Standard Operating Procedure for the Analysis of Microplastics in Larval Fish Diets †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Preparation of the Samples and Equipment
- -
- Dissecting microscope with 80× magnification
- -
- Microscope slides, 25 mm × 75 mm
- -
- Cover slips, 22 mm × 22 mm
- -
- Microscope slide box
- -
- Vials, 20 mL and 3.7 mL
- -
- Vial box
- -
- Fine tipped probes
- -
- Minuten pins
- -
- Tweezers
- -
- Eyedropper
- -
- Ethanol 99%, 100 mL
- -
- Permount™ Mounting Media, 100 mL
- -
- Glycerin-Alcohol 50:50, 100 mL
2.3. Larvae Fish Dissection
2.4. Diets Removal and Slide Preparation
2.5. Counting Particles
3. SOP Application
3.1. Scope and Objectives
3.2. Sample Selection
3.3. MPs Analysis
4. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cózar, A.; Echevarría, F.; González-Gordillo, J.I.; Irigoien, X.; Úbeda, B.; Hernández-León, S.; Palma, A.T.; Navarro, S.; García-de-Lomas, J.; Ruiz, A.; et al. Plastic debris in the open ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 10239–10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleansers. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Free, C.M.; Jensen, O.P.; Mason, S.A.; Eriksen, M.; Williamson, N.J.; Boldgiv, B. High-levels of microplastic pollution in a large, remote, mountain lake. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betts, K. Why Small Plastic Particles May Pose a Big Problem in the Oceans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boerger, C.M.; Lattin, G.L.; Moore, S.L.; Moore, C.J. Plastic ingestion by planktivorous fishes in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davison, P.; Asch, R.G. Plastic ingestion by mesopelagic fishes in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 432, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Rowe, D.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion decreases energy reserves in marine worms. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R1031–R1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, M.A.; Niven, S.J.; Galloway, T.S.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Microplastic moves pollutants and additives to worms, reducing functions linked to health and biodiversity. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochman, C.M.; Hoh, E.; Kurobe, T.; Teh, S.J. Ingested plastic transfers hazardous chemicals to fish and induces hepatic stress. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hämer, J.; Gutow, L.; Köhler, A.; Saborowski, R. Fate of microplastics in the marine isopod Idotea emarginata. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 13451–13458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazurais, D.; Ernande, B.; Quazuguel, P.; Severe, A.; Huelvan, C.; Madec, L.; Mouchel, O.; Soudant, P.; Robbens, J.; Huvet, A.; et al. Evaluation of the impact of polyethylene microbeads ingestion in European sea bass (Dicentrarchus labrax) larvae. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 112, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellas, J.; Martínez-Armental, J.; Martínez-Cámara, A.; Besada, V.; Martínez-Gómez, C. Ingestion of microplastics by demersal fish from the Spanish Atlantic and Mediterranean coasts. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 109, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rummel, C.D.; Löder, M.G.; Fricke, N.F.; Lang, T.; Griebeler, E.M.; Janke, M.; Gerdts, G. Plastic ingestion by pelagic and demersal fish from the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 102, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Takada, H. Microplastic fragments and microbeads in digestive tracts of planktivorous fish from urban coastal waters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ory, N.C.; Sobral, P.; Ferreira, J.L.; Thiel, M. Amberstripe scad Decapterus muroadsi (Carangidae) fish ingest blue microplastics resembling their copepod prey along the coast of Rapa Nui (Easter Island) in the South Pacific subtropical gyre. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 586, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Zhang, H.; Fu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Dai, Z.; Li, Y.; Chen, T.; Luo, Y. The distribution and morphology of microplastics in coastal soils adjacent to the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Geoderma 2018, 322, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biginagwa, F.J.; Mayoma, B.S.; Shashoua, Y.; Syberg, K.; Khan, F.R. First evidence of microplastics in the African Great Lakes: Recovery from Lake Victoria Nile perch and Nile tilapia. J. Great Lakes Res. 2016, 42, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva-Cavalcanti, J.S.; Silva, J.D.B.; de França, E.J.; de Araújo, M.C.B.; Gusmão, F. Microplastics ingestion by a common tropical freshwater fishing resource. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabeen, K.; Su, L.; Li, J.; Yang, D.; Tong, C.; Mu, J.; Shi, H. Microplastics and mesoplastics in fish from coastal and fresh waters of China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 221, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSantiago, R. Foraging Strategy May Predict Anthropogenic Debris Consumption in Wetland Fishes; NCUR: Edmond, OK, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lönnstedt, O.M.; Eklöv, P. Environmentally relevant concentrations of microplastic particles influence larval fish ecology. Science 2016, 352, 1213–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steer, M.; Cole, M.; Thompson, R.C.; Lindeque, P.K. Microplastic ingestion in fish larvae in the western English Channel. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 226, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, S.Y.; Lee, C.M.; Weinstein, J.E.; van den Hurk, P.; Klaine, S.J. Trophic transfer of microplastics in aquatic ecosystems: Identifying critical research needs. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 13, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, D.M.; Fefer, S.I.; Sileo, L. Ingestion of plastic debris by Laysan albatrosses and wedge-tailed shearwaters in the Hawaiian Islands. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 1987, 18, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksson, C.; Burton, H. Origins and biological accumulation of small plastic particles in fur seals from Macquarie Island. AMBIO A J. Hum. Environ. 2003, 32, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA (Environmental Protection Agency). Microplastics Expert Workshop Report. Trash Free Waters Dialogue Meeting. EPA Office of Wetlands, Oceans and Watersheds. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2018-03/documents/microplastics_expert_workshop_report_final_12-4-17.pdf (accessed on 8 August 2022).
- Baldwin, A.K.; Corsi, S.R.; Mason, S.A. Plastic debris in 29 Great Lakes tributaries: Relations to watershed attributes and hydrology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driedger, A.G.; Dürr, H.H.; Mitchell, K.; Van Cappellen, P. Plastic debris in the Laurentian Great Lakes: A review. J. Great Lakes Res. 2015, 41, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, M.; Mason, S.; Wilson, S.; Box, C.; Zellers, A.; Edwards, W.; Farley, A.; Amato, S. Microplastic pollution in the surface waters of the Laurentian Great Lakes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 77, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L. Distribution and degradation of fresh water plastic particles along the beaches of Lake Huron, Canada. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2011, 220, 365–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zbyszewski, M.; Corcoran, P.L.; Hockin, A. Comparison of the distribution and degradation of plastic debris along shorelines of the Great Lakes, North America. J. Great Lakes Res. 2014, 40, 288–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munno, K.; Helm, P.A.; Rochman, C.; George, T.; Jackson, D.A. Microplastic contamination in Great Lakes fish. Conserv. Biol. 2022, 36, e13794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Deng, D.F.; Huang, F.; Casu, F.; Kraco, E.; Newton, R.J.; Mendoza, L.M.R. Chronic exposure to high-density polyethylene microplastic through feeding alters the nutrient metabolism of juvenile yellow perch (Perca flavescens). Anim. Nutr. 2022, 9, 143–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesch, C.; Barthel, A.K.; Braun, U.; Klein, R.; Paulus, M. No microplastics in benthic eelpout (Zoarces viviparus): An urgent need for spectroscopic analyses in microplastic detection. Environ. Res. 2016, 148, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabaka, S.H.; Ghobashy, M.; Marey, R.S. Identification of marine microplastics in Eastern Harbor, Mediterranean Coast of Egypt, using differential scanning calorimetry. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2019, 142, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| 1. Sample Pools Selection |
|
| 2. Microscopic Analysis |
|
| 3. Statistical Analysis and Interpretation of Results |
|
| Particle | Characteristics | Images |
|---|---|---|
| Bead | Hard, Rounded |  |
| Fiber | Thin, fibrous, linear | 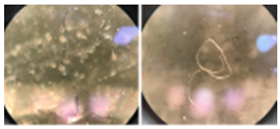 |
| Fragment | Hard, jagged |  |
| Film | Thin, flimsy |  |
| Foam | Lightweight, sponge like | 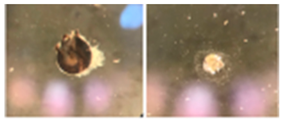 |
| Site | Species | Samples (#) | Ingestion Rate (%) | Particle Count (#) | Particle Types | Particle Size (Mean) | Particle Color | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (Fiber) | Area (Bead, Fragment, Foam) | |||||||
| S1 | Rainbow smelt | 20 | 45% | 10 | Bead (1), Fragment (1) fiber (8) | 912.6 nm | 22,855.4 nm2 | Orange, black, blue, red |
| Burbot | 28 | 53.6% | 29 | Fragment (7), fiber (22) | 1424.0 nm | 15,685.6 nm2 | Red, black, blue, transparent | |
| S2 | Yellow perch | 30 | 80% | 58 | Fragment (3), foam (3), fiber (52) | 1208.3 nm | 52,942.9 nm2 | Red, orange, black, blue, transparent |
| Rainbow smelt | 30 | 56.7% | 34 | Fiber (34) | 1610.2 | - | Red, blue, black, orange | |
| Burbot | 28 | 17.9% | 6 | Fragment (2), fiber (4) | 2106.9 nm | 5576.4 nm2 | Red, black, blue | |
| S3 | Cyprinidae | 20 | 25% | 5 | Fiber (5) | 691.1 nm | - | Black, blue, red |
| Rainbow smelt | 30 | 60% | 35 | Fragment (2), fiber (33) | 1367.0 nm | 4100.2 nm2 | Red, blue, black, orange | |
| Yellow perch | 33 | 72.7% | 52 | Fragment (1), fiber (51) | 1405.5 nm | 2092.0 nm2 | Blue, black, red, transparent | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maione, C. Standard Operating Procedure for the Analysis of Microplastics in Larval Fish Diets. Med. Sci. Forum 2023, 19, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023019001
Maione C. Standard Operating Procedure for the Analysis of Microplastics in Larval Fish Diets. Medical Sciences Forum. 2023; 19(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023019001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaione, Carol. 2023. "Standard Operating Procedure for the Analysis of Microplastics in Larval Fish Diets" Medical Sciences Forum 19, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023019001
APA StyleMaione, C. (2023). Standard Operating Procedure for the Analysis of Microplastics in Larval Fish Diets. Medical Sciences Forum, 19(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/msf2023019001






