Targeting AKT Kinase in Hydroxytamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Cells and Reagents
2.2. Evaluation of Antiproliferative Activity
2.3. Immunoblotting
2.4. Reporter Assay
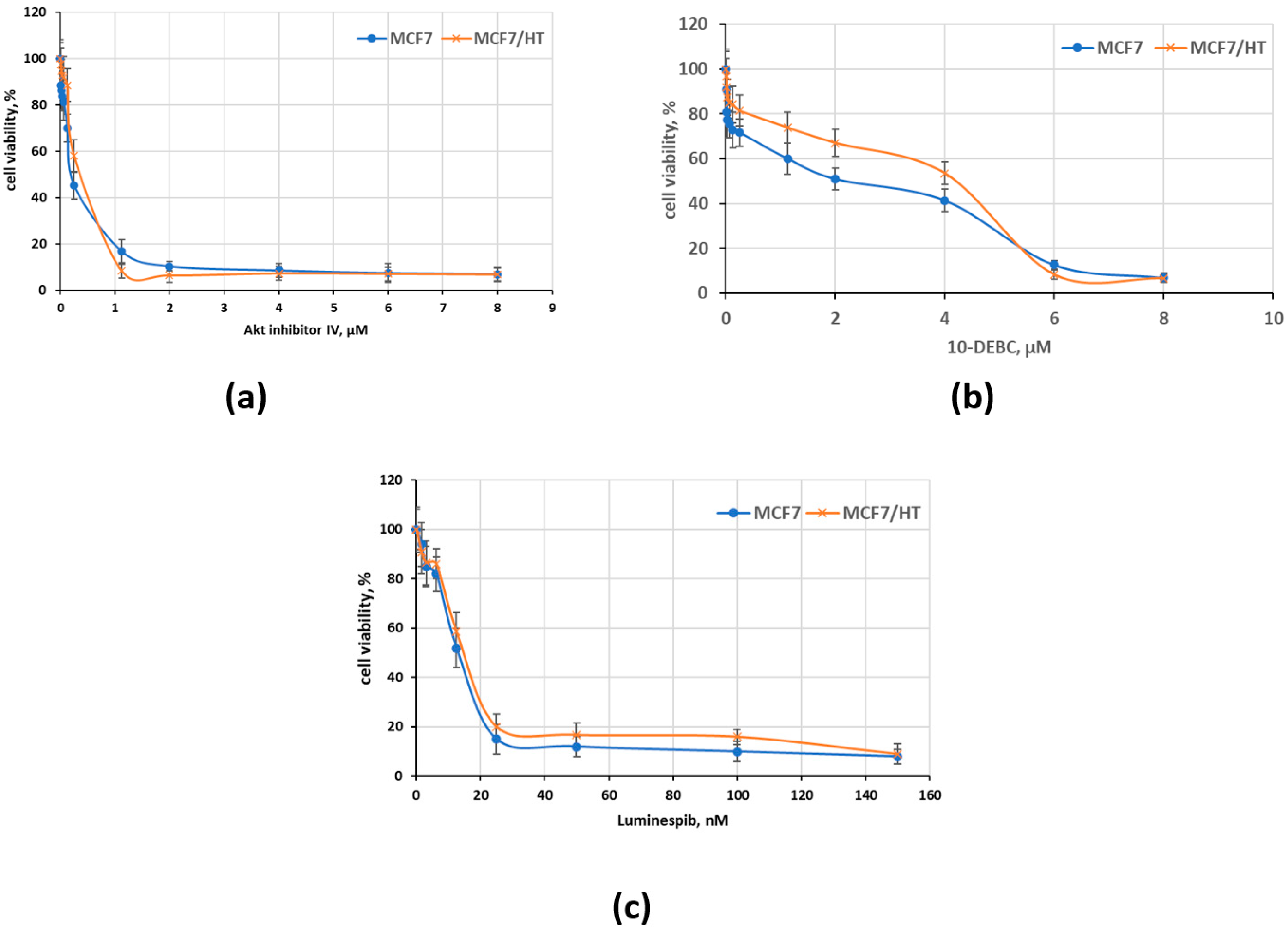
3. Results and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hua, H.; Zhang, H.; Kong, Q.; Jiang, Y. Mechanisms for estrogen receptor expression in human cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 7, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heel, R.C.; Brogden, R.N.; Speight, T.M.; Avery, G.S. Tamoxifen: A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use in the treatment of breast cancer. Drugs 1978, 16, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Calhoun, S.J.; Perez, R.E.; Macias, V.; Mir, F.; Gattuso, P.; Maki, C.G. Prolylcarboxypeptidase promotes IGF1R/HER3 signaling and is a potential target to improve endocrine therapy response in estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbakov, A.M.; Krasil’nikov, M.A.; Kushlinskii, N.E. Molecular mechanisms of hormone resistance of breast cancer. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2013, 155, 384–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, V.C. 50th anniversary of the first clinical trial with ICI 46,474 (tamoxifen): Then what happened? Endocr. -Relat. Cancer 2021, 28, R11–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Q.; Xu, B. Endocrine Therapy-Based Strategies for Metastatic Breast Cancer with Different Endocrine Sensitivity Statuses: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 6100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, H.K.; Bihani, T. Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) in cancer treatment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 186, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Becerra, R.; Santos, N.; Díaz, L.; Camacho, J. Mechanisms of resistance to endocrine therapy in breast cancer: Focus on signaling pathways, miRNAs and genetically based resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 14, 108–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanker, A.B.; Sudhan, D.R.; Arteaga, C.L. Overcoming Endocrine Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 496–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, L.; Gathani, T. Understanding breast cancer as a global health concern. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20211033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherbakov, A.M.; Basharina, A.A.; Sorokin, D.V.; Mikhaevich, E.I.; Mizaeva, I.E.; Mikhaylova, A.L.; Bogush, T.A.; Krasil’nikov, M.A. Targeting hormone-resistant breast cancer cells with docetaxel: A look inside the resistance. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilovaisky, A.I.; Scherbakov, A.M.; Merkulova, V.M.; Chernoburova, E.I.; Shchetinina, M.A.; Andreeva, O.E.; Salnikova, D.I.; Zavarzin, I.V.; Terent’ev, A.O. Secosteroid-quinoline hybrids as new anticancer agents. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2023, 228, 106245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherbakov, A.M.; Lobanova, Y.S.; Shatskaya, V.A.; Onopchenko, O.V.; Gershtein, E.S.; Krasil’nikov, M.A. Activation of mitogenic pathways and sensitization to estrogen-induced apoptosis: Two independent characteristics of tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells? Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2006, 100, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mruk, D.D.; Cheng, C.Y. Enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) for routine immunoblotting: An inexpensive alternative to commercially available kits. Spermatogenesis 2011, 1, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C.; Berkelman, T.; Yadav, G.; Hammond, M. A defined methodology for reliable quantification of Western blot data. Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 55, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Hübner, M.R.; Métivier, R.; Brand, H.; Denger, S.; Manu, D.; Beaudouin, J.; Ellenberg, J.; Gannon, F. Cyclic, proteasome-mediated turnover of unliganded and liganded ERalpha on responsive promoters is an integral feature of estrogen signaling. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkaria, J.N.; Miller, E.M.; Parker, C.J.; Jordan, V.C.; Mulcahy, R.T. 4-Hydroxytamoxifen, an active metabolite of tamoxifen, does not alter the radiation sensitivity of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells irradiated in vitro. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 1994, 30, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokunaga, E.; Kimura, Y.; Mashino, K.; Oki, E.; Kataoka, A.; Ohno, S.; Morita, M.; Kakeji, Y.; Baba, H.; Maehara, Y. Activation of PI3K/Akt signaling and hormone resistance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer 2006, 13, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Oh, J.H.; Kim, M.H. HOXA5 confers tamoxifen resistance via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in ER-positive breast cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 4626–4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadneh, L.; Abuarqoub, R.; Alhusban, A.; Bahader, M. Upregulation of PI3K/AKT/PTEN pathway is correlated with glucose and glutamine metabolic dysfunction during tamoxifen resistance development in MCF-7 cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.A.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Seo, J.H. The functional implications of Akt activity and TGF-beta signaling in tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitton, A.; Zheng, Y.; Houston, J.P.; Houston, K.D. Investigating differences between tamoxifen resistant and sensitive breast cancer cells with flow cytometry. Cytometry Part A J. Int. Soc. Anal. Cytol. 2021, 99, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Yang, Q.; Chen, Z.; Fu, W. Role of β1-integrin in promoting cell motility and tamoxifen resistance of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Asia-Pac. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022; Early View. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, H.; Zhang, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Y. Targeting Akt in cancer for precision therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miricescu, D.; Totan, A.; Stanescu, S., II; Badoiu, S.C.; Stefani, C.; Greabu, M. PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Breast Cancer: From Molecular Landscape to Clinical Aspects. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saatci, O.; Huynh-Dam, K.T.; Sahin, O. Endocrine resistance in breast cancer: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic strategies. J. Mol. Med. 2021, 99, 1691–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.H.; Page, Y.L.; Percevault, F.; Ferrière, F.; Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F. Apigenin, a Partial Antagonist of the Estrogen Receptor (ER), Inhibits ER-Positive Breast Cancer Cell Proliferation through Akt/FOXM1 Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Shi, Q.; et al. Tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cells are resistant to DNA-damaging chemotherapy because of upregulated BARD1 and BRCA1. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cells | 17β-Estradiol-Induced Luciferase Activity, Rel. Units |
|---|---|
| MCF7 | 2985 ± 301 |
| MCF7/HT | 2008 ± 191 * |
| Resistance index | 1.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scherbakov, A.M.; Bogdanov, F.B.; Mikhaylova, A.L.; Andreeva, O.E.; Salnikova, D.I. Targeting AKT Kinase in Hydroxytamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 20, 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECC2023-14224
Scherbakov AM, Bogdanov FB, Mikhaylova AL, Andreeva OE, Salnikova DI. Targeting AKT Kinase in Hydroxytamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Medical Sciences Forum. 2023; 20(1):4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECC2023-14224
Chicago/Turabian StyleScherbakov, Alexander M., Fedor B. Bogdanov, Alexandra L. Mikhaylova, Olga E. Andreeva, and Diana I. Salnikova. 2023. "Targeting AKT Kinase in Hydroxytamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells" Medical Sciences Forum 20, no. 1: 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECC2023-14224
APA StyleScherbakov, A. M., Bogdanov, F. B., Mikhaylova, A. L., Andreeva, O. E., & Salnikova, D. I. (2023). Targeting AKT Kinase in Hydroxytamoxifen-Resistant Breast Cancer Cells. Medical Sciences Forum, 20(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.3390/IECC2023-14224








