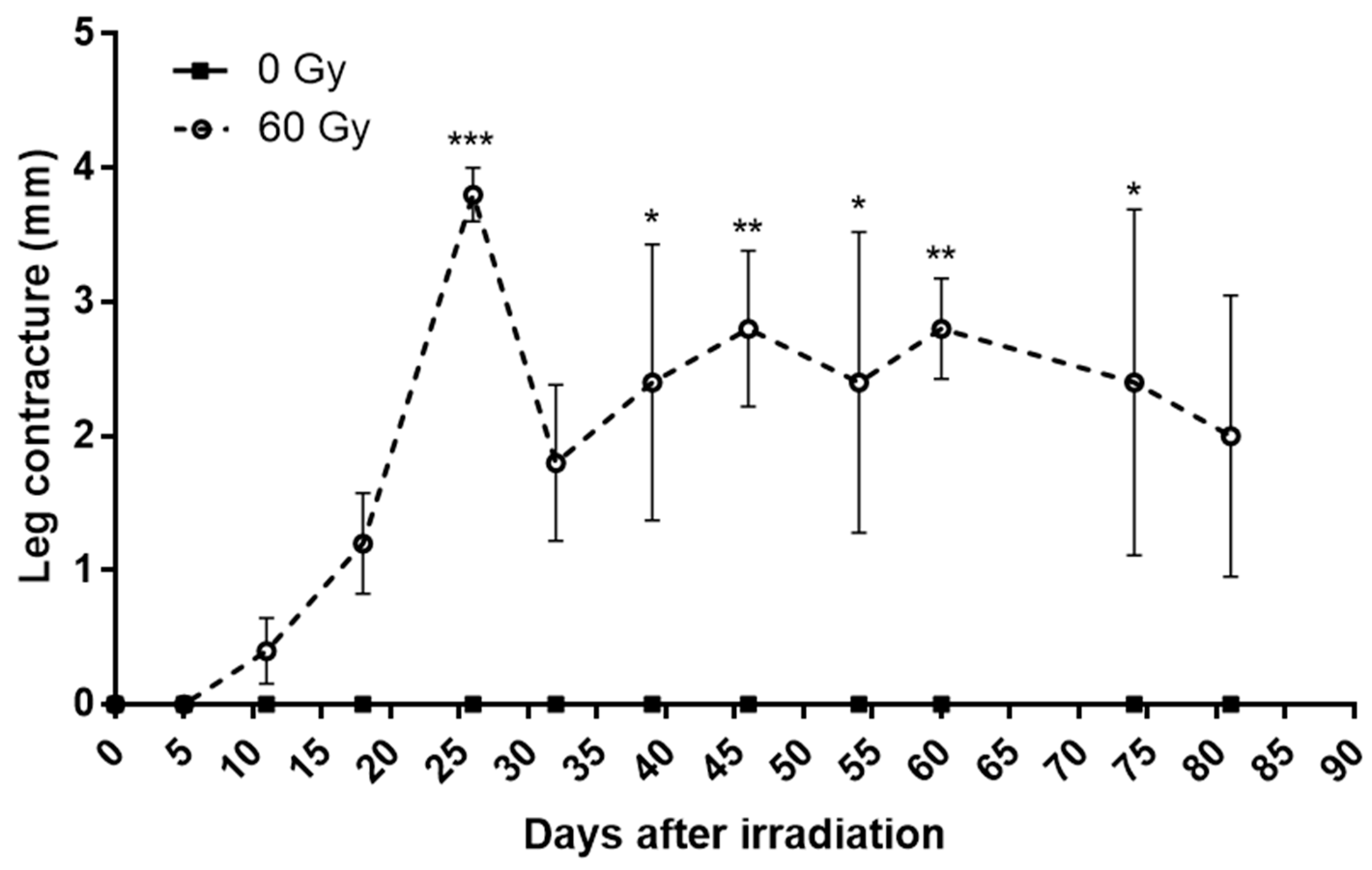
In a similar way, the contracture of the mice’s legs increases after irradiation to reach a peak around 25 days with inter-individual heterogeneity (Figure 2). Interestingly, we notice that the evolution of the skin score and contracture significantly and positively correlated for four mice out of five, according to the Pearson’s test. The mouse that shows no correlation is the least affected. This finding has been described in the literature [15]. These data suggest that paw contracture may be related to a loss of elasticity of the lesional skin, but other parameters should need to be studied, such as localized inflammation or the production of reactive oxygen species.
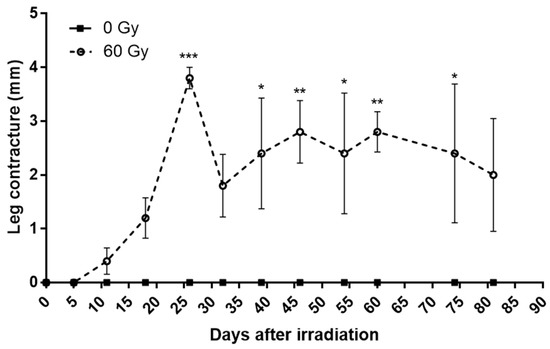
Figure 2.
Weekly evolution of paw contracture in control group and irradiated group. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM at each time. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
3.2. Muscle Weight and Size of Myofibers
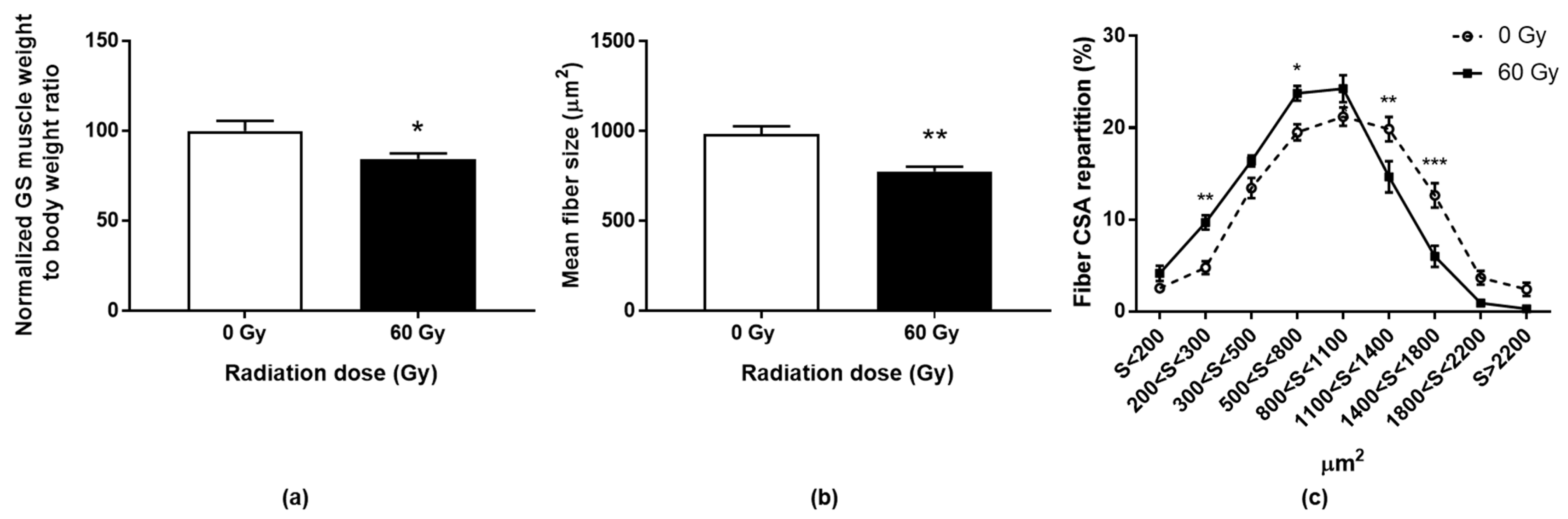
The GS muscles were harvested and weighed at day 90. An average decrease of almost 15% in muscle mass (normalized to body weight) was measured in the irradiated legs compared to the control group (Figure 3a).

Figure 3.
Gastrocnemius/soleus muscle weight normalized to total body weight 90 days post-irradiation (a). Data are expressed as percentages of control group ± SEM. Mean cross-sectional area (CSA) (b) and myofibers CSA repartition (c) in irradiated or sham GS muscles, 90 days post-irradiation. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001.
Anatomopathological observation of the irradiated muscle sections revealed no necrotic nor regenerating areas (centered nucleus). Nevertheless, an impairment can be illustrated by a decrease in the mean fiber cross-sectional area (CSA) of 21.2% compared to non-irradiated mice (Figure 3b). More specifically, a shift to the left of the distribution of CSA was shown, which indicates a decrease in the number of larger fibers in favor of smaller fibers in irradiated animals (Figure 3c). This could be explained by an alteration of the largest muscle fibers or a change in fibrillar typology. Indeed, Hardee and colleagues have shown that glycolytic type IIb fibers have a greater sensitivity to irradiation than more oxidative fibers (IIa) [11]. In our model, such a difference in fiber radiosensitivity could be at the origin of muscle remodeling with atrophy of the large fast-twitch fibers (type II fibers; 50% of the gastrocnemius muscle fibers) and lesser atrophy of the slow-twitch fibers (type I fibers; mainly composing the soleus muscle).
3.3. Expression of Specific Genes after Radiation Exposure
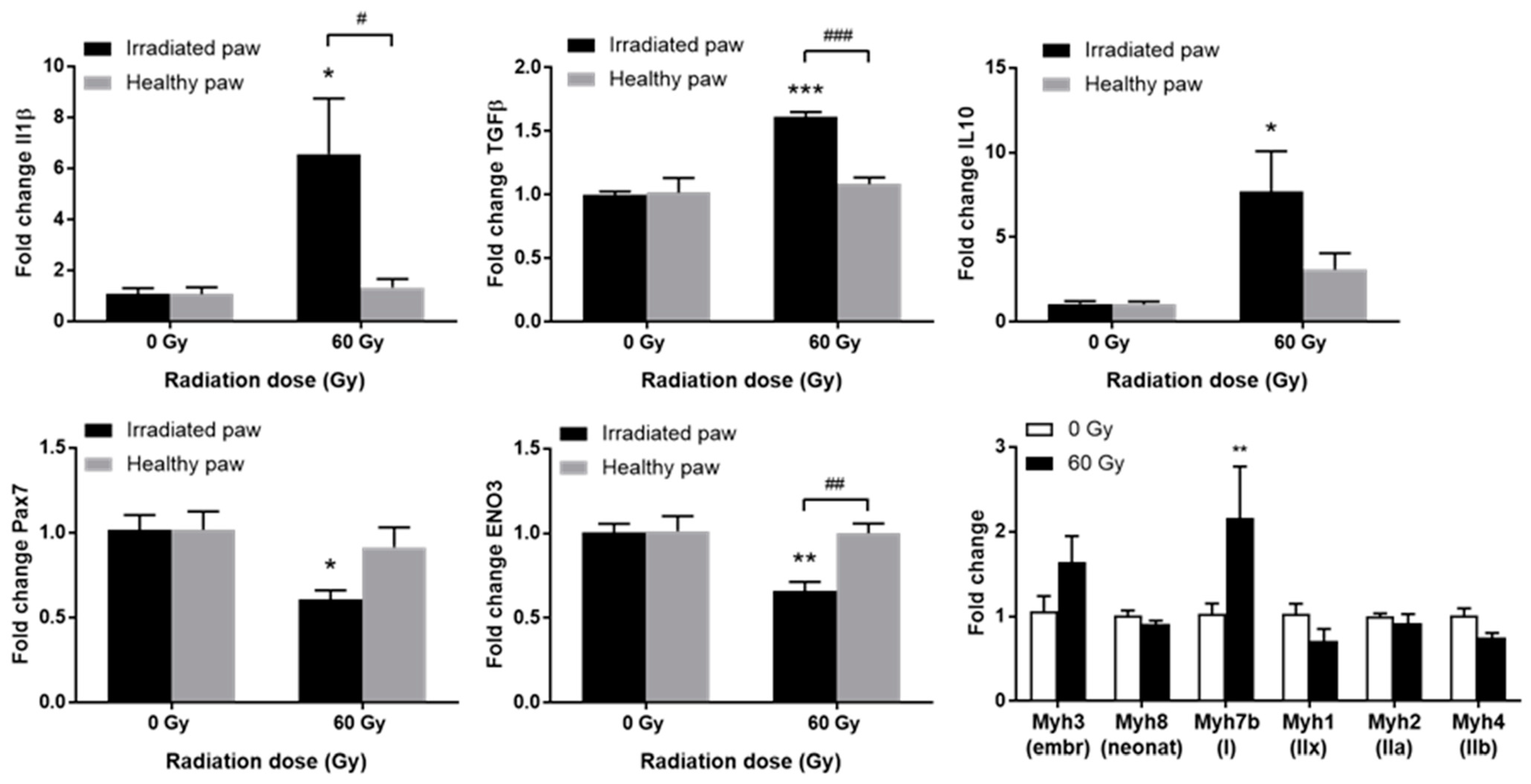
Among genes involved in inflammation and fibrotic phenomena, a significant increase in the expression of IL-1beta, TGFbeta1, and IL-10 was observed in the irradiated paw compared to the contralateral paw and to non-irradiated animals (Figure 4, top). The overexpression of IL-1beta and TGFbeta1 could reflect the establishment of a fibrotic pathological process in a localized inflammatory context. It has been shown that fibrosis and even necrosis are associated with an overexpression of IL-1beta and TGFbeta1 after localized high-dose irradiation of the muscle [10,12,16]. Moreover, the increase in IL-10 expression could be associated with a concomitant regenerative process, as previously observed in pigs treated with MSCs [10,16].
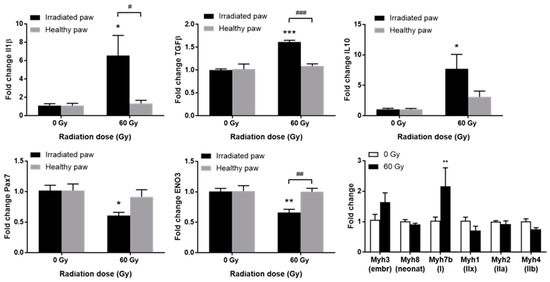
Figure 4.
Expression of inflammatory/fibrotic genes IL-1beta, TGFbeta1, and IL-10; (top) myogenic genes Pax7 and ENO3 (bottom left and center) or myosin isoform genes (bottom right) in irradiated or sham GS muscles, 90 days post-irradiation. Data are expressed as mean fold change ± SEM. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; *** p < 0.001 (60 Gy irradiated vs. 0 Gy sham paw) and # p < 0.05; ## p < 0.01; ### p < 0.001 (irradiated vs. contralateral paw).
Deregulation of the gene expression of several myogenic factors was observed. Pax7, a specific transcription factor of satellite cells, is significantly less expressed in irradiated paws (Figure 4, bottom left). The myogenic determination gene Myf5 shows a similar profile, while Pax3 does not vary significantly. No variation is observed for MYOD1, and a non-significant decrease is observed for MyoG. Overexpression of Myh3, generally associated with embryonic development and post-traumatic repair processes, was observed. Moreover, a significant increase in Myh7b, associated with slow-twitch myofibers, was shown, as well as a trend towards a decrease in Myh1 and Myh4, highly expressed in fast glycolytic IIx/IIb fibers, respectively (Figure 4, bottom right). Finally, a significant decrease in ENO3 was shown in the exposed muscle (Figure 4, bottom center). This gene codes for beta enolase, an enzyme involved in glycogen storage in glycolytic fibers IIx and IIb, and to a lesser extent in IIa fibers [17].
Thus, these variations in gene expression of myogenic markers, essential to the regenerative capacity of the muscle, suggest that deregulation may be observed compared to control animals.
4. Conclusions
This preliminary study shows a functional impairment of the muscle, a decrease in the GS mass, modification of the distribution of CSA, and deregulation of the gene expression of the inflammation and the myogenic markers after localized irradiation at 60 Gy. All these elements lead us to conclude that muscle homeostasis is altered in our model. To better describe the physiopathology (biomarkers and progression kinetics) of radiation-induced muscle injury, a longitudinal study is currently underway from very early to late times after irradiation. This model could then be used to identify new therapeutic targets and evaluate new medical countermeasures to treat radiation-induced muscle damage.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ECB2023-14280/s1, Slides: A new murine highly localized high dose muscle radiation model: a tool to develop innovative countermeasures to treat radio induced muscular lesions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, N.J. and E.R.G.; validation, N.J., M.D., S.F. and D.R.; experiments realization, N.J., E.R.G. and M.G.; writing—original draft preparation, N.J. and E.R.G.; writing—review and editing, N.J., E.R.G. and S.F.; project administration, N.J.; funding acquisition, N.J. and D.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by French Direction Générale de l’Armement (Paris, France).
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was conducted according to French and EU guidelines for animal care. The protocols were approved by the French Armed Forces Health Service Ethics Committee (Project No. IRBA2018-13).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all authors involved in this study.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data are not public. Data analyzes are presented in this paper and in the presentation cited in the Supplementary Data Section.
Acknowledgments
We wish to express our deep thanks to the French Direction Générale de l’Armement (Paris, France) for granting our work, to IRBA Animal Unit team for their help in the daily management of mice, to IRBA Structure for Animal Welfare headed by the Chief Veterinary Officer Fanny MAGISSON for their help in the protocols set up, and to Krisztina Nikovics, Aurélie Trignol, and Nathalie Guatto for their advice and their help for histological staining and immunohistochemical labeling.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors report no conflict of interest. They are entirely responsible for the content of the paper.
References
- Lefaix, J.L.; Delanian, S. Menace Terroriste Nucléaire: Approche Médicale; John Libbey Eurotext Plc: Arcueil, France, 2005; pp. 87–95. (In French) [Google Scholar]
- Hopewell, J.W. The Skin: Its Structure and Response to Ionizing Radiation. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 1990, 57, 751–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lataillade, J.; Doucet, C.; Bey, E.; Carsin, H.; Huet, C.; Clairand, I.; Bottollier-Depois, J.; Chapel, A.; Ernou, I.; Gourven, M.; et al. New approach to radiation burn treatment by dosimetry-guided surgery combined with autologous mesenchymal stem cell therapy. Regen. Med. 2007, 2, 785–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bey, E.; Prat, M.; Duhamel, P.; Benderitter, M.; Brachet, M.; Trompier, F.; Battaglini, P.; Ernou, I.; Boutin, L.; Gourven, M.; et al. Emerging therapy for improving wound repair of severe radiation burns using local bone marrow-derived stem cell administrations. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, E.H.; Baciu, F.; Benderitter, M.; Lataillade, J.J.; Bey, E.; Trompier, F.; Tamarat, R. Medical Response to Radiological Accidents in Latin America and International Assistance. Radiat. Res. 2016, 185, 359–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauro, A. Satellite cell of skeletal muscle fibers. J. Cell Biol. 1961, 9, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zammit, P.S.; Partridge, T.A.; Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. The Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cell: The Stem Cell That Came in From the Cold. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2006, 54, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawke, T.J.; Garry, D.J. Myogenic satellite cells: Physiology to molecular biology. J. Appl. Physiol. 2001, 91, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linard, C.; Brachet, M.; L’Homme, B.; Strup-Perrot, C.; Busson, E.; Bonneau, M.; Lataillade, J.-J.; Bey, E.; Benderitter, M. Long-term effectiveness of local BM-MSCs for skeletal muscle regeneration: A proof of concept obtained on a pig model of severe radiation burn. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccobono, D.; Agay, D.; François, S.; Scherthan, H.; Drouet, M.; Forcheron, F. Contribution of INTRAMUSCULAR autologous adipose tissue-derived stem cell injections to treat cutaneous radiation syndrome: Preliminary results. Health Phys. 2016, 111, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardee, J.P.; Puppa, M.J.; Fix, D.K.; Gao, S.; Hetzler, K.L.; Bateman, T.A.; Carson, J.A. The effect of radiation dose on mouse skeletal muscle remodeling. Radiol. Oncol. 2014, 48, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viana, W.; Lambertz, D.; Borges, E.; Melo, J.; Lambertz, K.; Amaral, A. Late Effects of Radiation on Skeletal Muscle: An Open Field of Research. J. Biomed. Sci. Eng. 2015, 08, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulpin, B.; Dolivet, G.; Marie, P.-Y.; Poussier, S.; Gallet, P.; Leroux, A.; Graff, P.; Groubach, F.; Bravetti, P.; Merlin, J.-L.; et al. Re-assessment of chronic radio-induced tissue damage in a rat hindlimb model. Exp. Ther. Med. 2010, 1, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Wright, L.; Buijs, J.T.; Kim, H.-S.; E Coats, L.; Scheidler, A.M.; John, S.K.; She, Y.; Murthy, S.; Ma, N.; Chin-Sinex, H.J.; et al. Single-Limb Irradiation Induces Local and Systemic Bone Loss in a Murine Model. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2015, 30, 1268–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, H.B. Leg contracture in mice: An assay of normal tissue response. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 1984, 10, 1053–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccobono, D.; Nikovics, K.; François, S.; Favier, A.-L.; Jullien, N.; Schrock, G.; Scherthan, H.; Drouet, M. First Insights Into the M2 Inflammatory Response After Adi-pose-Tissue-Derived Stem Cell Injections in Radiation-Injured Muscles. Health Phys. 2018, 115, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.; Demeurie, J.; Merkulova, T.; Gérard, G.; Charlotte, C.-G.; Marguerite, L.; François-Patrick, C. Fibre-type distribution and subcellular localisation of alpha and beta enolase in mouse striated muscle. Biol. Cell. 2000, 92, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).